Revisit of a Case Study of Spilled Oil Slicks Caused by the Sanchi Accident (2018) in the East China Sea
Abstract
1. Introduction
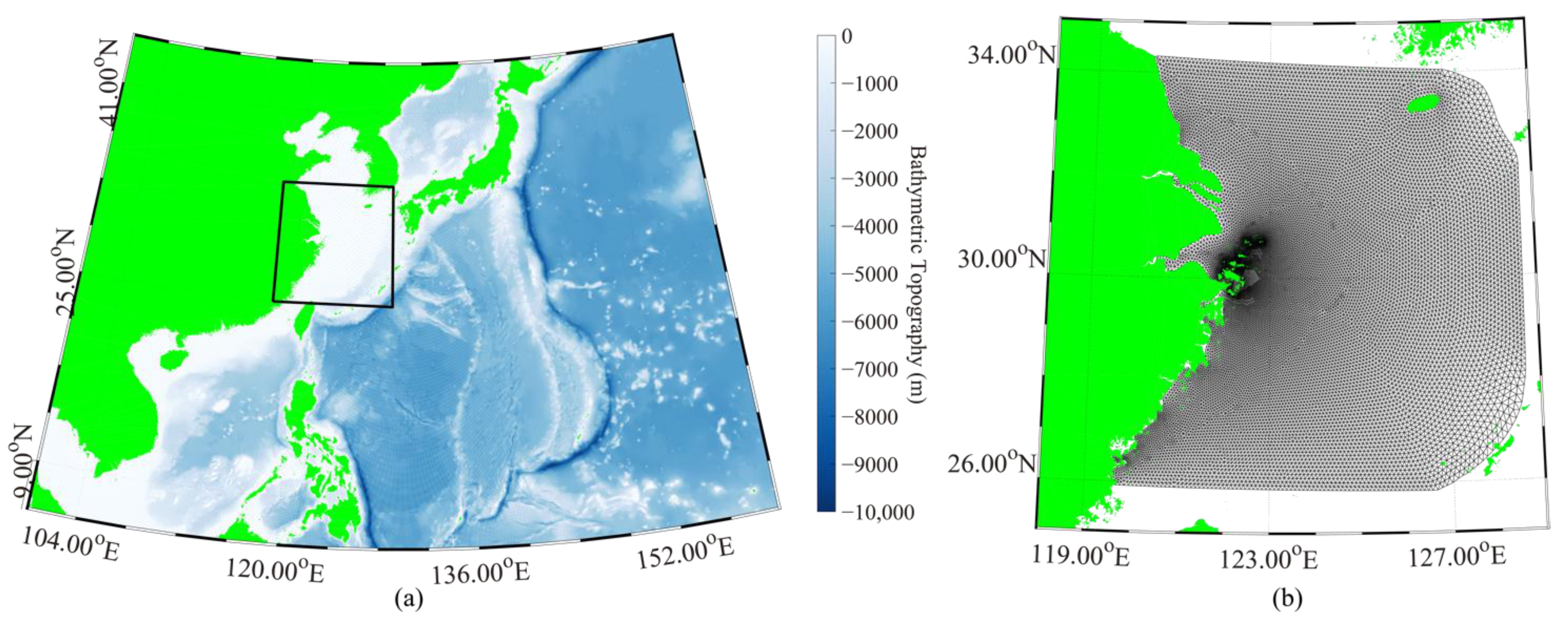
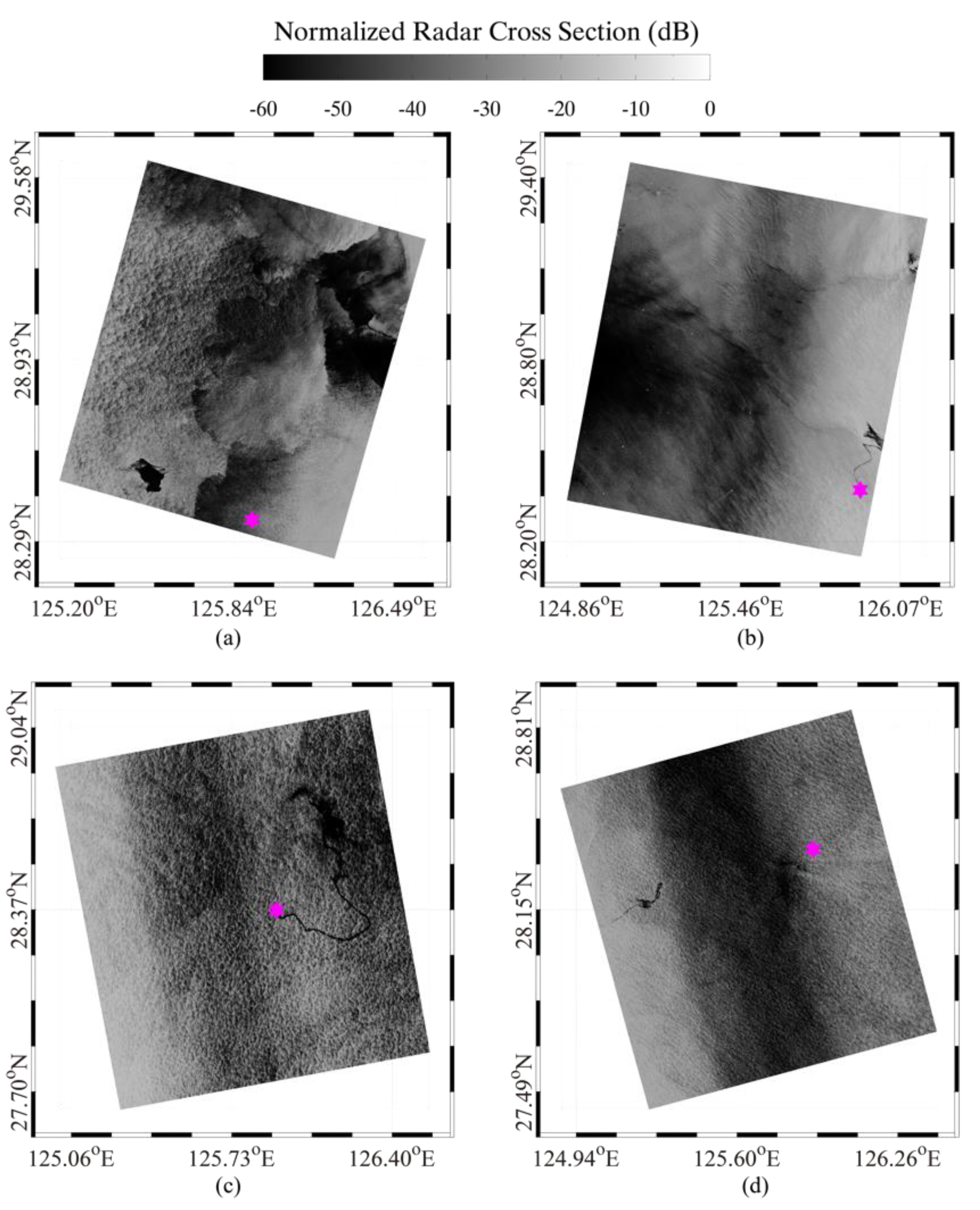
2. Dataset Collection
3. Method and Results
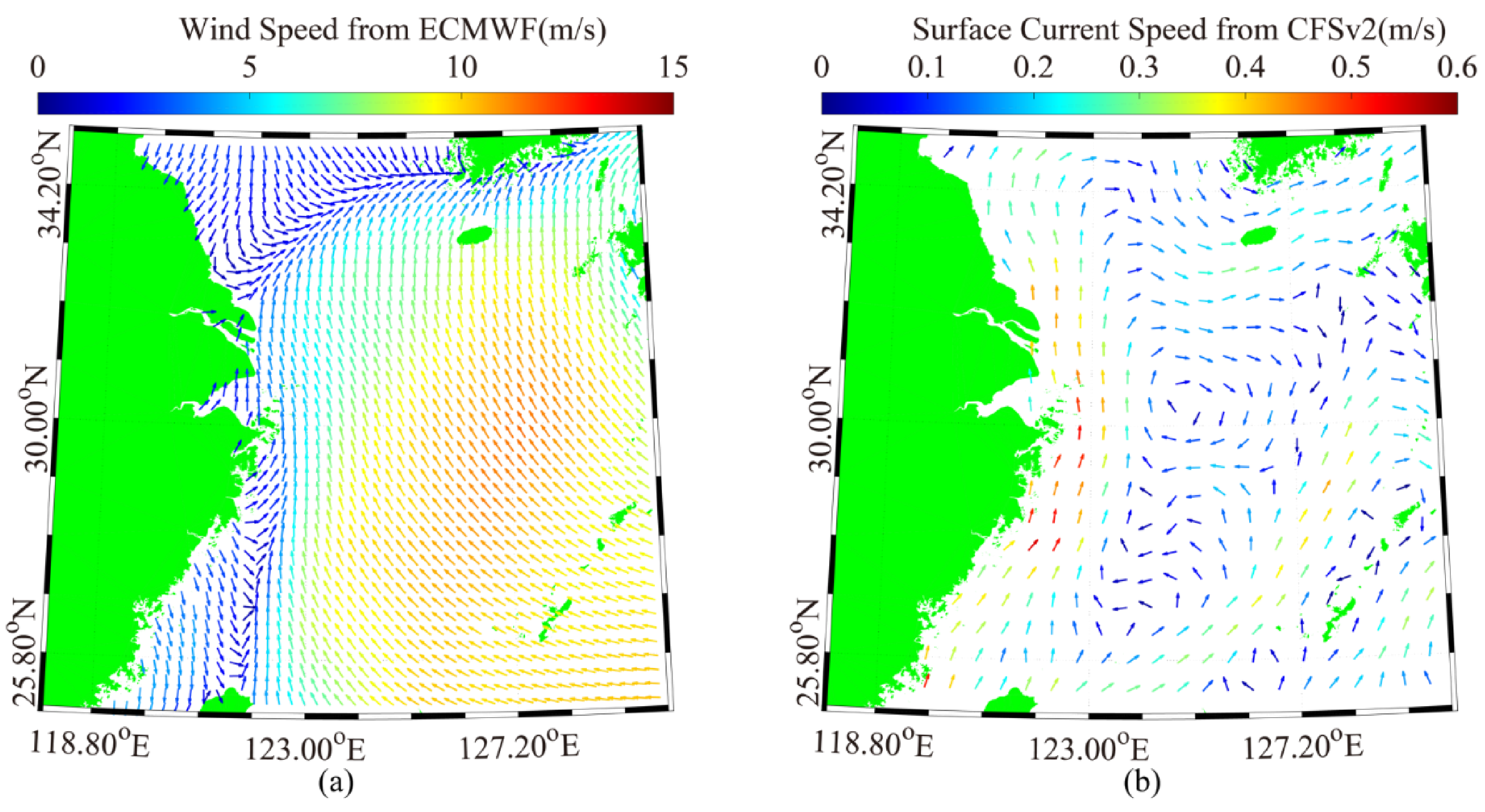
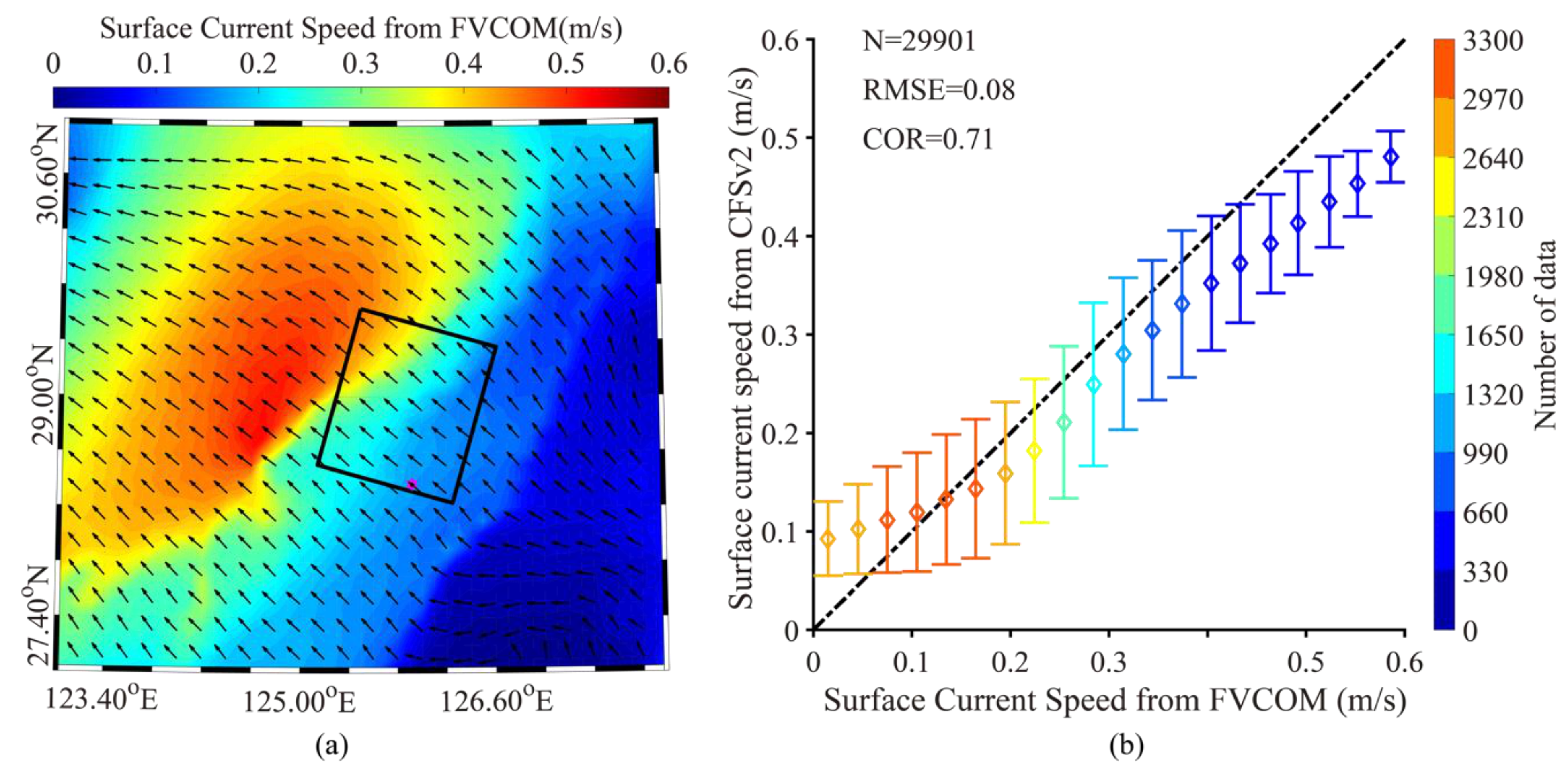
3.1. Simulation of Sea-Surface Current
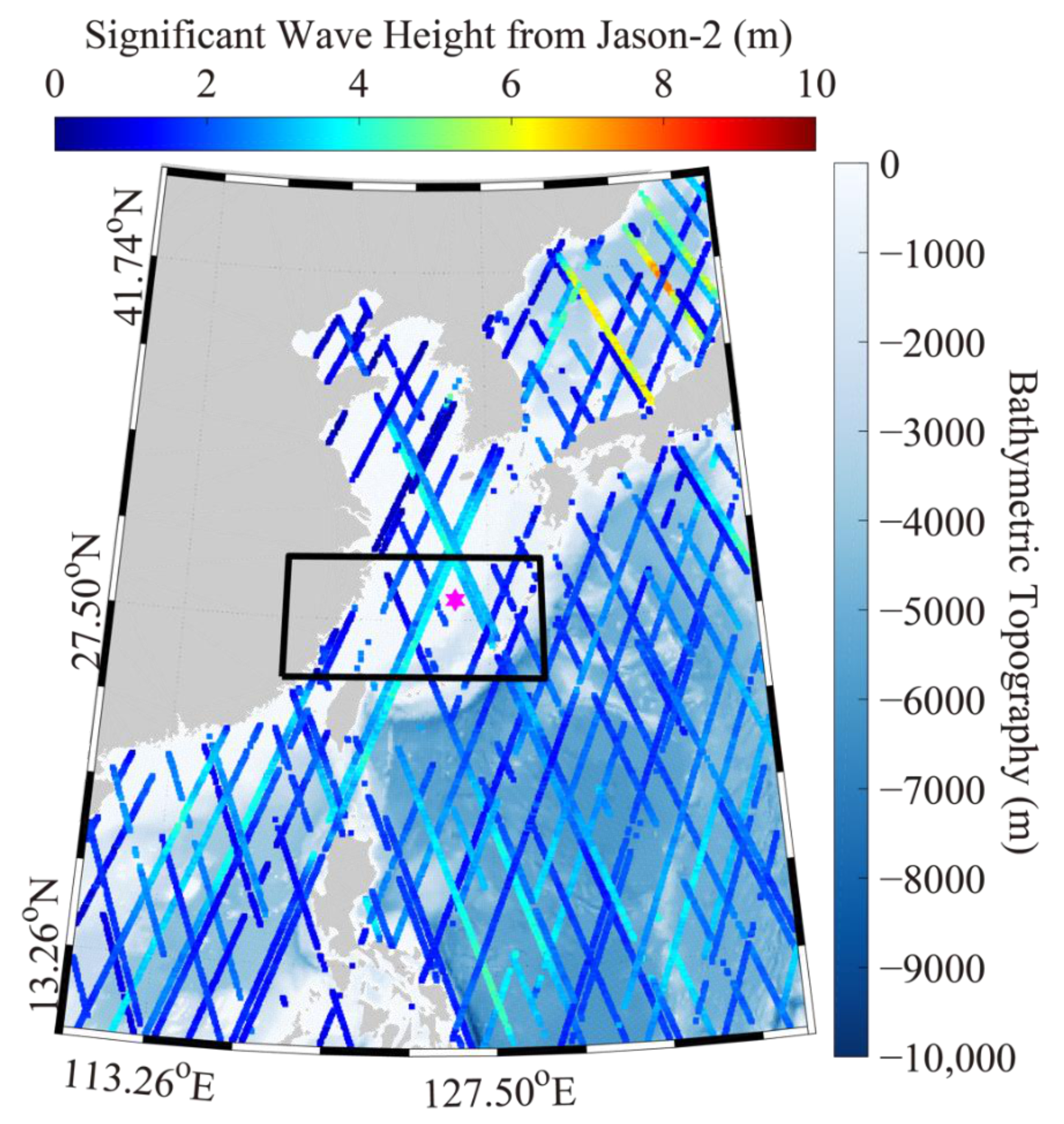
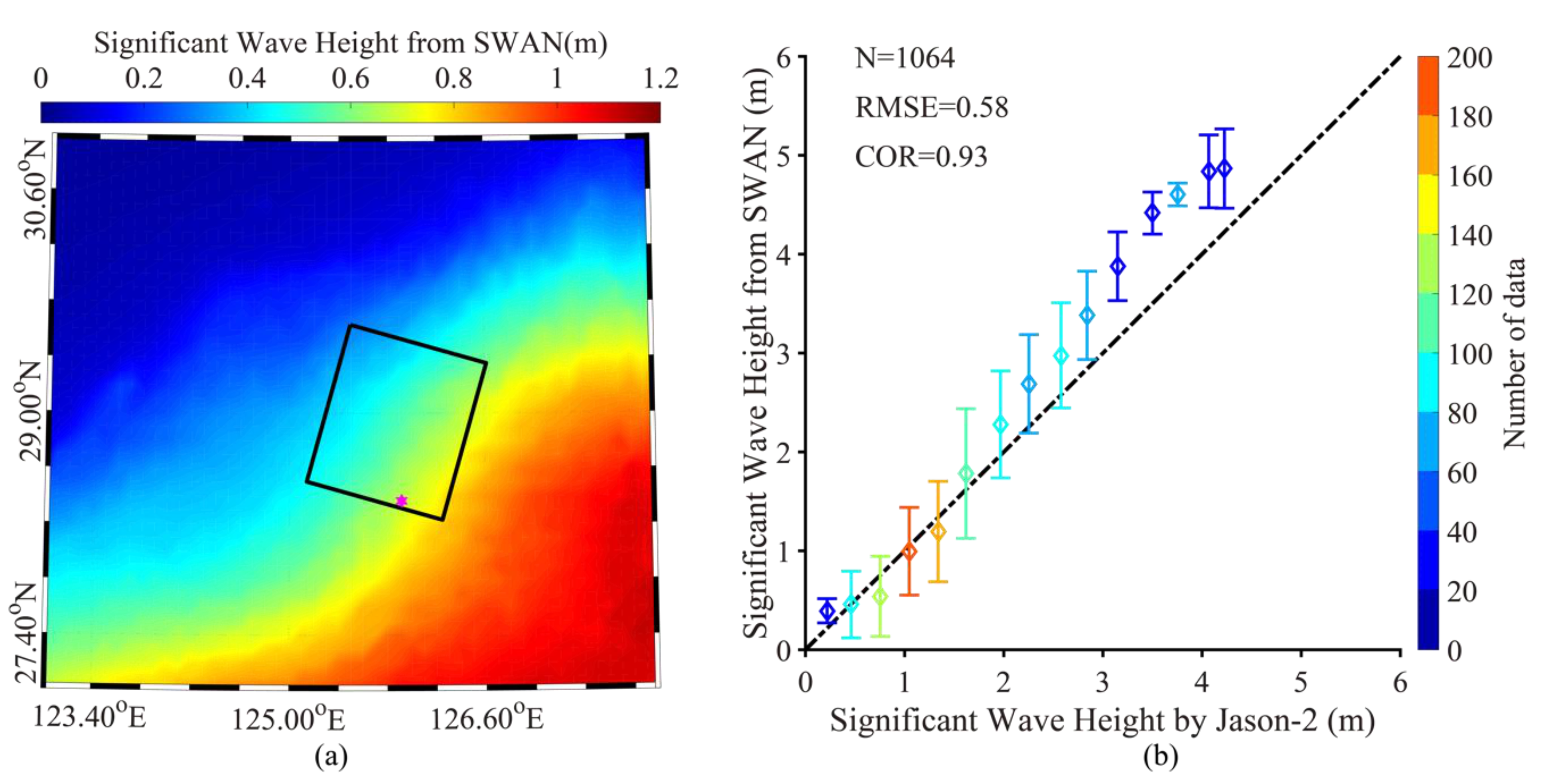
3.2. Simulation of Sea-Surface Wave
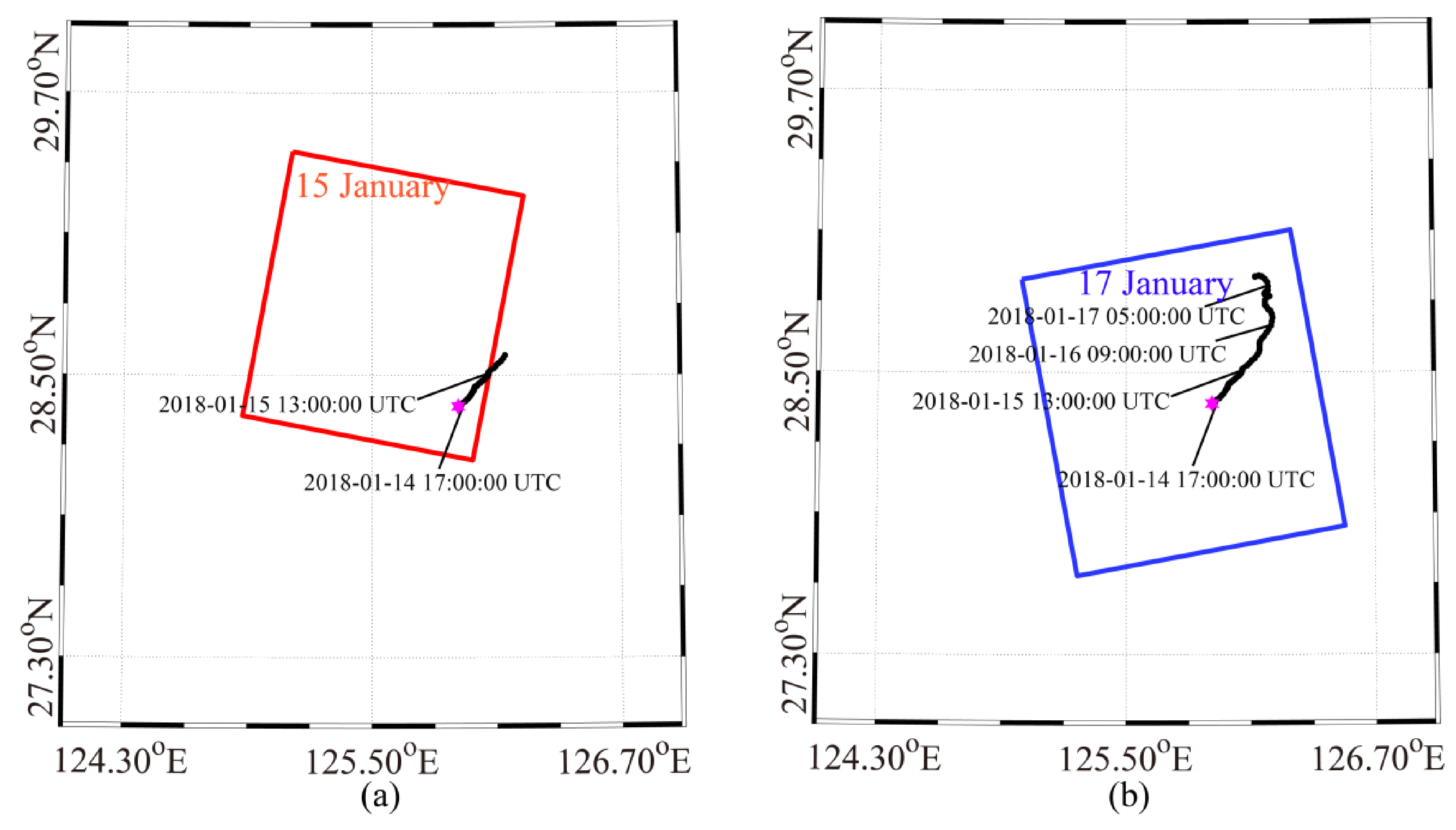
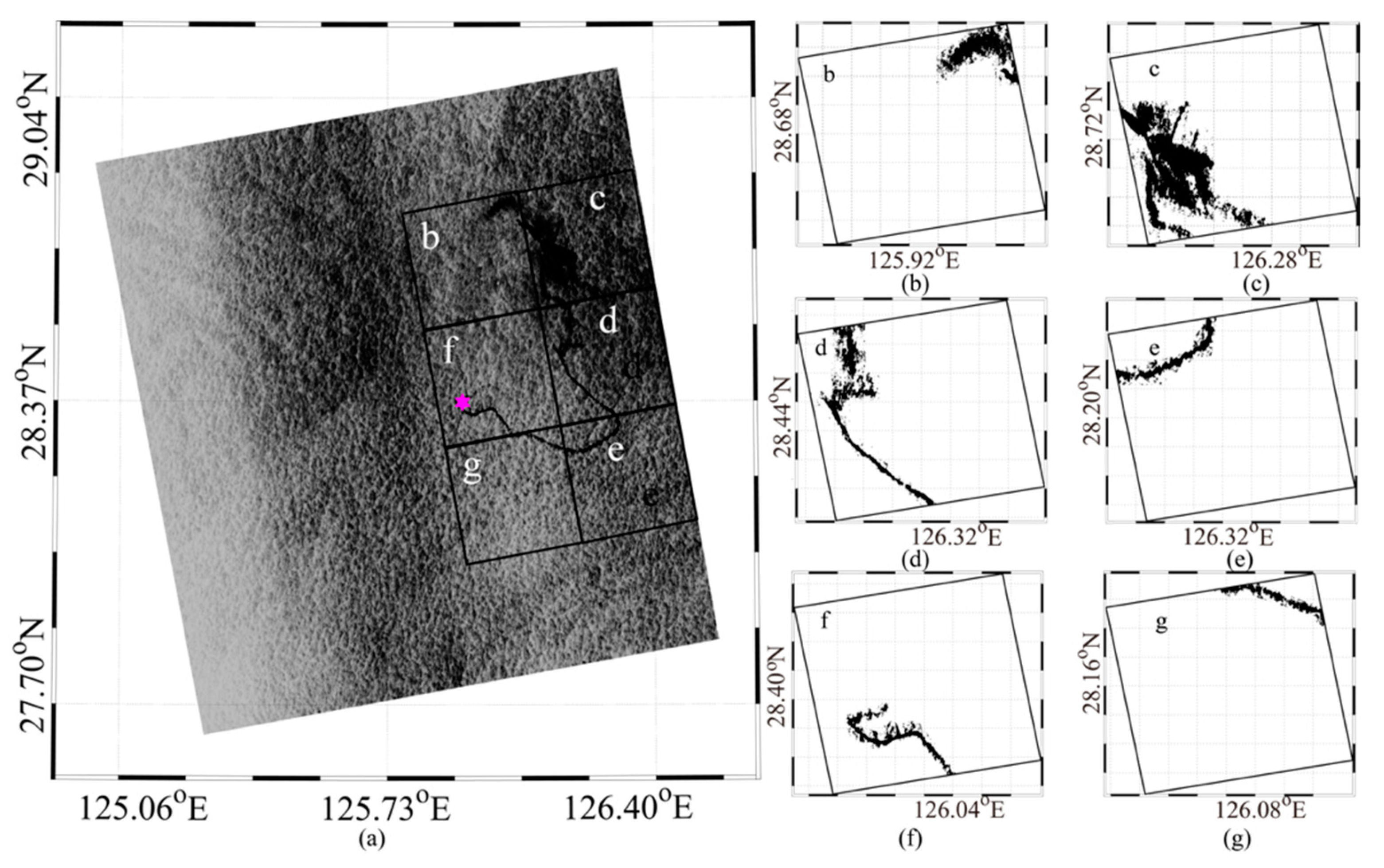
3.3. Simulation of Spilled Oil-Slicks
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
- (1)
- Any scattering unit in a pixel size will not affect other scattering units to a large extent.
- (2)
- The phase of each scattering unit obeys the uniform distribution on [-π, π].
- (3)
- The phase random variables of each scattering unit are not related to each other, and some related scattering units naturally form a scattering center.
- (4)
- There is no correlation between the amplitude random variable and the phase random variable of each scattering unit.
References
- Qiao, F.L.; Wang, G.; Yin, L.; Zeng, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Xiao, B.; Jiang, S.; Chen, H.; Chen, G. Modelling oil trajectories and potentially contaminated areas from the Sanchi oil spill. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 685, 856–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, A.; Dabrowski, T.; Lyons, K. The oil spill model OILTRANS and its application to the Celtic sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 2489–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Wu, G.; Jiang, M.; Xu, T.; Yang, Z.; Xie, M.; Chen, X. A modified probabilistic oil spill model and its application to the Dalian new port accident. Ocean Eng. 2016, 121, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fingas, M.; Fieldhouse, B. Formation of water-in-oil emulsions and application to oil spill modelling. J. Hazard. Mater. 2004, 107, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mccay, D.F. Development and application of damage assessment modeling: Example assessment for the north cape oil spill. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 47, 341–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yapa, P.D.; Shen, H.T. Modelling river oil spills: A review. J. Hydraul. Res. 1994, 32, 765–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fingas, M.F. A literature review of the physics and predictive modelling of oil spill evaporation. J. Hazard. Mater. 1995, 42, 157–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afenyo, M.; Veitch, B.; Khan, F. A state-of-the-art review of fate and transport of oil spills in open and ice-covered water. Ocean Eng. 2016, 119, 233–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasimu, A.; Dong, J.; Bian, Y.; Wu, D. Simulate oil spill weathering with system dynamic model. Front. Eng. Man. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, A.; Nikova, A.; Venkataraman, P.; John, V.; Bose, A. Oil emulsification using surface-tunable carbon black particles. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2013, 5, 3094–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, A.; Hurford, N.; Penn, C. Shear diffusion and the spreading of oil slicks. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1986, 17, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Wang, Y. A numerical oil spill model based on a hybrid method. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2009, 58, 726–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stopa, J.E.; Cheung, K.F. Intercomparison of wind and wave data from the ECMWF reanalysis interim and the NCEP climate forecast system reanalysis. Ocean Model. 2014, 75, 65–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.H.; Shao, W.Z.; Ding, Y.Y.; Shi, J.; Ji, Q.Y. Wave simulation by the SWAN model and FVCOM considering the sea-water level around the Zhoushan islands. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y.X.; Shao, W.Z.; Li, S.Q.; Zhang, Y.M.; Yang, H.W.; Zuo, J.C. Evaluation of typhoon waves simulated by WaveWatch-III model in shallow waters around Zhoushan Islands. J. Ocean Univ. China 2019, 18, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, W.Z.; Sheng, Y.X.; Li, H.; Shi, J.; Ji, Q.Y.; Tan, W.; Zuo, J.C. Analysis of wave distribution simulated by WAVEWATCH-III model in typhoons passing Beibu Gulf, China. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.Y.; Shao, W.Z.; Shi, J.; Sun, J.; Ji, Q.Y.; Cai, L.N. Analysis of the typhoon wave distribution simulated in WAVEWATCH-III model in the context of Kuroshio and wind-induced current. J. Oceanol. Limn. 2020, 38, 1692–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Liu, J.; Cai, L.N.; Zhou, M.R.; Bu, J.; Xu, J. Satellites HY-1C and Landsat 8 combined to observe the influence of bridge on sea surface temperature and suspended sediment concentration in Hangzhou Bay, China. Water 2020, 12, 2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.N.; Bu, J.; Tang, D.L.; Zhou, M.R.; Yao, R.; Huang, S. Geosynchronous Satellite GF-4 Observations of Chlorophyll-a Distribution Details in the Bohai Sea, China. Sensors 2020, 20, 5471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, R.; Cai, L.N.; Liu, J.; Zhou, M.R. GF-1 Satellite observations of suspended sediment injection of Yellow River Estuary, China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaraja Rao, C.; Stowe, L.; Mcclain, E. Remote sensing of aerosols over the oceans using AVHRR data theory, practice and applications. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1988, 10, 743–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esaias, W.; Abbott, M.; Barton, I.; Brown, O.; Minnett, P. An overview of MODIS capabilities for ocean science observations. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1998, 36, 1250–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.F.; Wu, Q.; Chen, G. Validation of HY-2A remotely sensed wave heights against buoy data and Jason-2 altimeter measurements. J. Atmos. Ocean. Tech. 2015, 32, 1270–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quilfen, Y.; Bentamy, A.; Elfouhaily, T.; Katsaros, K.; Tournadre, J. Observation of tropical cyclones by high-resolution scatterometry. J. Geophys. Res. 1998, 103, 7767–7786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpers, W.; Ross, D.B.; Rufenach, C.L. On the detectability of ocean surface waves by real and synthetic radar. J. Geophys. Res. 1981, 86, 10529–10546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.F.; Zhang, J.A.; Yang, X.F.; Pichel, W.G.; DeMaria, M.; Long, D.; Li, Z.W. Tropical cyclone morphology from spaceborne synthetic aperture radar. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2013, 94, 215–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espedal, H. Satellite SAR oil spill detection using wind speed history information. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1999, 20, 49–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliaccio, M.; Gambardella, A.; Tranfaglia, M. SAR polarimetry to observe oil spills. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 506–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghadosi, M.; Hasanlou, M.; Eftekhari, K. Soil salinity mapping using dual-polarized SAR Sentinel-1 imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 40, 237–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santi, F.; Luciani, G.; Bresciani, M.; Giardino, C.; Carolis, G. Synergistic use of synthetic aperture radar and optical imagery to monitor surface accumulation of cyanobacteria in the Curonian Lagoon. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2019, 7, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, K.; Wang, Y. A deep convolutional neural network for oil spill detection from spaceborne SAR images. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirvany, R. Ship and oil-spill detection using the degree of polarization in linear and hybrid/compact dual-pol SAR. IEEE J. Sel. Topics Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2012, 5, 885–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsey, E.; Rangoonwala, A.; Suzuoki, Y.; Jones, C.E. Oil Detection in a Coastal Marsh with Polarimetric Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR). Remote Sens. 2011, 3, 2630–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, C.M.; Huang, C.J.; Wu, L.C.; Zhang, Y.L.J.; Chuang, L.Z.H.; Fan, Y.M.; Yu, H.C. Forecasting of oil-spill trajectories by using SCHISM and X-band radar. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 137, 566–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Huang, W.M.; Gleason, S. Dual antenna space-based GNSS-R ocean surface mapping: Oil slick and tropical cyclone sensing. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Fu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, H. Modification of CFAR algorithm for oil spill detection from SAR data. Intell. Autom. Soft Comput. 2015, 21, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velotto, D.; Migliaccio, M.; Nunziata, F.; Lehner, S. Dual-polarized TerraSAR-X data for oil-spill observation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 4751–4762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunziata, F.; Migliaccio, M.; Gambardella, A. Pedestal height for sea oil slick observation. IET Radar Sonar. Nav. 2011, 5, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Li, X.; Perrie, W.; Garcia-Pineda, O. Compact polarimetric synthetic aperture radar for marine oil platform and slick detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 1407–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Chen, J.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y. Oil spill forecast model based on uncertainty analysis: A case study of Dalian oil spill. Ocean Eng. 2012, 54, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.l.; Lu, Y.C.; Liu, Y.X.; Wang, M.Q.; Hu, C.M. Tracking an oil tanker collision and spilled oils in the East China Sea using multisensor day and night satellite imagery. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 3212–3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutin, J.; Siefridt, L.; Etcheto, J.; Barnier, B. Comparison of ECMWF and satellite ocean wind speeds from 1985 to 1992. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 17, 2897–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saket, A.; Etemad-Shahidi, A.; Moeini, M. Evaluation of ECMWF wind data for wave hindcast in Chabahar zone. J. Coastal Res. 2013, 65, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.S.; Huang, H.; Beardsley, R.C.; Liu, H.; Xu, Q.; Cowles, G. A finite-volume numerical approach for coastal ocean circulation studies: Comparisons with finite difference models. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, C03018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akpınar, A.; Vledder, G.; Kömürcü, M.; Özger, M. Evaluation of the numerical wave model (SWAN) for wave simulation in the Black Sea. Cont. Shelf Res. 2012, 50, 80–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Qiao, F.L. The long-term prediction of the oil-contaminated water from the Sanchi collision in the East China Sea. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2018, 3, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, W.Z.; Zhu, S.; Sun, J.; Yuan, X.Z.; Sheng, Y.X.; Zhang, Q.J.; Ji, Q.Y. Evaluation of wind retrieval from co-polarization Gaofen-3 SAR imagery around China seas. J. Ocean. Univ. China 2019, 18, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, W.Z.; Hu, Y.Y.; Zheng, G.; Cai, L.N.; Zou, J.C. Sea state parameters retrieval from cross-polarization Gaofen-3 SAR data. Adv. Space Res. 2019, 65, 1025–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschetti, G.; Iodice, A.; Riccio, D.; Ruello, G.; Siviero, R. SAR raw signal simulation of oil slicks in ocean environments. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 1935–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, W.Z.; Jiang, X.W.; Nunziata, F.; Marino, A.; Corcione, V. Analysis of waves observed by synthetic aperture radar across ocean fronts. Ocean. Dynam. 2020, 70, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehr, W.; Fraga, R.; Belen, M.; Cekirge, H. A new technique to estimate initial spill size using a modified fay-type spreading formula. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1984, 15, 326–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, J.W. Stokes drift and the fully developed sea. J. Geophys. Res. 1970, 75, 2847–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, F.; Wu, K.J.; Zhang, Y.M. Effect of Stokes drift on Ekman transport in the open sea. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2012, 6, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, B.; Wei, Y.Y. Modeling of oil spill beaching along the coast of the Bohai sea, China. Front. Earth Sci. 2015, 9, 637–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
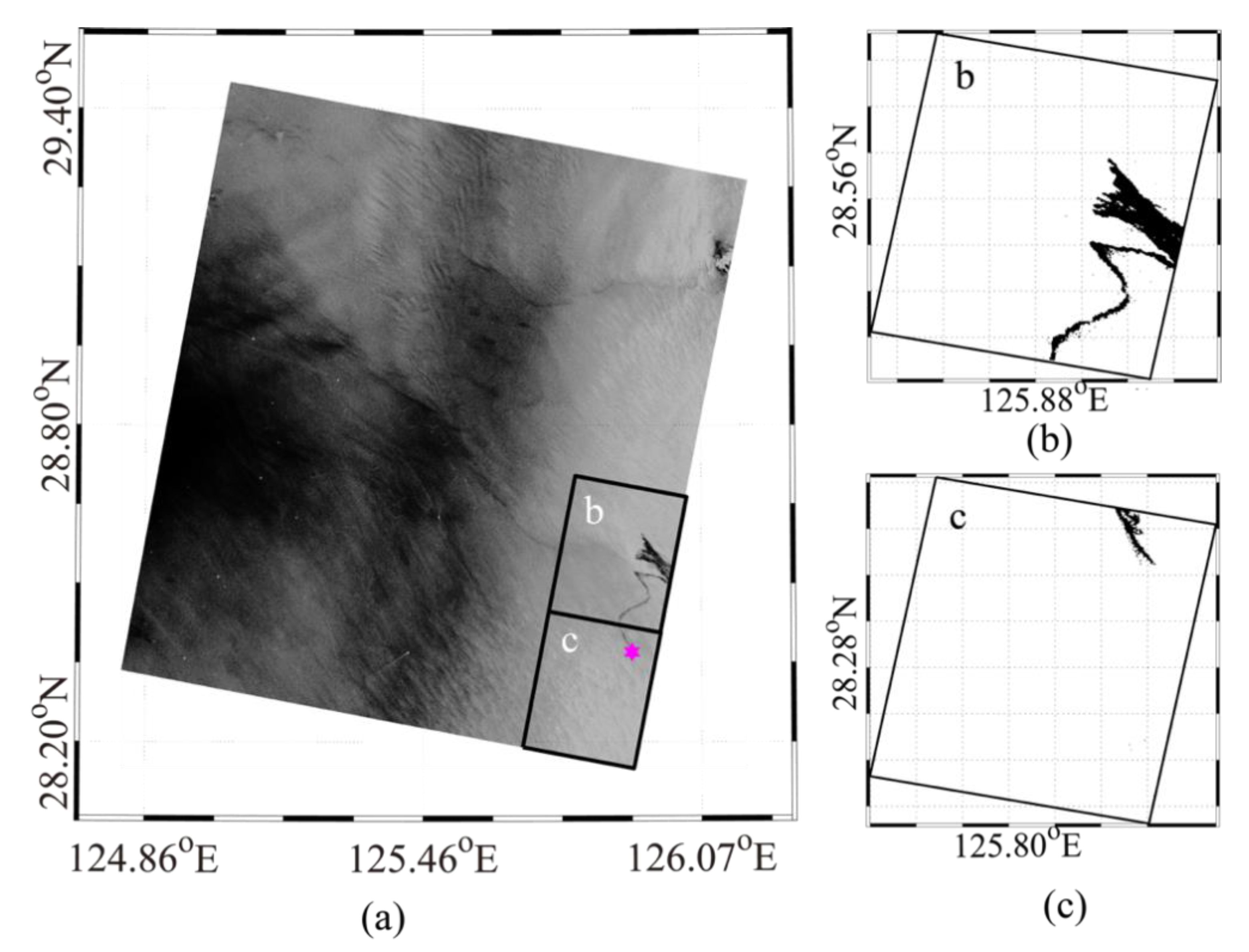
| Imaging Mode | SAR Acquisition Time (YYYY-MM-DD) | SAR Oil Area (km2) | Model Acquisition Time (YYYY-MM-DD) | Model-Simulated Oil Area (km2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FSII | 2018-1-15 21:39 | 83.78 | 2018-1-15 22:00 | 82.31 |
| SS | 2018-1-17 09:42 | 364.70 | 2018-1-17 10:00 | 363.56 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Z.; Shao, W.; Hu, Y.; Ji, Q.; Li, H.; Zhou, W. Revisit of a Case Study of Spilled Oil Slicks Caused by the Sanchi Accident (2018) in the East China Sea. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 279. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9030279
Yang Z, Shao W, Hu Y, Ji Q, Li H, Zhou W. Revisit of a Case Study of Spilled Oil Slicks Caused by the Sanchi Accident (2018) in the East China Sea. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2021; 9(3):279. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9030279
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Zhehao, Weizeng Shao, Yuyi Hu, Qiyan Ji, Huan Li, and Wei Zhou. 2021. "Revisit of a Case Study of Spilled Oil Slicks Caused by the Sanchi Accident (2018) in the East China Sea" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 9, no. 3: 279. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9030279
APA StyleYang, Z., Shao, W., Hu, Y., Ji, Q., Li, H., & Zhou, W. (2021). Revisit of a Case Study of Spilled Oil Slicks Caused by the Sanchi Accident (2018) in the East China Sea. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 9(3), 279. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9030279







