An Analysis of Ship-Source Marine Pollution in Nigeria Seaports
Abstract
:1. Introduction
The Research Problem
- To determine the significant physico-chemical and microbiological parameters of ship generated wastewater from vessels berthed at the ports.
- To compare the values of these parameters with Nigeria’s Department of Petroleum Resources (DPR) standards for Effluent Discharge from marine vessels.
- To examine the significant effects of the parameters (by the type of wastewater) on the marine environment.
2. Conceptual and Literature Review
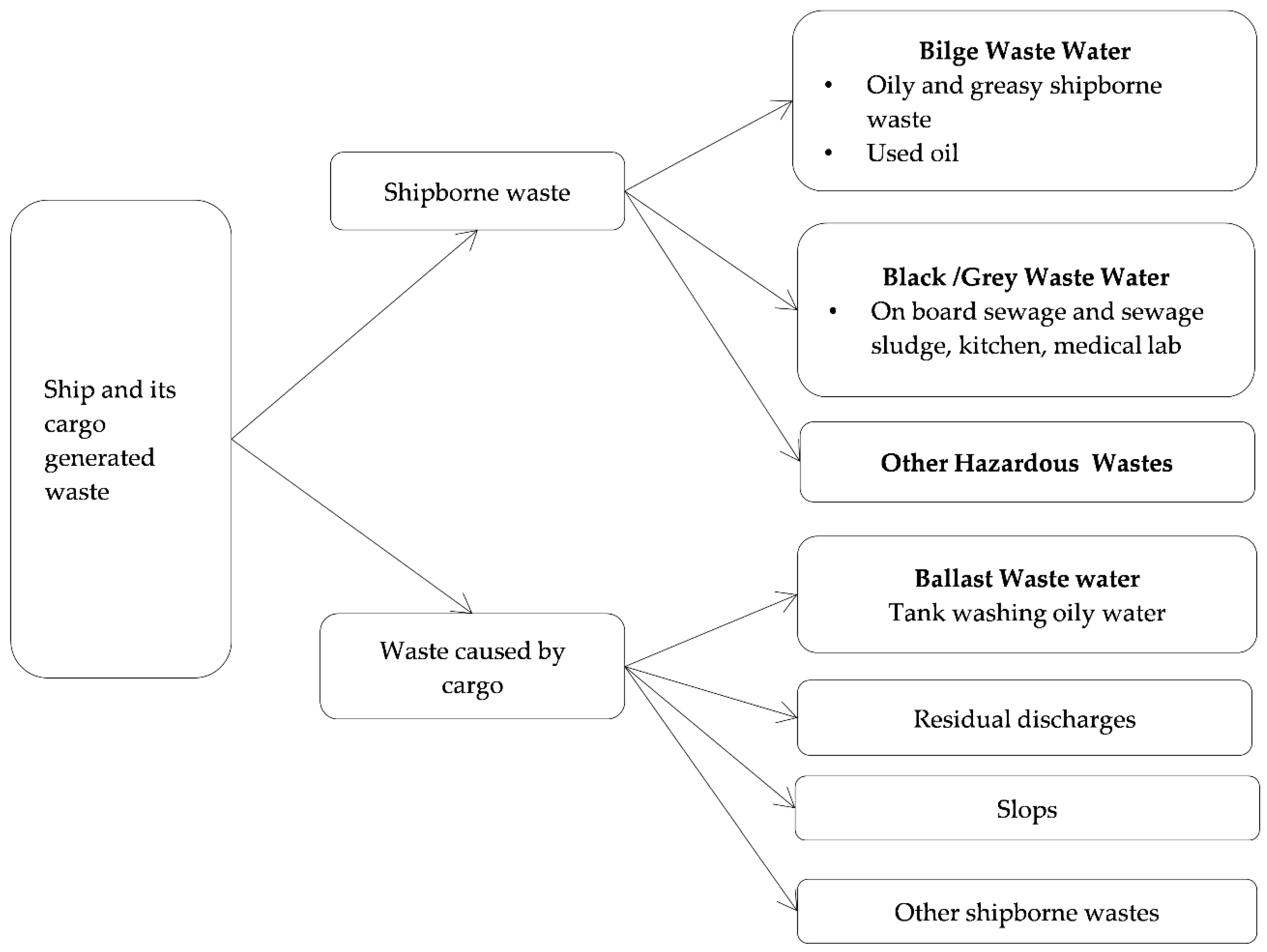
2.1. Sources of Marine Pollution
- Pollution by oil and hazardous or toxic substances from incidental, operational and illegal discharges;
- Air pollution through emissions and particulate matter from engine exhaust gases and cargo tanks which may be carried over long distances;
- Discharge of operational waste from ships, including discharge of raw sewage and garbage (litter);
- Release of toxic chemicals used in anti-fouling paints and leaching of heavy metals from anodes;
- The introduction of non-indigenous organisms through ships’ ballast water and associated sediments, and fouling on ships’ hulls;
- Pollution and physical impact through loss of ships and cargo;
- Physical and other impacts including noise and collision with marine mammals.
2.1.1. Black Waste Water
2.1.2. Bilge Waste Water
2.1.3. Ballast Wastewater
2.2. The International and Nigeria’s Legal Framework for Controlling Marine Pollution
2.3. Review of Empirical Studies on Marine Pollution
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Sample Collection
3.2. Laboratory Analysis
3.3. Determination of the Physico-Chemical and Microbiological Parameters
4. Presentation of Results
4.1. Comparative Analysis of Physico-Chemical Parameters with the DPR Permissible Limit
4.2. Discussion of Results
4.3. Development of Integrated Pollution Control Model
5. Conclusions
6. Recommendation
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Procedures Followed in Preparation of the Sample Prior to the Analysis pH (APHA 4500 H+)
Temperature
Turbidity (APHA 213°B)
Dissolved Oxygen
Conductivity/TDS (APHA-2540-C)
Total Dissolved Solids (TDS)
Total Suspended Solids (APHA 2540-D)
Heavy Metals (APHA 3030 E)
Mercury
Chemical Oxygen Demand (APHA 5220 B)
Biochemical Oxygen Demand (APHA 5210B)
- BOD = [DOB − DOA] − [DOSB − DOSA] D
- Where
- D = dilution factor usually 0.5
- DOB= DO of sample before incubation
- D = DO of sample after incubation
- DOSB = DO of sample blank before incubation
- DOSA = DO of sample blank after incubation
Oil and Grease (API-RP45)
Total and Faecal Coliform
Total Heterotrophic Bacteria and Fungi
Precautions Taken on Media Preparation
- Accurate weighing of powder and water measurement was ensured.
- The powder and water mixture was covered with a cotton wool (wrapped with an aluminum foil to prevent moisture accumulation on wool) plug as soon as possible to prevent contamination.
- The media on preparation and dishes were sterilized in the autoclave at 121° for 15 min.
- The media were allowed to cool to a certain temperature before pouring into plates to avoid steam formation on plates which contain contamination.
References
- Helen, S.; Bloor, M.; Baker, S.; Dahlgren, K. Greener shipping? A consideration of the issues associated with the introduction of emission control areas. Marit. Policy Manag. 2016, 43, 295–308. [Google Scholar]
- Umo, I.; Nitonye, S. Effects and Solutions of Marine Pollution from Ships in Nigerian Waterways. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Res. 2015, 6, 81–90. [Google Scholar]
- Kloff, S.; Wicks, C. Environmental Management of Offshore Oil Development and Maritime Oil Transport: A Background Document for Stakeholders of the West African Marine Eco Region. A Research Report by IUCN Commission on Environmental, Economic and Social Policy. 2004. Available online: http://cmsdata.iucn.org/downloads/offshore_oil_eng.pdf. (accessed on 10 February 2017).
- Szepes, M. MARPOL 73/78: The Challenges of Regulating Vessel-Source Oil Pollution. Manch. Stud. Law Rev. 2013, 2, 73–109. [Google Scholar]
- Momoh, B.C. An Investigation on Ship Generated Waste in Tin Can Island Port. Unpublished Thesis, Nigeria Institute of Safety, 2013. Available online: https://www.academia.edu/14642108/An_Investigation_on_Ship_Generated_Waste_in_Tin_Can_Island_Port (accessed on 14 March 2017).
- Carpenter, A. The Reduction of Ship-Generated Waste in the North Sea: A Contemporary Analysis. Unpublished Ph.D. Thesis, University of Leeds, Leeds, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Anstey, F. Ballast Water Management: A Time for Action. 2008. Available online: http://web.deu.edu.tr/maritime/imla2008/Papers/36.pdf (accessed on 23 March 2017).
- Barns-Dabban, H.; Koppen, K.V.; Mol, A. Environmental Reform of West and Central Africa Ports: The Influence of Colonial Legacies. Marit. Policy Manag. 2017, 44, 565–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.S. Port Development in Nigeria, International Symposium on Maritime Economy and Transport Services in West and Central Africa Countries. 2009. Available online: http://www.nigerianports.org/dynamicdata/uploads/MD (accessed on 10 March 2017).
- Group of Experts on the Scientific Aspects of Marine Environmental Protection. Ocean at Risk? GESAMP Statement of 1998 Concerning Marine Pollution Problems. 1999. Available online: http://gesamp.imo.org/ocean.htm (accessed on 2 March 2017).
- Ware, K. Assessment of the Impacts of Shipping on the Marine Environment. A Research Report Presented to OSPAR Commission. 2009. Available online: http://qsr2010.ospar.org/media/assessments/p00440_Shipping_Assessment.pdf (accessed on 24 March 2017).
- Donau, V. Danube Ports. 2010. Available online: http://www.danubeports.info (accessed on 31 May 2012).
- Berger, H. Waste Management for Inland Navigation on the Danube. 2012. Available online: http://www.donauschiffahrt.de/de/100078442/unsere_flotte.html (accessed on 28 March 2017).
- ICES, International Council for the Exploration of the Sea. Report on the Ices Advisory Committee on the Marine Environment. Copenhagen, 1994. Available online: http://ices.dk/sites/pub/Publication%20Reports/Cooperative%20Research%20Report%20(CRR)/crr239/CRR239.pdf (accessed on 22 February 2017).
- Berger, H.; Horvat, I.; Simongáti, G. Ship Waste Management along the Danube: The Way towards an International Danube Ship Waste Convention. Waste Manag. Environ. 2014, 180, 53–64. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, N.; Maes, F. Prevention of Vessel-Source Marine Pollution: A Note on the Challenges and Prospects for Chinese Practice under International Law. Ocean Dev. Int. Law 2011, 42, 356–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadafa, A.A.; Zakaria, M.P.; Othman, F. Oil Spillage and Pollution in Nigeria: Organizational Management and Institutional Framework. J. Environ. Earth Sci. 2012, 2, 22–30. [Google Scholar]
- Elenwo, E.I.; Akankali, J.A. The Effects of Marine Pollution on Nigerian Coastal Resources. J. Sustain. Dev. Stud. 2015, 8, 209–224. [Google Scholar]
- Bouaoun, D.; Nabbout, R. Study of Physical and Chemical Parameters of Oustouan River, North Lebanon. J. Coast. Zone Manag. 2016, 19, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekhaise, F.O.; Anyasi, C.C. Influence of Breweries Effluent Discharge on the Microbiological and Physicochemical Quality of Ikpoba River, Nigeria. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2005, 4, 1062–1065. [Google Scholar]
- Chukwu, O. Analysis of Groundwater Pollution from Abattoir Waste in Minna, Nigeria. Res. J. Diary Sci. 2008, 2, 74–77. [Google Scholar]
- Crowther, J.; Kay, D.; Wyer, M.D. Relationships between Microbial Water Quality and Environmental Conditions in Coastal Recreational Water: The Fylde Coast, UK. Water Res. 2001, 35, 4029–4038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Type of Vessel | Average Amount of Bilge Water (m3/Service) |
|---|---|
| Motorised Cargo Vessel | 3.7 |
| Tanker ships | 4 |
| Push boats | 3.5 |
| Passenger liner | 1.8 |
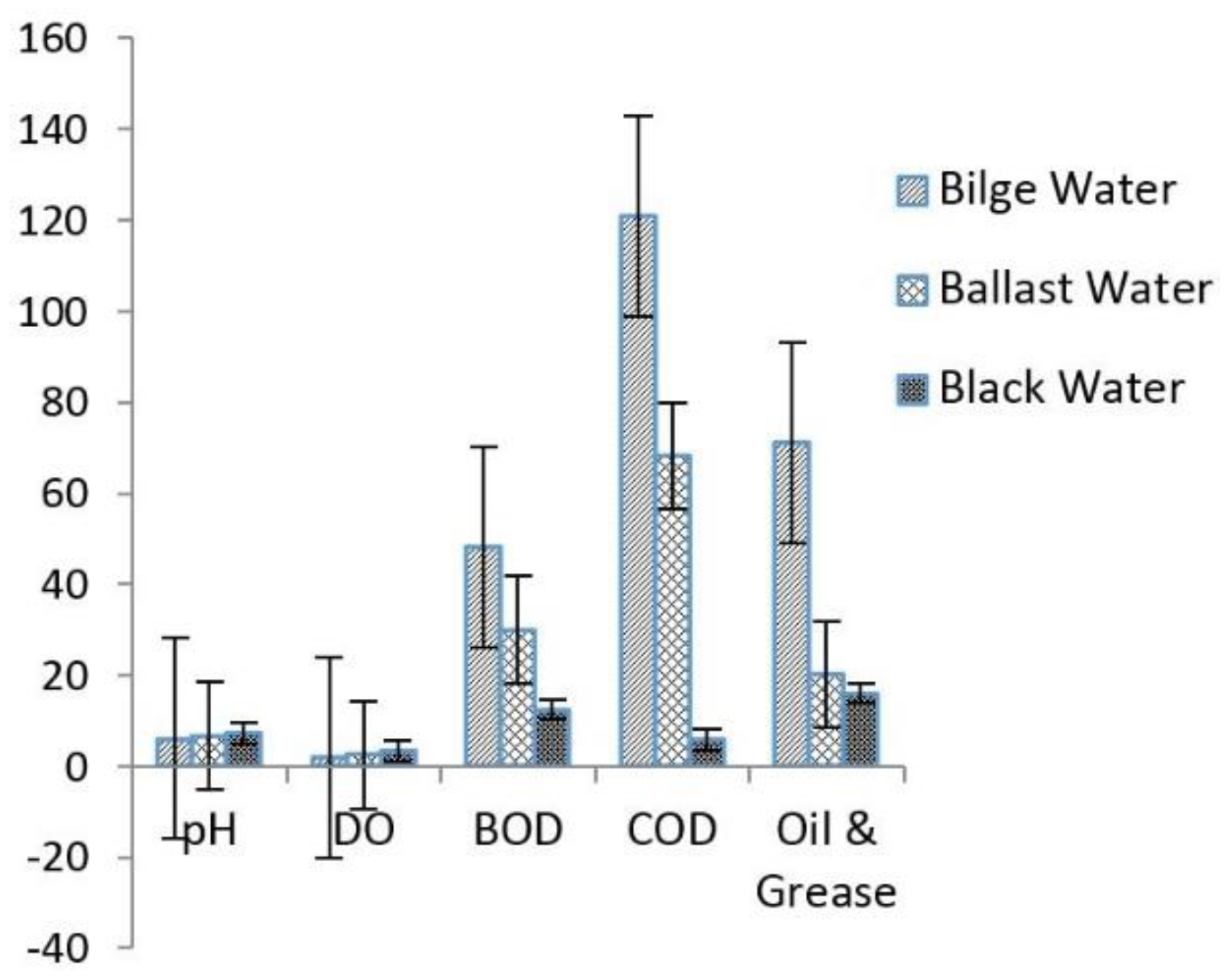
| Parameters | Bilge Water | Ballast Water | Black Waste | Mean * | Std. Mean Err. | DPR * Std. | Significant (Mean * > DPR Limit) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 6.04 | 6.73 | 7.4 | 6.72 | ±0.28 | 6.5–8.5 | No |
| Temperature °C | 28.1 | 27.1 | 27.9 | 27.7 | ±0.216 | 30 | No |
| Conductivity, µS/cm | 356.8 | 150.1 | 500.01 | 335.6 | ±3.48 | 100 | Yes |
| TDS, mg/L | 189.04 | 130.2 | 1500 | 606.4 | ±5.79 | <2000 | No |
| TSS, mg/L | 202 | 137.01 | 2000 | 779.67 | ±21.87 | 50 | Yes |
| Turbidity, NTU | 256.9 | 160 | 20.6 | 145.8 | ±1.54 | 10 | Yes |
| DO, mg/L | 2.01 | 2.5 | 3.39 | 2.63 | ±0.28 | 5.0 | No |
| BOD, mg/L | 48.22 | 30 | 12.5 | 30.24 | ±7.30 | 30 | Yes |
| COD, mg/L | 120.9 | 68.2 | 5.97 | 65.02 | ±40.68 | 40 | Yes |
| Oil and Grease, µg/L | 71.25 | 20.11 | 16.05 | 35.8 | ±12.57 | 48 | No |
| Copper, µg/L | 1.56 | 0.75 | 1.2 | 1.17 | ±0.21 | 1.5 | No |
| Iron, µg/L | 3.98 | 1.72 | 2.02 | 2.57 | ±40.75 | 0.3 | Yes |
| Lead, µg/L | 0.447 | 0.12 | n.a | 0.507 | ±0.11 | 0.05 | Yes |
| Zinc, µg/L | 1.99 | 0.82 | 0.04 | 0.95 | ±0.40 | 1.0 | No |
| Aluminium, µg/L | 0.045 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.025 | ±0.01 | 0.2 | No |
| Cadmium, µg/L | 0.113 | 0.09 | 0.25 | 0.151 | ±0.05 | 0.003 | Yes |
| Mercury, µg/L | n.a | n.a | n.a | n.a | n.a | 0.1 | n.a |
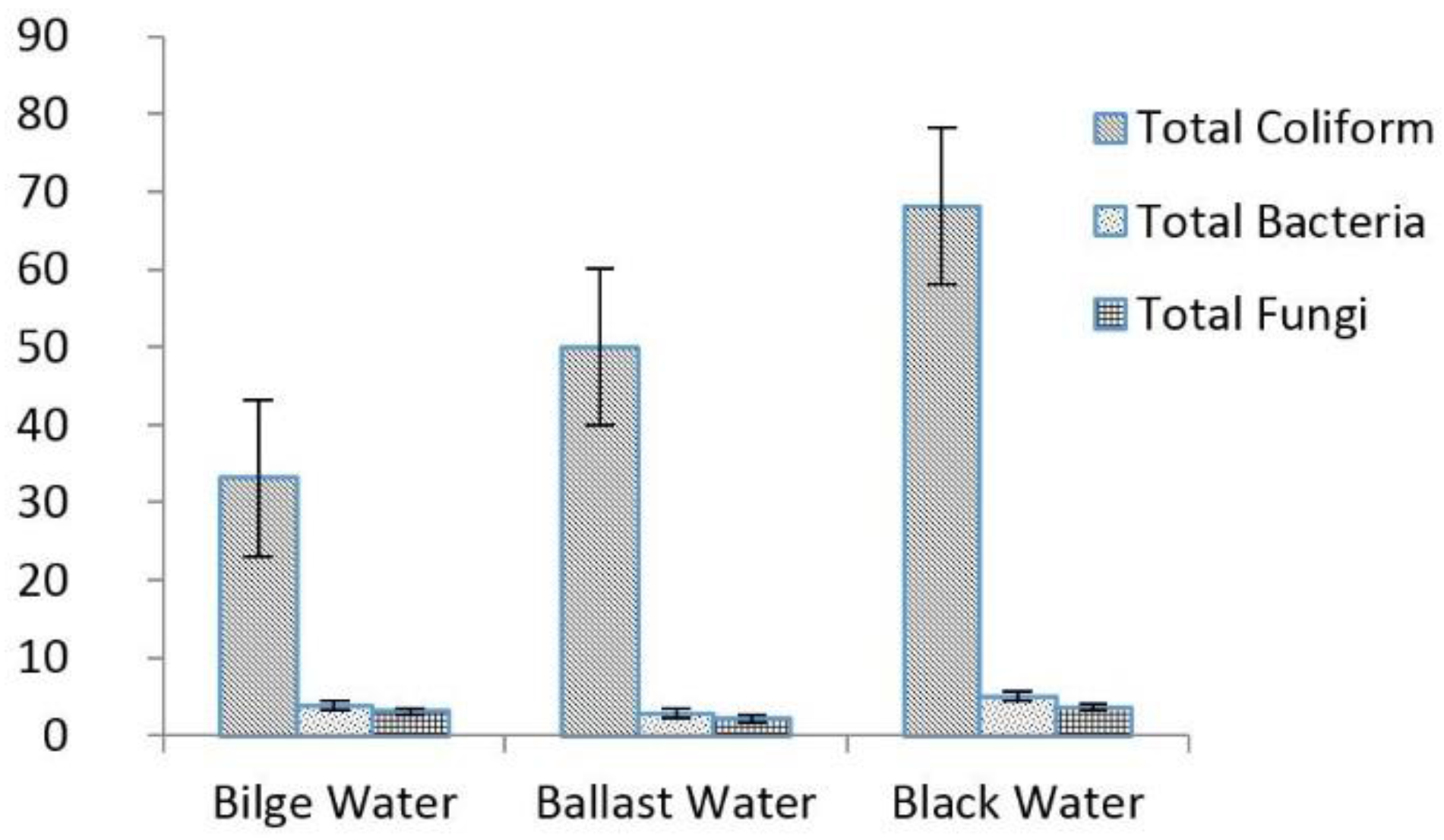
| Total Coliform, MPN/100 mL | 1100 | 2500 | 4635 | 2745 | ±72.76 | - | n.a |
| Total Heterotrophic Fungi, ×105 cfu/mL | 15.1 | 8.1 | 25.1 | 16 | ±6.98 | 100 | No |
| Total Heterotrophic Bacteria, ×106 cfu/mL | 9.6 | 4.5 | 0.02 | 4.71 | ±1.96 | 100 | No |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Onwuegbuchunam, D.E.; Ebe, T.E.; Okoroji, L.I.; Essien, A.E. An Analysis of Ship-Source Marine Pollution in Nigeria Seaports. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2017, 5, 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse5030039
Onwuegbuchunam DE, Ebe TE, Okoroji LI, Essien AE. An Analysis of Ship-Source Marine Pollution in Nigeria Seaports. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2017; 5(3):39. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse5030039
Chicago/Turabian StyleOnwuegbuchunam, D. E., T. E. Ebe, L. I. Okoroji, and A. E. Essien. 2017. "An Analysis of Ship-Source Marine Pollution in Nigeria Seaports" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 5, no. 3: 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse5030039
APA StyleOnwuegbuchunam, D. E., Ebe, T. E., Okoroji, L. I., & Essien, A. E. (2017). An Analysis of Ship-Source Marine Pollution in Nigeria Seaports. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 5(3), 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse5030039




