Benthic Ostracods as Indicators of Nearshore Pollution: An Example from Hurghada Bay, Red Sea Coast, Egypt
Abstract
1. Introduction
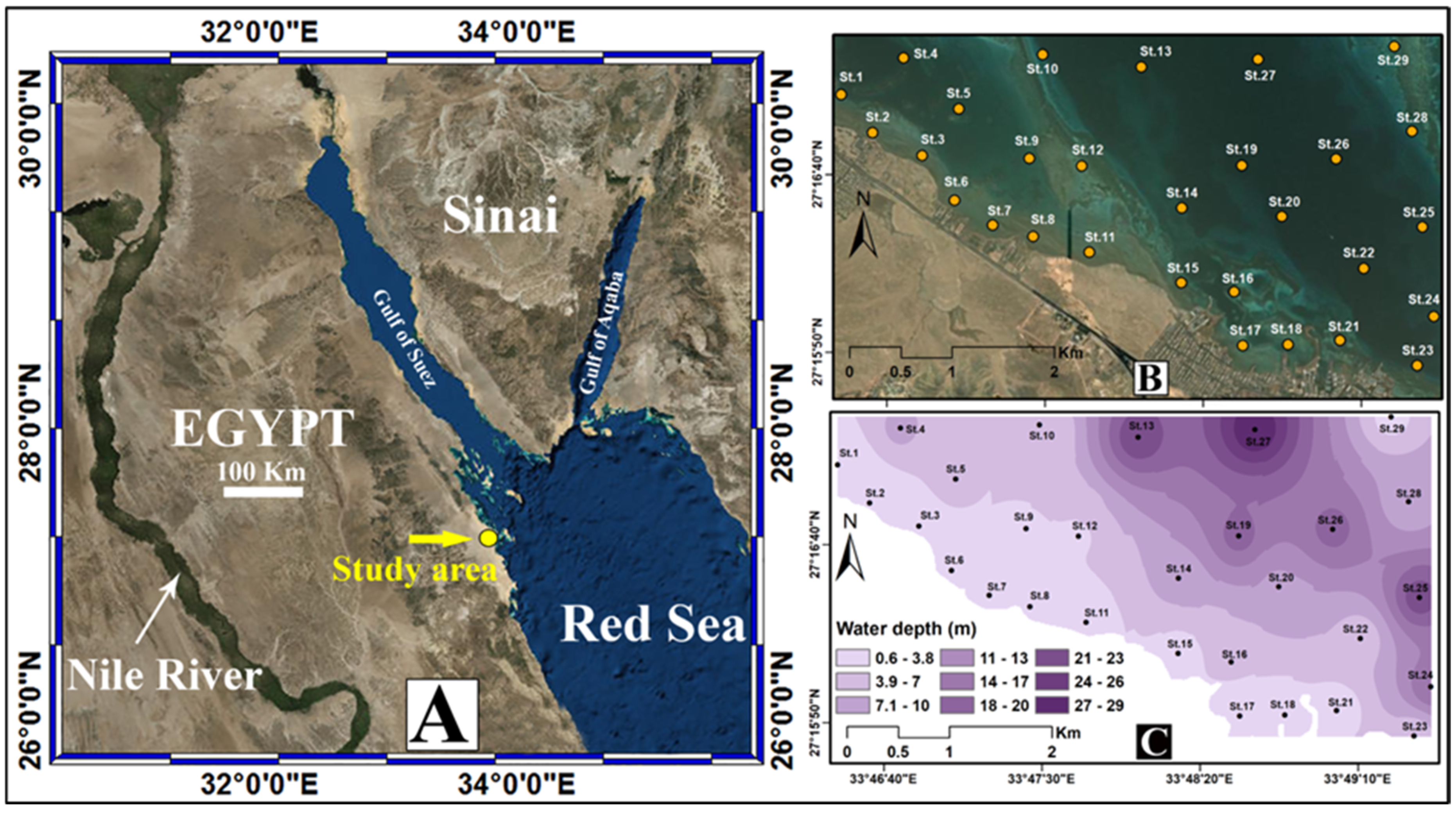
2. Study Area Description
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Sampling and Processing
3.2. Data Analysis
4. Results
4.1. Bottom Sediments Characteristics
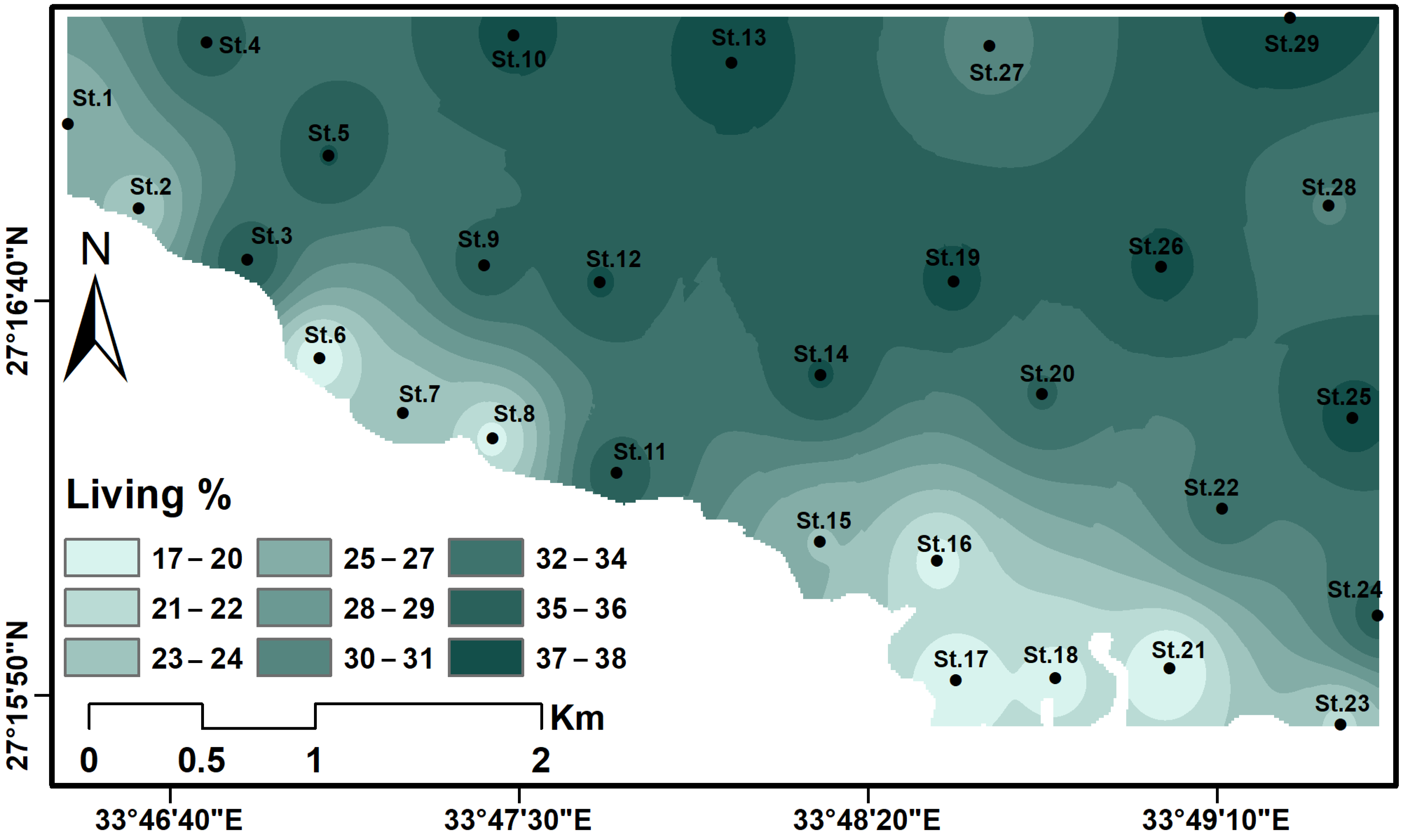
4.2. Hydrological Features
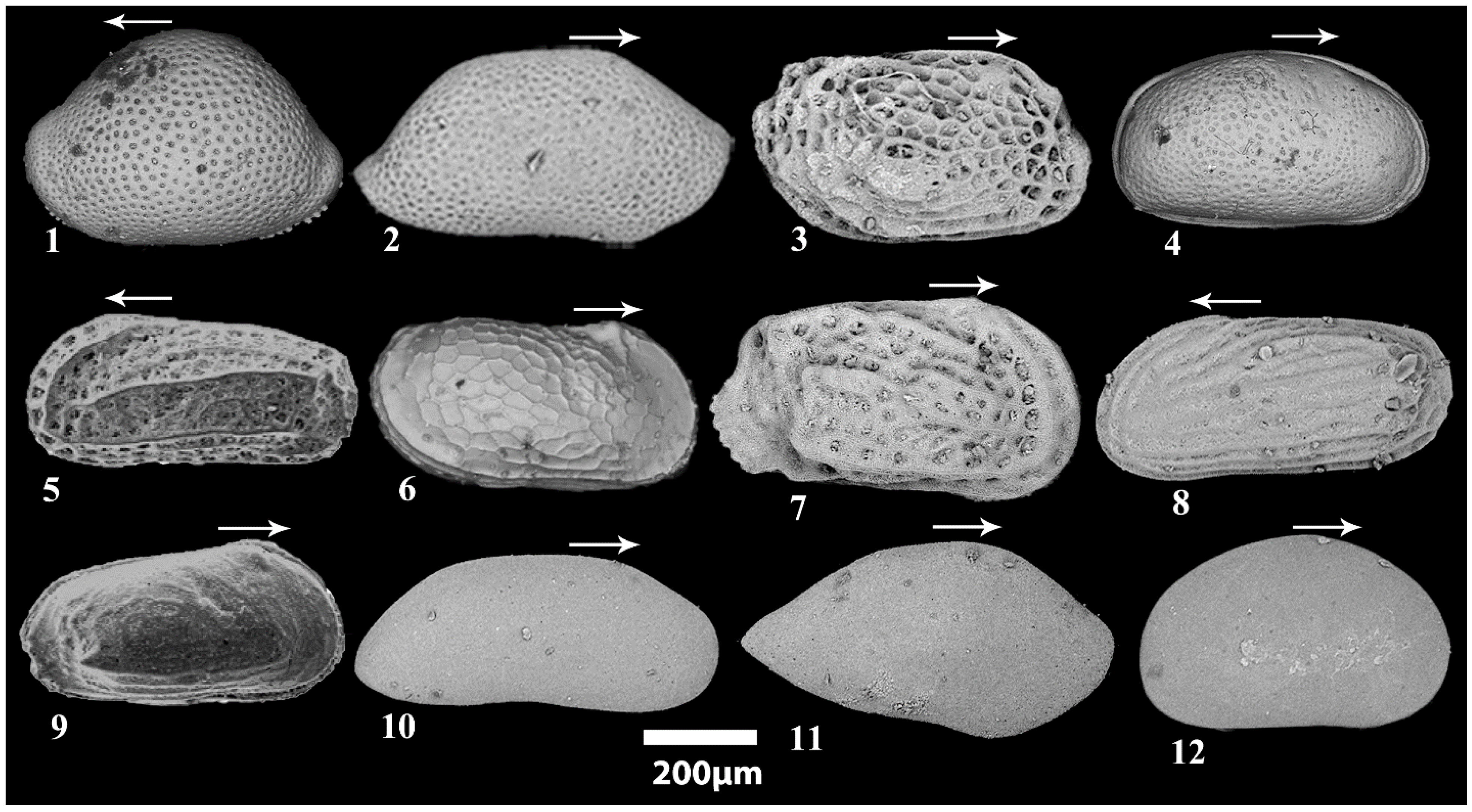
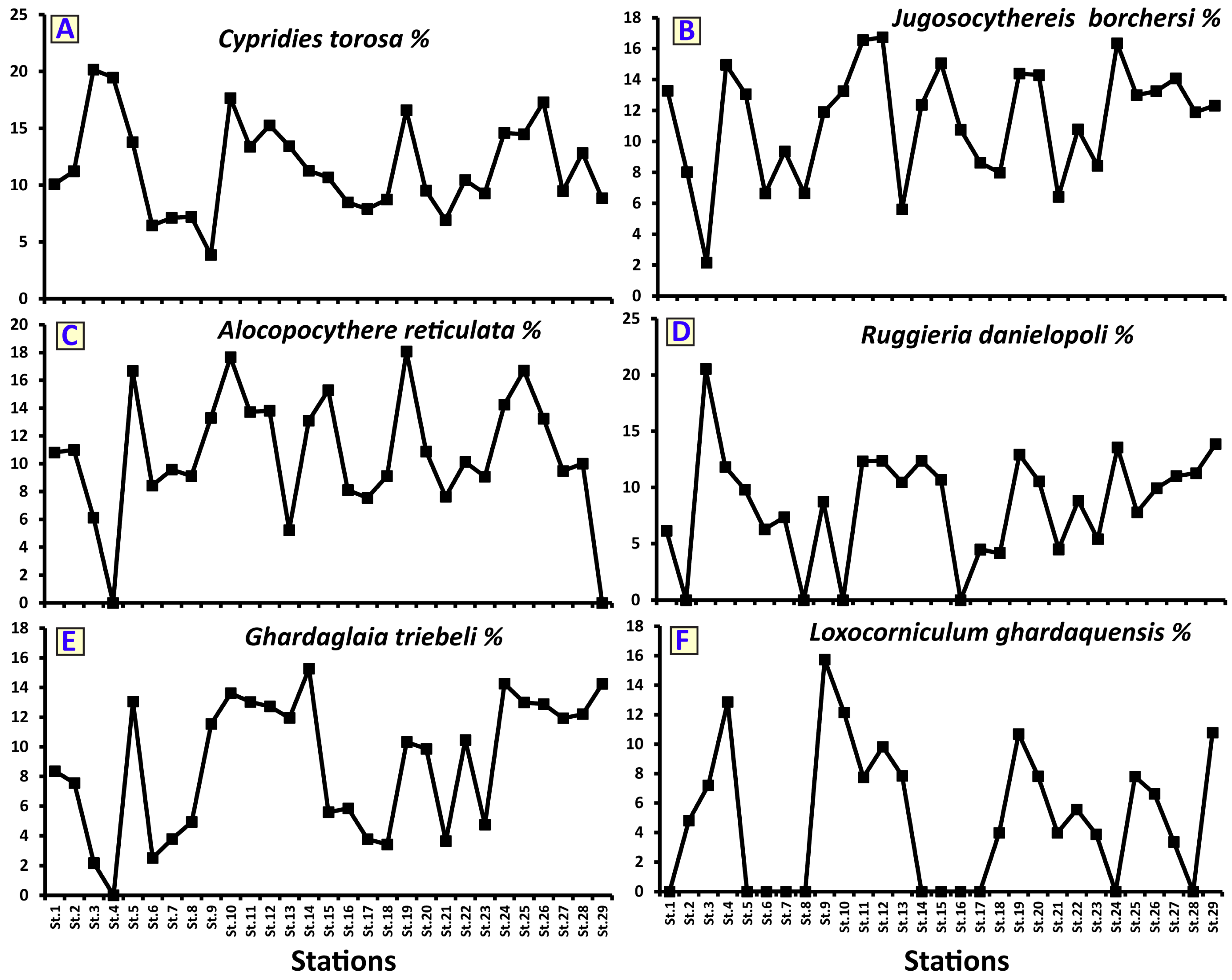
4.3. Ostracod Analysis
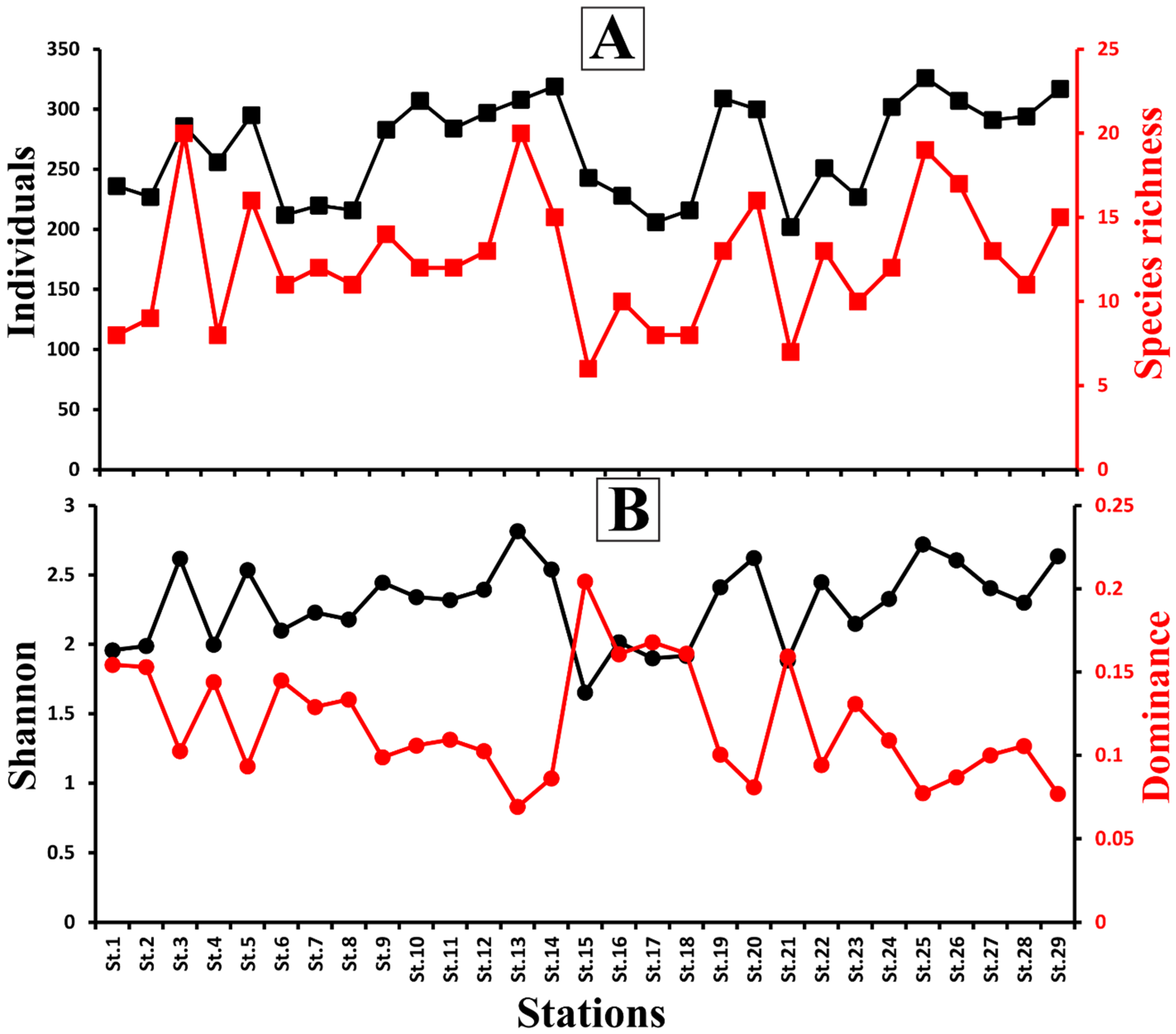
4.4. Benthic Ostracods Diversity Indices
4.5. Ordination Analysis
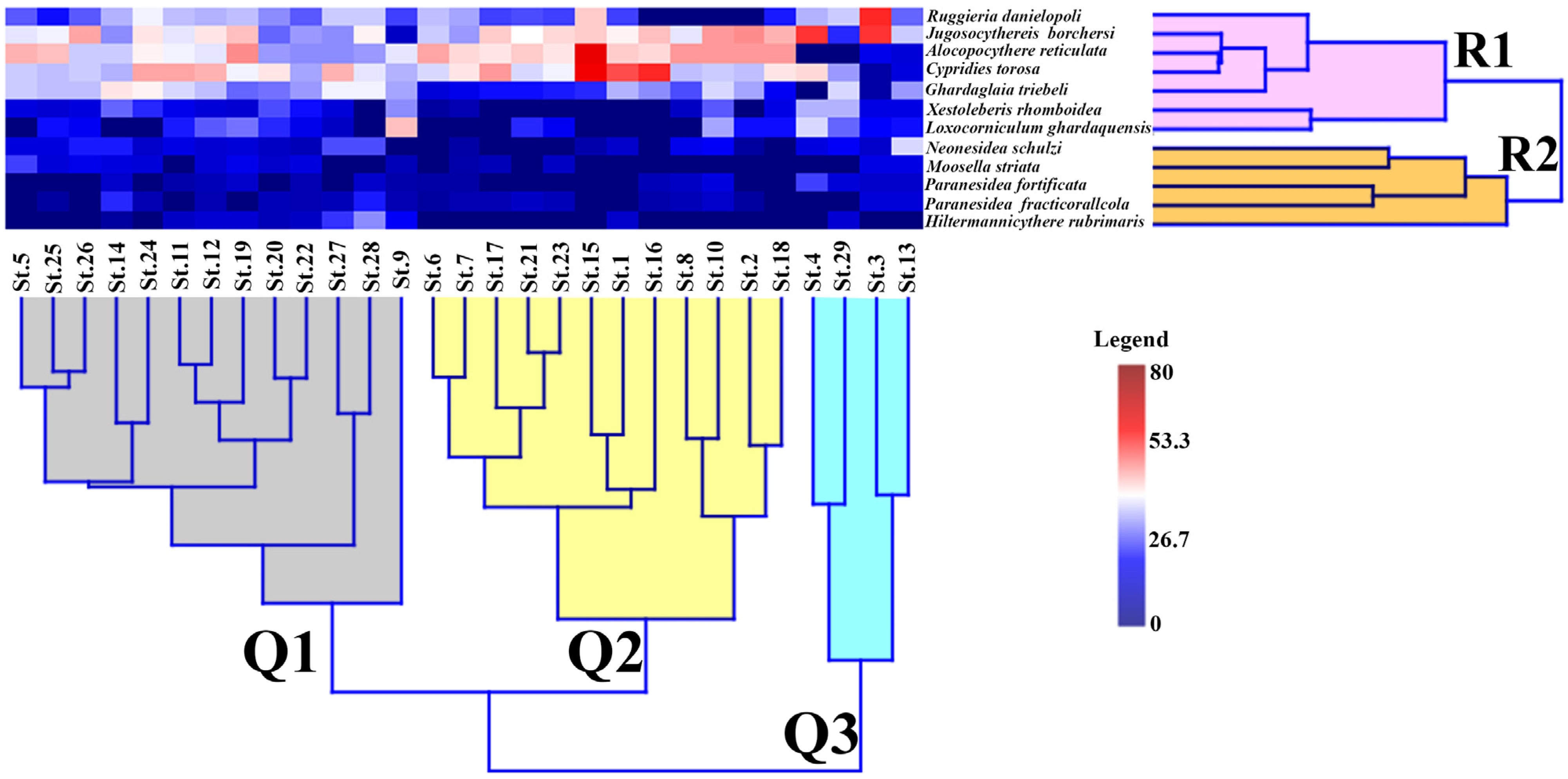
4.5.1. Hierarchical Cluster Analysis (HCA)
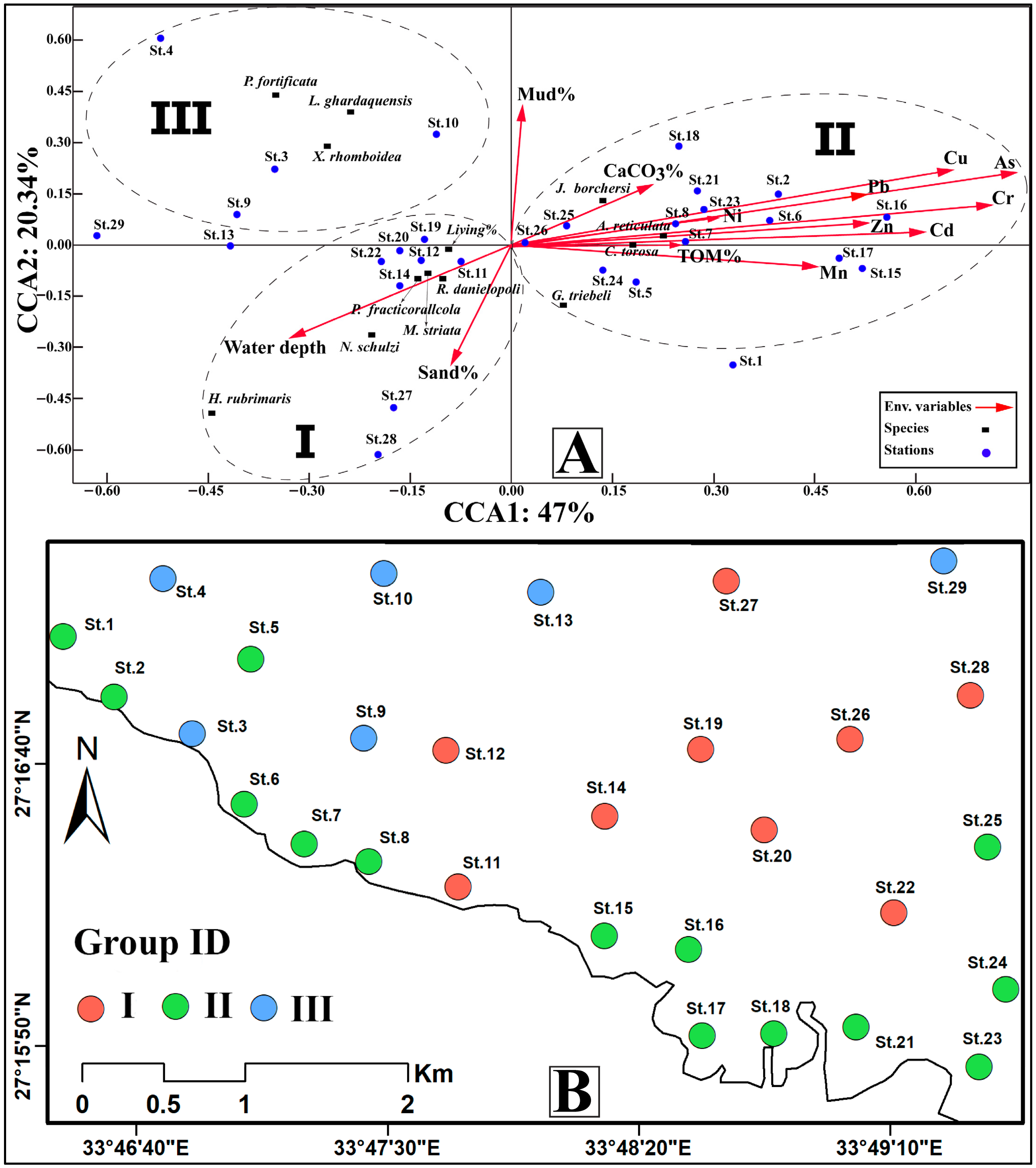
4.5.2. Canonical Correspondence Analysis (CCA)
5. Discussion
5.1. Heavy Metal Influence on Benthic Ostracods
5.2. Data Limitations and Future Directions
6. Conclusions and Recommendations
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aljahdali, M.H.; El-Kahawy, R.M.; Elhag, M.; Al-Mur, B.A.; Quicksall, A.N.; Alsaaq, F.; Ghandour, I.M. Benthic Ostracods as Pollution Indicator: A Case Study from Sharm Obhur, Red Sea Coast, Saudi Arabia. Earth Syst. Environ. 2024, 8, 1615–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fares, I.; El-Kahawy, R.M.; Hussein, A.W.; Abu El Ghar, M.S.; Helal, S.A. Benthic Foraminiferal Distribution in the Red Sea Coastal Sediments, Shalateen Area, Egypt: Environmental Biomonitoring Implications. J. King Saud Univ.–Mar. Sci. 2025, 34, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghandour, I.M.; El-Kahawy, R.M.; Murgulet, D.; Bantan, R.A.; Althagafi, A.A.; Al-Mur, B.A.; Aljahdali, M.H. Benthic foraminifera as ecological quality status biomonitors in Sharm Obhur, red sea Coast, Saudi Arabia. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2025, 51, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Asmar, H.M.; Ahmed, M.H.; El-Kafrawy, S.B.; Oubid-Allah, A.H.; Mohamed, T.A.; Khaled, M.A. Monitoring and assessing the coastal ecosystem at Hurghada, Red Sea coast, Egypt. Environ. Earth Sci 2015, 5, 144–160. [Google Scholar]
- El-Kahawy, R.M.; Mabrouk, M.S. Benthic foraminifera as bioindicators for the heavy metals in the severely polluted Hurghada Bay, Red Sea coast, Egypt. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 70437–70457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Ye, J.; Gao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, H. Integrated ecological quality assessment of the sea area adjacent to the Yellow River estuary under multiple pollutants. Front. Mar. Sci. 2025, 12, 1542611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, S.; Verma, A.K. Anthropogenic activities and Biodiversity threats. Int. J. Biol. Innov. IJBI 2022, 4, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathod, P.B.; Singh, M.P.; Taware, A.S.; Deshmukh, S.U.; Tagad, C.K.; Kulkarni, A.; Kanagare, A.B. Comprehensive insights into water remediation: Chemical, biotechnological, and nanotechnological perspectives. Environ. Pollut. Bioavailab. 2024, 36, 2329660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Cai, J.; Ma, W.; Li, B.; Feng, W. Distribution, sources and risk assessment of heavy metals in Yangshan port and its adjacent sea areas. Front. Mar. Sci. 2025, 11, 1512115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Hilal, A.H.; Badran, M.M. Effect of pollution sources on metal concentration in sediment cores from the Gulf of Aqaba (Red Sea). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1990, 21, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sharkawy, M.; Alotaibi, M.O.; Li, J.; Du, D.; Mahmoud, E. Heavy Metal Pollution in Coastal Environments: Ecological Implications and Management Strategies: A Review. Sustainability 2025, 17, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, S.M.; Shaker, I.M. Assessment of heavy metals pollution in water and sediments and their effect on Oreochromis niloticus in the northern delta lakes, Egypt. In Proceedings of the 8th International Symposium on Tilapia in Aquaculture, Cairo, Egypt, 12–14 October 2008; pp. 475–490. [Google Scholar]
- Martins, S.E.; Fillmann, G.; Lillicrap, A.; Thomas, K.V. Ecotoxicity of organic and organo-metallic antifouling co-biocides and implications for environmental hazard and risk assessments in aquatic ecosystems. Biofouling 2018, 34, 34–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiello, G.; Barra, D.; Parisi, R.; Arienzo, M.; Donadio, C.; Ferrara, L.; Toscanesi, M.; Trifuoggi, M. Infralittoral ostracoda and benthic foraminifera of the Gulf of Pozzuoli (Tyrrhenian Sea, Italy). Aquat. Ecol. 2021, 55, 955–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, O.; Alivernini, M.; Yasuhara, M.; Frenzel, P. Ostracoda (Crustacea) as indicators of anthropogenic impacts—A review. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2025, 263, 105049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parameswari, E.; Davamani, V.; Kalaiarasi, R.; Ilakiya, T.; Arulmani, S. Utilization of ostracods (Crustacea) as bioindicator for environmental pollutants. Int. Res. J. Pure Appl. Chem. 2020, 21, 73–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, M.; Keyser, D. Recent ostracods from the tidal flats of the coast of Aden City, Yemen. Mar. Biodivers. 2012, 42, 247–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, F.; Abad, M.; Bodergat, A.; Carbonel, P.; Rodríguez-Lázaro, J.; González-Regalado, M.; Toscano, A.; García, E.; Prenda, J. Freshwater ostracods as environmental tracers. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 10, 1115–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Gouramanis, C.; Pham, T.; Hoang, D.; Switzer, A.D. Ostracods as pollution indicators in Lap An Lagoon, central Vietnam. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 278, 116762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Börner, N.; De Baere, B.; Akita, L.G.; Francois, R.; Jochum, K.P.; Frenzel, P.; Zhu, L.; Schwalb, A. Stable isotopes and trace elements in modern ostracod shells: Implications for reconstructing past environments on the Tibetan Plateau, China. J. Paleolimnol. 2017, 58, 191–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormick, L.R.; Levin, L.A.; Oesch, N.W. Vision is highly sensitive to oxygen availability in marine invertebrate larvae. J. Exp. Biol. 2019, 222, jeb200899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieri, V.; Vandekerkhove, J.; Goi, D. Ostracoda (Crustacea) as indicators for surface water quality: A case study from the Ledra River basin (NE Italy). Hydrobiologia 2012, 688, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuhara, M.; Yamazaki, H. The impact of 150 years of anthropogenic pollution on the shallow marine ostracode fauna, Osaka Bay, Japan. Mar. Micropaleontol. 2005, 55, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvi, G.; Buosi, C.; Arbulla, D.; Cherchi, A.; De Giudici, G.; Ibba, A.; De Muro, S. Ostracoda and foraminifera response to a contaminated environment: The case of the Ex-Military Arsenal of the La Maddalena Harbour (Sardinia, Italy). Micropaleontology 2015, 61, 115–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samir, A.M. The response of benthic foraminifera and ostracods to various pollution sources: A study from two lagoons in Egypt. J. Foraminifer. Res. 2000, 30, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, O.; Mehlhorn, P.; Finch, J.; Haberzettl, T.; Hahn, A.; Hill, T.; Kretschmer, K.; Frenzel, P. Ostracoda and Foraminifera as bioindicators of (aquatic) pollution in the protected area of uMlalazi estuary, South Africa. Rev. Micropaléontol. 2024, 83, 100771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussa, A.; El-Askary, M.; Nasr, S.; El-Mamoney, M. Unconsolidated reefal sediments in the Jubal Strait region, Red Sea, Egypt. Mar. Geol. 1991, 97, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgson, E. Coral reef community structure at Al-Ghardaqa, Red Sea. Bull Inst Ocean. Fish ARE 1983, 9, 116–123. [Google Scholar]
- Radwan, G.E. Impact of human activities on coral reef sedimentary environment along Hurghada Coast-Red Sea. Master’s Thesis, Geology Department-Cairo University, Giza, Egypt, 2003; p. 132. [Google Scholar]
- Beltagy, A.; Ali, Y.; Lotfi, I. Geochemistry of the Red Sea shelf sediments at Al-Ghardaqa. I—Abundance and distribution of chemical constituents. Bull Inst Ocean. Fish ARE 1986, 12, 57–80. [Google Scholar]
- CRI. Report on studies and recommendations for alleviating the negative impacts of the infringements on the coastal zone shoreline located between km 15 to km 23.7 Hurghada/Safaga road on the Red Sea. Tech. Rep. 1994, 1, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, R.C. Treatise on Invertebrate Paleontology: Pt. Q Arthropoda 3, Crustacea, Ostracoda; Geological Society of America, University Kansas Press: Lawrence, KS, USA, 1961. [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann, G. Zur Kenntnis der Ostracoden des Roten Meeres: Ergebnisse Nr. 11 der Reise von A. Remane und E. Schulz ach dem Roten Meer. Kiel. Meeresforsch.-Sonderh. 1964, 1, 35–127. [Google Scholar]
- Martens, K.; Horne, D. Ostracoda. Encycl. Inland Waters 2009, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folk, R.L.; Ward, W.C. Brazos River bar [Texas]; a study in the significance of grain size parameters. J. Sediment. Res. 1957, 27, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šmilauer, P.; Lepš, J. Multivariate Analysis of Ecological Data Using CANOCO 5; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hammer, Ø.; Harper, D.A.T. Past: Paleontological statistics software package for educaton and data anlysis. Palaeontol. Electron. 2001, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz, F.; González-Regalado, M.; Baceta, J.; Muñoz, J. Comparative ecological analysis of the ostracod faunas from low-and high-polluted southwestern Spanish estuaries: A multivariate approach. Mar. Micropaleontol. 2000, 40, 345–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, E.; Bergamin, L.; Croudace, I.; Pierfranceschi, G.; Sesta, G.; Ausili, A. Measuring anthropogenic impacts on an industrialised coastal marine area using chemical and textural signatures in sediments: A case study of Augusta Harbour (Sicily, Italy). Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasier, M. Phylum Crustacea. Ostracods. In Microfossils; Armstrong, H., Brasier, M., Eds.; Wiley-Blackwell Publishing: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1979; pp. 219–248. [Google Scholar]
- Mischke, S.; Zhang, C. Holocene cold events on the Tibetan Plateau. Glob. Planet. Change 2010, 72, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokorný, V. Ostracoda. In Introduction to Marine Micropaleontology; Haq, B., Boersma, A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1978; pp. 109–149. [Google Scholar]
- Sell, J. Carapace shape variability in the ostracode Heterocypris salinus (Brady) from Polish populations. In What About Ostracoda! Actes du 3e Congre’s Europe én des Ostracodologistes, 1996, Bulletin des Centres de Recherche, Exploration, Production Elf—Aquitaine, Mémoirs; Crasquin Soleau, S., Braccini, E., Lethiers, F., Eds.; Elf Aquitaine: Paris, France, 1998; pp. 125–129. [Google Scholar]
- Helal, S.A.; Mohamed, A.E.-W. Distribution of podocopid ostracods in mangrove ecosystems along the Egyptian Red Sea Coast. Crustaceana 2012, 85, 1669–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kahawy, R.; El-Shafeiy, M.; Helal, S.; Aboul-Ela, N.; Abd El-Wahab, M. Benthic ostracods (crustacean) as a nearshore pollution bio-monitor: Examples from the Red Sea Coast of Egypt. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 31975–31993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglikowska, A.; Pawłowska, J. The adaptations of the foraminifera and ostracoda to fresh water colonisation. In Impact of Climate Changes on Marine Environments; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 91–113. [Google Scholar]
- Barbieri, G.; Rossi, V.; Ghosh, A.; Vaiani, S.C. Conservation paleobiology as a tool to define reference conditions in naturally stressed transitional settings: Micropaleontological insights from the Holocene of the Po coastal plain (Italy). Water 2020, 12, 3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandekerkhove, J.; Martens, K.; Rossetti, G.; Mesquita-Joanes, F.; Namiotko, T. Extreme tolerance to environmental stress of sexual and parthenogenetic resting eggs of Eucypris virens (Crustacea, Ostracoda). Freshw. Biol. 2013, 58, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorissen, F.J.; de Stigter, H.C.; Widmark, J.G. A conceptual model explaining benthic foraminiferal microhabitats. Mar. Micropaleontol. 1995, 26, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alve, E. Benthic foraminifera in sediment cores reflecting heavy metal pollution in Sorfjord, western Norway. J. Foraminifer. Res. 1991, 21, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whatley, R.C.; Pyne, R.S.; Wilkinson, I.P. Ostracoda and palaeo-oxygen levels, with particular reference to the Upper Cretaceous of East Anglia. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2003, 194, 355–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannier, J.; Abe, K.; Ikuta, K. Feeding in myodocopid ostracods: Functional morphology and laboratory observations from videos. Mar. Biol. 1998, 132, 391–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, F.; Abad, M.; Bodergat, A.-M.; Carbonel, P.; Rodríguez-Lázaro, J.; Yasuhara, M. Marine and brackish-water ostracods as sentinels of anthropogenic impacts. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2005, 72, 89–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winding Hansen, B. Copepod embryonic dormancy: “An egg is not just an egg”. Biol. Bull. 2019, 237, 145–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kahawy, R.; El-Shafeiy, M.; Helal, S.; Aboul-Ela, N.; El-Wahab, M.A. Morphological deformities of benthic foraminifera in response to nearshore pollution of the Red Sea, Egypt. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauzielly, L.; Irizuki, T.; Sampei, Y. Spatial distribution of recent ostracode assemblages and depositional environments in Jakarta Bay, Indonesia, with relation to environmental factors. Paleontol. Res. 2013, 16, 267–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irizuki, T.; Takimoto, A.; Sako, M.; Nomura, R.; Kakuno, K.; Wanishi, A.; Kawano, S. The influences of various anthropogenic sources of deterioration on meiobenthos (Ostracoda) over the last 100 years in Suo-Nada in the Seto Inland Sea, southwest Japan. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 2030–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirto, S.; Danovaro, R.; Mazzola, A. Microbial and meiofaunal response to intensive mussel-farm biodeposition in coastal sediments of the western Mediterranean. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2000, 40, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguera, S.G.; Hendrickx, M. Distribution and abundance of meiofauna in a subtropical coastal lagoon in the south-eastern Gulf of California, Mexico. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1997, 34, 582–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Kuang, X.; Shan, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Tong, Y.; Zou, Y. Recent ostracods as ecological indicators and its applications: An example from the southern Tibetan Plateau. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 143, 109326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Lo, H.-S.; Wong, H.-M.; Zhou, M.; Wong, C.-Y.; Tam, N.F.-Y.; Cheung, S.-G. Heavy metals contamination of sedimentary microplastics in Hong Kong. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 153, 110977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Yu, Z.; Zeng, G.; Jiang, M.; Yang, Z.; Cui, F.; Zhu, M.; Shen, L.; Hu, L. Effects of sediment geochemical properties on heavy metal bioavailability. Environ. Int. 2014, 73, 270–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, R.; Sun, D.; Sun, L.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, J.; Zang, S. Sediment record of heavy metals over the last 150 years in Northeast China: Implications for regional anthropogenic activities. Ecotoxicology 2021, 30, 1354–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.-H.M.; Yasuhara, M.; Iwatani, H.; Yamaguchi, T.; Yamada, K.; Mamo, B. Deep-sea ostracod faunal dynamics in a marginal sea: Biotic response to oxygen variability and mid-Pleistocene global changes. Paleobiology 2019, 45, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuhara, M.; Yamazaki, H.; Tsujimoto, A.; Hirose, K.J.L.; Oceanography. The effect of long-term spatiotemporal variations in urbanization-induced eutrophication on a benthic ecosystem, Osaka Bay, Japan. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2007, 52, 1633–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldrighi, E.; Pizzini, S.; Punzo, E.; Santelli, A.; Strafella, P.; Scirocco, T.; Manini, E.; Fattorini, D.; Vasapollo, C. Multi-benthic size approach to unveil different environmental conditions in a Mediterranean harbor area (Ancona, Adriatic Sea, Italy). PeerJ 2023, 11, e15541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedepohl, K. Environmental influences on the chemical composition of shales and clays. Phys. Chem. Earth 1971, 8, 307–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, R.G. The level of heavy metals in the the Red Sea after 50 years. Sci. Total Environ. 1992, 125, 417–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| TOM% | Sand% | Mud% | Cu | Pb | Zn | Cd | Ni | Mn | Cr | As | C. tor. | J. bor. | A. retic. | R. dan. | L. gha. | G. trieb. | Spec. Rich. | Indiv. | % Liv. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TOM% | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Sand% | −0.56 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Mud% | 0.54 | −0.95 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||
| Cu | 0.40 | −0.23 | 0.22 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||
| Pb | 0.72 | −0.54 | 0.46 | 0.38 | 1 | |||||||||||||||
| Zn | 0.65 | −0.29 | 0.26 | 0.43 | 0.78 | 1 | ||||||||||||||
| Cd | 0.69 | −0.38 | 0.37 | 0.68 | 0.66 | 0.70 | 1 | |||||||||||||
| Ni | 0.55 | −0.49 | 0.48 | 0.54 | 0.56 | 0.44 | 0.55 | 1 | ||||||||||||
| Mn | 0.18 | −0.24 | 0.20 | 0.36 | 0.34 | 0.37 | 0.42 | 0.52 | 1 | |||||||||||
| Cr | 0.41 | −0.27 | 0.28 | 0.58 | 0.52 | 0.74 | 0.74 | 0.51 | 0.61 | 1 | ||||||||||
| As | 0.63 | −0.52 | 0.43 | 0.62 | 0.76 | 0.74 | 0.81 | 0.48 | 0.48 | 0.80 | 1 | |||||||||
| C. torosa | 0.59 | −0.03 | 0.14 | 0.46 | 0.49 | 0.52 | 0.65 | 0.33 | 0.43 | 0.41 | 0.30 | 1 | ||||||||
| J. borchersi | −0.01 | 0.20 | −0.39 | 0.27 | 0.20 | 0.16 | 0.20 | 0.12 | 0.29 | 0.31 | 0.34 | 0.03 | 1 | |||||||
| A. reticulata | 0.62 | 0.14 | 0.46 | 0.56 | 0.53 | 0.58 | 0.36 | 0.43 | 0.28 | 0.66 | 0.42 | 0.28 | 0.48 | 1 | ||||||
| R. danielopoli | −0.04 | 0.41 | −0.27 | −0.33 | −0.21 | −0.16 | −0.15 | −0.24 | −0.47 | −0.39 | −0.45 | −0.06 | −0.16 | −0.35 | 1 | |||||
| L. ghardaquensis | −0.23 | −0.18 | 0.20 | −0.23 | −0.30 | −0.41 | −0.31 | −0.01 | −0.22 | −0.44 | −0.38 | −0.09 | −0.33 | −0.39 | −0.03 | 1 | ||||
| G. triebeli | −0.21 | 0.30 | −0.43 | −0.25 | −0.21 | −0.24 | −0.28 | −0.14 | 0.11 | −0.34 | −0.27 | −0.42 | 0.15 | 0.17 | −0.22 | −0.11 | 1 | |||
| Species richness | −0.29 | 0.17 | −0.04 | −0.55 | −0.30 | −0.40 | −0.47 | −0.37 | −0.28 | −0.54 | −0.60 | −0.24 | −0.70 | −0.40 | 0.24 | 0.21 | 0.26 | 1 | ||
| Individuals | −0.54 | 0.45 | −0.42 | −0.68 | −0.57 | −0.66 | −0.75 | −0.52 | −0.38 | −0.83 | −0.85 | −0.20 | −0.31 | −0.36 | 0.30 | 0.32 | 0.55 | 0.74 | 1 | |
| % Living | −0.53 | 0.42 | −0.37 | −0.61 | −0.64 | −0.71 | −0.73 | −0.46 | −0.40 | −0.82 | −0.87 | −0.15 | −0.38 | −0.48 | 0.35 | 0.46 | 0.40 | 0.71 | 0.94 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
El-Kahawy, R.M.; Heinz, P.; Sayed, M.M.; Mannaa, A.; Haredy, R.A.; Wagreich, M. Benthic Ostracods as Indicators of Nearshore Pollution: An Example from Hurghada Bay, Red Sea Coast, Egypt. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 1555. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13081555
El-Kahawy RM, Heinz P, Sayed MM, Mannaa A, Haredy RA, Wagreich M. Benthic Ostracods as Indicators of Nearshore Pollution: An Example from Hurghada Bay, Red Sea Coast, Egypt. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(8):1555. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13081555
Chicago/Turabian StyleEl-Kahawy, Ramadan M., Petra Heinz, Mostafa M. Sayed, Ammar Mannaa, Rabea A. Haredy, and Michael Wagreich. 2025. "Benthic Ostracods as Indicators of Nearshore Pollution: An Example from Hurghada Bay, Red Sea Coast, Egypt" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 8: 1555. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13081555
APA StyleEl-Kahawy, R. M., Heinz, P., Sayed, M. M., Mannaa, A., Haredy, R. A., & Wagreich, M. (2025). Benthic Ostracods as Indicators of Nearshore Pollution: An Example from Hurghada Bay, Red Sea Coast, Egypt. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(8), 1555. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13081555







