A Mapping Approach to Identify Player Types for Game Recommendations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Preparation of Game Data
2.1. Game Data Collection
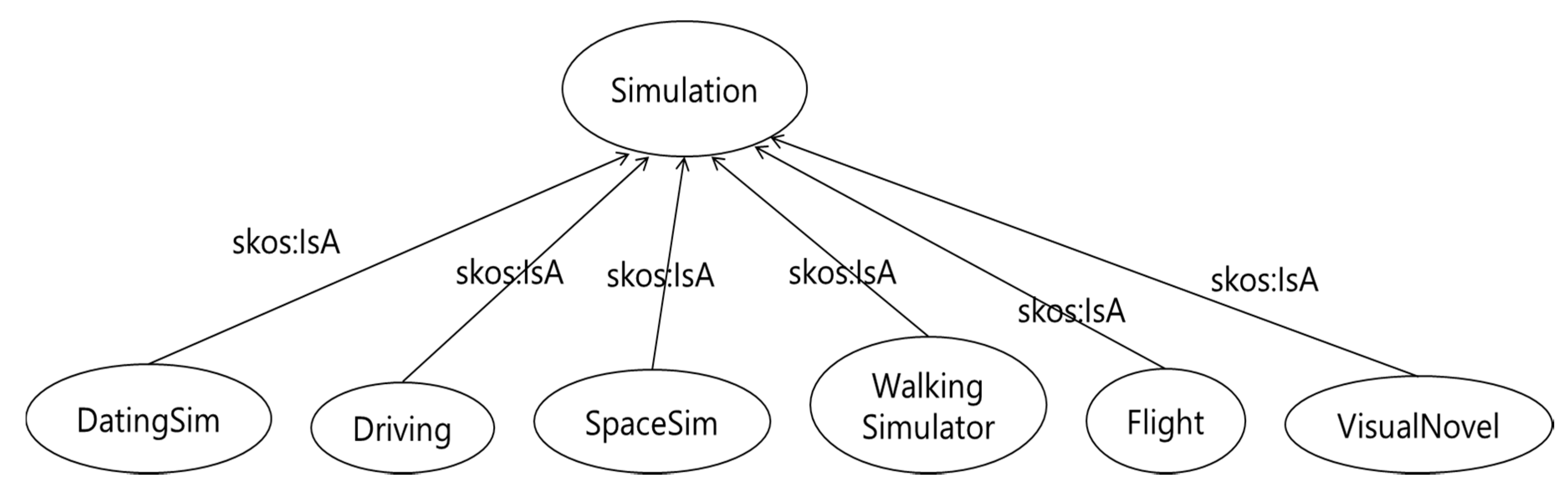
2.2. Game Tag Information
3. The Proposed Model for Mapping
3.1. Personality Diagnosis
3.2. Player Type
3.3. OCEAN Personality Analysis and Player Type Mapping
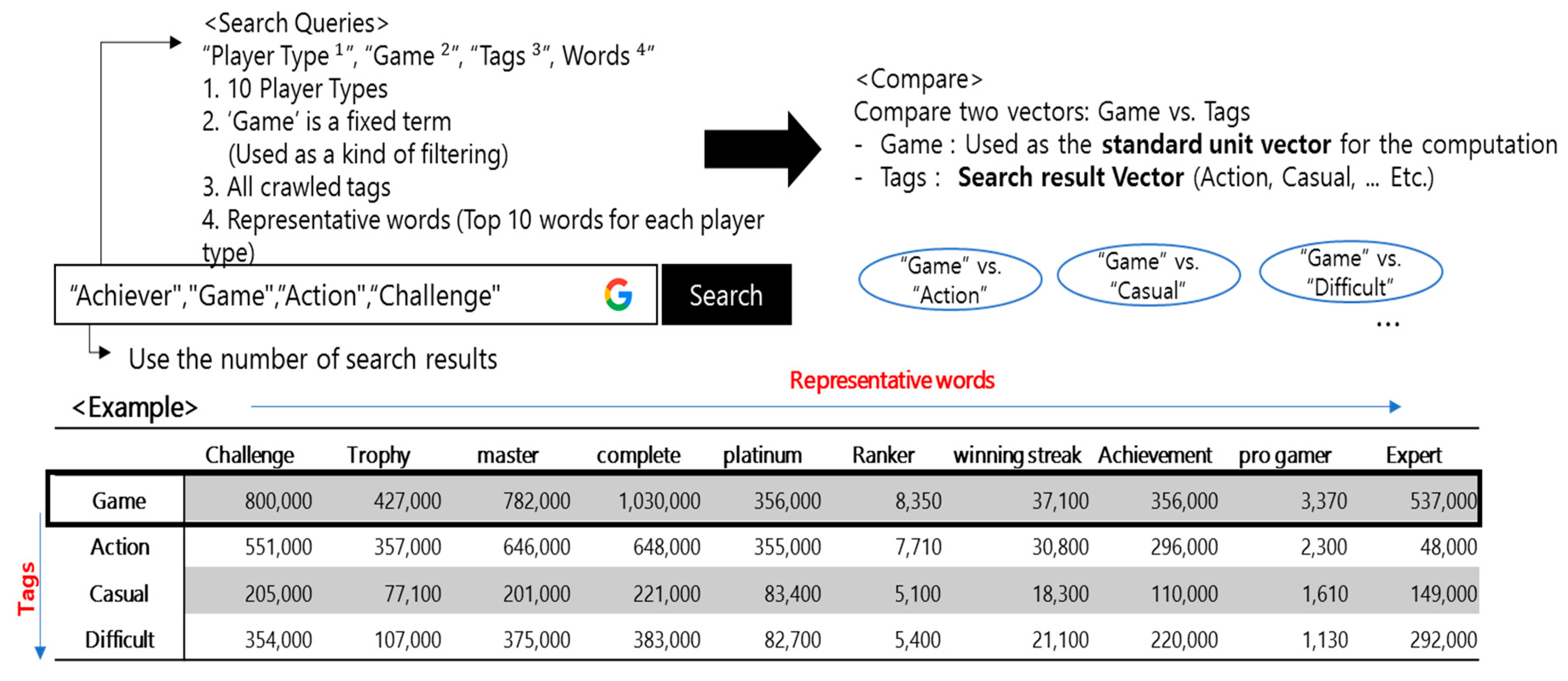
3.4. Mapping between Game Tags and Player Types
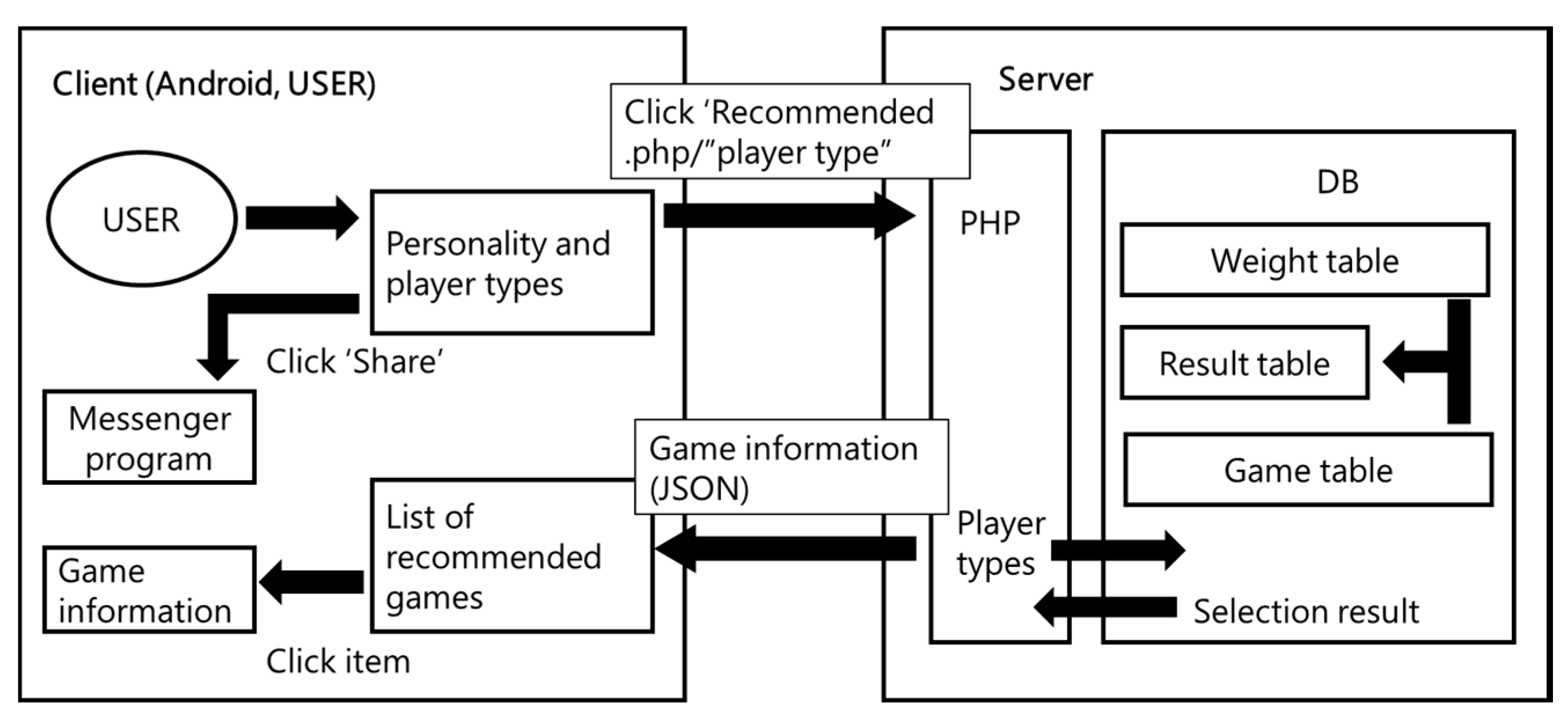
4. Overview of Game Recommendation System
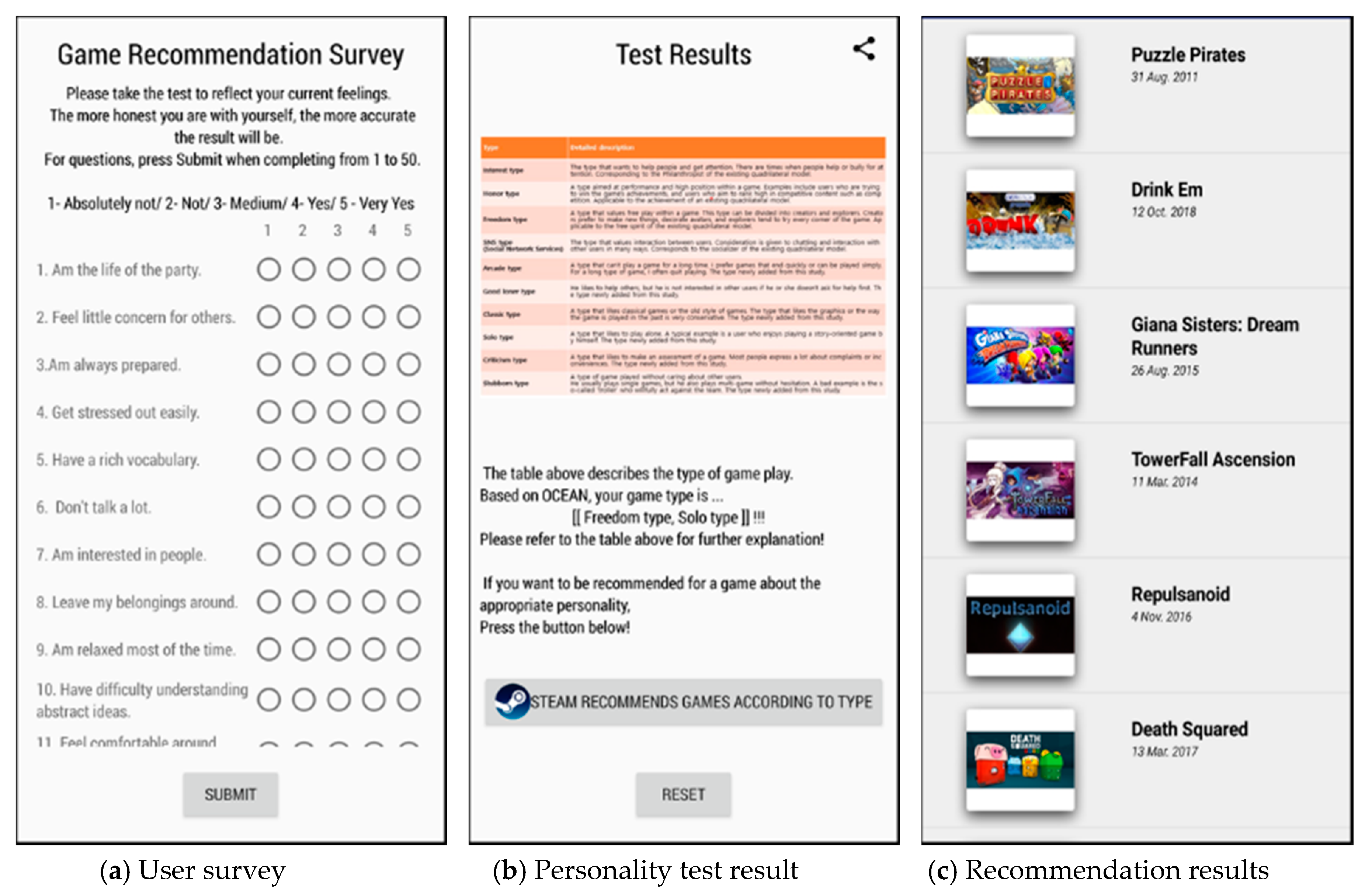
4.1. User Interfaces in Android App
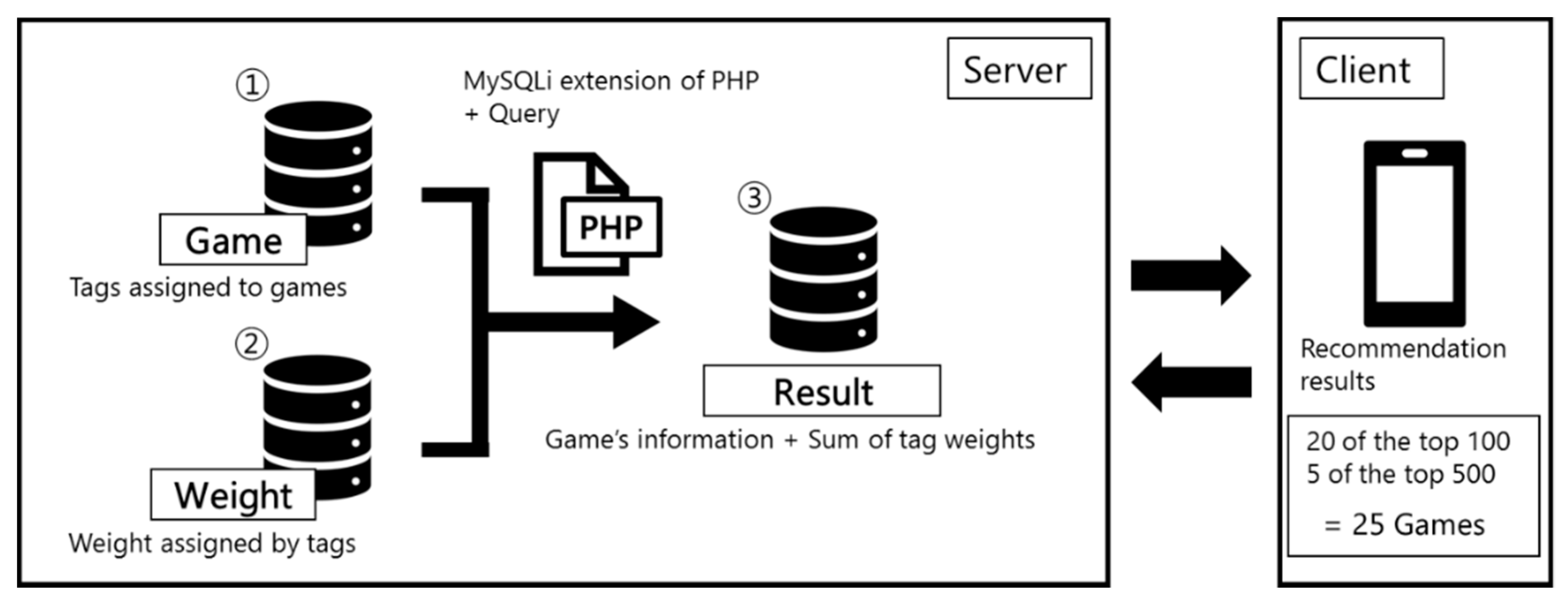
4.2. Server-Side Data Flow
4.3. Comparison with Other Recommendation Systems
5. Experimental Results
5.1. Player Type Analysis
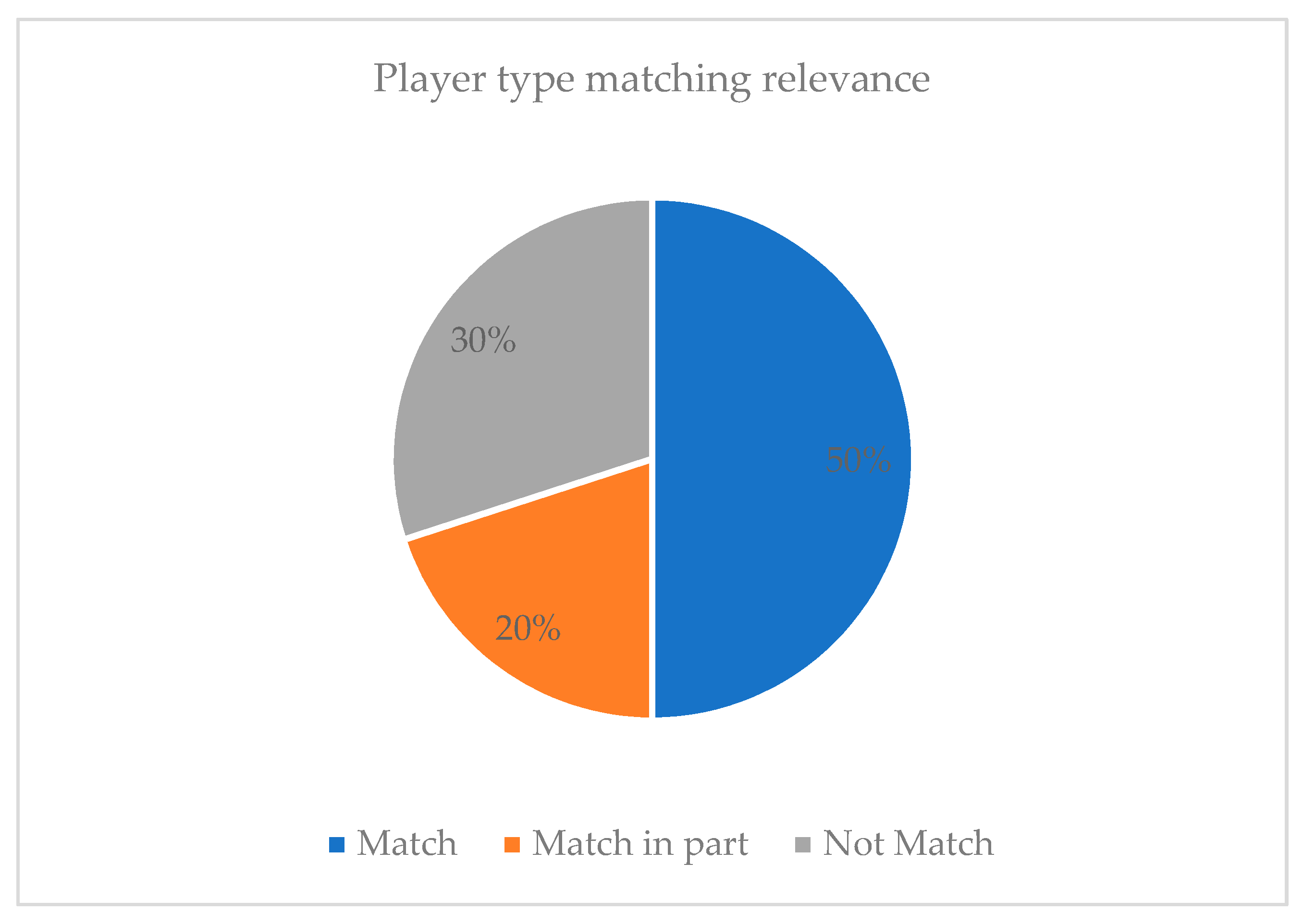
5.2. Game Recommendation Based on the Identified Player Type
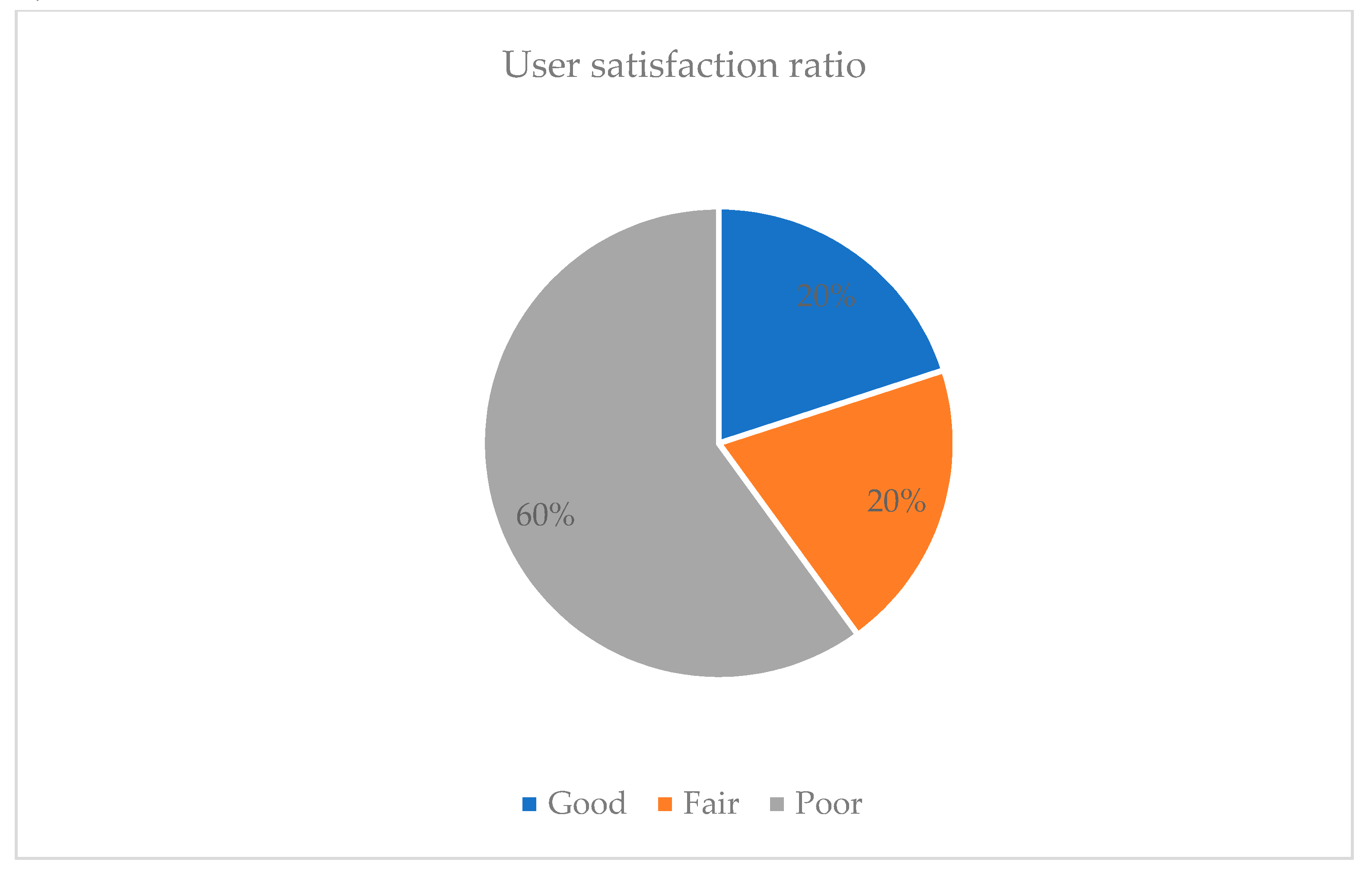
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wijman, T. The Global Games Market Will Generate $152.1 Billion in 2019 as the U.S. Overtakes China as the Biggest Market | Newzoo. Available online: https://newzoo.com/insights/articles/the-global-games-market-will-generate-152-1-billion-in-2019-as-the-u-s-overtakes-china-as-the-biggest-market/ (accessed on 9 January 2019).
- Statista Number of Games Released on Steam Worldwide from 2004 to 2018. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/552623/number-games-released-steam/ (accessed on 11 October 2019).
- Anwar, S.M.; Shahzad, T.; Sattar, Z.; Khan, R.; Majid, M. A game recommender system using collaborative filtering (GAMBIT). In Proceedings of the Proceedings of 2017 14th International Bhurban Conference on Applied Sciences and Technology, IBCAST, Islamabad, Pakistan, 10–14 January 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Ye, F.; Xu, J. A personalized recommendation algorithm based on the user’s implicit feedback in e-commerce. Futur. Internet 2018, 19, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Q.; Azizi, V.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y. Learning heterogeneous knowledge base embeddings for explainable recommendation. Algorithms 2018, 11, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roccas, S.; Sagiv, L.; Schwartz, S.H.; Knafo, A. The Big Five personality factors and personal values. Personal. Soc. Psychol. Bull. 2002, 28, 789–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Seibert, S.E. The big five personality dimensions and entrepreneurial status: A meta-analytical review. J. Appl. Psychol. 2006, 91, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bollegala, D.; Matsuo, Y.; Ishizuka, M. Measuring semantic similarity between words using web search engines. In Proceedings of the 16th International World Wide Web Conference, WWW 2007, Banff, AB, Canada, 8–12 May 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Cilibrasi, R.L.; Vitányi, P.M.B. The Google similarity distance. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2007, 19, 370–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soper, T. Valve Reveals Steam’s Monthly Active User Count and Game Sales by Region. Available online: https://www.geekwire.com/2017/valve-reveals-steams-monthly-active-user-count-game-sales-region/ (accessed on 9 October 2019).
- Goldberg, L.R. The Development of Markers for the Big-Five Factor Structure. Psychol. Assess. 1992, 4, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gow, A.J.; Whiteman, M.C.; Pattie, A.; Deary, I.J. Goldberg’s “IPIP” Big-Five factor markers: Internal consistency and concurrent validation in Scotland. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2005, 39, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartle, R. Hearts, Clubs, Diamonds, Spades: Players who Suit Muds. J. MUD Res. 1996, 1, 19. [Google Scholar]
- Bartle, R.A. Designing Virtual Worlds; New Riders Publishing: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Tondello, G.F.; Wehbe, R.R.; Diamond, L.; Busch, M.; Marczewski, A.; Nacke, L.E. The gamification user types Hexad scale. In Proceedings of the CHI PLAY 2016—the 2016 Annual Symposium on Computer-Human Interaction in Play, Austin, TX, USA, 16–19 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Singhal, A. Modern Information Retrieval: A Brief Overview. IEEE Data Eng. Bull. 2001, 24, 35–43. [Google Scholar]
- Adrian Tache Big-Five-Personality-Test. Available online: https://github.com/adriantache/Big-Five-Personality-Test (accessed on 9 October 2019).
- PHP MySQL Improved Extension. Available online: https://secure.php.net/manual/en/book.mysqli.php (accessed on 9 October 2019).
- Sarwar, B.; Karypis, G.; Konstan, J.; Riedl, J. Item-based collaborative filtering recommendation algorithms. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on World Wide Web, WWW, Hong Kong, China, 1–5 May 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Linden, G.; Smith, B.; York, J. Amazon.com recommendations: Item-to-item collaborative filtering. IEEE Internet Comput. 2003, 7, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazzani, M.J.; Billsus, D. Content-based recommendation systems. In The Adaptive Web; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, D.; Luo, Z.; Zhang, F. A novel approach for collaborative filtering to alleviate the new item cold-start problem. In Proceedings of the 11th International Symposium on Communications and Information Technologies, ISCIT, Hangzhou, China, 12–14 October 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, J.; He, J.; Chen, K.; Zhou, Y.; Tang, Z. Collaborative filtering and deep learning based recommendation system for cold start items. Expert Syst. Appl. 2017, 69, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, R. Hybrid recommender systems: Survey and experiments. User Model. User Adapt. Interact. 2002, 12, 331–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quadrana, M.; Karatzoglou, A.; Hidasi, B.; Cremonesi, P. Personalizing session-based recommendations with hierarchical recurrent neural networks. In Proceedings of the RecSys 2017—the 11th ACM Conference on Recommender Systems, Como, Italy, 27–31 August 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Pasumarthi, R.K.; Bruch, S.; Wang, X.; Li, C.; Bendersky, M.; Najork, M.; Pfeifer, J.; Golbandi, N.; Anil, R.; Wolf, S. TF-Ranking: Scalable TensorFlow Library for Learning-to-Rank. In Proceedings of the 25th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, Anchorage, AK, USA, 4–8 August 2018. [Google Scholar]

| Name (Game Title) | Text (Detailed Description of the Game) | Date (Release Date) | Tags (Features of the Game/Genre) | Image URL (Game Title Image URL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLAYER UNKNOWN’S BATTLEGROUNDS | PLAYERUNKNOWN’S BATTLEGROUNDS is a battle royale shooter that pits 100 players against each other in a struggle for survival. Gather supplies and outwit your opponents to become the last person standing. | Dec 21, 2017 | /Survival/Shooter/Multiplayer/PvP/Third-PersonShooter/FPS/ Action/OnlineCo-Op/BattleRoyale/FPS/ Tactical/Co-op/First-Person/EarlyAccess/ Strategy/Competitive/ ThirdPerson/Team-Based/Difficult/ Simulation/Stealth | https://steamcdn-a.akamaihd.net/steam/apps/578080/header.jpg?t=1544485873 |
| MONSTER HUNTER: WORLD | Welcome to a new world! In Monster Hunter: World, the latest installment in the series, you can enjoy the ultimate hunting experience, using everything at your disposal to hunt monsters in a new world teeming with surprises and excitement. | Aug 9, 2018 | /Action/Hunting/Co-op/Multiplayer/OpenWorld/ThirdPerson/RPG/Adventure/Fantasy/ CharacterCustomization/Difficult/Singleplayer/ActionRPG/Exploration/GreatSoundtrack/ReplayValue/Atmospheric/HackandSlash/JRPG/ Souls-like | https://steamcdn-a.akamaihd.net/steam/apps/582010/header.jpg?t=1544082685 |
| Total Number of Unique Tags | Maximum Frequency of Occurrence | Minimum Frequency of Occurrence | Average Frequency of Occurrence |
|---|---|---|---|
| 351 | 6754 | 1 | 233.79 |
| Type | Detailed Description |
|---|---|
| Interest type | The type that seeks attention and wants to help people. There are times when people help or bully for attention. Corresponds to the philanthropist of the existing quadrilateral model. |
| Honor type | A type that focuses on performance and achieving a high position within a game. Examples include users who try to complete the game’s achievements and those who aim to rank high in competitions. Applicable to the achiever of the existing quadrilateral model. |
| Freedom type | A type that values free play within a game. This type can be divided into creators and explorers. Creators prefer to create new things and decorate avatars, and explorers tend to explore every corner of the game. Applicable to the free spirit of the existing quadrilateral model. |
| SNS type (Social Network Services) | The type that values interaction between users. Importance is given to chatting and interacting with other users in many ways. Corresponds to the socializer of the existing quadrilateral model. |
| Arcade type | A type that cannot play a game for a long time. They prefer games that end quickly or are simple to play, otherwise they quit. This type has been newly added to this study. |
| Good loner type | They like to help others but are not interested in doing so if other users do not ask for help first. The type has been newly added from this study. |
| Classic type | A type that likes classical games or old-style games. They like the graphics or the conservative style of gameplay. The type has been newly added from this study. |
| Solo type | A type that likes to play alone. A typical example is a user who enjoys playing a story-oriented game by themselves. The type has been newly added from this study. |
| Criticism type | A type that likes to make an assessment regarding a game. Most of them complain excessively about inconveniences. The type has been newly added from this study. |
| Stubborn type | A type that plays without regard for other users. They usually play single-player games, but they also play multi-player games without hesitation. An example is the so-called ’troll’ who willfully acts against the team. The type has been newly added from this study. |
| BEST | SECOND | WORST | TYPE |
|---|---|---|---|
| O | C | E | Freedom type |
| A | Freedom, SNS type | ||
| N | Freedom, SNS type | ||
| A | E | Freedom, Solo type | |
| C | Arcade, Interest type | ||
| N | Freedom, SNS type | ||
| E | N | Freedom, SNS type | |
| C | Arcade type | ||
| A | SNS type | ||
| N | A | Freedom type | |
| E | Freedom type | ||
| C | Arcade type | ||
| C | O | E | Honor, Freedom type |
| A | SNS type | ||
| N | SNS type | ||
| A | E | Good loner type | |
| O | Honor, Interest type | ||
| N | SNS, Interest type | ||
| E | N | SNS type | |
| O | Honor, Interest type | ||
| A | SNS type | ||
| N | A | Honor type | |
| E | Honor type | ||
| O | Honor type | ||
| A | C | E | Good loner type |
| O | Interest, Honor type | ||
| N | Interest type | ||
| O | E | Freedom, Solo type | |
| C | Arcade, Interest type | ||
| N | Interest, Freedom, SNS type | ||
| E | N | Interest type | |
| C | SNS, Arcade, Interest type | ||
| O | Interest type | ||
| N | O | Interest, Classic type | |
| E | Honor, Good loner type | ||
| C | Arcade, Interest type | ||
| E | C | O | Interest type |
| A | SNS, Stubborn type | ||
| N | SNS type | ||
| A | O | Interest, Honor type | |
| C | SNS type | ||
| N | SNS type | ||
| O | N | SNS type, Freedom type | |
| C | SNS, Arcade, Interest type | ||
| A | Freedom, SNS type | ||
| N | A | Freedom, SNS, Honor type | |
| O | Interest Classic type | ||
| C | SNS, Criticism type | ||
| N | C | E | Honor type |
| A | Honor type | ||
| O | Classic, Honor, Interest type | ||
| A | E | Honor, Freedom, Solo type | |
| C | Criticism, Arcade, Interest type | ||
| O | Classic, Interest type | ||
| E | O | Classic, Interest type | |
| C | SNS type | ||
| A | Honor, SNS, Stubborn type | ||
| O | A | Honor, Freedom, SNS type | |
| E | Honor, Freedom, Solo type | ||
| C | Arcade, Interest type | ||
| |||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, Y.; Jung, Y. A Mapping Approach to Identify Player Types for Game Recommendations. Information 2019, 10, 379. https://doi.org/10.3390/info10120379
Lee Y, Jung Y. A Mapping Approach to Identify Player Types for Game Recommendations. Information. 2019; 10(12):379. https://doi.org/10.3390/info10120379
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Yeonghun, and Yuchul Jung. 2019. "A Mapping Approach to Identify Player Types for Game Recommendations" Information 10, no. 12: 379. https://doi.org/10.3390/info10120379
APA StyleLee, Y., & Jung, Y. (2019). A Mapping Approach to Identify Player Types for Game Recommendations. Information, 10(12), 379. https://doi.org/10.3390/info10120379






