An LSTM Model for Predicting Cross-Platform Bursts of Social Media Activity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Data
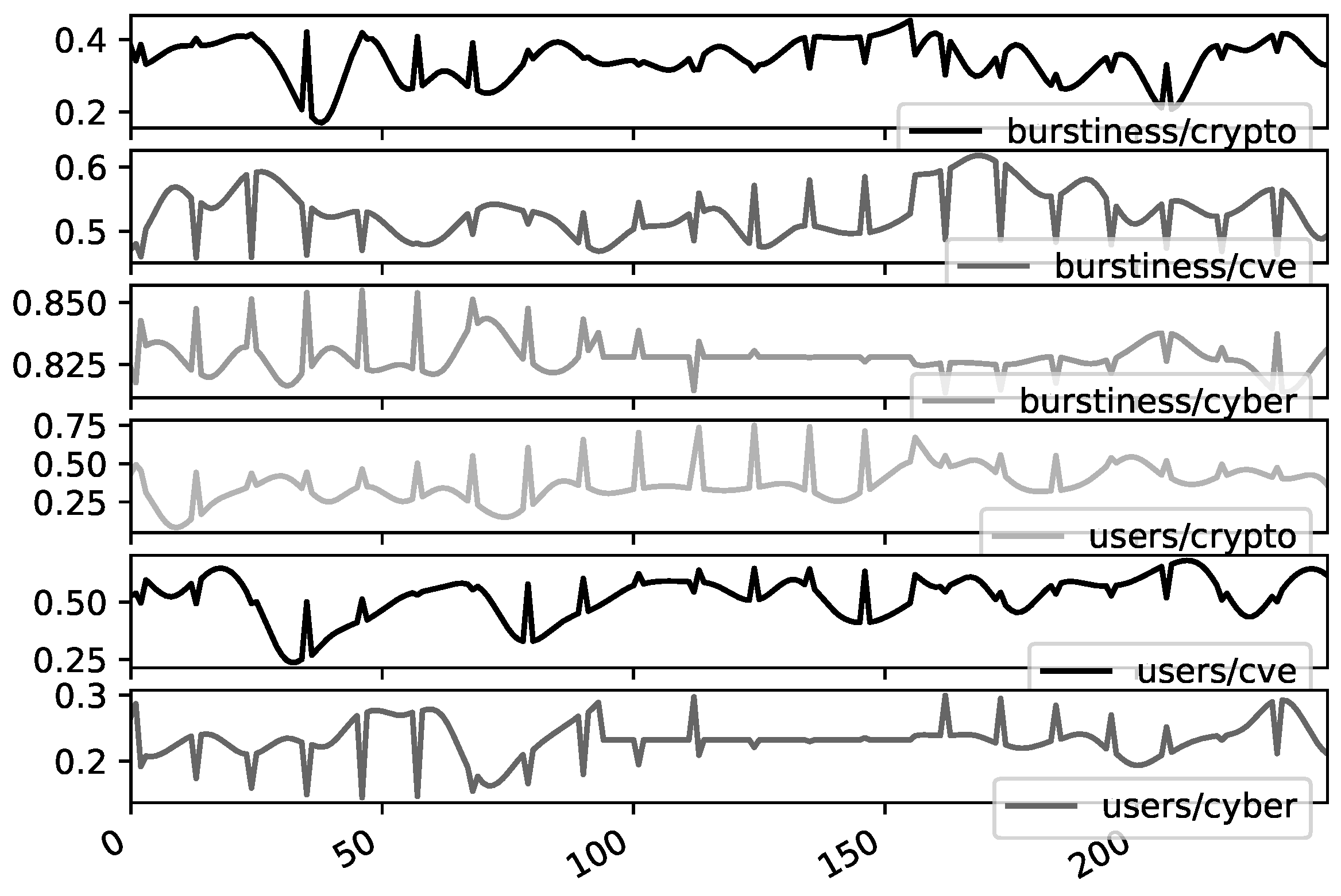
Data Preprocessing
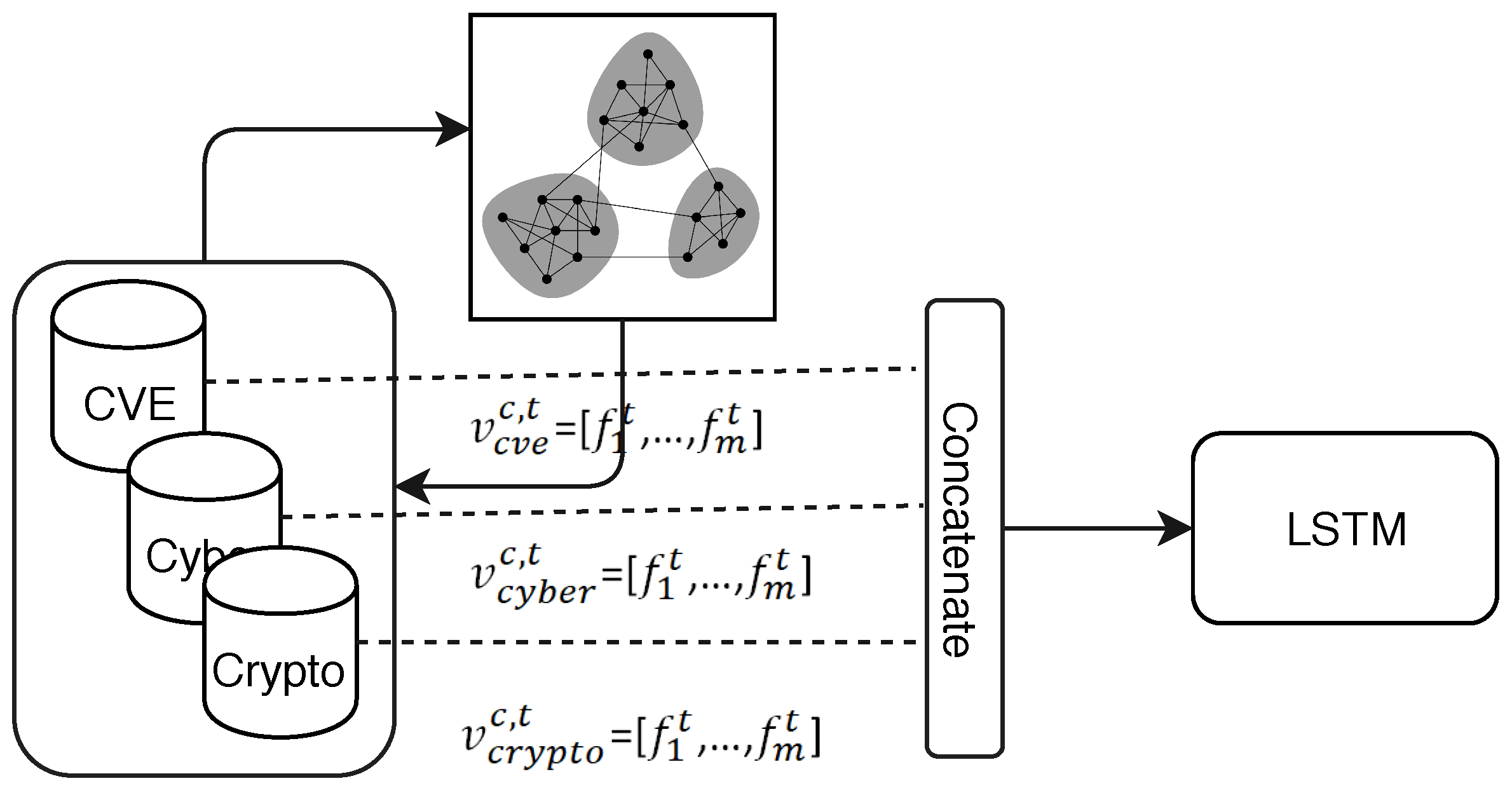
4. Methodology
4.1. LSTM Model vs. Markov Chain
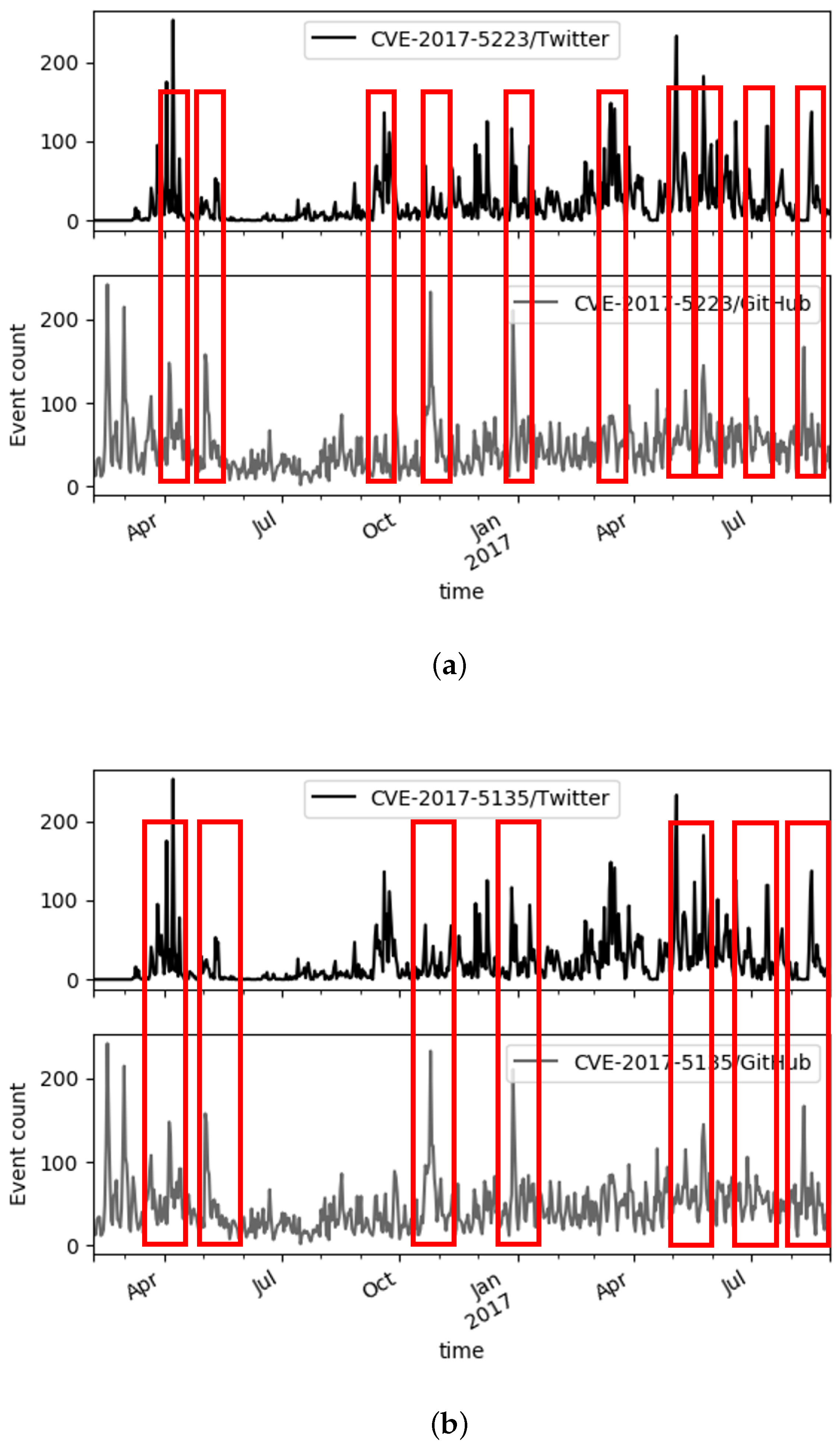
5. Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, J.; Counts, S. Predicting the speed, scale, and range of information diffusion in twitter. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Weblogs and Social Media, Washington, DC, USA, 23–26 May 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Friedkin, N. A test of structural features of Granovetter’s strength of weak ties theory. Soc. Netw. 1980, 2, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wu, J.; Xu, K. Weak ties: Subtle role of information diffusion in online social networks. Phys. Rev. E 2010, 82, 016105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mooney, P.; Winstanley, A.C.; Corcoran, P. Evaluating Twitter for use in environmental awareness campaigns. In Winstanley, Adam (Hg.): Proceedings of the China-Ireland Information and Communications Technologies Conference (CIICT 2009), Maynooth, Ireland, 19–21 August 2009; National University of Ireland: Galway, Ireland, 2009; pp. 83–86. [Google Scholar]
- Del Vicario, M.; Bessi, A.; Zollo, F.; Petroni, F.; Scala, A.; Caldarelli, G.; Stanley, H.E.; Quattrociocchi, W. The spreading of misinformation online. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 554–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, C.; Mantzaris, A.; Garibay, I. Exploring How Homophily and Accessibility Can Facilitate Polarization in Social Networks. Information 2018, 9, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friggeri, A.; Adamic, L.; Eckles, D.; Cheng, J. Rumor cascades. In Proceedings of the International AAAI Conference on Weblogs and Social Media, Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 1–4 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Starbird, K.; Palen, L. (How) Will the Revolution be Retweeted?: Information Diffusion and the 2011 Egyptian Uprising. In Proceedings of the ACM Conference on Computer Supported Cooperative Work, Seattle, WA, USA, 11–15 February 2012; pp. 7–16. [Google Scholar]
- Barabasi, A.L. The origin of bursts and heavy tails in human dynamics. Nature 2005, 435, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasilescu, B.; Filkov, V.; Serebrenik, A. Stack Overflow and GitHub: Associations between Software Development and Crowdsourced Knowledge. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Social Computing, Beijing, China, 20–23 August 2013; pp. 188–195. [Google Scholar]
- Mantzaris, A.V. Uncovering nodes that spread information between communities in social networks. EPJ Data Sci. 2014, 3, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Yan, Z.; Hu, X.; Philip, S.Y.; Li, Z. Burst time prediction in cascades. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Austin, TX, USA, 25–30 January 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Higham, D.; Mantzaris, A.V.; Grindrod, P.; Otley, A.; Laflin, P. Anticipating activity in social media spikes. In Proceedings of the International AAAI Conference on Web and Social Media, Oxford, UK, 26–29 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Alsaedi, N.; Burnap, P.; Rana, O. Automatic summarization of real world events using twitter. In Proceedings of the Tenth International AAAI Conference on Web and Social Media, Cologne, Germany, 17–20 May 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Li, Q.; D’Agostino, G.; Havlin, S.; Stanley, H.E.; Van Mieghem, P. Effect of the interconnected network structure on the epidemic threshold. Phys. Rev. E 2013, 88, 022801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mucha, P.J.; Porter, M.A. Communities in multislice voting networks. Chaos 2010, 20, 041108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasserman, S.; Faust, K. Social Network Analysis: Methods and Applications; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1994; Volume 8. [Google Scholar]
- Salehi, M.; Sharma, R.; Marzolla, M.; Magnani, M.; Siyari, P.; Montesi, D. Spreading processes in multilayer networks. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2015, 2, 65–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Sun, Y.; Philip, S.Y. A survey of heterogeneous information network analysis. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2017, 29, 17–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, S.A.; Zhu, C.; Leskovec, J. Information diffusion and external influence in networks. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Beijing, China, 12–16 August 2012; pp. 33–41. [Google Scholar]
- Krijestorac, H.; Garg, R.; Mahajan, V.; Ter Hofstede, F. Cross-Platform Spillover Effects in Consumption of Viral Content: A Quasi-Experimental Analysis Using Synthetic Controls. SSRN 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christodoulou, G.; Georgiou, C.; Pallis, G. The role of Twitter in Youtube videos diffusion. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Web Information Systems Engineering, Paphos, Cyprus, 28–30 November 2012; pp. 426–439. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Jiang, C.; Guan, S.; Xu, L.; Ren, Y. Big Data Driven Similarity Based U-Model for Online Social Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Global Communications Conference, Singapore, 4–8 December 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Tumasjan, A.; Sprenger, T.O.; Sandner, P.G.; Welpe, I.M. Predicting Elections with Twitter: What 140 characters Reveal About Political Sentiment. In Proceedings of the Fourth International AAAI Conference on Weblogs and Social Media, Washington, DC, USA, 23–26 May 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Asur, S.; Huberman, B.A. Predicting the future with social media. In Proceedings of the IEEE/WIC/ACM International Conference on Web Intelligence and Intelligent Agent Technology, IEEE Computer Society, Toronto, ON, Canada, 31 August–3 September 2010; pp. 492–499. [Google Scholar]
- Gruhl, D.; Guha, R.; Kumar, R.; Novak, J.; Tomkins, A. The predictive power of online chatter. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery in Data Mining, Chicago, IL, USA, 21–24 August 2005; pp. 78–87. [Google Scholar]
- Bollen, J.; Mao, H.; Zeng, X. Twitter mood predicts the stock market. J. Comput. Sci. 2011, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupavskii, A.; Ostroumova, L.; Umnov, A.; Usachev, S.; Serdyukov, P.; Gusev, G.; Kustarev, A. Prediction of retweet cascade size over time. In Proceedings of the ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, Maui, HI, USA, 29 October–2 November 2012; pp. 2335–2338. [Google Scholar]
- Pourebrahim, N.; Sultana, S.; Thill, J.C.; Mohanty, S. Enhancing Trip Distribution Prediction with Twitter Data: Comparison of Neural Network and Gravity Models. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGSPATIAL International Workshop on AI for Geographic Knowledge Discovery, Seattle, WA, USA, 6 November 2018; pp. 5–8. [Google Scholar]
- Hakim, M.A.N.; Khodra, M.L. Predicting information cascade on Twitter using support vector regression. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Data and Software Engineering (ICODSE), Bandung, Indonesia, 26–27 November 2014; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng-yu, T.L.; Poo, M.m.; Dan, Y. Burst spiking of a single cortical neuron modifies global brain state. Science 2009, 324, 643–646. [Google Scholar]
- Myers, S.A.; Leskovec, J. The bursty dynamics of the Twitter information network. In Proceedings of the International Conference on World Wide Web, Seoul, Korea, 7–11 April 2014; pp. 913–924. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, M.; Spagna, S.; Huici, F.; Niccolini, S. A peek into the future: Predicting the evolution of popularity in user generated content. In Proceedings of the ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, Rome, Italy, 4–8 February 2013; pp. 607–616. [Google Scholar]
- Bauckhage, C.; Kersting, K.; Hadiji, F. Mathematical models of fads explain the temporal dynamics of internet memes. In Proceedings of the International AAAI Conference on Weblogs and Social Media, Cambridge, MA, USA, 8–11 July 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara, Y.; Sakurai, Y.; Prakash, B.A.; Li, L.; Faloutsos, C. Rise and fall patterns of information diffusion: Model and implications. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Beijing, China, 12–16 August 2012; pp. 6–14. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Leskovec, J. Modeling information diffusion in implicit networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Data Mining, Sydney, Australia, 13 December 2010; pp. 599–608. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, J.; Adamic, L.A.; Kleinberg, J.M.; Leskovec, J. Do cascades recur? In Proceedings of the International Conference on World Wide Web, Montreal, QC, Canada, 11–15 April 2016; pp. 671–681. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, S.; Cha, M.; Jung, K.; Chen, W.; Wang, Y. Prominent features of rumor propagation in online social media. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Data Mining, Dallas, TX, USA, 7–10 December 2013; pp. 1103–1108. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Livshits, B. The anatomy of a cryptocurrency pump-and-dump scheme. In Proceedings of the USENIX Security Symposium, Santa Clara, CA, USA, 14–16 August 2019; pp. 1609–1625. [Google Scholar]
- Kleinberg, J. Bursty and hierarchical structure in streams. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2003, 7, 373–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, N.; Hinton, G.; Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Salakhutdinov, R. Dropout: A Simple Way to Prevent Neural Networks from Overfitting. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2014, 15, 1929–1958. [Google Scholar]
- Schiappa, M.; Chantry, G.; Garibay, I. Cyber Security in a Complex Community: A Social Media Analysis on Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures. In Proceedings of the 6th Int Conference on Social Network Analysis, Management and Security (SNAMS 2019), Granada, Spain, 22–25 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
| GitHub | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Actors | Events | Actors | Events | Actors | Events | |
| Mean | 223.7 | 487.52 | 199.05 | 261.55 | 14.5 | 19 |
| Median | 162.5 | 339 | 195 | 270 | 11 | 14.5 |
| Std | 224.36 | 507.24 | 134.58 | 187.79 | 9.7 | 12.15 |
| () | (2, 0.50) | (2, 0.75) | (3, 0.50) | (3, 0.75) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Mean | Std | Mean | Std | Mean | Std | Mean | Std |
| a_LSTM | 0.09 | 0.20 | 0.11 | 0.22 | 0.08 | 0.20 | 0.09 | 0.21 |
| MCM | 0.36 | 0.25 | 0.29 | 0.18 | 0.37 | 0.21 | 0.39 | 0.28 |
| Model | Optimizer | Activation Function | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Linear | Softmax | ||||
| Mean | Std | Mean | Std | ||
| a_LSTM | adam | 0.010 | 0.018 | 0.015 | 0.032 |
| rmsprop | 0.021 | 0.41 | 0.010 | 0.016 | |
| LSTM | adam | 0.022 | 0.28 | 0.025 | 0.041 |
| rmsprop | 0.030 | 0.41 | 0.20 | 0.021 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hajiakhoond Bidoki, N.; Mantzaris, A.V.; Sukthankar, G. An LSTM Model for Predicting Cross-Platform Bursts of Social Media Activity. Information 2019, 10, 394. https://doi.org/10.3390/info10120394
Hajiakhoond Bidoki N, Mantzaris AV, Sukthankar G. An LSTM Model for Predicting Cross-Platform Bursts of Social Media Activity. Information. 2019; 10(12):394. https://doi.org/10.3390/info10120394
Chicago/Turabian StyleHajiakhoond Bidoki, Neda, Alexander V. Mantzaris, and Gita Sukthankar. 2019. "An LSTM Model for Predicting Cross-Platform Bursts of Social Media Activity" Information 10, no. 12: 394. https://doi.org/10.3390/info10120394
APA StyleHajiakhoond Bidoki, N., Mantzaris, A. V., & Sukthankar, G. (2019). An LSTM Model for Predicting Cross-Platform Bursts of Social Media Activity. Information, 10(12), 394. https://doi.org/10.3390/info10120394






