Analysis of Cultural Meme Characteristics for Big Data of Cultural Relics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Relation Work
3. Data and Methods
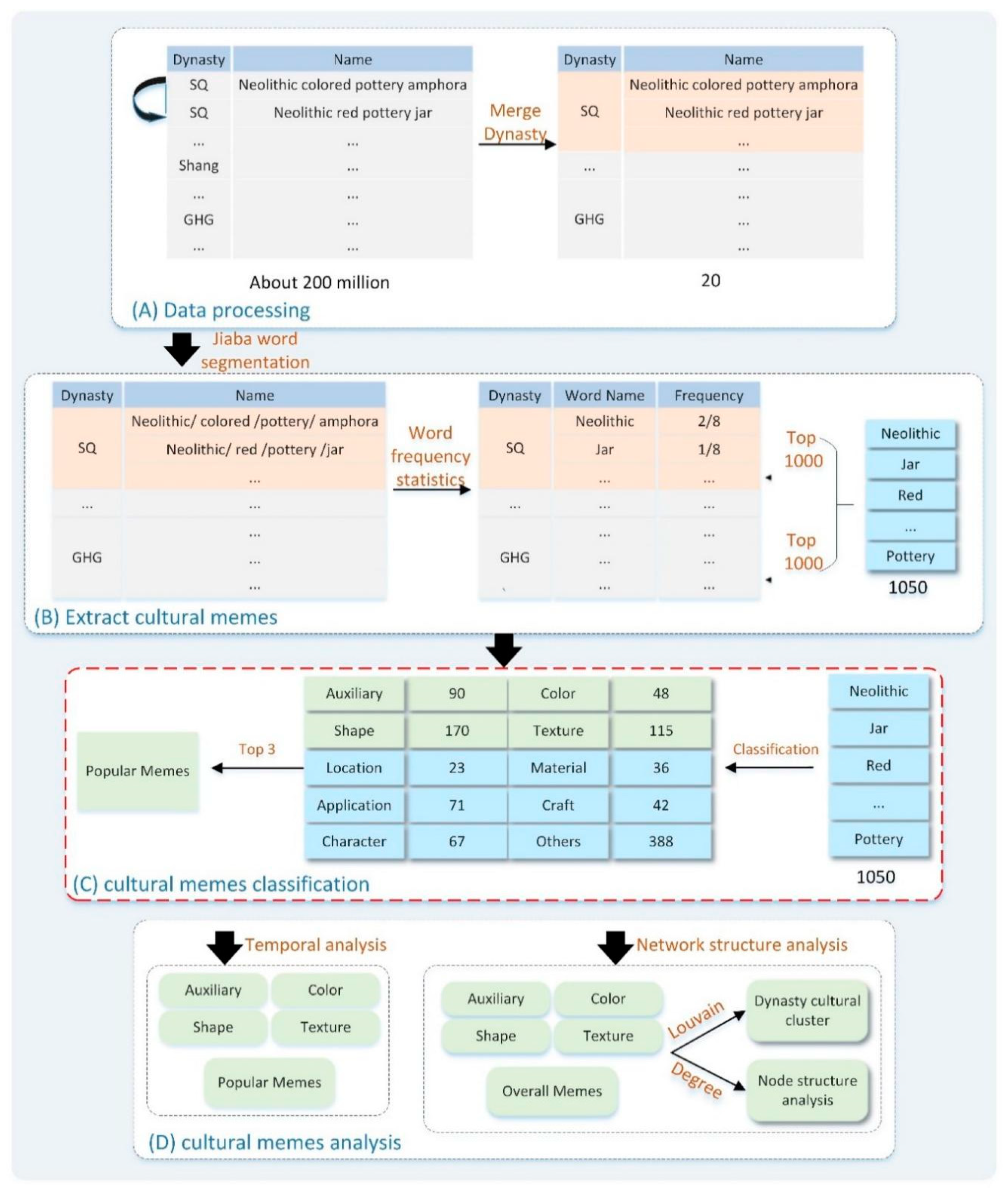
3.1. Data Sources and Processing
3.2. Relevant Concepts
3.2.1. Cultural Meme
3.2.2. Cultural Meme Types
3.2.3. Prevalence Memes
3.3. Research Framework
3.4. Method
3.4.1. Cultural Meme Extraction
3.4.2. Louvain Community Detection Algorithm
3.4.3. Degree of Centrality Analysis
4. Analysis of Cultural Characteristics of Dynasties
4.1. Timing Analysis of Cultural Meme Characteristics
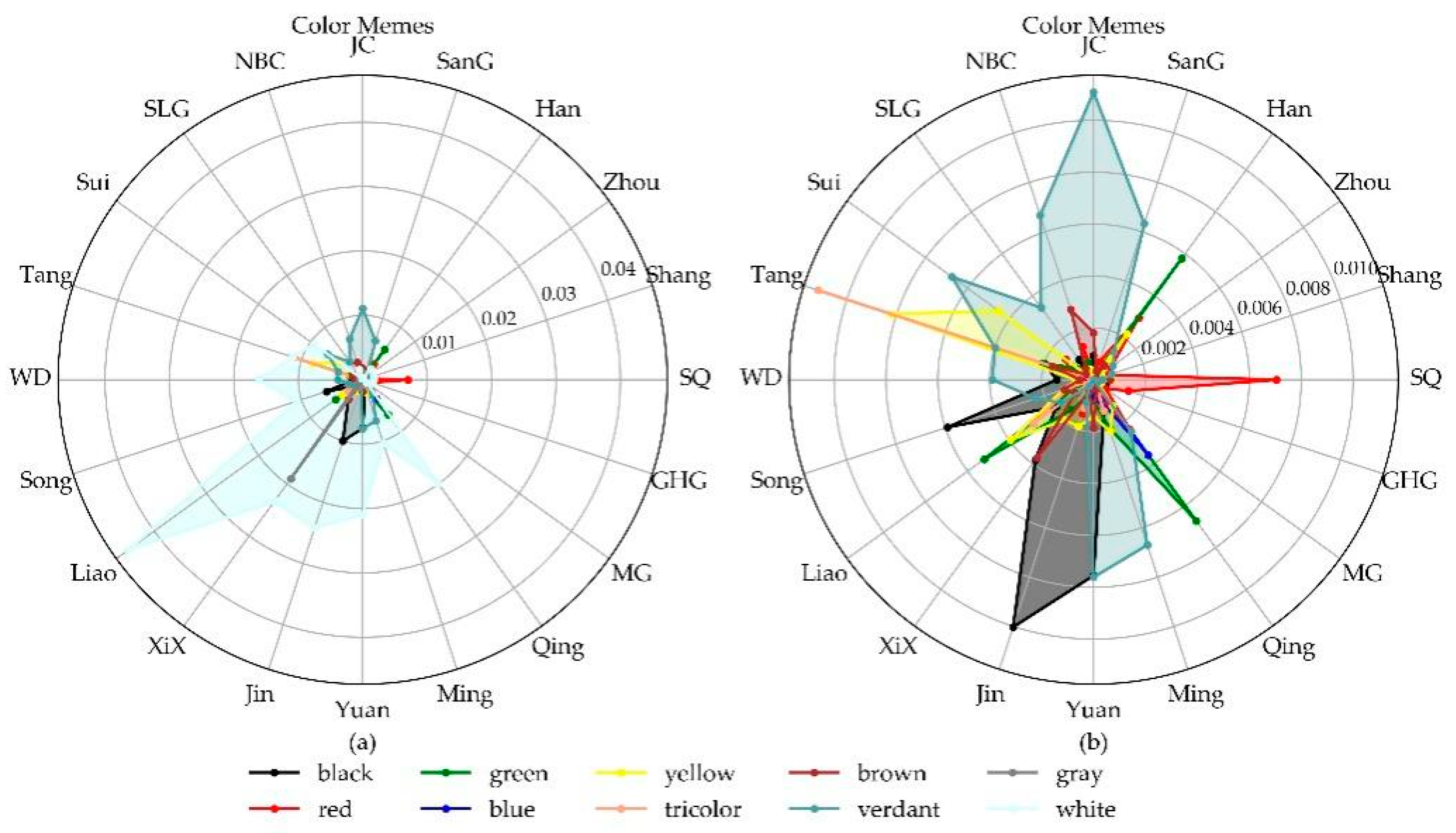
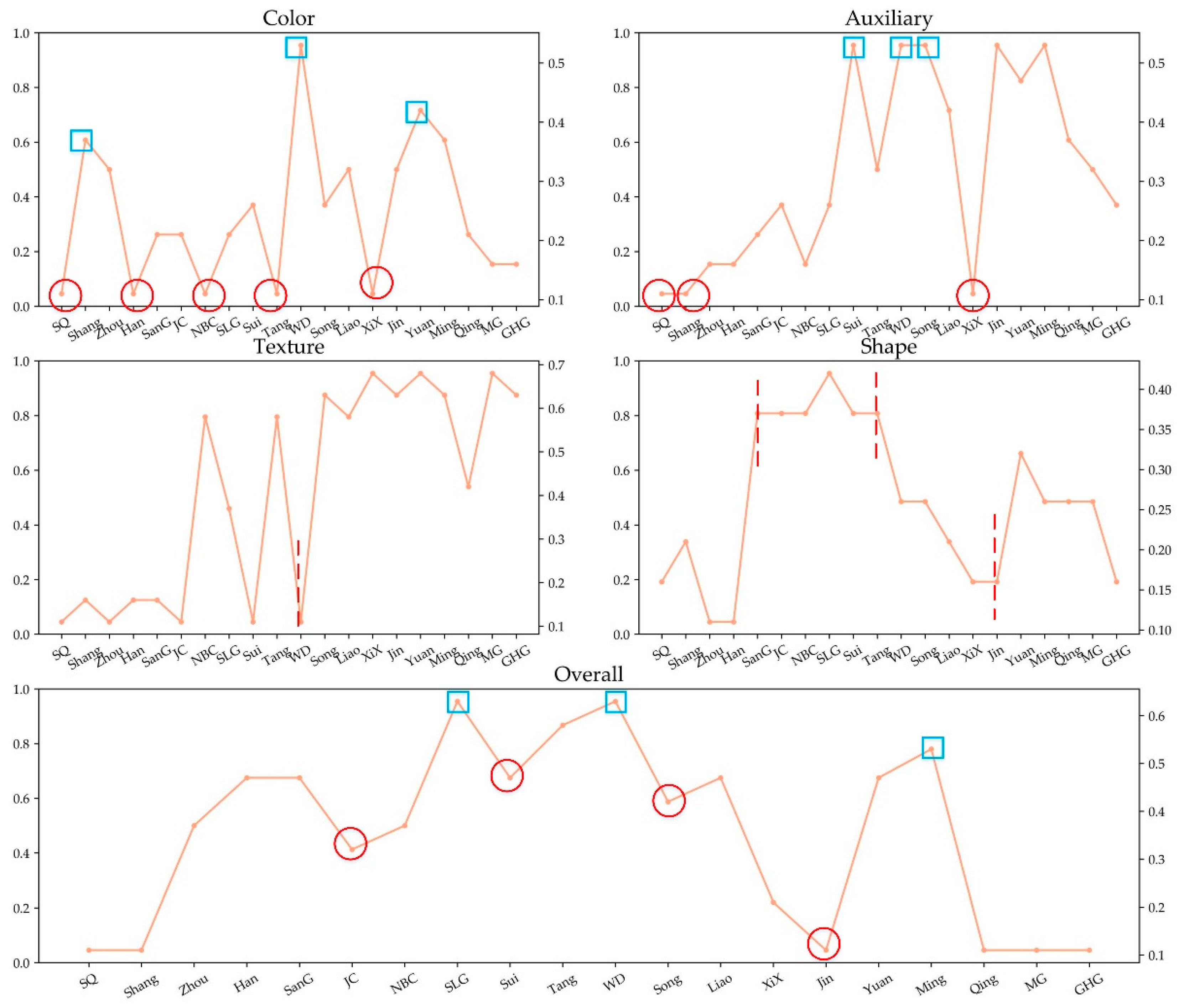
4.1.1. Color Memes
4.1.2. Texture Memes
4.1.3. Auxiliary Memes
4.1.4. Shape Memes
4.1.5. Prevalence Memes
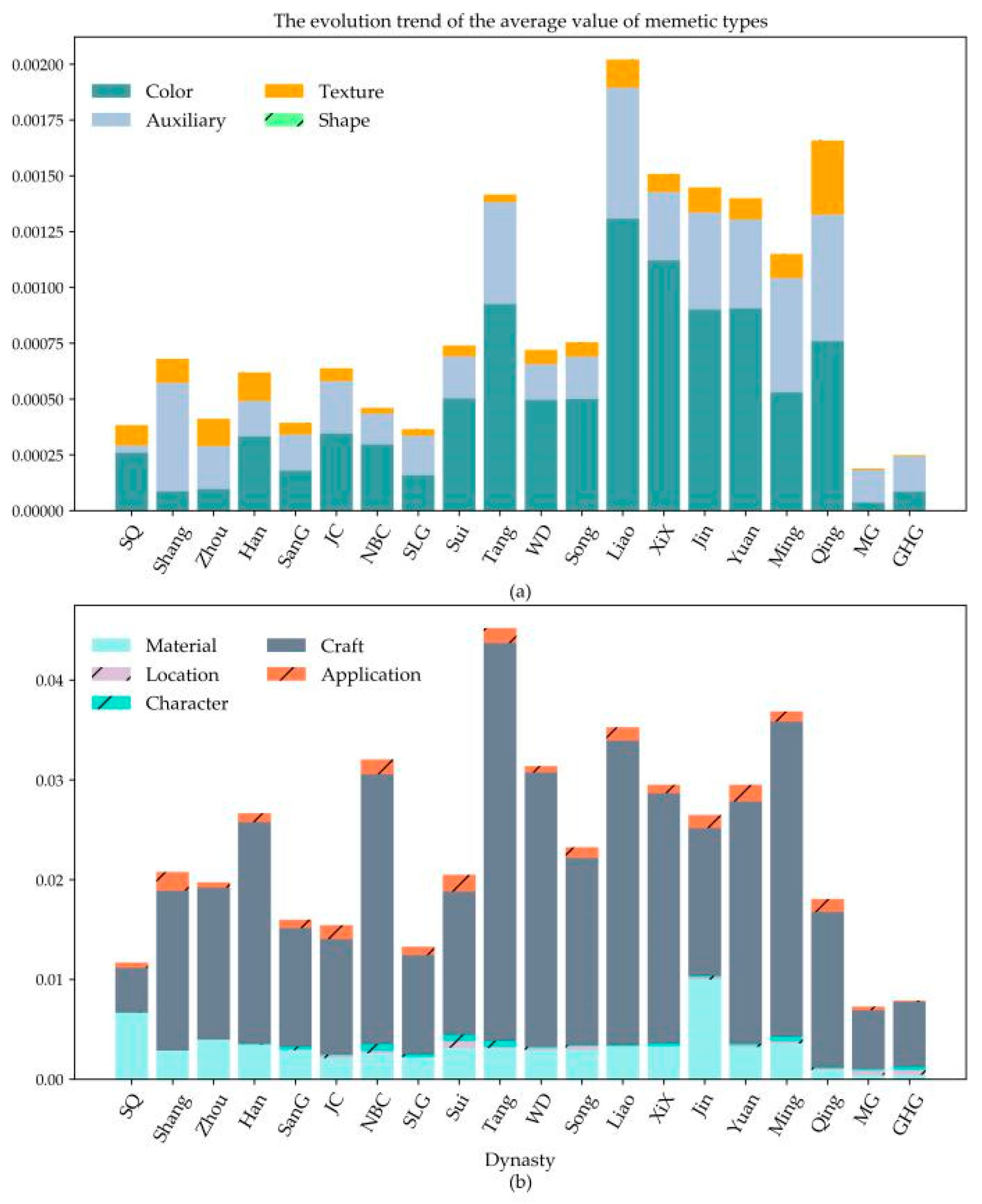
4.2. Analysis of the Characteristic Structure of Cultural Memes
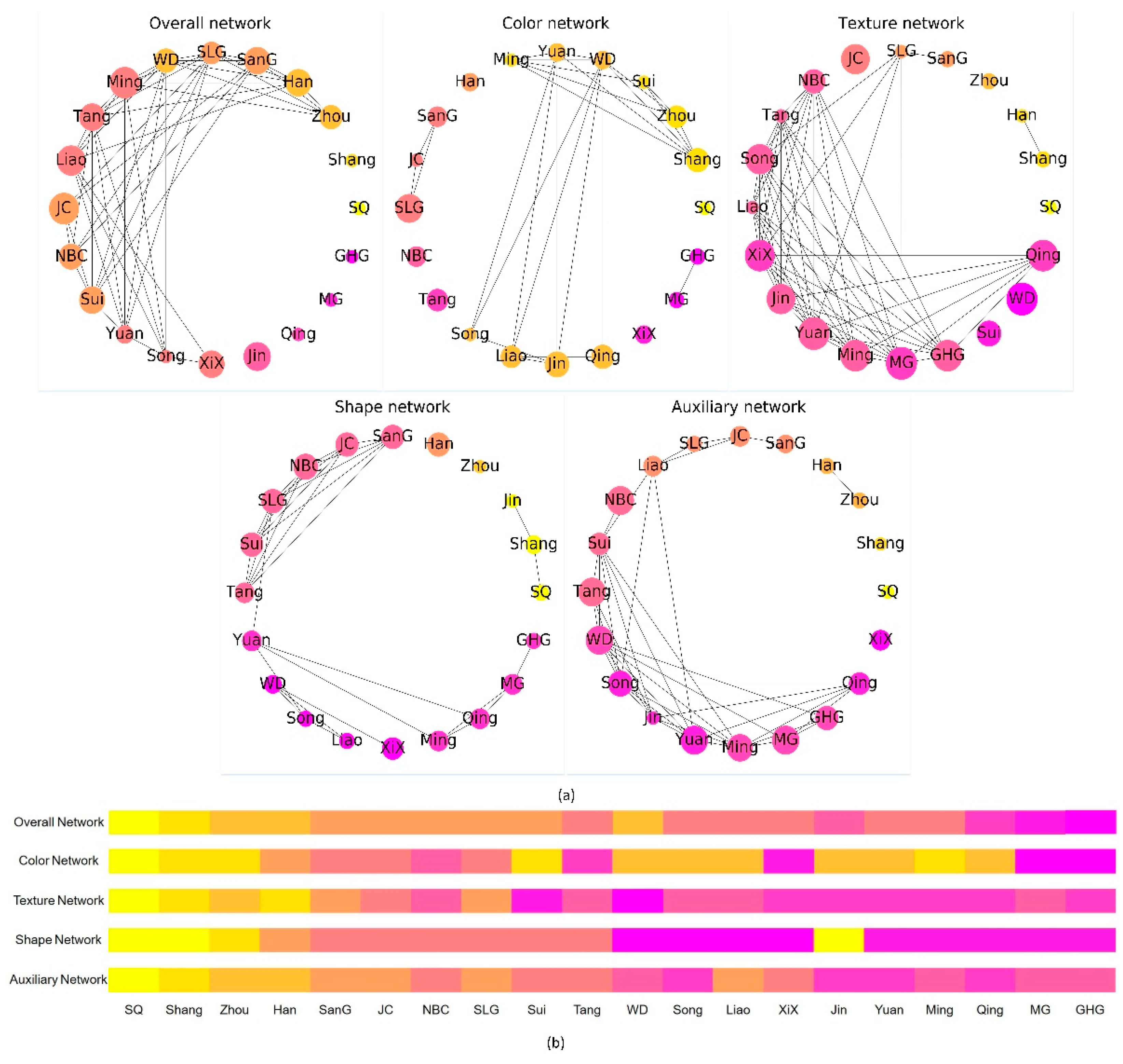
4.2.1. Clustering of Dynasties′ Cultures
4.2.2. Features of the Cultural Structure of Dynasties
5. Conclusions and Discussions
- The temporal variation of cultural meme types expounds the cultural characteristics of the coexistence of inheritance and differences between the dynasties. Among them, the color meme reflects that the color culture of dynasties is closely related to the five virtues advocated by dynasties, verifying the possibility of reflecting the culture of the dynasty from the names of relics. Auxiliary memes and texture memes reflected the transformation of people’s pursuit from simple life needs to spiritual development.
- By calculating the average value of cultural meme types of dynasties, it is found that craft, material, and application memes were very popular in all dynasties. After the Tang dynasty, color memes were more popular and abundant than it during the previous dynasties. Texture memes showed a U-shaped distribution trend on the whole, which represented the inheritance of prevalence memes in all dynasties.
- Statistical analysis of prevalence memes of successive dynasties helped to determine the popular cultural memes of a dynasty’s culture and define the culture of the dynasties. To a certain extent, it helped us reproduce the cultural characteristics of the dynasties, which is conducive to a more comprehensive understanding of dynasty culture.
- The Louvain community detection algorithm was used to obtain the cultural similarity of clusters of dynasties in five different types of cultural meme networks. It was found that the cultural similarity of dynasties belonging to the same community cluster presented continuous characteristics.
- By analyzing the level of centrality of dynasty nodes in different networks, we could not only detect the similarity clusters of different culture types, but also find out the most important dynasty nodes within a cluster, and could judge the similarity and uniqueness of dynasty culture in different types of cultures.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Dynasty Name | Abbreviation | Dynasty Name | Abbreviation | Dynasty Name | Abbreviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stone Age | SQ | The period of the Sixteen States | SLG | Jin dynasty | Jin |
| Shang dynasty | Shang | Sui dynasty | Sui | Yuan dynasty | Yuan |
| Zhou dynasty | Zhou | Tang dynasty | Tang | Ming dynasty | Ming |
| Han dynasty | Han | The period of the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms | WD | Qing dynasty | Qing |
| The period of the Three Kingdoms | SanG | Song dynasty | Song | Republic of China | MG |
| Jurchen Jin dynasty | JC | Liao dynasty | Liao | The People′s Republic of China | GHG |
| The Northern and Southern dynasties | NBC | The Western Xia | XiX |
References
- Nisbett, R.E.; Masuda, T. Culture and point of view. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 11163–11170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mead, R.; Jones, C.J. Cross-Cultural Communication. In The Blackwell Handbook of Cross-Cultural Management; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 283–291. [Google Scholar]
- Henrich, J.; McElreath, R. The evolution of cultural evolution. Evol. Anthropol. 2003, 12, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assmann, A. Cultural memory. In Social Trauma–An Interdisciplinary Textbook; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 25–36. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y.Y. Cultural evolution and spatial-temporal distribution of archaeological sites from 9.5–2.3 ka BP in the Yan-Liao region, China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2019, 29, 449–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.-L. The Remains of Material Culture in Liao Dynasty and Its Silk Road Cultural Factors. J. Chifeng Univ. 2019, 8, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Mizoguchi, K. Making Sense of Material Culture Transformation: A Critical Long-Term Perspective from Jomon- and Yayoi-Period Japan. J. World Prehistory 2020, 33, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. A Study on Tourism Development of Shanxi Intangible Cultural Heritages Based on Geographical Influence. J. Jincheng Inst. Technol. 2019, 5, 70–72. [Google Scholar]
- Heredia-Carroza, J.; Martos, L.P.; Aguado, L.F. How to Measure Intangible Cultural Heritage Value? The Case of Flamenco in Spain. Empir. Stud. Arts 2020, 027623742090786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, D.; Naquin, S. The Material Manifestations of Regional Culture. J. Chin. Hist. 2019, 3, 363–379. [Google Scholar]
- De Wever, P.; Guiraud, M. Geoheritage and museums. In Geoheritage; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 129–145. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, K. Introduction: Museum management. In Museum Management; Routledge: London, UK, 2005; pp. 12–23. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F. The Concept and the Study Methods of Regional Culture. Zhejiang Soc. Sci. 2008, 4, 63–66. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, K. The Museum and the Intangible Cultural Heritage. Mus. Int. 2004, 56, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windhager, F.; Federico, P.; Schreder, G.; Glinka, K.; Dörk, M.; Miksch, S.; Mayr, E. Visualization of cultural heritage collection data: State of the art and future challenges. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2018, 25, 2311–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briola, D.; Deufemia, V.; Mascardi, V.; Paolino, L. Agent-oriented and ontology-driven digital libraries: The IndianaMAS experience. Softw. Pract. Exp. 2017, 47, 1773–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gossa, L.; Boer, V.D.; Aart, C.J.V. Exploring West African Folk Narrative Texts Using Machine Learning. Information 2020, 11, 236. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Yang, H.; Li, J.Y.; Kolmani, S. Preliminary Study on the Knowledge Graph Construction of Chinese Ancient History and Culture. Information 2020, 11, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankovic, R. Machine Learning Models for Cultural Heritage Image Classification: Comparison Based on Attribute Selection. Information 2019, 11, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawkins, R. The Selfish Gene; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ghawi, R.; Pfeffer, J. Extraction Patterns to Derive Social Networks from Linked Open Data Using SPARQL. Information 2020, 11, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ampornphan, P.; Tongngam, S. Exploring Technology Influencers from Patent Data Using Association Rule Mining and Social Network Analysis. Information 2020, 11, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.L.; Huang, Y.; Hu, D.Y.; Wan, D. Evaluation of social network conservation in historical areas of mountainous towns in Chongqing, China. J. Mt. Sci. 2020, 17, 1763–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suaib, N.; Ismail, N.; Sadimon, S.; Yunos, Z.M. Cultural heritage preservation efforts in Malaysia: A survey. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 979, 012008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jewell, E.J.; Abate, F.R.; Mckean, E. The New Oxford American Dictionary. Ref. Rev. 2002, 33, 20–21. [Google Scholar]
- Heylighen, F.; Chielens, K. Cultural Evolution and Memetics. In Encyclopedia of Complexity and Systems Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Mundinger, P.C. Animal cultures and a general theory of cultural evolution. Ethol. Sociobiol. 1980, 1, 183–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heylighen, F. What Makes a Meme Successful? Selection Criteria for Cultural Evolution. 1998. Available online: http://pespmc1.vub.ac.be/Papers/Memetics-Namur.pdf (accessed on 17 December 2020).
- Malhotra, N. An Empirical Analysis of “Tort Tales” How Cultural Memes Influence Attitudes on Tort Reform. J. Law Court. 2015, 3, 149–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.-J. Powerful Memes of Culture and Their Application to Trademarks. J. Wuxi Vocat. Inst. Commer. 2018, 2, 100–103. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, S.; Park, J. Evolutionary Dynamics of Cultural Memes and Application to Massive Movie Data. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1903.02197. [Google Scholar]
- Theisen, W.; Brogan, J.; Thomas, P.B.; Moreira, D.; Phoa, P.; Weninger, T.; Scheirer, W. Automatic discovery of political meme genres with diverse appearances. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2001.06122. [Google Scholar]
- Day, M.-Y.; Lee, C.-C. Deep learning for financial sentiment analysis on finance news providers. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Advances in Social Networks Analysis and Mining (ASONAM), San Francisco, CA, USA, 18–21 August 2016; pp. 1127–1134. [Google Scholar]
- Que, X.; Checconi, F.; Petrini, F.; Gunnels, J.A. Scalable Community Detection with the Louvain Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Parallel and Distributed Processing Symposium, Hyderabad, India, 25–29 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez, D.L.; Revuelta, J.; Prieta, F.D.L.; Gil-González, A.B.; Dang, C. Twitter User Clustering Based on Their Preferences and the Louvain Algorithm. PAAMS 2016, 473, 349–356. [Google Scholar]




| Dynasty | Copper | KuiLong | Yellow | … | Binaural | Accessories | Hollow Out |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SQ | 0.000105 | 0.000192 | … | 0.014313 | 0.000051 | 0.000158 | |
| Shang | 0.041962 | 0.001783 | 0.000047 | … | 0.001821 | 0.00049 | 0.00033 |
| Zhou | 0.103191 | 0.001135 | 0.000138 | … | 0.001607 | 0.000634 | 0.000744 |
| … | |||||||
| Qing | 0.012381 | 0.00135 | 0.000941 | … | 0.001338 | 0.000311 | 0.000303 |
| MG | 0.004657 | 0 | 0.000213 | … | 0.000239 | 0 | 0.00018 |
| GHG | 0.004407 | 0 | 0.000323 | … | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Dynasty | Five Virtue Attributes | Five Color Attributes | Top Three Colors | Dynasty | Five Virtue Attributes | Five Color Attributes | Top Three Colors |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SQ | Red Black White | Red White Yellow | Tang | Earth Fire | Yellow Red | White Tricolor Yellow | |
| Shang | Gold | White | White Verdant Red | WD | Gold Earth Water Wood | White Yellow Black Verdant | White Verdant Black |
| Zhou | Fire | Red | White Verdant Red | Song | Fire | Red | White Black Verdant |
| Han | Water Soil Fire | Black Yellow Red | Green Red Yellow | Liao | Water | Black | White Green Yellow |
| SG | Soil Fire | Yellow Red | Verdant Red Brown | Jin | Gold Earth | White Yellow | White Black Yellow |
| JinC | Gold | White | Verdant Brown Black | Yuan | Gold | White | White Verdant Black |
| NBC | Water Wood Fire | Black Verdant Red | Verdant Brown White | Ming | Fire | Red | White Verdant Yellow |
| SLG | Fire Water Wood Gold | Red Black Verdant White | Verdant Black Gray | Qing | Water | Black | White Green Blue |
| Sui | Fire | Red | White Verdant Yellow |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.; Shi, Z.; Chen, L.; Cui, Z.; Li, S.; Zhao, L. Analysis of Cultural Meme Characteristics for Big Data of Cultural Relics. Information 2020, 11, 584. https://doi.org/10.3390/info11120584
Li H, Shi Z, Chen L, Cui Z, Li S, Zhao L. Analysis of Cultural Meme Characteristics for Big Data of Cultural Relics. Information. 2020; 11(12):584. https://doi.org/10.3390/info11120584
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Haifeng, Zuoqin Shi, Li Chen, Zhenqi Cui, Sumin Li, and Ling Zhao. 2020. "Analysis of Cultural Meme Characteristics for Big Data of Cultural Relics" Information 11, no. 12: 584. https://doi.org/10.3390/info11120584
APA StyleLi, H., Shi, Z., Chen, L., Cui, Z., Li, S., & Zhao, L. (2020). Analysis of Cultural Meme Characteristics for Big Data of Cultural Relics. Information, 11(12), 584. https://doi.org/10.3390/info11120584






