1. Introduction
Energy and environment are key issues for humans and their development. Due to the problems of environmental pollution and energy deficit, the development and utilization of renewable energy have received strong attention by more and more countries [
1,
2]. Benefiting from the advantages of wide distribution, large reserves, renewable and no pollution, wave energy has received extensive attention. Barstow et al. [
3] reported that wave energy can provide more than 2 TW, which is the same order of the world’s electricity consumption.
Wave energy is usually captured by motions of a wave energy converter (WEC) [
4]. While development of modern wave energy converter dates back to 1799 [
5], the technology did not receive worldwide attention until the 1970s, when an oil crisis occurred and Stephen Salter published a notable paper about the technology in Nature in 1974 [
6]. Early research mainly focused on the oscillating water column WECs, but the device is (1) expensive to build, (2) has low conversion efficiency (10–30%) and (3) high cost of power generation [
7,
8,
9]. At present, the main focus is on the oscillating float-type (point absorption) WECs [
10,
11,
12]. The float-absorber-type WEC reflects a simple but robust technology, which consists of buoys or floating bodies to capture the wave’s motion. A point absorber with a direct drive power take-off (PTO) system is the most efficient and beneficial in converting the low-speed oscillating motion of ocean waves [
13]. Bhatta et al. [
14] carried out numerical study on the cylindrical shape point absorption WEC, and analyzed the hydrodynamic performance under different degrees of freedom such as surge, heave and pitch by using the mathematical technique method. Zheng et al. [
15,
16] studied the diffraction and radiation of a square floating structure under the condition of three-dimensional wave incidence, and analyzed the influence of different incident wave directions on the force and hydrodynamic performance of the WEC by using the eigenfunction expansion matching method. Shen et al. [
17] used a semi-analytical method to solve the parameters of the wave excitation force and additional mass of the cylindrical WEC. Vantorre et al. [
18] employed a software named AQUA+ to study floating structures with cylindrical, conical and hemispherical shapes at the bottom. The numerical results show that the WEC energy capture efficiency of the tapered bottom structure is higher. However, Backer et al. [
19] carried out their research by boundary element method and shows that the difference in WEC energy capture efficiency between different shapes of float structures is small.
Consequently, the analysis of motion response of WEC in waves and its hydrodynamic performance is especially important. For hydrodynamic studies, analytical and semi-analytical methods have been used for wave-structure interaction, especially for simple geometries [
20,
21]. Potential flow theory is another widely used numerical approach. Since potential flow solvers are not easy to take the viscous effect into account, which may affect the accuracy of numerical results [
22,
23,
24]. Recently, CFD (Computational Fluid Dynamics) method has been widely used to simulate the complicated interaction between strong nonlinear waves and floating bodies. Yu et al. [
25] studied a two-body floating-point absorber (FPA) WEC system, and analyzed the hydrodynamic response and the power absorption performance of the system in regular waves. The study showed that the nonlinear effects could significantly decrease the power output and the motion of the FPA system, particularly in larger waves. However, this study does not show the relationship between WEC power absorption and resonance condition. Gallizio et al. [
26] studied the dynamics of an inertial wave energy converter by coupled a CFD method with a dynamic model of the power generation system. Coe et al. [
27] predicted extreme loading in a two-body WEC using a combination of a time-domain model based on linearized potential theory and CFD method based on unsteady Reynolds-averaged Navier–Stokes equation. CFD is considered to be a good choice to analyze the hydrodynamic performance of WEC especially for real sea situation [
28,
29]. Recently, a commercial CFD solver, STAR-CCM+ becomes popular and powerful in ocean engineering [
30,
31,
32]. In the present paper, the STAR-CCM+ was employed to analyze a WEC’s motion in waves.
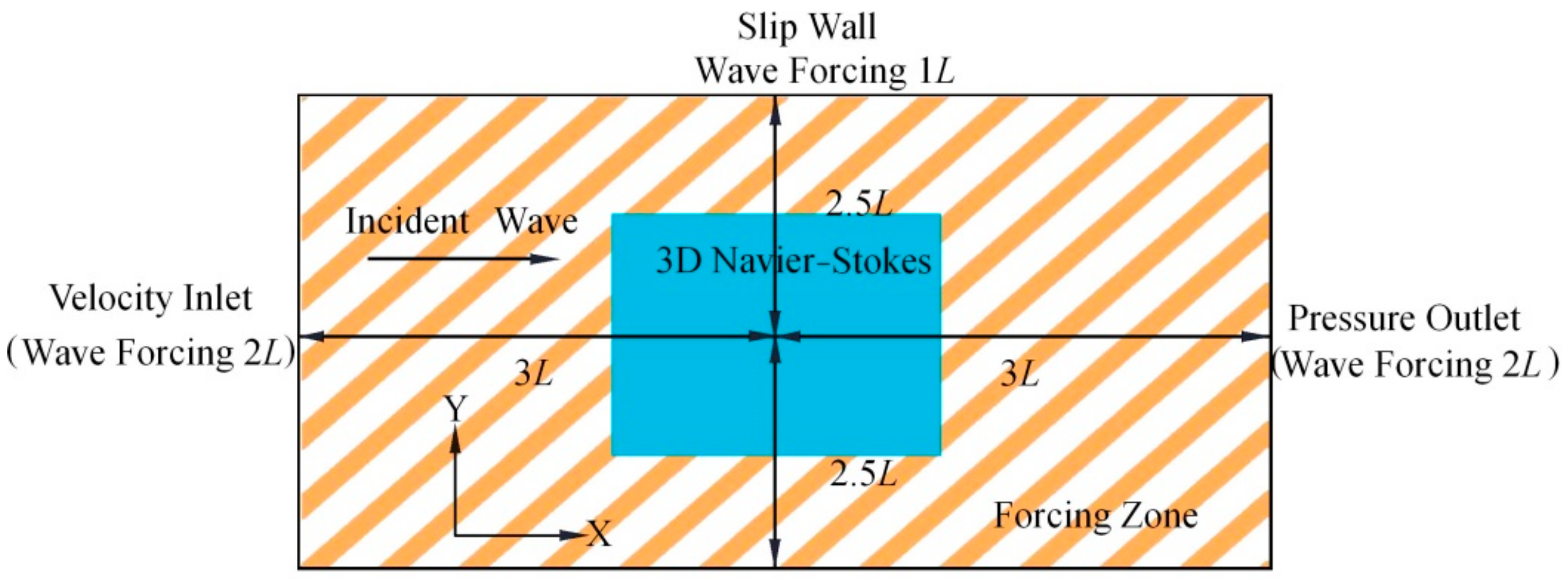
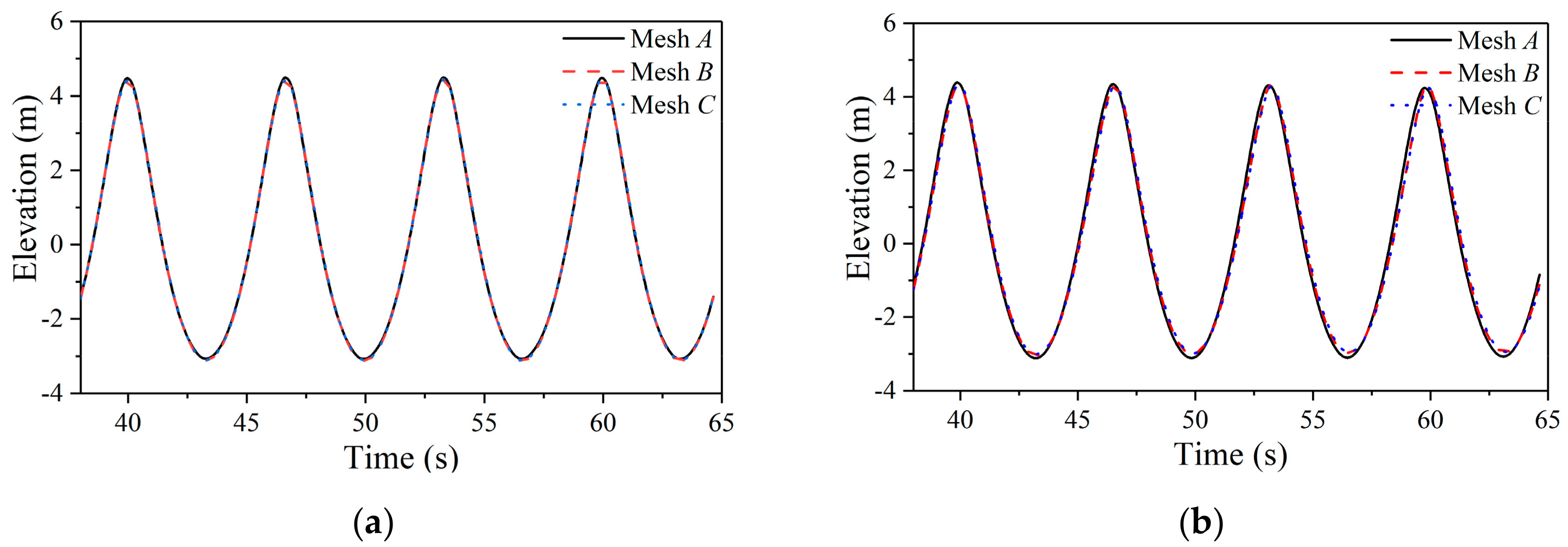
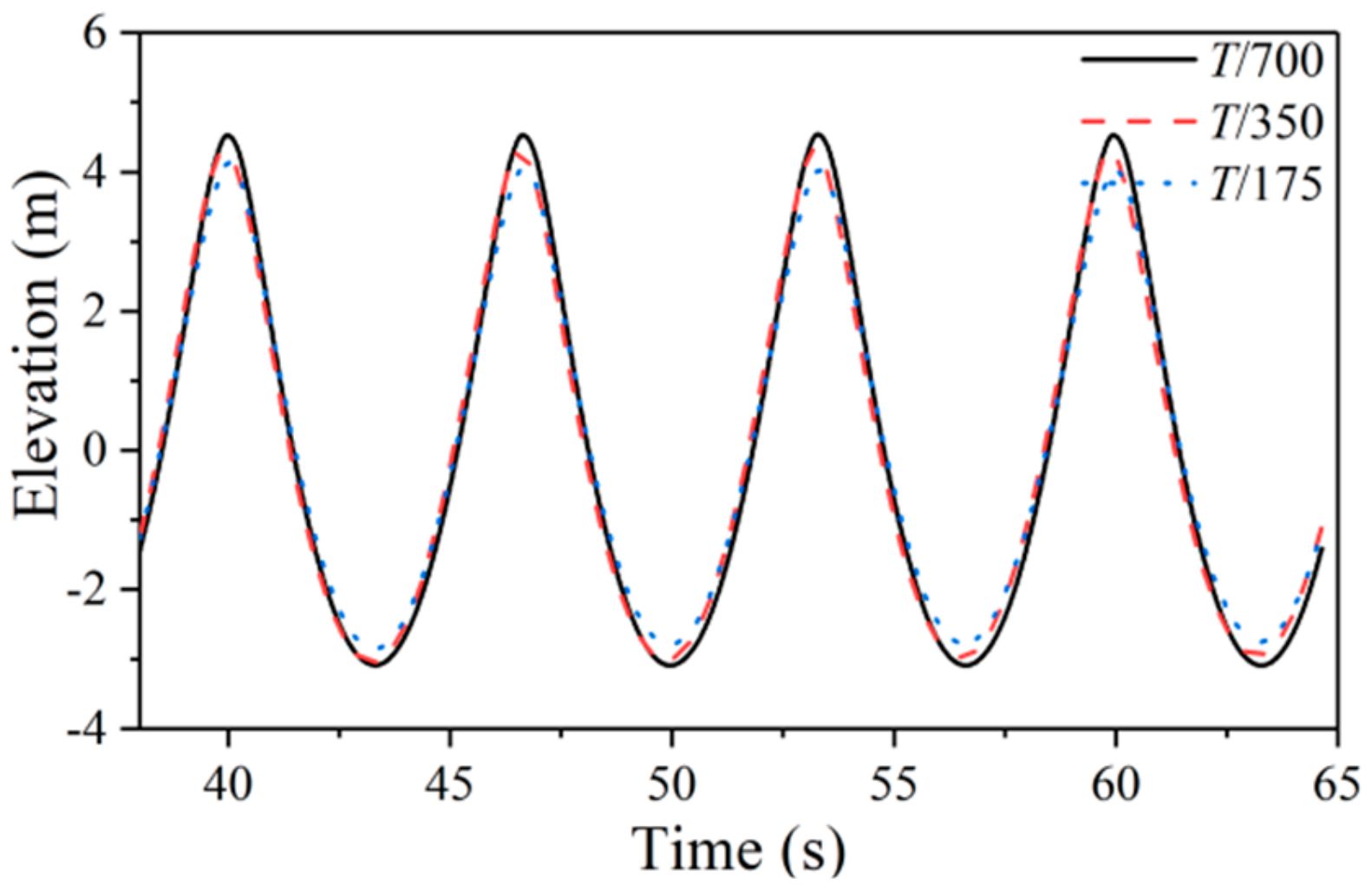
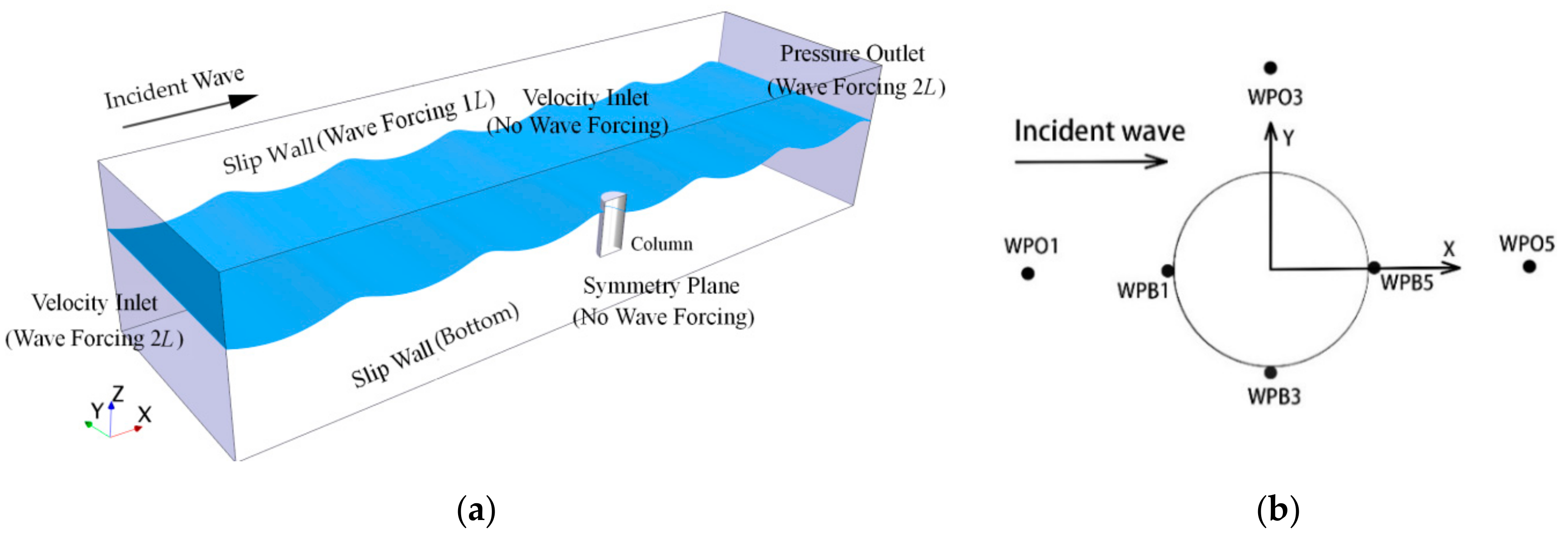
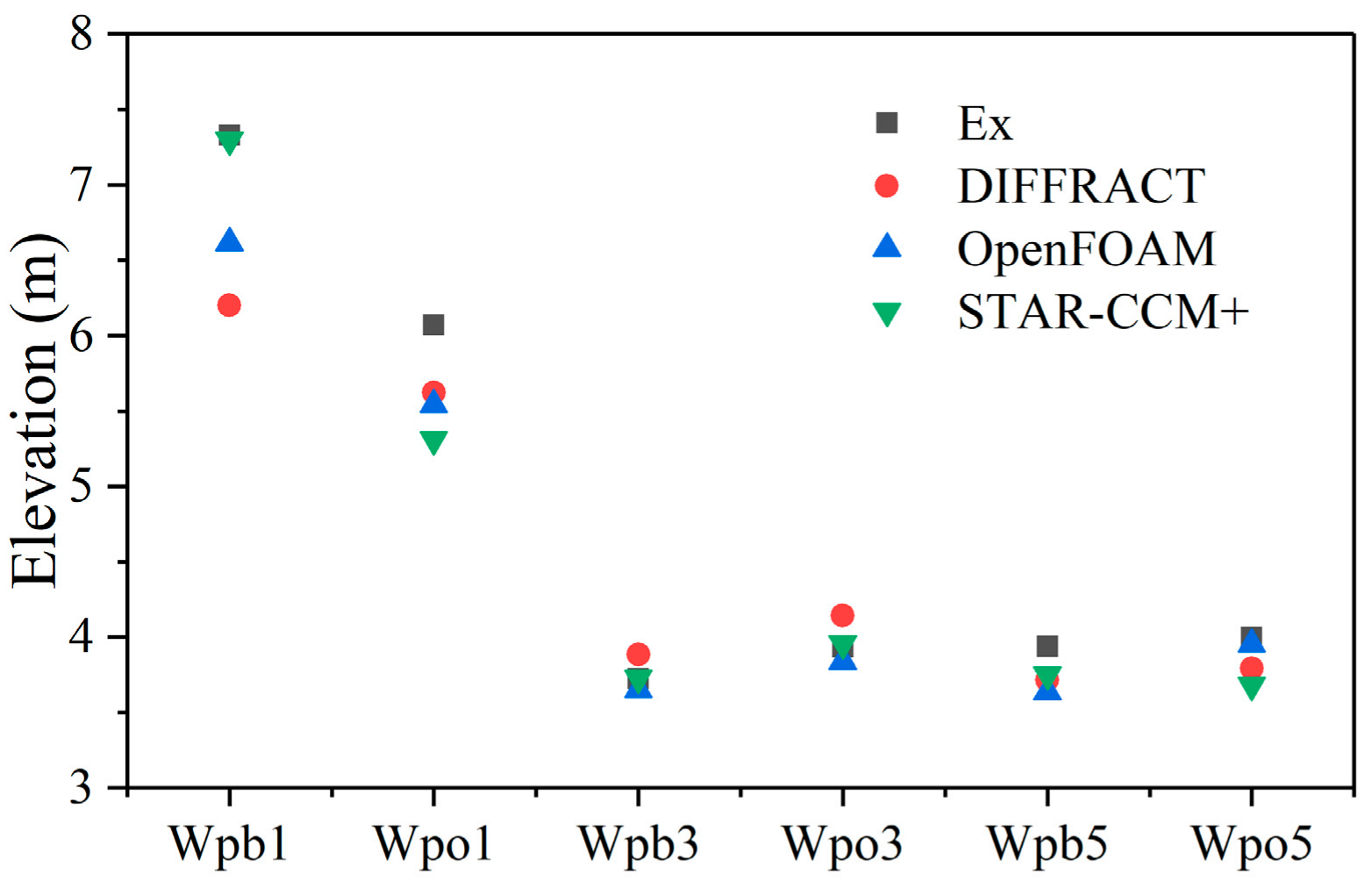
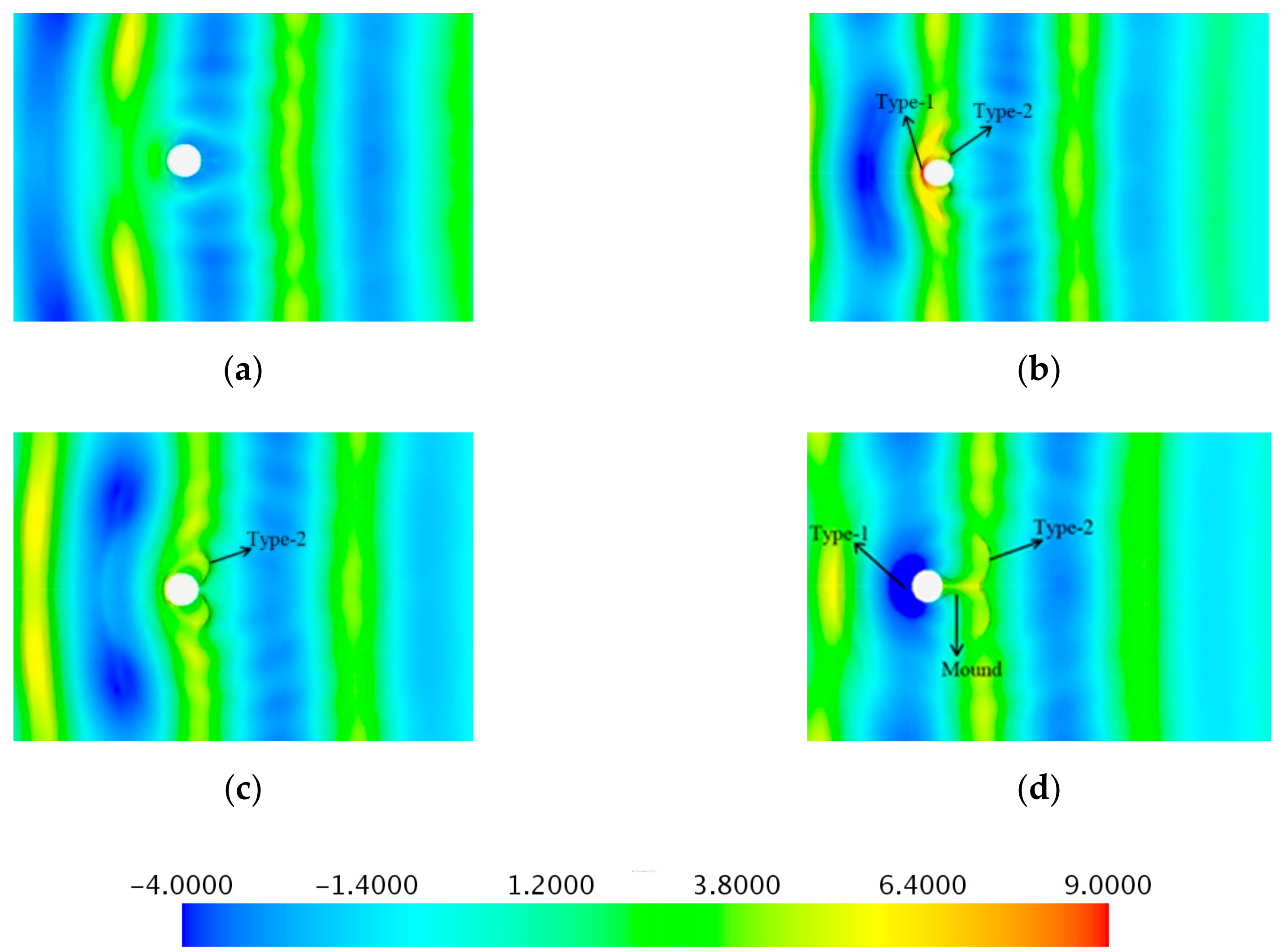
Firstly, a three-dimensional numerical wave tank was established by STAR-CCM+, then convergence studies with respect to mesh and time step were verified. The problem of a truncated column in regular waves was simulated and compared with a potential flow solver DIFFRACT and a CFD tool OpenFOAM [
33] and available experimental data from MOERI [
34]. Secondly, the resonance condition of a particular float was solved not only by numerical method but also by analytical method. The numerical results and the analytical results were mutually verified. The velocity and displacement of a float without damping constant were investigated against various wave numbers. Finally, the relationship between the optimal damping constants and wave number was studied. Some conclusions and future research directions were then considered.
5. Discussion
In this paper, a numerical model for calculating the hydrodynamic performance of a float was established. First, the numerical accuracy and reliability of the established multiphase flow numerical wave tank were verified by the convergence studies. Then the wave-surface elevations surrounding a truncated column in waves were simulated and compared with the corresponding experimental data from MOERI [
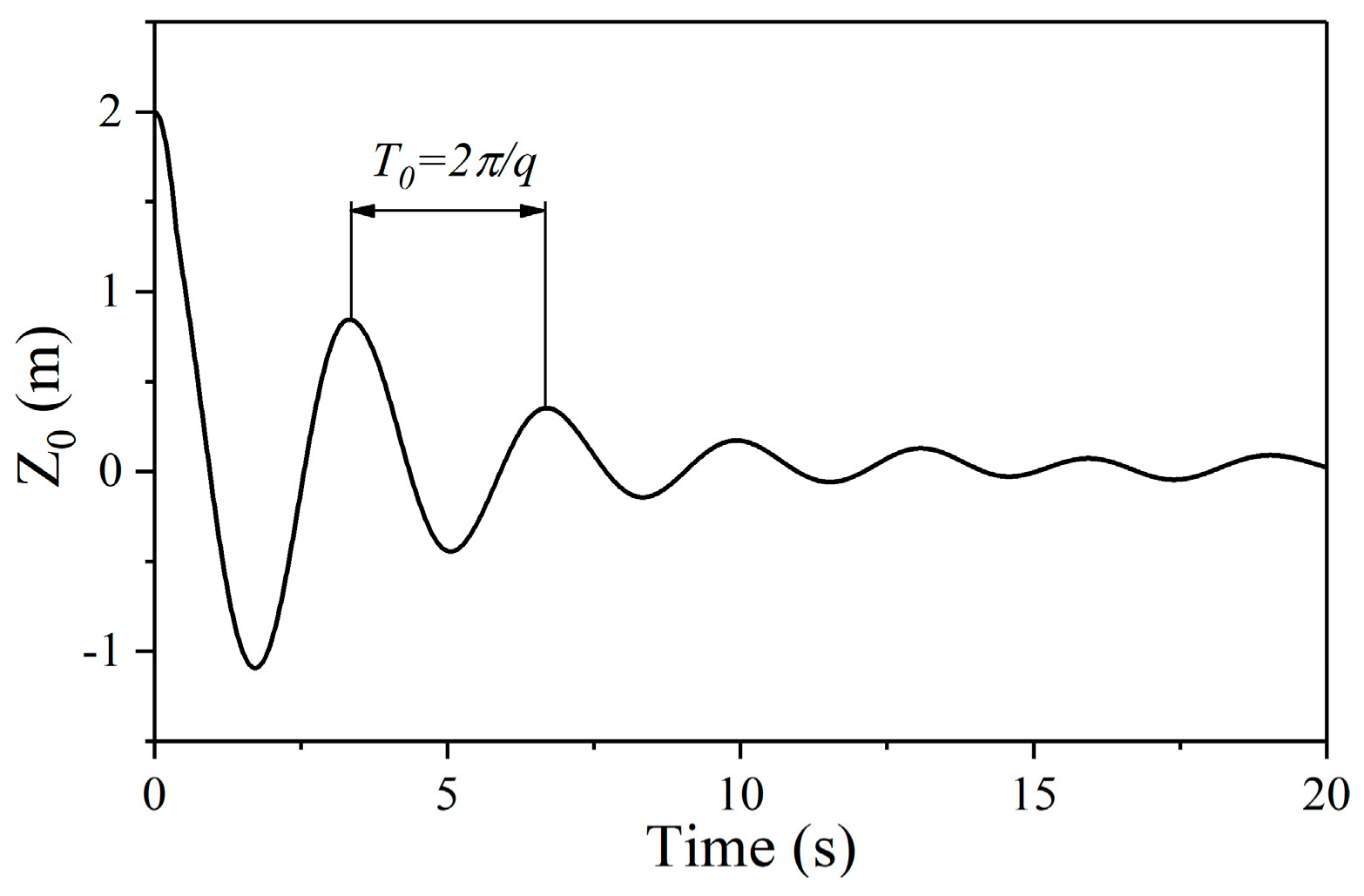
34]. After, the resonance condition of a particular float was solved not only by numerical method but also by analytical method. The results are in good agreement, which verify the reliability of the analytical process. Then, the hydrodynamic forces and motion response of the float without the damping constants in different waves were evaluated, and the power absorption performance of the float considering the damping constants in different waves were studied.
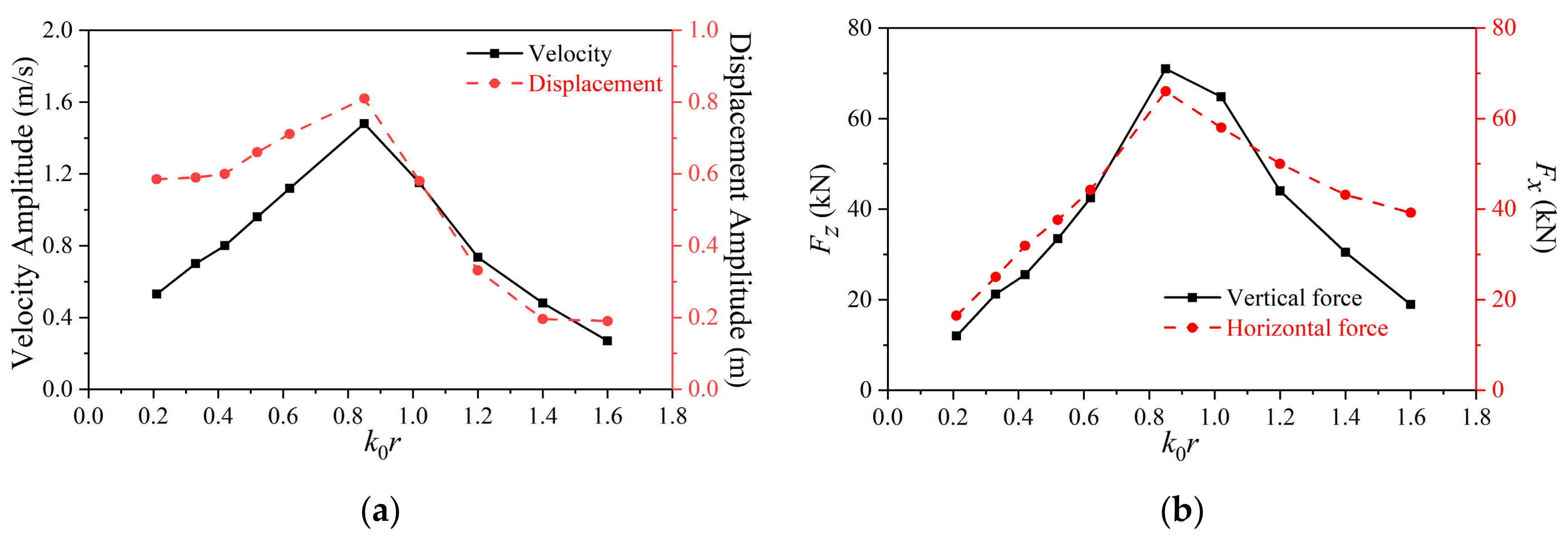
The velocity amplitude and the displacement amplitude of a float without damping constant were investigated against various wave numbers. It was found that velocity amplitude and the displacement amplitude increase first and then decrease with the increases of wave number, with the turning point being near k0r = 0.85 rather than 1.02. This means that the damping factor can affect the motion response of the float and the wave force it receives.
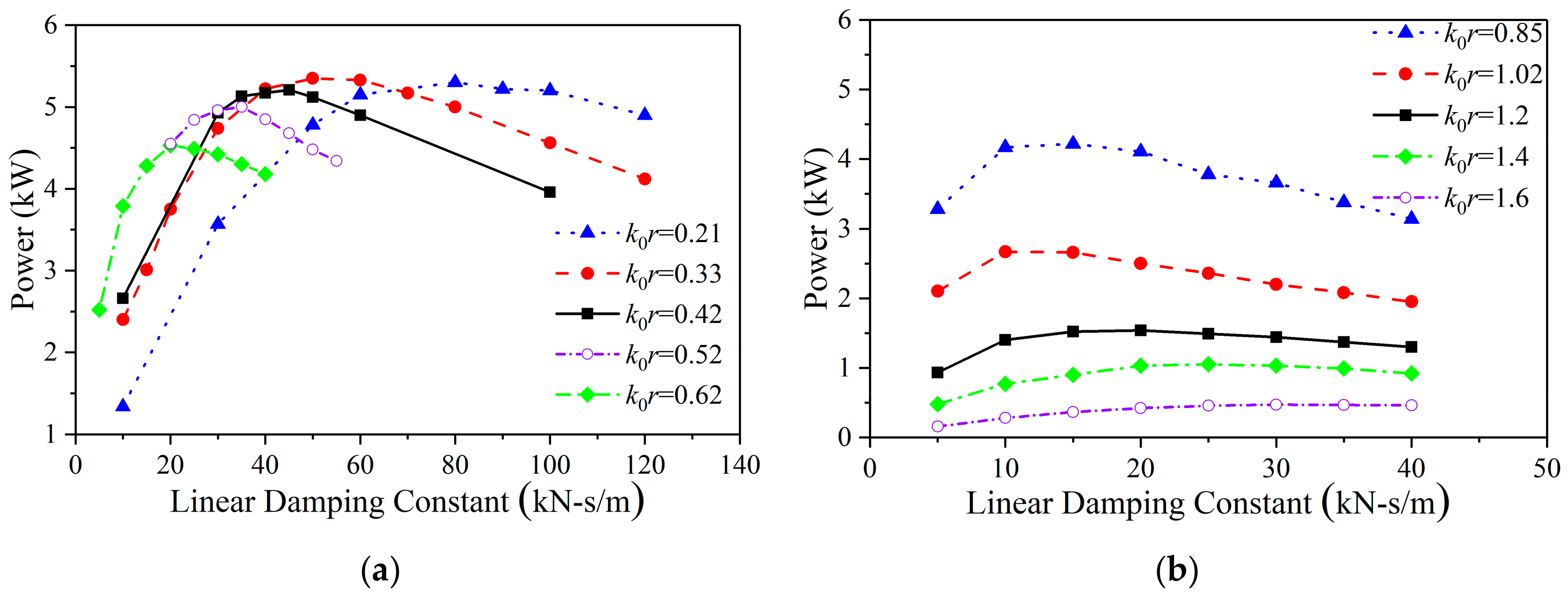
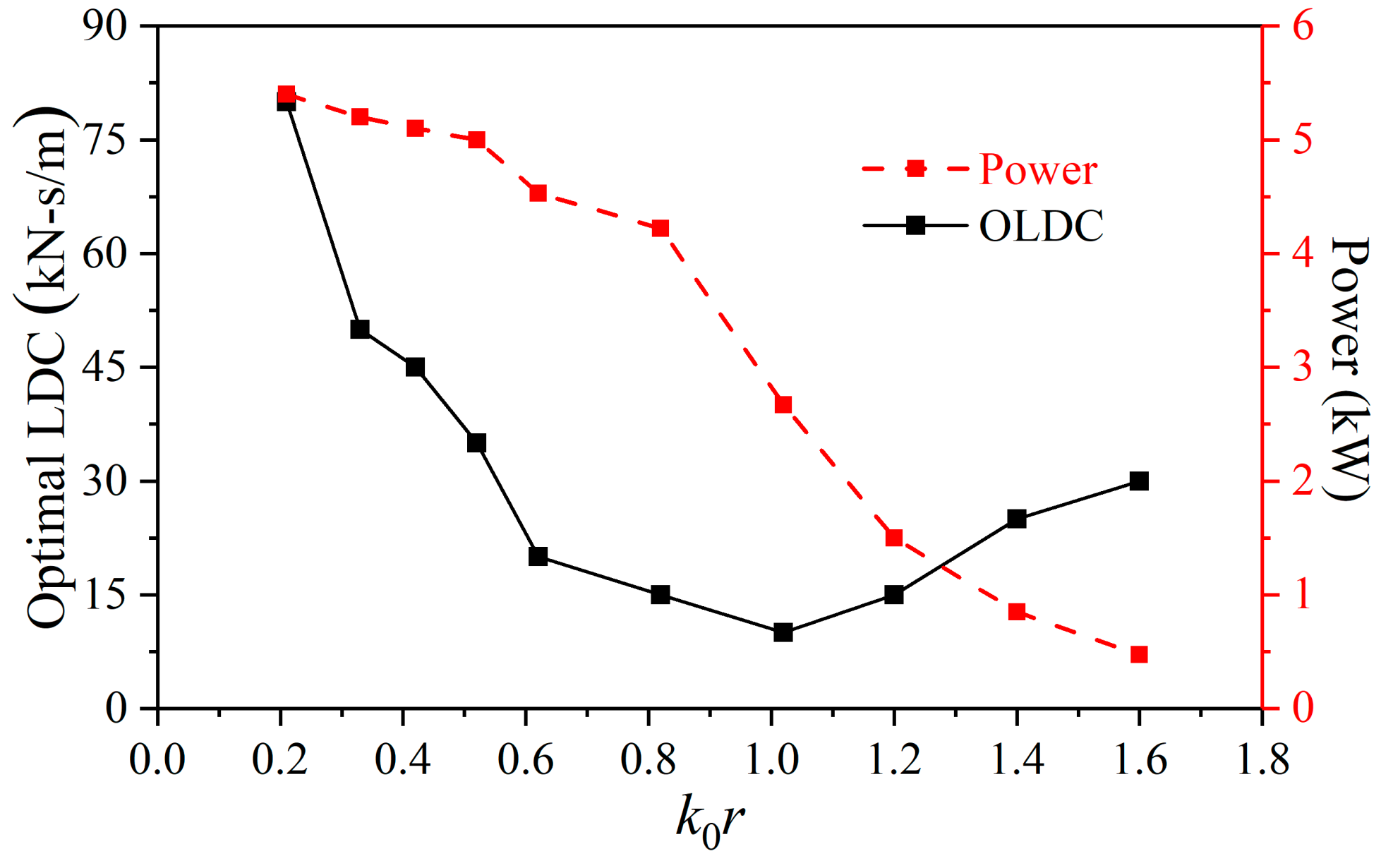
The relationship between the optimal damping constant and the wave number was obtained. When k0r > 1.02, the optimal damping constant increases as the wave number increases. When k0r < 1.02, the optimal damping constant decreases as the wave number increases. In other words, the turning point of optimal linear damping constants is near k0r = 1.02; this value is the analytical natural heaving frequency without consideration of damping. This means that the damping factor does not affect the wave number turning point of the optimal damping constant.
The power of the float generator under the optimal damping constant decreases as the wave number increases. When k0r < 0.42, the absorption power of the float at the optimal damping constant is basically the same (5.5 kW).
The study provided an analytical approach to solving the resonance condition of a specific float, and provided an insight into the hydrodynamic performance of a WEC system and its power generation with optimal linear damping constant in different waves.