Abstract
This paper investigates the surrounding control problem of multiple unmanned surface vehicles (USVs) against false data injection (FDI) attacks and proposes a learning-based prescribed performance control (PPC) integrated with a dynamic event-triggering (DET) mechanism. First, a predefined-time observer (PTO) is designed to estimate the injected false data. Then, the constrained surrounding tracking error of multi-USVs is first formulated based on an exponential prescribed performance function. To facilitate the control law design, the constrained surrounding problem is transformed into an unconstrained space using a hyperbolic tangent function. Based on adaptive dynamic programming (ADP) and the DET mechanism, a prescribed performance time-varying surrounding control scheme is developed. Finally, the effectiveness and superiority of the proposed control strategy are demonstrated through rigorous theoretical analysis and simulation experiments, while Zeno behavior in the event-triggered mechanism is excluded.
1. Introduction
In recent years, multi-agent systems (MASs) control has emerged as a significant research focus due to the inherent flexibility, scalability, and intelligent emergence characteristics of MASs. The MASs control technology has been widely used in the formation control of unmanned systems [1], surrounding control of unmanned surface vehicles (USVs) [2], and reconnaissance missions of multiple unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) [3].
Multi-USV systems have attracted significant research attention globally, owing to the advantages of their low cost, high maneuverability, and operational reliability. An equal-distance surrounding control strategy was proposed to address the encirclement tasks of multi-USVs with collision avoidance in [4]. Skjetne et al. [5] designed an adaptive recursive control scheme for nonlinear USV systems with parameter uncertainties. In [6], a distributed prescribed performance formation control method with obstacle avoidance was presented for multiple USVs under parameter uncertainties and external disturbances. However, the above-mentioned control methods, such as sliding mode control, adaptive control, and backstepping control, fail to account for the trade-off between control performance and control cost. Moreover, in practical applications, the communication networks of multi-USVs may be vulnerable to cyber-attacks, and the closed-loop systems (CLSs) are required to achieve good steady-state and transient performance. Therefore, it is significant to design a robust, secure, and optimal control scheme with prescribed performance to address the surrounding control problem of multiple USVs under network attacks.
In [7], a fixed-time extended state observer (FTESO) was designed to estimate the velocities and disturbances of multi-USVs, and a FTESO-based fixed-time distributed formation control method was developed. In [8], a leader–follower formation control strategy based on event-triggered mechanism and artificial potential function was proposed for multiple autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs) in a three-dimensional environment. The authors investigated the formation control problem of multiple USVs under constraints on line-of-sight range and angular measurements, and a fault-tolerant finite-time formation control method based on time-varying tangent barrier Lyapunov function was proposed in [9]. Formation control methods are generally used to realize cooperative tasks. However, the surrounding control and containment control methods can be utilized to address the MASs control problem involving non-cooperative targets [10]. Xu et al. [11] developed an event-triggered control method to address the surrounding-formation control problem with multiple dynamic targets; Zeno behavior did not occur in the event-triggered mechanism. Reference [12] proposed a sampled-data-based containment control strategy to solve the second-order multi-agent control problem involving a dynamic leader with nonzero input, ultimately guaranteeing that all followers converge within the convex hull formed by the dynamic leader. In practical applications, USVs are typically powered by lithium batteries, which are limited in capacity due to the constraints of the USV’s size and structure. Therefore, designing control schemes that minimize energy consumption while maintaining USV performance is of significant value. In [13], an optimal tracking control scheme was designed for USV dead-zone input nonlinearity and external disturbances, which can balance the control cost and performance. In [14], the authors addressed the control problem of fixed-wing UAVs subjected to both matched and unmatched disturbances, and an adaptive optimal control method based on the adaptive gain generalized super-twisting algorithm was proposed to mitigate the negative impact of disturbances on the CLSs.
The aforementioned works primarily focus on designing control methods to ensure the steady-state performance of control systems. However, these control methods do not simultaneously account for both steady-state and transient performance, including factors such as convergence accuracy, convergence speed, and overshoot in the CLSs. In [15], a prescribed performance control (PPC) method was first designed for MIMO nonlinear systems, which can ensure that the state of CLSs remains within the range defined by a prescribed performance function. A reinforcement learning (RL)-based prescribed performance optimal control scheme was presented to deal with the constrained tracking control problem of USV [16]. An adaptive fault-tolerant control scheme based on PPC techniques for spacecraft in the presence of external disturbances and actuator failures in [17]. In [18], a RL-based prescribed performance attitude control method was designed for spacecraft attitude control systems under disturbances and state constraints, and a neural network (NN) weight update law without persistent excitation (PE) conditions was proposed in the RL algorithm. In [19], a leader–follower prescribed performance formation control approach was developed to solve second-order MASs output feedback control problems without velocity measurement. In [20], a FTESO-based PPC method was proposed to handle the path-tracking problem of USVs via sliding mode control (SMC) techniques. An event-triggered-based reinforcement learning PPC method was presented for the underactuated USV in [21]. The event-triggered strategies in the aforementioned works primarily are mainly static triggering mechanisms. To further reduce the number of event triggers, reference [22] employed a dynamic event-triggered (DET) mechanism to design a finite-time formation control method for USVs.
Multi-UAVs are one branch of cyber-physical systems (CPSs); malicious cyberattacks can have severe negative impacts on their security and stability [23,24]. The cyberattacks are mainly categorized into denial of service (DoS) attacks [25] that destroy data availability, and false data injection (FDI) attacks [26] that damage data integrity. Compared to DoS attacks, FDI attacks are more covert and destructive. Considering the consensus control problem of multiple UAVs under deception attacks, a memory-based event-triggered control strategy was proposed by incorporating an averaging mechanism to suppress event mis-triggering caused by deception attacks [27]. For smart grid systems subjected to FDI attacks, a deep-learning-based intelligent detection algorithm was designed to identify the behavioral characteristics of false data using historical measurement data in [28]. He et al. [29] proposed a pulse-synchronization-based secure control method for MASs under deception attacks. For MASs under composite attacks combining FDI and information replay, an adaptive observer-based distributed leader–follower resilient control scheme was proposed in [30]. A periodic event-triggered resilient control strategy was developed for the consensus control problem of linear MASs under FDI and DoS attacks [31]. In [32], a fully distributed resilient control protocol was developed for the formation-containment control problem of higher-order heterogeneous MASs under unbounded FDI attacks. In [33], a distributed resilient containment control method was proposed for MASs against FDI attacks. Zhang et al. [34] designed a predictive sliding mode control method to address the output tracking problem of higher-order fully actuated systems in the presence of FDI attacks. In [35], considering the higher-order fully actuated MASs under FDI attacks, a predictive sliding mode control approach was proposed to ensure the stability and security of CLSs.
By analyzing the aforementioned works, it can be observed that there is relatively little research on the surrounding control problem of multi-USVs under FDI cyberattacks. Inspired by the above studies, this paper proposes a learning-based resilient DET surrounding control strategy for multi-USVs under FDI attacks. The main contributions of this work are as follows:
1. A novel predefined-time observer (PTO) is proposed to estimate false data in the communication network of multi-USVs, and a PTO-based resilient control scheme is designed. In contrast to the asymptotic convergence FDI observer presented in [27], the proposed PTO can estimate the false data within a user-predefined time and does not require the assumption that the false data are bounded.
2. Based on the information from the PTO, a prescribed performance time-varying surrounding control method is designed for multi-USVs within the adaptive dynamic programming (ADP) framework. In [16], an RL-based control method for the tracking control problem of USVs was proposed using the NN weight update law under the persistent excitation condition (PE). In contrast, the NN weight update law in this paper relaxes the PE requirement by incorporating the system’s state into the learning rate, thereby accelerating the convergence of the weight update law.
3. Compared to these control schemes for USVs in [4,11,16], this work proposes an ADP-based prescribed performance controller integrated with the DET mechanism. In contrast to the time-sampling controller in [4,11], and the static event-triggering strategy in [16], the proposed DET scheme further reduces the event-triggering numbers to reduce energy consumption. Moreover, by combining the ADP and PPC techniques, the proposed optimal surrounding controller effectively balances control cost and performance while considering both the steady-state and transient performance of the CLSs.
2. Materials and Methods
This paper investigates the surrounding control problem of multiple unmanned surface vehicles (USVs) against false data injection (FDI) attacks and the control structure diagram of the multi-USVs against FDI attacks is given in Figure 1. The false data are injected into the communication network between USVs to degrade the performance of CLSs. The proposed FDI compensation observer can effectively detect false signals to mitigate the impact of FDI attacks. Ultimately, combining the framework of adaptive dynamic programming and the dynamic event-triggered mechanism, a resilient prescribed performance surrounding control method is designed for multi-USVs.
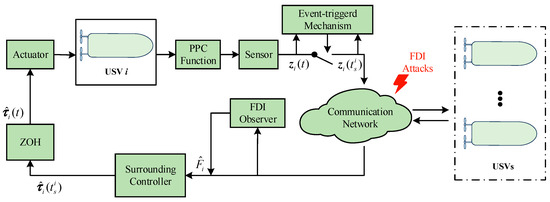
Figure 1.
The structure illustration of surrounding control for multi-USVs under FDI attacks.
2.1. Communication Network Diagram of USV
The time-varying surrounding control problem of multi-USVs is investigated in this work. Considering the multi-USVs with N agents, the directed communication network of USVs is defined as , where denotes the node set and is the edge set among the directed graph . The symbol is defined as the adjacency matrix of multi-USVs, where denotes the connection weight between the ith USV and jth USV. If , that means the ith USV can acquire the state of jth USV, , otherwise . The diagonal matrix is denoted as the in-degree matrix of USVs, where . The Laplacian matrix is given by .
Consider the state of target USV as , if the state information of target USV can flow to the ith USV, , otherwise . For a digraph with agents, the directed graph contains the target USV and N pursuer USVs. The Laplacian matrix of digraph is defined as , where .
Assumption 1.
For the digraph , there exists at least one path from the target USV to any pursuer USV. Also, a directed spanning tree is rooted at the target USV in the .
2.2. The Dynamical Model of USV
The simplified schematic diagram of the unmanned surface vehicle (USV) is shown in Figure 2, where represents the Earth-fixed coordinate and denotes the body-fixed coordinate of the USV.
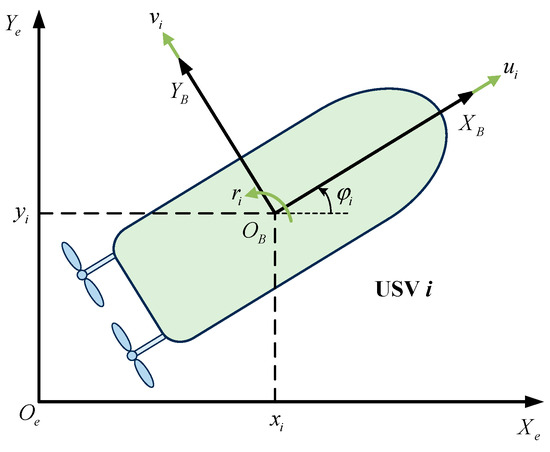
Figure 2.
Construction and frame of the unmanned surface vehicle (USV).
According to references [6,16], the kinematic and dynamic models of the USVs are given as follows:
where denotes the state of the ith USV, is the position state and is the yaw angle. is the velocity vector, are the surge, sway, yaw velocities, respectively. is the control input. represents the inertia matrix, satisfying , is the skew-symmetric Coriolis force matrix, , and is the damping matrix. is the rotation matrix from to , defined as follows:
where the rotation matrix has the property . The matrices , , are expressed as follows:
with , , , , is the mass of the ith USV, denotes the inertia term in the z-axis, is the gravity of the USV, and these variables are the added masses. , . , , , are the linear damping coefficients of USV, and denote the quadratic damping coefficients.
Next, according to the Euler-Lagrange modeling method [36,37], the dynamical model (1) of the USV is transformed as follows:
Taking the derivative of Equation (4), we obtain the following equation:
Substituting (5) into (1), we can obtain the following:
where , .
In this work, the control inputs under the FDI attacks are represented as follows:
where denotes the false information injected by the attacker, is the FDI attacks probability matrix, , , and denote random variables that follow the Bernoulli distribution. The probability distribution of the random variable satisfies the following:
where , , and .
Substituting (7) into (6), we can obtain the dynamic systems of multiple USVs under FDI attacks as follows:
2.3. The Surrounding Control for Multi-USVs
Definition 1
[38]. There exists a set that belongs to a convex set . In the convex set , there exists a convex hull .
Definition 2.
The time-varying surrounding control of multi-USVs is achieved, if for any pursuer USV satisfying the following equation:
where denotes the state of target USV, the time-varying surrounding function , , .
Figure 3 illustrates the process of multiple USVs moving from their initial states to uniformly encircling the target. It can be observed that the target USV is finally distributed into the convex hull spanned by the pursuer USVs.
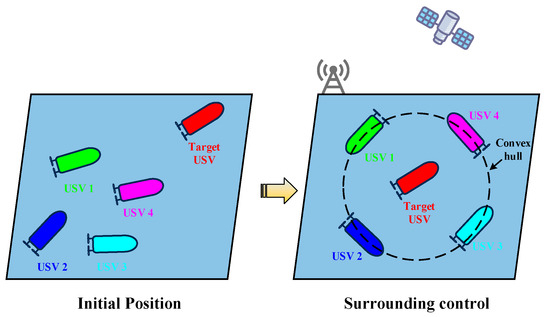
Figure 3.
Schematic diagram of surrounding control for multi-USVs.
Lemma 1
[39]. Consider the dynamic system , where represents the system state and is the control input. For any positive constants and , there exists a positive-definite Lyapunov function satisfying the following:
with . The system state will converge to the origin within the user-predefined time .
2.4. Design of a Preset Time Controller Based on ADP and Dynamic Event-Triggering Mechanism
2.4.1. Predefined-Time FDI Attack Observer Design
This work considers the surrounding control problem of multi-USVs under FDI attacks. If the false information in the communication network of USVs is not handled properly, it will lead to the performance degradation of the closed-loop system. To mitigate the impact of FDI attacks, a predefined-time attack compensation observer will be designed for the multi-USVs. One auxiliary variable is defined as follows:
where is a positive constant. Taking the time derivative of Equation (12), we obtain the following expression:
where .
Theorem 1.
Based on the auxiliary variable and its derivative , which are specifically defined in Equations (12) and (13), a predefined-time observer is designed as follows:
with , , , . According to Equations (13) and (14), to alleviate the impact of FDI attacks on the closed-loop system of USVs, the following predefined-time FDI observer is given as follows:
Under the observer (15), the estimation error will converge to zero within the predefined time .
Proof.
The function is selected as the Lyapunov function, and the can be obtained as follows:
According to Lemma 1, it can be derived that as the time . When , can be obtained. Based on Equations (13) and (15), we can obtain the following:
Based on the above analysis, it can be concluded that the estimation error of the false data will converge to zero within the predefined time . □
2.4.2. Tracking Error Subsystem of USVs
Considering the second-order Euler-Lagrange dynamic model of the USV in Equation (6), the following controller is given as follows:
where the denotes the ADP-based controller, the feedforward control law is defined as , and is the surrounding position vector of the ith USV relative to the target.
The position vector of the target USV is set as , and is the velocity vector of the target. Next, the surrounding tracking error model for the multi-USVs will be established. The position error of the ith USV relative to its neighbor is formulated as follows:
where denotes the relative position between ith USV and jth USV, .
The velocity tracking error is defined as follows:
Take the derivative of Equation (20) with respect to time, it can yield the following:
with , , . One can determine that and when time . According to (20) and (21), a combined dynamic system is defined as follows:
where , , , , .
In this paper, to ensure that the surrounding tracking error of USVs has both great steady-state and transient performance, the following prescribed performance function is designed:
where , , , , . The surrounding tracking error can be expressed as follows:
where is a monotonically increasing smooth function such that , . The mapping function is designed as follows:
Because , it can be deduced that from Equation (25). Furthermore, we can obtain the following:
From (26), the inverse function of the variable is given as follows:
The time derivative of Equation (27) can be given as follows:
with , , , , . Substituting Equation (20) into (28), we obtain the following:
where , . According to (24) and (27), can be derived.
2.4.3. ADP-Based Optimal Time-Varying Surrounding Control
To save the energy of the USV, this paper adopts a dynamic event-triggered control strategy to reduce communication frequency and state sampling times between USVs. The sampling time sequence for the ith USV is defined as , satisfying , . The sampling error of ith USV is designed as follows:
where represents the previous sampling time of ith USV. To facilitate the design of the event-triggered control strategy in the following discussion, we define . The performance index function for the ith USV is designed as follows:
where and . If the ith USV has an optimal control scheme , the cost function in Equation (27) can be transformed into the following form:
We conduct the time derivative of the optimal cost function in (32), it yields the following:
where is the partial derivative of with respect to . Using Equation (33), the optimal control strategy is obtained as follows:
According to the definition of in (30), the event-triggered optimal controller is obtained as follows:
Substituting (35) into (33), the HJB equation of ith USV under the event-triggered strategy is given as follows:
Based on the above analysis, we can obtain the event-triggered optimal control strategy by solving the HJB Equation (36). However, the HJB equation is highly nonlinear and contains partial differential terms, making it difficult to obtain an analytical solution. Therefore, we use a neural network to approximate the optimal cost function, which can be formulated as follows:
where is the optimal weight vector of the NN, represents the activation function, and is the approximation error of the NN. Utilizing (37), the optimal event-triggered control strategy in (35) is re-expressed as follows:
The optimal weight vector is unknown, which makes it impossible to directly obtain the optimal cost function . Then, we design the to estimate the , and is defined as the estimation of . Therefore, the actual optimal control strategy is given as follows:
According to (33) and , the Hamiltonian function can be rewritten as follows:
Furthermore, based on Equations (33), (37) and (40), we can obtain the following:
where . According to (40) and (41), we can obtain the following:
with and .
Assumption 2.
The activation function of the NN and the approximation error are both bounded, satisfying , , where and are constant values.
Assumption 3.
The activation function satisfies the Lipschitz continuous [40]; we obtain the following:
where is a positive constant.
Theorem 2.
Considering the transformed subsystem (29) of the USVs, an event-triggered control strategy (39) based on reinforcement learning is designed. The dynamic event-triggering condition is designed as follows:
where , , , , . The dynamic variable in (44) is given as follows:
where , , . The NN weight update law without PE condition is given as follows:
with , , , and being positive constants. The state tracking error and the NN weight estimation error are ensured to be uniformly ultimately bounded (UUB) under the optimal control law (39) and the weight update law (46). Furthermore, the proposed dynamic event-triggered control strategy does not exhibit Zeno behavior.
Proof.
According to Equations (44) and (45), we can obtain . Furthermore, from one, we obtain . Based on the above analysis, a positive-definite Lyapunov function for the ith USV is chosen as follows:
The following analysis will be divided into two parts: (1) the stability analysis; (2) the exclusion of Zeno behavior.
(1) Stability Analysis: The time derivative of the Lyapunov function is given as follows:
According to Equations (33), (46) and (48) can be further derived into the following form:
According to [18], the ideal weight is bounded. Furthermore, we can obtain , where . Based on the weight update law (46) and Equation (49), the following inequality can be obtained:
where and . is the upper bound of the ideal weight , and is the upper bound of Substituting (50) into (49), we obtain the following:
According to Equations (34) and (37), the time-sampling-based control strategy is obtained as follows:
And further from (39) and (52), the following inequality can be derived as follows:
Substituting (53) into (52), Equation (51) can be reformulated as follows:
where and are shown as follows:
Based on the dynamic event-triggering conditions (44) and (45), Equation (54) can be re-expressed in the following form:
where , . Based on the above analysis, it is known that the variables and are UUB. It is reasonable to assume that the position tracking error is , where is a positive constant. Therefore, we can obtain the following:
According to the definition of encirclement control and Equation (53), it can be concluded that multiple unmanned ships will successfully complete the encirclement control task for the target.
(2) Exclusion of Zeno behavior: Taking the derivative of the event-triggered sampling error with respect to time , we obtain the following:
From the proof results given above, it is known that these variables are bounded. Therefore, Equation (58) can be written in the following form:
where . Since time is within the interval , integrating both sides of Equation (59) yields the following expression:
According to (60), there is no Zeno behavior in the proposed DETC. □
Remark 1.
The predefined-time FDI attacks observer was first proposed in this work for multi-USVs under FDI network attacks. Compared to the asymptotic convergence, finite-time, and fixed-time observers [1,7,27], the proposed observer allows for a predefined convergence time while maintaining a simple structure. In [41], the prescribed-time observer may encounter singularity issues at the prescribed time point. This occurs because measurement errors in the system state can lead to an infinite gain. Compared to [41], the predefined-time approach proposed in this paper overcomes the singularity problem.
Remark 2.
Compared to these multi-USVs surrounding control strategies in [4,11,42], this paper proposes a prescribed-performance time-varying surrounding control scheme based on ADP for the first time. In the proposed control strategy, multi-USVs can achieve time-varying even encirclement of the target, meaning that all the pursuer USVs are evenly distributed on a circle with the encirclement radius and move in a circular motion around the target.
Remark 3.
Reference [16] proposed a reinforcement learning-based prescribed-performance tracking control strategy for USV, which requires the assumption of a weight update law with persistent excitation. Compared to [16], this paper introduces an NN weight update law that does not require the persistently excited condition. Additionally, a system state is incorporated into the NN weight update law, which accelerates the convergence of the NN weights.
Remark 4.
Compared to the static event-triggered control strategy proposed in [21] for the USV tracking problem, this paper introduces an improved dynamic event-triggered mechanism (IDETM) to further reduce the number of triggers. Moreover, through rigorous theoretical proof, Zeno behavior is eliminated. The proposed reinforcement learning control method based on IDETM significantly reduces the energy consumption of multi-USVs caused by the controller and communication.
3. Results and Discussion
In this section, numerical simulations are used to verify the effectiveness of the proposed control strategy. The computer specifications for this simulation are as follows: an AMD Ryzen 9-7945HX processor running at 2.5 GHz and 16 GB of RAM. The simulation is implemented in MATLAB/Simulink (R2016B) and MATLAB/Simscape (R2023B) with a fixed-step sampling method, where the step size is 0.01 and the total simulation time is 100 s. In the simulation, four pursuer USVs () and one target are designed. Figure 4 shows the communication topology of the multi-USVs.
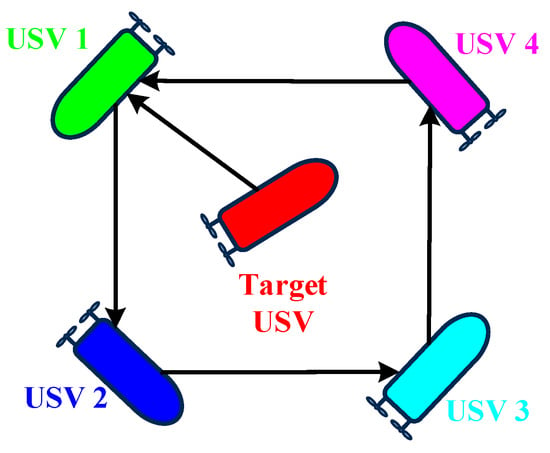
Figure 4.
The communication topology of the multi-USVs.
The settings for the inertia matrix , Coriolis term , and damping matrix of the dynamics model of the unmanned surface vehicle refer to [5], with specific values listed in Table 1. The parameters for the prescribed performance function are set as , , . Additionally, the initial values of USV states, NN weights, the weight matrix, control parameters, and the parameters of the predefined-time FDI observer are provided in Table 2. The vector is expanded as , and is set as the NN activation function. The desired motion trajectory for the target is set as , while the time-varying surrounding configuration of the pursuer USVs relative to the target is given in Table 3. Assuming the false data are , the attack probability constants are set as , , .

Table 1.
Parameters of USVs.

Table 2.
Parameters for simulation.

Table 3.
Time-varying surrounding function.
Considering the surrounding control problem of multi-USVs under FDI attacks, this work proposes an ADP-based prescribed performance time-varying encirclement control strategy. This subsection verifies the effectiveness and superiority of the proposed scheme through numerical simulations and comparative experiments.
Figure 5 shows the 2D trajectory of multi-USVs. From Figure 5, it can be seen that at the initial moment, the target is located outside the four pursuer USVs. Under the proposed control method, the four pursuer USVs successfully form a square configuration to encircle the target unmanned ship. Furthermore, from Figure 5, it can be observed that the formation of the configuration of pursuer USVs is time-varying, meaning that each pursuer USV performs a circular motion around the target unmanned ship, ultimately resulting in the target being enclosed within the convex hull formed by the pursuing unmanned ships.
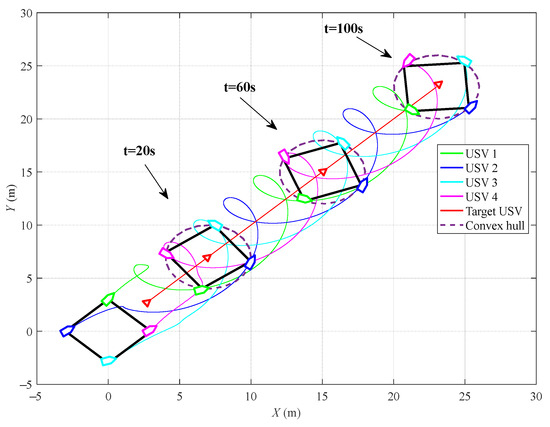
Figure 5.
Trajectories of multiple USVs with a time-varying surrounding configuration.
To demonstrate the superior performance of the proposed ADP-based prescribed-performance control method (PPCADP), Figure 6 presents comparative simulation results with three different control approaches, including the traditional ADP control method (TADP) in [38], the model predictive control strategy (MPC) in [43], and the sliding mode control method (SMC) in [44]. Figure 6 illustrates the simulation results of the state tracking error under different controllers. From Figure 6, it can be seen that the state tracking errors under the PPCADP strategy remain strictly within the prescribed bounds, indicating the superior control performance of the proposed PPCADP. Figure 6b–d show the simulation results of the state tracking errors under the TADP, MPC, and SMC methods, respectively. The three control methods without prescribed performance constraints fail to confine the state tracking errors within the predefined bounds.
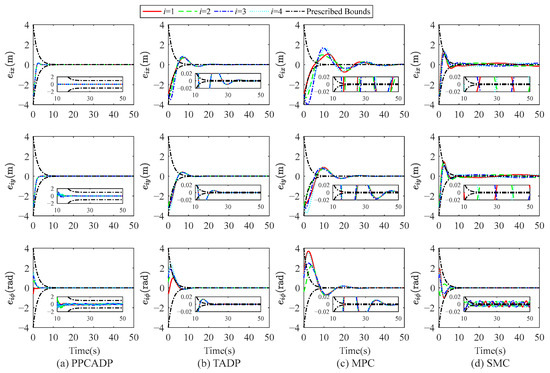
Figure 6.
Comparison of state tracking error results under different controllers.
To sum up, it can be observed from Figure 6 that the proposed PPCADP approach achieves faster convergence, higher convergence accuracy, and smaller overshoot compared with the other three control strategies.
In order to quantitatively compare the energy consumption results, a unified control energy cost function has been designed in the manuscript for different control methods: , where , , . Figure 7 presents comparative simulation results of energy consumption under different control strategies.
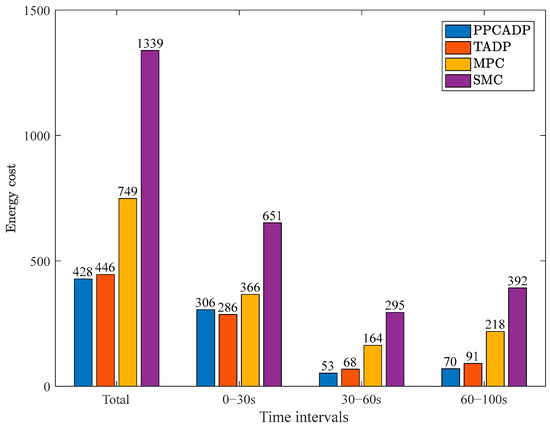
Figure 7.
Energy consumption results under different control strategies.
As observed from Figure 7, the PPCADP strategy achieves the lowest energy consumption, reducing energy cost by 12.8%, 49.3%, and 71.6% compared to the TADP, MPC, and SMC methods, respectively. This improvement is attributed to the incorporation of both control performance and control cost in the design of the cost function for the proposed PPCADP.
Figure 8 shows the control input curves. It can be observed that the resilient control strategy designed in this work ensures the stable performance of the multi-USVs under FDI attacks, and the control inputs converge to the origin within 10 s.
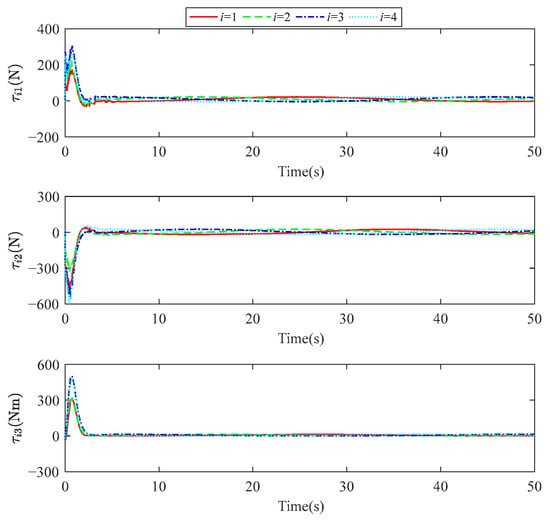
Figure 8.
Time response of control input achieved by PPCADP.
Figure 9 illustrates the time response of the NN weights. It can be seen that the weights converge from initial values to a constant value, indicating that the weights remain stable as the state convergence of CLSs.
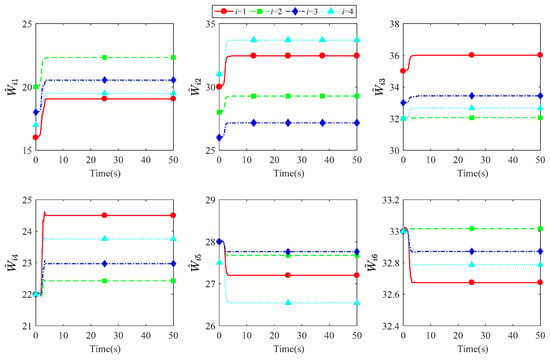
Figure 9.
Time response of NN weight achieved by PPCADP.
The time response results of the attack variable that satisfy the Bernoulli probability distribution are shown in Figure 10.
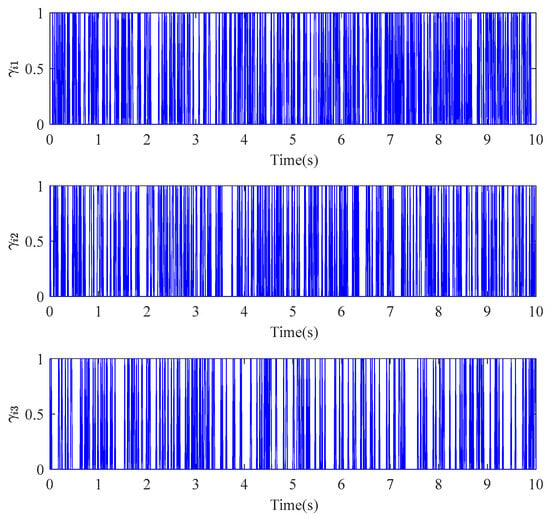
Figure 10.
The time response results of random variable .
Figure 11 shows the estimation error of the predefined-time FDI observer for the injected false data. It can be observed that the FDI observer’s estimation error converges to zero within 10 s (the predefined convergence time), verifying the effectiveness and rapidity of the proposed predefined-time FDI observer.
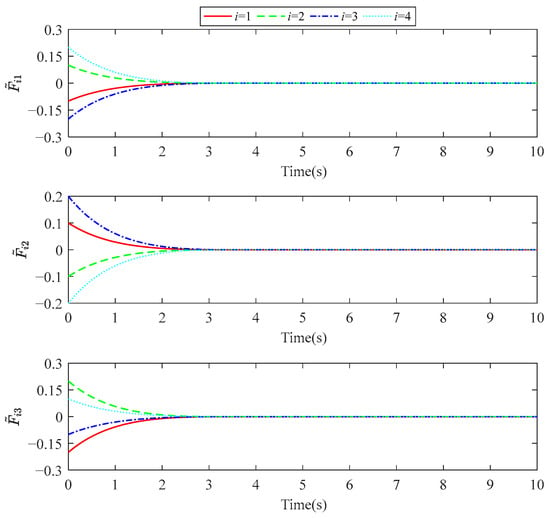
Figure 11.
Estimation error of the predefined-time FDI observer.
Figure 12 presents a comparison of the number of sampling between the proposed dynamic event-triggered control scheme (DETC), and the event-triggered reinforcement learning control (ETC) method proposed in [40]. The ETC method [40] is applied to the USV model in simulation, and all parameters of the multi-USVs are kept consistent with the settings mentioned above. In Figure 12, the blue bar represents the results under the DETC, while the orange-red bar is the results under the ETC. It can be observed that the four USVs have fewer event-trigger numbers under DETC. The dynamic event-triggering strategy proposed in this paper reduces the total number of triggers by 31.5% compared to the ETC in [40].
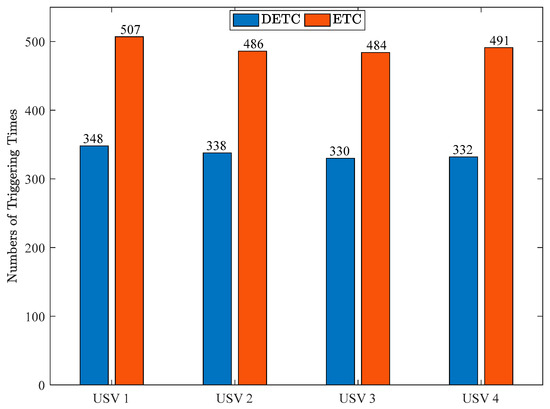
Figure 12.
The event-triggered number used in DETC and ETC.
Figure 13 shows the time response curves of the dynamic event-triggering condition (44) and trigger threshold . It can be observed that the value of the event-triggering condition is always less than or equal to the trigger threshold, and the and gradually converge to zero as the closed-loop system state stabilizes.
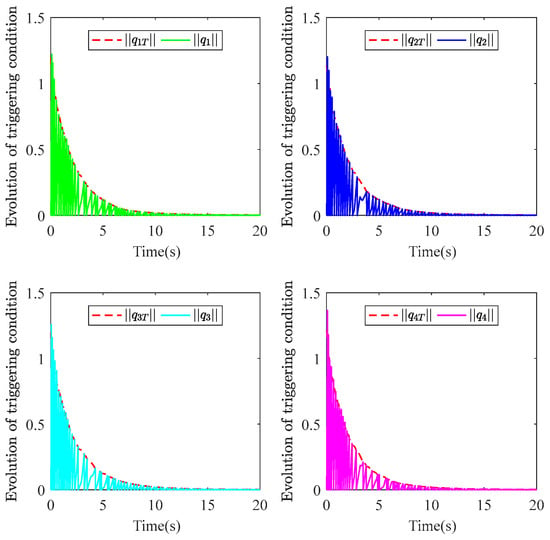
Figure 13.
The results of event-triggering condition and trigger threshold under the DETC.
In summary, the theoretical proofs and simulation results given above validate the effectiveness and superiority of the proposed control method (18). This method can effectively solve the time-varying surrounding control problem of multi-USVs under FDI attacks.
To further validate the engineering applicability of the proposed PPCADP control method, a 3D semi-physical simulation model of multiple USVs was developed using the Simscape simulation platform. The mass is , the inertial matrix of USV is , and the control parameters were kept consistent with those used in the previous Simulink simulations. Figure 14 and Figure 15 show the motion trajectories of the USVs and the time responses of the state tracking errors in the Simscape environment, respectively. These results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed PPCADP in the Simscape-based multi-USVs simulation.
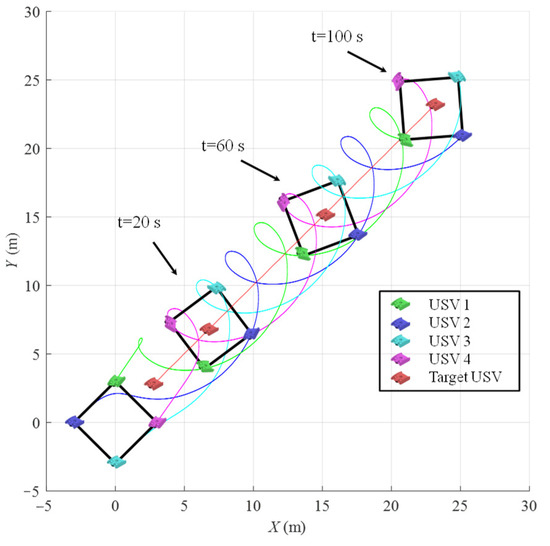
Figure 14.
The collaborative surrounding process of multi-USVs under Simscape simulation.
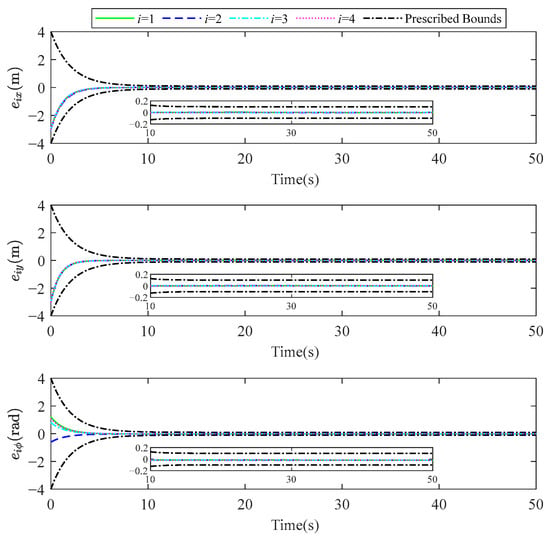
Figure 15.
State tracking errors achieved by PPCADP under Simscape simulation.
Although the above simulation results verify the effectiveness and superiority of the proposed control method, sensitivity analysis was not conducted [45,46]. In future work, we plan to further investigate the reliability of the algorithm under varying simulation parameters through box plots and Monte Carlo simulations.
4. Conclusions
This paper integrated an IDETM with the ADP algorithm and proposed a prescribed-performance time-varying surrounding control scheme for multiple unmanned surface vehicles (multi-USVs) under false data injection (FDI) attacks. First, a predefined-time FDI observer was developed to estimate the injected false data within a user-specified time, thereby removing the conventional assumption of bounded false data. Subsequently, an ADP-based control strategy utilizing the IDETM was designed. Within the learning framework of ADP, a weight update law was constructed without requiring the persistency of the excitation condition, enhancing the generality of the proposed method. Finally, theoretical analysis and numerical simulations demonstrated that the proposed approach enables the pursuer USVs to achieve time-varying surrounding configuration of the target while avoiding Zeno behavior in the DETC. Future work will explore the surrounding control problem of multi-USVs in the presence of actuator failures.
Author Contributions
Y.Z. put forward the general framework of the article and provided the writing ideas, conceived and supervised the research and experiments, and made many constructive comments for the improvement and revision of the article. D.W. consulted the references, performed the validation, and completed the writing and revision of this article. Q.H. guided the structure of the paper and provided suggestions for revisions. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 61673259, in part by the Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai under Grant 25ZR1401159, in part by the Open Project Funds for the Key Laboratory of Space Photoelectric Detection and Perception (Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics), Ministry of Industry and Information Technology under Grant NJ2024027-3, in part by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities under Grant NJ2024027, also in part by the Shanghai Key Laboratory of Intelligent Information Processing, Fudan University. Grant No. IIPL-2025-RD5-01.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in this article (tables and figures).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the College of Information Engineering and the Institute of Logistics Science and Engineering of Shanghai Maritime University for their support. The author would also like to thank the anonymous reviewers for their helpful suggestions and comments to improve the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| USVs | Unmanned surface vehicles |
| FDI | False data injection |
| PPC | Prescribed performance control |
| DET | Dynamic event-triggering |
| PTO | Predefined-time observer |
| MASs | Multi-agent systems |
| FTESO | Fixed-time extended state observer |
| CLSs | Closed-loop systems |
| RL | Reinforcement learning |
| NN | Neural network |
| SMC | Sliding mode control |
| PE | Persistent excitation |
| IDETM | improved dynamic event-triggered mechanism |
| PPCADP | Prescribed-performance control ADP |
| TADP | Traditional ADP |
| DETC | Dynamic event-triggered control |
| Symbols and terms. | |
| The directed communication network of USVs | |
| The node set among the directed graph | |
| The edge set among the directed graph | |
| The adjacency matrix of multi-USVs, | |
| The connection weight between the ith USV and jth USV | |
| The in-degree matrix of USVs | |
| The Laplacian matrix of USV | |
| The Laplacian matrix of digraph | |
| The state of ith USV | |
| the state of target USV | |
| The position state of ith USV | |
| The yaw angle of ith USV | |
| The surge, sway, yaw velocities | |
| The velocity vector of ith USV | |
| The control input | |
| The inertia matrix | |
| The skew-symmetric Coriolis force matrix | |
| The damping matrix | |
| ) | |
| The false information injected by the attacker | |
| The FDI attacks probability matrix | |
| Random variables that follow the Bernoulli distribution | |
| The time-varying surrounding function | |
| The RL-based controller | |
| The feedforward control law | |
| The estimation error | |
| The position error of ith USV relative to its neighbor | |
| The velocity tracking error of ith USV relative to its neighbor | |
| The prescribed performance function | |
| The sampling error of ith USV | |
| The performance index function for the ith USV | |
References
- Zhao, J.; Li, X.; Yu, X.; Wang, H. Finite-Time Cooperative Control for Bearing-Defined Leader-Following Formation of Multiple Double-Integrators. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2022, 52, 13363–13372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.-B.; Zhang, H.-T. Bearing-Only Motional Target-Surrounding Control for Multiple Unmanned Surface Vessels. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 69, 3988–3997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, B.; Wang, B.; Fan, H.; Liu, L.; Hu, H.; Wang, Y. Fully distributed prescribed performance formation control for UAVs with unknown maneuver of leader. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2022, 130, 107886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.-B.; Zhang, H.-T.; Wang, J. Multiple-Target Surrounding and Collision Avoidance With Second-Order Nonlinear Multiagent Systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 68, 7454–7463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skjetne, R.; Fossen, T.I.; Kokotović, P.V. Adaptive maneuvering, with experiments, for a model ship in a marine control laboratory. Automatica 2005, 41, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Wang, M.; Dai, S.-L.; Luo, F. Leader–Follower Formation Control of USVs With Prescribed Performance and Collision Avoidance. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2019, 15, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Fan, Y.; Liu, J. Distributed fixed-time formation tracking control for multiple underactuated USVs with lumped uncertainties and input saturation. ISA Trans. 2024, 154, 186–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhu, D.; Pang, W.; Luo, C. A Novel Obstacle Avoidance Consensus Control for Multi-AUV Formation System. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2023, 10, 1304–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X. Fault tolerant finite-time leader–follower formation control for autonomous surface vessels with LOS range and angle constraints. Automatica 2016, 68, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.; Zhang, Y. Time-Varying Formation-Surrounding Control for Multiquadrotors Pursuit–Evasion Games With Disturbances and Collision Avoidance. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2025, 61, 522–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Zhang, H.-T.; Ding, Y.; Ren, W. Event-Triggered Surrounding Formation Control of Multiagent Systems for Multiple Dynamic Targets. IEEE Trans. Control Netw. Syst. 2023, 10, 752–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Ren, W. Sampled-data containment control for double-integrator agents with dynamic leaders with nonzero inputs. Syst. Control Lett. 2020, 139, 104673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, H.; Ahn, C.K. Reinforcement Learning-Based Optimal Tracking Control of an Unknown Unmanned Surface Vehicle. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2021, 32, 3034–3045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, G.; Dong, Q. Adaptive dynamic programming-based adaptive-gain sliding mode tracking control for fixed-wing unmanned aerial vehicle with disturbances. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control. 2023, 33, 1065–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechlioulis, C.P.; Rovithakis, G.A. Robust Adaptive Control of Feedback Linearizable MIMO Nonlinear Systems With Prescribed Performance. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2008, 53, 2090–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, X. Data-Driven Performance-Prescribed Reinforcement Learning Control of an Unmanned Surface Vehicle. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2021, 32, 5456–5467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Shao, X.; Guo, L. Adaptive Fault-Tolerant Attitude Tracking Control of Spacecraft With Prescribed Performance. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2018, 23, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, B.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Z.; Cao, L. Fixed-Time Fault-Tolerant Optimal Attitude Control of Spacecraft With Performance Constraint via Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2023, 59, 7715–7724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Li, B.; Yang, Y.; Xiao, B.; Ran, D. Leader-following output-feedback consensus for second order multiagent systems with arbitrary convergence time and prescribed performance. ISA Trans. 2023, 141, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Sheng, C.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, C. Anti-saturation distributed fixed-time prescribed performance sliding mode formation control based on FXESO for uncertain USVs. Ocean Eng. 2025, 318, 120101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Chen, Y.; Tian, X.; Mai, Q. Reinforcement learning control for USVs using prescribed performance sliding surfaces and an event-triggered strategy. Ocean Eng. 2024, 306, 118045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, K.; Li, K.; Li, Y. Finite-Time Formation Tracking Control for USVs Based on Dynamic Event-triggered Mechanism. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Unmanned Systems (ICUS), Hefei, China, 13–15 October 2023; pp. 1148–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Che, W.; Deng, C. Event-triggered model-free adaptive control for nonlinear cyber-physical systems with false data injection attacks. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 2022, 32, 2442–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Zhang, Y. Secrecy Rate Optimization for Multi-User Secure Communication Assisted by Intelligent Reflecting Surfaces (IRS) Under Imperfect CSI Conditions. Trans. Emerg. Telecommun. Technol. 2025, 36, 70117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, W.; Miao, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Z.-G.; Wang, Y. Event-Triggered Finite-Time Formation Control for Networked Nonholonomic Mobile Robots Under Denial-of-Service Attacks. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2023, 10, 354–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Gao, X.; Zhong, W.; Qian, F. Secure impulsive synchronization control of multi-agent systems under deception attacks. Inf. Sci. 2018, 459, 354–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, X.; Gu, Z.; Lu, Q. Memory-event-triggered consensus control for multi-UAV systems against deception attacks. ISA Trans. 2023, 139, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Mendis, G.J.; Wei, J. Real-Time Detection of False Data Injection Attacks in Smart Grid: A Deep Learning-Based Intelligent Mechanism. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2017, 8, 2505–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Mo, Z.; Han, Q.-L.; Qian, F. Secure impulsive synchronization in Lipschitz-type multi-agent systems subject to deception attacks. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2020, 7, 1326–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahoun, A.; Arafa, M. Cooperative control for cyber–physical multi-agent networked control systems with unknown false data-injection and replay cyber-attacks. ISA Trans. 2021, 110, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, A.; Mohammadi, A.; Asif, A.; Hou, M.; Plataniotis, K.N. Fault-Tolerant Periodic Event-Triggered Consensus Under Communication Delay and Multiple Attacks. IEEE Syst. J. 2022, 16, 6338–6349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, S.; Yue, D. Resilient Output Formation Containment of Heterogeneous Multigroup Systems Against Unbounded Attacks. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2022, 52, 1902–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, S.; Yue, D. Resilient Containment of Multigroup Systems Against Unknown Unbounded FDI Attacks. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 69, 2864–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.-W.; Liu, G.-P. Predictive sliding-mode control of networked high-order fully actuated systems under random deception attacks. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2023, 66, 190204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.-W.; Liu, G.-P. Predictive Sliding-Mode Control for Networked High-Order Fully Actuated Multiagents Under Random Deception Attacks. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2024, 54, 484–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhang, W.; He, W.; Li, C.; Ge, S.S. Two-Layer Distributed Formation-Containment Control of Multiple Euler–Lagrange Systems by Output Feedback. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2019, 49, 675–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Li, C.; Xiao, B.; Guo, Y. Formation-containment control of networked Euler–Lagrange systems: An event-triggered framework. ISA Trans. 2019, 86, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, H.; Zhang, Y. Reinforcement learning-based formation-surrounding control for multiple quadrotor UAVs pursuit-evasion games. ISA Trans. 2024, 145, 205–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Huang, H.; Xiao, B.; Dong, K. Command-filtered incremental backstepping attitude control of spacecraft with predefined-time stability. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2024, 155, 109552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, S.; Luo, B.; Liu, D. Event-Triggered Adaptive Dynamic Programming for Zero-Sum Game of Partially Unknown Continuous-Time Nonlinear Systems. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2020, 50, 3189–3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Gong, W.; Xiao, B.; Yang, Y. Distributed prescribed-time leader-following formation control for second-order multi-agent systems with mismatched disturbances. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 2023, 33, 9781–9803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.; Zhang, Y. Dynamic Event-Triggering Formation-Surrounding Control for Multiagent Pursuit-Evasion Games under DoS Attacks. IEEE Internet Things J. 2025, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Li, H. Distributed Model Predictive Contouring Control of Unmanned Surface Vessels. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2024, 71, 13012–13019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Guo, G. Fixed-time sliding mode formation control of AUVs based on a disturbance observer. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2020, 7, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owais, M.; Moussa, G.S. Global sensitivity analysis for studying hot-mix asphalt dynamic modulus parameters. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 413, 134775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idriss, L.K.; Owais, M. Global sensitivity analysis for seismic performance of shear wall with high-strength steel bars and recycled aggregate concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 411, 134498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).