Deep-Water Evolution in the Southwest Indian Ocean and Its Response to Global Climate Change During the Last 300 ka: Evidence from Sedimentary and Stable Isotopic Records
Abstract
1. Introduction
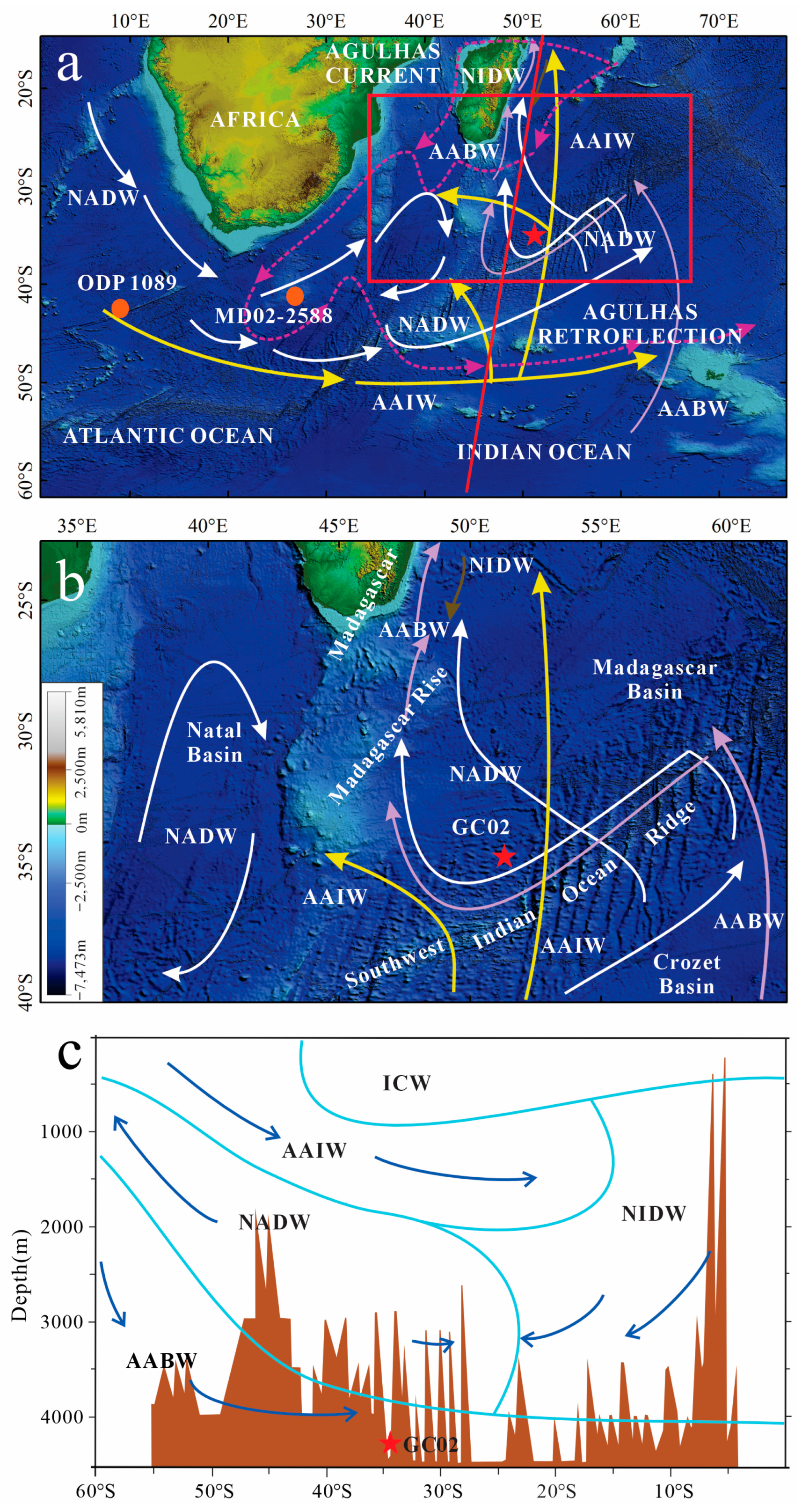
2. Study Area
3. Materials and Methods
4. Results
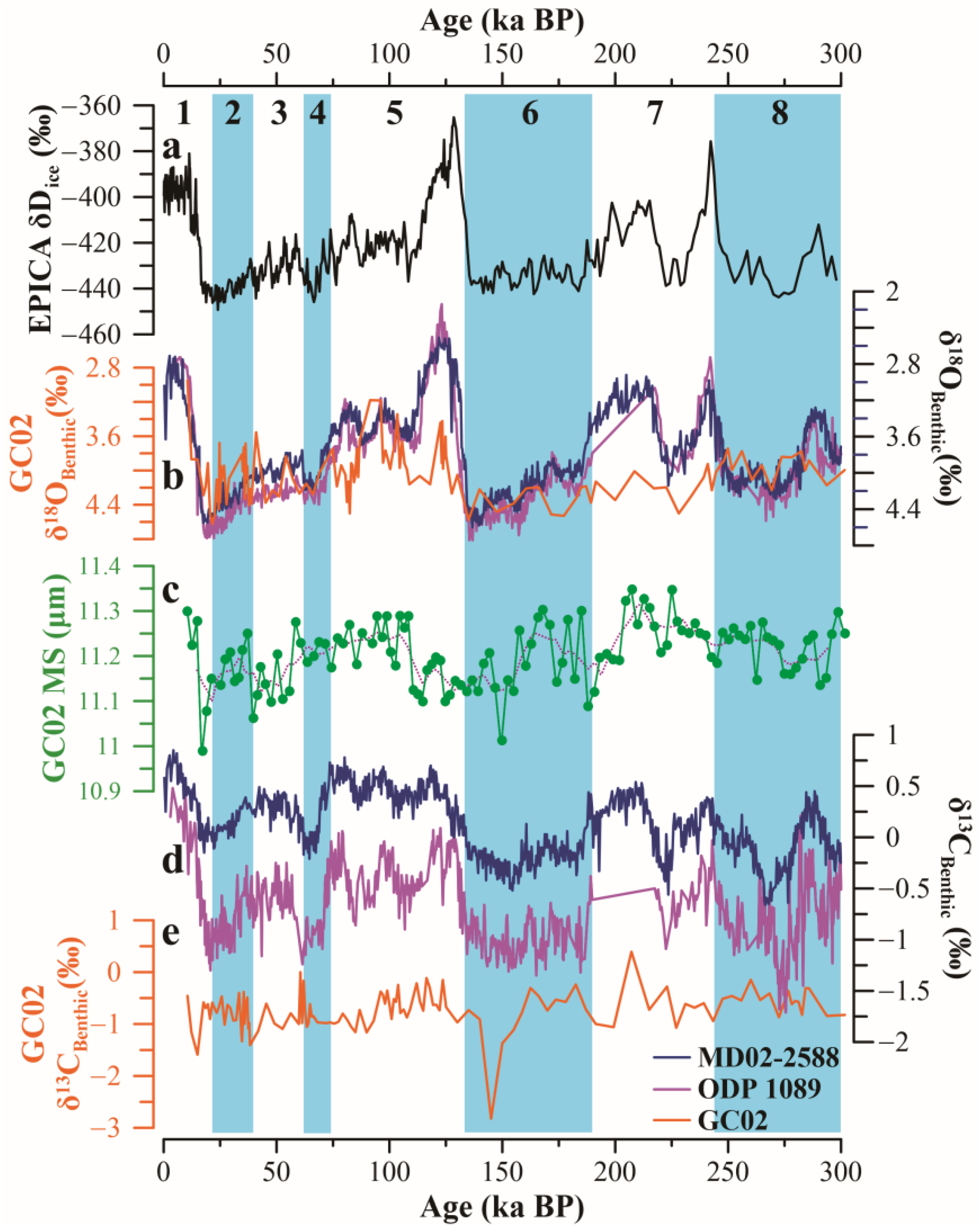
4.1. Chronology of GC02
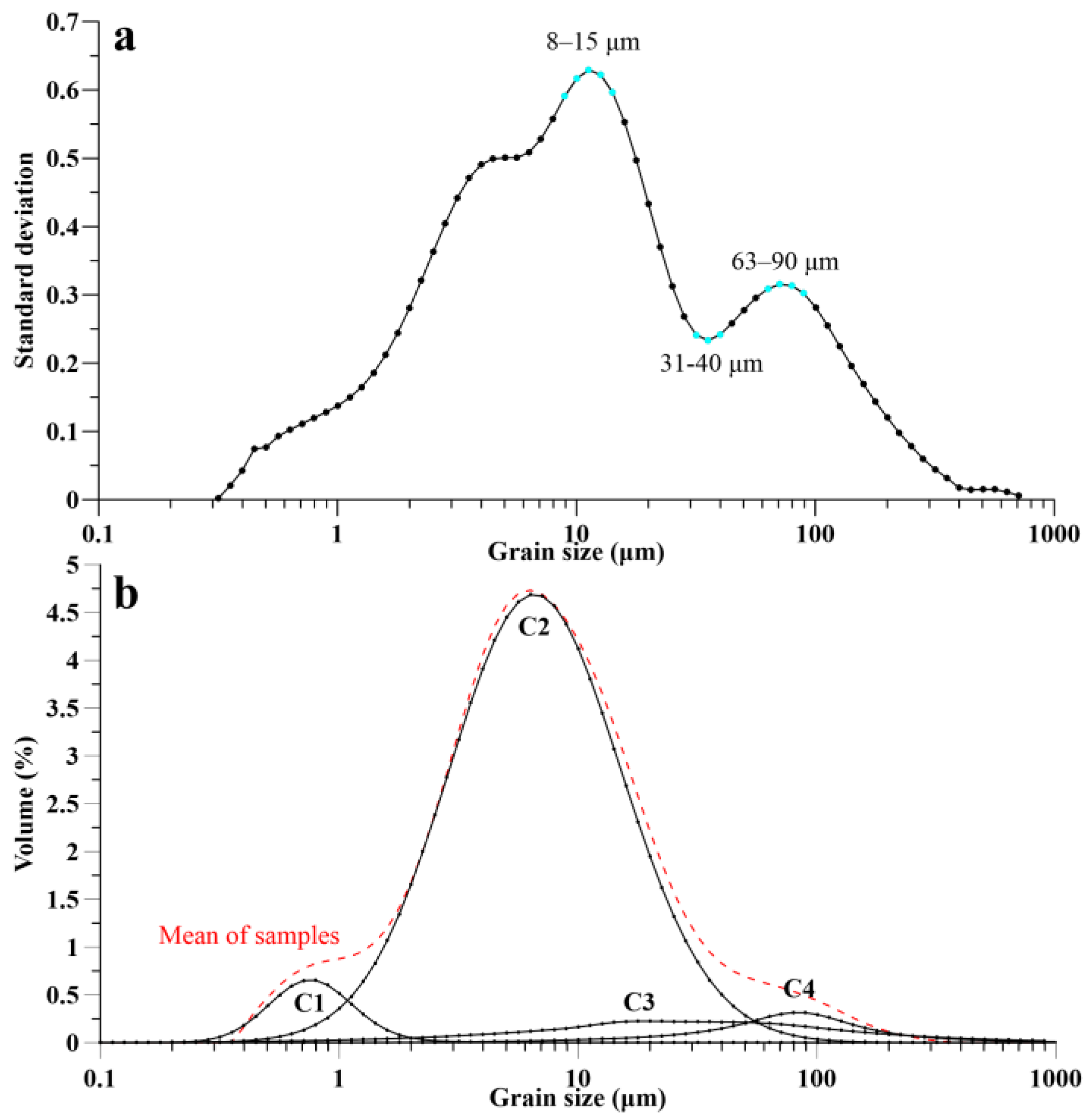
4.2. Main Sensitive Grain Mean Size of Sortable Silt
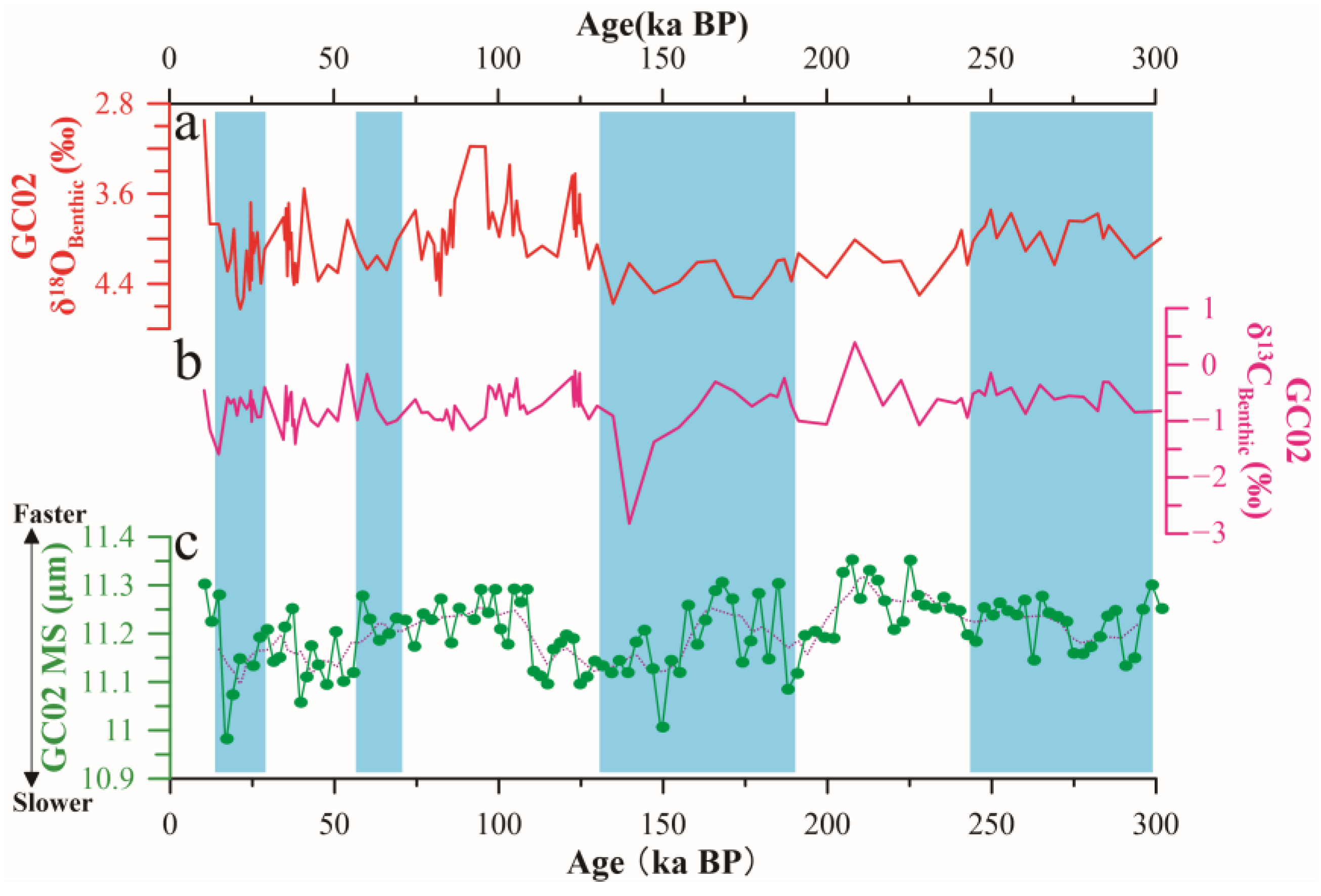
4.3. Stable Isotope
5. Discussion
5.1. Characteristics of AABW Masses near SWIR
5.2. Characteristics and Comparison of Regional Deep Water
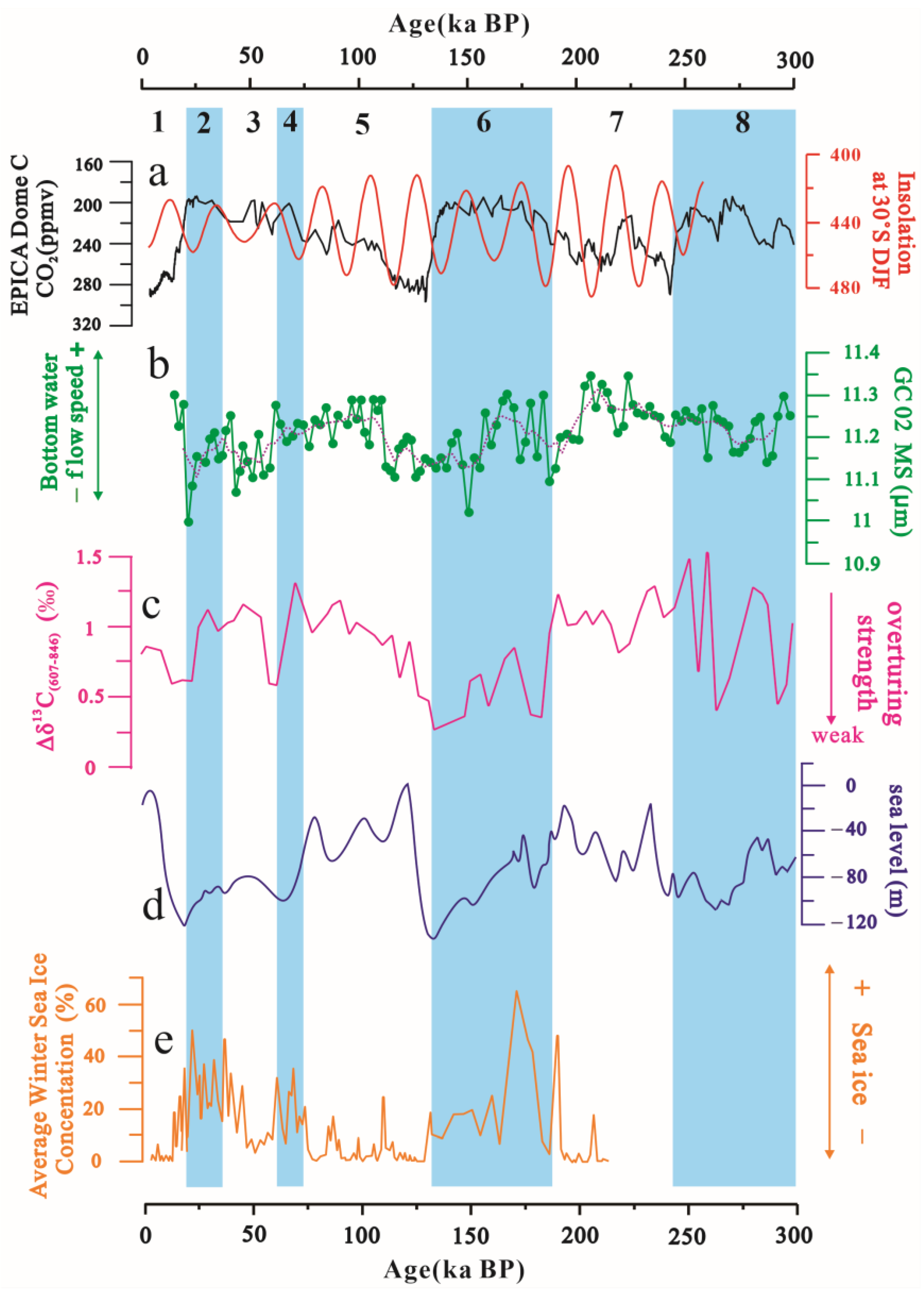
5.3. Driving Mechanism in Climate and Water Mass
6. Conclusions
- Variations in the GC02 MS values reflect changes in the bottom water flow speed and the degree of AABW impact. Decreased MS values indicate weakened AABW during the late glacial periods. Conversely, increased MS values suggest enhanced AABW during the interglacial periods. Meanwhile, it indicates the phenomenon of strengthening during the early stages of the glacial periods.
- Except for MIS 1, the MS record is particularly synchronous with benthic δ18O in GC02, indicating that the temperature and salinity of bottom water in the Southwest Indian Ocean are mainly controlled by the AABW. In contrast to adjacent areas, our analysis indicates that the AABW exerts a significant influence on the climate of the study area during glacial–interglacial periods during the last 300 ka.
- By controlling the ventilation of water masses and polar heat transport in the Indian Ocean, changes in AABW intensity and Southern Ocean ice volume result from changes in AMOC, which itself arises from orbital modulation. In the Southwest Indian Ocean, the AMOC has a more significant effect on ice volume during glacial periods, while its effect on AABW is relatively strong during interglacial periods.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MS | mean grain size |
| SS | sortable silt |
| SWIR | Southwest Indian Ocean mid-ridge |
| AABW | Antarctic Bottom Water |
| AMOC | Atlantic meridional overturning circulation |
| WSI | winter sea ice |
| THC | Oceanic thermohaline circulation |
| NADW | North Atlantic Deep Water |
| ICW | Indian Central Water |
| AMS | accelerator mass spectrometry |
References
- Johnson, G.C. Quantifying Antarctic Bottom Water and North Atlantic Deep Water Volumes. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2008, 113, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, C.D.; Fairbanks, R.G. Evidence from Southern Ocean Sediments for the Effect of North Atlantic Deep-Water Flux on Climate. Nature 1992, 355, 416–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickson, R.R.; Brown, J. The Production of North Atlantic Deep Water: Sources, Rates, and Pathways. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1994, 99, 12319–12341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jullion, L.; Garabato, A.C.N.; Bacon, S.; Meredith, M.P.; Brown, P.J.; Torres-Valdés, S.; Speer, K.G.; Holland, P.R.; Dong, J.; Bakker, D.; et al. The contribution of the Weddell Gyre to the lower limb of the Global Overturning Circulation. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2014, 119, 3357–3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solodoch, A.; Stewart, A.L.; Hogg, A.M.C.; Morrison, A.K.; Kiss, A.E.; Thompson, A.F.; Purkey, S.G.; Cimoli, L. How Does Antarctic Bottom Water Cross the Southern Ocean? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2021GL097211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.I.; Liu, Z.; Otto-Bliesner, B.L.; Kutzbach, J.E.; Vavrus, S.J. Southern Ocean Sea-Ice Control of the Glacial North Atlantic Thermohaline Circulation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapter 4 Circulation and Water Masses of the Southern Ocean: A Review. In Developments in Earth and Environmental Sciences; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; Volume 8, pp. 85–114. [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, M.; Lourens, L.J.; Tuenter, E.; Hilgen, F.; Reichart, G.J.; Weber, N. Precession Phasing Offset between Indian Summer Monsoon and Arabian Sea Productivity Linked to Changes in Atlantic Overturning Circulation. Paleoceanography 2010, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curry, W.B.; Oppo, D.W. Glacial Water Mass Geometry and the Distribution of δ13C of ΣCO2 in the Western Atlantic Ocean. Paleoceanography 2005, 20, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarnthein, M.; Winn, K.; Jung, S.J.A.; Duplessy, J.C.; Labeyrie, L.; Erlenkeuser, H.; Ganssen, G. Changes in East Atlantic Deepwater Circulation over the Last 30,000 Years: Eight Time Slice Reconstructions. Paleoceanography 1994, 9, 209–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molyneux, E.G.; Hall, I.R.; Zahn, R.; Diz, P. Deep Water Variability on the Southern Agulhas Plateau: Interhemispheric Links over the Past 170 Ka. Paleoceanography 2007, 22, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krueger, S.; Leuschner, D.C.; Ehrmann, W.; Schmiedl, G.; Mackensen, A. North Atlantic Deep Water and Antarctic Bottom Water Variability during the Last 200 Ka Recorded in an Abyssal Sediment Core off South Africa. Glob. Planet. Change 2012, 80–81, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, T.; Laughton, A.S.; Flemming, N.C.; McCave, I.N.; Kiefer, T.; Thornalley, D.J.R.; Elderfield, H. Deep Flow in the Madagascar–Mascarene Basin over the Last 150000 Years. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2005, 363, 81–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, J.L. On the Total Geostrophic Circulation of the South Atlantic Ocean: Flow Patterns, Tracers, and Transports. Prog. Oceanogr. 1989, 23, 149–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orsi, A.H.; Whitworth, T.; Nowlin, W.D. On the Meridional Extent and Fronts of the Antarctic Circumpolar Current. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 1995, 42, 641–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GEBCO Bathymetric Compilation Group. The GEBCO_2024 Grid—A Continuous Terrain Model of the Global Oceans and Land; NERC EDS British Oceanographic Data Centre NOC: Liverpool, UK, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stramma, L.; Lutjeharms, J.R.E. The Flow Field of the Subtropical Gyre of the South Indian Ocean. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1997, 102, 5513–5530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, A.L.; Henderson, G.M.; Robinson, L.F. Interpretation of the 231Pa/230Th Paleocirculation Proxy: New Water-Column Measurements from the Southwest Indian Ocean. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2006, 241, 493–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, M.; Diz, P.; Hall, I.R.; Zahn, R. Millennial-Scale Changes in Atmospheric CO2 Levels Linked to the Southern Ocean Carbon Isotope Gradient and Dust Flux. Nat. Geosci. 2013, 6, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortese, G.; Abelmann, A.; Gersonde, R. The Last Five Glacial-Interglacial Transitions: A High-Resolution 450,000-Year Record from the Subantarctic Atlantic. Paleoceanography 2007, 22, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, W.H.; Parker, F.L. Diversity of Planktonic Foraminifera in Deep-Sea Sediments. Science 1970, 168, 1345–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCorkle, D.C.; Keigwin, L.D. Depth Profiles of δ13C in Bottom Water and Core Top C. Wuellerstorfi on the Ontong Java Plateau and Emperor Seamounts. Paleoceanography 1994, 9, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch-Stieglitz, J.; Adkins, J.F.; Curry, W.B.; Dokken, T.; Hall, I.R.; Herguera, J.C.; Hirschi, J.J.M.; Ivanova, E.V.; Kissel, C.; Marchal, O.; et al. Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation During the Last Glacial Maximum. Science 2007, 316, 66–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackensen, A.; Rudolph, M.; Kuhn, G. Late Pleistocene Deep-Water Circulation in the Subantarctic Eastern Atlantic. Glob. Planet. Change 2001, 30, 197–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manighetti, B.; McCave, I.N. Late Glacial and Holocene Palaeocurrents around Rockall Bank, NE Atlantic Ocean. Paleoceanography 1995, 10, 611–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCave, I.N.; Hall, I.R. Size Sorting in Marine Muds: Processes, Pitfalls, and Prospects for Paleoflow-Speed Proxies. Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 2006, 7, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Chang, Z.; Si, B.; Qin, X.; Itoh, S.; Lomtatidze, Z. Partitioning of the grain-size components of Dali Lake core sediments: Evidence for lake-level changes during the Holocene. J. Paleolimnol. 2009, 42, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, J.J.; Walker, M. Reconstructing Quaternary Environments, 3rd ed.; Routledge: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisiecki, L.E.; Raymo, M.E. A Pliocene-Pleistocene Stack of 57 Globally Distributed Benthic δ18O Records. Paleoceanography 2005, 20, PA1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuiver, M.; Reimer, P.J. Extended 14C Data Base and Revised CALIB 3.0 14C Age Calibration Program. Radiocarbon 1993, 35, 215–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, D.J.; Piotrowski, A.M.; Galy, A.; McCave, I.N. A Boundary Exchange Influence on Deglacial Neodymium Isotope Records from the Deep Western Indian Ocean. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2012, 341–344, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouzel, J.; Masson-Delmotte, V.; Cattani, O.; Dreyfus, G.; Falourd, S.; Hoffmann, G.; Minster, B.; Nouet, J.; Barnola, J.M.; Chappellaz, J.; et al. Orbital and millennial Antarctic climate variability over the past 800,000 years. Science 2007, 317, 793–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodell, D.A.; Venz, K.A.; Charles, C.D.; Ninnemann, U.S. Pleistocene Vertical Carbon Isotope and Carbonate Gradients in the South Atlantic Sector of the Southern Ocean. Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 2003, 4, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spooner, P.T.; Thornalley, D.J.R.; Ellis, P. Grain Size Constraints on Glacial Circulation in the Southwest Atlantic. Paleoceanogr. Paleoclimatol. 2018, 33, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bali, H.; Gupta, A.K.; Joseph, S.; Kaushik, A. Exploring the deep water mass turnovers in the eastern indian ocean since the late oligocene: Significance of ocean gateways and paleoclimate. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2024, 657, 112607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, I.R.; McCave, I.N.; Shackleton, N.J.; Weedon, G.P.; Harris, S.E. Intensified Deep Pacific Inflow and Ventilation in Pleistocene Glacial Times. Nature 2001, 412, 809–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bard, E.; Rickaby, R.E.M. Migration of the Subtropical Front as a Modulator of Glacial Climate. Nature 2009, 460, 380–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, A.L. Long-Term Variations of Caloric Insolation Resulting from the Earth’s Orbital Elements. Quat. Res. 1978, 9, 139–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruddiman, W.F.; Raymo, M.E.; Martinson, D.G.; Clement, B.M.; Backman, J. Pleistocene Evolution: Northern Hemisphere Ice Sheets and North Atlantic Ocean. Paleoceanography 1989, 4, 353–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mix, A.C.; Le, J.; Shackleton, N.J. Benthic foraminiferal stable isotope stratigraphy of site 846: 0-1.8 Ma. In Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results; Pisias, N.G., Mayer, L.A., Janecek, T.R., Palmer-Julson, A., van Andel, T.H., Eds.; Ocean Drilling Program: College Station, TX, USA, 1995; Volume 138, pp. 839–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skumryev, V.; Stoyanov, S.; Zhang, Y.; Hadjipanayis, G.; Givord, D.; Nogués, J. Beating the Superparamagnetic Limit with Exchange Bias. Nature 2003, 423, 850–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosta, X.; Sturm, A.; Armand, L.; Pichon, J.J. Late Quaternary Sea Ice History in the Indian Sector of the Southern Ocean as Recorded by Diatom Assemblages. Mar. Micropaleontol. 2004, 50, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrag, D.P.; Adkins, J.F.; McIntyre, K.; Alexander, J.L.; Hodell, D.A.; Charles, C.D.; McManus, J.F. The Oxygen Isotopic Composition of Seawater during the Last Glacial Maximum. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2002, 21, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diz, P.; Hall, I.R.; Zahn, R.; Molyneux, E.G. Paleoceanography of the Southern Agulhas Plateau during the Last 150 Ka: Inferences from Benthic Foraminiferal Assemblages and Multispecies Epifaunal Carbon Isotopes. Paleoceanography 2007, 22, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oppo, D.W.; Horowitz, M. Glacial deep water geometry: South Atlantic benthic foraminiferal Cd/Ca and d13C evidence. Paleoceanography 2000, 15, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustin, L.; Barbante, C.; Barnes, P.R.F.; Marc Barnola, J.; Bigler, M.; Castellano, E.; Cattani, O.; Chappellaz, J.; Dahl-Jensen, D.; Delmonte, B.; et al. Eight Glacial Cycles from an Antarctic Ice Core. Nature 2004, 429, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uemura, R.; Motoyama, H.; Masson-Delmotte, V.; Jouzel, J.; Kawamura, K.; Goto-Azuma, K.; Fujita, S.; Kuramoto, T.; Hirabayashi, M.; Miyake, T.; et al. Asynchrony between Antarctic Temperature and CO2 Associated with Obliquity over the Past 720,000 Years. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
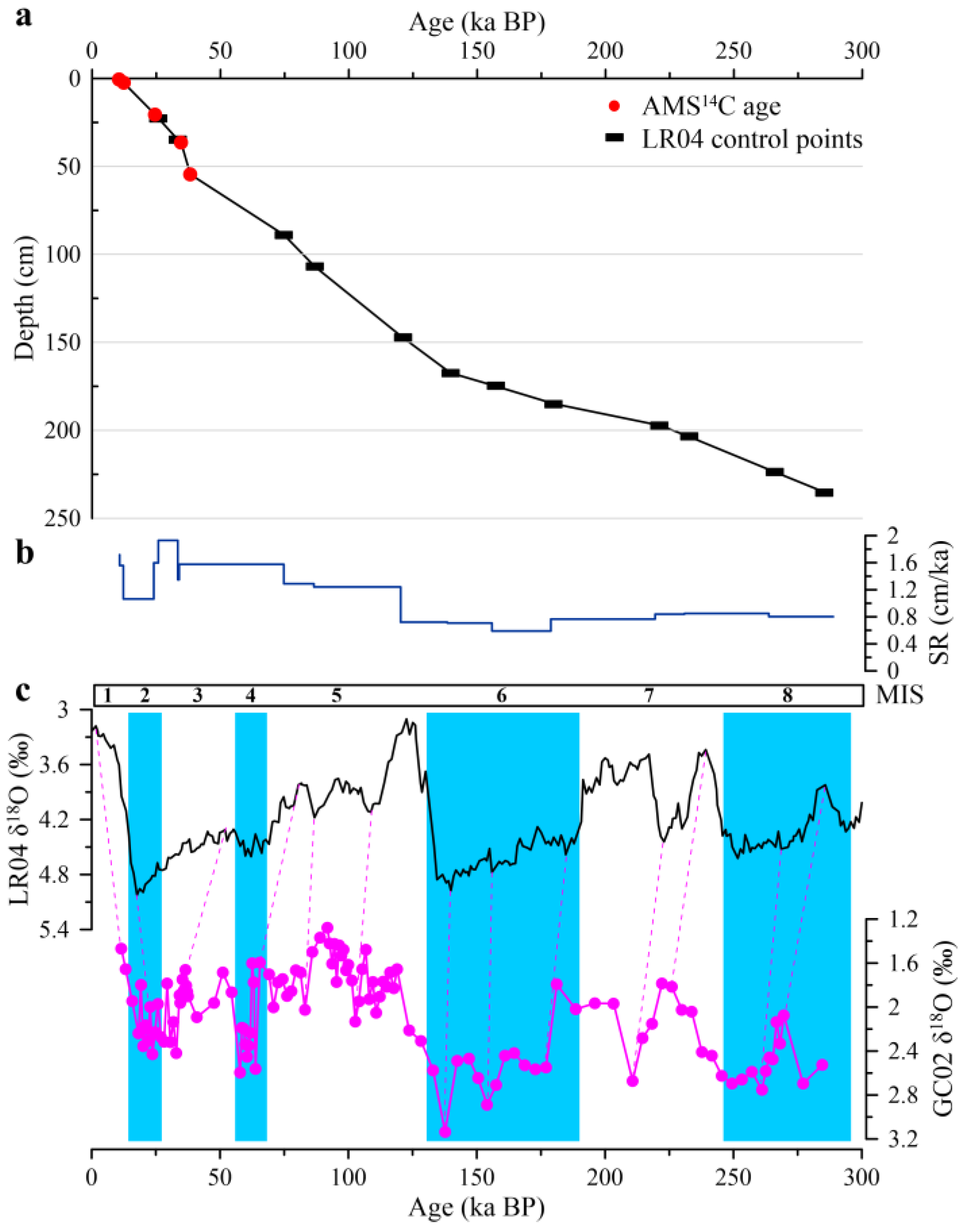
| Lab Code | Depth, cm | Conventional 14C Age, a | ±1SD, a | Calibrated 14C Age, a | ±1SD, a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beta-461852 | 1 | 10,120 | ±30 | 10,530 | ±30 |
| Beta-461853 | 3 | 11,890 | ±40 | 12,290 | ±40 |
| Beta-461854 | 21 | 24,020 | ±90 | 24,430 | ±90 |
| Beta-461855 | 37 | 34,260 | ±240 | 34,660 | ±240 |
| Beta-461856 | 55 | 37,850 | ±370 | 38,260 | ±370 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Zhao, M.; Liu, G.; Yang, J.; Dada, O.A.; Lin, Z. Deep-Water Evolution in the Southwest Indian Ocean and Its Response to Global Climate Change During the Last 300 ka: Evidence from Sedimentary and Stable Isotopic Records. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2026, 14, 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse14010056
Zhao M, Liu G, Yang J, Dada OA, Lin Z. Deep-Water Evolution in the Southwest Indian Ocean and Its Response to Global Climate Change During the Last 300 ka: Evidence from Sedimentary and Stable Isotopic Records. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2026; 14(1):56. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse14010056
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Mengwei, Guanyu Liu, Jichao Yang, Olusegun A. Dada, and Zhen Lin. 2026. "Deep-Water Evolution in the Southwest Indian Ocean and Its Response to Global Climate Change During the Last 300 ka: Evidence from Sedimentary and Stable Isotopic Records" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 14, no. 1: 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse14010056
APA StyleZhao, M., Liu, G., Yang, J., Dada, O. A., & Lin, Z. (2026). Deep-Water Evolution in the Southwest Indian Ocean and Its Response to Global Climate Change During the Last 300 ka: Evidence from Sedimentary and Stable Isotopic Records. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 14(1), 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse14010056






