Study on the Influence of Fluid Fields on the Impact Force of Ships Colliding with Bridges
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Numerical Simulation of Container Ship and Bridge Collision
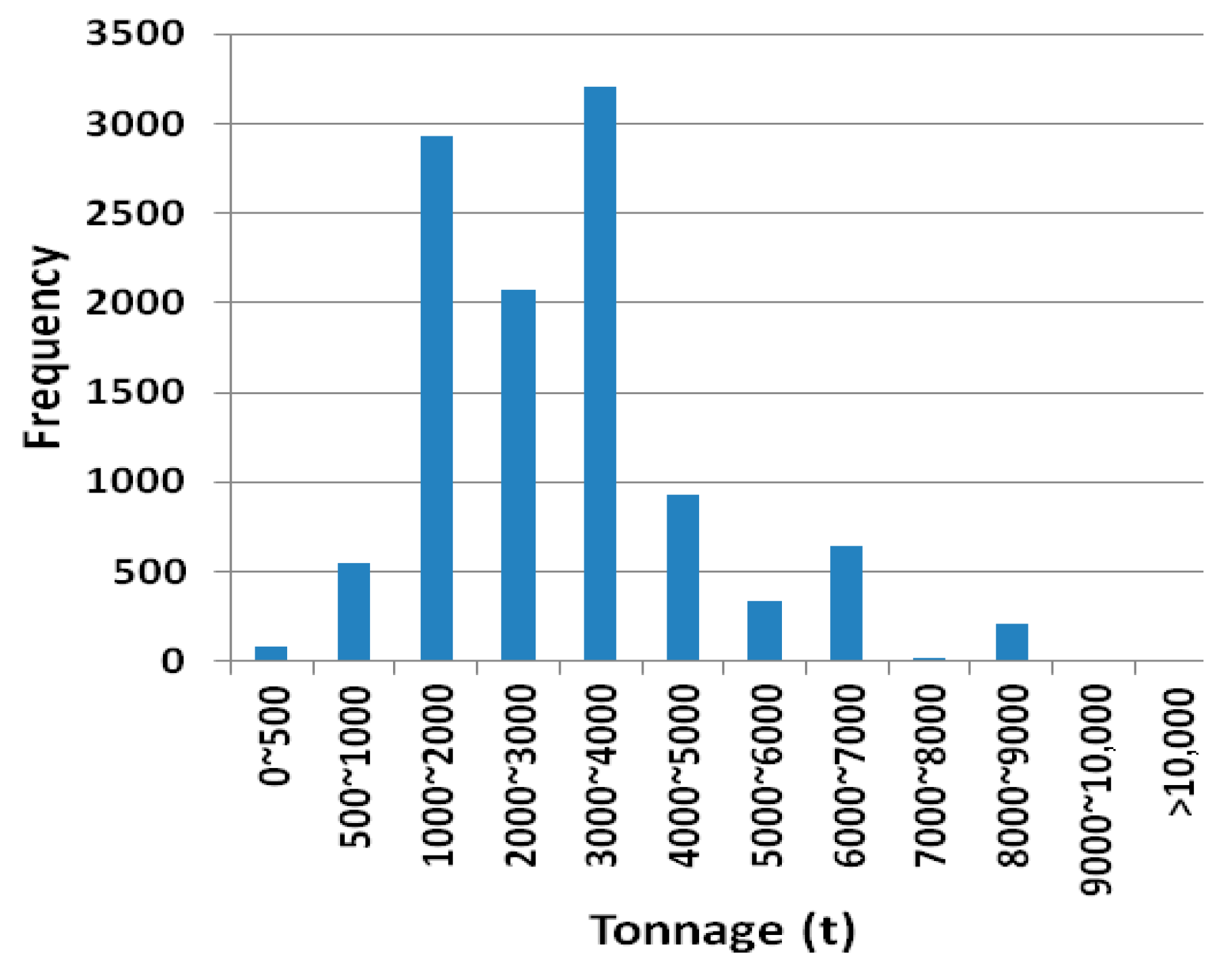
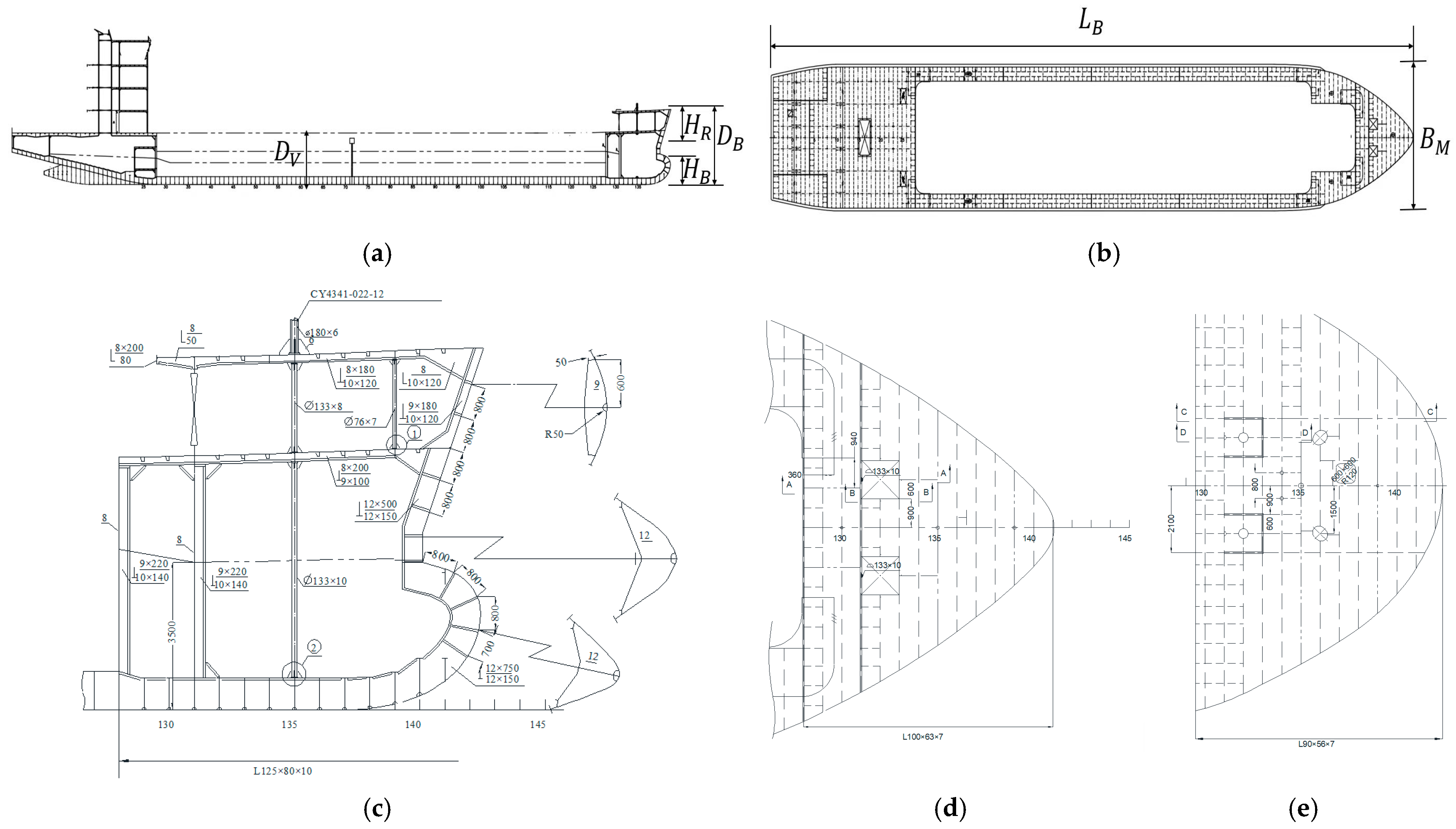
2.1. Description of the Container Ship
2.2. Finite-Element Models
2.3. Modeling of the Water Surrounding the Ship
2.3.1. Constant Added-Mass Method (CAM)
- (1)
- Theoretical calculation: A theoretical analysis is conducted based on fluid-mechanics principles and the geometric shape of the object, and the additional mass coefficient is estimated in conjunction with boundary conditions.
- (2)
- Empirical formulae and charts: Empirical formulae or charts from industry standard literature and research findings are used. These resources provide reference values for the additional mass coefficient of objects of different types and sizes at various speeds and attitudes.
- (3)
- Numerical simulation: Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) with high resolution is used to simulate the dynamic behavior of the ship in fluid to determine the additional mass effect.
- (4)
- Experiment: Using a physical model experiment in a tank to determine the added-mass coefficient by measuring the acting forces during motion, see Table 1.
2.3.2. Fluid–Structure Interaction Method (FSI)
2.4. Load Conditions
3. Numerical Results Analysis
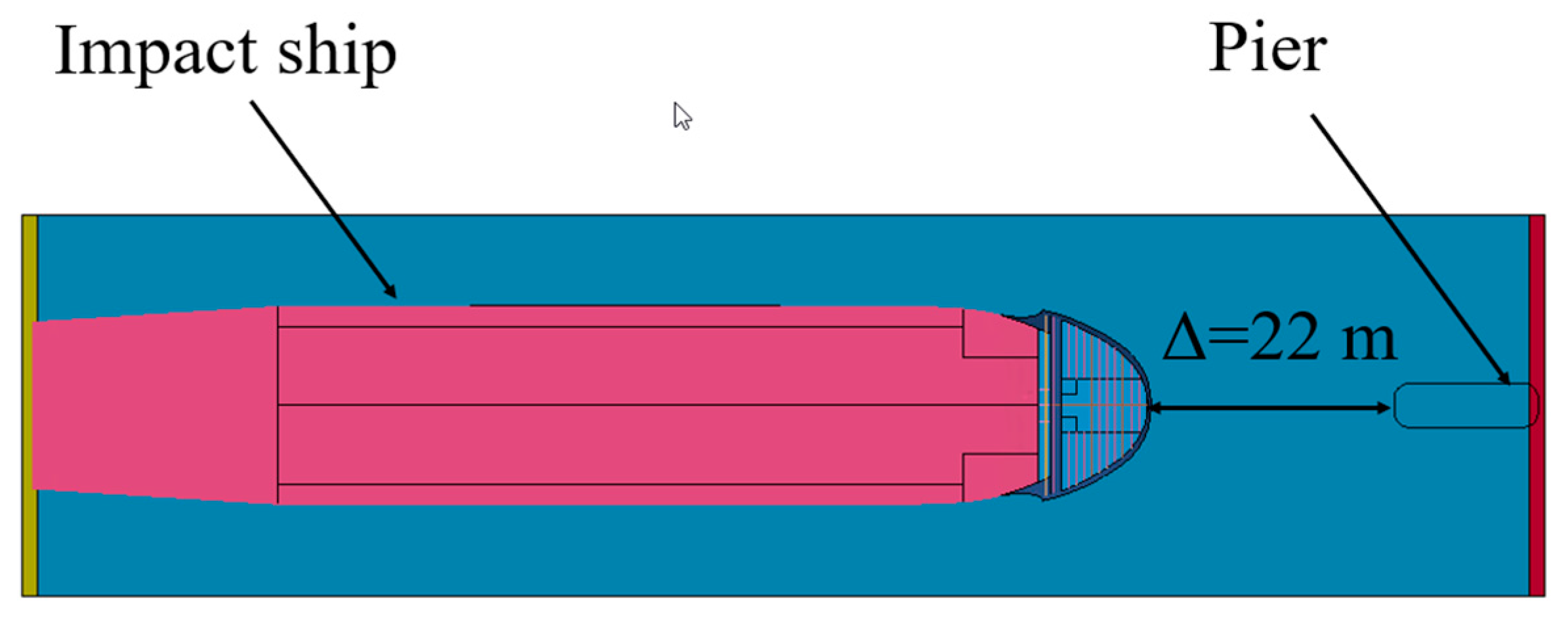
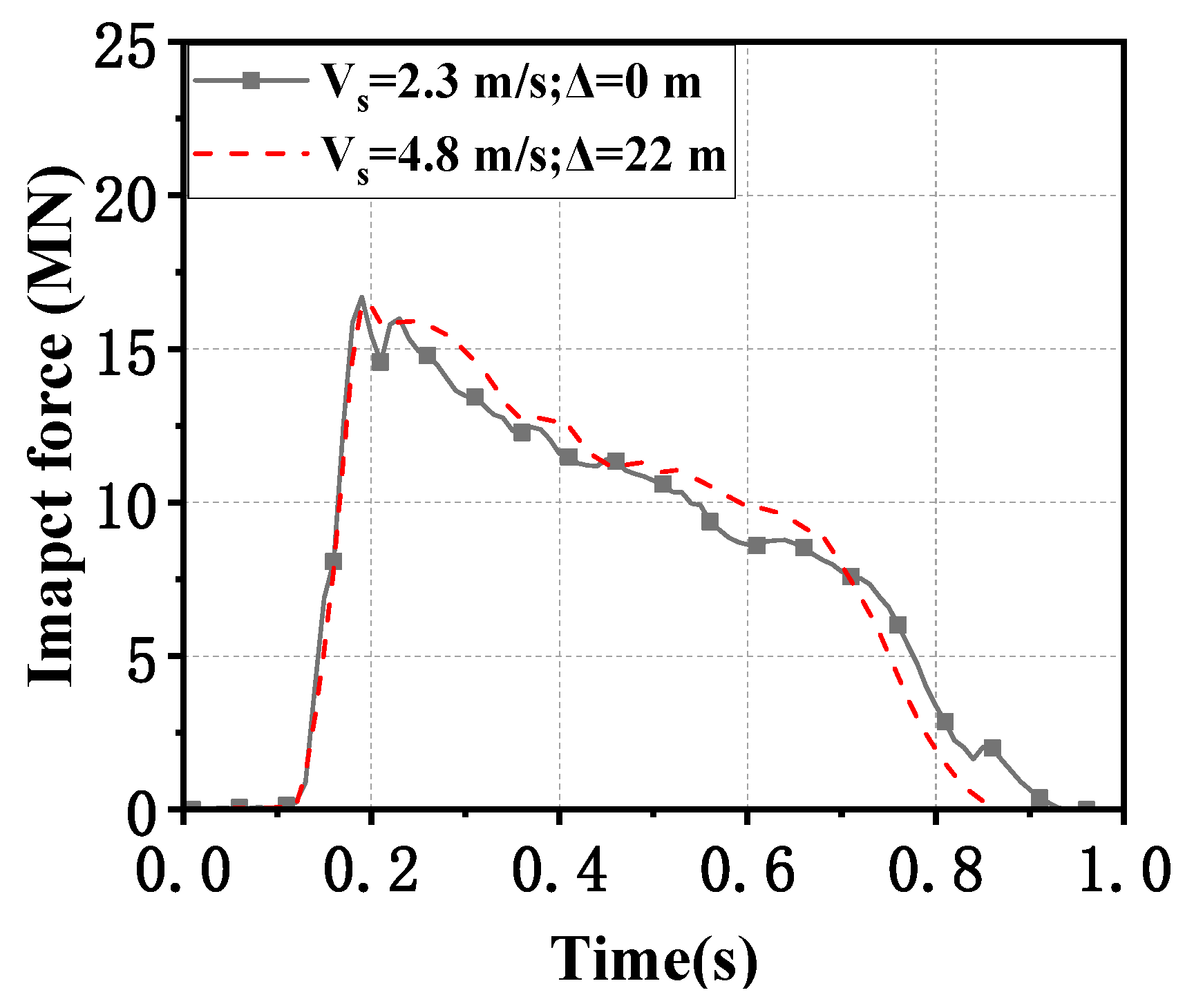
3.1. Effect of Initial Distance
3.2. Effect of Impact Velocity
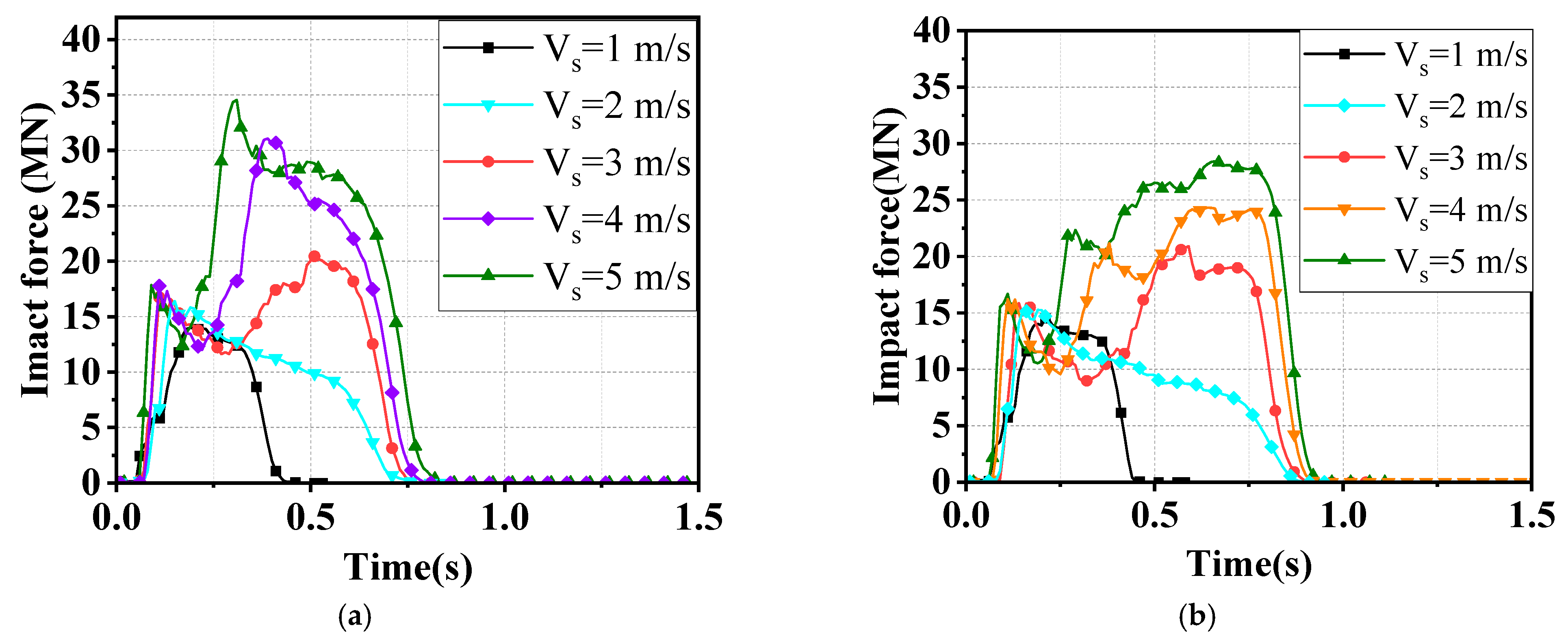
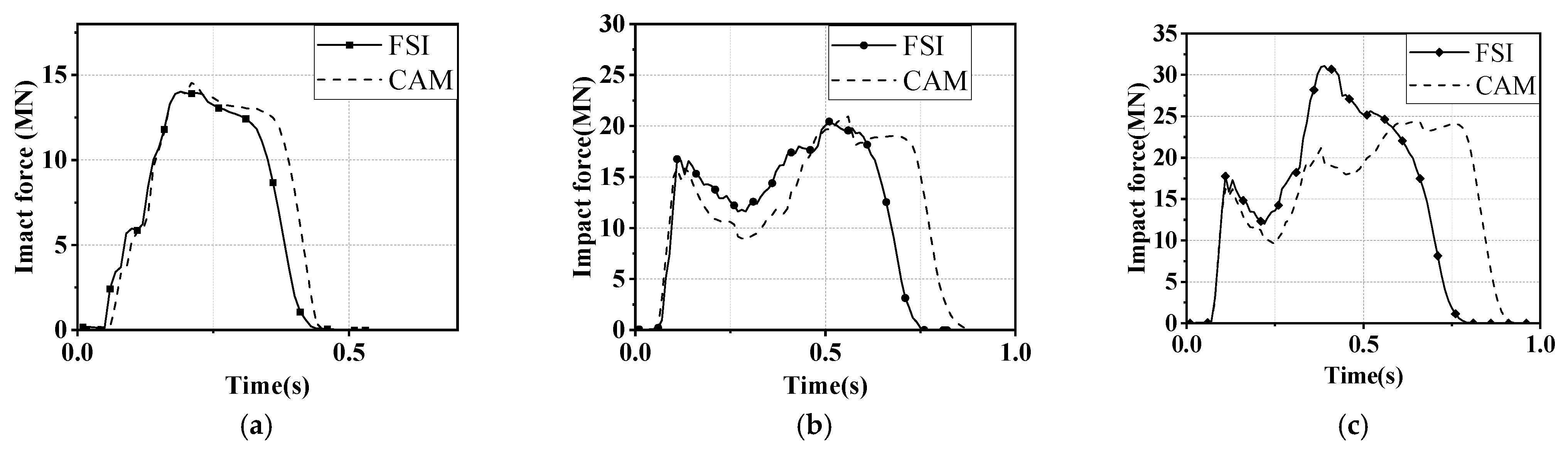
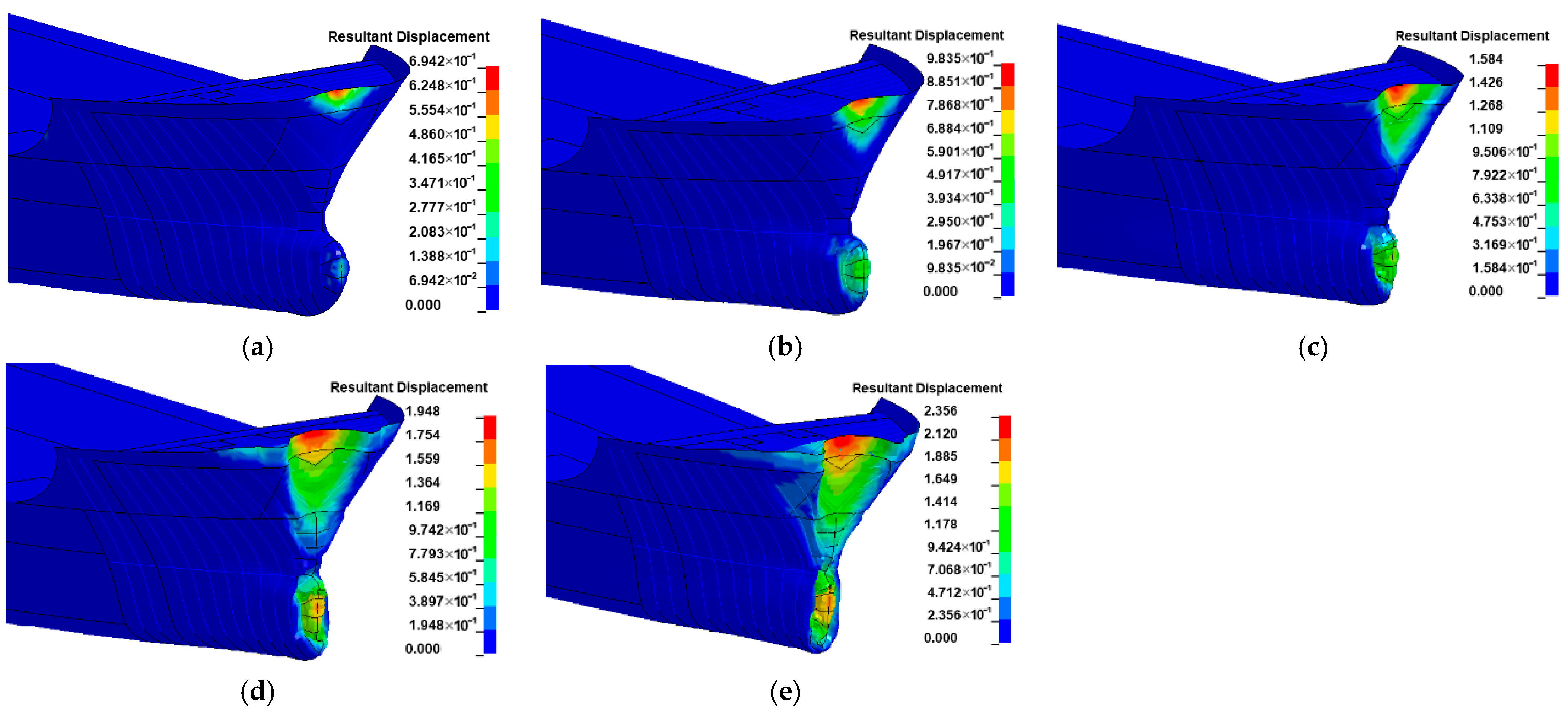
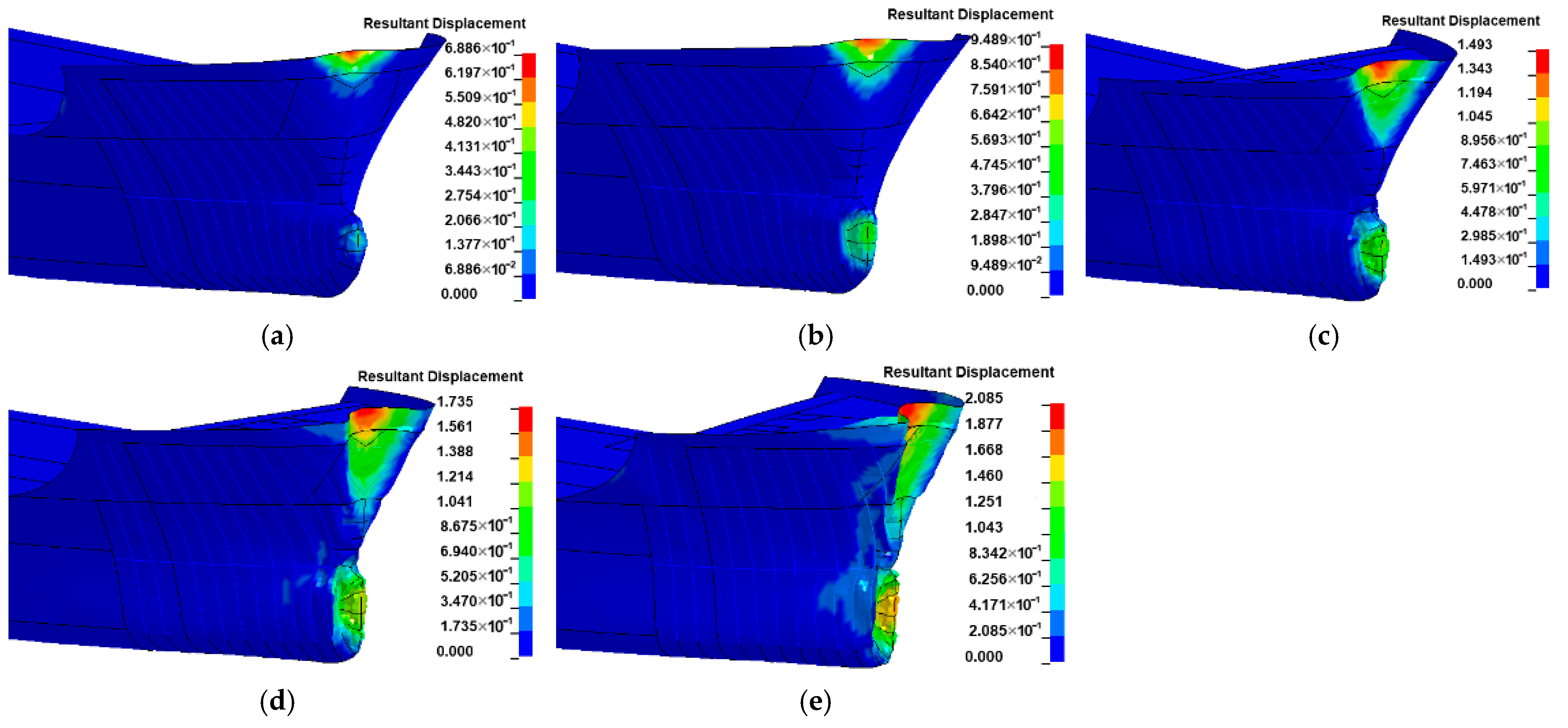
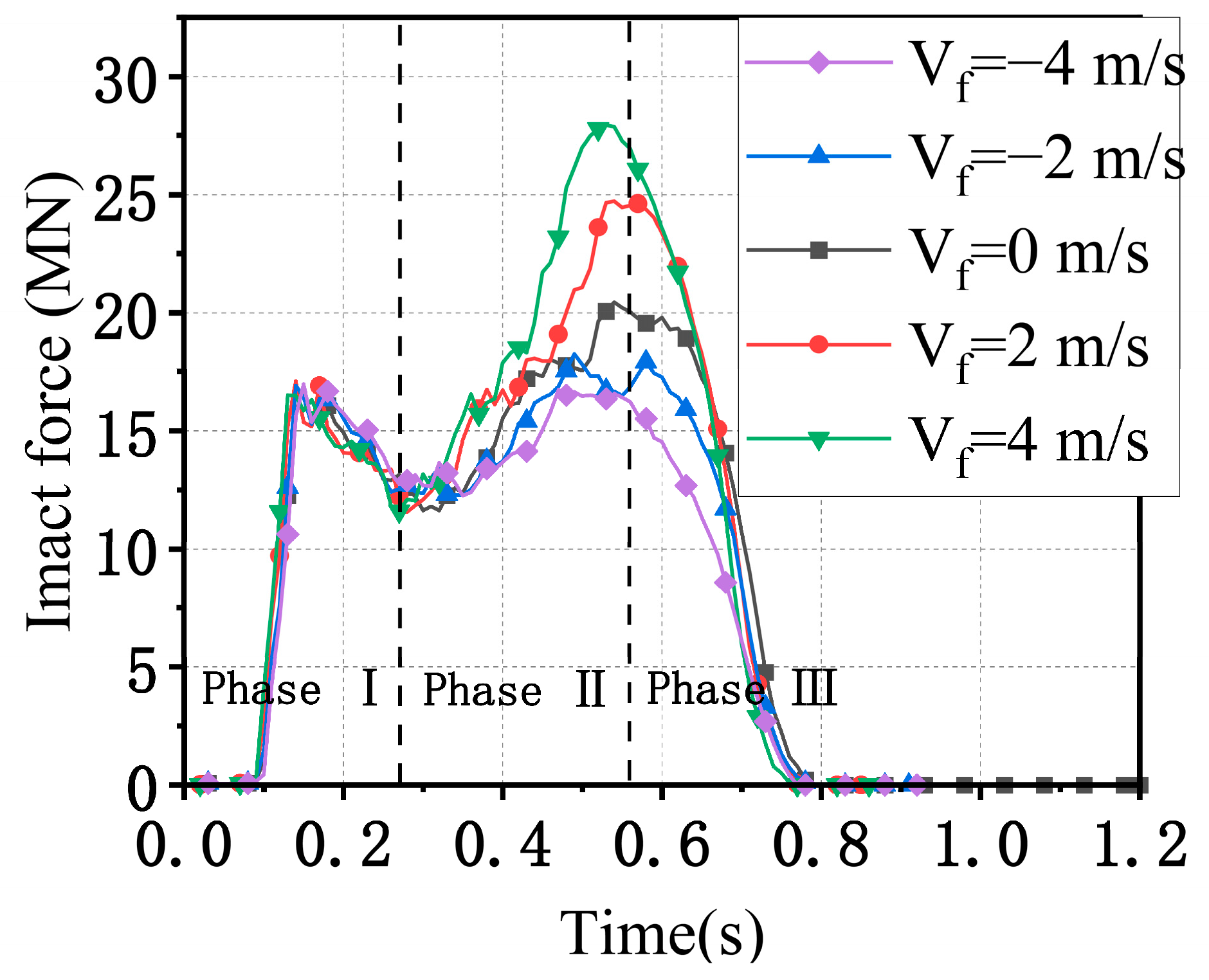
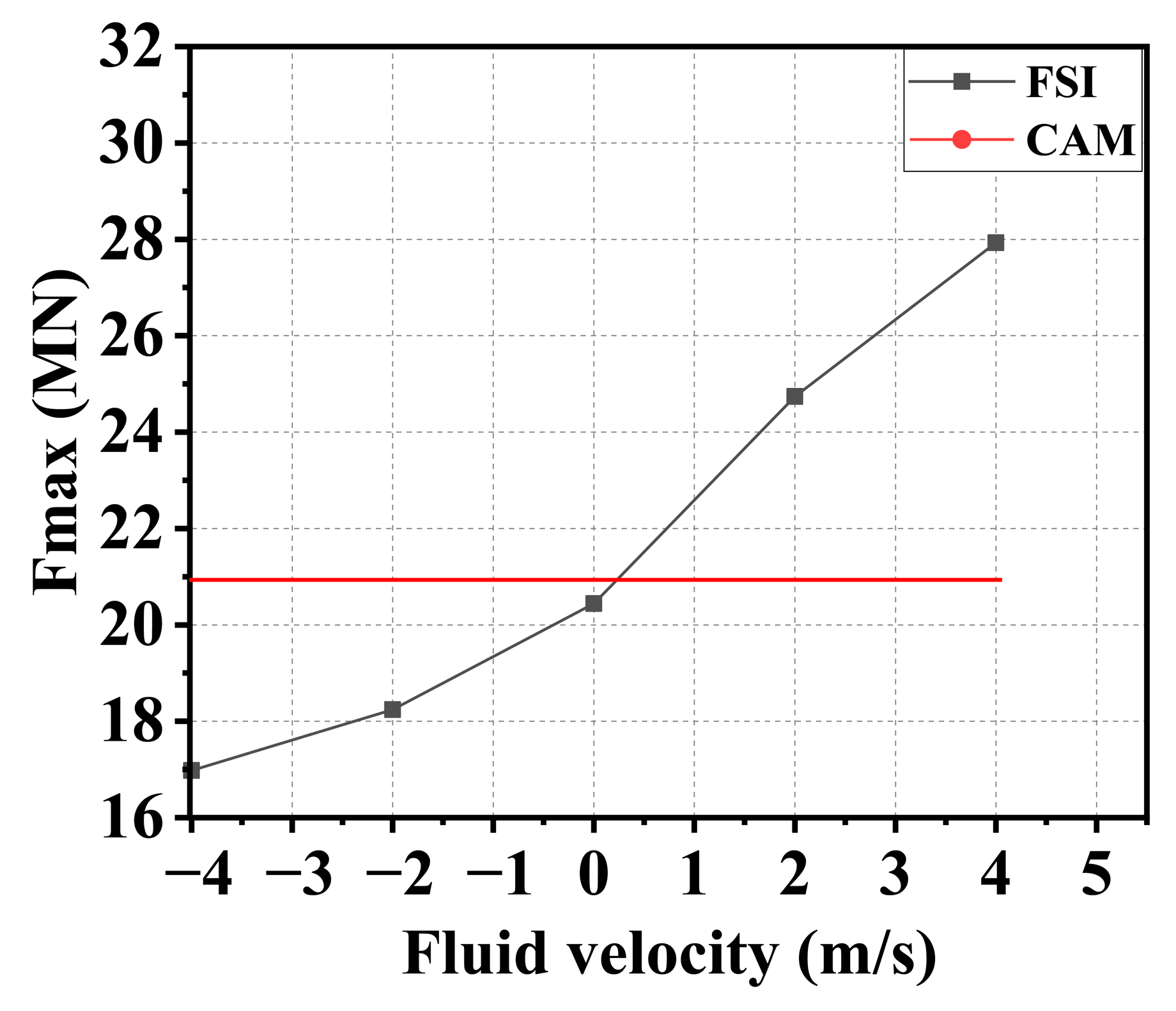
3.3. Effect of Water-Flow Velocity
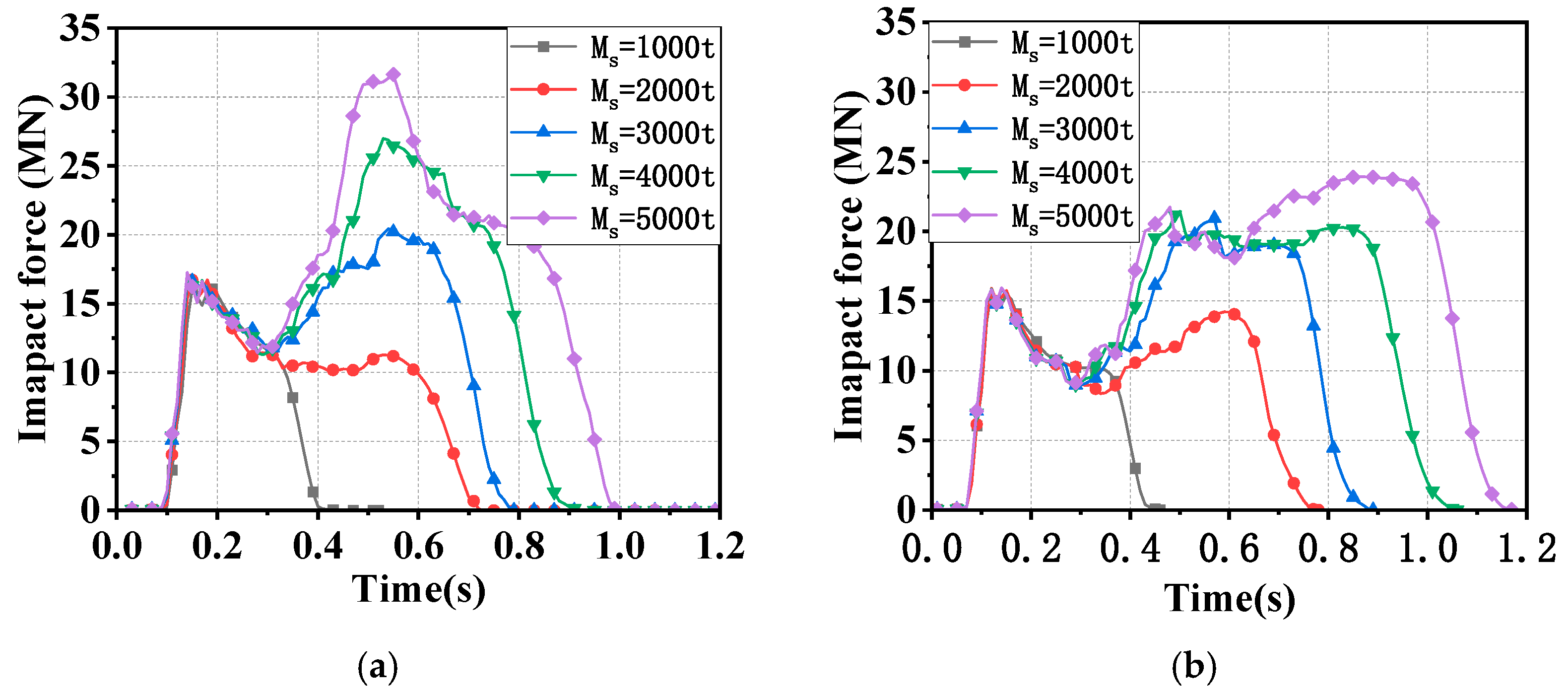
3.4. Effect of Ship Displacement Weight
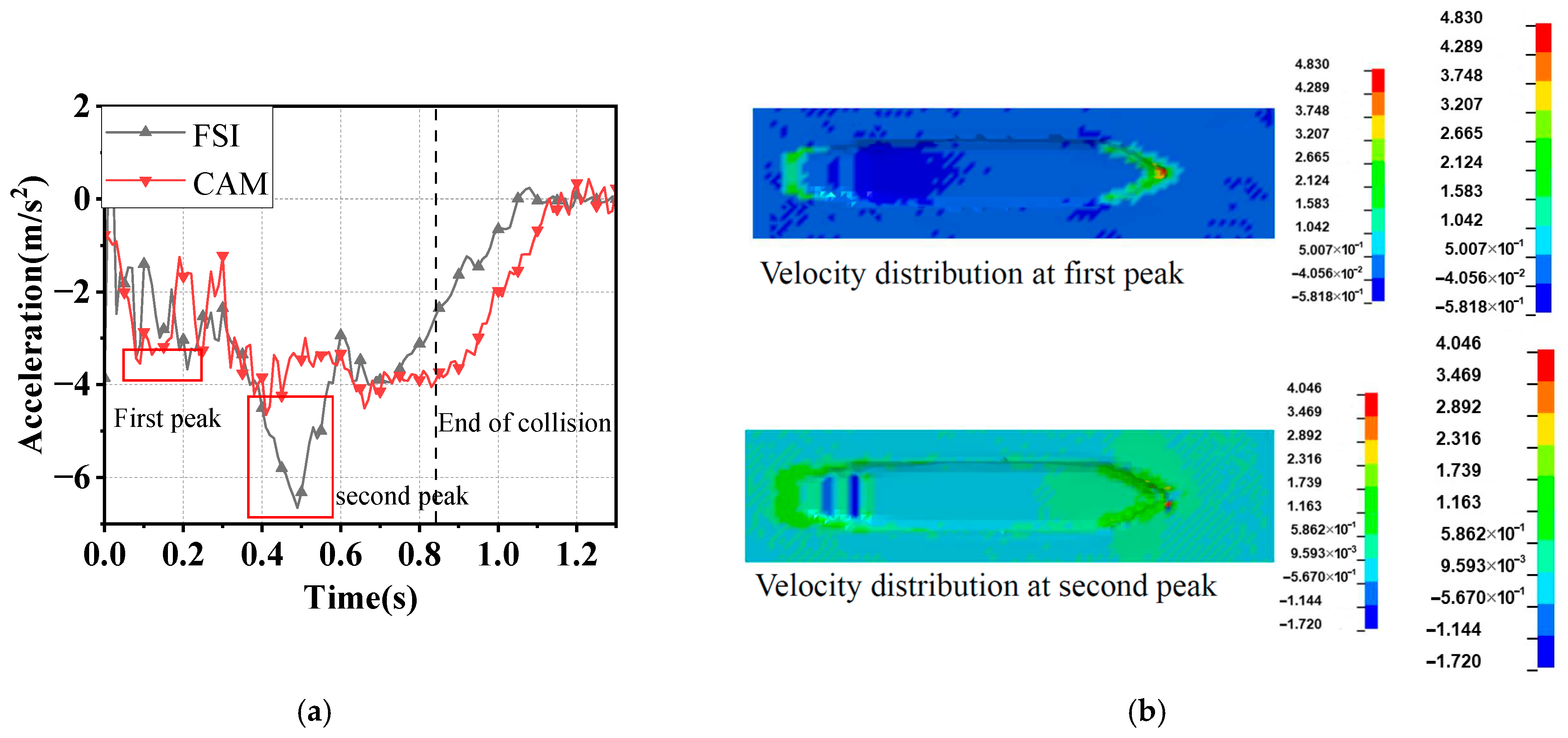
3.5. Influence of Kinematic Energy
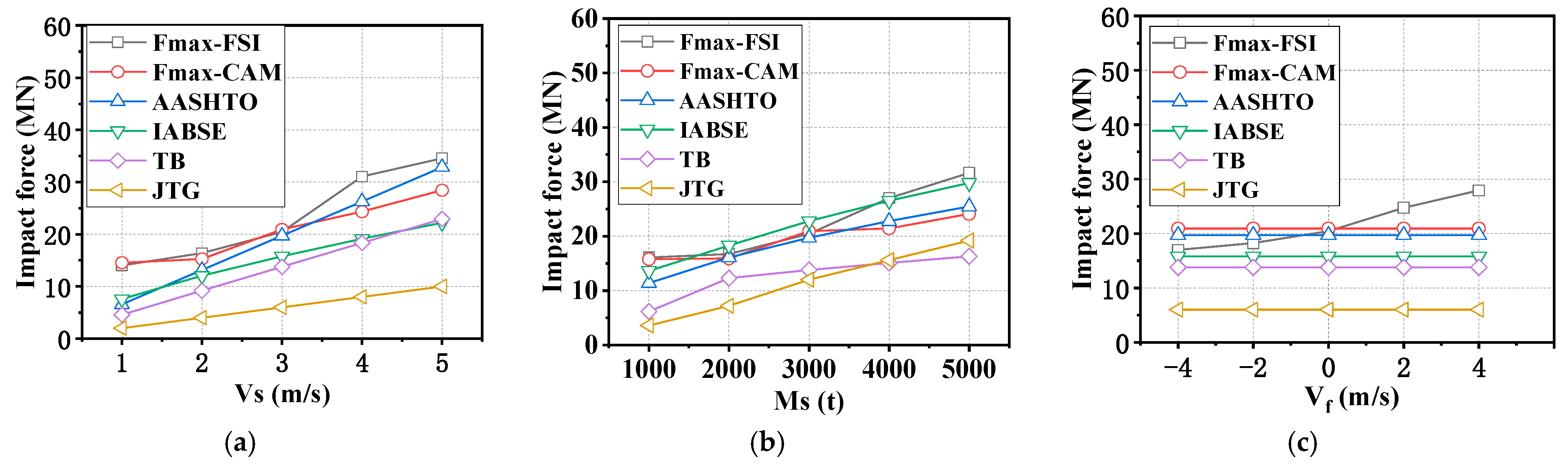
4. Impact Force with Various Methods
4.1. Empirical Formulae
4.2. Comparative Analysis of Impact Forces
5. Conclusions
- The wave and current of water caused by the ship’s movement during sailing slightly influence the impact force; hence, the initial position of the ship can be close to the bridge pier to save computation time.
- The velocity of the water current larger than 3 m/s significantly affects the impact force of the ship, which should be considered using the FSI method instead of the CAM method. Further experiments considering the influence of water current are suggested to be conducted to verify this conclusion.
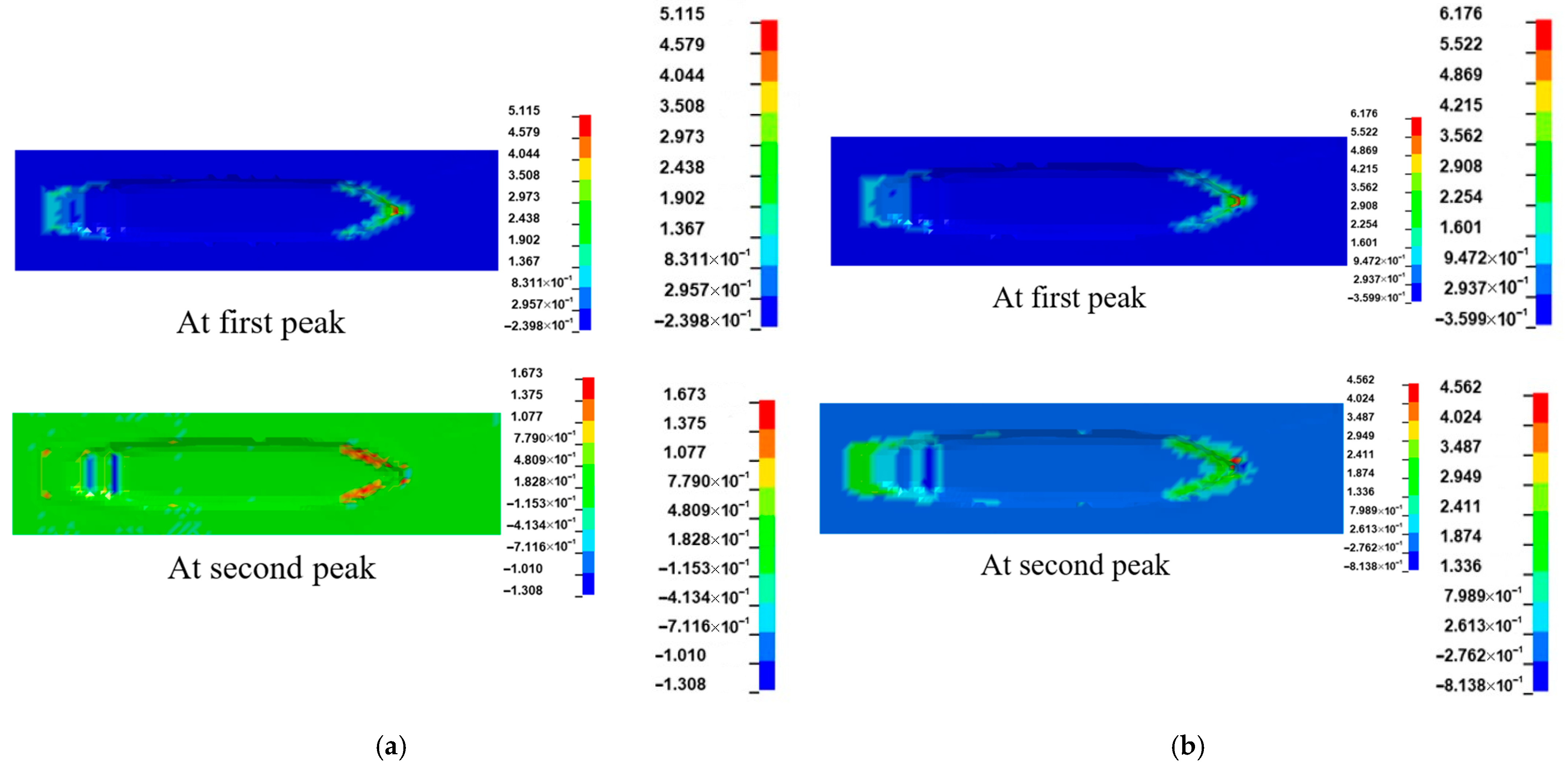
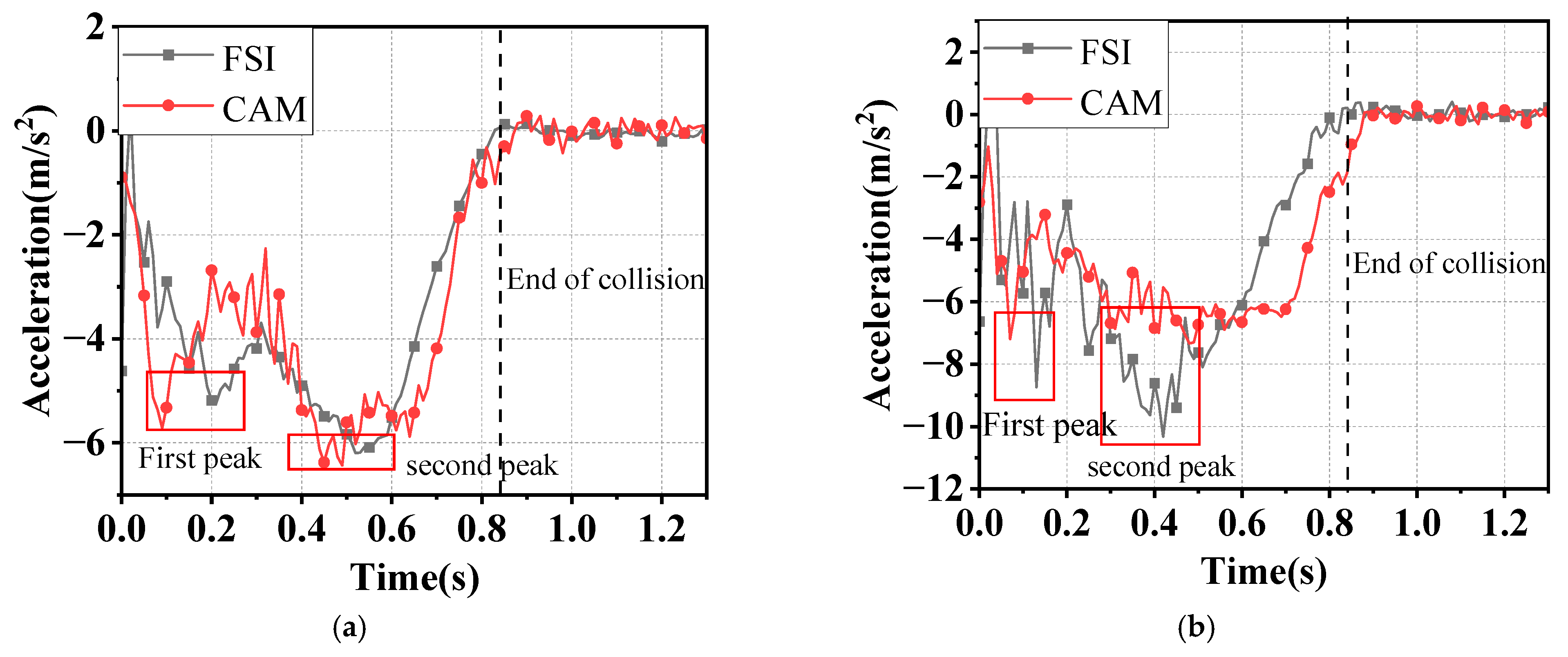
- Since the water could push the ship at the stern and prevent the ship at the bow during impact at the same time, the added water mass of a ship–bridge collision is not constant. Since the FE analysis with the CAM method is not able to consider the hydrodynamic effect, to save computation time, it is suggested that limitation conditions with a small velocity of the ship (<3 m/s) and water flow (<2 m/s) be adopted.
- When the ship is in still water, the impact forces assessed by the AASHTO requirement are the closest to those of the numerical results. For bridge anti-collision design, the existing requirement formulae for predicting impact force need to be improved to consider the influence of water-flow velocity.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Perera, L.P.; Soares, C.G. Collision risk detection and quantification in ship navigation with integrated bridge systems. Ocean Eng. 2015, 109, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, O.D. Ship Collision with Bridges: The Interaction Between Vessel Traffic and Bridge Structures; IABSE: Copenhagen, Denmark, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Copenhagen, I.C. Ship Collision with Bridges and Offshore Structures; IABSE: Zurich, Switzerland, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, N. Structural Aspects of Ship Collisions; Structural crashworthiness: London, UK, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Minorsky, V.U. An Analysis of Ship Collisions with Reference to Protection of Nuclear Power Plants; Sharp (George G.) Inc. New York: New York, NY, USA, 1959. [Google Scholar]
- Woisin, G. Die Kollisionsversuche Der Gkss; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Carlebur, A.F.C. Full-scale collision tests. Saf. Sci. 1995, 19, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, Y.; Hao, H. Laboratory tests and numerical simulations of barge impact on circular reinforced concrete piers. Eng. Struct. 2013, 46, 593–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guide Specifications and Commentary for Vessel Collision Design of Highway Bridges, 2nd ed.; AASHTO: Washington, DC, USA, 2009.
- TB 10002.1; Fundamental Code for the Design of Railway Bridge and Culvert. Railway Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2005.
- JTG D60; General Code for the Design of Railway Bridge and Culvert. Communications Press: Beijing, China, 2004.
- Pan, J.; Huang, S.W.; Xu, M.C. Numerical analysis for impact force in high-energy ship-bridge pier collision. In Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering, Busan, Republic of Korea, 19–24 June 2016; p. 55119. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, W.; Shen, D.; Huang, X.; Sun, Y. Reinforced concrete bridge structures under barge impacts: FE modeling, dynamic behaviors, and UHPFRC-based strengthening. Ocean Eng. 2020, 216, 108116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantrales, G.C.; Consolazio, G.R.; Wagner, D. Experimental and analytical study of high-level barge deformation for barge–bridge collision design. J. Bridge Eng. 2016, 21, 04015039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.J.; Song, Y.C.; Wang, W. Calibrations of numerical models by experimental impact tests using scaled steel boxes. Eng. Struct. 2018, 173, 481–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Bu, L.; Cao, C. Code formulas for ship-impact design of bridges. J. Bridge Eng. 2012, 17, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholipour, G.; Zhang, C.; Mousavi, A.A. Nonlinear numerical analysis and progressive damage assessment of a cable-stayed bridge pier subjected to ship collision. Mar. Struct. 2020, 69, 102662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, P.; Harik, I.E. One-dimensional model for multi-barge flotillas impacting bridge piers. Comput.-Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2008, 23, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harik, I.; Yuan, P.; Davidson, M. Equivalent Barge and Flotilla Impact Forces on Bridge Piers; Kentuky Transportation Center, College of Engineering, University of Kentuky: Lexington, KY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Motora, S. On the measurement of added mass and added moment of inertia for ship motions. J. Zosen Kiokai 1959, 105, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, M.J. Dynamics of ship collisions. Ocean Eng. 1982, 9, 295–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, P.T.; Zhang, S. On impact mechanics in ship collisions. Mar. Struct. 1998, 11, 429–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Storheim, M.; Amdahl, J. Laboratory experiments on shared-energy collisions between freshwater ice blocks and a floating steel structure. Ships Offshore Struct. 2017, 12, 530–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagnon, R.E.; Wang, J. Numerical simulations of a tanker collision with a bergy bit incorporating hydrodynamics, a validated ice model and damage to the vessel. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2012, 81, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Ma, J.; Huang, Y. Fluid-structure interaction analysis of ship-ship collisions. Mar. Struct. 2017, 55, 121–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.L.; Wu, H.; Fang, Q. Impact force models for bridge under barge collisions. Ocean Eng. 2022, 259, 111856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Fan, W.; Sha, Y. Fluid-structure interaction analysis of oblique ship-bridge collisions. Eng. Struct. 2023, 274, 115129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Wang, Y.; Huang, S.; Xu, M.C. Statistical Investigation of the Influential Parameters for Probability Analysis of Ship-bridge Collision Based on AIS Data. In Proceedings of the International Ocean and Polar Engineering Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 25 June 2017. ISOPE-I-17-714. [Google Scholar]
- Standard, N. Design of Steel Structures; Standards Norway: Oslo, Norway, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Alsos, H.S.; Amdahl, J. On the resistance of tanker bottom structures during stranding. Mar. Struct. 2007, 20, 218–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, N. Structural Impact; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sha, Y.; Hao, H. Nonlinear finite element analysis of barge collision` with a single bridge pier. Eng. Struct. 2012, 41, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Wang, T.; Huang, S.W. Investigation of assessment method of axial crushing force of rake bow for bridge against ship collision. Ocean Eng. 2023, 269, 113498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Kim, E.; Amdahl, J. A comparative analysis of the fluid-structure interaction method and the constant added mass method for ice-structure collisions. Mar. Struct. 2016, 49, 58–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eurocode 1: Actions on structures-Part 1–7: General actions-Accidental actions. Eur. Comm. Stand. 2006, 54, 18–20.
- Zhao, H.O. LS-DYNA Dynamics Analysis Guide; The Publishing House of Ordnance Industry: Beijing, China, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.H.; Xiao, Q.Y.; Pan, J.; Xu, M.C. Nonlinear dynamics of ship-bridge pier collisions using FSI method. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Collision and Grounding of Ships and Offshore Structures, Shanghai, China, 16–19 September 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Consolazio, G.R.; Cook, R.A.; McVay, M.C. Barge Impact Testing of the St. George Island Causeway Bridge, Phase III: Physical Testing and Data Interpretation, Engineering and Industrial Experiment Station; University of Florid: Gainesville, FL, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]







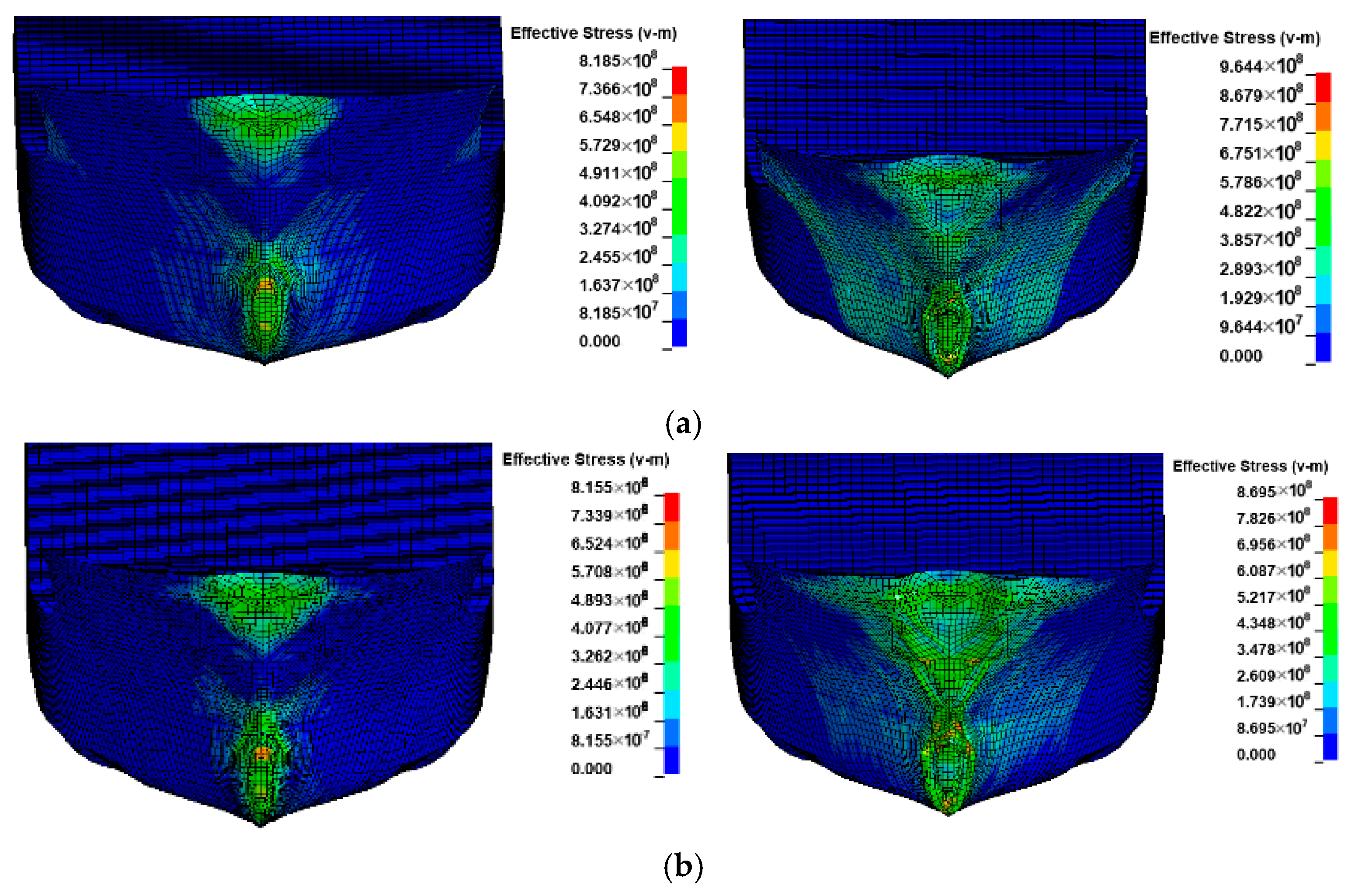

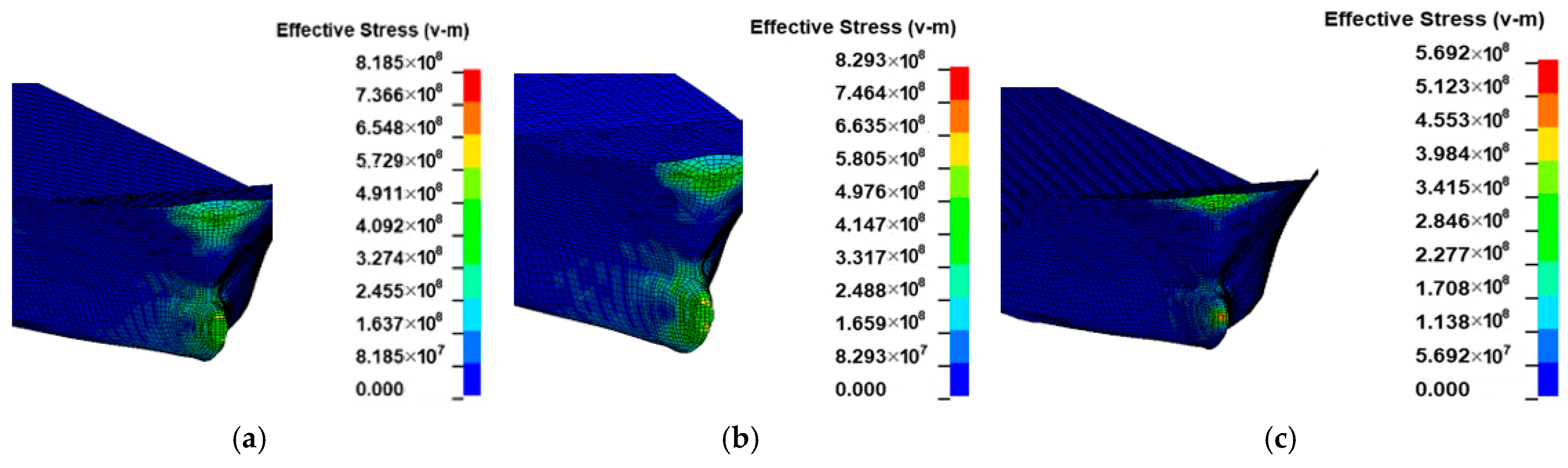
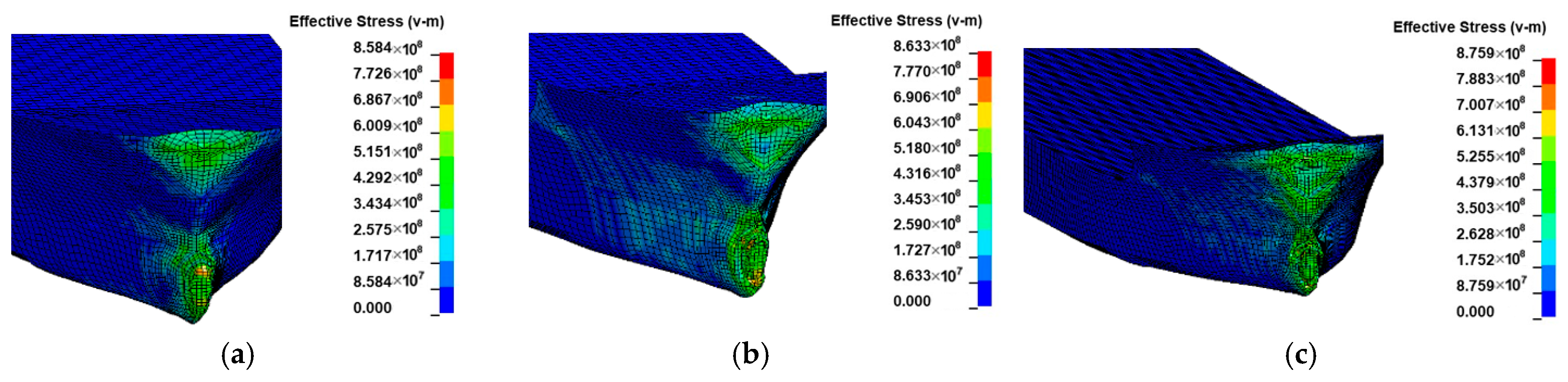
| Motion Mode | Added-Mass Coefficient | Author | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sway | 0.4 | Minorsky [5] | |
| Surge | 0.02–0.07 | Motora [20] | |
| Sway | 0.4–1.3 | Motora [20] | |
| Sway | 0.50 | Petersen [21] | |
| Surge | 0.05 | Petersen [21] | |
| Surge | 0.05 | AASHTO [9] | large underkeel clearances (≥0.5 × Draft) |
| Surge | 0.25 | AASHTO [9] | small underkeel clearances (≤0.1 × Draft) |
| Surge | 0.1 | European standard [35] |
| NO. | Ms/t | Vf/(m/s) | Vs/(m/s) | Fmax-FSI (MN) | Fmax-CAM (MN) | Errors |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3000 | −4 | 3 | 16.98 | 20.92 | −23% |
| 2 | 3000 | −2 | 3 | 18.24 | 20.92 | −15% |
| 3 | 3000 | 0 | 3 | 20.44 | 20.92 | −2% |
| 4 | 3000 | 2 | 3 | 24.74 | 20.92 | 15% |
| 5 | 3000 | 4 | 3 | 27.93 | 20.92 | 25% |
| 6 | 3000 | 0 | 1 | 14.02 | 14.53 | −4% |
| 7 | 3000 | 0 | 2 | 16.39 | 15.26 | 7% |
| 8 | 3000 | 0 | 4 | 31.06 | 24.33 | 22% |
| 9 | 3000 | 0 | 5 | 34.55 | 28.43 | 18% |
| 10 | 1000 | 0 | 3 | 16.09 | 15.78 | 2% |
| 11 | 2000 | 0 | 3 | 16.73 | 15.92 | 5% |
| 12 | 4000 | 0 | 3 | 26.99 | 21.43 | 21% |
| 13 | 5000 | 0 | 3 | 31.64 | 24.10 | 24% |
| 14 | 1000 | 0 | 5.2 | 19.78 | 20.31 | −3% |
| 15 | 5000 | 0 | 2.3 | 21.21 | 20.55 | 3% |
| No. | Ms/t | Vf/(m/s) | Vs/(m/s) | Fmax-FSI | Fmax-CAM | AASHTO | IABSE | TB | JTG |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3000 | 0 | 1 | 14.02 | 14.53 | 6.57 | 7.59 | 4.59 | 2 |
| 2 | 3000 | 0 | 2 | 16.39 | 15.26 | 13.15 | 12.05 | 9.18 | 4 |
| 3 | 3000 | 0 | 3 | 20.44 | 20.92 | 19.72 | 15.79 | 13.77 | 6 |
| 4 | 3000 | 0 | 4 | 31.06 | 24.33 | 26.29 | 19.13 | 18.35 | 8 |
| 5 | 3000 | 0 | 5 | 34.55 | 28.43 | 32.86 | 22.19 | 22.94 | 10 |
| 6 | 1000 | 0 | 3 | 16.09 | 15.78 | 11.38 | 13.62 | 6.156 | 3.6 |
| 7 | 2000 | 0 | 3 | 16.73 | 15.92 | 16.1 | 18.29 | 12.31 | 7.2 |
| 8 | 3000 | 0 | 3 | 20.44 | 20.92 | 19.72 | 22.77 | 13.77 | 12 |
| 9 | 4000 | 0 | 3 | 26.99 | 21.43 | 22.77 | 26.518 | 15.07 | 15.6 |
| 10 | 5000 | 0 | 3 | 31.64 | 24.1 | 25.45 | 29.8 | 16.28 | 19.2 |
| 11 | 3000 | −4 | 3 | 16.98 | 20.92 | 19.72 | 15.79 | 13.77 | 6 |
| 12 | 3000 | −2 | 3 | 18.24 | 20.92 | 19.72 | 15.79 | 13.77 | 6 |
| 13 | 3000 | 0 | 3 | 20.44 | 20.92 | 19.72 | 15.79 | 13.77 | 6 |
| 14 | 3000 | 2 | 3 | 24.74 | 20.92 | 19.72 | 15.79 | 13.77 | 6 |
| 15 | 3000 | 4 | 3 | 27.93 | 20.92 | 19.72 | 15.79 | 13.77 | 6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jia, E.; Chen, Y.; Ren, S.; Xu, M.; Pan, J.; Fang, H. Study on the Influence of Fluid Fields on the Impact Force of Ships Colliding with Bridges. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 1573. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13081573
Jia E, Chen Y, Ren S, Xu M, Pan J, Fang H. Study on the Influence of Fluid Fields on the Impact Force of Ships Colliding with Bridges. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(8):1573. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13081573
Chicago/Turabian StyleJia, Enshi, Yuheng Chen, Shuxia Ren, Mingcai Xu, Jin Pan, and Hai Fang. 2025. "Study on the Influence of Fluid Fields on the Impact Force of Ships Colliding with Bridges" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 8: 1573. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13081573
APA StyleJia, E., Chen, Y., Ren, S., Xu, M., Pan, J., & Fang, H. (2025). Study on the Influence of Fluid Fields on the Impact Force of Ships Colliding with Bridges. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(8), 1573. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13081573






