Impulse Wave Generation: Comparison of Free Granular with Mesh-Packed Slides
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Previous Research and Experimental Setup
2.1. Impulse Product Parameter
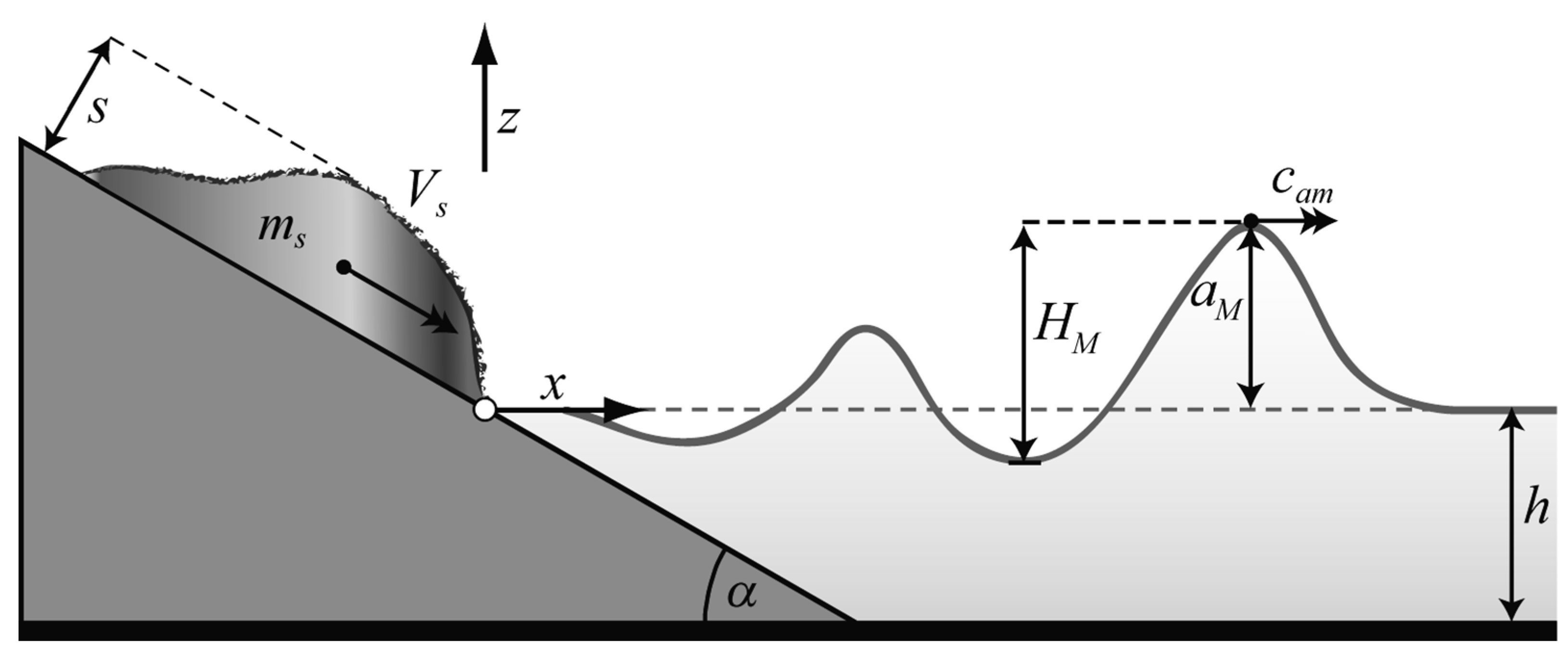
2.2. Wave Characteristics
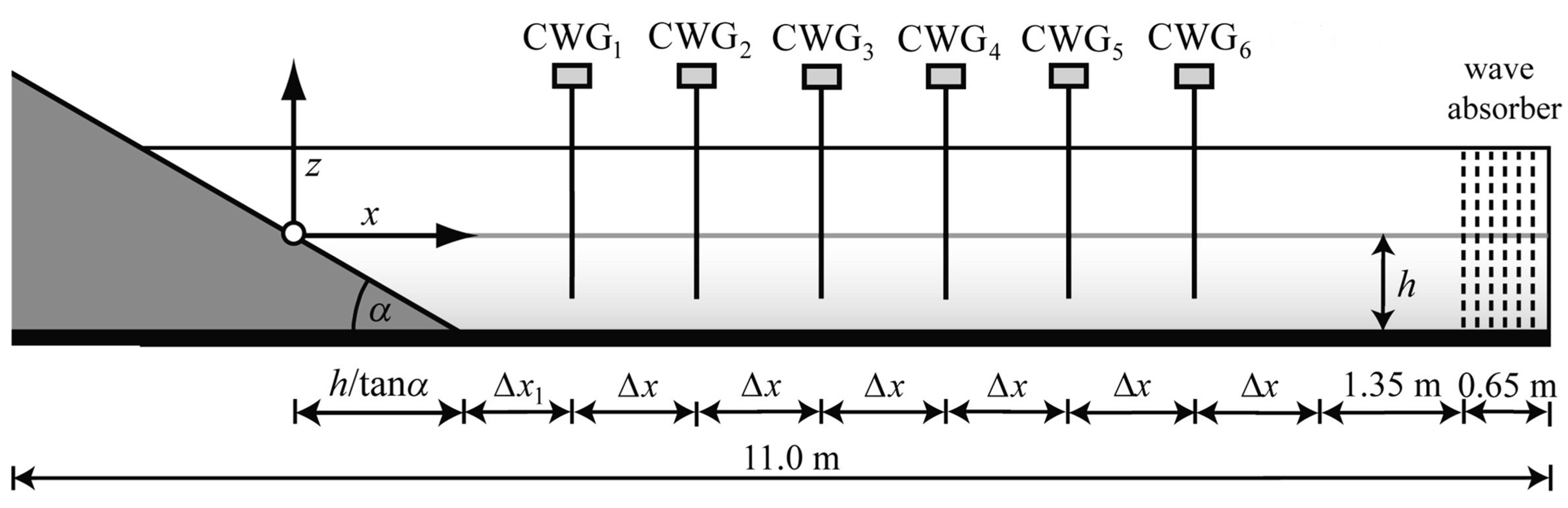
2.3. Experimental Setup and Procedure
| Parameter | Free Granular Slides [4] | Mesh-Packed Slides |
|---|---|---|
| h [m] | 0.15, 0.20, 0.30, 0.45, 0.60, 0.675 | 0.20, 0.30, 0.40 |
| s [m] | 0.05–0.249 | 0.062–0.145 |
| Vs [m/s] | 2.06–8.77 | 1.2–9.2 |
| ms [kg] | 10.09–113.30 | 19.5–20.1 |
| α [°] | 30, 45, 60 | 30, 45, 60 |
| F [-] | 0.86–6.83 | 0.70–5.36 |
| S [-] | 0.09–1.64 | 0.16–0.65 |
| M [-] | 0.11–10.02 | 0.24–1.01 |
| P [-] | 0.17–8.13 | 0.26–2.78 |
3. Results and Discussion
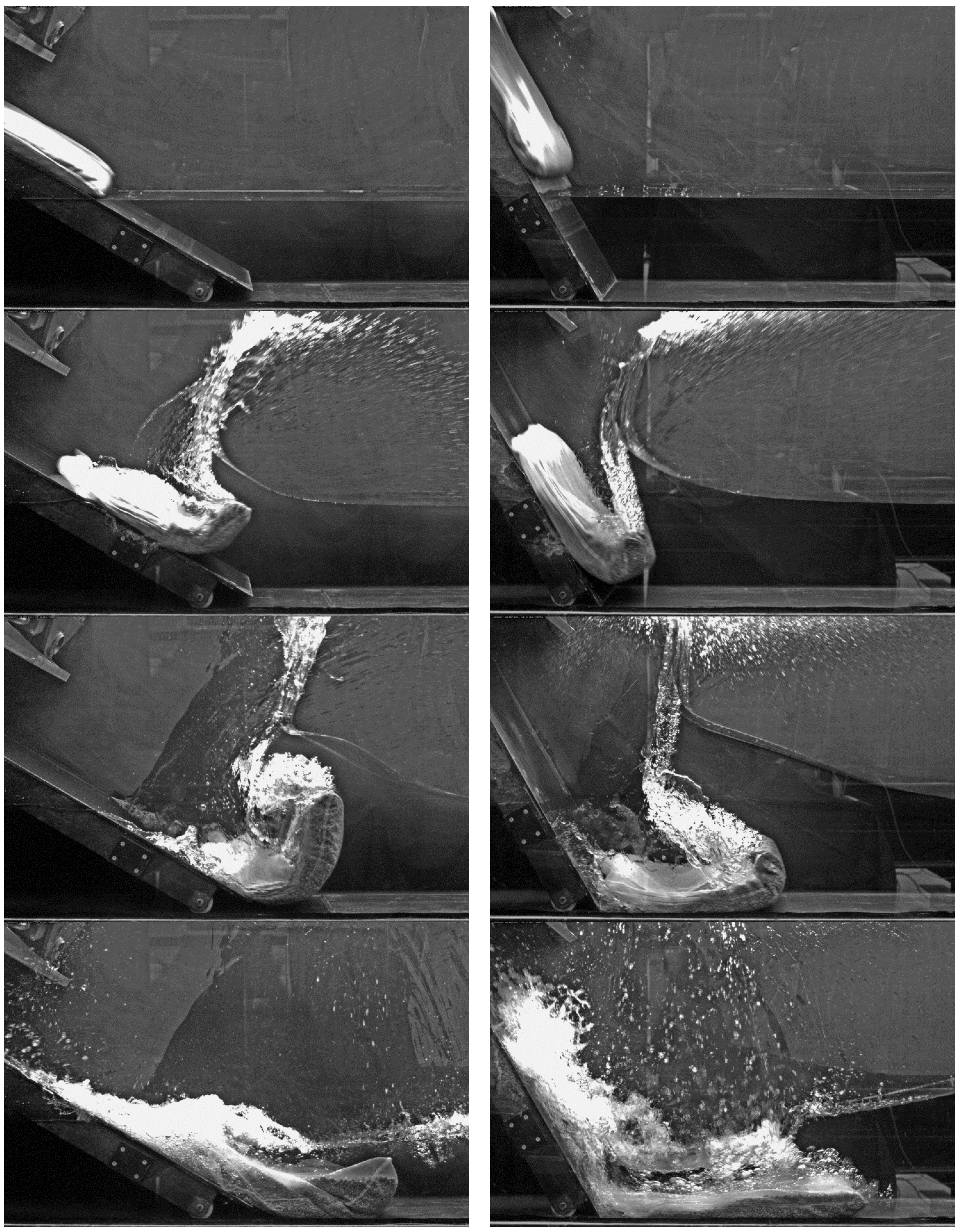
3.1. Slide Impact and Wave Generation Process
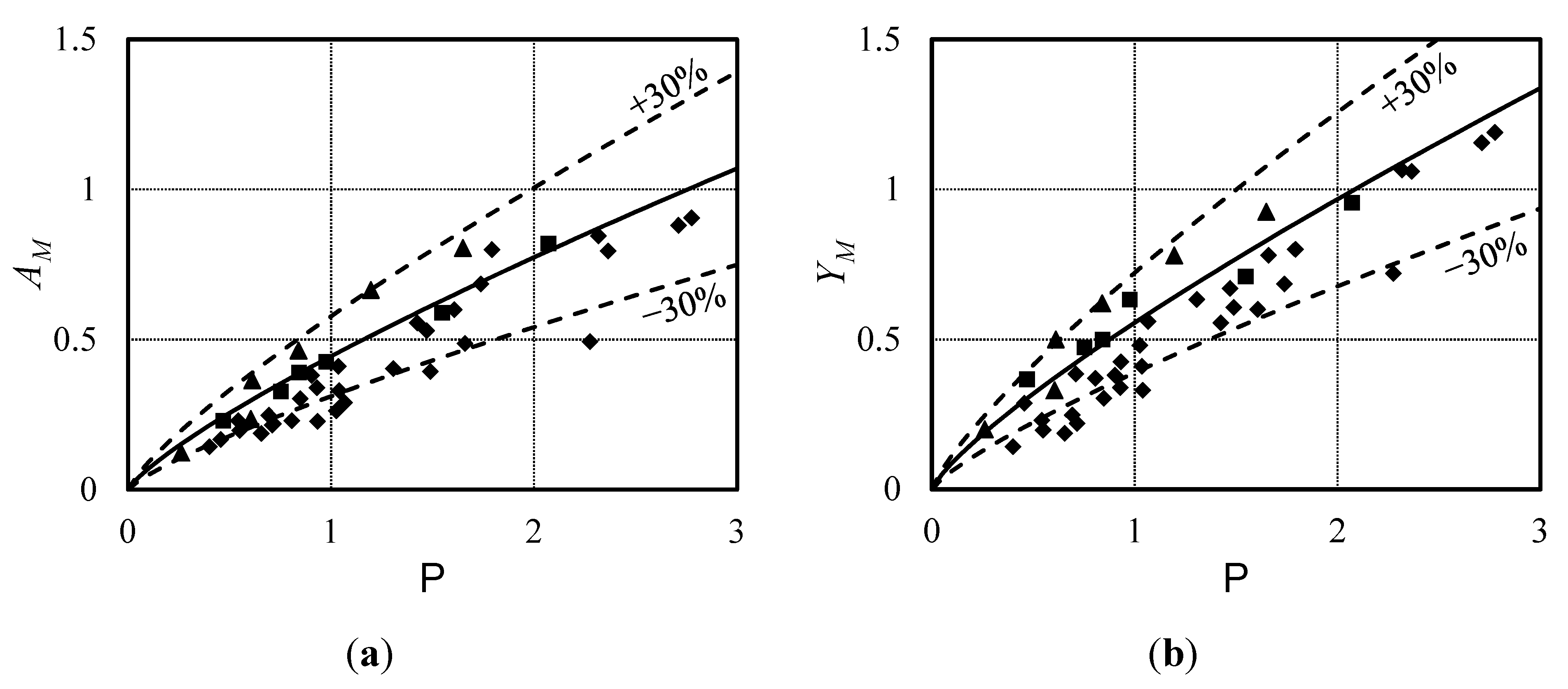
3.2. Maximum Wave Amplitude and Height
3.3. Wave Amplitude and Height Decay
3.4. Wave Crest Celerity
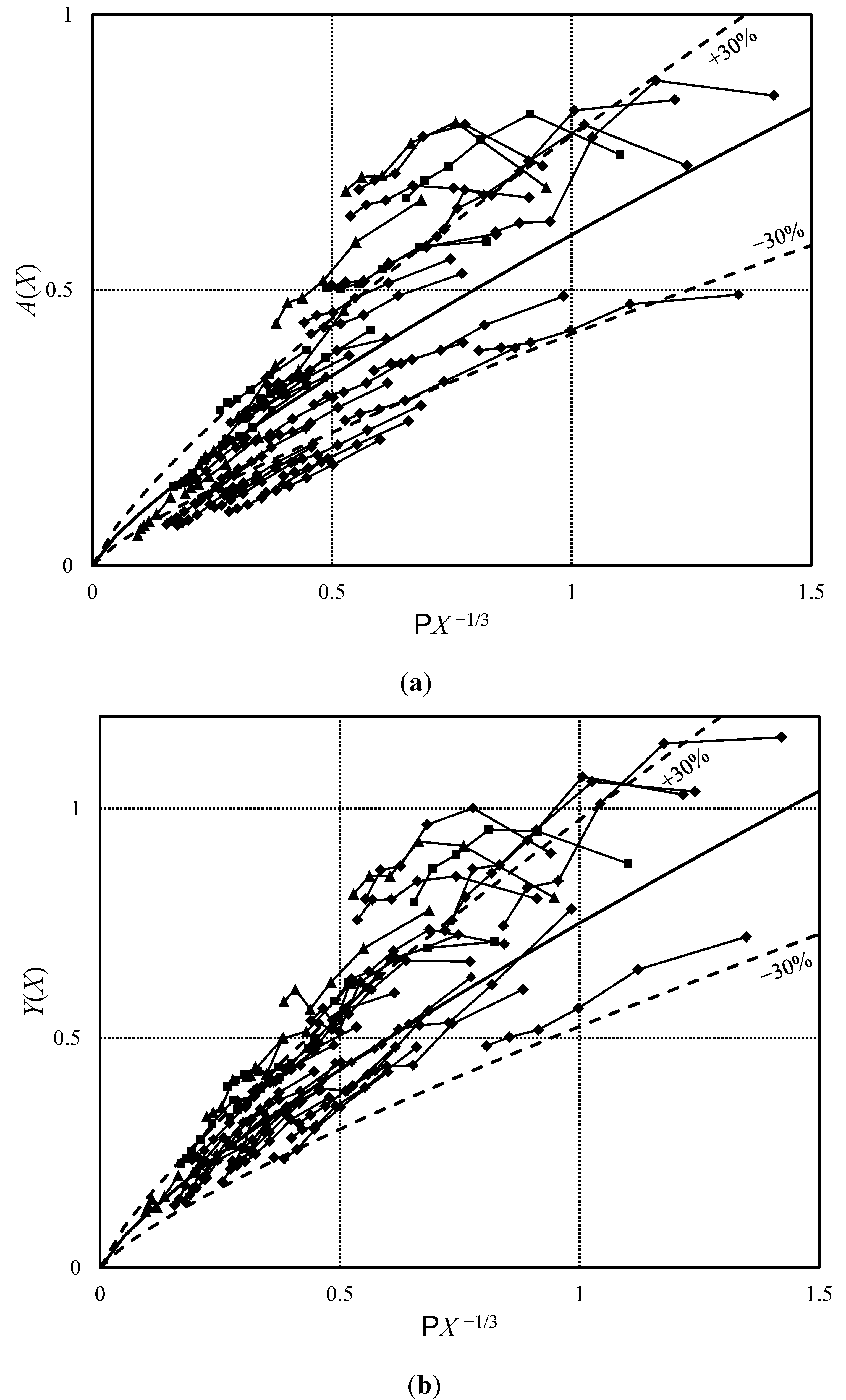

4. Conclusions
- The impulse product parameter P describes adequately both waves generated by mesh-packed and free granular slides;
- Waves generated by mesh-packed slides follow a ±30% scatter around the equations derived from experiments with free granular material. This scatter applies equally to free granular slides;
- For small values of P, the present data may undercut the −30% range. This behavior applies also for the corresponding ranges of free granular slides; and
- For values of PX−1/3 ranging between 0.5 and 1, the present data may exceed the +30% range, similar as for free granular slides.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heller, V.; Hager, W.H.; Minor, H.-E. Landslide generated impulse waves in reservoirs: Basics and computation. In VAW-Mitteilung 211; Minor, H.-E., Ed.; ETH Zurich: Zürich, Switzerland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Heller, V.; Spinneken, J. Improved landslide-tsunami prediction: Effects of block model parameters and slide model. J. Geophys. Res.-Oceans 2013, 118, 1489–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritz, H.M. Initial phase of landslide generated impulse waves. In VAW-Mitteilung 178; Minor, H.-E., Ed.; ETH Zurich: Zürich, Switzerland, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Heller, V. Landslide generated impulse waves: Prediction of near field characteristics. In VAW-Mitteilung 204; Minor, H.-E., Ed.; ETH Zurich: Zürich, Switzerland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed, F.; Fritz, H.M. Physical modeling of tsunamis generated by three-dimensional deformable granular landslides. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, C11015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viroulet, S.; Sauret, A.; Kimmoun, O. Tsunami generated by a granular collapse down a rough inclined plane. Europhys. Lett. 2014, 105, 34004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Risio, M.; De Girolamo, P.; Bellotti, G.; Panizzo, A.; Aristodemo, F.; Molfetta, M.G.; Petrillo, A.F. Landslide-generated tsunamis runup at the coast of a conical island: New physical model experiments. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, C01009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamphuis, J.W.; Bowering, R.J. Impulse waves generated by landslides. In Proceedings of the 12th Coastal Engineering Conference, Washington, DC, USA; 1970; pp. 575–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, E. Water waves generated by landslides. J. Waterway Div.-ASCE 1970, 96, 835–855. [Google Scholar]
- Panizzo, A.; de Girolamo, P.; Petaccia, A. Forecasting impulse waves generated by subaerial landslides. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110, C12025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sælevik, G.; Jensen, A.; Pedersen, G. Experimental investigation of impact generated tsunami; related to a potential rock slide, Western Norway. Coast. Eng. 2009, 56, 897–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viroulet, S.; Cébron, D.; Kimmoun, O.; Kharif, C. Shallow water waves generated by subaerial solid landslides. Geophys. J. Int. 2013, 193, 747–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ataie-Ashtiani, B.; Nik-Khah, A. Impulsive waves caused by subaerial landslides. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2008, 8, 263–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zweifel, A. Impulswellen: Effekte der Rutschdichte und der Wassertiefe (Impulse waves: Effects of slide density and water depth). In VAW-Mitteilung 186; Minor, H.-E., Ed.; ETH Zurich: Zürich, Switzerland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Slingerland, R.L.; Voight, B. Evaluating hazard of landslide-induced water waves. J. Waterw. Port C. Div. 1982, 108, 504–512. [Google Scholar]
- Davidson, D.D.; Whalin, R.W. Potential landslide-generated water waves, Libby Dam and Lake Koocanusa, Montana; Technical Report H-74–15; Waterway Experiment Station, U.S. Army Corps of Engineers: Vicksburg, MO, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Heller, V.; Hager, W.H. Impulse product parameter in landslide generated impulse waves. J. Waterw. Port C-ASCE 2010, 136, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritz, H.M.; Moser, P. Pneumatic landslide generator. Int. J. Fluid Power 2003, 4, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Evers, F.M.; Hager, W.H. Impulse Wave Generation: Comparison of Free Granular with Mesh-Packed Slides. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2015, 3, 100-110. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse3010100
Evers FM, Hager WH. Impulse Wave Generation: Comparison of Free Granular with Mesh-Packed Slides. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2015; 3(1):100-110. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse3010100
Chicago/Turabian StyleEvers, Frederic M., and Willi H. Hager. 2015. "Impulse Wave Generation: Comparison of Free Granular with Mesh-Packed Slides" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 3, no. 1: 100-110. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse3010100
APA StyleEvers, F. M., & Hager, W. H. (2015). Impulse Wave Generation: Comparison of Free Granular with Mesh-Packed Slides. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 3(1), 100-110. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse3010100





