Severe Weather-Induced Exchange Flows through a Narrow Tidal Channel of Calcasieu Lake Estuary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data
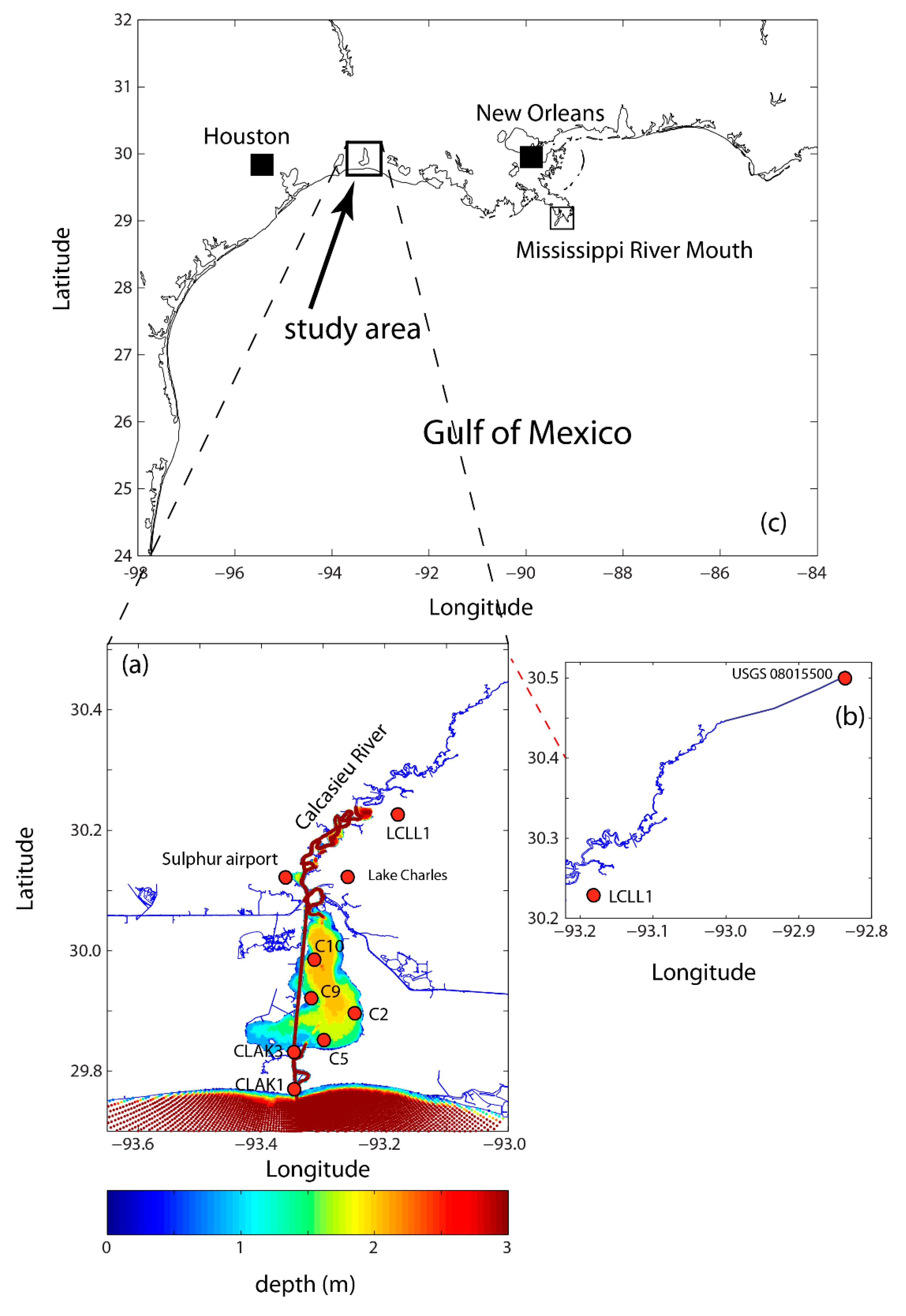
2.1. Study Area
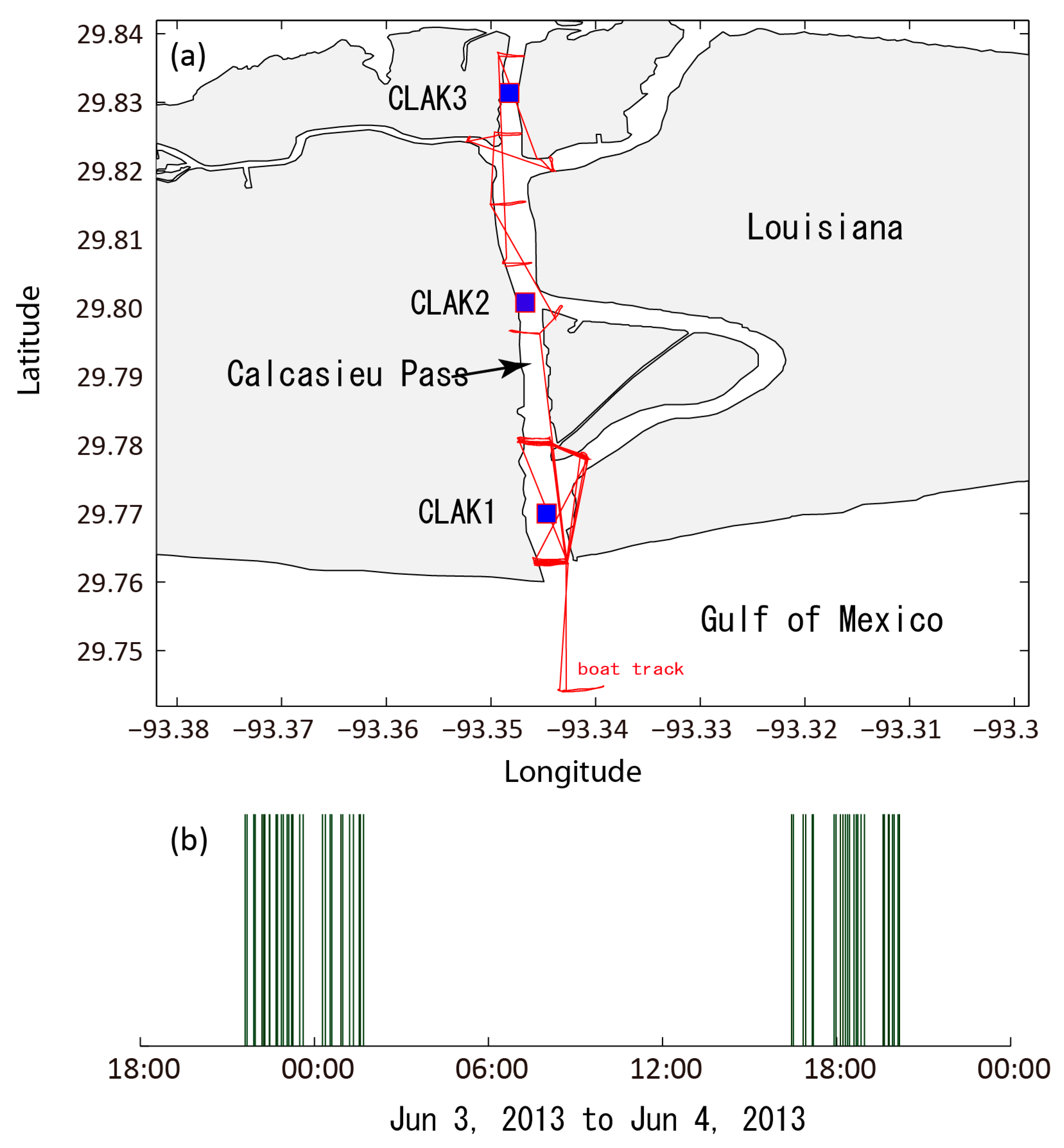
2.2. Data and Processing
3. Data Analysis
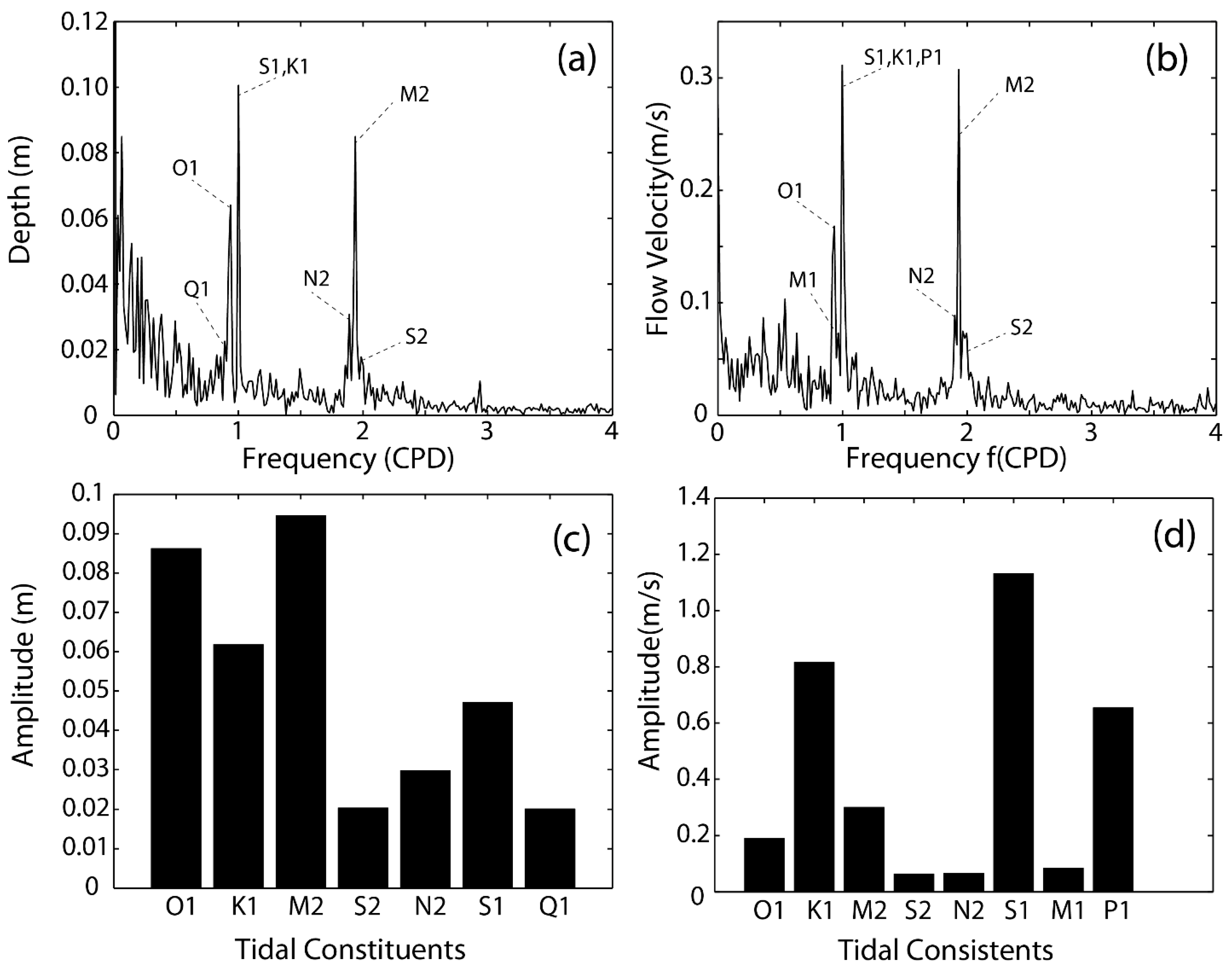
3.1. Fourier and Harmonic Analysis
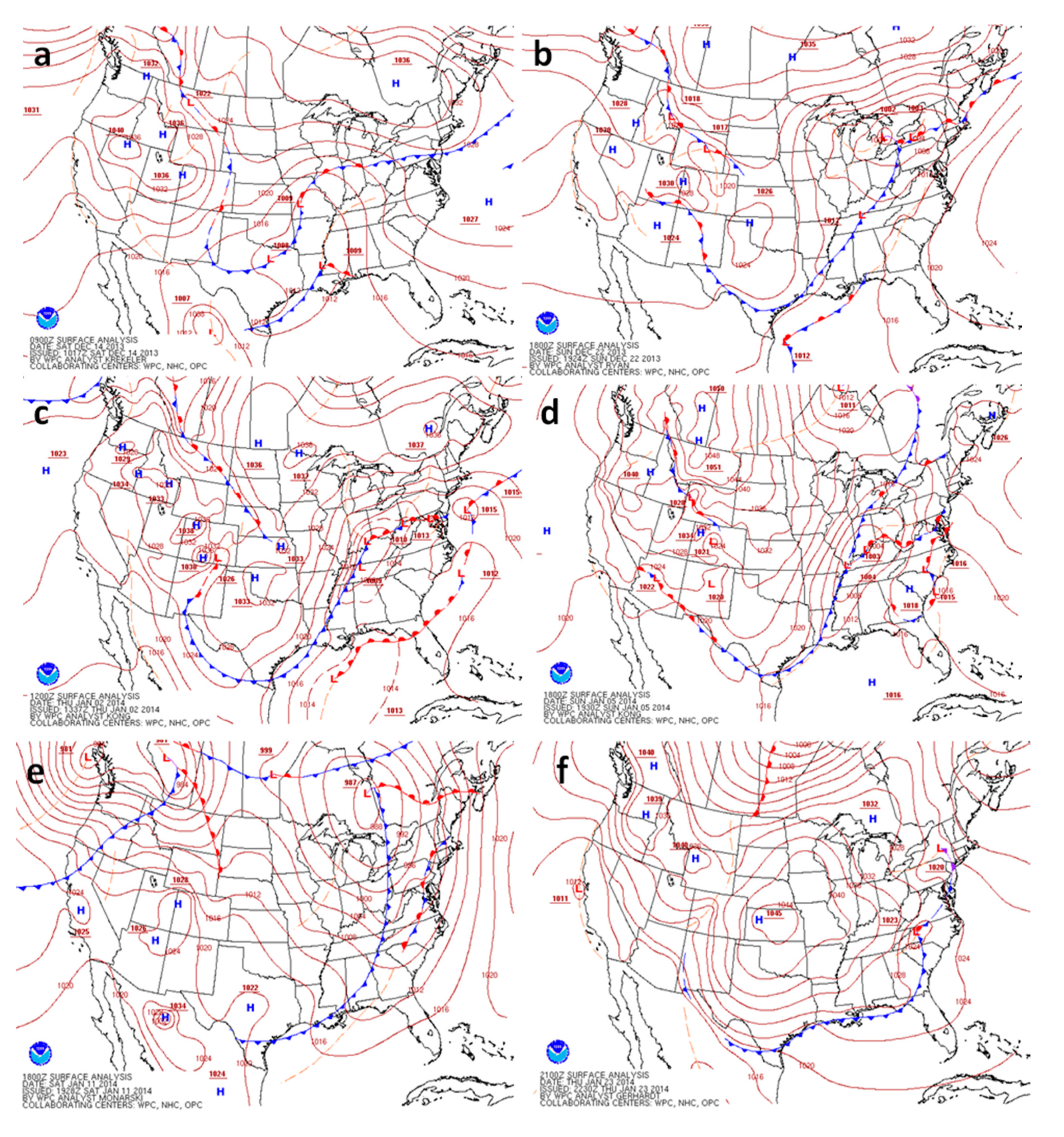
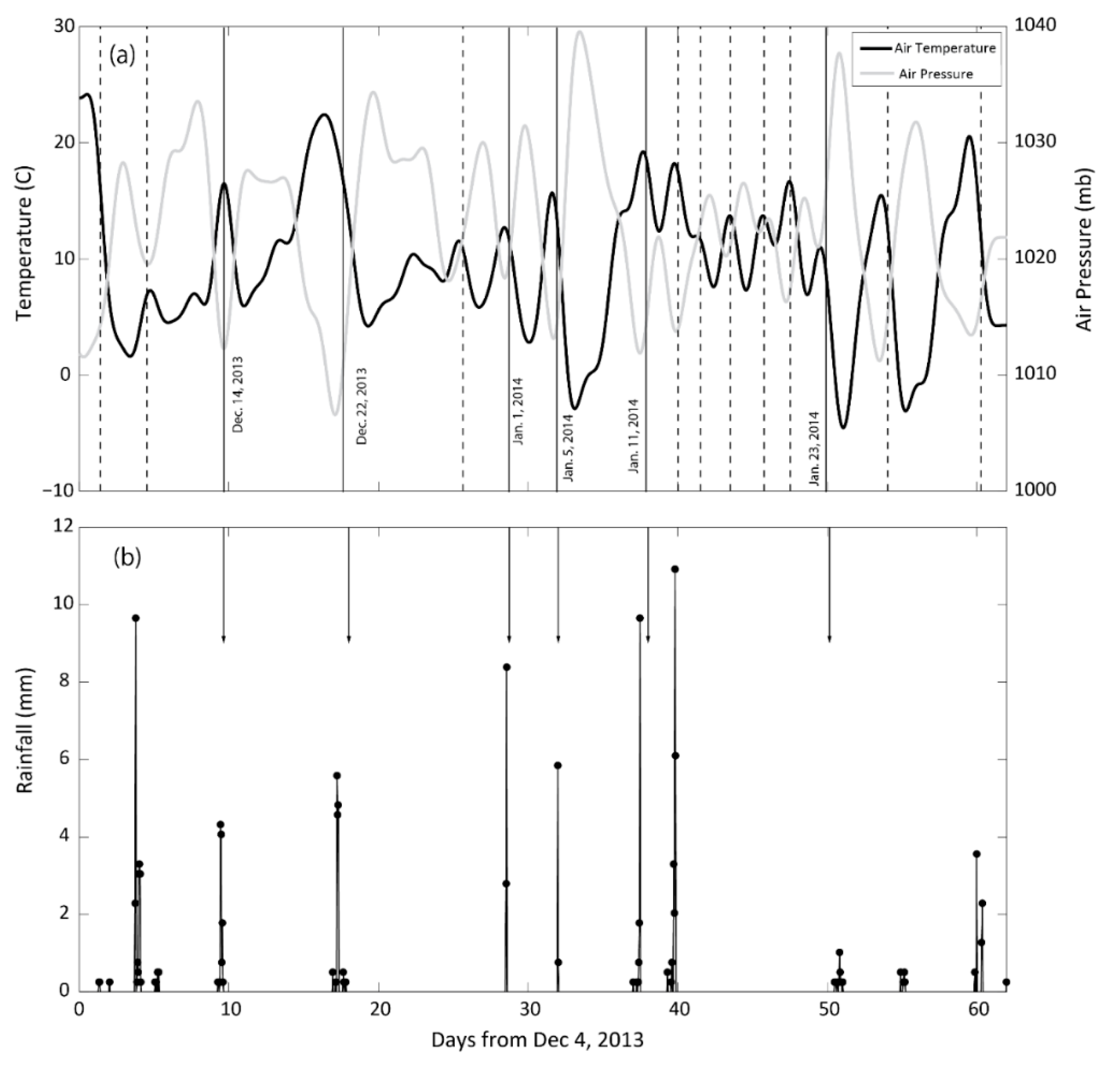
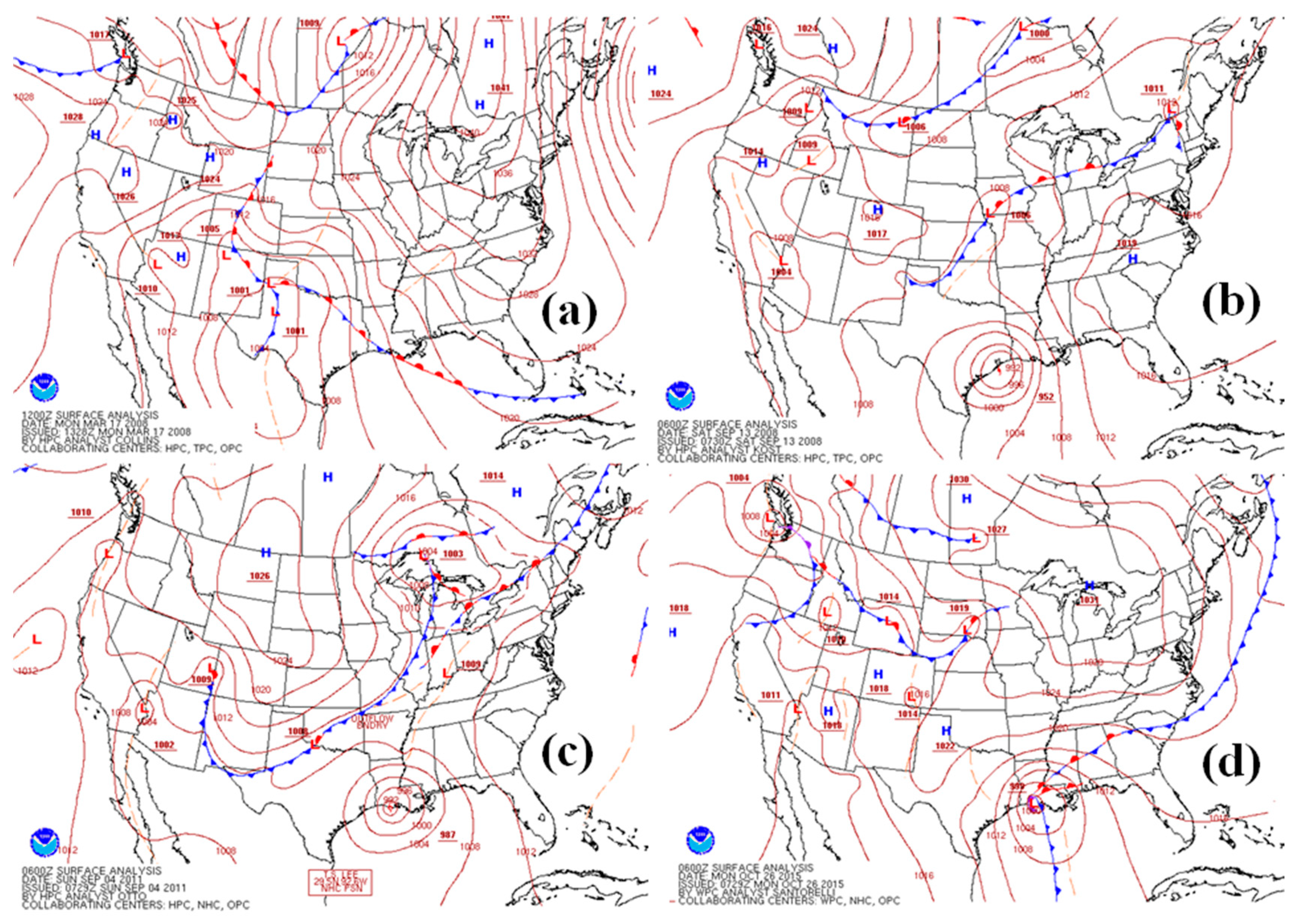
3.2. Weather Background
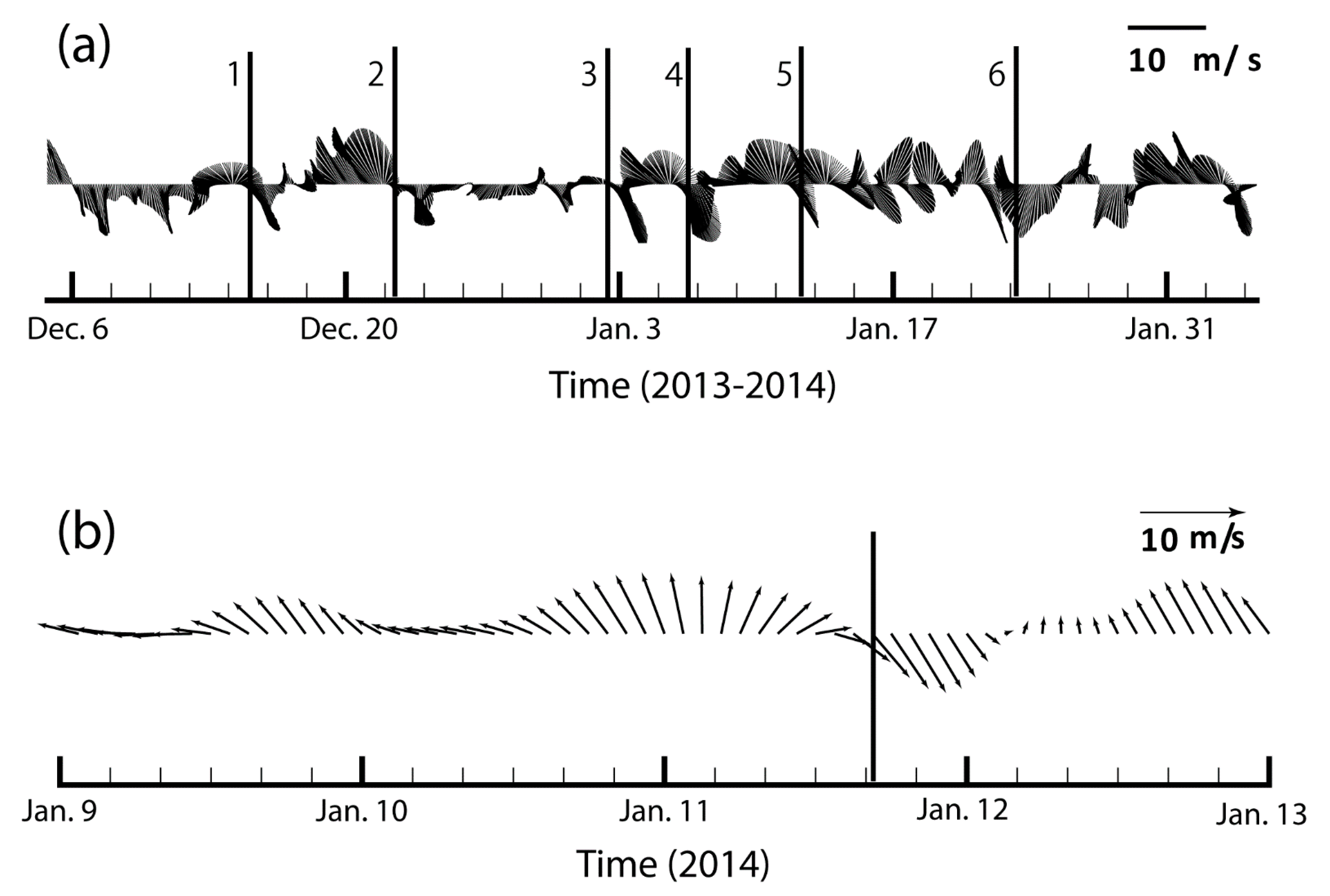
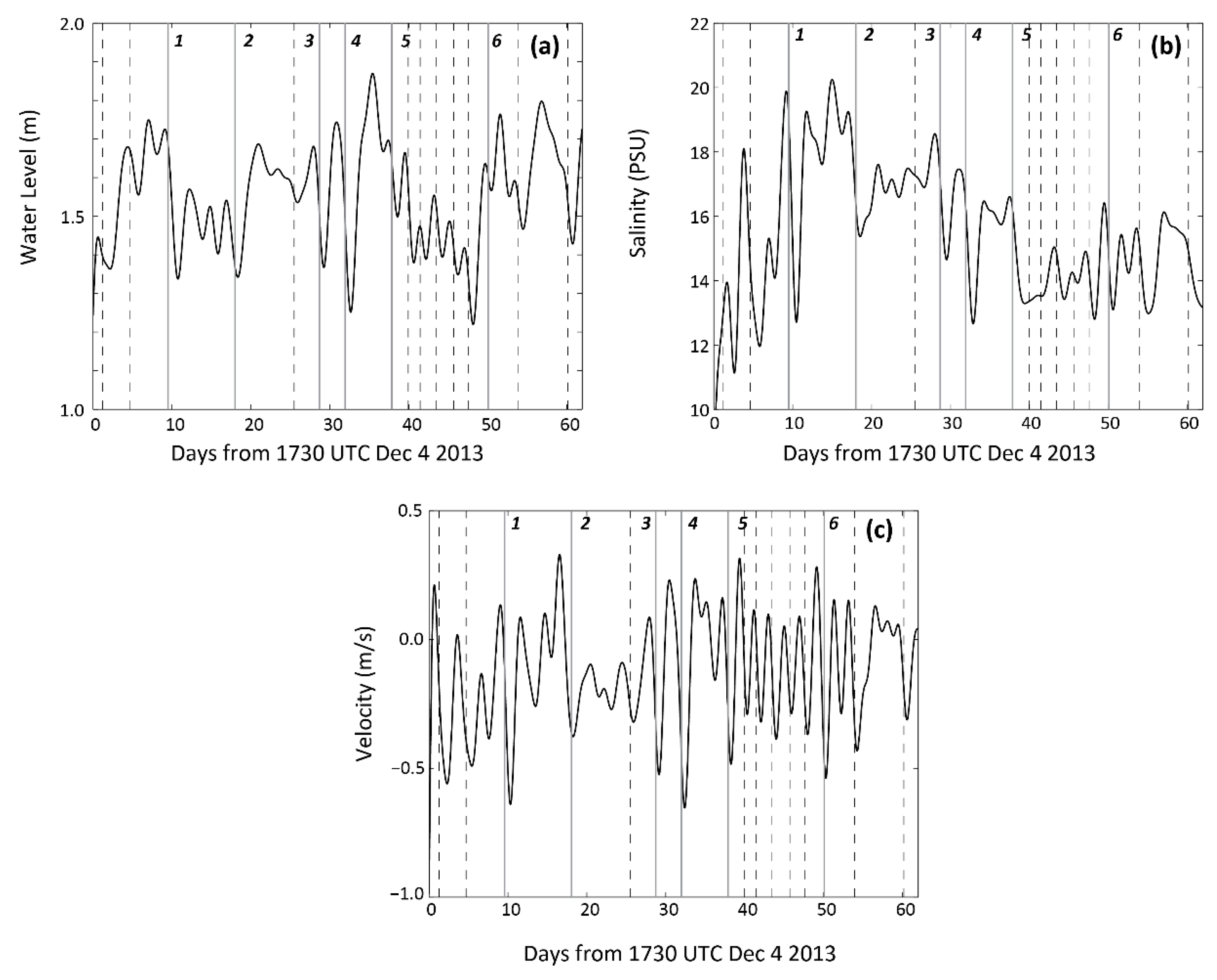
3.3. Response to Cold Fronts
3.4. Transport Response to Cold Fronts
Transport Regression
3.5. Correlation Analysis
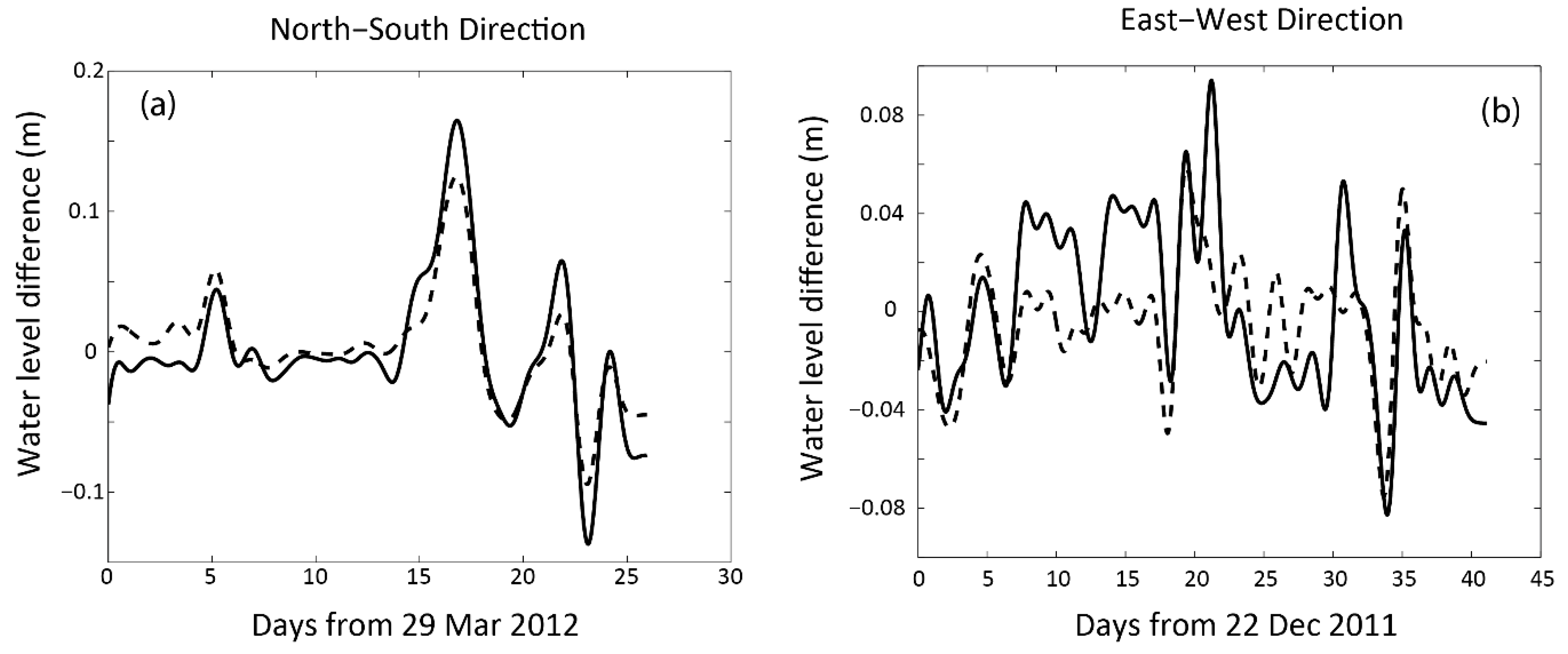
4. Conceptual Model
5. Regression Model and Case Studies
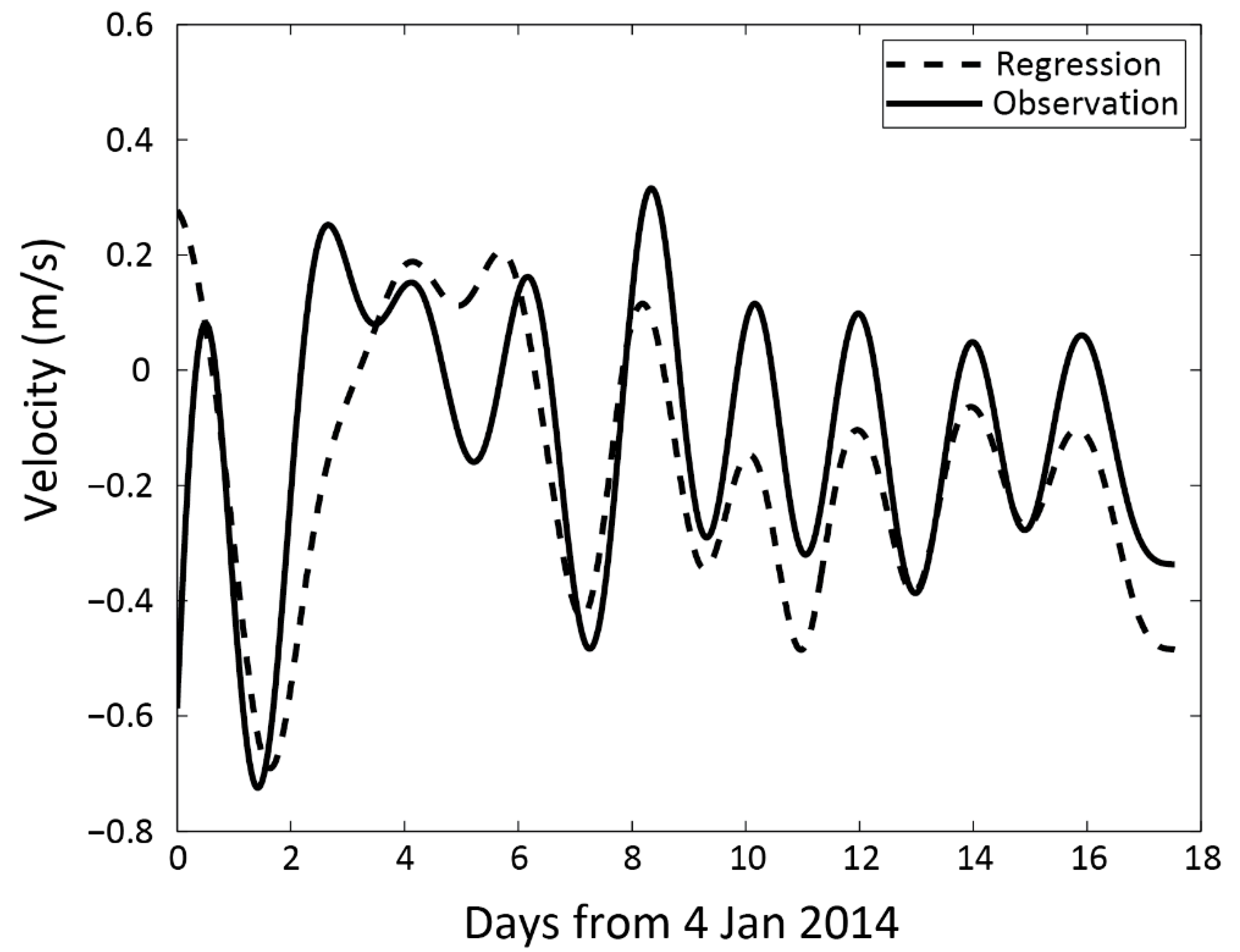
5.1. Regression Model
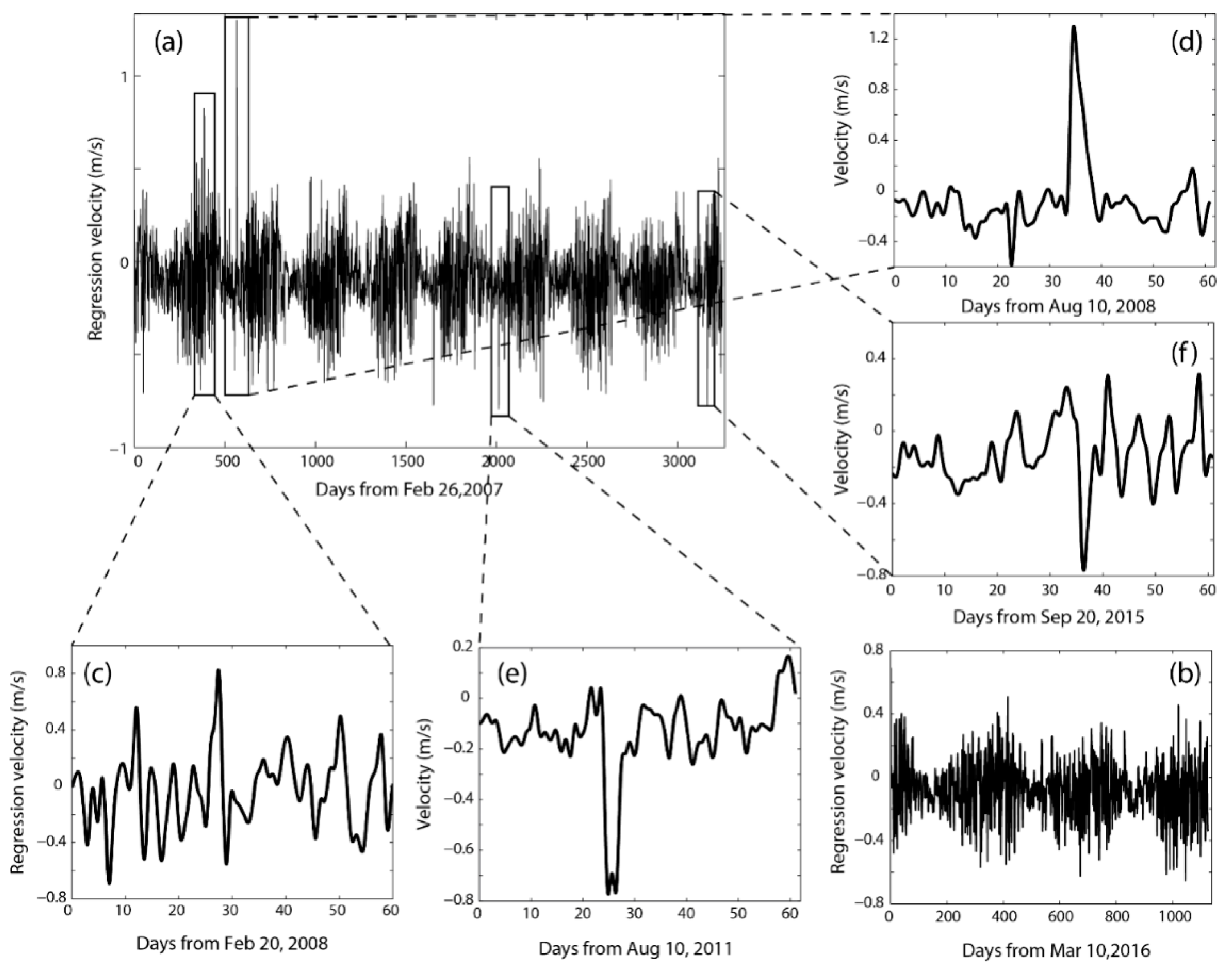
5.2. A 12-Year Regression and Case Studies
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stone, G.W.; Grymes, J.M.; Dingler, J.R.; Pepper, D.A. Overview and Significance of Hurricanes on the Louisiana Coast, U.S.A. J. Coast. Res. 1997, 13, 656–669. [Google Scholar]
- Penland, S.; Roberts, H.H.; Williams, S.J.; Sallenger, A.H., Jr.; Cahoon, D.R.; Davis, D.W.; Groat, C.G. Coastal land loss in Louisiana. Gulf Coast Assoc. Geol. Soc. 1990, 40, 685–699. [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard, D.W. Salinity distribution and circulation in The Chesapeake Bay Estuarine system. J. Mar. Res. 1952, 11, 106–123. [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard, D.W. A study of the salt balance in a coastal plain estuary. J. Mar. Res. 1954, 13, 133–144. [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard, D.W. The dynamic structure of a coastal plain Estuary. J. Mar. Res. 1956, 15, 33–42. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, D.V.; Rattray, M., Jr. Gravitational circulation in straits and estuaries. J. Mar. Res. 1965, 23, 104–122. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, K.-C. On the nature of transverse variability in a coastal plain estuary. J. Geophys. Res. 1994, 99, 14209–14222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valle-Levinson, A.; Reyes, C.; Sanay, R. Effects of Bathymetry, Friction and Rotation on Estuary-Ocean Exchange. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2003, 3, 2375–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasai, A.; Hill, A.E.; Fujiwara, T.; Simpson, J.H. Effect of the earth’s rotation on the circulation in regions of freshwater influence. J. Geophys. Res. 2000, 105, 16961–16969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjerfve, B.; Proehl, J.A. Velocity variability in a cross-section of a well-mixed estuary. J. Mar. Res. 1979, 37, 409–418. [Google Scholar]
- Ianniello, J.P. Non-Linearly induced Residual Currents in Tidally Dominated Estuaries. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Connecticut, Mansfield, CT, USA, 1977; p. 250. [Google Scholar]
- Ianniello, J.P. Tidally induced residual currents in estuaries of constant breadth and depth. J. Mar. Res. 1977, 35, 755–786. [Google Scholar]
- Bowers, D.G.; Al-Barakati, A. Tidal Rectification on Drying Estuarine Sandbanks. Estuaries 1997, 20, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; O’Donnell, J. Tidally driven residual circulation in shallow estuaries with lateral depth variation. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 27915–27929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, A.J. Observations of the Meteorologically induced circulation in the Potomac Estuary. Estuar. Coast. Mar. Sci. 1978, 6, 285–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garvine, R.W. A simple model of estuarine subtidal fluctuations forced by local and remote wind stress. J. Geophys. Res. 1985, 90, 11945–11948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelund, F. Steady Wind Set-up in Prismatic Lakes. In: Environmental Hydraulics: Stratified Flows. Lect. Notes Coast. Estuar. Stud. 1986, 18, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Li, C. Cold-front-induced Flushing of the Louisiana Bays. J. Mar. Res. 2010, 82, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, M.; Abell, J.; Hamilton, D. Wind forced circulation and sediment disturbance in a temperate lake. N. Z. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2016, 50, 209–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C. Subtidal water flux through a multiple-inlet system: Observations before and during a cold front event and numerical experiments. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2013, 118, 1877–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Huang, W.; Milan, B. Atmospheric Cold Front Induced Exchange Flows through a Microtidal Multi-inlet Bay: Analysis using Multiple Horizontal ADCPs and FVCOM Simulations. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2019, 36, 443–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, H.H.; Huh, O.K.; Hsu, S.A.; Rouse, L.J., Jr.; Rickman, D.A. Winter storm impacts on the Chenier Plain Coast of Southwestern Louisiana. In Proceedings of the Gulf Coast Association of Geological Societies and Gulf Coast Section of SEPM Meeting, Corpus Christi, TX, USA, 25–27 October 1989; pp. 515–522. [Google Scholar]
- Crout, R.L.; Hamiter, R.D. Response of bottom waters on the west Louisiana shelf to transient wind events and resulting sediment transport. Gulf Coast Assoc. Geol. Soc. Trans. 1981, 31, 273–278. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Wiseman, W.; Kelly, F.J. Barotropic, subtidal exchange between Calcasieu Lake and the Gulf of Mexico. Estuaries 1990, 13, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Weeks, E.; Huang, W.; Milan, B. Weather-Induced Transport through a Tidal Channel Calibrated by an Unmanned Boat. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2018, 35, 261–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crout, R.L. Wind-Driven, Near-Bottom Currents over the West Louisiana Inner Continental Shelf. LSU Historical Dissertations and Theses. 1983. Available online: https://digitalcommons.lsu.edu/gradschool_disstheses/3840 (accessed on 1 June 2019).
- Cochrane, J.D.; Kelly, F.J. Low-frequency circulation on the Texas-Louisiana continental shelf. J. Geophys. Res. 1986, 91, 10645–10659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dingler, J.R.; Reiss, T.E. Cold-front driven storm erosion and overwash in the central part of the Isles Dernieres, a Louisiana barrier-island arc. Mar. Geol. 1990, 91, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Roberts, H.; Stone, G.W.; Weeks, E.; Luo, Y. Wind surge and saltwater intrusion in Atchafalaya Bay during onshore winds prior to cold front passage. Hydrobiologia 2011, 658, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Li, C.; Boswell, K.M.; Kimball, M.; Rozas, L. Examination of winter circulation in a northern Gulf of Mexico estuary. Estuaries Coasts 2016, 39, 879–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, N.D.; Hammack, A.B. Impacts of winter storms on circulation and sediment transport: Atchafalaya-Vermilion Bay region, Louisiana, U.S.A. J. Coast. Res. 2000, 16, 996–1010. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Li, C.; Li, X. Remote Sensing Studies of Suspended Sediment Concentration Variations in a Coastal Bay During the Passages of Atmospheric Cold Fronts. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 2608–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weeks, E.; Robinson, M.E.; Li, C. Quantifying cold front induced water transport of a bay with in situ observations using manned and unmanned boats. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2018, 37, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Boswell, K.M.; Chaichitehrani, N.; Huang, W.; Wu, R. Weather induced subtidal flows through multiple inlets of an arctic microtidal lagoon. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2019, 38, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Zheng, Z.C.; Yadagiri, S. A hydrodynamic simulation for the circulation and transport in coastal watersheds. Comput. Fluids 2011, 47, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Li, C. Cold Front Driven Flows Through Multiple Inlets of Lake Pontchartrain Estuary. J. Geophys. Res. 2017, 122, 8627–8645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Li, C.; White, J.R.; Bargu, S.; Milan, B.; Bentley, S. Numerical Experiments on variation of freshwater plume and leakage effect from Mississippi River diversion in the Lake Pontchartrain Estuary. J. Geophys. Res. 2020, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, X.; Zhang, G.; Boswell, K.M.; Kimball, M.E.; Shen, D.; Lin, J. Estuarine plume: A case study by satellite SAR observations and in situ measurements. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 2276–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Li, C. Spatial Variation of Cold Front Wind-driven Circulation and Quasi-steady State Balance in Lake Pontchartrain Estuary. Estuar. Coast Shelf Sci. 2019, 31, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| No. | * Starting Time (UTC) | CL Time (UTC) | *Ending Time (UTC) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2100 05 Dec 2013 | 0300 06 Dec 2013 | 0000 07 Dec 2013 |
| 2 | 0300 09 Dec 2013 | 0600 09 Dec 2013 | 1200 09 Dec 2013 |
| 3 | 0000 14 Dec 2013 | 0900 14 Dec 2013 | 2100 14 Dec 2013 |
| 4 | 1200 21 Dec 2013 | 0000 22 Dec 2013 | 0900 22 Dec 2013 |
| 5 | 1900 22 Dec 2013 | 1800 22 Dec 2013 | 0900 23 Dec 2013 |
| 6 | 2100 20 Dec 2013 | 0900 30 Dec 2013 | 2100 30 Dec 2013 |
| 7 | 0600 02 Jan 2014 | 1200 02 Jan 2014 | 1500 02 Jan 2014 |
| 8 | 1200 05 Jan 2014 | 1800 05 Jan 2014 | 0000 06 Jan 2014 |
| 9 | 0600 11 Jan 2014 | 1800 11 Jan 2014 | 2100 11 Jan 2014 |
| 10 | 1500 13 Jan 2014 | 1800 13 Jan 2014 | 0000 14 Jan 2014 |
| 11 | 2100 14 Jan 2014 | 0600 15 Jan 2014 | 2100 15 Jan 2014 |
| 12 | 0000 17 Jan 2014 | 0600 17 Jan 2014 | 1200 17 Jan 2014 |
| 13 | 0000 21 Jan 2014 | 0600 21 Jan 2014 | 1200 21 Jan 2014 |
| 14 | 0000 23 Jan 2014 | 2100 23 Jan 2014 | 0000 24 Jan 2014 |
| 15 | 0900 27 Jan 2014 | 1800 27 Jan 2014 | 2100 27 Jan 2014 |
| 16 | 0300 02 Feb 2014 | 0000 03 Feb 2014 | 0900 03 Feb 2014 |
| Cold Fronts (Sequence Number) | Air Pressure (mba) | Wind Speed (m/s) | Passing Time (Hour) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max | Min | Max | Min | ||
| First | 1033 | 1013 | 7.1 | 2.8 | 21 |
| Second | 1035 | 1007 | 6.0 | 1.3 | 14 |
| Third | 1031 | 1019 | 8.9 | 0.5 | 9 |
| Fourth | 1039 | 1013 | 8.7 | 3.5 | 12 |
| Fifth | 1021 | 1012 | 6.5 | 0.9 | 15 |
| Sixth | 1038 | 1021 | 8.5 | 0.3 | 24 |
| No. | Parameter Pair | Correlation * |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | north wind, near-surface velocity | 0.75 |
| 2 | east wind, near-surface velocity | −0.45 |
| 3 | north wind, lower velocity | 0.44 |
| 4 | east wind, lower velocity | −0.55 |
| 5 | north wind, sensor depth | 0.35 |
| 6 | east wind, sensor depth | −0.50 |
| 7 | pressure, sensor depth | 0.12 |
| 8 | pressure, near-surface velocity | −0.01 (p = 0.68) |
| 9 | delayed pressure, sensor depth | 0.68 |
| 10 | delayed pressure, near-surface velocity | 0.37 |
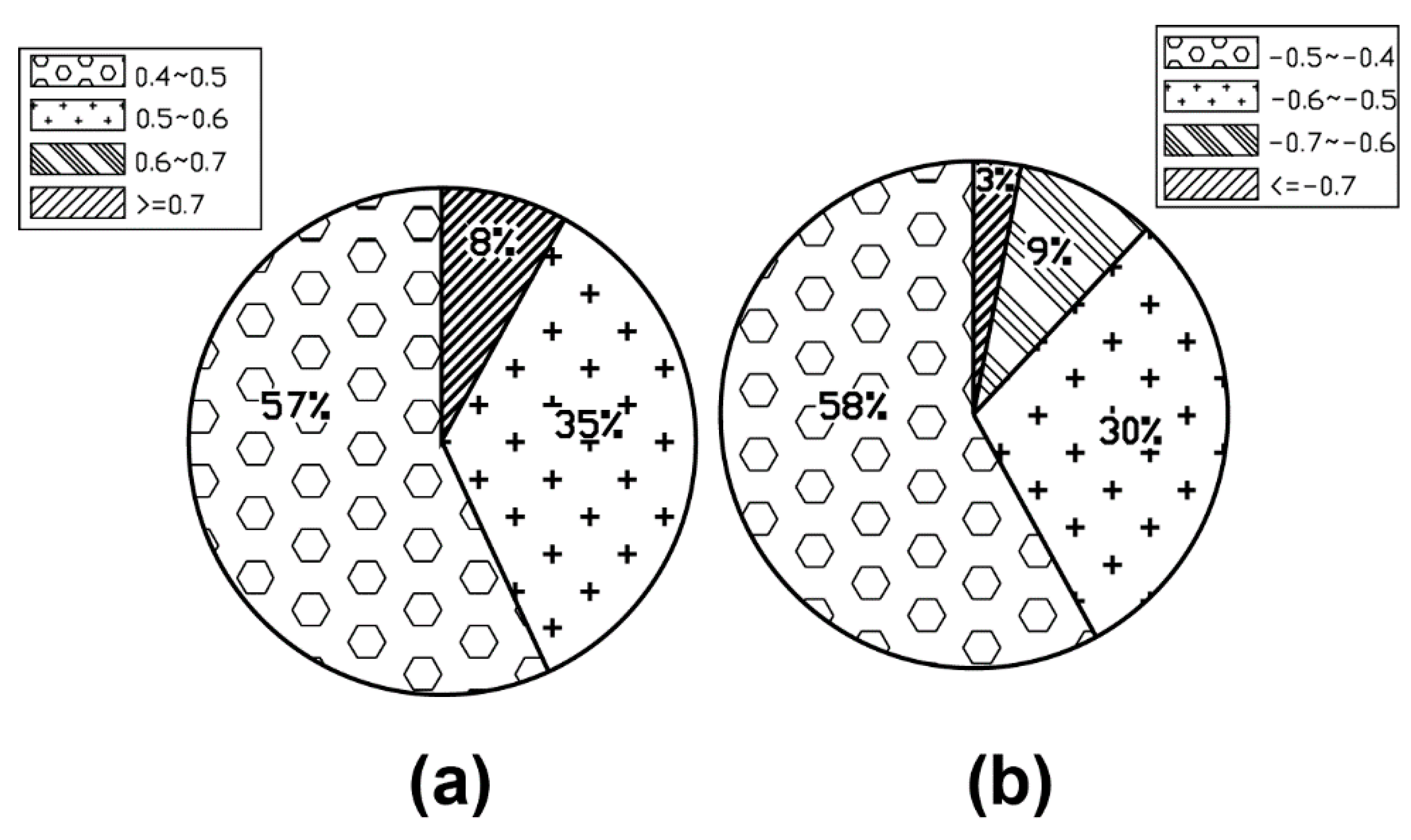
| No. | Inflow Velocity (m/s) | Number | Outflow Velocity (m/s) | Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.4~0.5 | 13 | −0.4~−0.5 | 123 |
| 2 | 0.5~0.6 | 8 | −0.5~−0.6 | 63 |
| 3 | 0.6~0.7 | 0 | −0.6~−0.7 | 19 |
| 4 | > = 0.7 | 2 | < = −0.7 | 7 |
| Total | 23 | 212 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Li, C.; Xu, F.; Huang, W. Severe Weather-Induced Exchange Flows through a Narrow Tidal Channel of Calcasieu Lake Estuary. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8020113
Wang J, Li C, Xu F, Huang W. Severe Weather-Induced Exchange Flows through a Narrow Tidal Channel of Calcasieu Lake Estuary. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2020; 8(2):113. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8020113
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jie, Chunyan Li, Fumin Xu, and Wei Huang. 2020. "Severe Weather-Induced Exchange Flows through a Narrow Tidal Channel of Calcasieu Lake Estuary" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 8, no. 2: 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8020113
APA StyleWang, J., Li, C., Xu, F., & Huang, W. (2020). Severe Weather-Induced Exchange Flows through a Narrow Tidal Channel of Calcasieu Lake Estuary. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 8(2), 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8020113





