Abstract
The hilly and mountainous regions of Nepal provide a suitable environment for the cultivation of large cardamom, a high-value cash crop with significant global market potential. However, climate change poses significant threats to its production and the livelihoods of farmers dependent on this crop. To cope with these challenges, adopting climate-resilient agricultural practices is essential, particularly among smallholder farmers of rural communities. However, the extent of their implementation remains largely unknown. We surveyed 158 households in Ilam and Tehrathum districts to assess the adoption intensity of climate-resilient practices among large cardamom farmers using the Ordered Probit Model. Findings revealed considerable variation in the adoption intensity of climate-resilient practices. Traditional practices like tillering, weeding, and irrigation were highly adopted, while more innovative, knowledge-intensive methods were less adopted. Education was found to have a positive influence on the high adoption intensity of climate-resilient practices. Each additional unit of year of schooling increases the probability of high adoption of practices by 3.4%. Membership in farmers’ groups increases the likelihood of high adoption by 12.9%, while labor availability and regular extension contact rises by 21.9% and 17.8%, respectively. Similarly, age shows a smaller but significant effect, increasing adoption by 0.5% at p-value = 0.08. The use of traditional practices is common; however, the uptake of scientifically recommended practices for climate resilience remains limited. Policy initiatives focusing on farmer education, promoting farmer organizations, addressing labor shortages, and strengthening extension services are important for enhancing resilience in the large cardamom sector of Nepal.
1. Introduction
Climate change and unsustainable agricultural practices remain among the biggest global challenges that significantly impact the agricultural sector of the hilly and mountainous regions in the world [1]. Climate change has significantly affected the livelihoods of small-holder farmers from rural communities in developing countries like Nepal [2]. Nepal remains one of the top five climate-vulnerable nations in the world [3]. The farmers have been witnessing climate variabilities, such as intense rainfall, prolonged droughts, an increase in new pests and diseases, and rising temperatures, which have threatened the production and productivity of the crops [4]. The economy of Nepal is mainly based on agriculture, where agriculture contributes about 21.87% to the national GDP [5]. Out of various agricultural commodities, large cardamom has been widely cultivated over the past two decades, becoming very popular among farmers due to its high cash value in both domestic and international markets. Large cardamom (Amomum subulatum Roxb.) is one of the world’s oldest spices and is known as Black Gold or the Queen of Spices [6,7]. According to FAO [8], Nepal ranks as one of the largest producers of cardamom in the world [9], and cardamom farming supports rural livelihoods [10]. The cardamom was first imported from Sikkim, India [11], and then introduced in the Ilam district, and has since been expanded to more than 50 districts in Nepal [12]. However, the primary production regions are Ilam, Tehrathum, Panchthar, and Sankhuwasabha. They make up 87.04% of the country’s total output, with data indicating that around 125,000 households are involved in cardamom cultivation [10,12].
Large cardamom is considered one of Nepal’s key commodities, with the potential to reduce poverty and promote sustainable rural development substantially [13]. However, the production of large cardamom has decreased globally in recent years due to factors such as diseases and a changing climate [6,12]. It is a crop highly sensitive to climate; it thrives best in temperatures between 7 and 30 degrees Celsius, with annual rainfall of 3000–3500 mm, requiring a cool, humid environment with shade [6]. However, the production, market values, and income sources of farmers associated with the quality of cardamom are threatened by the effects of climate change [14]. To ensure the sustainable production of important crops like large cardamom and livelihood security, communities need to implement climate-resilient farming practices [1,4].
Climate-resilient practices are those methods of farming that reduce the climate risks, help to mitigate and adapt to climate change impacts, and maintain productivity and ecological sustainability [15]. In Nepal, the International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) released a manual on implementing climate-resilient practices for large cardamom cultivation, designed to significantly enhance the sustainability of large cardamom farming [16]. ICIMOD, in partnership with the Environment Conservation and Development Forum, has been providing various trainings, demonstrations, and on-site coaching to the local cardamom growers to increase awareness on the adoption of climate-resilient practices [17]. While these climate-resilient practices are proven to support sustainable cardamom production in the context of climate change, their adoption by farmers remains inconsistent, likely due to various socio-economic, demographic, and institutional factors [3]. There are limited studies on factors influencing the adoption intensity of climate-resilient practices among the cardamom farmers in Nepal. Most of the research has focused on the value chain and economic analyses of cardamom production or marketing. The extent to which farmers are adopting and integrating such recommended practices into their farming systems and the factors influencing high adoption intensity remain poorly examined. It is important to address this gap for designing effective interventions that foster climate-resilient, sustainable livelihoods among the cardamom farmers and sustain planetary health through achieving food security, ecosystem well-being, and community health. Therefore, this study aims to fill the research gap by examining the status of adoption intensity of climate-resilient practices and understanding the socio-economic, demographic, and institutional factors that influence the adoption of these practices. This study adds to the existing literature on climate-resilient agriculture and provides evidence to assist policymakers in developing targeted policies for enhancing climate resilience in the large cardamom sector of Nepal.
2. Materials and Methods
We conducted the study in the Ilam and Tehrathum districts of Koshi Province of Nepal during the year 2023/24 (Figure 1). Ilam and Tehrathum are purposively chosen for the study because they are among the top producers of large cardamoms in the country. The study focused on specific municipalities within these two districts, which are the Rong Rural Municipality of Ilam and Laligurans Municipality of Tehrathum district (Figure 1). These areas have a higher concentration of cardamom farmers and the availability of farmer support programs.
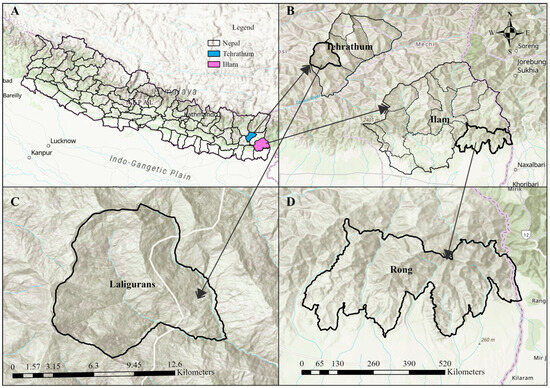
Figure 1.
Location of the study areas: Laligurans Municipality (C) and Rong Rural Municipality (D) within the respective Tehrathum and Ilam districts (B) of Nepal (A).
Both municipalities feature mid-hill agro-ecology, where large cardamom agroforestry is a main land-use system [18]. For the cultivation of cardamom, the feasible elevation ranges from 500 to 1500 m above sea level [19]. Ilam has an elevation ranging from 140 to more than 3600 m, offering various climatic zones that are favorable to tea and large cardamom. Tehrathum has its elevation ranging from 169 to 3038 m, and it has tropical, alpine, and cold climate conditions that make the cultivation of large cardamom suitable. Both study areas lie within the foothills of the Himalayas and are considered part of the larger Himalayan region in Nepal. Cardamom is a main source of cash income and livelihoods for many farmers in the study area. Additionally, various governmental and non-governmental organizations are involved in the study area actively to promote climate-resilient agriculture (CSA), making them relevant for exploring the adoption of sustainable agricultural practices.
2.1. Data Collection and Analysis
We used a multi-stage sampling procedure to select the study areas. In the first stage, the Ilam and Tehrathum districts were purposively chosen. In the second stage, Rong Rural Municipality and Laligurans Municipality were selected because they have a high number of cardamom growers and are active sites for climate resilience projects. The sampling frame included all households that took part in training programs on climate-resilient practices for large cardamom farming in the study area. The partner organizations provided the list of the beneficiaries upon request. We focused on trained beneficiaries because it could help assess the factors influencing the adoption intensity of promoted climate-smart practices directly. We determined the sample size for each municipality using the formula given by [20] as shown in Equations (1) and (2).
where
For the total population (N = 198) representing trained beneficiaries at Rong Municipality (N = 130) and Laligurans Municipality (N = 68), we assumed a 95% confidence level (Z = 1.96) with a 5% margin of error (E) and the sample proportion representing at least 50% of the population at each site (p = 0.5). Using these parameters, we randomly selected 158 household samples, 99 from Rong Rural Municipality of Ilam district, and 59 from Laligurans Municipality of Tehrathum. This sampling process ensured that the sample size was representative of the sampling frame. For the data collection, primary datasets were collected from farmers’ household surveys using a pre-tested, semi-structured questionnaire. Before doing the survey, all the respondents were provided with verbal consent, and we assured them that their data would remain confidential and their identity would be anonymous throughout the study process. The researchers directly involved in the study had access to the raw survey data to ensure adherence to ethical standards. The secondary data were collected from a review of both published and unpublished reports from governmental and non-governmental organizations, such as annual reports from the Ministry of Agriculture and Livestock Development (MOALD), district statistical records, ICIMOD publications, and peer-reviewed journal articles. The information from the secondary data collection helped to contextualize the study, confirm the primary data findings, and provide background on production trends and program interventions.
2.2. Variables in the Econometric Model and Their Measurement
The survey questionnaire had a set of quantitative and qualitative questions. At first, we gathered quantitative data on the independent variables covering demographic, socio-economic, and institutional support variables. Among all variables, “Age” (total age in years of the respondent) and “Education” (formal years of schooling of the respondent) were continuous variables. “Gender”, a categorical variable, was coded as 1 = male and 0 = female. “Experience” (years of cardamom farming experience of the respondent), “Farm size” (the total farm acreage in hectares), and “Income” (the annual income of the respondent in USD) were also continuous. Other variables were binary (1 = Yes and 0 = No), which include “Membership” (active member in the farmer’s group organizations), “Credit” (access to the loans from financial institutions like cooperatives, banks, microfinances, or through informal sources like farmer cooperatives for investment on cardamom farming), “Labor” (access to those human workers who are accessible and willing to do necessary farm-related tasks when needed), “Extension” (a regular contact of farmer with the extension worker), and “ICT” (use of any of the information and communication technologies like radio, television, mobile phones, internet platforms).
We also gathered quantitative data on the adoption intensity of thirteen climate-resilient practices. These practices were based on the climate-smart agricultural guide created and promoted by ICIMOD for the large cardamom sector and their relevance to the study area [21,22]. Each of these 13 climate-resilient practices was coded as a binary variable (1 = adopted, 0 = not adopted), based on their “Yes/No” responses. The practices assessed were: “Manure application”, which refers to the use of well-decomposed dung as manure while discarding any manure that contains insects/pests like white grub to prevent the field infestation; “Irrigation”, refers to the use of sprinkler or drip irrigation applied at least twice weekly during dry periods; and “Weeding”, carried out before flowering and harvesting phase, and using those weeds as mulch. “Intercropping” involved growing nitrogen-fixing crops like pulses, beans, Siris (A. julibrissin), and Phaledo (E. stricta), etc., to enrich the soils with surplus nitrogen for the crop growth, while “Shade trees” refers to the adoption of species like Alnus, Albizia, and Artemisia that provide shade to the cardamom and maintain microclimate. “Slashing tillers” refers to practices like carefully cutting the fruiting tillers and spreading the trimmed parts around the bushes. “Weed growing (winter)” refers to an innovative practice that involves keeping the existing weeds intact in higher altitude areas, mainly in winter, to protect the new shoots from frost damage and cold weather conditions. “Harvesting” refers to the practice of gently harvesting cardamom without damaging new shoots for better fruiting in the next year. “Disease monitoring” is the practice of watching for pests/diseases year-round and timely isolating the affected plants. “Mulching” referred to the practice of using slashed stems, weeds, or residues as mulch for protection and nutrients, while “Green Manuring” denoted the practice of planting leguminous shrubs/trees as live fences or insect repellents like Dhaincha (Sesbania bispinosa), Ipil Ipil (Leucaena leucocephala), Crotalaria spp., etc. “Drying” denoted the practice of using dry hardwood for uniform drying, avoiding moisture, and reshuffling the capsules often, and “Post-harvest storage” referred to keeping harvested cardamom in dry, ventilated rooms to avoid fungal infestation and maintain quality. All these variables were treated as an equally weighted index for analysis, reflecting a focus on the overall adoption of climate-resilient practices. We interviewed the farmers with follow-up questions to reveal their perceptions, attitudes, knowledge, and constraints. These follow-up questions helped to enrich our findings by uncovering the underlying reasons behind their adoption behaviors and decisions.
2.3. Data Analysis
We analyzed the data collected using descriptive and inferential statistical methods in STATA software (version 17) and Excel 2021. The descriptive analysis included the means and standard deviations that summarized the socio-economic characteristics of the respondents and the adoption rates of the individual climate-resilient practices. For the econometric model chosen, adoption intensity of climate-resilient practices is the dependent variable. We chose the dependent variable in two steps. Initially, we prepared an adoption index for each household by summing the total number of independent variables implemented by the household farmers. This resulted in an index score ranging from 0 to 13. Secondly, we employed the mean and standard deviation method to move beyond a simple count and categorize the farmers into different groups based on adoption intensity. It is a standard procedure in such research where the subjects are grouped into similar categories for ease of analysis [23].
Based on the index scores generated, we placed the total respondent households into three groups using a threshold of 0.5 standard deviations. They are Low Adopters (LA), Medium Adopters (MA), and High Adopters (HA). Those respondent households that had an adoption score below, within, and above the 0.5 standard deviations from the mean were categorized as LA, MA, and HA, respectively. This classification resulted in an ordered, categorical dependent variable where the categories have a clear, fixed rank (Low < Medium < High), but the intervals between them are not necessarily equal.
Given the ordered nature of the dependent variable, we chose an Ordered Probit Model for the analysis because of its capacity to handle a case of more than two-category outcomes of a dependent variable that have a natural ordering system, like low, medium, and high adoption rates, as in our study [24]. The cumulative normal distribution is used in Probit for interpreting the results. Although there are several other econometric models, such as Ordinary Least Squares (OLS) and multinomial logit (MNL) models, we chose the OPM. OLS would treat the ranked categories as equal distances apart, leading to biased and inconsistent estimates [25], and MNL wouldn’t consider the natural order of the categories. This oversight could result in a loss of statistical efficiency [26].
OPM assumes an underlying, unobservable latent variable, y* [27], which represents a household’s propensity to adopt a higher intensity of climate-resilient practices. This latent variable is determined by a vector of explanatory variables (X) and an error term (ε), specified as Equation (3) given by.
where y*ᵢ is the unobserved adoption propensity for ith farm household; Xᵢ is the vector of independent socio-economic and institutional variables; β is the vector of parameters to be estimated; and εᵢ is the random error term, assumed to be independent and normally distributed with a mean of zero and a variance of one [εᵢ ~ N(0, 1)].
y*ᵢ = β′Xᵢ + εᵢ
3. Results
Table 1 presents the demographic, socio-economic, and institutional characteristics of the 158 surveyed cardamom farmers. The demographic data revealed that the average age of the respondents was 49.5 years, indicating that most of the farmers were experienced and aging farmers in the hilly region of Nepal. The majority were male (73.4%), and the average formal education level was 7.31 years. The average farm size was 0.56 hectares, which is slightly lower than the national average of 0.6 hectares for small-scale farmers [28]. The respondents had an average of 9.63 years of experience in farming, and they had a mean annual household income of USD 2958.05.

Table 1.
Descriptive statistics of the independent variables used in the study.
Regarding institutional access, 60.1% of farmers reported they had membership in farmers’ groups, while 62.6% had access to credit, and 45.5% maintained regular contact with agricultural extension workers (Table 1). Approximately 60.1% of respondents reported that they have access to labor. Moreover, 74.0% of the respondents reported using information and communication technologies (ICT) for agricultural purposes, such as mobile phones and FM radio.
The adoption intensity of climate-resilient practices among cardamom farmers varied widely (Table 2). Our research showed that all farmers (100%) practiced the slashing of tillers. This is a common farming method that farmers have been adopting for a long time in the study area. Weeding was among the most frequently adopted practices by farmers, reported to be adopted by 89.2% respondents. Harvesting (88.6%), drying (88.6%), manure application (86.7%), and irrigation (86.7%) were also highly adopted practices by the large cardamom farmers. Farmers also widely adopted mulching and disease monitoring practices, with 75.9% and 70.2% of respondents reporting each, respectively. However, moderate adoption was found in green manuring (36.7%), shade tree planting (36.0%), and post-harvest storage (34.8%) (Table 2). However, intercropping with the nitrogen-fixing crops was adopted by only about 5.6% of the respondents. Winter weed growing practices were not adopted at all.

Table 2.
Descriptive statistics of climate-resilient practices being used by cardamom farmers in Ilam and Tehrathum districts of Nepal.
The average adoption score for the practices was 7.99, with a standard deviation of 0.14. Based on this, scores below seven are classified as low intensity, a score of eight as medium intensity, and nine or higher as high intensity. The study revealed that adoption scores ranged from 5 to 11, with no respondent scoring exactly seven. Overall, 40.50% of participants were classified as high-intensity adopters, 24.05% as medium-intensity, and 35.45% as low-intensity.
Table 3 presents the results of the Ordered Probit Model that identified the factors influencing the adoption intensity of climate-resilient practices. We have reported both the estimated coefficients and marginal effects in Table 3. The likelihood ratio statistics of 120.82 were found significant at 1% level. It meant that the coefficients of the explanatory variables jointly influence the decisions of farmers to adopt climate-resilient practices. The Pseudo R2 value of 0.355 showed a good explanatory power of the independent variable used in the study, and the two cutoff points estimated are significantly different, which reveals that the outcome categories are distinct and valid for the model.

Table 3.
Parameter estimates and marginal effects of the Ordered Probit Model analysis of factors influencing the adoption intensity of climate-resilient practices for large cardamom farmers in Nepal.
The variable “Age” exhibited a positive but marginally significant effect on the high adoption intensity of climate-resilient practices at a 10% level of significance. The marginal effect of farmers’ age on adopting such practices is 0.005, meaning the likelihood of high adoption increases by 0.5% for each year above the average age of the farmers. The variable “Education” was found to have a positive and significant effect at a 1% significance level. Suggesting that, relative to uneducated farmers, raising the educational level through formal education significantly increases the probability that households will adopt various practices. Results showed that the marginal effect of education level on households practicing high-intensity adoption is 0.034, suggesting that higher education levels increase the likelihood of farmers adopting climate-resilient practices. The variable “Membership” played a significant role in the likelihood of farmers adopting climate-resilient practices. The coefficient on “Membership” was positive and significant at 5%, and it predicts higher adoption intensity of those farmers who are members of a farmer’s group compared to non-members.
Similarly, we found that the availability of “Labor” significantly and positively influences the level of adoption at 1% level of significance. A slight increase in the availability of labor for farming raised the likelihood of high adoption of practices by 21.9%, assuming other factors remain unchanged. The variable “Extension” was found to be another positive and significant factor influencing the high adoption intensity at 1% significance level. The value marginal effect for households that regularly interact with extension workers and highly adopt climate-resilient practices is 0.178. This means that, all other variables being constant, households with regular contact are 17.8% more likely to adopt those practices compared to those without regular contact with the extension workers. Other factors, such as gender, farming experience, farm size, income, access to credit, and ICT use, did not have a significant impact on adoption intensity.
4. Discussion
These findings revealed that farmers primarily focused on traditional practices that directly improve yield and require less technical knowledge; however, the scientifically recommended package of practices for climate resilience and ecological sustainability is still less adopted [19]. For instance, slashing the tillers, weeding, harvesting, drying, manure application, and irrigation were the basic agronomic practices adopted widely as these help in bringing resilience and sustainability in cardamom farming amid climate change conditions [29]. The moderate adoption of mulching and disease monitoring practices corresponds to the growing level of awareness of the pest and moisture management needs. Contrastingly, more complex and ecologically important practices, such as green manuring, shade tree planting, post-harvest storage, and intercropping, were adopted unevenly across the study area. Farmers reported that the technical and labor-intensive nature of those recommended practices, and the absence of immediate yield benefits, limited the adoption of these practices. Farmers also stated financial and policy constraints, like the government providing subsidies for using chemical fertilizers over organic alternatives like green manuring, further discouraged adoption [6,30,31]. Intercropping practices require technical knowledge and a good support of extension agents to train farmers [29], while the labor constraints and the unavailability of enough land spaces were additional barriers [32]. Similarly, post-harvest storage infrastructure was unaffordable for smallholder farmers, and their preference was to stick with the traditional methods [6]. Moreover, farmers perceived risks in adopting the recommended winter weeds growing practices due to fear of pests/fungus infestation and outbreak of new diseases [33].
Multiple factors influenced the adoption intensity of climate-resilient practices among large cardamom farmers. Age showed a positive effect on high adoption intensity, indicating that older farmers are more likely to adopt climate-resilient practices than the younger ones, which could be attributed to their longer years of experience in farming, a higher ability to manage risks and uncertainties, access to land, and social resources [34,35,36,37]. This finding was similar to the results of research conducted in Eastern Kenya, where older farmers were more likely to adopt sustainable farming practices [38]. Education also played an important role in adoption behavior [39], as farmers with formal education can read materials and advertisements provided during training and workshops, engage with extension workers, and understand the long-term benefits of adopting climate-resilient practices [24,40,41]. This finding is in line with studies across South Asia [42,43,44], which found that educated farmers are more likely to recognize the long-term advantages of climate-resilient practices and tend to be more receptive to adopting innovative farming methods. This reveals that education level differentiates the adoption outcomes, where less-educated farmers may significantly lag compared to the highly educated farmers. Proportionally, younger farmers were found to be highly educated compared to the older farmers. This highlights a generational difference where older farmers with accumulated knowledge through years of farming experience, and highly educated younger farmers, both play an important role in shaping the high adoption intensity of climate-resilient practices [45].
Membership in farmers’ groups significantly enhanced adoption intensity, similar to the studies conducted across Africa and Latin America, which confirm that social networks are important for agricultural growth, and these organizations act as essential platforms for peer learning, exchanging information, and collaborative efforts [40,46,47]. Organizational backing and peer support enhanced access to resources, training, and technical assistance for adopting climate-resilient practices [48]. Similarly, labor availability significantly influenced the adoption intensity, suggesting that households with sufficient labor could adopt complex, labor-intensive, yet ecologically sustainable practices like manure application, agroforestry, mulching, weed growing in winter, and intensive weeding [49]. Labor shortages, often resulting from out-migration or demographic changes, restrict the ability to carry out new or additional work necessary for climate-resilient practices [47]. This is especially true in the context of Nepal, where high out-migration of young men to urban areas or foreign countries has been a leading problem, causing labor shortages and increasing the involvement of women in agriculture [50]. This causes the women and elderly people of the family to manage the farms, and they face barriers to land ownership, access to extension agents, and social networks, thereby limiting the adoption intensity of many practices [51,52]. Although migrants send remittances that can partly offset labor shortages, that income is mostly used for household use, education, or debt repayment, which limits its use in the agricultural sector [53]. This trend of labor migration has significant socio-cultural implications, and it remains a constraint in adopting climate-resilient practices. This scenario is not just unique to Nepal, but also in other developing regions like the Ecuadorian Andes [54] and Ethiopia [55], where labor out-migration has reduced labor in farming and reshaped gender roles. Regular contact with the extension agents also significantly influenced the high adoption intensity, highlighting the vital role of extension services in raising awareness, reducing information gaps, and providing technical support [56]. This finding aligns with the study from Nigeria, demonstrating that strong engagement of extension agents with farmers increases confidence in recognizing, understanding, and implementing climate-resilient agricultural practices [57]. Moreover, our findings align with the global evidence that extension services and training for farmers are influential characteristics of sustainable practices adoption [58].
The absence of significant effects of factors like farm size, income, access to credit, gender, and ICT use suggests that financial and structural factors play a less significant role than the human and social capital factors in shaping the adoption behavior. Smaller farms were more likely to adopt the climate-resilient practices, consistent with cross-regional studies [44,59]. Access to credit negatively influenced the adoption of climate-resilient practices, similar to the findings from Ethiopia [60]. It could be attributed to the strict requirements linked to these financial products or a significant aversion to the perceived risks of new agricultural technologies [61]. Farmers tend to avoid taking loans from formal credit sources due to high-risk loan terms, rigid repayment plans, demanding collateral requirements, and strict eligibility criteria, which make these institutions less accessible for small-scale farmers [62,63]. Gender had a low value marginal effect showing a weaker influence, with a unit increase in the gender “male” increasing the likelihood of adopting the practices by 2.7%. Male farmers were more likely to adopt climate-resilient practices due to their role as household heads and decision makers. This finding was similar to the results of a study conducted in Kenya, a developing country [37], while contrasting with the findings of the study conducted in the US Midwest [64]. This highlights the need for gender-responsive policies and programs that empower women farmers and reduce the gender disparities in access and adoption of climate-resilient practices [65]. ICT usage was high, which suggests the increasing importance of digital tools in rural agricultural systems [66,67,68]. However, its insignificant effect on adoption intensity indicates that digital tools are not yet effectively integrated into farm management due to barriers like a lack of relevant information on time tailored to the specific needs of the farmer, poor literacy in using the digital tools, and limited availability of skilled extension agents to train the farmers [66,69]. Moreover, we found that about 26% of farmers do not use ICT, and this could be due to barriers like higher costs of technologies like internet services [70]. Strengthening these factors is important for enhancing resilience, not just in Nepal but across the global smallholder farming sector.
This study suggest four primary phases through which these climate-resilient practices adoption could be enhanced: (i) restoring agricultural extension services to offer long-term, tailored, site-specific, hands-on technical assistance, on-site demonstrations; (ii) enhancing the local farmer groups and cooperatives to encourage farmer-to-farmer training, and collective action, offering easier credit access to farmers; and (iii) integrating functional literacy and farm management education into rural development programs, strengthening vocational training; (iv) adopt a dual strategy that promotes either labor-saving or labor-efficient resilient practices, along with more community-focused approaches to labor sharing. Governmental policies in developing these strategies could prove beneficial for increasing the adoption intensity of climate-resilient practices. If these constraints remain unaddressed, even the well-informed and motivated farmers are unlikely to implement a comprehensive set of resilient practices. Beyond the government’s role, the involvement of the private sector is equally important. Agribusiness companies, cooperatives, and other value-chain actors can facilitate farmers’ access to improved technologies, extension services, credit, markets, and crop insurance, which are essential to reduce risk perception and uncertainty among farmers [71]. Fostering scientific and academic collaboration with regional and international organizations can provide opportunities for knowledge transfer, capacity building, and technology sharing. Collaborative approaches, like cross-country partnerships and joint research, can strengthen institutional capacities and enable farmers to benefit from innovative practices and lessons learned in local and global contexts. For achieving this, it is important to have collaboration and coordination among all governmental, non-governmental, universities, and private companies.
This study has three limitations. First, the geographic scope includes only two districts, Illam and Tehrathum of Eastern Nepal. This restricts the generalizability of our research findings to all cardamom-growing regions of the country. The results, therefore, reflect the context of trained beneficiaries in these districts and may not capture the broader diversity of production systems across the eastern hills. Second, this study was designed as a cross-sectional survey, which restricts the ability to track changes in adoption over time. Third, the findings from the study are generalizable primarily to the trained beneficiaries and may not extend to the untrained farmers or other regions with different socio-economic and ecological conditions. Future studies should adopt a longitudinal study design that follows the same beneficiaries over multiple years to assess adoption dynamics and the long-term impacts of interventions. Expanding the study area to include other major production districts, such as Sankhuwasabha and Panchthar, would strengthen the generalizability and provide a more representative picture of adoption patterns across the cardamom belt. Finally, comparative regional studies between Nepal and India, particularly with cardamom-growing areas of Sikkim, would help identify transferable good practices and policy lessons. Such cross-regional studies could help in formulating policies that enhance the resilience and sustainability of large cardamom farming in Nepal.
5. Conclusions
This study explored the socio-economic and institutional factors influencing the adoption intensity of climate-resilient practices among large cardamom farmers of the eastern mid-hills of Nepal. The Ordered Probit Model revealed that the main factors influencing high adoption intensity are education, age, social networks, labor availability, and extension services. These findings conclude that promoting climate-resilient agriculture is influenced not only by individual awareness but also by access to social networks, collective action, and institutional support systems. Together, these factors enable farmers to adopt the recommended scientific practices and adapt to climate change more effectively. The key takeaway from this research is that strengthening community-based organizations like farmers’ groups and cooperatives, improving extension services, and addressing labor constraints are essential strategies for enhancing the adoption of climate-resilient practices and fostering sustainable production of high-value crops in the Himalayan region. Empowering farmers through continuous learning, participatory approaches, and providing access to resources will help bridge the adoption gap. At the same time, addressing these factors will enhance both livelihood security, like food and income security, and ecosystem health. Enhancing the adoption of climate-resilient practices in large cardamom farming contributes directly to soil conservation, reduced carbon emissions, increased carbon sequestration, and enhanced biodiversity, thereby connecting agricultural sustainability with ecosystem and human well-being. Moreover, this study supports the broader global efforts of achieving the Sustainable Development Goals, particularly SDG 13 (Climate Action), SDG 2 (Zero Hunger), and SDG 15 (Life on Land). Since Nepal’s Himalayan landscapes represent fragile, ecologically sensitive, and globally important ecosystems, fostering resilience through effective policies not only brings local livelihood sustainability but also protects planetary health. Evidence from the United States further supports this linkage, suggesting that governance-led land management efforts at the local level can deliver measurable improvements in ecosystem services [72]. Thus, promoting climate-resilient farming in the large cardamom sector exemplifies how local adaptation efforts can contribute to global sustainability.
Author Contributions
All authors participated in developing the study conception and design. Conceptualization, S.P. and B.P.M.; methodology, B.P.M.; software, B.P.M.; validation, S.P. and S.B. and B.P.M.; formal analysis, S.P. and B.P.M.; investigation, B.P.M.; resources; data curation, S.P., S.B.; writing—original draft preparation, S.P. and B.P.M.; writing—review and editing, S.P.; visualization, S.B., S.P. and B.P.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors state that they did not receive any funds, grants, or additional support while preparing this manuscript.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) at Nepal Polytechnic Institute (approval code: NPI-IRB-2023-01; approval date: 5 January 2023).
Informed Consent Statement
All participants in the study provided informed consent.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used or analyzed in this study are not publicly available due to respondent privacy concerns, but they can be obtained from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank all the enumerators, officials from different institutions, and respondents who participated in the survey and helped to make this study possible. The authors sincerely thank Suraj Upadhaya, Buddhi Gyawali, Kentucky State University for their valuable guidance throughout the research and manuscript preparation.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ramalingam, S.; Tanaka, K.; Tarakaramu, N.; Murugan, M.; Kaliyaperumal, A.; Khan, M.I. Assessing Multi-Decadal Climatic Variability and Its Impact on Cardamom Cultivation in the Indian Cardamom Hills. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 29283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, J. Promoting Climate Resilient Agriculture in Nepal: Building Climate Change Resilient Communities through Private Sector Participation. 2018. Available online: https://www.cif.org/sites/cif_enc/files/knowledge-documents/cif_case_study_nepal_1.pdf (accessed on 15 June 2025).
- Gairhe, J.J.; Adhikari, M. Intervention of Climate Smart Agriculture Practices in Farmers Field to Increase Production and Productivity of Winter Maize in Terai Region of Nepal. J. Inst. Agric. Anim. Sci. 2018, 35, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, B.R.; Erskine, W.; Acciaioli, G. Hybrid Knowledge and Climate-Resilient Agriculture Practices of the Tharu in the Western Tarai, Nepal. Front. Polit. Sci. 2022, 4, 969835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Bank Organization. Nepal-Agriculture, Value Added (% of GDP). 2024. Available online: https://tradingeconomics.com/nepal/agriculture-value-added-percent-of-gdp-wb-data.html (accessed on 11 June 2025).
- Kattel, R.R.; Regmi, P.P.; Sharma, M.D.; Thapa, Y.B. Factors Influencing Adoption of Major Post-Harvest Handling Practices of Large Cardamom in Nepal. Cogent Food Agric. 2020, 6, 1796201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, J.; Chandrasekaran, S.; Preetha, G.; Kuttalam, S.; Jasmine, R.S. Estimation of Diafenthiuron Residues in Cardamom (Elettaria cardamomum (L.) Maton) Using Normal Phase HPLC: Dissipation Pattern and Safe Waiting Period in Green and Cured Cardamom Capsules. Chromatogr. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 289747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO). The State of Food and Agriculture 2023- Revealing the True Cost of Food to Transform Agrifood Systems. 2023. Available online: https://openknowledge.fao.org/items/1516eb79-8b43-400e-b3cb-130fd70853b0 (accessed on 7 August 2025).
- Shrestha, K.P.; Shrestha, J. Value Chain Analysis of Large Cardamom in Ilam District of Nepal. Azarian J. Agric. 2018, 5, 179–189. [Google Scholar]
- Prasain, K. Large Cardamom Could Be Nepal’s Trade Booster; The Kathmandu Post. 2025. Available online: https://kathmandupost.com/money/2024/06/25/large-cardamom-could-be-nepal-s-trade-booster (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- The Kathmandu Post. Nepali Large Cardamom Being Pushed out of World Markets. 2018. Available online: https://kathmandupost.com/money/2018/03/02/nepali-large-cardamom-being-pushed-out-of-world-markets (accessed on 8 October 2025).
- Shrestha, J.; Prasai, H.K.; Timsina, K.P.; Shrestha, K.P.; Pokhrel, D.; Poudel, K.; Yadav, M. Large Cardamom in Nepal: Production Practice and Economics, Processing and Marketing. 2018. ISBN 9789937050982. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/339311342 (accessed on 11 July 2025).
- Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO). Nepal Investment Cases and Interventions. 2025. Available online: https://www.fao.org/hand-in-hand/hih-investment-forum-2025/nepal/en (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Pun, A.B. A Review on Different Factors of Large Cardamom Decline in Nepal. Asian J. Res. Crop Sci. 2019, 2, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvar-Beltrán, J.; Elbaroudi, I.; Gialletti, A.; Heureux, A.; Neretin, L.; Soldan, R. Climate Resilient Practices: Typology and Guiding Material for Climate Risk Screening; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.; Joshi, S.R.; Gurung, M.B. Climate-Resilient Practices for Sustainability of Large Cardamom Production Systems in Nepal: Resource Book for Farmers; ICIMOD Manual 2017/6. 2017. Available online: https://lib.icimod.org/records/p9rst-j8063 (accessed on 23 July 2025).
- Gurung, M.B.; Joshi, S.R.; Chilwal, H.C.C.C. Climate Smart Practices Revive Cardamom Farming in Eastern Himalayas. Available online: https://dialogue.earth/en/food/climate-smart-practices-revive-cardamom-farming-in-eastern-himalayas/ (accessed on 23 July 2025).
- Joshi, B.; Joshi, G.R. Factors Influencing the Adoption of Large Cardamom-Based Agroforestry System in the Eastern Hills of Nepal. Res. J. Agric. For. Sci. 2016, 4, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- ICIMOD Reviving and Sustaining Large Cardamom Production in Nepal. 2023. Available online: https://weadapt.org/solutions-portal/reviving-and-sustaining-large-cardamom-production-in-nepal/ (accessed on 15 June 2025).
- Wayne, D.W. Biostatistics: A Foundation for Analysis in the Health Sciences, 7th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1999; ISBN 0471163864/9780471163862. [Google Scholar]
- Khatri-Chhetri, A.; Aggarwal, P.K.; Joshi, P.K.; Vyas, S. Farmers’ Prioritization of Climate-Smart Agriculture (CSA) Technologies. Agric. Syst. 2017, 151, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.; Joshi, S.; Gurung, M. Package of Practices for Promoting Climate Resilient Cardamom Value Chains in Nepal. 2016. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/326506616_Package_of_Practices_for_Promoting_Climate_Resilient_Cardamom_Value_Chains_in_Nepal (accessed on 15 June 2025).
- Arel-Bundock, V.; Greifer, N.; Heiss, A. How to Interpret Statistical Models Using Marginal Effects for R and Python. J. Stat. Softw. 2024, 111, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzira, R.; Tenywa, J.S.; Basamba, T.A. Using the Ordered Probit Model to Predict Drivers for Adoption of Multiple Soil Fertility Management and Conservation Technologies in Potato Production Systems in Uganda. Open Acess Libr. J. 2021, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, W.H. Econometric Analysis, 5th ed.; Pearson Education, Inc.: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2002; ISBN 9783540776482. [Google Scholar]
- Wooldridge, J.M. Econometric Analysis of Cross Section and Panel Data, 2nd ed.; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2010; ISBN 9780262232586. [Google Scholar]
- Guneri, O.I.; Durmus, B.; Aynur, I. Ordered Choice Models: Ordinal Logit and Ordinal Probit. Lumbini Agric. J. 2024, 3, 21–41. [Google Scholar]
- National Statistics Office. National Sample Census of Agriculture; Office of the Prime Minister and Council of Ministers: Kathmandu, Nepal, 2023. Available online: https://www.scribd.com/document/858501522/National-Sample-Census-of-Agriculture-National-Report (accessed on 11 June 2025).
- Abdullah, M.; Parvin, S.S. Sustainable Strategies for Large Cardamom Cultivation in the Sikkim Himalayas: Addressing Climate, Socioeconomic, and Biodiversity Challenges. Appl. Agric. Sci. 2024, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanal, D.; Banjade, D.; Joshi, L.P.; Shrestha, A.; Khatri, S. Adoption of Technology in Cardamom Cultivation in Taplejung District, Nepal. Int. J. Environ. Agric. Biotechnol. 2025, 10, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakal, S.; Chaulagain, B.; Bhattarai, R.K.; Pandit, A.; Dangi, B.; Dahal, R. Organic Approaches for Preserving Soil Health in the Mountainous Agro-Ecosystem of Nepal: A Review. Trends Agric. Sci. 2024, 3, 329–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.; Partap, U.; Dahal, D.R.; Sharma, D.P.; Sharma, E. Declining Large-Cardamom Production Systems in the Sikkim Himalayas: Climate Change Impacts, Agroeconomic Potential, and Revival Strategies. Mt. Res. Dev. 2016, 36, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sony, K.C.; Upreti, B.R. The Political Economy of Cardamom Farming in Eastern Nepal: Crop Disease, Coping Strategies, and Institutional Innovation. SAGE Open 2017, 7, 2158244017705422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruba, U.B.; Talucder, M.S.A.; Zaman, M.N.; Montaha, S.; Tumpa, M.F.A.; Duel, M.A.K.; Puja, R.S.; Triza, A.H. The Status of Implemented Climate Smart Agriculture Practices Preferred by Farmers of Haor Area as a Climate Resilient Approach. Heliyon 2024, 10, e25780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, M.; Abdulai, A. The Drivers of Adoption and Impact of Climate-Smart Agricultural Practices on Livestock Farmers’ Household Welfare in Pakistan. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2025, 9, 1604899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upendram, S.; Regmi, H.P.; Cho, S.H.; Mingie, J.C.; Clark, C.D. Factors Affecting Adoption Intensity of Climate Change Adaptation Practices: A Case of Smallholder Rice Producers in Chitwan, Nepal. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2023, 6, 1016404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziro, J.S.; Kichamu-Wachira, E.; Ross, H.; Palaniappan, G. Adoption of Climate Resilient Agricultural Practices among the Giriama Community in South East Kenya: Implications for Conceptual Frameworks. Front. Clim. 2023, 5, 1032780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asule, P.A.; Musafiri, C.; Nyabuga, G.; Kiai, W.; Kiboi, M.; Nicolay, G.; Ngetich, F.K. Awareness and Adoption of Climate-Resilient Practices by Smallholder Farmers in Central and Upper Eastern Kenya. Heliyon 2024, 10, e38368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rijal, S.; Singh, O.P.; Pandeya, S.; Bhatta, S.; Sapkota, S.; Mishra, B.P. Factors Affecting the Adoption of Good Agricultural practices (GAP) Among Smallholder Vegetable Farmers in Surkhet District, Nepal. J. Agric. For. Univ. 2025, 6, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassie, M.; Jaleta, M.; Shiferaw, B.; Mmbando, F.; Mekuria, M. Adoption of Interrelated Sustainable Agricultural Practices in Smallholder Systems: Evidence from Rural Tanzania. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2013, 80, 525–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abegunde, V.O.; Sibanda, M.; Obi, A. Determinants of the Adoption of Climate-Smart Agricultural Practices by Small-Scale Farming Households in King Cetshwayo District Municipality, South Africa. Sustainability 2020, 12, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jena, P.R.; Tanti, P.C.; Maharjan, K.L. Determinants of Adoption of Climate Resilient Practices and Their Impact on Yield and Household Income. J. Agric. Food Res. 2023, 14, 100659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveen, N.; Datta, P.; Behera, B.; Rahut, D.B. Climate-Smart Agriculture in South Asia: Exploring Practices, Determinants, and Contribution to Sustainable Development Goals. Mitig. Adapt. Strateg. Glob. Change 2024, 29, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandeya, S.; Gajurel, A.; Mishra, B.P.; Devkota, K.; Gyawali, B.R.; Upadhaya, S. Determinants of Climate-Smart Agriculture Adoption Among Rice Farmers: Enhancing Sustainability. Sustainability 2024, 16, 10247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandeya, S.; Gyawali, B.R.; Upadhaya, S. Factors Influencing Precision Agriculture Technology Adoption Among Small-Scale Farmers in Kentucky and Their Implications for Policy and Practice. Agriculture 2025, 15, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mnukwa, M.L.; Mdoda, L.; Mudhara, M. Assessing the Adoption and Impact of Climate-Smart Agricultural Practices on Smallholder Maize Farmers’ Livelihoods in Sub-Saharan Africa: A Systematic Review. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2025, 9, 1543805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizik, T. Climate-Smart Agriculture on Small-Scale Farms: A Systematic Literature Review. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbar, A.; Liu, W.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Peng, J.; Liu, J. Enhancing Adaptation to Climate Change by Fostering Collective Action Groups among Smallholders in Punjab, Pakistan. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2023, 7, 1235726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Rahut, D.B. Climate-Smart Agriculture: Adoption, Impacts, and Implications for Sustainable Development. Mitig. Adapt. Strateg. Glob. Change 2024, 29, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gartaula, H.N.; Visser, L.; Niehof, A. Socio-Cultural Dispositions and Wellbeing of the Women Left Behind: A Case of Migrant Households in Nepal. Soc. Indic. Res. 2012, 108, 401–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghimire, D.J.; Axinn, W.G.; Bhandari, P. Social Change, out-Migration, and Exit from Farming in Nepal. Popul. Environ. 2021, 42, 302–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gartaula, H.; Niehof, A.; Visser, L. Shifting Perceptions of Food Security and Land in the Context of Labour Out-Migration in Rural Nepal. Food Secur. 2012, 4, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.; Paudel, K.P. Migration, Remittance, and Adoption of Conservation Practices. Environ. Manag. 2020, 66, 1072–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, C.L. Rural Out-Migration and Smallholder Agriculture in the Southern Ecuadorian Andes. Popul. Environ. 2009, 30, 193–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dessalegn, M.; Debevec, L.; Nicol, A.; Ludi, E. A Critical Examination of Rural Out-Migration Studies in Ethiopia: Considering Impacts on Agriculture in the Sending Communities. Land 2023, 12, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryal, J.P.; Jat, M.L.; Sapkota, T.B.; Khatri-Chhetri, A.; Kassie, M.; Rahut, D.B.; Maharjan, S. Adoption of Multiple Climate-Smart Agricultural Practices in the Gangetic Plains of Bihar, India. Int. J. Clim. Change Strateg. Manag. 2018, 10, 407–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozor, N.; Cynthia, N. The Role of Extension in Agricultural Adaptation to Climate Change in Enugu State, Nigeria. J. Agric. Ext. Rural Dev. 2011, 3, 42–50. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.L.; Orton, G.; Lu, P. Global Meta-Analysis of Innovation Attributes Influencing Climate-Smart Agriculture Adoption for Sustainable Development. Climate 2024, 12, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakaria, A.; Alhassan, S.I.; Kuwornu, J.K.M.; Azumah, S.B.; Derkyi, M.A.A. Factors Influencing the Adoption of Climate-Smart Agricultural Technologies among Rice Farmers in Northern Ghana. Earth Syst. Environ. 2020, 4, 257–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiros, S.; Meshesha, G.B. Factors Affecting Farmers’ Access to Formal Financial Credit in Basona Worana District, North Showa Zone, Amhara Regional State, Ethiopia. Cogent Econ. Financ. 2022, 10, 2035043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Custer, C.; Healey, A.; Meyer, H.; Smith, R. Bridging the Regenerative Agriculture Financing Gap. 2024. Available online: https://cbey.yale.edu/sites/default/files/2024-02/Bridging%20the%20Regenerative%20Agriculture%20Financing%20Gap_FinalRev.pdf (accessed on 29 September 2025).
- Makate, C.; Makate, M.; Mutenje, M.; Mango, N.; Siziba, S. Synergistic Impacts of Agricultural Credit and Extension on Adoption of Climate-Smart Agricultural Technologies in Southern Africa. Environ. Dev. 2019, 32, 100458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalba, R.; Joshi, G.; Daum, T.; Venus, T.E. Financing Climate-Smart Agriculture: A Case Study from the Indo-Gangetic Plains. Mitig. Adapt. Strateg. Glob. Change 2024, 29, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhaya, S.; Arbuckle, J.G. Examining Factors Associated with Farmers’ Climate-Adaptive and Maladaptive Actions in the US Midwest. Front. Clim. 2021, 3, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.V.; Dhungana, A.R.; Khand, P.B. Gender Perspective on Climate Change Adaption Strategies in Livestock Farming in Gandaki Province, Nepal. Open Vet. J. 2024, 14, 3363–3374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhungana, S.M. Information and Communication Technologies (ICTs) in Farming and Its Determinants: A Reference of Dhankuta, Nepal. OCEM J. Manag. Technol. Soc. Sci. 2024, 3, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachkain, R.; Karki, T. Status and Prospects of Ict Among Nepalese Smallholder Farmers. Acta Inform. Malays. 2022, 6, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Padaria, R.N.; Burman, R.R.; Velayudhan, P.K.; Mahra, G.S.; Aditya, K.; Sahu, S.; Saini, S.; Mallick, S.; Quader, S.W.; et al. Global Trends in ICT-Based Extension and Advisory Services in Agriculture: A Bibliometric Analysis. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2025, 9, 1430336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigdel, U.P.; Pyakuryal, K.N.; Devkota, D.; Ojha, G.P. Constraints on the Use and Adoption of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) Tools and Farm Machinery by Paddy Farmers in Nepal. J. Agric. For. Univ. 2022, 5, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touray, A.; Salminen, A.; Mursu, A. ICT Barriers and Critical Success Factors in Developing Countries. Electron. J. Inf. Syst. Dev. Ctries. 2013, 56, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osumba, J.J.L.; Recha, J.W.; Oroma, G.W. Transforming Agricultural Extension Service Delivery through Innovative Bottom-up Climate-Resilient Agribusiness Farmer Field Schools. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandeya, S.; Gyawali, B.R.; Upadhaya, S.; Zourarakis, D. Patterns of Change: Land Use/Land Cover Dynamics in Priority vs. Non-Priority Watersheds in Eastern Kentucky. Environ. Chall. 2025, 20, 101264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).