A Broad-Scale Summer Spatial Structure of Pelagic Fish Schools as Acoustically Assessed Along the Turkish Aegean Coast
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection
2.1.1. Acoustics
2.1.2. Environments
2.2. Data Processing
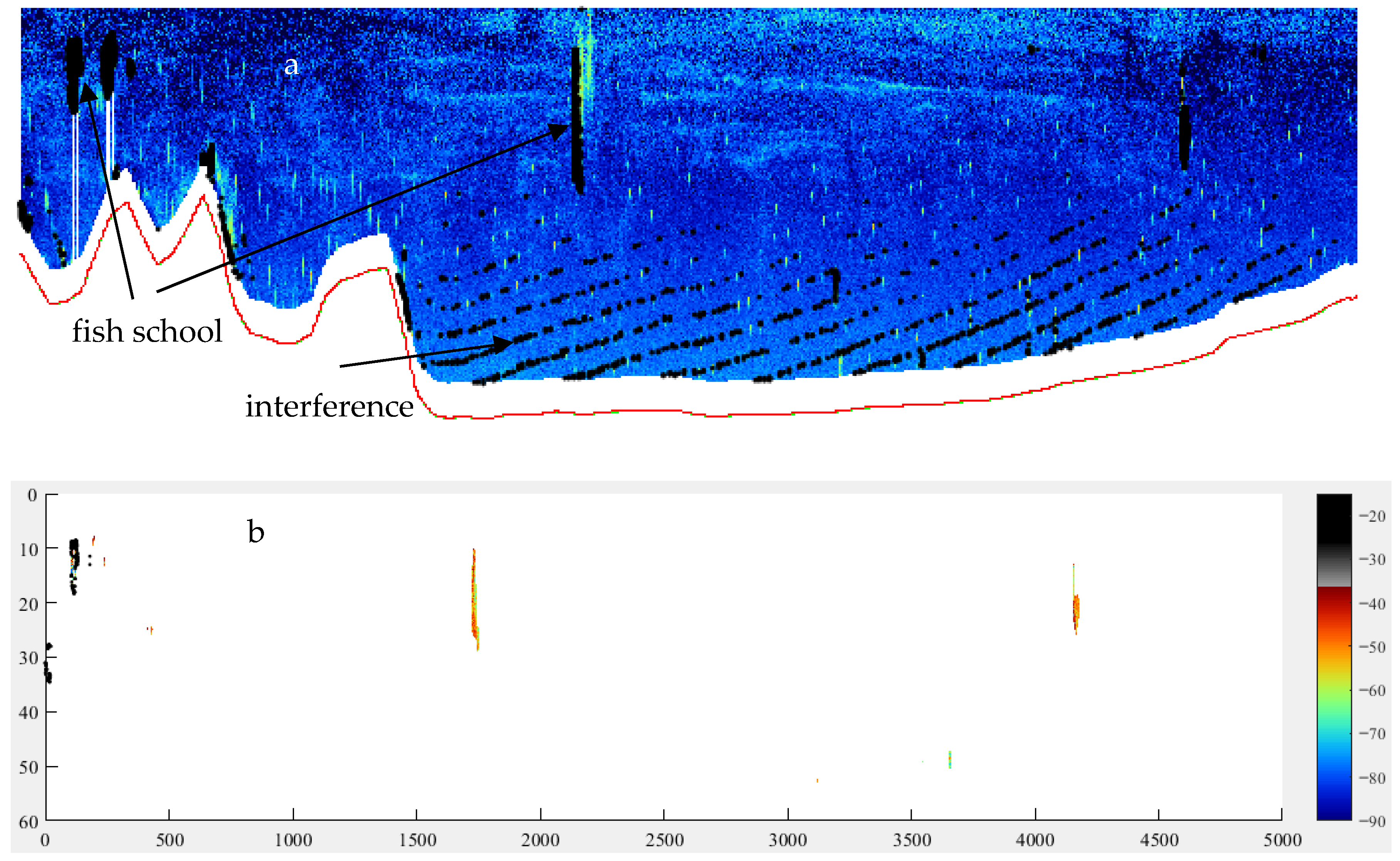
2.2.1. Acoustics
- School identification using Sv values between −50 and −33 dB.
- School separation: Fewer than 20 successive vertical counts or horizontal pings indicate the same school; otherwise, it is considered a separate school. This threshold, determined through iterative analysis of the entire acoustic dataset, has proven highly effective in eliminating interference.
- Exclusion of small sample schools: Schools with fewer than 20 echoes were excluded. This threshold, along with the following criteria, was established to ensure statistically significant analyses by eliminating samples with insufficient size.
- Exclusion of small-area schools: schools with lateral areas smaller than 20 m2.
- i.
- School shape: defined by amorphous polygons in meters (depth and geographic distance)
- ii.
- A: School lateral area (m2), +
- iii.
- SH: School height (m), +
- iv.
- SW: School width (m), +
- v.
- SvE (dB/m3): Sv at polygon edge (min, max, mean*), +
- vi.
- SvI (dB/m3): Sv inside polygon (min, max, mean*),
- vii.
- Sv (dB/m3): Total Sv of polygon (min, max, mean*),
- viii.
- HFB (m): Height from the bottom to the school’s deepest point, +
- ix.
- MnD (m): Minimum (shallowest) school depth from the surface, +
- x.
- MxD (m): Maximum (deepest) school depth toward bottom, +
- xi.
- Sa/sa (dB/m2 and m2/m2): Backscattering strength and coefficient per unit area, +
- xii.
- Sv/sv (dB/m3 and m2/m3): Volume backscattering strength and coefficient per unit volume, +
- xiii.
- NASC (m2/nm2): Nautical Area Scattering Coefficient, +
- xiv.
- TS (dB/individual): Target strengthTS was converted to fish length using Love’s formula [61].
2.2.2. Environment
2.3. Statistical Analyses
2.3.1. Acoustics
2.3.2. Environment
3. Results
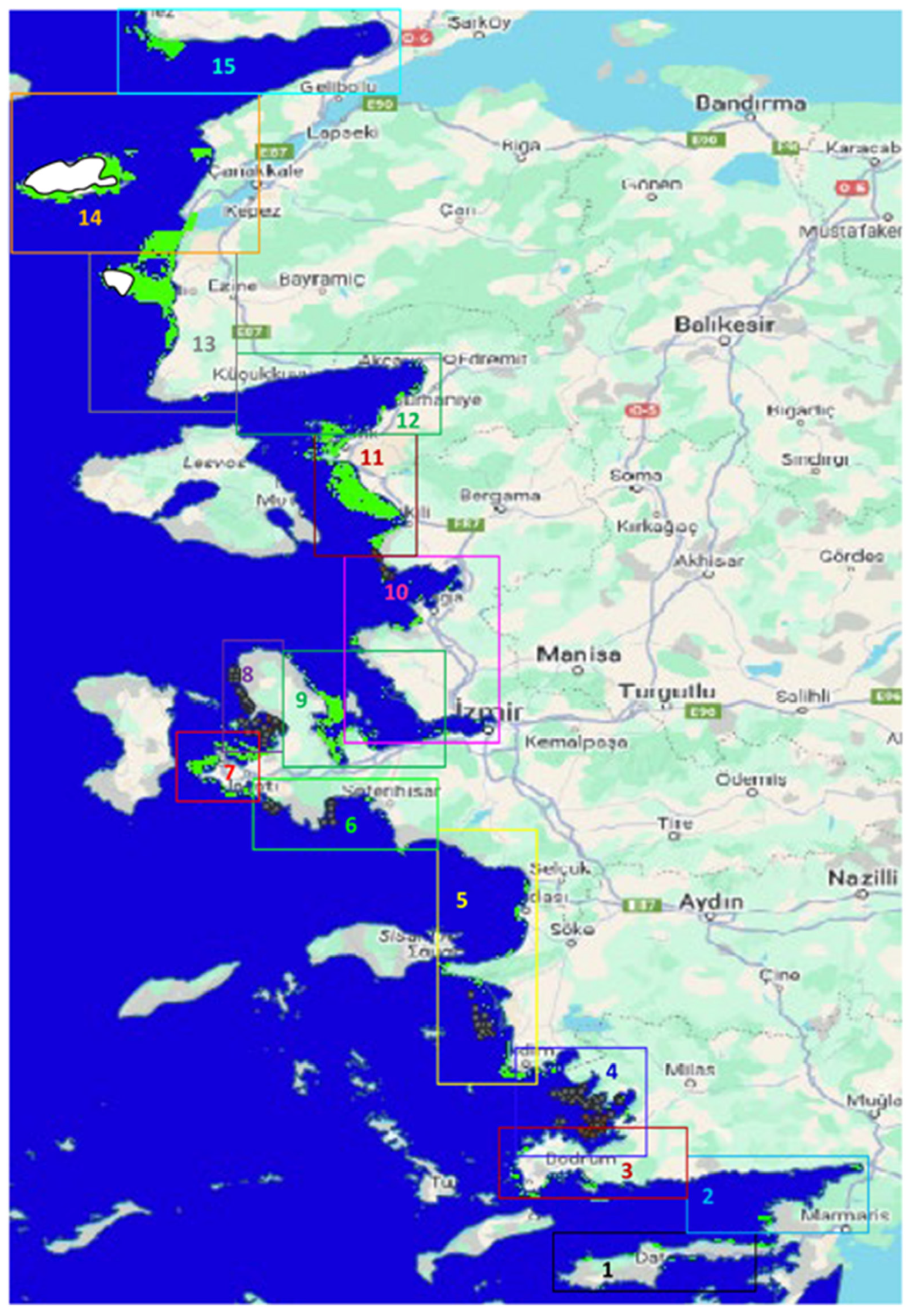
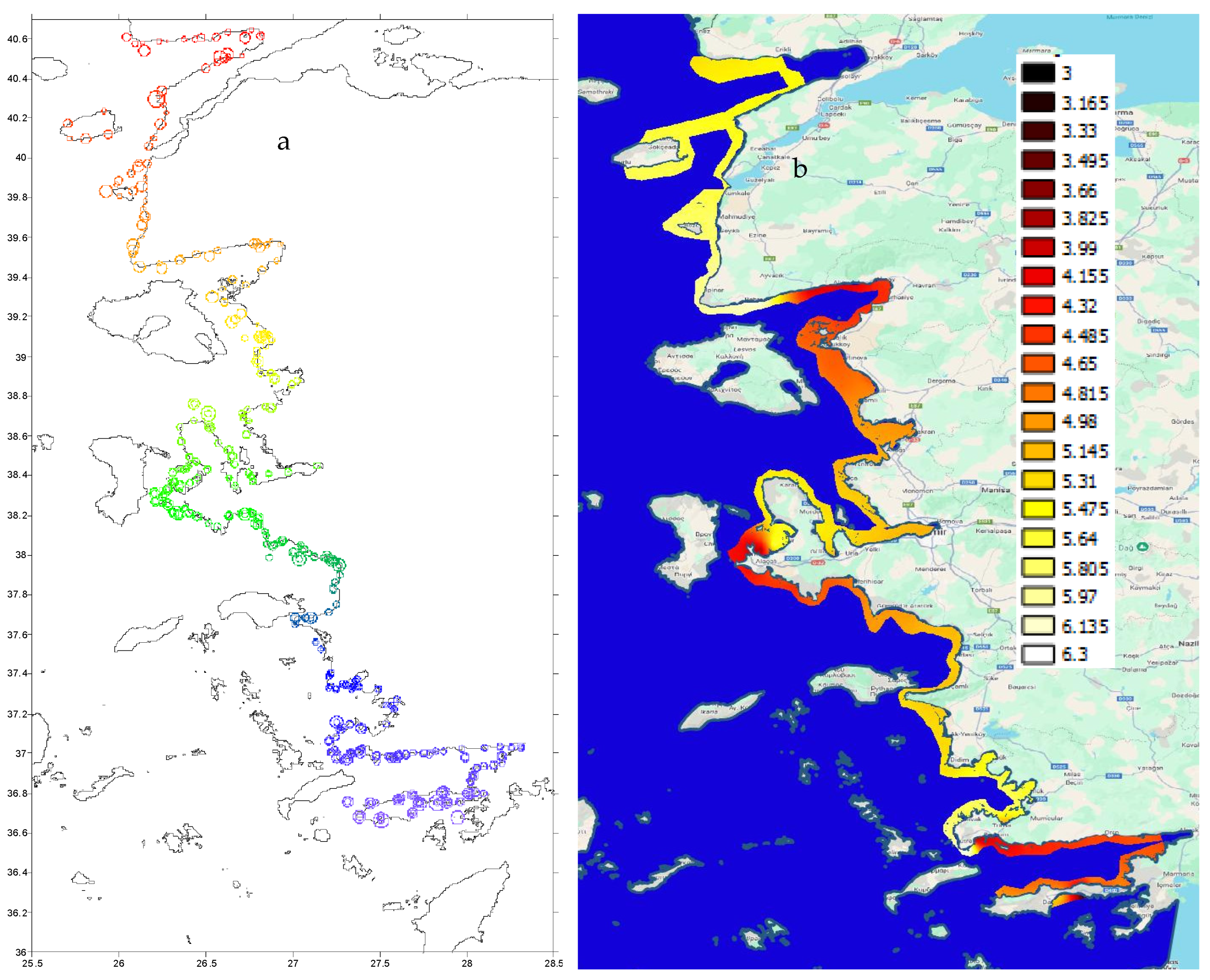
3.1. Study Area
3.1.1. Bottom Depth and Coastline Features
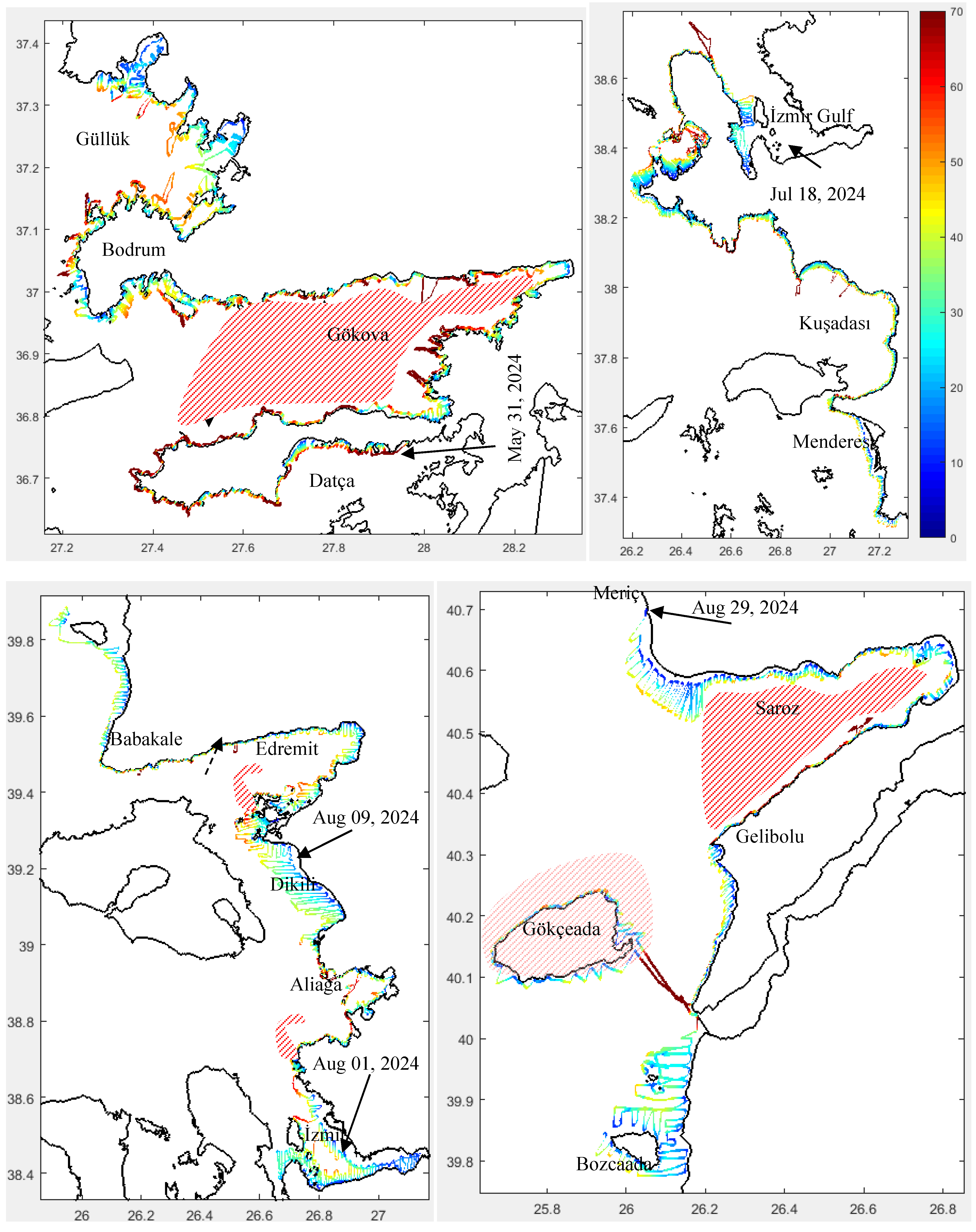
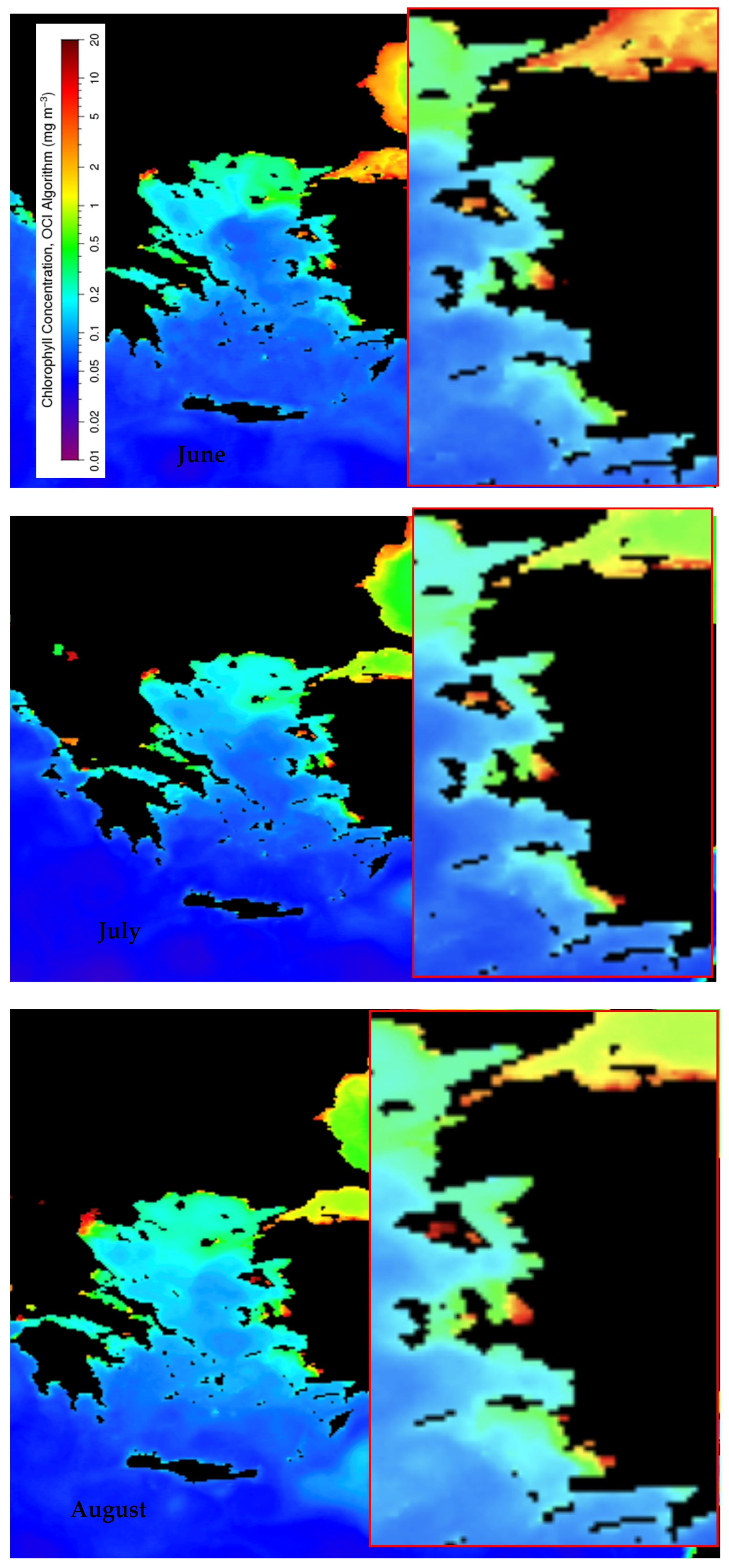
3.1.2. Chlorophyll
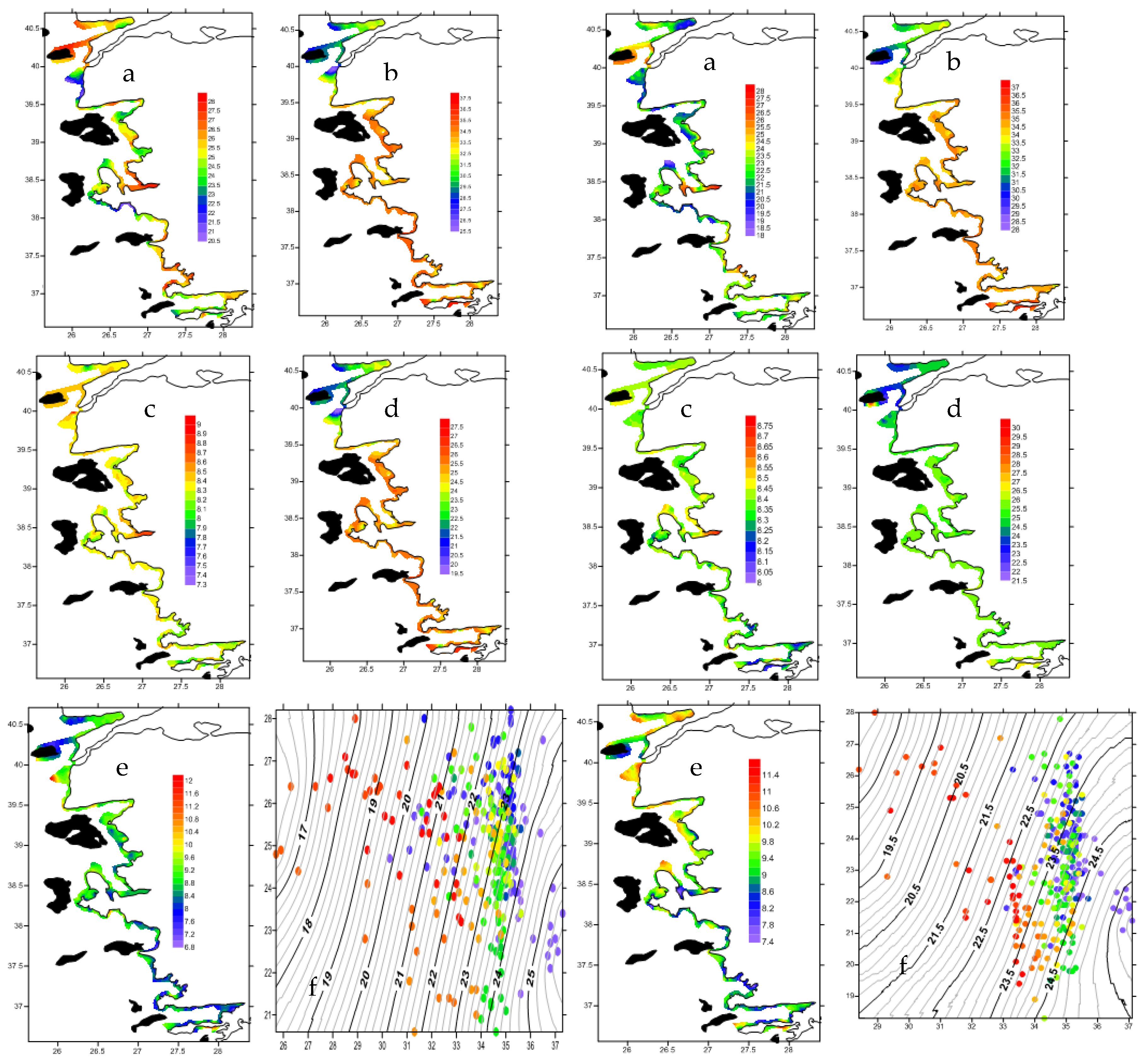
3.1.3. Physics
3.1.4. Optics: Secchi Disk Depth (m) and PAR
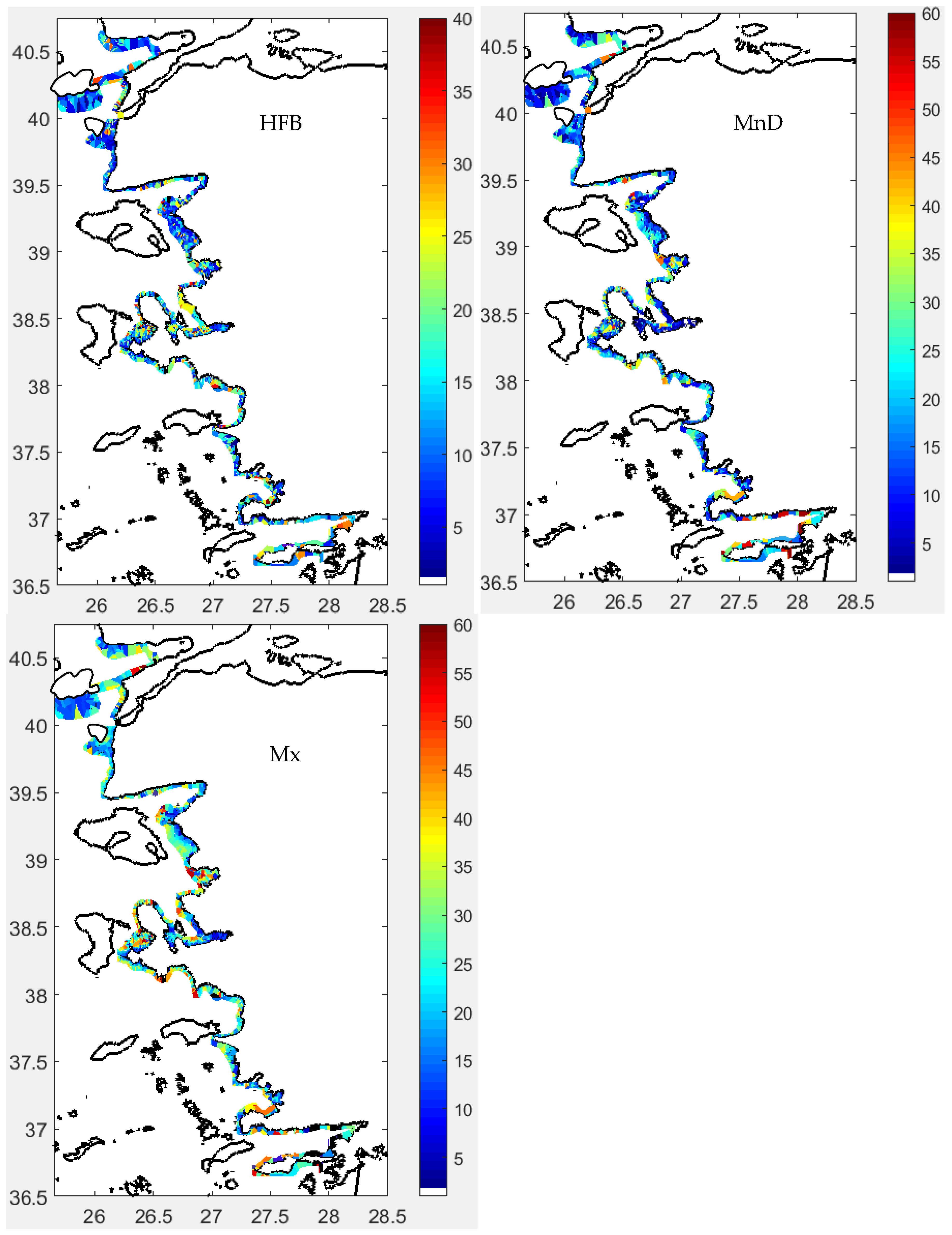
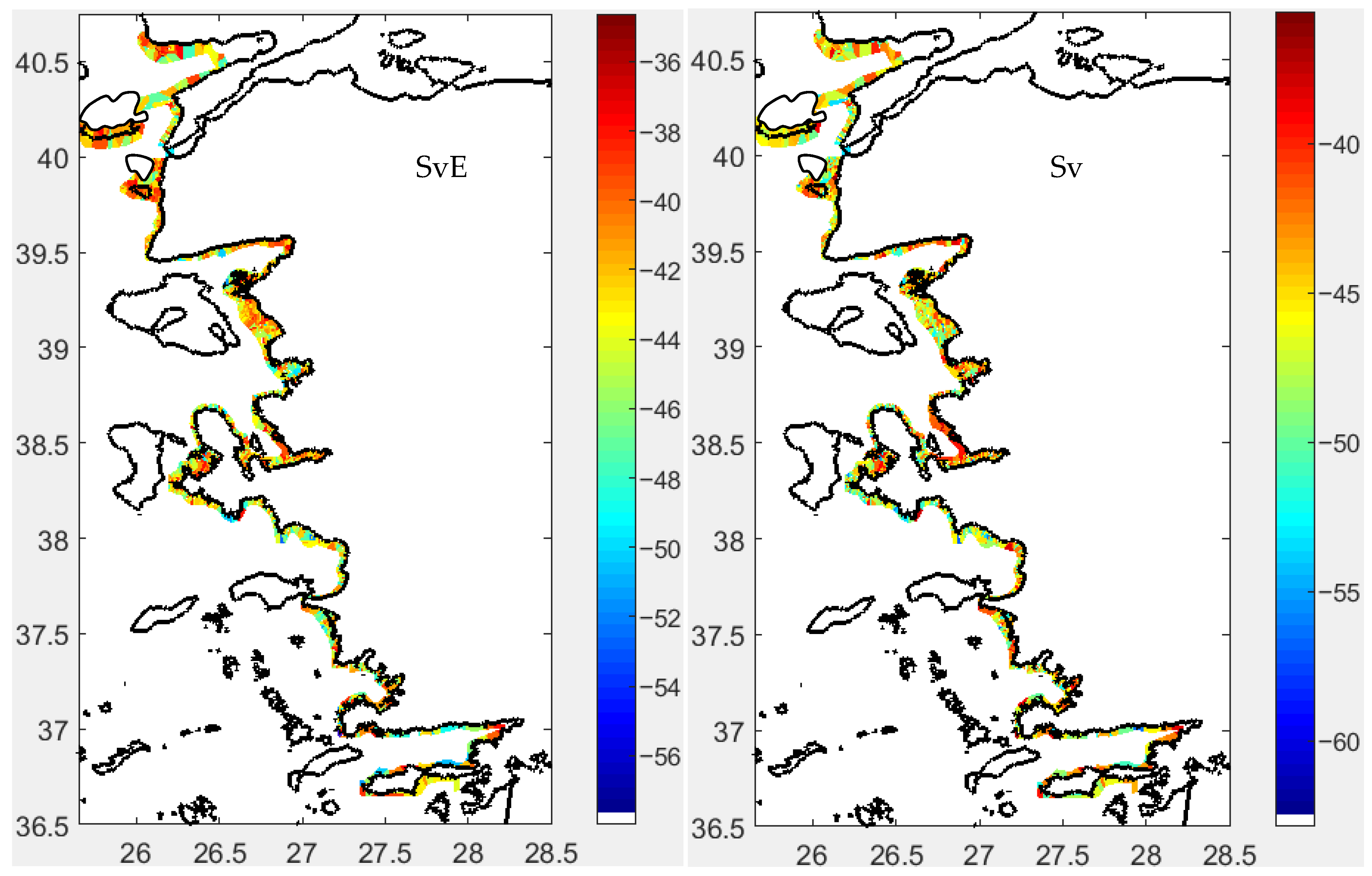
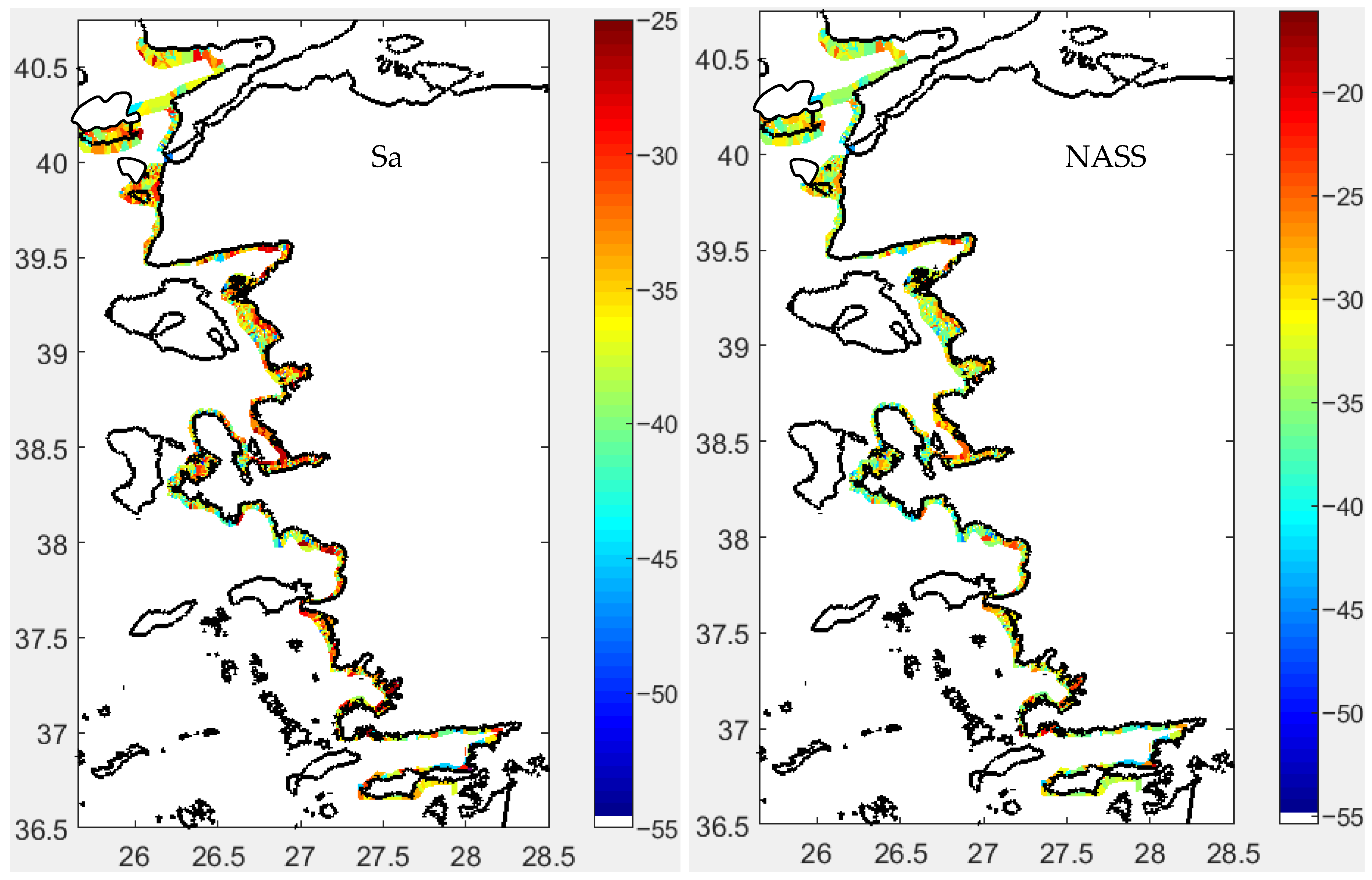
3.2. Fish Schools
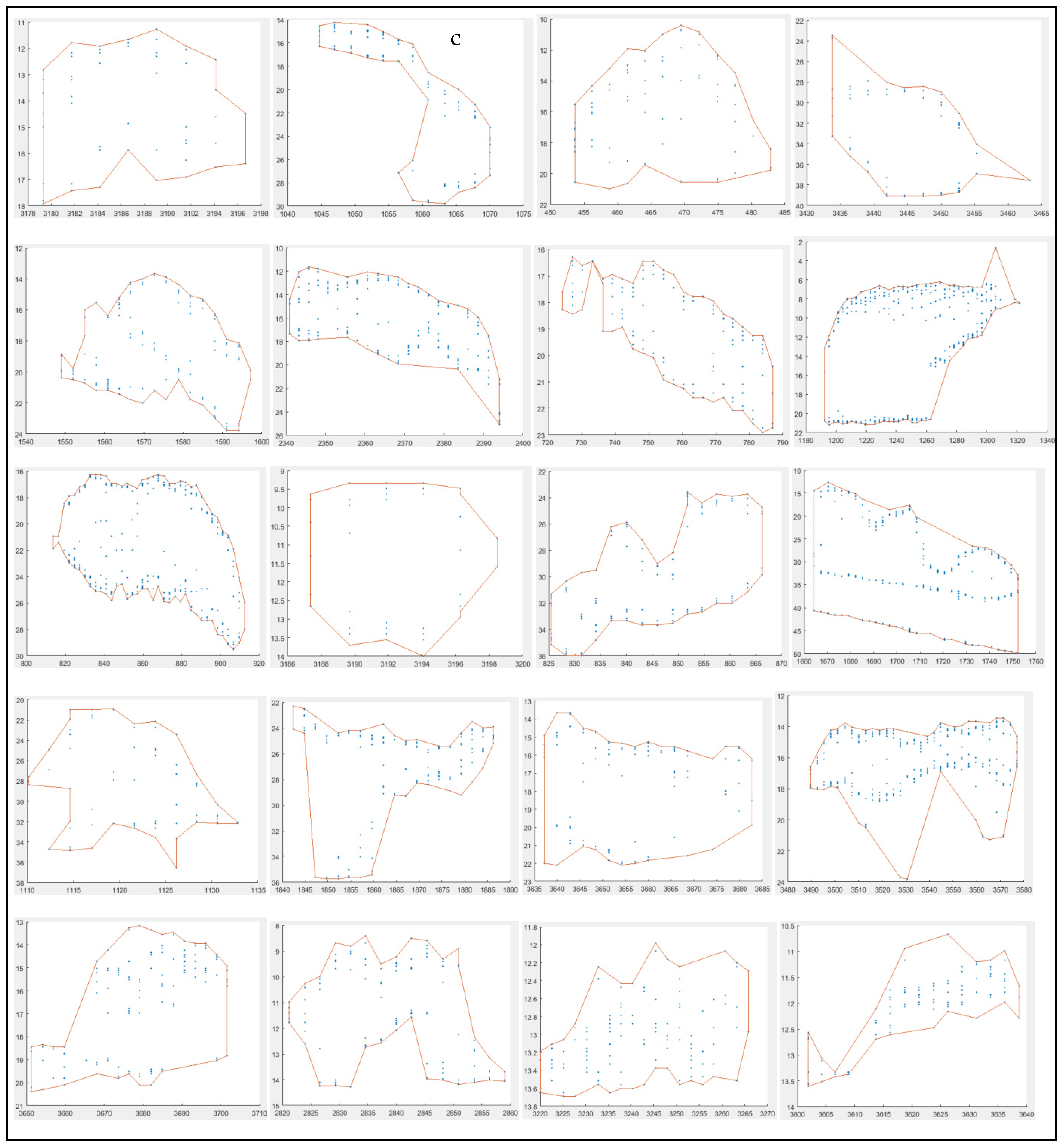
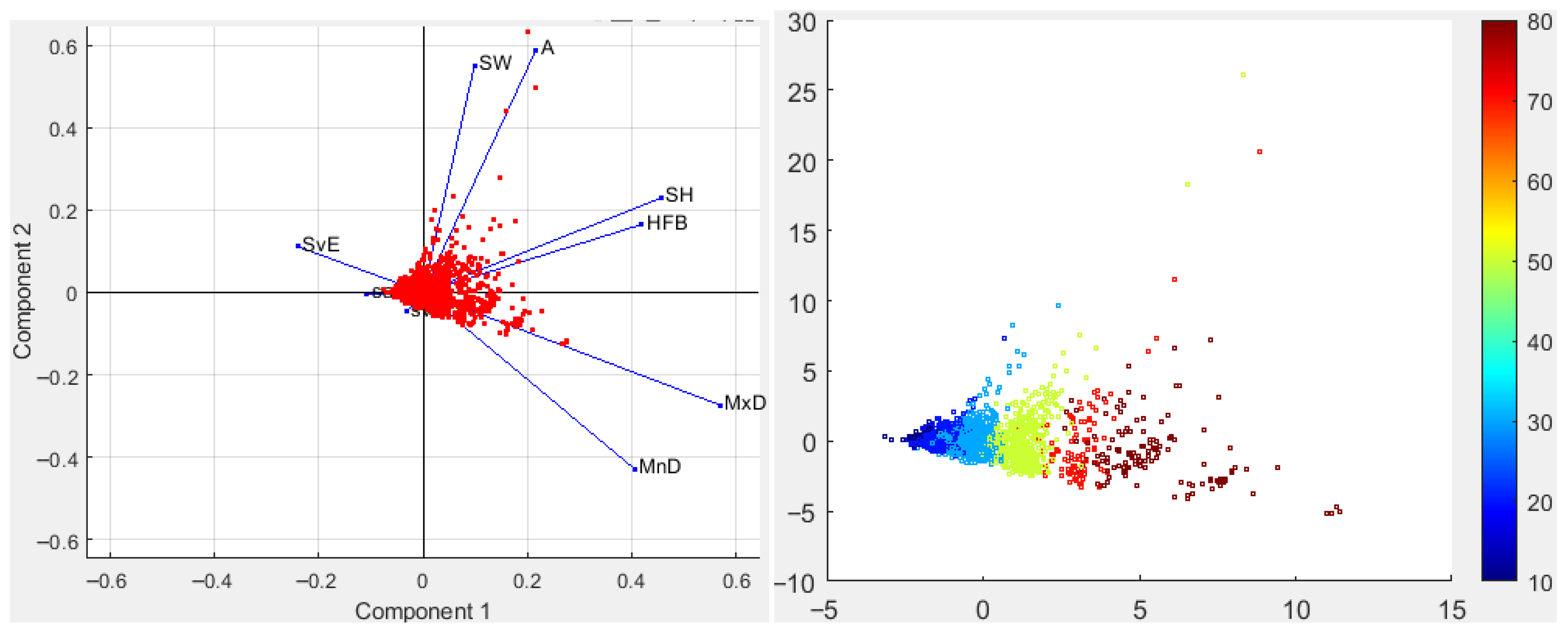
3.2.1. Morphometrical Structure
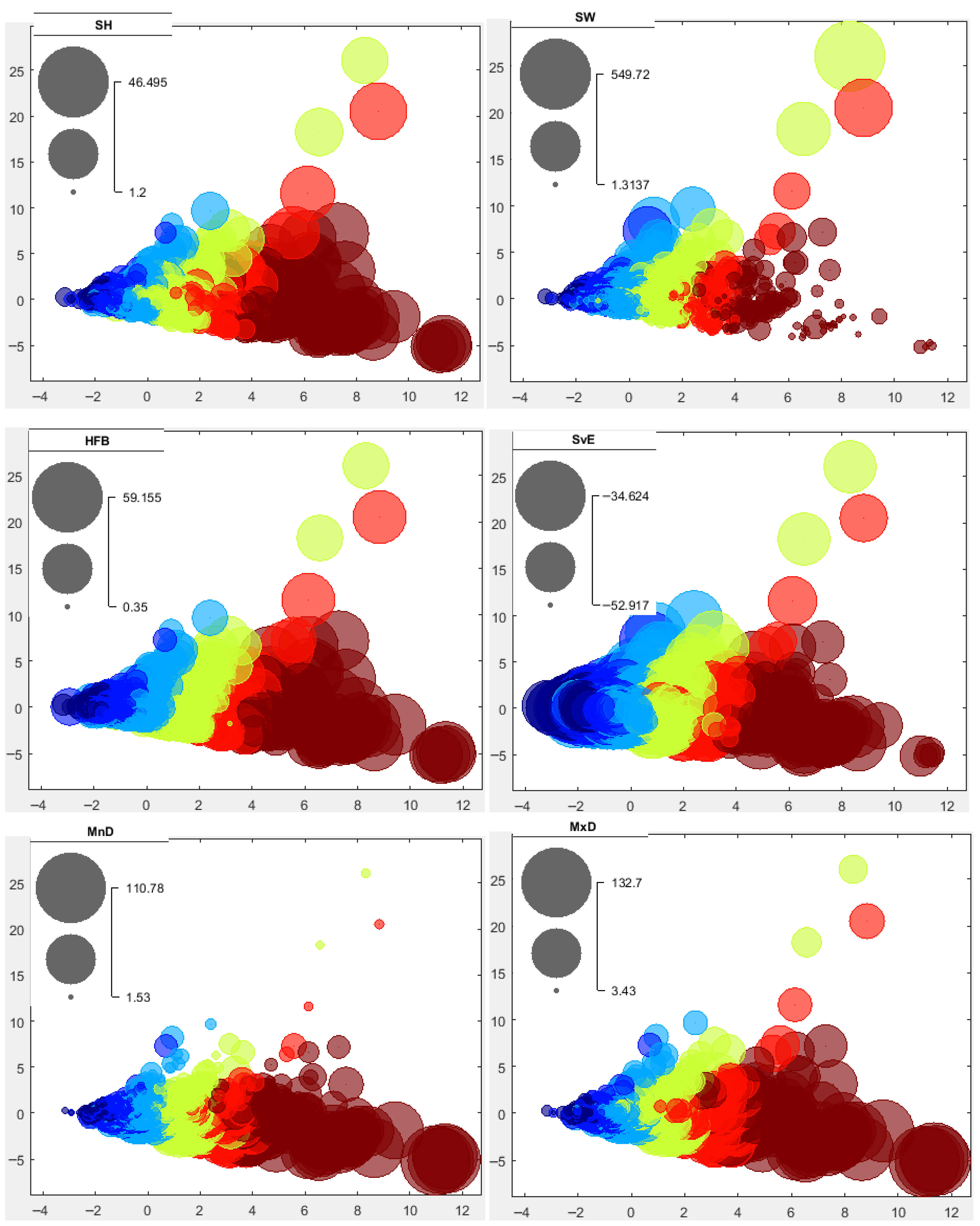
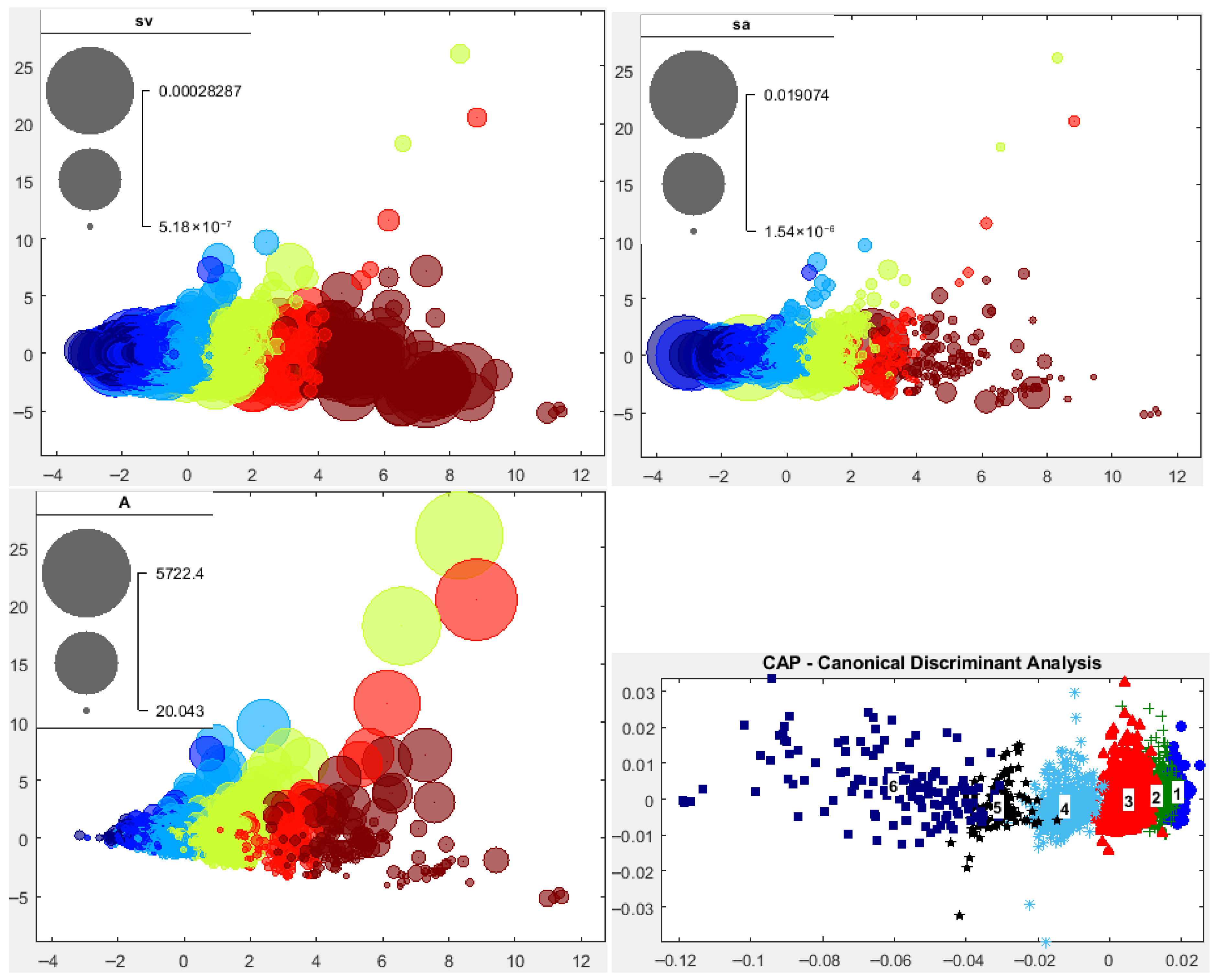
3.2.2. School Morphs
3.2.3. Depth-Related Morphologies
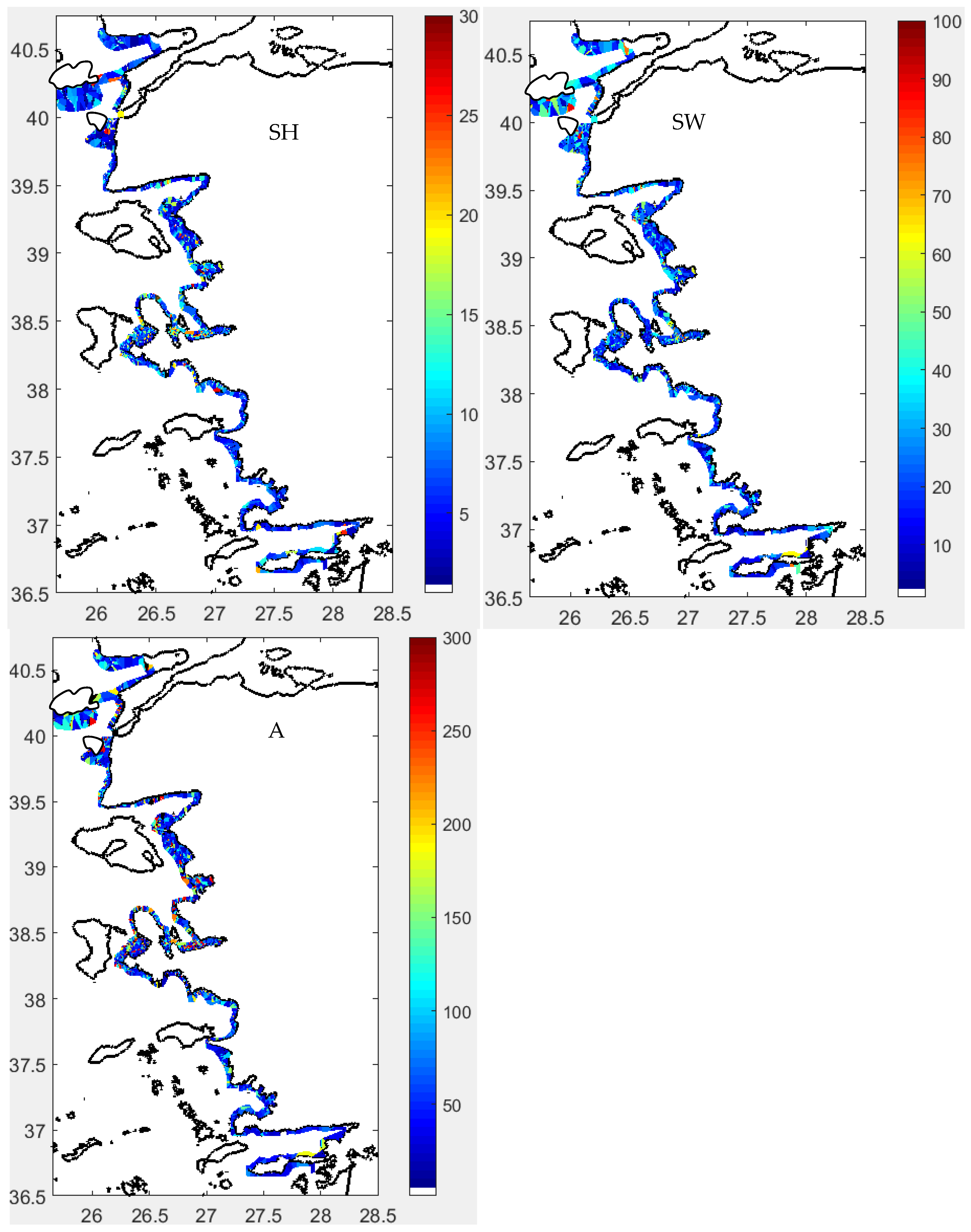
3.3. Spatial Distribution
Acoustical Structure
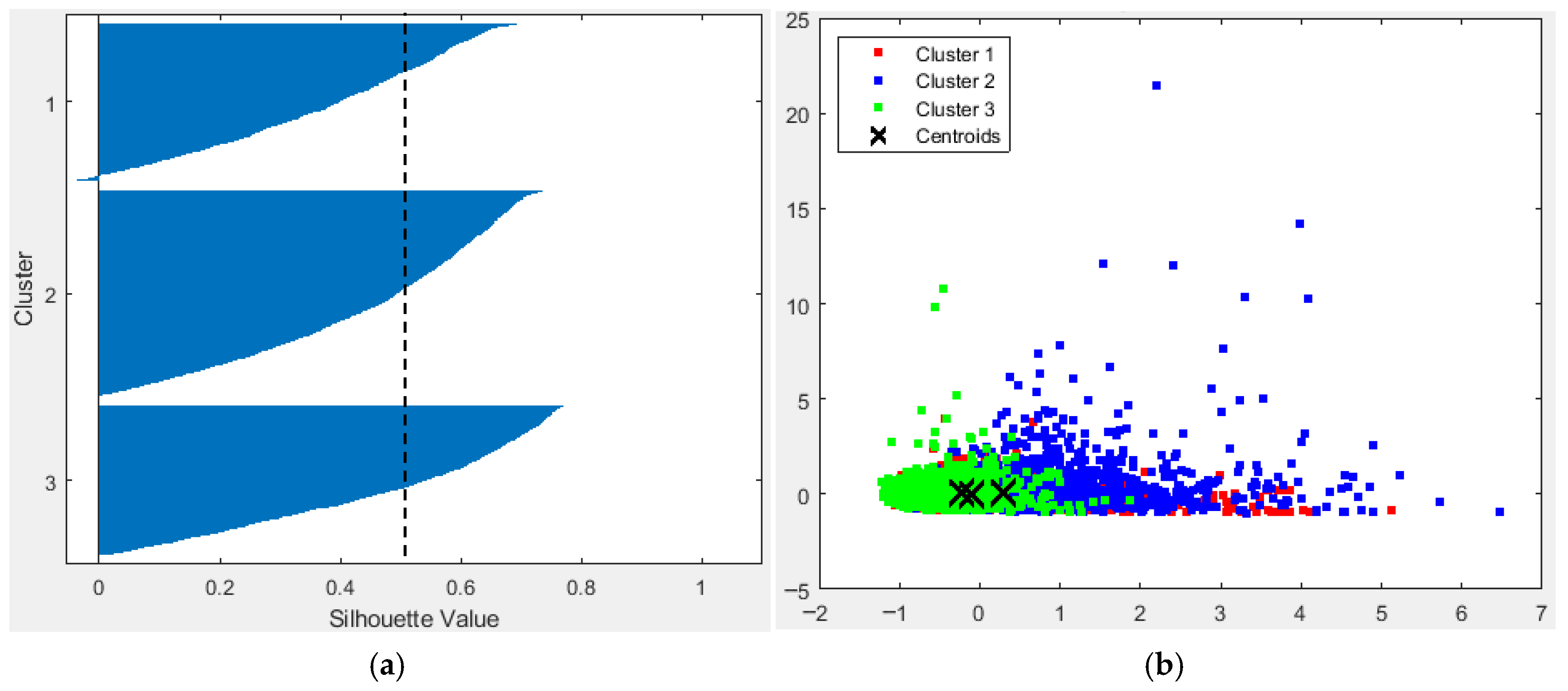
3.4. Statistical Structure
3.4.1. Fish Clusters
3.4.2. Depth-Wise Structure Analysis
| Variable | PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC4 | PC5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SH | 0.457 | 0.230 | −0.092 | −0.416 | −0.138 |
| SW | 0.098 | 0.550 | −0.049 | 0.481 | 0.065 |
| HFB | 0.419 | 0.165 | −0.079 | −0.517 | −0.002 |
| SvE | −0.241 | 0.112 | −0.516 | 0.013 | −0.588 |
| MnD | 0.406 | −0.429 | −0.094 | 0.439 | 0.017 |
| MxD | 0.569 | −0.273 | −0.126 | 0.197 | −0.048 |
| sv | −0.032 | −0.047 | −0.748 | 0.050 | 0.046 |
| sa | −0.108 | −0.003 | −0.363 | −0.140 | 0.785 |
| A | 0.216 | 0.587 | 0.013 | 0.270 | 0.103 |
| Sea Surface | Depth | T | S | pH | TSM | DO | σt | Secchi |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Morphs | ||||||||
| SH | 0.113 | −0.050 | −0.136 | −0.025 | −0.144 | 0.122 | −0.020 | 0.042 |
| SW | 0.078 | −0.047 | −0.406 | 0.190 | −0.401 | 0.329 | −0.314 | 0.042 |
| A | 0.051 | −0.076 | −0.410 | 0.250 | −0.410 | 0.344 | −0.251 | −0.004 |
| Bathymetrics | ||||||||
| HFB | 0.077 | 0.133 | 0.323 | −0.285 | 0.324 | −0.265 | 0.195 | 0.017 |
| MnD | 0.098 | −0.137 | 0.273 | −0.190 | 0.270 | −0.054 | 0.230 | 0.210 |
| MxD | 0.124 | −0.161 | 0.223 | −0.169 | 0.217 | −0.021 | 0.231 | 0.204 |
| Acoustics | ||||||||
| SvE | −0.046 | −0.007 | −0.351 | 0.185 | −0.346 | 0.186 | −0.276 | −0.133 |
| sv | −0.004 | 0.145 | 0.062 | −0.121 | 0.073 | 0.006 | −0.042 | −0.100 |
| sa | −0.155 | 0.067 | 0.204 | −0.073 | 0.211 | −0.142 | 0.145 | −0.166 |
| Near bottom | ||||||||
| Morphs | ||||||||
| SH | −0.059 | −0.062 | −0.010 | −0.047 | 0.053 | 0.053 | ||
| SW | −0.143 | −0.435 | 0.135 | −0.414 | 0.307 | −0.231 | ||
| A | −0.169 | −0.399 | 0.219 | −0.396 | 0.290 | −0.161 | ||
| Bathymetrics | ||||||||
| HFB | 0.150 | 0.364 | −0.170 | 0.356 | −0.224 | 0.196 | ||
| MnD | −0.109 | 0.235 | −0.152 | 0.226 | 0.066 | 0.250 | ||
| MxD | −0.140 | 0.197 | −0.129 | 0.191 | 0.072 | 0.263 | ||
| Acoustics | ||||||||
| SvE | −0.007 | −0.351 | 0.185 | −0.346 | 0.186 | −0.276 | ||
| sv | 0.095 | 0.163 | −0.097 | 0.162 | −0.030 | 0.035 | ||
| sa | 0.157 | 0.328 | −0.046 | 0.313 | −0.208 | 0.114 |
4. Discussion
- Enclosure index—the ratio of the length of the area’s coastline to the length of the boundary line of the study area,
- Mean bottom depth,
- Coefficient of variation (CV) of bottom depth, and
- Subarea size, expressed in nautical miles2.
- (i) Range (as)—the maximum size of fish patches [80],
- (ii) Nugget effect (cop)—derived from omnidirectional variograms on a relative scale (cop/model variance, %),
- (iii) Surface area enclosed by the 100% standardized data variance contour,
- (iv) Anisotropy ratio—the ratio of the major to the minor axis of the best-fitted ellipse around the 100% variance contour,
- (v) Anisotropy direction—the tangent of the anisotropy angle of the major axis of the fitted ellipse, indicating how the maximum spatial structure of fish schools changes with direction,
- (vi) Surface ratio—the ratio of the area enclosed by 60% of the variance contour to that of the 100% contour, which quantifies the heterogeneity of fish school distribution. A low ratio indicates a heterogeneous spatial structure, whereas a high ratio suggests a more homogeneous distribution.
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Woillez, M.; Petitgas, P.; Rivoirard, J.; Fernandes, P.; ter Hoftstede, R.; Korsbrekke, K.; Orlowski, A.; Spedicato, M.-T.; Politou, C.Y. Relationships Between Population Spatial Occupation and Population Dynamics. In Proceedings of the ICES Annual Science Conference, Maastricht, The Netherlands, 19 September 2006; CM 2006/O:05, 24376. pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Katara, I.; Pierce, G.J.; Illian, J.; Scott, B.E. Environmental drivers of the anchovy/sardine complex in the Eastern Mediterranean. Hydrobiologia 2011, 670, 49–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valavanis, V.D. Essential Fish Habitat Mapping in the Mediterranean. Hydrobiologia 2008, 612, 300. [Google Scholar]
- Leonori, I.; Tičina, V.; Giannoulaki, M.; Hattab, T.; Iglesias, M.; Bonanno, A.; Costantini, I.; Canduci, G.; Machias, A.; Ventero, A.; et al. History of hydroacoustic surveys of small pelagic fish species in the European Mediterranean Sea. Medit. Mar. Sci. 2021, 22, 751–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petitgas, P.; Reid, D.; Carrera, P.; Iglesias, M.; Georgakarakos, S.; Liorzou, B.; Massé, J. On the relation between schools, clusters of schools, and abundance in pelagic fish stocks. ICES J. Mar. Res. 2001, 58, 1150–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICES. Report of the Working Group on Acoustic and Egg Surveys for Sardine and Anchovy in ICES Areas 7, 8, and 9. In Wgacegg Report 2016 Capo; International Council for the Exploration of the Sea: Sicily, Granitola, Italy, 2016; ICES CM 2016/SSGIEOM:31; 326p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machias, A.; Tsimenides, N. Anatomical and physiological factors affecting the swim-bladder cross-section of the sardine Sardina pilchardus. Canadian J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1996, 53, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsagarakis, K.; Pyrounaki, M.M.; Giannoulaki, M.; Somarakis, S.; Machias, A. Ontogenetic shift in the schooling behaviour of sardines, Sardina pilchardus. Anim. Behav. 2012, 84, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacCall, A. Dynamic Geography of Marine Fish Populations; University of Washington Press: Seattle, WA, USA, 1990; 153p. [Google Scholar]
- Calò, A.; Félix-Hackradt, F.C.; Garcia, J.; Hackradt, C.W.; Rocklin, D.; Otón, C.T.; Charton, J.A.G. A review of methods to assess connectivity and dispersal between fish populations in the Mediterranean Sea. Adv. Oceanogr. Limnol. 2013, 4, 150–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Relini, G. Fishery and Aquaculture Relationship in the Mediterranean: Present and Future. Medit. Mar. Sci. 2003, 4, 125–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheaves, M. Consequences of ecological connectivity: The coastal ecosystem mosaic. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2009, 391, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiadis, M.; Mavraki, N.; Koutsikopoulos, C.; Tzanatos, E. Spatio-temporal dynamics and management implications of the nightly appearance of Boops boops (Acanthopterygii, Perciformes) juvenile shoals in the anthropogenically modified Mediterranean littoral zone. Hydrobiologia 2014, 734, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barra, M.; Bonanno, A.; Hattab, T.; Saraux, C.; Iglesias, M.; Leonori, I.; Tičina, V.; Basilone, G.; De Felice, A.; Ferreri, R.; et al. Effects of sampling intensity and biomass levels on the precision of acoustic surveys in the Mediterranean Sea. Medit. Mar. Sci. 2021, 22, 769–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldé, B.S.; Brehmer, P.; Faye, S.; Diop, P. Population Structure, Age and Growth of Sardine (Sardina pilchardus, Walbaum, 1792) in an Upwelling Environment. Fishes 2022, 7, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paramo, J.; Roa, R. Acoustic-geostatistical assessment and habitat-abundance relations of small pelagic fish from the Colombian Caribbean. Fish. Res. 2003, 60, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Seo, Y.I.; Oh, T.Y.; Lee, K.; Zhang, H.; Kang, M. 2016. Anchovy Distributional Properties by Time and Location: Using Acoustic Data from A Primary Trawl Survey in The South Sea of South Korea. J. Mar. Sci. Technol. 2016, 24, 864–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Report of the FAO Working Group on the Assessment of Small Pelagic Fish off Northwest Africa. Banjul, The Gambia, 26 June–1 July 2018. FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Report, No. R1247; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2019; p. 321. [Google Scholar]
- Tiedemann, M.; Ndour, I.; Sow, F.N.; Bagøien, E.; Krakstad, J.-O.; Ostrowski, M.; Stenevik, E.K.; Ensrud, T.; Isari, S. Asynchronized spawning responses of small pelagic fishes to a short-term environmental change. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2022, 696, 85–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingel, F.; Mutlu, E.; Gücü, A.C. Shifts in fish ecosystem in the Turkish Seas as inferred statistically. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Oceanography of the Eastern Mediterranean and Black Sea: Similarities and Differences of Two Interconnected Basins, Ankara, Turkey, 14–18 October 2002; pp. 903–909. [Google Scholar]
- Brehmer, P.; Gerlotto, F.; Samb, B. Measuring fish avoidance during surveys. In Proceedings of the ICES CM 2000: Annual Science Conference, Copenhagen, Denmark, 15–17 June 2000. ICES CM 2000/K. [Google Scholar]
- Muinoz, R.; Carrera, P.; Petitgas, P.; Beare, D.J.; Georgakarakos, S.; Haralambous, J.; Iglesias, M.; Liorzou, B.; Masse, J.; Reid, D.G. Consistency in the correlation of school parameters across years and stocks. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2003, 60, 164–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soria, M.; Bahri, T.; Gerlotto, F. Effect of externalfactors (environment and survey vessel) on fish school characteristics observed by echosounder and multibeamsonar in the Mediterranean Sea. Aquat. Living. Resour. 2003, 16, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmonds, E.J.; MacLennan, D.N. Fisheries Acoustics: Theory and Practice; Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Ben, A.L.; Barra, M.; Gaamour, A.; Khemiri, S.; Genovese, S.; Mifsud, R.; Basilone, G.; Fontana, I.; Giacalone, G.; Aronica, S.; et al. Small pelagic fish assemblages in relation to environmental regimes in the Central Mediterranean. Hydrobiologia 2018, 821, 113–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, C.A.; Caserta, V.; Salzeri, P.; Bonanno-Ferraro, G.; Pecoraro, F.; Lucchetti, A.; Boitani, L.; Blasi, M.F. Acoustic deterrent devices as mitigation tool to prevent dolphin-fishery interactions in the Aeolian Archipelago (Southern Tyrrhenian Sea, Italy). Medit. Mar. Sci. 2021, 22, 408–421. [Google Scholar]
- Coetzee, J. Use of a shoal analysis and patch estimation system (SHAPES) to characterise sardine schools. Aquat. Living. Resour. 2000, 13, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenkel, V.M.; Ressler, P.H.; Jech, M.; Giannoulaki, M.; Taylor, C. Underwater acoustics for ecosystem-based management: State of the science and proposals for ecosystem indicators. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2011, 442, 285–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerckhove, D.T.de.; Shuter, B.J. Predation on schooling fish is shaped by encounters between prey during school formation using an Ideal Gas Model of animal movement. Ecol. Model. 2022, 470, 110008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Castaneda, J.C.; Ventero, A.; García-M´arquez, M.G.; Iglesias, M. Spatial and temporal analysis (2009–2020) of the biological parameters, abundance and distribution of Trachurus mediterraneus (Steindachner, 1868) in the Western Mediterranean. Fish. Res. 2022, 256, 106483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corgnati, L.P.; Mantovani, C.; Griff, A.; Berta, M.; Penna, P.; Celentano, P.; Bellomo, L.; Carlson, D.F.; D’Adamo, R. Implementation and Validation of the ISMAR High-Frequency Coastal Radar Network in the Gulf of Manfredonia (Mediterranean Sea). IEEE J. Ocean Engineer. 2019, 44, 424–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brehmer, P.; Gorka, S.; Trygonis, V.; Itano, D.; Dalen, J.; Fuchs, A.; Faraj, A.; Taquet, M. Towards an Autonomous Pelagic Observatory: Experiences from Monitoring Fish Communities around Drifting FADs. Thalassas 2019, 35, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basilone, G.; Ganias, K.; Ferreri, R.; D’Elia, M.; Quinci, E.M.; Mazzola, S.; Bonanno, A. Application of GAMs and multinomial models to assess the spawning pattern of fishes with daily spawning synchronicity: A case study inthe European anchovy (Engraulis encrasicolus) in the central Mediterranean Sea. Fish. Res. 2015, 167, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palermino, A.; De Felice, A.; Canduci, G.; Biagiotti, I.; Costantini, I.; Malavolti, S.; Leonori, I. First target strength measurement of Trachurus mediterraneus and Scomber colias in the Mediterranean Sea. Fish. Res. 2021, 240, 105973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brehmer, P.; Lafont, T.; Georgakarakos, S.; Josse, E.; Gerlotto, F.; Collet, C. Omnidirectional multibeam sonar monitoring: Applications in fisheries science. Fish Fisher. 2006, 7, 165–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brehmer, P.; Georgakarakos, S.; Josse, E.; Trygonis, V.; Dalen, J. Adaptation of fisheries sonar for monitoring schools of large pelagic fish: Dependence of schooling behaviour on fish finding efficiency. Aquat. Living. Resour. 2007, 20, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trygonis, V.; Georgakarakos, S.; Simmonds, E.J. An operational system for automatic school identification on multibeam sonar echoes. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2009, 66, 935–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackinson, S.; Nøttestad, L.; Guénette, S.; Pitcher, T.J.; Misund, O.A.; Fernö, A. Cross-scale observations on distribution and behavioural dynamics of ocean feeding Norwegian spring spawning herring (Clupea harengus L.). ICES J. Mar. Sci. 1999, 56, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brehmer, P.; Gerlotto, F.; Rouault, A. In situ interstandardisation of acoustic data: An integrated database for fish school behavioural studies. Acta Acoust. 2002, 88, 730–734. [Google Scholar]
- Mutlu, E. Acoustical identification of the concentration layer of a copepod species, Calanus euxinus. Mar. Biol. 2003, 142, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutlu, E. A comparison of the contribution of zooplankton and nekton taxa to the near-surface acoustic structure of three Turkish seas. Mar. Ecol. 2005, 26, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutlu, E. Diel vertical migration of Sagitta setosa as inferred acoustically in the Black Sea. Mar. Biol. 2006, 149, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brehmer, P.; Gerlotto, F.; Laurent, C.; Cotel, P.; Achury, A.; Sam, B. Schooling behaviour of small pelagic fish: Phenotypic expression of independent stimuli. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2007, 334, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SIMFAMI. Species Identification Methods from Acoustic Multi-frequency Information 1st Annual Progress Report; The European Commission’s Fifth Framework Programme (SIMFAMI project; Grant No. Q5RS-2001-02054): Aberdeen, UK, 2002; pp. 1–61. [Google Scholar]
- Zwolinski, J.; Mason, E.; Oliveira, P.B.; Stratoudakis, Y. Fine-scale distribution of sardine (Sardina pilchardus) eggs and adults during a spawning event. J. Sea Res. 2006, 56, 294–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, S.; Lowerre-Barbieri, S.; Bickford, J.; Mann, D. Using a passive acoustic survey to identify spotted sea trout spawning sites and associated habitat in Tampa Bay, Florida. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2009, 138, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowerre-Barbieri, S.K.; Walters, S.; Bickford, J.; Cooper, W.; Muller, R. Site fidelity and reproductive timing at a spotted sea trout spawning aggregation site: Individual versus population scale behavior. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2013, 481, 181–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, D.; Simmonds, E. Image analysis techniques for the study of fish school structure from acoustic survey data. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1993, 50, 1264–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, D.; Scalabrin, C.; Petitgas, P.; Masse, J.; Aukland, R.; Carrera, P.; Georgakarakos, S. Standard protocols for the analysis of school based data from echosounder surveys. Fish. Res. 2000, 47, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsagarakis, K.; Giannoulaki, M.; Pyrounaki, M.M.; Machias, A. Species identification of small pelagic fish schools by means of hydroacoustics in the Eastern Mediterranean Sea. Medit. Mar. Sci. 2015, 16, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpentieri, P.; Bonanno, A.; Scarcella, G. Technical guidelines for scientific surveys in the Mediterranean and the Black Sea. In FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Technical Papers; no 641; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutlu, E. A package of script codes, POSIBIOM, for vegetation acoustics: POSIdonia BIOMass. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannoulaki, M.; Machias, A.; Somarakis, S.; Tsimenides, N. The spatial distribution of anchovy and sardine in the northern Aegean Sea in relation to hydrographic regimes. Belg. J. Zool. 2005, 135, 151–156. [Google Scholar]
- Dereli, H.; Ünal, V.; Ulman, A.; Gıovos, I.; Tosunoğlu, Z.; Prodromıtıs, G.; Moutopoulos, D.K. Towards Cross-Border Fisheries Management: An Analysis of Fleet Structures and Species-Specific Regulatory Measures in the Aegean Sea. Medit. Mar. Sci. 2024, 25, 418–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TUİK. Türkiye İstatistik Kurumu. Available online: https://data.tuik.gov.tr/Bulten/Index?p=Su-Urunleri-2023-53702 (accessed on 2 June 2025).
- Stergiou, K.I.; Papaconstantinou, C.; Jeanthous, M.K.; Fourtouni, A. The relative abundance and distribution of small pelagic fishes in the Aegean Sea. Fresenius. Envir. Bull. 1993, 2, 357–362. [Google Scholar]
- Somarakis, S.; Machias, A.; Giannoulaki, M.; Siapatis, A.; Torre, M.; Anastasopoulou, K.; Vassilopoulou, V.; Kalianiotis, A.; Papaconstantinou, C. Ichthyoplanktonic and Acoustic Biomass Estimates of Anchovy in the Aegean Sea (June 2003 and June 2004); General Fisheries Commission for the Mediterranean, GFCM, Technical Report; FAO: Rome, Italy, 26–30 September 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Somarakis, S.; Schismenou, E.; Siapatis, A.; Giannoulaki, M.; Kallianiotis, A.; Machias, A. High variability in the Daily Egg Production Method parameters of an eastern Mediterranean anchovy stock: Influence of environmental factors, fish condition and population density. Fish. Res. 2012, 117–118, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Politikos, D.; Somarakis, S.; Tsiaras, K.P.; Giannoulaki, M.; Petihakis, G.; Machias, A.; Triantafyllou, G. Simulating anchovy’s full life cycle in the northern Aegean Sea (eastern Mediterranean): A coupled hydro-biogeochemical–IBM model. Prog. Oceanogr. 2015, 138, 399–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannoulaki, M.; Machias, A.; Koutsikopoulos, C.; Somarakis, S. The effect of coastal topography on the spatial structure of anchovy and sardine. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2006, 63, 650–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, R.H. Dorsal-aspect target strength of an individual fish. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1971, 49, 816–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutlu, E. Ecological gradients of epimegafaunal distribution along the sectors of Gulf of İzmir, Aegean Sea. COMU J. Mar. Sci. Fish. 2021, 4, 130–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutlu, E.; Bingel, F.; Gücü, A.C.; Tuğrul, S.; Beşiktepe, Ş.T. Selection of Marine Fish Culture Sites that Will not Influence the Environmental Quality of the Bays Along the Coast of of Muğla; Project no: YDABAG-102Y058, Final report; TUBITAK: Ankara, Turkey, 2005; p. 157. (In Turkish) [Google Scholar]
- Palialexis, A.; Georgakarakos, S.; Karakassis, I.; Lika, K.; Valavanis, V.D. Prediction of marine species distribution from presence–absence acoustic data: Comparing the fitting efficiency and the predictive capacity of conventional and novel distribution models. Hydrobiologia 2011, 670, 241–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutlu, E.; Akçalı, B.; Özvarol, Y.; Narlı, Z.; Aslan, B.E.; Zabun, Z. Recent plant traits of Caulerpa taxifolia var. distichophylla in the Turkish Aegean Sea. Aquatic Sci. Engin. 2025, 40, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trygonis, V.; Kapelonis, Z. Corrections of fish school area and mean volume backscattering strength by simulation of an omnidirectional multi-beam sonar. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2018, 75, 1496–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonanno, A.; Giannoulaki, M.; Barra, M.; Basilone, G.; Machias, A.; Genovese, S.; Goncharov, S.; Popov, S.; Rumolo, P.; Di Bitetto, M.; et al. Habitat Selection Response of Small Pelagic Fish in Different Environments. Two Examples from the Oligotrophic Mediterranean Sea. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannoulaki, M.; Machias, A.; Tsimenides, N. Ambient luminance and vertical migration of the sardine Sardina pilchardus. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1999, 178, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwolinski, J.P.; Oliveira, P.B.; Quintino, V.; Stratoudakis, Y. Sardine potential habitat and environmental forcing off western Portugal. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2010, 67, 1553–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beare, D.J.; Reid, D.G.; Petitgas, P.; Carrera, P.; Georgakarakos, S.; Haralambous, J.; Iglesias, M.; Liorzou, B.; Masse, J.; Muino, R. Spatio-Temporal Patterns in Pelagic Fish School Abundance and Size: A Study of Pelagic Fsh Aggregation Using Acoustic Surveys from Senegal to Shetland; CM 2000/K:03; Incorporation of External Factors in Marine Resource Surveys; International Council for the Exploration of the Sea: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Tsagarakis, K.; Giannoulaki, M.; Somarakis, S.; Machias, M. Variability in positional, energetic and morphometric descriptors of European anchovy Engraulis encrasicolus schools related to patterns of diurnal vertical migration. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2012, 446, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Elia, M.; Bernardo, P.; Sulli, A.; Tranchida, G.; Bonanno, A.; Basilone, S.; Giacalone, G.; Fontana, I.; Genovese, S.; Guisande, C.; et al. Distribution and spatial structure of pelagic fish schools in relation to the nature of the seabed in the Sicily Straits (Central Mediterranean). Mar. Ecol. 2009, 30 (Suppl. 1), 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannoulaki, M.; Pyrounaki, M.M.; Liorzou, B.; Leonori, I.; Valavanis, V.D.; Tsagarakis, K.; Bigot, J.L.; Roos, D.; De Felice, A.; Campanella, F.; et al. Habitat suitability modelling for sardine juveniles (Sardina pilchardus) in the Mediterranean Sea. Fish. Oceanogr. 2011, 20, 367–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannoulaki, M.; Iglesias, M.; Tugores, M.P.; Bonanno, A.; Patti, B.; De Felice, A.; Leonori, L.; Bigot, J.L.; Tic Ina, V.; Pyrounaki, M.M.; et al. Characterizing the potential habitat of European anchovy Engraulis encrasicolus in the Mediterranean Sea, at different life stages. Fish. Oceanogr. 2013, 22, 69–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barra, M.; Petitgas, P.; Bonanno, A.; Somarakis, S.; Woillez, M.; Machias, A.; Mazzola, S.; Basilone, G.; Giannoulaki, M. Interannual Changes in Biomass Affect the Spatial Aggregations of Anchovy and Sardine as Evidenced by Geostatistical and Spatial Indicators. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somarakis, S.; Ganias, K.; Siapatis, A.; Koutsikopoulos, C.; Machias, A.; Papaconstantinou, C. Spawning habitat and daily egg production of sardine (Sardina pilchardus) in the eastern Mediterranean. Fish. Oceanogr. 2006, 15, 4, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannoulaki, M.; Pyrounaki, M.M.; Bourdeix, J.-H.; Ben Abdallah, L.; Bonanno, A.; Basilone, G.; Iglesias, M.; Ventero, A.; De Felice, A.; Leonori, I.; et al. Habitat Suitability Modeling to Identify the Potential Nursery Grounds of the Atlantic Mackerel and Its Relation to Oceanographic Conditions in the Mediterranean Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beare, D.J.; Burns, F.; Greig, A.; Jones, E.G.; Peach, K.; Kienzle, M.; McKenzie, E.; Reid, D.G. Long-term increases in prevalence of North Sea fishes having southern biogeographic affinities. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2004, 284, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palermino, A.; De Felice, A.; Canduci, G.; Biagiotti, I.; Costantini, I.; Centurelli, M.; Leonori, I. Application of an analytical approach to characterize the target strength of ancillary pelagic fish species. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 15182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyrounaki, Μ.M.; Machias, A.; Giannoulaki, Μ. Target Strength Equations for anchovy (Engraulis encrasicolus) and sardine (Sardina pilchardus) from Acoustic Surveys in Aegean Sea. Available online: http://62.217.127.53/xmlui/handle/123456789/1256?locale-attribute=en (accessed on 9 June 2025).


| Echosounder Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer and model | BioSonics (Seattle, WA,USA) and DT-X |
| Acoustic frequency | 206 kHz |
| Transducer type and shape | Split and circle |
| Source level | 220.4 dB re µPa at 1 m |
| Receive sensitivity, narrow-beam | −51.0 dB re counts per µPa |
| Receive sensitivity, wide-beam | −56.0 dB re counts per µPa |
| Beam width | 6.8 × 6.8° |
| System noise floor | −140 dB |
| Echosounder settings | |
| Transducer draft | 2.5 m from the surface water |
| Ping rate | 5 pings s−1 |
| Sound speed * | calculated by Visual Acquisition |
| Absorption coefficient * | calculated by Visual Acquisition |
| Data collection threshold | −140 dB |
| Pulse width | 0.1 ms |
| Maximum depth | 70 (200 in cases) m |
| Cls | SH | SW | HFB | SvE | MnD | MxD | sv | sa | A |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.2983 | 0.0604 | 0.3284 | −0.0707 | −0.28 | −0.1207 | −0.2421 | −0.1077 | 0.1341 |
| 2 | −0.2172 | 0.0362 | −0.2457 | 0.4633 | −0.0938 | −0.2165 | 0.2097 | 0.1214 | −0.0574 |
| 3 | −0.0966 | −0.0825 | −0.1006 | −0.3242 | 0.4735 | 0.3482 | −0.114 | −0.0404 | −0.0636 |
| Variable | PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC4 | PC5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SH | 0.489 | −0.106 | −0.116 | −0.404 | 0.117 |
| SW | 0.279 | −0.473 | −0.051 | 0.490 | −0.076 |
| HFB | 0.416 | −0.071 | −0.123 | −0.554 | 0.052 |
| SvE | −0.252 | −0.250 | −0.431 | 0.012 | 0.574 |
| MnD | 0.244 | 0.547 | −0.167 | 0.387 | 0.011 |
| MxD | 0.441 | 0.434 | −0.201 | 0.156 | 0.063 |
| sv | −0.115 | 0.003 | −0.712 | 0.075 | 0.115 |
| sa | −0.149 | −0.045 | −0.456 | −0.152 | −0.785 |
| A | 0.397 | −0.455 | −0.016 | 0.295 | −0.120 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mutlu, E. A Broad-Scale Summer Spatial Structure of Pelagic Fish Schools as Acoustically Assessed Along the Turkish Aegean Coast. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 1807. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13091807
Mutlu E. A Broad-Scale Summer Spatial Structure of Pelagic Fish Schools as Acoustically Assessed Along the Turkish Aegean Coast. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(9):1807. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13091807
Chicago/Turabian StyleMutlu, Erhan. 2025. "A Broad-Scale Summer Spatial Structure of Pelagic Fish Schools as Acoustically Assessed Along the Turkish Aegean Coast" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 9: 1807. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13091807
APA StyleMutlu, E. (2025). A Broad-Scale Summer Spatial Structure of Pelagic Fish Schools as Acoustically Assessed Along the Turkish Aegean Coast. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(9), 1807. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13091807







