Measuring Language Distance of Isolated European Languages
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Phylogenetics and Lexicostatistics
2.2. Corpus-Based Approaches
3. The Methods
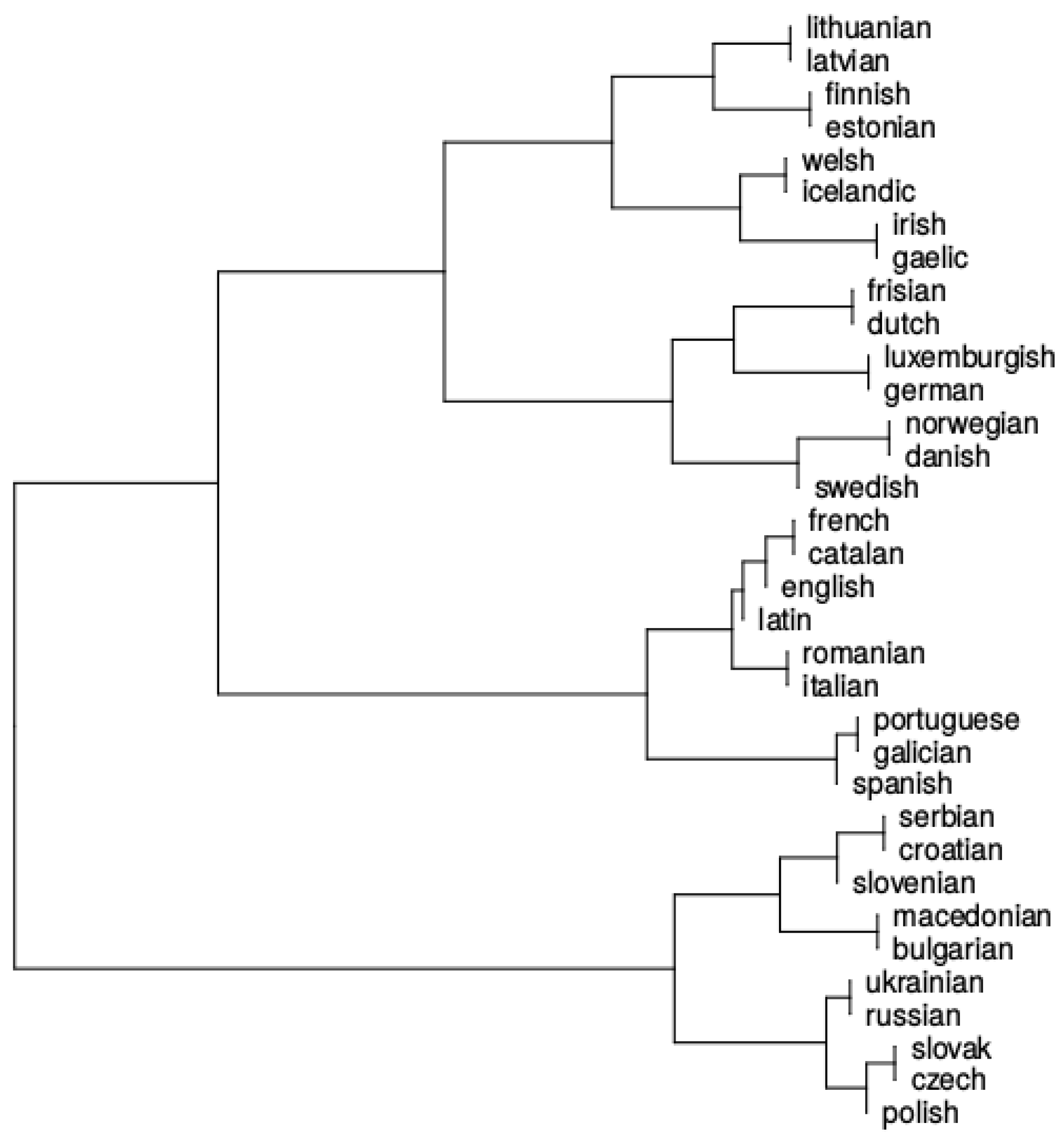
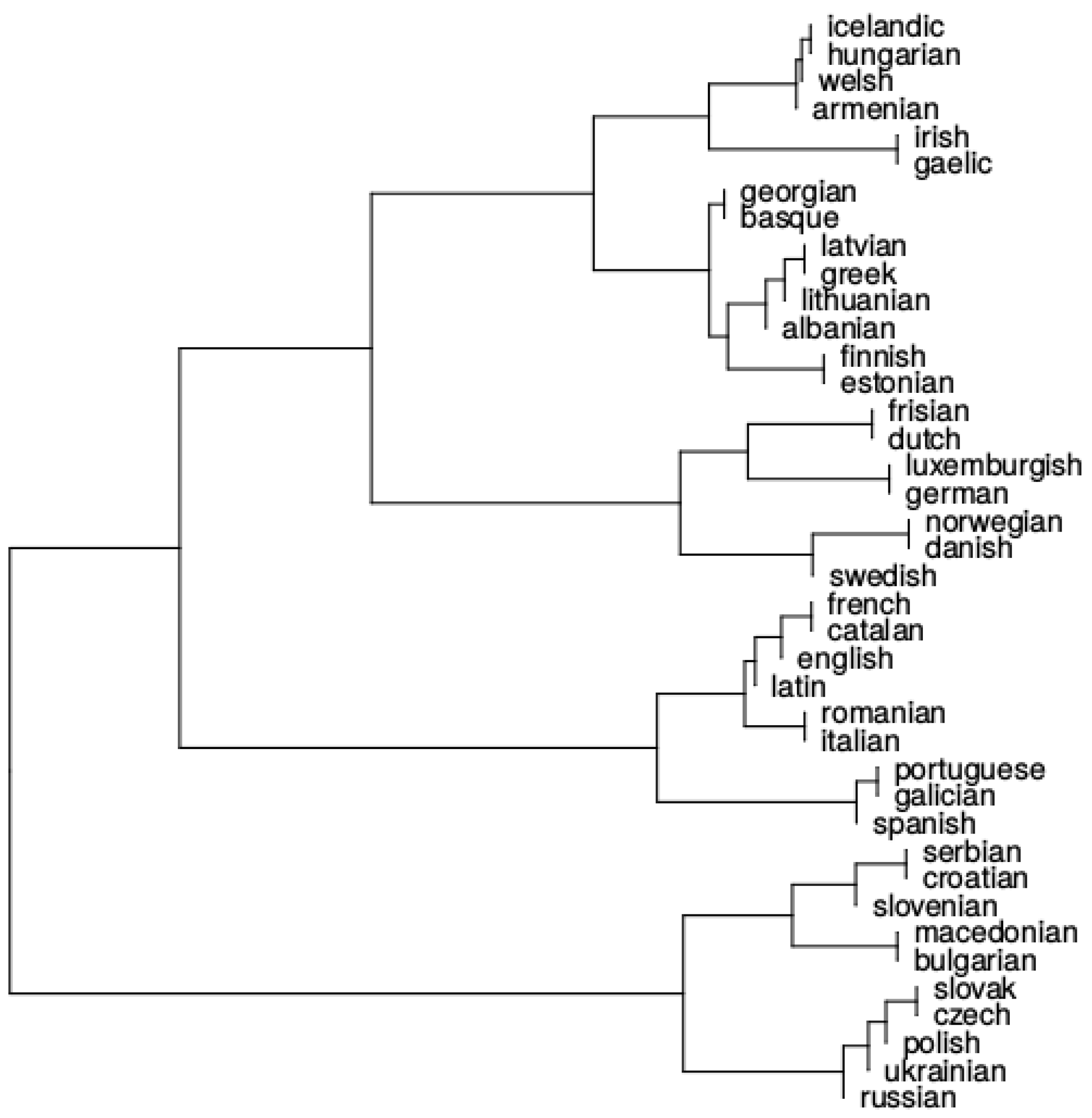
3.1. Language Clustering
3.2. Language Distance Measures
3.2.1. Perplexity
3.2.2. Kullback–Leibler
3.2.3. Rank-Based
3.2.4. Distance Metrics Mean
3.2.5. Average Language Distance
4. Experiments
4.1. The Corpus
4.2. Development and Configuration
4.3. Results
4.4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nichols, J.; Warnow, T.J. Tutorial on Computational Linguistic Phylogeny. Lang. Linguist. Compass 2008, 2, 760–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swadesh, M. Lexicostatistic dating of prehistoric ethnic contacts. In Proceedings of the American Philosophical Society; American Philosophical Society: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1952; pp. 452–463. [Google Scholar]
- Wichmann, S. Genealogical classification in historical linguistics. In Oxford Research Encyclopedias of Linguistics; Aronoff, M., Ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Clackson, J. Indo-European Linguistics: An Introduction; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbançon, F.; Evans, S.; Nakhleh, L.; Ringe, D.; Warnow, T. An experimental study comparing linguistic phylogenetic reconstruction methods. Diachronica 2013, 30, 143–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starostin, G. Preliminary Lexicostatistics as a Basis for Language Classification: A New Approach. J. Lang. Relatsh. 2010, 3, 79–116. [Google Scholar]
- Bakker, D.; Muller, A.; Velupillai, V.; Wichmann, S.; Brown, C.H.; Brown, P.; Egorov, D.; Mailhammer, R.; Grant, A.; Holman, E.W. Adding typology to lexicostatistics: A combined approach to language classification. Linguist. Typol. 2009, 13, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holman, E.; Wichmann, S.; Brown, C.; Velupillai, V.; Muller, A.; Bakker, D. Explorations in automated lexicostatistics. Folia Linguist. 2008, 42, 331–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.H.; Holman, E.W.; Wichmann, S.; Velupilla, V. Automated classification of the world’s languages: A description of the method and preliminary results. Lang. Typol. Univers. Sprachtypol. Universalienforschung 2008, 61, 285–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakhleh, L.; Ringe, D.; Warnow, T. Perfect Phylogenetic Networks: A New Methodology for Reconstructing the Evolutionary History of Natural Languages. Language 2005, 81, 382–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petroni, F.; Serva, M. Measures of lexical distance between languages. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2010, 389, 2280–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nerbonne, J.; Hinrichs, E. Linguistic Distances. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Linguistic Distances; Association for Computational Linguistics, Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 3–4 July 2006; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Michael, L.D.; Chousou-Polydouri, N.; Bartolomei, K.; Donnelly, E.; Meira, S.; Wauters, V.; O’hagan, Z. A Bayesian Phylogenetic Classification of Tupí-Guaraní. LIAMES Líng. Indíg. Am. 2015, 15, 193–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carling, G.; Larsson, F.; Cathcart, C.; Johansson, N.; Holmer, A.; Round, E.; Verhoeven, R. Diachronic Atlas of Comparative Linguistics (DiACL)—A database for ancient language typology. PLoS ONE 2018, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgari, E.; Mofrad, M.R.K. Comparing Fifty Natural Languages and Twelve Genetic Languages Using Word Embedding Language Divergence (WELD) as a Quantitative Measure of Language Distance. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Multilingual and Cross-lingual Methods in NLP, Association for Computational Linguistics, Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 7–12 August 2016; pp. 65–74. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Liang, W.; Shi, Y.; Huang, Q. Comparison of directed and weighted co-occurrence networks of six languages. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2014, 393, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Cong, J. Language clustering with word co-occurrence networks based on parallel texts. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2013, 58, 1139–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christodoulopoulos, C.; Steedman, M. A massively parallel corpus: The Bible in 100 languages. Lang. Resour. Eval. 2015, 49, 375–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamallo, P.; Pichel, J.R.; Alegria, I. From Language Identification to Language Distance. Phys. A 2017, 484, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamallo, P.; Alegria, I.; Pichel, J.R.; Agirrezabal, M. Comparing Two Basic Methods for Discriminating Between Similar Languages and Varieties. In The Third Workshop on NLP for Similar Languages, Varieties and Dialects (VarDial3); The COLING 2016 Organizing Committee: Osaka, Japan, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Pichel, J.R.; Gamallo, P.; Alegria, I. Measuring diachronic language distance using perplexity: Application to English, Portuguese, and Spanish. Nat. Lang. Eng. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmasi, S.; Zampieri, M.; Ljubešić, N.; Nakov, P.; Ali, A.; Tiedemann, J. Discriminating between Similar Languages and Arabic Dialect Identification: A Report on the Third DSL Shared Task. In Proceedings of the 3rd Workshop on Language Technology for Closely Related Languages, Varieties and Dialects (VarDial), Osaka, Japan, 11–16 December 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Daelemans, W.; Kestemont, M.; Manjavancas, E.; Potthast, M.; Rangel, F.; Rosso, P.; Specht, G.; Stamatatos, E.; Stein, B.; Tschuggnall, M.; et al. Overview of PAN 2019: Author Profiling, Celebrity Profiling, Cross-domain Authorship Attribution and Style Change Detection. In Proceedings of the Tenth International Conference of the CLEF Association (CLEF 2019), Lugano, Switzerland, 9–12 September 2019; Crestani, F., Braschler, M., Savoy, J., Rauber, A., Müller, H., Losada, D., Heinatz, G., Cappellato, L., Ferro, N., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zampieri, M.; Malmasi, S.; Scherrer, Y.; Samardžić, T.; Tyers, F.; Silfverberg, M.; Klyueva, N.; Pan, T.L.; Huang, C.R.; Ionescu, R.T.; et al. A Report on the Third VarDial Evaluation Campaign. In Proceedings of the Sixth Workshop on NLP for Similar Languages, Varieties and Dialects, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 7 June 2019; Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2019; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evert, S.; Proisl, T.; Jannidis, F.; Reger, I.; Pielström, S.; Schöch, C.; Vitt, T. Understanding and explaining Delta measures for authorship attribution. Digit. Scholarsh. Humanit. 2017, 32, ii4–ii16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrows, J. Delta: A Measure of Stylistic Difference and a Guide to Likely Authorship. Lit. Ling. Comput. 2002, 17, 267–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, J.H. Hierarchical Grouping to Optimize an Objective Function. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1963, 58, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eder, M. Rolling stylometry. Digit. Scholarsh. Humanit. 2016, 31, 457–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo Tello, J. Entendiendo Delta desde las Humanidades. Caracteres Estud. Cult. Y Crit. De La Crit. Digit. 2016, 5, 140–176. [Google Scholar]
- Eder, M. Visualization in stylometry: Cluster analysis using networks. Digit. Scholarsh. Humanit. 2015, 32, 50–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kullback, S.; Leibler, R. On Information and Sufficiency. Ann. Math. Stat. 1951, 22, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanromán, Á.I.; Gamallo, P.; Simões, A. Estratégias Lexicométricas para Detetar Especificidades Textuais. Linguamática 2018, 10, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavnar, W.B.; Trenkle, J.M. N-gram-based text categorization. In Proceedings of the Third Symposium on Document Analysis and Information Retrieval, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 11–13 April 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Szmrecsanyi, B. Grammatical Variation in British English Dialects: A Study in Corpus-Based Dialectometry; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Sturua, N. On the Basque-Caucasian Hypothesis. Stud. Ling. 1991, 45, 164–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trask, R.L. The History of Basque; Psychology Press: East Sussex, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Tomić, O.M. The Balkan Sprachbund morpho-syntactic properties. In Balkan Syntax and Semantics; Tomić, O.M., Ed.; John Benjamins: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004; pp. 1–55. [Google Scholar]
| Rank | Danish (Ger) | Croatian (Sla) | Latin (Lat) | Irish (Cel) | Finnish (Fin) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | norwegian 0.00 | serbian 0.00 | french 0.25 | gaelic 0.01 | estonian 0.05 |
| 2 | swedish 0.23 | slovenian 0.22 | portuguese 0.32 | welsh 0.70 | |
| 3 | english 0.48 | macedonian 0.26 | italian 0.37 | ||
| 4 | french 0.48 | bulgarian 0.29 | spanish 0.37 | ||
| 5 | german 0.51 | basque 0.45 | galician 0.41 | ||
| 6 | luxemburgish 0.55 | georgian 0.47 | english 0.42 | ||
| 7 | frisian 0.71 | russian 0.57 | catalan 0.44 | ||
| 8 | dutch 0.73 | czech 0.58 | romanian 0.45 | ||
| 9 | icelandic 0.76 | ukrainian 0.61 | |||
| 10 | slovak 0.63 | ||||
| 11 | polish 0.66 | ||||
| 12 | latvian 0.70 |
| Rank | Albanian | Armenian | Basque | Georgian | Greek | Hungarian |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | czech 0.11 | basque 0.14 | georgian 0.03 | basque 0.02 | latvian 0.09 | albanian 0.06 |
| 2 | lithuanian 0.11 | latvian 0.17 | czech 0.07 | russian 0.06 | basque 0.10 | frisian 0.47 |
| 3 | portuguese 0.22 | dutch 0.21 | macedonian 0.10 | bulgarian 0.07 | swedish 0.15 | french 0.52 |
| 4 | catalan 0.24 | polish 0.22 | albanian 0.12 | czech 0.10 | czech 0.18 | polish 0.52 |
| 5 | french 0.25 | czech 0.22 | portuguese 0.13 | macedonian 0.11 | albanian 0.19 | macedonian 0.52 |
| 6 | bulgarian 0.26 | frisian 0.23 | russian 0.14 | serbian 0.15 | russian 0.22 | danish 0.52 |
| 7 | basque 0.27 | swedish 0.23 | bulgarian 0.15 | latvian 0.16 | french 0.23 | basque 0.53 |
| 8 | spanish 0.27 | danish 0.24 | greek 0.17 | lithuanian 0.19 | bulgarian 0.26 | finnish 0.53 |
| 9 | russian 0.28 | croatian 0.25 | spanish 0.18 | albanian 0.20 | georgian 0.30 | portuguese 0.53 |
| 10 | dutch 0.33 | finnish 0.26 | croatian 0.20 | greek 0.22 | spanish 0.31 | norwegian 0.54 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gamallo, P.; Pichel, J.R.; Alegria, I. Measuring Language Distance of Isolated European Languages. Information 2020, 11, 181. https://doi.org/10.3390/info11040181
Gamallo P, Pichel JR, Alegria I. Measuring Language Distance of Isolated European Languages. Information. 2020; 11(4):181. https://doi.org/10.3390/info11040181
Chicago/Turabian StyleGamallo, Pablo, José Ramom Pichel, and Iñaki Alegria. 2020. "Measuring Language Distance of Isolated European Languages" Information 11, no. 4: 181. https://doi.org/10.3390/info11040181
APA StyleGamallo, P., Pichel, J. R., & Alegria, I. (2020). Measuring Language Distance of Isolated European Languages. Information, 11(4), 181. https://doi.org/10.3390/info11040181






