An Ex-Situ Immobilization Experiment with Zn, Pb, and Cu in Dredged Marine Sediments from Bohai Bay, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection and Pretreatment of Marine Sediment Samples
2.2. Analytical Methods
2.3. Incubation Experiment
2.4. BCR Sequential Extraction Procedure
2.5. The Method Used to Evaluate the Immobilization Effect
2.6. Quality Control
3. Results
3.1. The Properties of the Marine Sediments
3.2. The Chemical Fractions of Metals in the Marine Sediments
4. Discussion
4.1. The Properties Influencing the Immobilization Effect
4.2. Immobilization Effect of Metals in Marine Sediments
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guevara-Riba, A.; Sahuquillo, A.; Rubio, R.; Rauret, G. Assessment of metal mobility in dredged harbour sediments from Barcelona, Spain. Sci. Total Environ. 2004, 321, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guern, M.L.; Dang, T.A.; Boutouil, M. Implementation and experimental monitoring of a subgrade road layer based on treated marine sediments. J. Soils Sediments 2017, 17, 1815–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibeum, K.; Woojin, Y.; Kyoungphile, N.; Kwon, C.J.; Jungyo, C.; Yongju, C. Prediction of long-term heavy metal leaching from dredged marine sediment applied inland as a construction material. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 27352–27361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurl, O.; Obbard, J.P. A review of pollutants in the sea-surface microlayer (SML): A unique habitat for marine organisms. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2004, 48, 1016–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Ran, W.; Teng, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H.; Yin, X.; Cao, R.; Wang, Q. Microplastic pollution in sediments from the Bohai Sea and the Yellow Sea, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 640, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raknuzzaman, M.; Ahmed, M.K.; Islam, M.S.; Habibullah-Al-Mamun, M.; Tokumura, M.; Sekine, M.; Masunaga, S. Trace metal contamination in commercial fish and crustaceans collected from coastal area of Bangladesh and health risk assessment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 17298–17310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Li, Y. Distributions and sources of heavy metals in sediments of the Bohai Sea, China: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 24753–24764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stalikas, C.D.; Pilidis, G.A.; Tzouwara-Karayanni, S.M.; Stalikas, C.D.; Pilidis, G.A.; Tzouwara-Karayanni, S.M. Use of a sequential extraction scheme with data normalisation to assess the metal distribution in agricultural soils irrigated by lake water. Sci. Total Environ. 1999, 236, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Lee, J.S.; Choi, Y.J.; Kim, J.G. In situ stabilization of cadmium-, lead-, and zinc-contaminated soil using various amendments. Chemosphere 2009, 77, 1069–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.Y.; Chen, W.H.; Shih, C.J. Heavy metal removal from wastewater using zero-valent iron nanoparticles. Water Sci. Technol. 2008, 58, 1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.S.; Song, K.H.; Choi, K.Y.; Kim, Y.I.; Kim, H.E.; Jung, J.M.; Kim, C.J. Variations in the concentrations of heavy metals through enforcement of a rest-year system and dredged sediment capping at the Yellow Sea-Byung dumping site, Korea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 124, 512–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giorgia, D.G.; Aldo, M.; Alessandra, P.; Raffaella, P. Enhanced electrokinetic treatment of different marine sediments contaminated by heavy metals. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2008, 43, 852–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammami, M.T.; Portet-Koltalo, F.; Benamar, A.; Duclairoir-Poc, C.; Wang, H.; Le, D.F. Application of biosurfactants and periodic voltage gradient for enhanced electrokinetic remediation of metals and PAHs in dredged marine sediments. Chemosphere 2015, 125, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doni, S.; Macci, C.; Peruzzi, E.; Iannelli, R.; Masciandaro, G. Heavy metal distribution in a sediment phytoremediation system at pilot scale. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 81, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doni, S.; Macci, C.; Martinelli, C. Combination of sediment washing and bioactivators as a potential strategy for dredged marine sediment recovery. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 125, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taneez, M.; Marmier, N.; Hurel, C. Use of neutralized industrial residue to stabilize trace elements (Cu, Cd, Zn, As, Mo, and Cr) in marine dredged sediment from South-East of France. Chemosphere 2016, 150, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamindy-Pajany, Y.; Geret, F.; Hurel, C.; Marmier, N. Batch and column studies of the stabilization of toxic heavy metals in dredged marine sediments by hematite after bioremediation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 5212–5219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauret, G.; Lo´pez-Sa´nchez, J.F.; Sahuquillo, A.; Rubio, R.; Davidson, C.; Ure, A.; Quevauviller, P. Improvement of the BCR three step sequential extraction procedure prior to the certification of new sediment and soil reference materials. J. Environ. Monitor. 1999, 1, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessier, A.; Campbell, P.G.C.; Bisson, M. Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particular trace elements. Anal. Chem. 1979, 15, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastami, K.D.; Neyestani, M.R.; Molamohyedin, N.; Shafeian, E.; Haghparast, S.; Shirzadi, I.A.; Baniamam, M. Bioavailability, mobility, and origination of metals in sediments from Anzali Wetland, Caspian Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 136, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, R.S. Applications of surfactant-modified zeolites to environmental remediation. Microporous Mesoporous Mat. 2003, 61, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiran, M.G.; Pakshirajan, K.; Das, G. Heavy metal removal from aqueous solution using sodium alginate immobilized sulfate reducing bacteria: Mechanism and process optimization. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 218, 486–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Zhang, P.; Alistair, B.; Chen, H.; Ni, J. Adsorption mechanisms of thallium(I) and thallium(III) by titanate nanotubes: Ion-exchange and co-precipitation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 423, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumpiene, J.; Lagerkvist, A.; Maurice, C. Stabilization of As, Cr, Cu, Pb and Zn in soil using amendments—A review. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparrevik, M.; Eek, E.; Grini, R.S.; Abriak, N.E.; Damidot, D.; Zentar, R. The importance of sulphide binding for leaching of heavy metals from contaminated Norwegian marine sediments treated by stabilization/solidification. Environ. Technol. 2009, 30, 831–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, B.; Sabino, D.G.; Rossella, C.; Francesco, T.; Michele, N.; Carmen, T. A life cycle assessment study on the stabilization/solidification treatment processes for contaminated marine sediments. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 201, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, W.; Kim, Y.K. Stabilization of heavy metal contaminated marine sediments with red mud and apatite composite. J. Soils Sediments 2016, 16, 726–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Liang, X.F.; Xu, Y.M.; Qin, X.; Huang, Q.Q.; Wang, L.; Sun, Y.B. Remediation of Heavy Metal-Polluted Agricultural Soils Using Clay Minerals: A Review. Pedosphere 2017, 27, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.S.; Bhattacharyya, K.G. Immobilization of Pb (II), Cd (II) and Ni (II) ions on kaolinite and montmorillonite surfaces from aqueous medium. J. Environ. Manag. 2008, 87, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- And, A.C.; Adriano, D.C. Mimicked In-Situ Stabilization of Metals in a Cropped Soil: Bioavailability and Chemical Form of Zinc. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1996, 30, 3294–3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaldi, P.; Santona, L.; Melis, P. Heavy metal immobilization by chemical amendments in a polluted soil and influence on white lupin growth. Chemosphere 2005, 60, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.H. Numerical simulation of aquatic Eco-environment of Bohai bay. J. Hydrodyn. 2006, 18, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, H.X.; Zhu, L.; Feng, J.F.; Yang, G.; Fan, J.F. Risk Assessment of Rotavirus Infection in Surface Seawater from Bohai Bay, China. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2014, 20, 929–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Qian, C.; Huang, R. Locating dry ports on a network: A case study on Tianjin Port. Marit. Policy Manag. 2018, 45, 71–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment. Bulletin on the State of Marine Ecological Environment in China in 2018; Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2018; pp. 27–28. [Google Scholar]
- Xuelu, G.; Chen-Tung Arthur, C. Heavy metal pollution status in surface sediments of the coastal Bohai Bay. Water Res. 2012, 46, 1901–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, W.; Qin, Y.; Zheng, B.; Zhang, L. Heavy metal pollution in Tianjin Bohai Bay, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2008, 20, 814–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.L.; Zhang, W.S.; Chi, G.X. Distribution and Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Sediment from Bohai Bay, China. Minerals 2019, 9, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Li, X.; Wai, O.W.H.; Huang, W.; Yan, W. Remobilization of trace metals from contaminated marine sediment in a simulated dynamic environment. Environ. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 19905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gang, Y.; Won, E.J.; Ra, K.; Jin, Y.C.; Lee, K.W.; Kim, K. Environmental assessment of contaminated marine sediments treated with solidification agents: Directions for improving environmental assessment guidelines. Mar. Environ. Res. 2018, 139, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.H.; Shan, S.C.; Shui, R.C.; Fang, T.C. Accumulation and remobilization of metals in superficial sediments in Tianjin, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 173, 917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guanghong, W.; Zheng, W.; Ruixian, S. Distribution, accumulation and mobility of mercury in superficial sediment samples from Tianjin, northern China. J. Environ. Monit. JEM 2011, 13, 2488–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Wang, L.; Weihua, L.I.; Qiu, X.; Luo, T. Study on the Passivating Effects of Applying Heavy Metal Passivation Agents to Cd and Pb in Vegetable-soil System. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2017, 26, 1242–1249. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, A.; Zhang, S.; Shan, X.Q. Time effect on the fractionation of heavy metals in soils. Geoderma 2005, 125, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.Z.; Zhong, H.; Liu, G.X.; Dai, Z.M.; Brookes, P.C.; Xu, J.M. Remediation of heavy metal contaminated soils by biochar: Mechanisms, potential risks and applications in China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252, 846–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Wu, C.; Wang, J. The effect of simulated acid rain on the stabilization of cadmium in contaminated agricultural soils treated with stabilizing agents. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 17499–17508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garau, G.; Castaldi, P.; Santona, L.; Deiana, P.; Melis, P. Influence of red mud, zeolite and lime on heavy metal immobilization, culturable heterotrophic microbial populations and enzyme activities in a contaminated soil. Geoderma 2007, 142, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabala, C.; Singh, B.R. Fractionation and mobility of copper, lead, and zinc in soil profiles in the vicinity of a copper smelter. J. Environ. Qual. 2001, 30, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svendsen, M.L.; Steinnes, E.; Blom, H.A. Partitioning of Zn, Cd, Pb, and Cu in organic-rich soil profiles in the vicinity of a zinc smelter. Chem. Speciat. Bioavail. 2011, 23, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.F.; Song, Y.H.; Yuan, P.; Cui, X.Y.; Qiu, G.L. The remediation of heavy metals contaminated sediment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 161, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, W.; Zhang, T.; Liu, Y.; Li, P.; He, L.; Chen, J. Distribution and partitioning of heavy metals in large anthropogenically impacted river, the Pearl River, China. Acta Geochim. 2019, 38, 216–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karikari-Yeboah, O.; Skinner, W.; Addai-Mensah, J. The impact of preload on the mobilisation of multivalent trace metals in pyrite-rich sediment. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, H.; Zang, S.; Xiao, H. Speciation and ecological risk of heavy metals and metalloid in the sediments of Zhalong Wetland in China. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 12, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Devi, P.; Saroha, A.K. Risk analysis of pyrolyzed biochar made from paper mill effluent treatment plant sludge for bioavailability and eco-toxicity of heavy metals. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 162, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabata-Pendias, A.; Pendias, H. Trace Elements in Soils and Plants, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000; pp. 161–182. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, J.; Peng, Z.; Liu, Y.; Fang, Y.; Zeng, G.M.; Zhang, S.Y. A case study of evaluating zeolite, CaCO3, and MnO2 for Cd-contaminated sediment reuse in soil. J. Soils Sediments 2017, 18, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Lin, C.; Jiang, Y.; Lu, W.; Si, C.; Liu, Y. Competitive removal of waterborne copper, zinc and cadmium by a CaCO3-dominated red mud. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 172, 1288–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiekens, L.; Alloway, B.J. Heavy Metals in Soils, 2nd ed.; Blackie Academic & Professional: Glasgow, UK, 1995; pp. 161–182. [Google Scholar]
- Won, J.; Burns, S.E. Role of Immobile Kaolinite Colloids in the Transport of Heavy Metals. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 2735–2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eigenberg, R.A.; Doran, J.W.; Nienaber, J.A.; Ferguson, R.B.; Woodbury, B.L. Electrical conductivity monitoring of soil condition and available N with animal manure and a cover crop. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2002, 88, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.Y.; Du, Y.J.; Li, F.S.; Guo, G.L.; Yan, X.L.; Li, C.P.; Arulrajah, A.; Wang, F.; Wang, S. Field evaluation of a new hydroxyapatite based binder for ex-situ solidification/stabilization of a heavy metal contaminated site soil around a Pb-Zn smelter. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 210, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, W.; Kang, S.; Wan, Y.; Sun, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, Y. Yellow river sediment as a soil amendment for amelioration of saline land in the yellow river delta. Land Degrad. Dev. 2016, 27, 1595–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, L.A.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, Z.; Mahar, A.; Li, R.; Kumar, A.M.; Ali, S.T.; Kumbhar, F.; Wang, P.; Shen, F. Potential use of lime combined with additives on (im)mobilization and phytoavailability of heavy metals from Pb/Zn smelter contaminated soils. Ecotox. Environ. Safe 2017, 145, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summa, V.; Margiotta, S.; Tateo, F. Correlation between geochemical, mineralogical and physical characters of sediments and salinization phenomena in a pilot area in the ionian plain (Southern Italy). Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2019, 10, 1139–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.; Khan, M.J.; Samad, A.; Noor, Y.; Rashid, M.; Jan, B. In-Situ Stabilization of Heavy Metals in Agriculture Soils Irrigated with Untreated Wastewater. J. Geochem. Explor. 2015, 159, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojeda, G.; Patrício, J.; Mattana, S.; Sobral, A.J.F.N. Effects of biochar addition to estuarine sediments. J. Soils Sediments 2016, 16, 2482–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotoky, P.; Bora, B.J.; Baruah, N.K.; Baruah, J.; Baruah, P.; Borah, G.C. Chemical fractionation of heavy metals in soils around oil installations, Assam. Chem. Speciat. Bioavail. 2003, 15, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasheen, M.R.; Ammar, N.S. Speciation of some heavy metals in River Nile sediments, Cairo, Egypt. Environmentalist 2009, 29, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabata-Pendias, A. Trace Elements in Soils and Plants, 4th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011; pp. 134–146. [Google Scholar]
- Udom, B.E.; Mbagwu, J.S.C.; Adesodun, J.K.; Agbim, N.N. Distributions of zinc, copper, cadmium and lead in a tropical ultisol after long-term disposal of sewage sludge. Environ. Int. 2004, 30, 467–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, F.; Wu, J.; Dai, Y.R.; Xiang, D.F.; Deng, Z.F.; Cheng, S.P. Responses of water quality and phytoplankton assemblages to remediation projects in two hypereutrophic tributaries of Chaohu Lake. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 248, 109276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
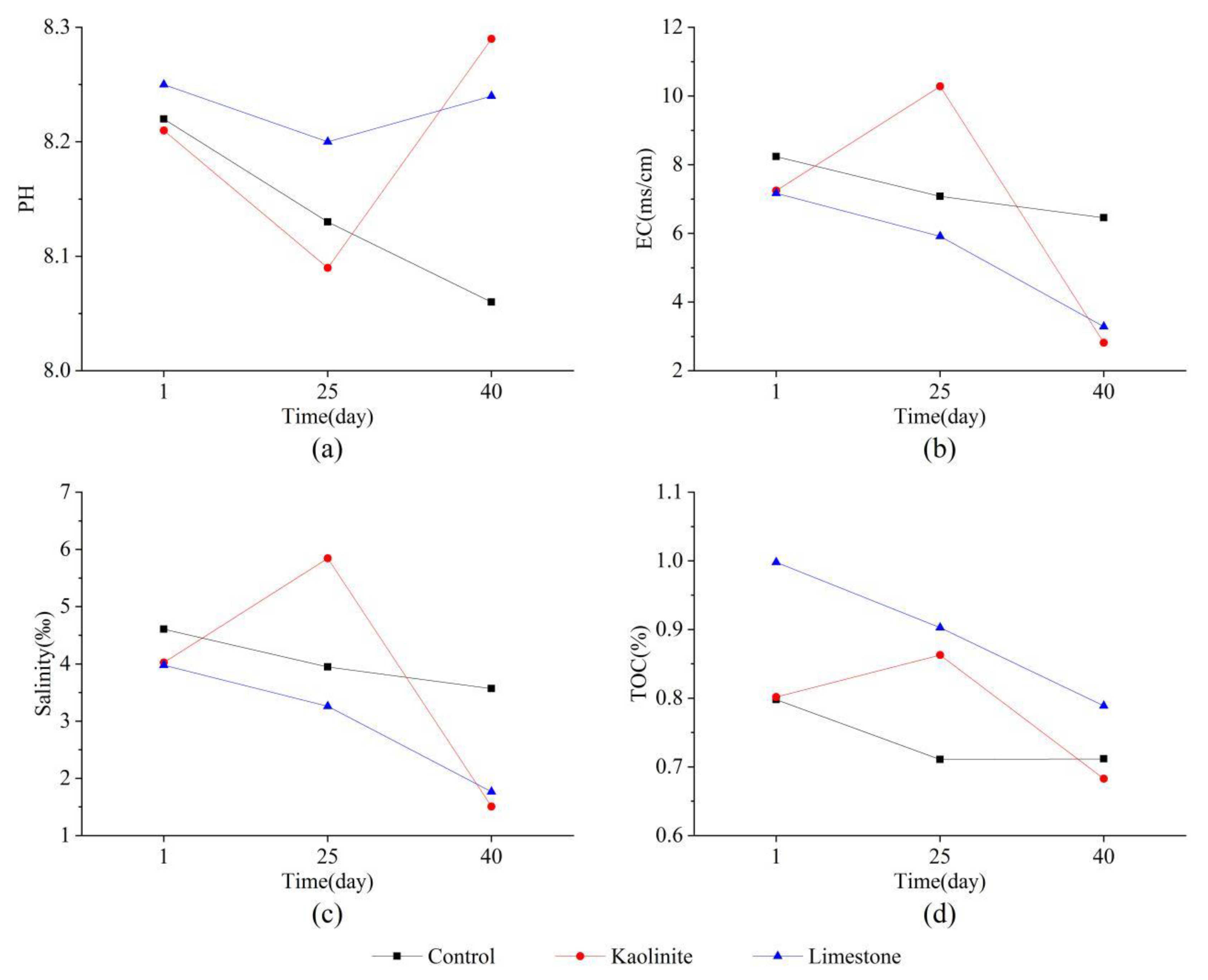
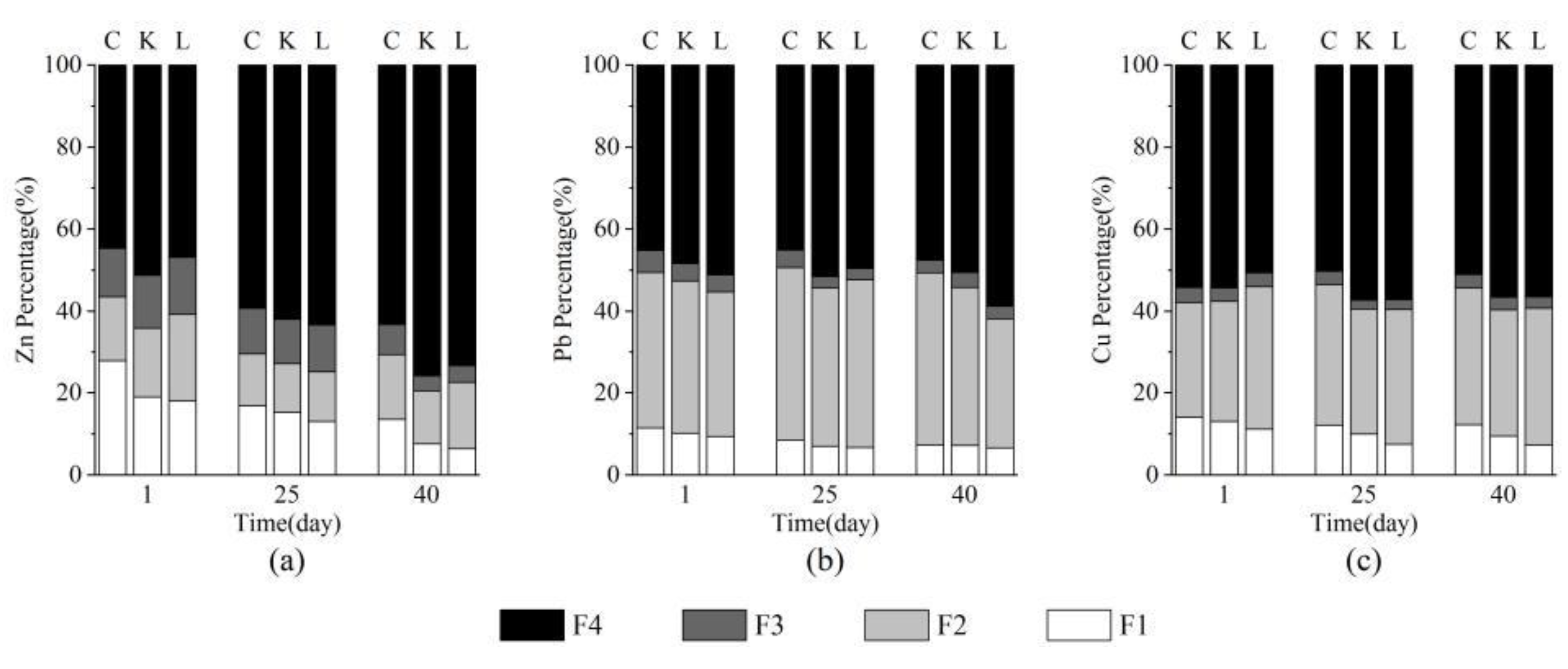
| Property | Sediment | |
|---|---|---|
| pH | 7.9 | |
| EC (ms/cm) | 8.08 | |
| Salinity (‰) | 4.50 | |
| TOC (%) | 0.78 | |
| Zn (mg/kg) | 132.50 | |
| Pb (mg/kg) | 30.85 | |
| Cu (mg/kg) | 34.15 | |
| Grain size | Sand | 4.47% |
| Silt | 57.46% | |
| Clay | 38.07% | |
| Immobilization Agents | Molecular Formula | pH | EC (ms/cm) | Salinity (‰) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| kaolinite | Al2Si2O5(OH)4 | 6.7 | 0.07 | 0.09 |
| limestone | CaCO3 | 9.2 | 0.14 | 0.12 |
| Step | Fraction | Reagent | Procedure |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | acid exchangeable fraction | 40 mL of 0.11 mol/L CH3COOH | 22 ± 5 °C for 16 h, 3000 rpm for 20 min |
| 2 | reducible fraction | 40 mL of 0.5 mol/L NH2OH·HCl | 22 ± 5 °C for 16 h, 3000 rpm for 20 min |
| 3 | oxidizable fraction | 10 mL of 8.8 mol/L H2O2, 50 mL of 1.0 mol/L CH3COONH4 | 1 h at 25 °C, 3 h at 85 ± 2 °C, twice; 22 ± 5°C for 16 h, 3000 rpm for 20 min |
| 4 | residual fraction | 0.1000 g remaining, 3 mL HCl, 2 mL HNO3, 1 mL of HClO4 and 3 mL of HF | 2 h at 110 °C, overnight, 2 h at 130 °C, increase to 150 °C until smoke gone, diluted to 10 mL |
| Fraction | Zn (mg/kg) | Pb (mg/kg) | Cu (mg/kg) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | certified | 205 | 3.18 | 49.3 |
| measured | 208.81 | 3.08 | 53.13 | |
| F2 | certified | 114 | 126 | 124 |
| measured | 113.45 | 118.63 | 122.36 | |
| F3 | certified | 46 | 9.3 | 55 |
| measured | 51.55 | 8.70 | 50.23 |
| Metals | Incubation Days | Control | Kaolinite | Limestone |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zn | 1 | 27.85% | 19.10% | 18.10% |
| 25 | 16.88% | 15.32% | 13.05% | |
| 40 | 13.56% | 7.68% | 6.48% | |
| Pb | 1 | 11.52% | 10.18% | 9.41% |
| 25 | 8.54% | 7.09% | 6.71% | |
| 40 | 7.33% | 7.25% | 6.67% | |
| Cu | 1 | 14.14% | 13.11% | 11.17% |
| 25 | 12.19% | 10.07% | 7.54% | |
| 40 | 12.30% | 9.56% | 7.32% |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, W.; Wang, X.; Liu, B. An Ex-Situ Immobilization Experiment with Zn, Pb, and Cu in Dredged Marine Sediments from Bohai Bay, China. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2019, 7, 394. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse7110394
Zhang W, Wang X, Liu B. An Ex-Situ Immobilization Experiment with Zn, Pb, and Cu in Dredged Marine Sediments from Bohai Bay, China. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2019; 7(11):394. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse7110394
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Wensi, Xiao Wang, and Baolin Liu. 2019. "An Ex-Situ Immobilization Experiment with Zn, Pb, and Cu in Dredged Marine Sediments from Bohai Bay, China" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 7, no. 11: 394. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse7110394
APA StyleZhang, W., Wang, X., & Liu, B. (2019). An Ex-Situ Immobilization Experiment with Zn, Pb, and Cu in Dredged Marine Sediments from Bohai Bay, China. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 7(11), 394. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse7110394




