Morphodynamic of Tidal Flat Profiles in an Erosion-to-Accretion Transitional Coastal Segment Under Wave–Current Interaction: A Case Study of Dafeng Port, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
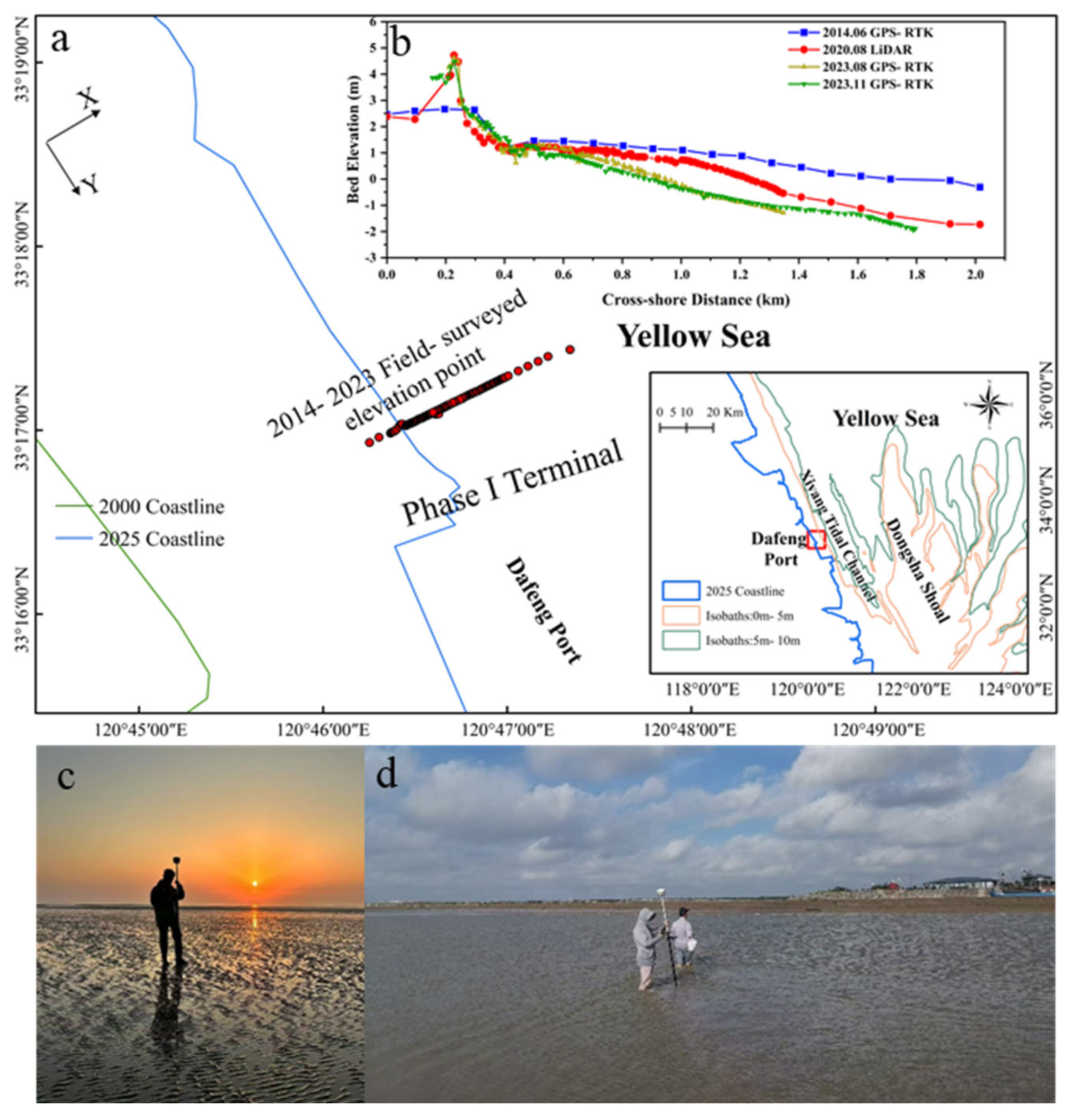
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Model Description and Configuration
2.3. Model Setup and Wave Conditions
2.3.1. Model Domain and Grid Configuration
2.3.2. Model Parameters and Boundary Forcing
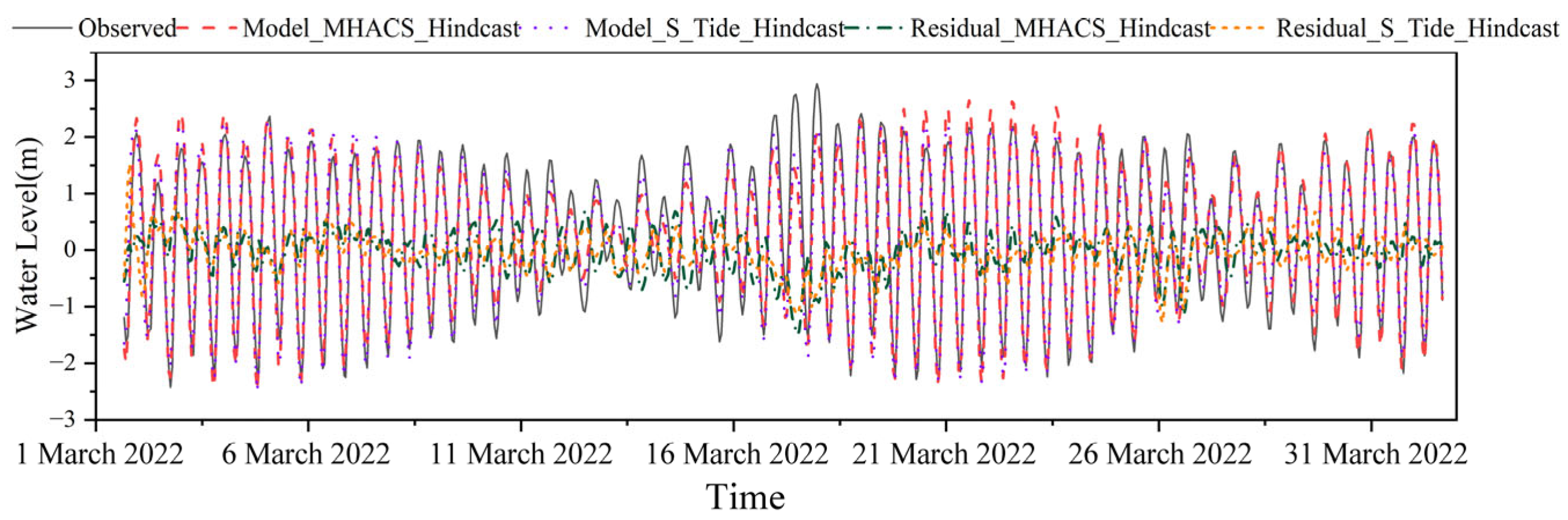
2.3.3. Evaluation Metric
3. Results
3.1. Topographic Validation
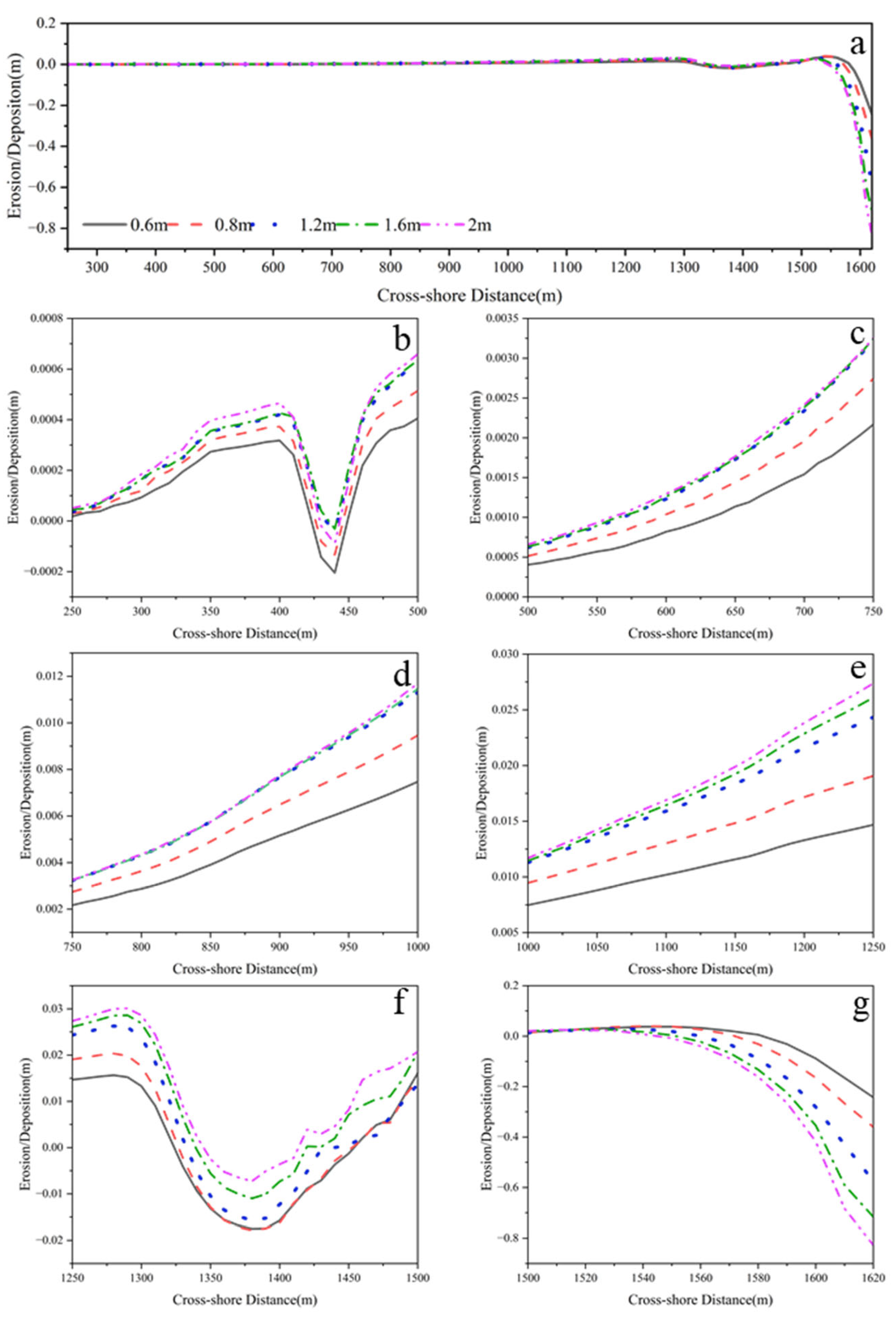
3.2. Influence of Significant Wave Height on Profile Erosion and Deposition
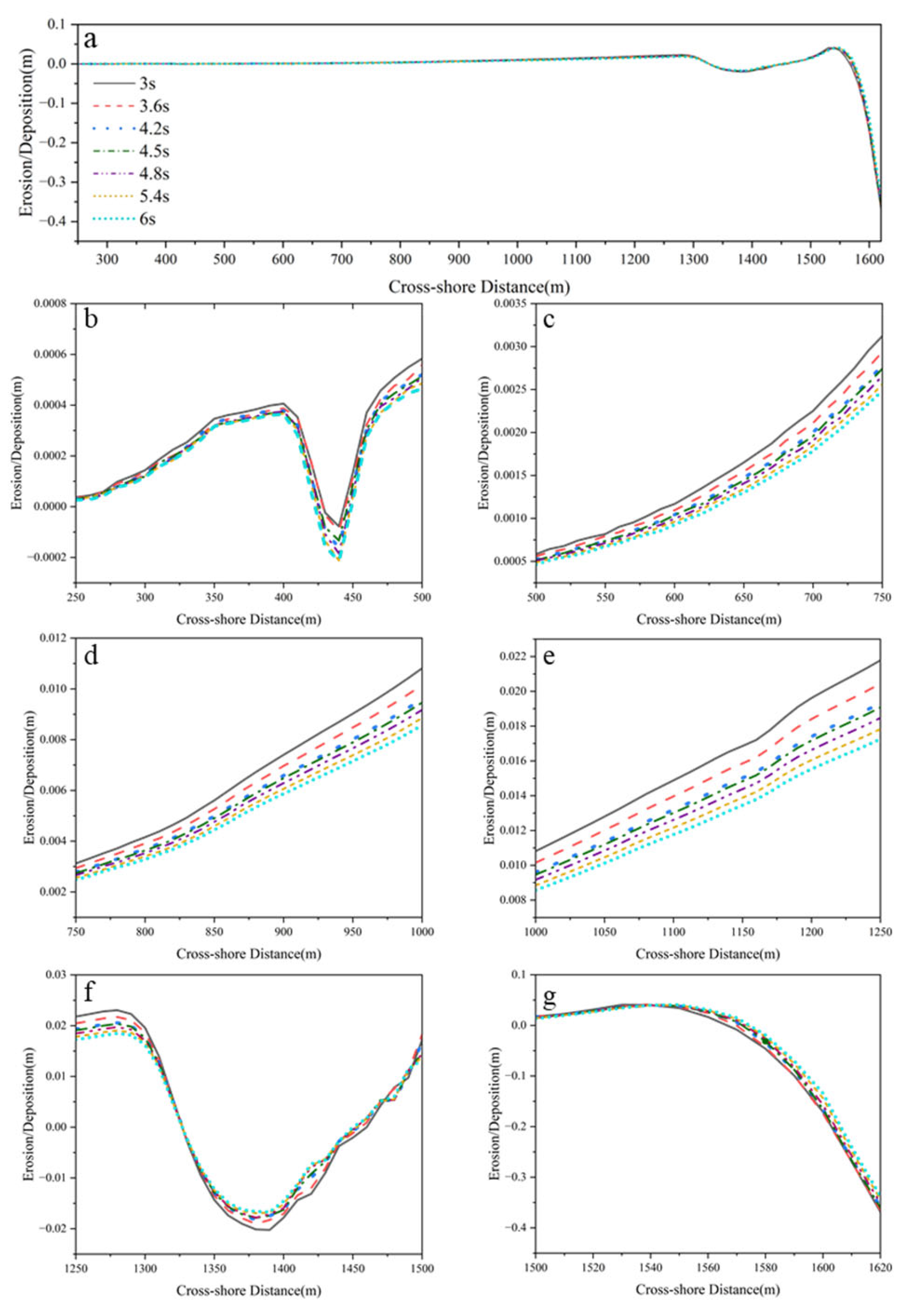
3.3. Influence of Peak Wave Period on Profile Erosion and Deposition
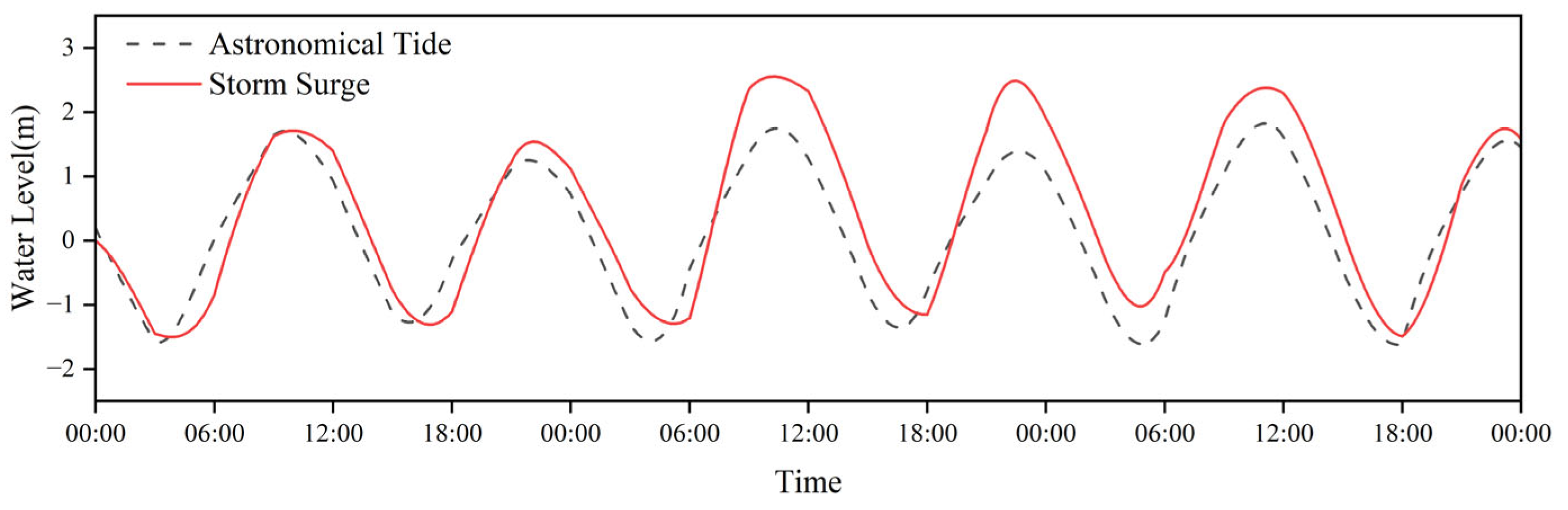
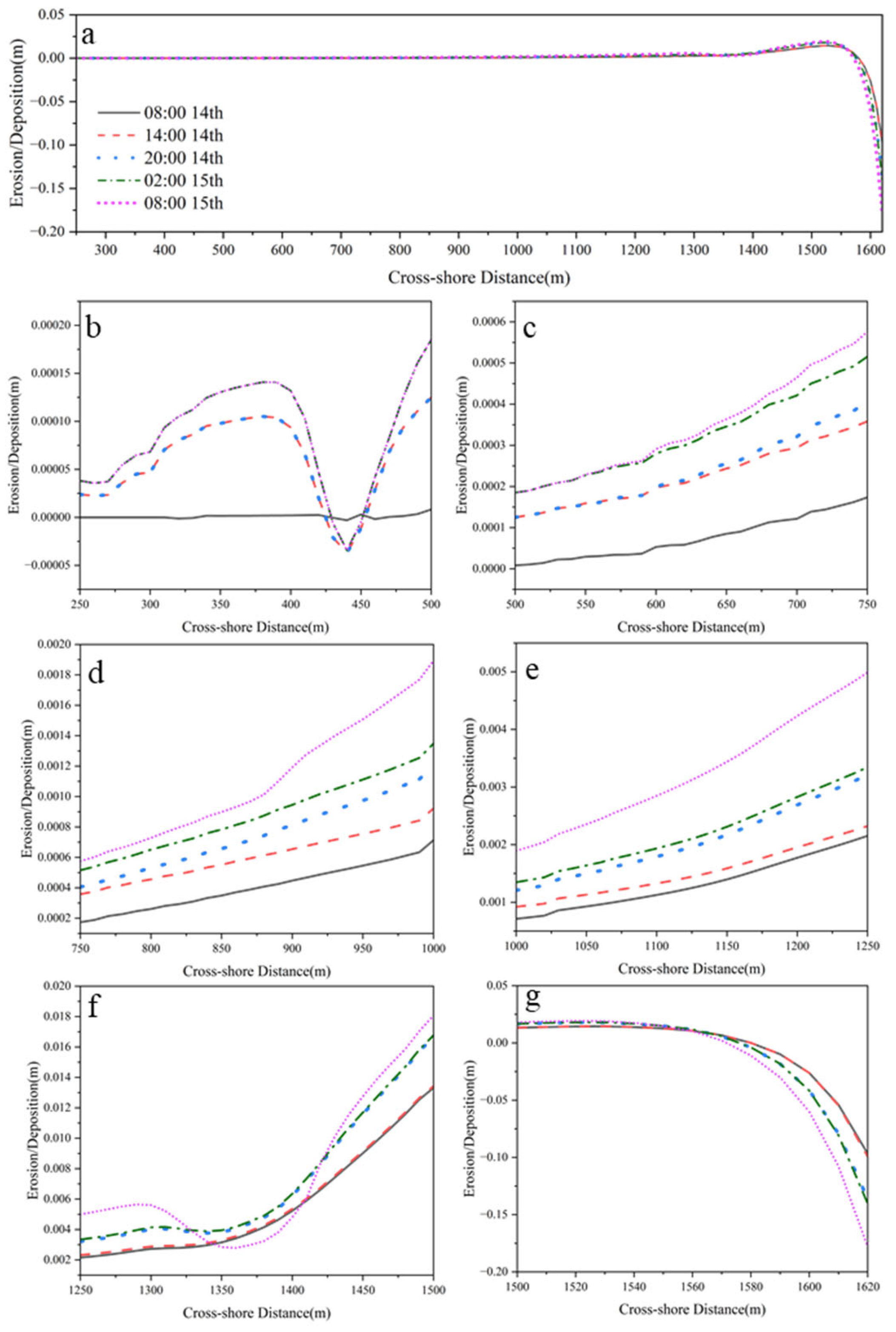
3.4. Changes in Profile Erosion and Deposition During Storm Tide Periods
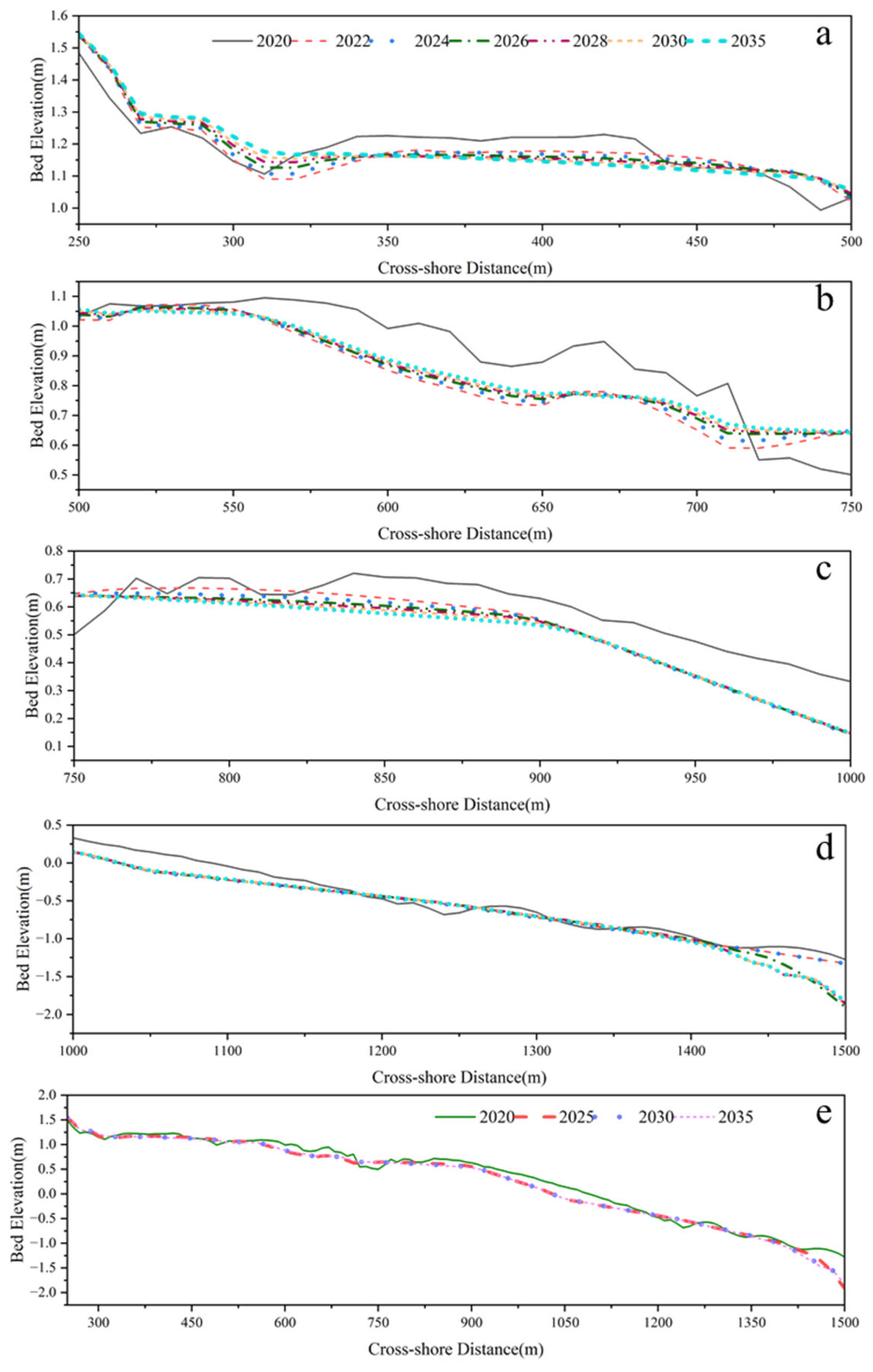
3.5. Profile Morphology Prediction
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
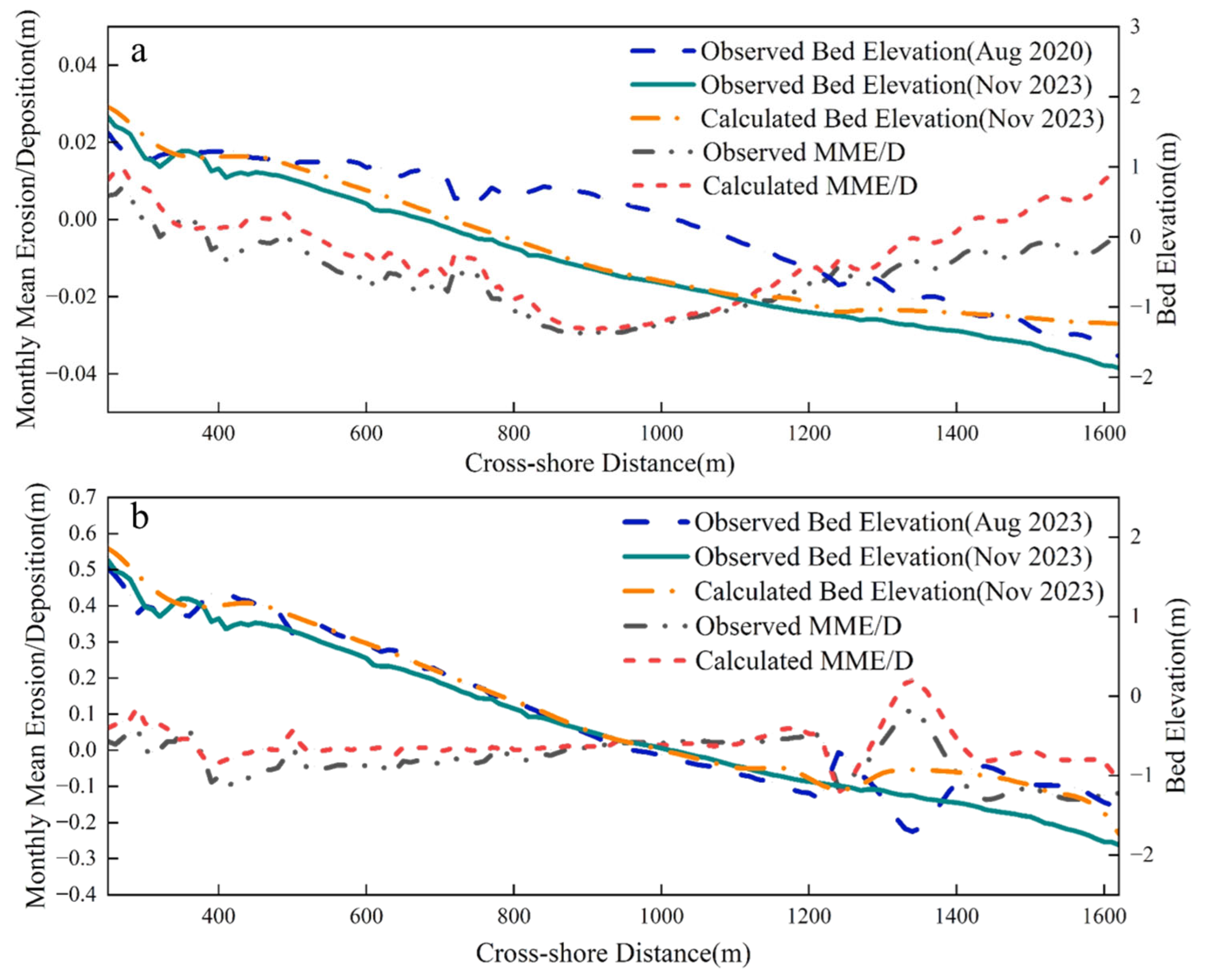
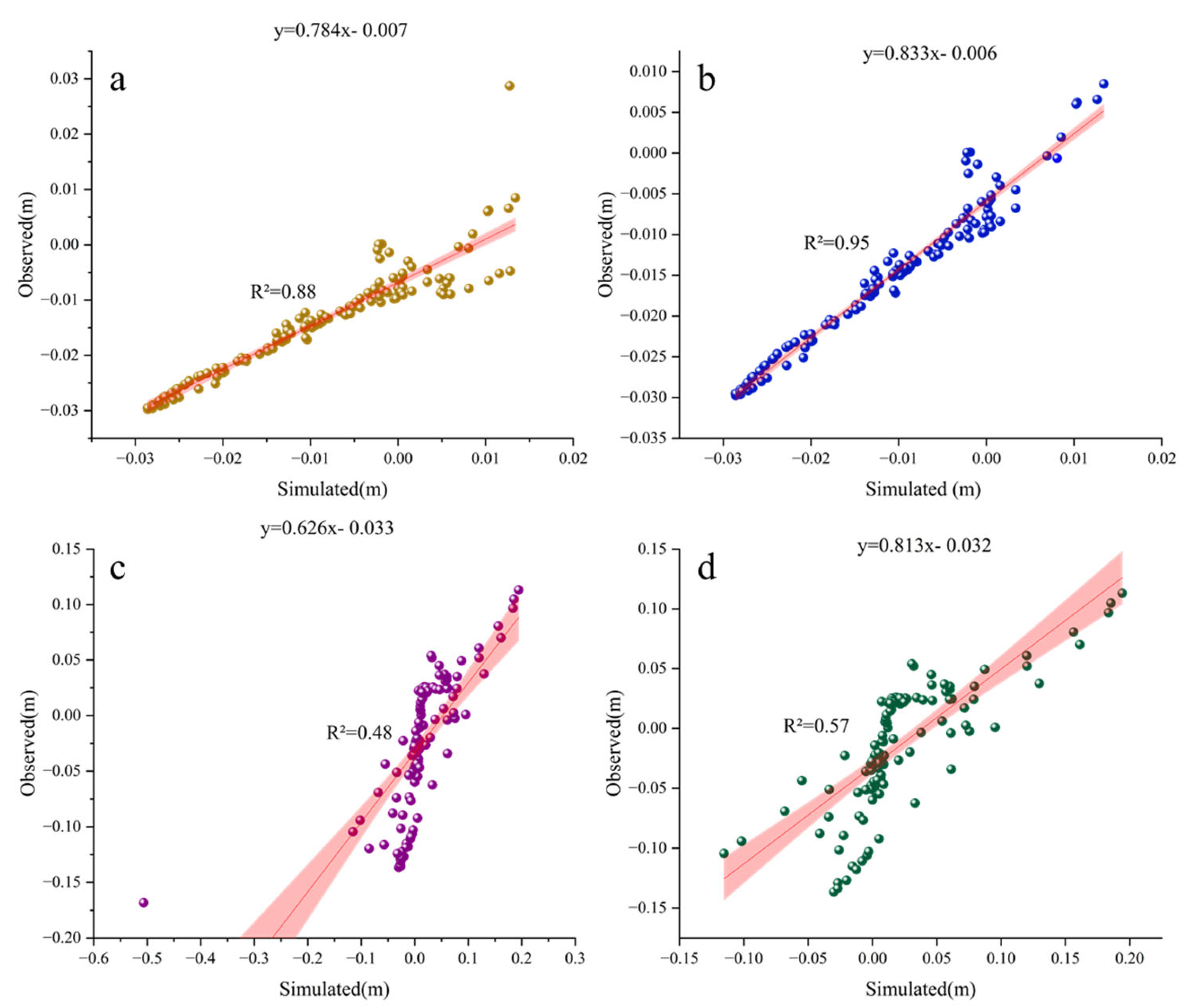
- The topographic validation results indicate that the constructed one-dimensional morphodynamic model can reliably reproduce the erosion–deposition evolution of the tidal flat profile along the Dafeng Port coast—currently in an accretion-to-erosion transition—on an interannual scale. In the main profile section (250–1500 m), the simulated results are highly consistent with the measured elevations, demonstrating high accuracy and reliability, making the model suitable for long-term morphological trend analysis and prediction. Although some discrepancies in erosion–deposition magnitude are observed on the monthly scale—mainly due to the exclusion of seasonal wave variations—the overall trends and spatial responses align well with field observations, providing a solid foundation for identifying the mechanisms of profile evolution.
- (2)
- The erosion and deposition processes of the profile exhibit significant nonlinear responses to wave parameters. Among them, critical transition points in sediment response efficiency appear around an effective wave height of 1.2 m and a peak period of 4.5 s, reflecting phased changes in the profile’s reaction to wave disturbances. Additionally, different profile segments display strong spatial heterogeneity under wave forcing, with clearly defined accretion and erosion zones, and some areas exhibiting non-monotonic response trends.
- (3)
- The upper tidal flat primarily undergoes erosion and deposition changes dominated by accretion during flood tide during storm tide events, with weakened responses during ebb tide. In contrast, the middle to lower tidal flat and shallow water zones experience significantly enhanced erosion during ebb tide, while sediment changes during flood tide are comparatively subdued, forming a differentiated pattern of “upper flood tide response and lower ebb tide response.”
- (4)
- Predictive results show persistent weak accretion in the upper intertidal zone, with shallow water areas transitioning from early erosion to recovery accretion. The middle section largely maintains dynamic equilibrium or slight erosion, and the rate of sediment change decreases annually, indicating that the profile is expected to remain relatively stable after 2026. The profile retains the typical “accretion above, erosion below” pattern. The upper section shows continuous accretion. The lower section transitions from erosion to accretion. The erosion–accretion boundary is likely around 900 m offshore (mean low water level). Under long-term hydrodynamic forcing, local morphological undulations gradually diminish. Eventually, the profile approaches a stable shape with minimal resistance.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Sample No. | Dx (16) (μm) | Dx (84) (μm) | Dx (50) (μm) | MZ (μm) | Latitude (°) | Longitude (°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DF 01 | 5.9 | 63.5 | 29.1 | 32.9 | 33.2838 | 120.7738 |
| DF 02 | 4.7 | 61.3 | 26.0 | 30.7 | 33.2841 | 120.7745 |
| DF 03 | 26.0 | 73.2 | 47.7 | 48.9 | 33.2842 | 120.7750 |
| DF 04 | 42.1 | 108.0 | 73.1 | 74.4 | 33.2844 | 120.7755 |
| DF 05 | 15.0 | 83.1 | 51.0 | 49.7 | 33.2846 | 120.7763 |
| DF 06 | 43.2 | 117.0 | 76.4 | 78.8 | 33.2848 | 120.7771 |
| DF 07 | 38.4 | 113.0 | 75.6 | 75.6 | 33.2851 | 120.7780 |
| DF 08 | 37.7 | 106.0 | 70.5 | 71.4 | 33.2855 | 120.7788 |
| DF 09 | 46.5 | 109.0 | 76.1 | 77.2 | 33.2859 | 120.7796 |
| DF 10 | 37.2 | 105.0 | 69.1 | 70.4 | 33.2865 | 120.7802 |
| DF 11 | 31.1 | 88.3 | 57.7 | 59.0 | 33.2870 | 120.7809 |
| DF 12 | 20.7 | 83.5 | 51.7 | 51.9 | 33.2874 | 120.7816 |
| DF 13 | 14.5 | 86.2 | 54.9 | 51.8 | 33.2878 | 120.7824 |
| DF 14 | 4.7 | 70.8 | 23.4 | 32.6 | 33.2882 | 120.7830 |
| (s) | (m) | Peak Enhancement Factor | Directional Spreading (°) | Direction (°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.5 | 0.6 | 3.3 | 25 | 90 |
| 0.8 | ||||
| 1.2 | ||||
| 1.6 | ||||
| 2.0 |
| (m) | (s) | Peak Enhancement Factor | Directional Spreading (°) | Direction (°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.8 | 3.0 | 3.3 | 25 | 90 |
| 3.6 | ||||
| 4.2 | ||||
| 4.5 | ||||
| 4.8 5.4 6.0 |
References
- Hulskamp, R.; Luijendijk, A.; van Maren, B.; Moreno-Rodenas, A.; Calkoen, F.; Kras, E.; Lhermitte, S.; Aarninkhof, S. Global distribution and dynamics of muddy coasts. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 8259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, N.J.; Phinn, S.R.; Dewitt, M.; Ferrari, R.; Johnston, R.; Lyons, M.B.; Clinton, N.; Thau, D.; Fuller, R.A. The global distribution and trajectory of tidal flats. Nature 2019, 565, 222–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Xu, L.; Okon, S.U.; Hu, P.; Li, W.; Shi, H.; He, Z. Sediment transport and bed erosion during storm surge using a coupled hydrodynamic and morphodynamic model considering wave and current interaction. Coast. Eng. 2024, 187, 104409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Bellerby, R.; Craft, C.; Widney, S.E. Coastal wetland loss, consequences, and challenges for restoration. Anthr. Coasts 2018, 1, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luque, P.; Gomez-Pujol, L.; Ribas, F.; Falqués, A.; Marcos, M.; Orfila, A. Shoreline response to sea-level rise according to equilibrium beach profiles. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 15789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirby, R. Practical implications of tidal flat shape. Cont. Shelf Res. 2000, 20, 1061–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieterse, A.; Puleo, J.A.; Mckenna, T.E. Hydrodynamics and sediment suspension in shallow tidal channels intersecting a tidal flat. Cont. Shelf Res. 2016, 119, 40–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Dai, Z.; Pang, W.; Wang, J.; Gao, S. Sedimentary zonation shift of tidal flats in a meso-tidal estuary. Sediment. Geol. 2020, 407, 105749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igor, O.L. Sediment transport and beach equilibrium profile. Coast. Eng. 1985, 9, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jara, M.S.; González, M.; Medina, R. Shoreline evolution model from a dynamic equilibrium beach profile. Coast. Eng. 2015, 99, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariotti, G.; Fagherazzi, S. A numerical model for the coupled long-term evolution of salt marshes and tidal flats. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2010, 115, 2009JF001326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Chi, Y.; Lu, H.; Sun, G.; Lu, Y.; Li, H.; Luo, Y. Effects of the comprehensive elimination of Spartina alterniflora along China’s coast on blue carbon scenario prediction after ecological restoration. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 369, 122283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Gu, W.; Shi, B.; Chen, Y.; Chatzipavlis, A.; Ding, J.; Zhang, W.; Chen, Q.; Wang, Y.P. Sediment dynamic responses of coastal salt marsh to wind waves swells in a semi-open tidal flat. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 954, 176562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Gao, S.; Zhao, Y.; Chatzipavlis, A.; Chen, Y.; Gao, J.; Zhao, Y. An eco-parametric method to derive sedimentation rates for coastal saltmarshes. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 770, 144756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Wang, Z.B.; Zitman, T.J.; Stive, M.J.F.; Bouma, T.J. Predicting long-term short-term tidal flat morphodynamics using a dynamic equilibrium theory. JGR Earth Surf. 2015, 120, 1803–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Zhu, D. A Preliminary Study on the Profiles of the Muddy Coast in Jiangsu. J. Nanjing Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 1988, 24, 75–84. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, S.; Jia, J.; Yu, Q. Theoretical framework for coastal accretion-erosion analysis: Material budgeting, profile morphology, shoreline change. Mar. Geol. Quat. Geol. 2023, 43, 42–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.; Li, C.; Archer, A.W. Temporal distribution of diastems in deposits of an open-coast tidal flat with high suspended sediment concentrations. Sediment. Geol. 2002, 152, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Chai, C.; Zhang, M. Numerical study on the influence of salt marsh plants on coastal wetland hydrodynamics and suspended sediment transport. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1180457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chu, A.; Dai, Z.; Nienhuis, J. Delft3D model-based estuarine suspended sediment budget with morphodynamic changes of the channel-shoal complex in a mega fluvial-tidal delta. Eng. Appl. Comput. Fluid Mech. 2024, 18, 2300763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Wu, S.; Yue, D.; Zhao, J.; Deng, M.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Liu, M.; Feng, W. Effects of upstream conditions on digitate shallow-water delta morphology. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2021, 134, 105333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Zeng, J.; Ge, Z.; Zuo, Y.; Li, S.-H.; Zhao, L.-H.; Han, Y.; Cheng, H.-F.; Xin, P. A model coupling ecological and hydrodynamic processes for simulating the biogeomorphology of a coastal salt marsh. Ecol. Model. 2024, 493, 110758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhtyar, R.; Maitaria, K.; Velissariou, P.; Trimble, B.; Mashriqui, H.; Moghimi, S.; Abdolali, A.; Van der Westhuysen, A.J.; Ma, Z.; Clark, E.P.; et al. A New 1D/2D Coupled Modeling Approach for a Riverine-Estuarine System Under Storm Events: Application to Delaware River Basin. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2020, 125, e2019JC015822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, C.; Eidam, E.; Seim, H.; Nienhuis, J. Effects of Sea Ice on Arctic Delta Evolution: A Modeling Study of the Colville River Delta, Alaska. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2024, 129, e2024JF007742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Wegen, M.; Jaffe, B.; Foxgrover, A.; Roelvink, D. Mudflat Morphodynamics and the Impact of Sea Level Rise in South San Francisco Bay. Estuaries Coasts 2017, 40, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Cai, H. Profile characteristics study of the Jiangsu coast. Ocean. Eng. 2010, 28, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Jin, S.; Sun, C.; Wei, X. Evolution of the topography of tidal flats and sandbanks along the Jiangsu coast from 1973 to 2016 observed from satellites. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 150, 27–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, K. Evolution of the Silt-Muddy Coastline and Land Reclamation along the Jiangsu Coast, 1985–2002. Mar. Geol. Front. 2010, 26, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Liu, Q.; Yu, C.; Chen, Z.; Dong, X.; Xu, M.; Zhao, Y. Extracting waterline and inverting tidal flats topography based on Sentinel-2 remote sensing images: A case study of the northern part of the North Jiangsu radial sand ridges. Geomorphology 2024, 461, 109323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Peng, Y.; Wang, Y. Seasonal and interannual evolution of geomorphology in middle Jiangsu tidal flat from 2017 to 2020. Mar. Geol. Quat. Geol. 2023, 43, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, Q.; Xu, M.; Wang, Z. Inter-annual variability of heavy metals pollution in surface sediments of Jiangsu coastal region, China: Case study of the Dafeng Port. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 150, 110720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Z.; Huang, S.; Hu, B.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Z. Evolution of tidal flat in response to storm surges:a case study from the central Jiangsu Coast. Adv. Water Sci. 2019, 30, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Q.; Cai, H.; Gao, S. Characteristics of tides and tidal currents at central Jiangsu coast, China. Mar. Sci. 2019, 43, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, P.; Wen, S.; Zhou, C. Comprehensive Evaluation of Coastline Development and Utilization Intensity-A case study of Dafeng China. IOP conference series. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 199, 22052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Best, Ü.S.N.; Van der Wegen, M.; Dijkstra, J.; Willemsen, P.W.J.M.; Borsje, B.W.; Roelvink, D.J.A. Do salt marshes survive sea level rise? Modelling wave action, morphodynamics and vegetation dynamics. Environ. Model. Softw. 2018, 109, 152–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hibma, A.; Schuttelaars, H.M.; Wang, Z.B. Comparison of longitudinal equilibrium profiles of estuaries in idealized and process-based models. Ocean. Dyn. 2003, 53, 252–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Ye, Q.; Coco, G. A one-dimensional biomorphodynamic model of tidal flats; sediment sorting, marsh distribution, and carbon accumulation under sea level rise. Adv. Water Resour. 2016, 93, 288–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Z.; Jin, C.; Zhang, C.; Li, H.; Xin, P. Surface elevation variation of the Jiangsu mudflats: Field observation. Adv. Water Sci. 2014, 25, 880–887. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, H.; Xu, T.; Wei, Z. Improved tidal estimates from short water level records via the modified harmonic analysis model. Ocean. Model. 2024, 189, 102372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Lv, X.; Wang, Y.; Matte, P.; Chen, H.; Jin, G. Exploration of Tidal-Fluvial Interaction in the Columbia River Estuary Using S_TIDE. J. Geophys. Res. 2018, 123, 6598–6619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, A.; Yuka, Y.; Kenji, H.; Toyofuku, T. Identifying storm surge deposits in the muddy intertidal zone of Ena Bay, Central Japan. Mar. Geol. 2020, 426, 106228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, Z.; Jin, L. Numerical Simulation of Muddy Beach Profile Erosion under Wave Action: A Case from Northern Jiangsu. Acta Oceanol. Sin. (Chin. Ed.) 1993, 4, 74–83. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Deng, A.; Feng, H.-C.; Wang, D.-W.; Guo, C.-S. Emerging Downdrift Erosion by Twin Long-Range Jetties on an Open Mesotidal Muddy Coast, China. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrichs, C.T. Tidal Flat Morphodynamics: A Synthesis. In Treatise on Estuarine and Coastal Science: Sedimentology and Geology; Flemming, B.W., Hansom, J.D., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 137–170. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.; Yao, P.; Van Der Wal, D.; Bouma, T.J. Patterns and drivers of daily bed-level dynamics on two tidal flats with contrasting wave exposure. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, B.; Cooper, J.R.; Pratolongo, P.D.; Gao, S.; Bouma, T.J.; Li, G.; Li, C.; Yang, S.L.; Wang, Y.P. Erosion and accretion on a mudflat: The importance of very shallow-water effects. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2017, 122, 9476–9499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, M.O.; Coco, G. Review of wave-driven sediment resuspension and transport in estuaries. Rev. Geophys. 2014, 52, 77–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.P.; Yu, Q.; Du, Z.; Wang, Z.B.; Gao, S. Sand-mud tidal flat morphodynamics influenced by alongshore tidal currents. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2019, 124, 3818–3836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, T.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, H.; Xu, M.; Cao, J. Morphodynamic of Tidal Flat Profiles in an Erosion-to-Accretion Transitional Coastal Segment Under Wave–Current Interaction: A Case Study of Dafeng Port, China. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 1746. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13091746
Li T, Zhao Y, Wang L, Zhang H, Xu M, Cao J. Morphodynamic of Tidal Flat Profiles in an Erosion-to-Accretion Transitional Coastal Segment Under Wave–Current Interaction: A Case Study of Dafeng Port, China. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(9):1746. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13091746
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Tianjun, Yifei Zhao, Lizhu Wang, Hong Zhang, Min Xu, and Jicheng Cao. 2025. "Morphodynamic of Tidal Flat Profiles in an Erosion-to-Accretion Transitional Coastal Segment Under Wave–Current Interaction: A Case Study of Dafeng Port, China" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 9: 1746. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13091746
APA StyleLi, T., Zhao, Y., Wang, L., Zhang, H., Xu, M., & Cao, J. (2025). Morphodynamic of Tidal Flat Profiles in an Erosion-to-Accretion Transitional Coastal Segment Under Wave–Current Interaction: A Case Study of Dafeng Port, China. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(9), 1746. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13091746







