A Fast Method for Estimating the Number of Clusters Based on Score and the Minimum Distance of the Center Point
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Background
4. The Estimation Method Based on Score and the Minimum Distance of Centers
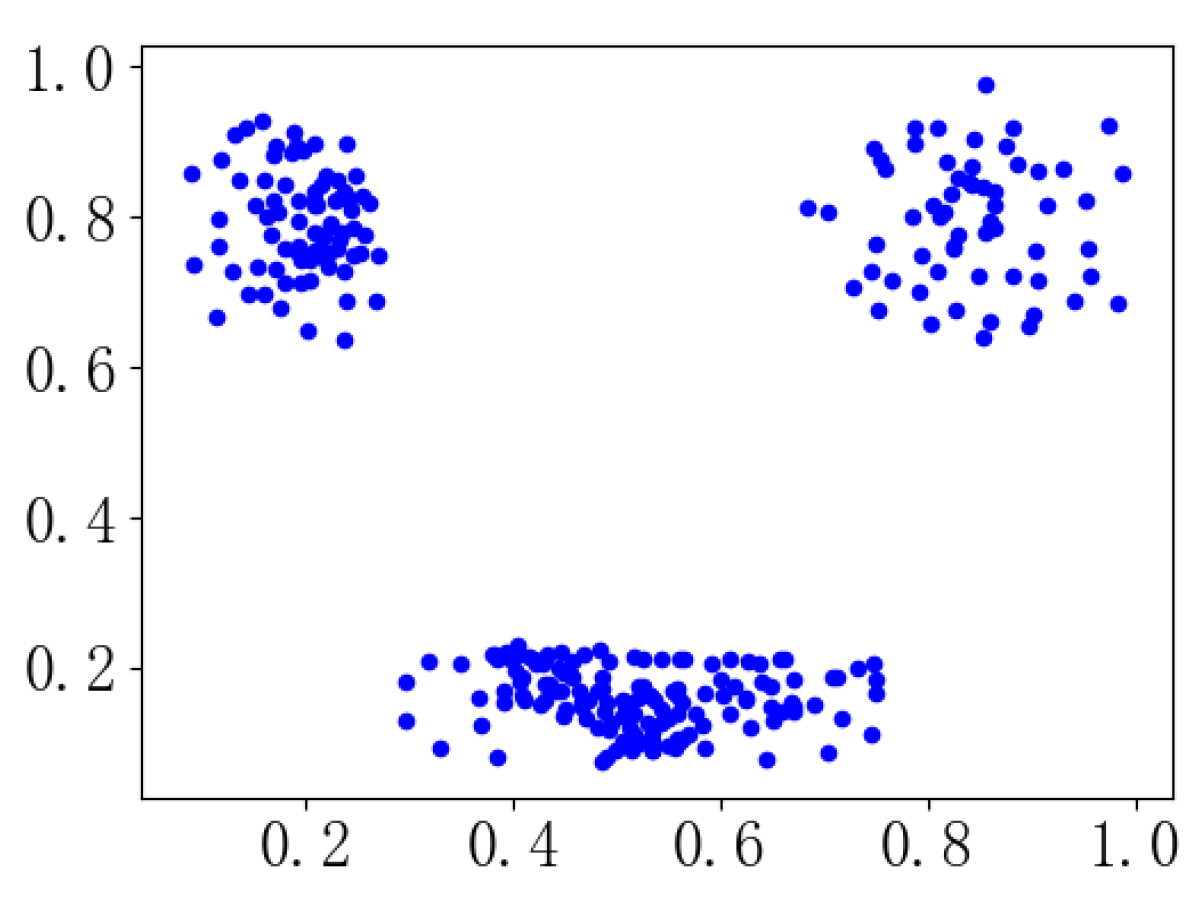
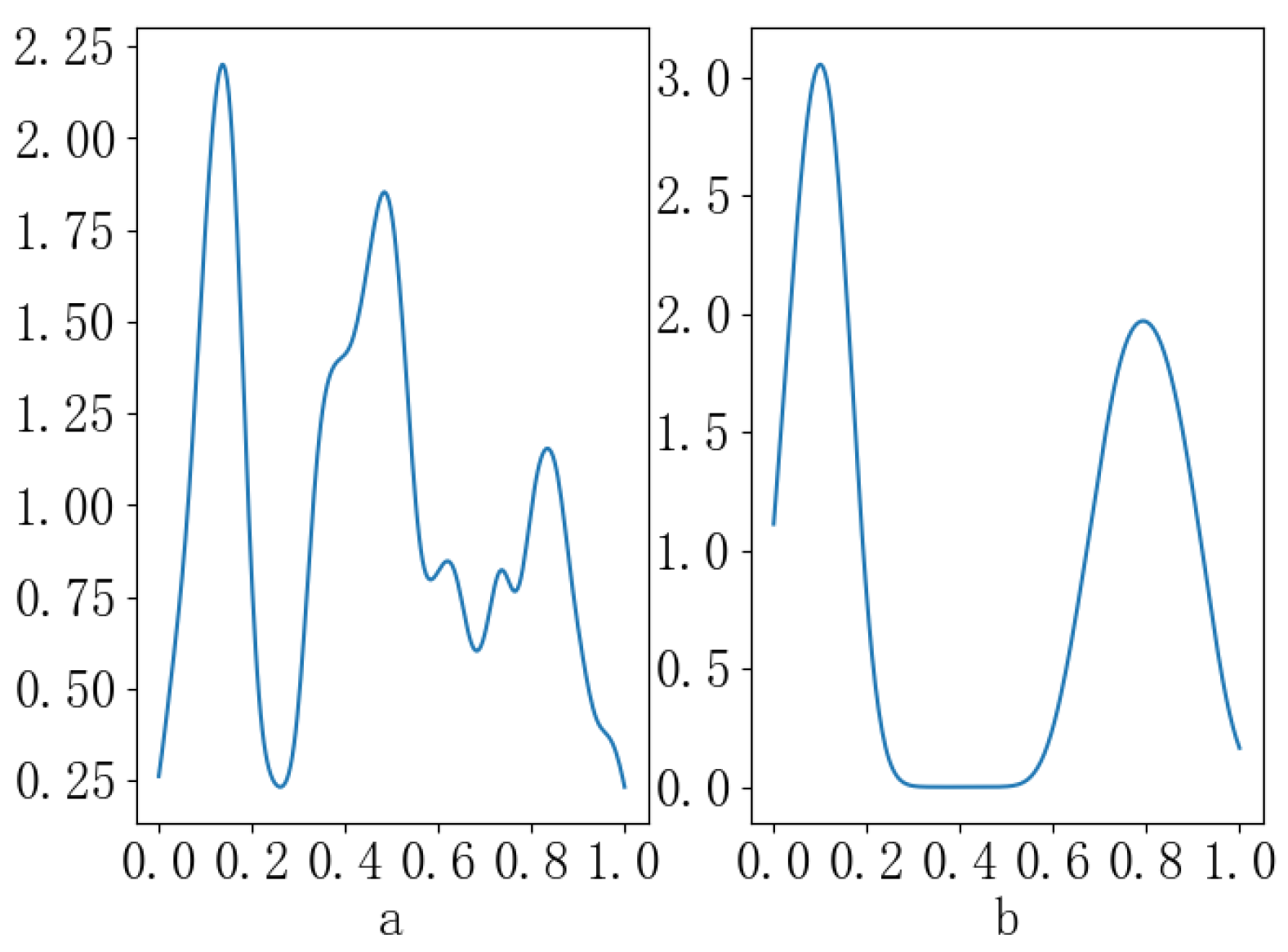
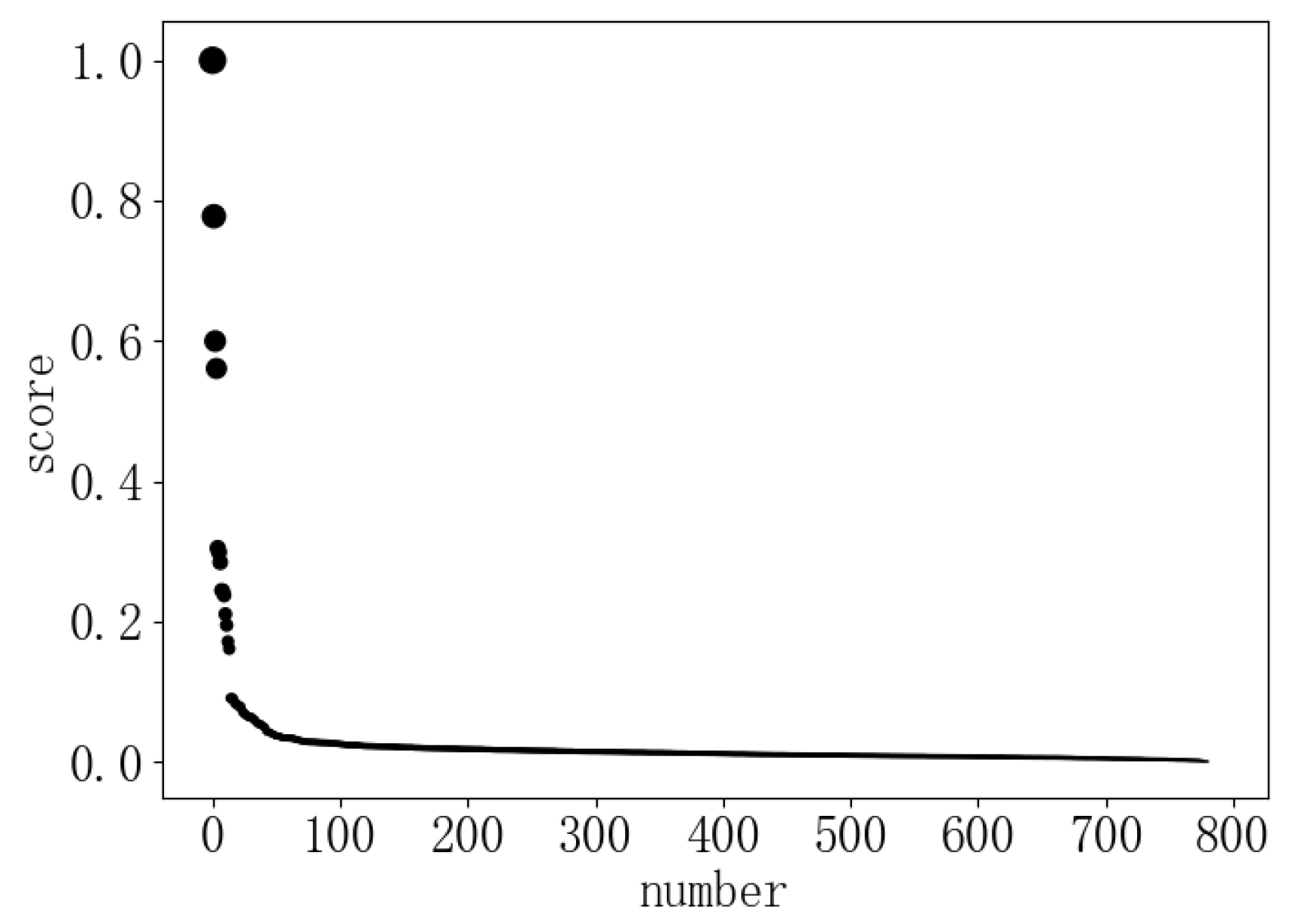
4.1. Gaussian Kernel Function Establishes Kmax
4.2. Calculation of Candidate Set of Center Points
4.3. Calculation of K Values
4.4. Framework for Cluster Number Estimation
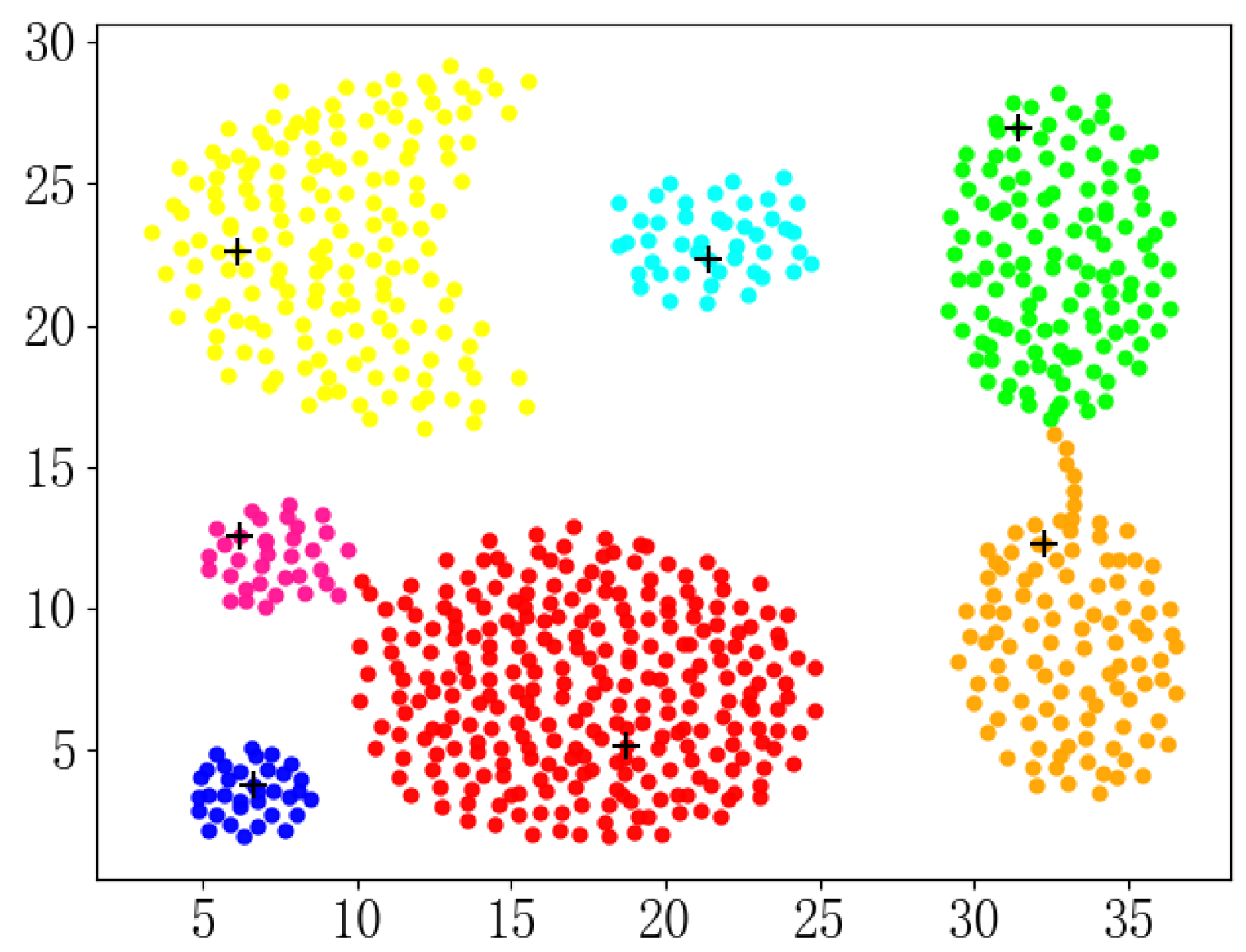
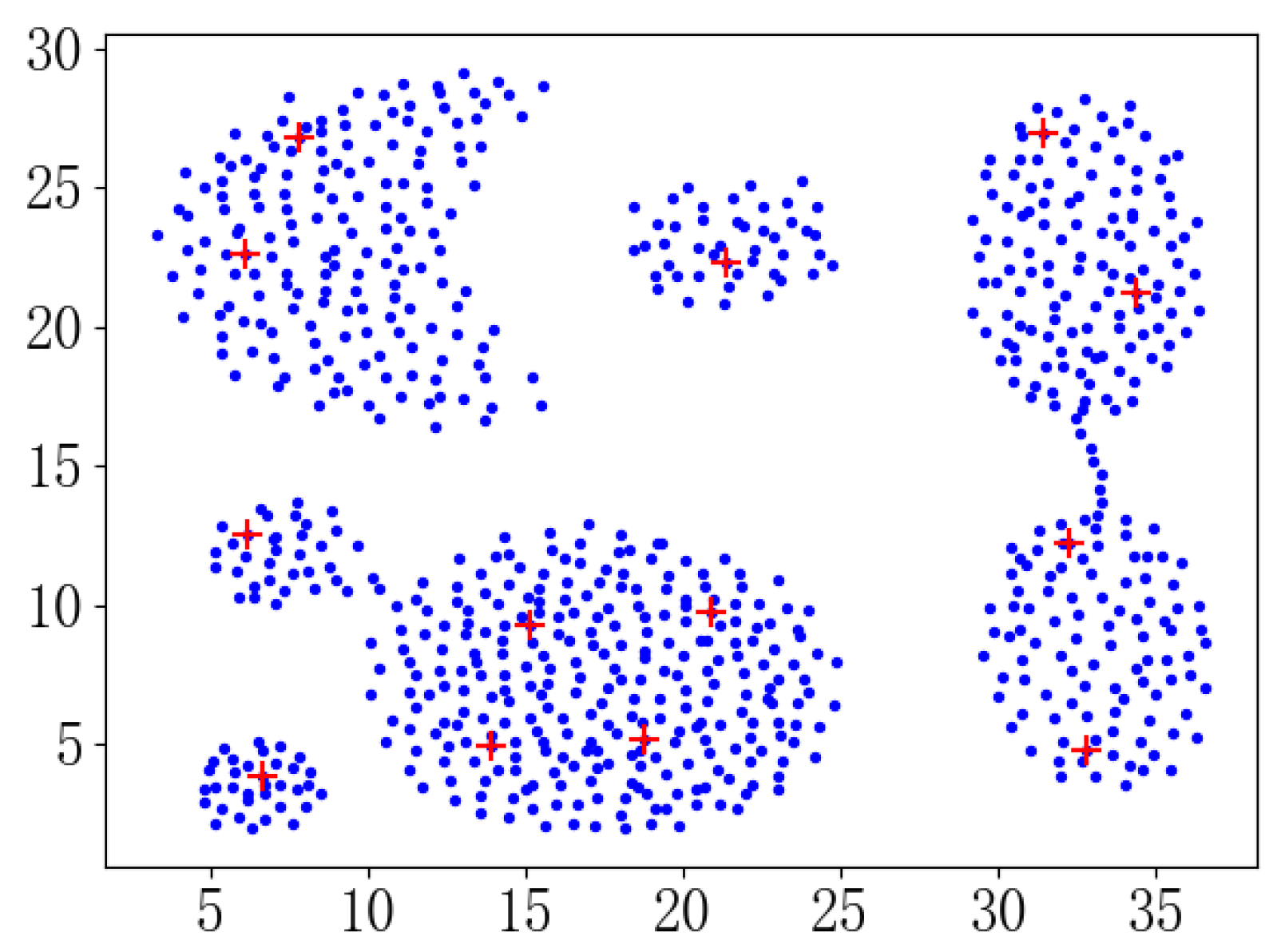
5. Experiments and Discussion
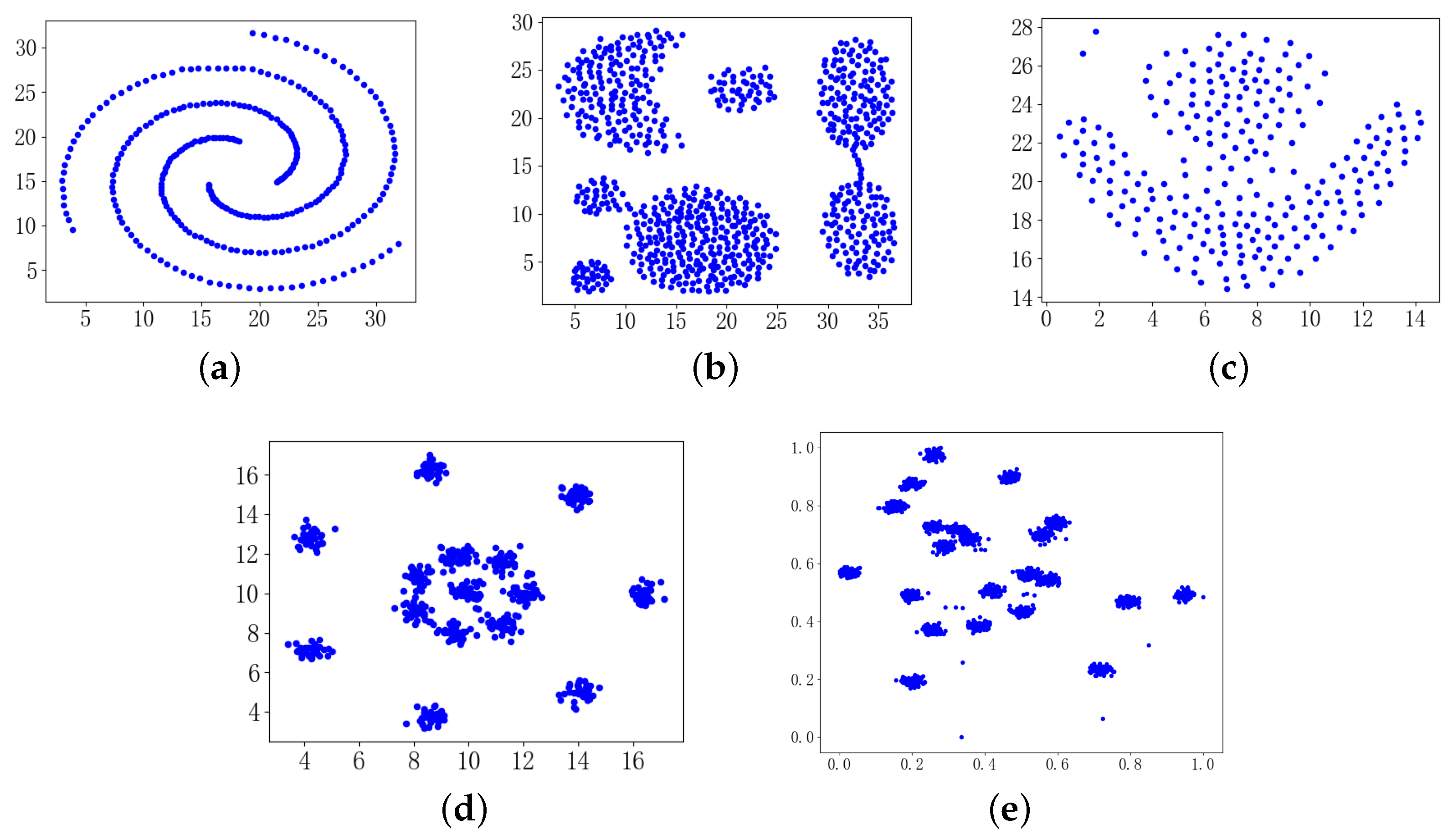
5.1. Experimental Environment, Dataset and Other Algorithms
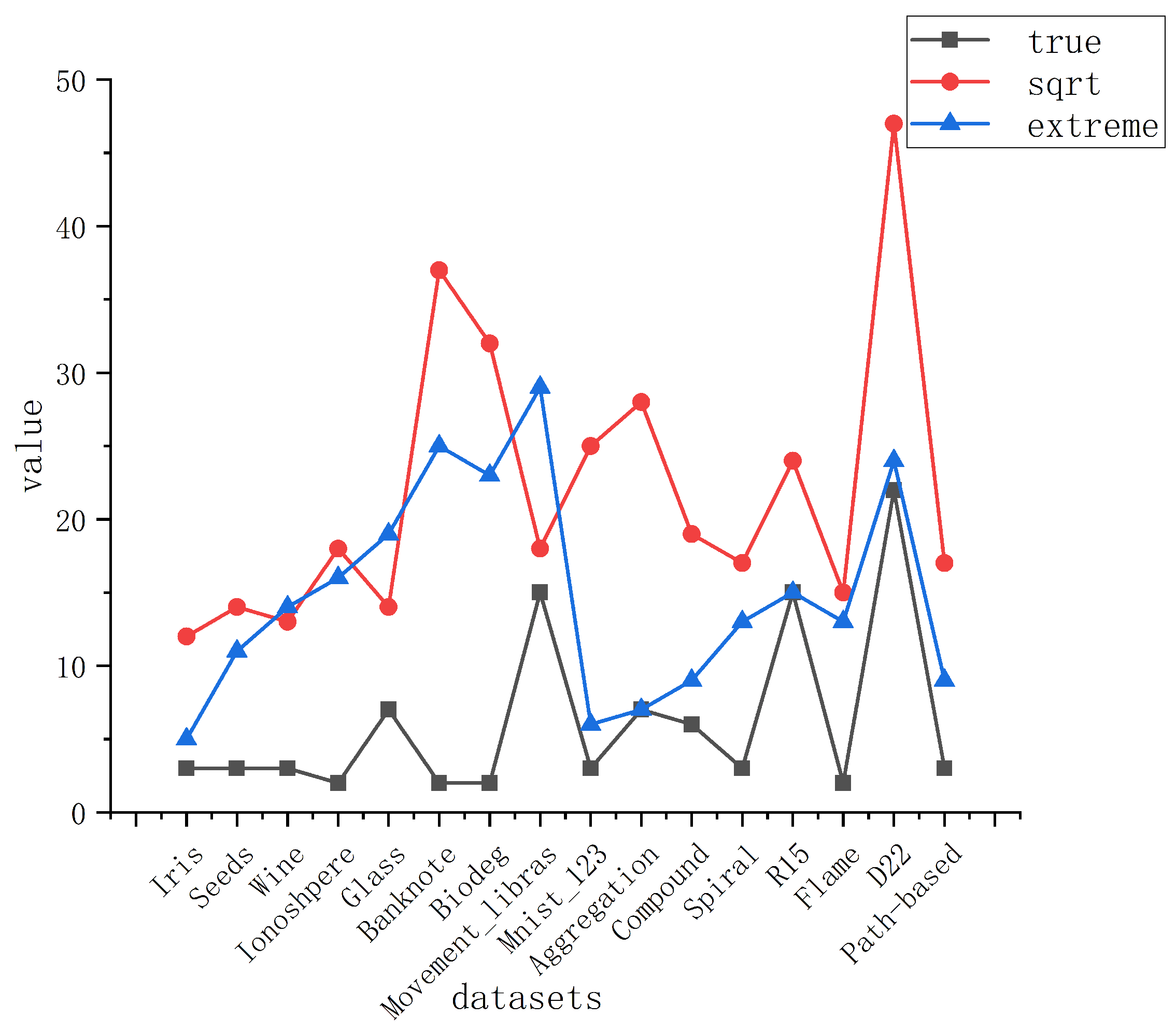
5.2. Experimental Results and Analysis
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jain, A.K. Data clustering: 50 years beyond K-means. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2010, 31, 651–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, M.; Liu, P.; Wang, Z.; Yi, J. A self-adaptive fuzzy c-means algorithm for determining the optimal number of clusters. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2016, 2016, 2647389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Miao, F.; Ma, H. Genetic algorithm with an improved initial population technique for automatic clustering of low-dimensional data. Information 2018, 9, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, A.; Laio, A. Machine learning Clustering by fast search and find of density peaks. Science 2014, 344, 1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.H.; Zhu, Q.P.; Huang, Y.J.; Xiao, J.; Wang, L.; Tong, F.C. Parameter-free Laplacian centrality peaks clustering. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2017, 100, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, A.; Takahashi, D.Y.; Patriota, A.G. A non-parametric method to estimate the number of clusters. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2014, 73, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maulik, U.; Bandyopadhyay, S. Performance evaluation of some clustering algorithms and validity indices. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2002, 24, 1650–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.L.; Beni, G. A validity measure for fuzzy clustering. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1991, 8, 841–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, D.L.; Bouldin, D.W. A cluster separation measure. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1979, 2, 224–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teklehaymanot, F.K.; Muma, M.; Zoubir, A.M. A Novel Bayesian Cluster Enumeration Criterion for Unsupervised Learning. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2017, 66, 5392–5406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masud, M.A.; Huang, J.Z.; Wei, C.; Wang, J.; Khan, I.; Zhong, M. I-nice: A new approach for identifying the number of clusters and initial cluster centres. Inf. Sci. 2018, 466, 129–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shi, Z.; Guo, X.; Liu, X.; Zhu, E.; Yin, J. Deep embedding for determining the number of clusters. In Proceedings of the Thirty-Second AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–7 February 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kingrani, S.K.; Levene, M.; Zhang, D. Estimating the number of clusters using diversity. Artif. Intell. Res. 2018, 7, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Xu, Z. A novel internal validity index based on the cluster centre and the nearest neighbour cluster. Appl. Soft Comput. 2018, 71, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liang, W.; Zhang, X.; Qing, S.; Chang, P.C. A cluster validity evaluation method for dynamically determining the near-optimal number of clusters. Soft Comput. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ünlü, R.; Xanthopoulos, P. Estimating the number of clusters in a dataset via consensus clustering. Expert Syst. Appl. 2019, 125, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Luo, Z.; Huang, J.Z.; Shahzad, W. Variable weighting in fuzzy k-means clustering to determine the number of clusters. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugar, C.A.; James, G.M. Finding the number of clusters in a dataset: An information-theoretic approach. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2003, 98, 750–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Q.; Li, X.; Yuan, B. A highly scalable clustering scheme using boundary information. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2017, 89, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Xu, Z.; Liu, F. Method for determining the optimal number of clusters based on agglomerative hierarchical clustering. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2016, 28, 3007–3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Datta, S.; Das, S. Fast automatic estimation of the number of clusters from the minimum inter-center distance for k-means clustering. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2018, 116, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverman, B.W. Density Estimation for Statistics and Data Analysis; Chapman and Hall: London, UK, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Caliński, T.; Harabasz, J. A dendrite method for cluster analysis. Commun. Stat.-Theory Methods 1974, 3, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezdek, J.C. Mathematical models for systematics and taxonomy. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Numerical; Freeman: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1975; Volume 3, pp. 143–166. [Google Scholar]
- Dave, R.N. Validating fuzzy partitions obtained through c-shells clustering. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 1996, 17, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezdek, J.C. Cluster validity with fuzzy sets. J. Cybernet. 1973, 3, 58–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakhira, M.K.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Maulik, U. Validity index for crisp and fuzzy clusters. Pattern Recognit. 2004, 37, 487–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Xu, M.; Fränti, P. Sum-of-squares based cluster validity index and significance analysis. In International Conference on Adaptive and Natural Computing Algorithms; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 313–322. [Google Scholar]


| Notions | Description |
|---|---|
| P | node set |
| min | the minimum value of a set of values |
| max | the maximum value of a set of values |
| maximum number of clusters | |
| the size of the candidate point set | |
| K | number of clusters |
| F | the value of Discreteness |
| center point set with the number of center points being K | |
| point i | |
| the score of the kth point in descending order | |
| the change of the kth point in score | |
| average of the top Kmax score changes | |
| Euclidean distance between point i and point j | |
| the degree of change of the minimum distance when the number of center points is from k to k + 1 |
| Number | Dataset | Features | Clusters | Instances |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Iris | 4 | 3 | 150 |
| 2 | Seeds | 7 | 3 | 210 |
| 3 | Wine | 13 | 3 | 178 |
| 4 | Ionoshpere | 34 | 2 | 351 |
| 5 | Banknote | 4 | 2 | 1372 |
| 6 | Glass | 9 | 7 | 214 |
| 7 | Biodeg | 41 | 2 | 1055 |
| 8 | Movement_libras | 91 | 15 | 366 |
| 9 | Mnist_123 | 784 | 3 | 649 |
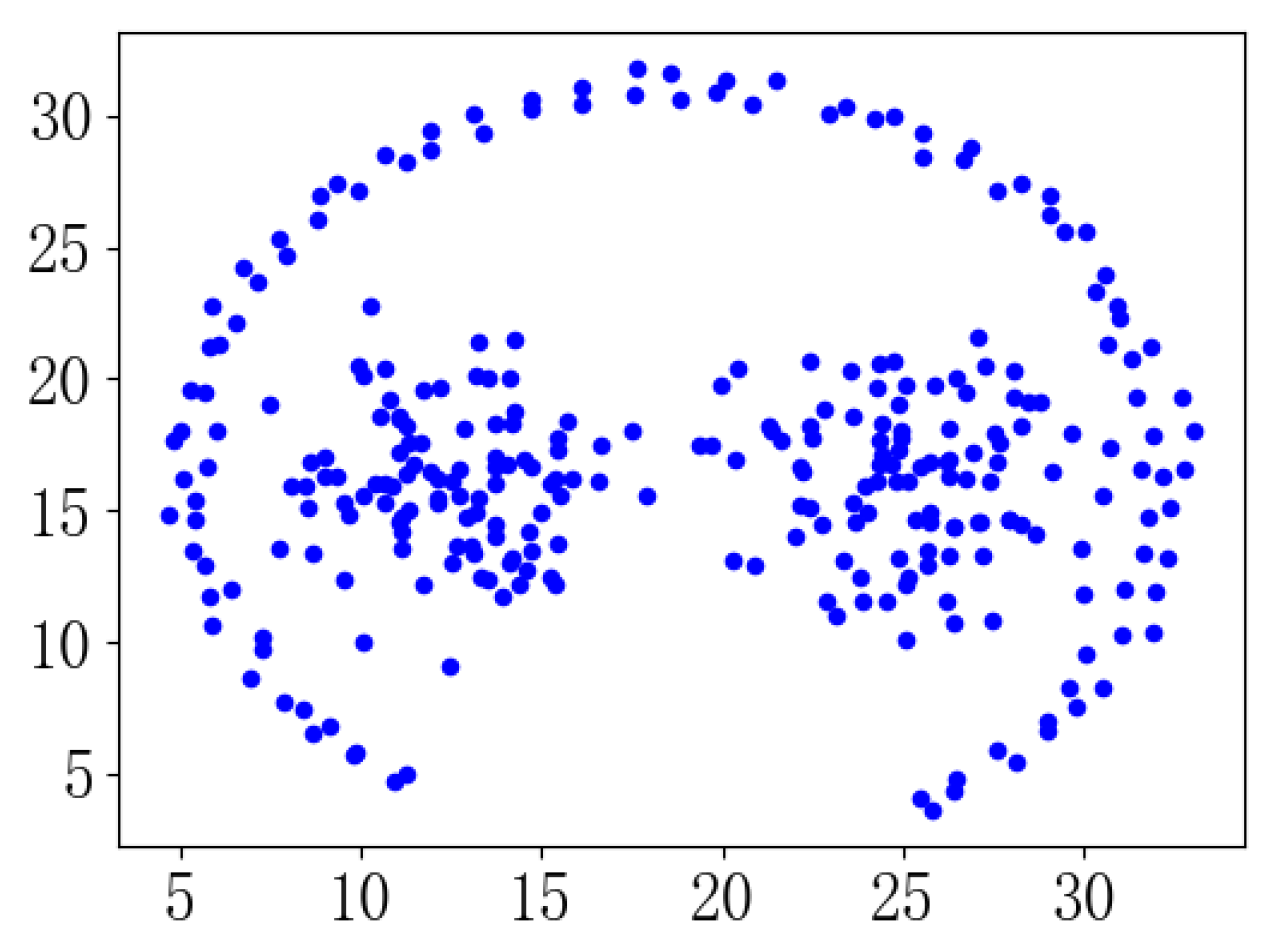
| 10 | Spiral | 2 | 3 | 312 |
| 11 | Aggregation | 2 | 7 | 788 |
| 12 | Flame | 2 | 2 | 240 |
| 13 | R15 | 2 | 15 | 600 |
| 14 | D22 | 2 | 22 | 2211 |
| Number | Approaches | Selection Criteria for K | Min No. of Clusters |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Bayesian Information Criterion (BIC) | max | 2 |
| 2 | Caliński Harabasz (CH) Index [23] | max | 2 |
| 3 | Classification Entropy (CE) [24] | min | 2 |
| 4 | Fuzzy Hypervolume (FHV) [25] | min | 1 |
| 5 | I Index [7] | max | 2 |
| 6 | Jump Method [18] | max | 2 |
| 7 | Partition Coefficient (PC) [26] | max | 2 |
| 8 | PBMF [27] | max | 2 |
| 9 | Zhao Xu Fränti (ZXF) Index [28] | Knee | 2 |
| 10 | Last leap (LL) [21] | max & 1 | 1 |
| 11 | Last Major Leap (LML) [21] | max & 1 | 1 |
| 12 | our approach | max & 1 | 1 |
| Approaches | Iris | Seeds | Wine | Ionoshpere | Banknote | Glass | Biodeg | Movement_libras | Mnist_123 | Spiral | Aggregation | Flame | R15 | D22 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BIC | 8–12 | 14 | 13 | 15–18 | 35–37 | 14 | 31/32 | 18 | 23–25 | 3 | 14 | 4 | 15 | 25–33 |
| CH | 3 | 3 | 13 | 2 | 2 | 14 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 15–17 | 26–28 | 8 | 15 | 23–25 |
| CE | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| FHV | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| I | 3 | 3 | 7 | 2 | 3 | 4–6 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 15 | 23 |
| Jump | 3 | 3 | 10–13 | 2 | 15–37 | 13 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 12–17 | 14–27 | 4 | 15 | 22 |
| PC | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 15 | 22 |
| PBMF | 3 | 3 | 12/13 | 3 | 15–37 | 13/14 | 4/5 | 3/4 | 2 | 7/8 | 4 | 4 | 15 | 23 |
| ZXF | 6 | 6 | 6 | 4–7 | 9 | 6 | 4/5 | 5-10 | 5-8 | 5/6 | 6 | 4 | 8 | 11 |
| LL | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1–11 | 2 | 2 | 1–31 | 2 | 1/24 | 1 | 6 | 4 | 15 | 23–26 |
| LML | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1–9 | 2 | 2 | 1/6 | 2–17 | 1 | 1 | 6 | 4 | 15 | 24–26 |
| our approach | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 7 | 2 | 15 | 3 | 3 | 7 | 2 | 15 | 22 |
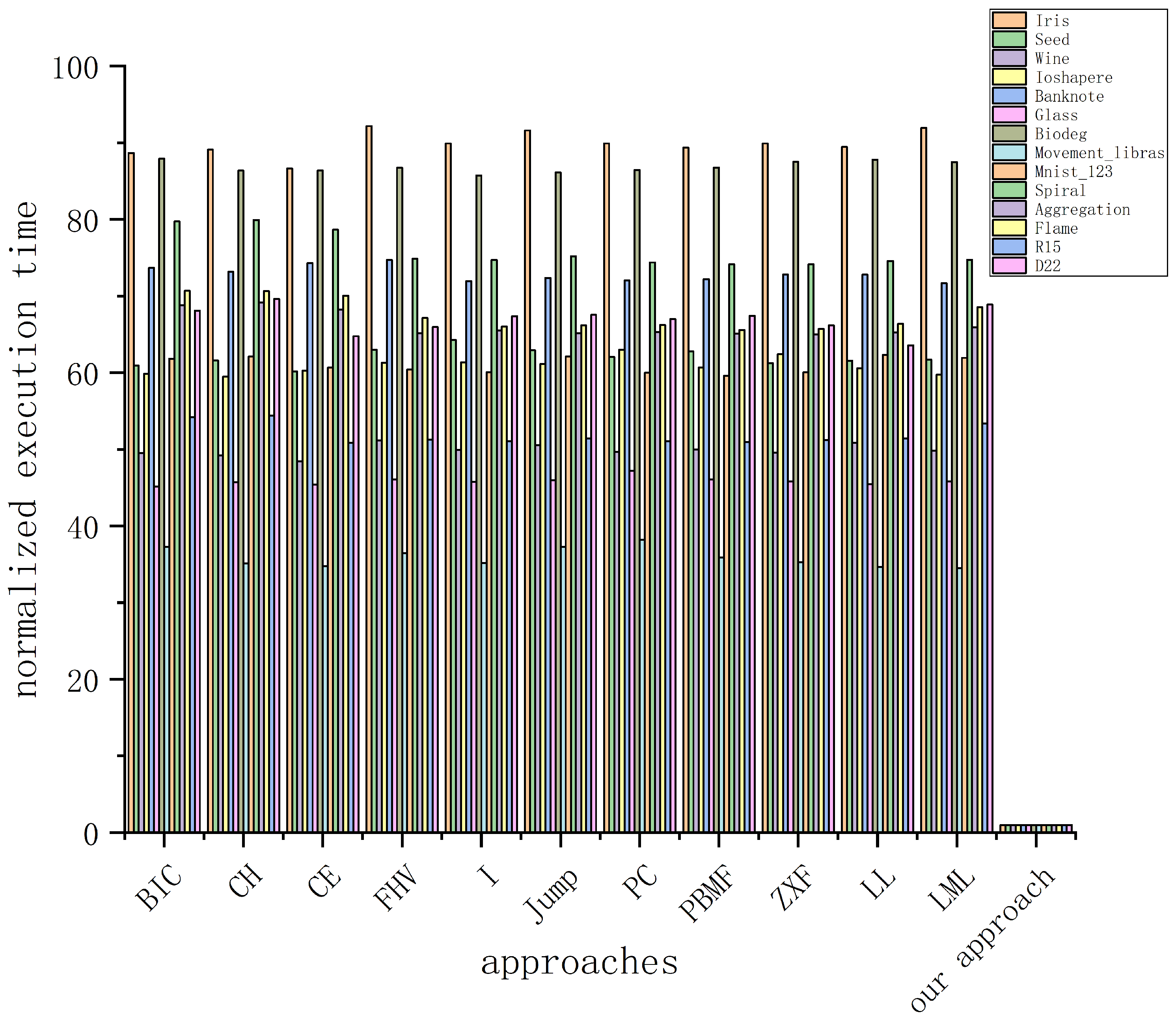
| Approaches | Iris | Seed | Wine | Ioshapere | Banknote | Glass | Biodeg | Movement_libras | Mnist_123 | Spiral | Aggregation | Flame | R15 | D22 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BIC | 1.348 | 2.017 | 1.570 | 3.962 | 24.023 | 2.134 | 20.821 | 4.025 | 37.340 | 3.533 | 10.150 | 2.411 | 5.720 | 42.149 |
| CH | 1.354 | 2.039 | 1.560 | 3.938 | 23.863 | 2.163 | 20.451 | 3.794 | 37.505 | 3.541 | 10.203 | 2.409 | 5.740 | 43.090 |
| CE | 1.317 | 1.991 | 1.534 | 3.990 | 24.229 | 2.148 | 20.455 | 3.757 | 36.636 | 3.484 | 10.061 | 2.389 | 5.367 | 40.092 |
| FHV | 1.401 | 2.085 | 1.622 | 4.059 | 24.359 | 2.179 | 20.541 | 3.939 | 36.479 | 3.317 | 9.612 | 2.290 | 5.409 | 40.817 |
| I | 1.367 | 2.127 | 1.583 | 4.060 | 23.458 | 2.166 | 20.299 | 3.797 | 36.261 | 3.308 | 9.659 | 2.251 | 5.386 | 41.698 |
| Jump | 1.393 | 2.083 | 1.603 | 4.048 | 23.603 | 2.175 | 20.391 | 4.025 | 37.504 | 3.332 | 9.605 | 2.257 | 5.427 | 41.829 |
| PC | 1.367 | 2.054 | 1.576 | 4.171 | 23.493 | 2.233 | 20.471 | 4.125 | 36.231 | 3.295 | 9.631 | 2.258 | 5.390 | 41.474 |
| PBMF | 1.359 | 2.078 | 1.585 | 4.017 | 23.542 | 2.178 | 20.548 | 3.879 | 36.009 | 3.285 | 9.602 | 2.236 | 5.378 | 41.730 |
| ZXF | 1.367 | 2.028 | 1.572 | 4.131 | 23.734 | 2.167 | 20.718 | 3.810 | 36.260 | 3.283 | 9.592 | 2.241 | 5.403 | 40.958 |
| LL | 1.360 | 2.038 | 1.613 | 4.008 | 23.737 | 2.151 | 20.789 | 3.744 | 37.625 | 3.304 | 9.624 | 2.263 | 5.423 | 39.356 |
| LML | 1.397 | 2.043 | 1.580 | 3.954 | 23.370 | 2.167 | 20.711 | 3.727 | 37.406 | 3.311 | 9.722 | 2.337 | 5.629 | 42.636 |
| our approach | 0.015 | 0.033 | 0.032 | 0.066 | 0.326 | 0.047 | 0.237 | 0.108 | 0.604 | 0.044 | 0.148 | 0.034 | 0.106 | 0.619 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, Z.; Jia, Z.; Zhang, X. A Fast Method for Estimating the Number of Clusters Based on Score and the Minimum Distance of the Center Point. Information 2020, 11, 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/info11010016
He Z, Jia Z, Zhang X. A Fast Method for Estimating the Number of Clusters Based on Score and the Minimum Distance of the Center Point. Information. 2020; 11(1):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/info11010016
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Zhenzhen, Zongpu Jia, and Xiaohong Zhang. 2020. "A Fast Method for Estimating the Number of Clusters Based on Score and the Minimum Distance of the Center Point" Information 11, no. 1: 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/info11010016
APA StyleHe, Z., Jia, Z., & Zhang, X. (2020). A Fast Method for Estimating the Number of Clusters Based on Score and the Minimum Distance of the Center Point. Information, 11(1), 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/info11010016





