Abstract
This study developed a model to predict ships with high deficiency risk under Port State Control (PSC) through machine learning techniques, particularly the Random Forest algorithm. The study utilized actual ship inspection data from the Port of Singapore, comprehensively considering various operational and safety indicators of ships, including but not limited to flag state, ship age, past deficiencies, and detention history. By analyzing these factors in depth, this research enhances the efficiency and accuracy of PSC inspections, provides decision support for port authorities, and offers strategic guidance for shipping companies to comply with international safety standards. During the research process, I first conducted detailed data preprocessing, including data cleaning and feature selection, to ensure the effectiveness of model training. Using the Random Forest algorithm, I identified key factors influencing the detention risk of ships and established a risk prediction model accordingly. The model validation results indicated that factors such as ship age, tonnage, company performance, and flag state significantly affect whether a ship exhibits a high deficiency rate. In addition, this study explored the potential and limitations of applying the Random Forest model in predicting high deficiency risk under PSC, and proposed future research directions, including further model optimization and the development of real-time prediction systems. By achieving these goals, I hope to provide valuable experience for other global shipping hubs, promote higher international maritime safety standards, and contribute to the sustainable development of the global shipping industry. This research not only highlights the importance of machine learning in the maritime domain but also demonstrates the potential of data-driven decision-making in improving ship safety management and port inspection efficiency. It is hoped that this study will inspire more maritime practitioners and researchers to explore advanced data analytics techniques to address the increasingly complex challenges of global shipping.
1. Introduction
In the era of globalization, maritime transport is not only a key driver of international trade and economic development but also the core of the global supply chain, connecting markets and cultures across the world. With the rapid expansion of global shipping, there is increasing concern about the safety and efficiency of vessels. Particularly in maintaining supply chain stability, promoting economic growth, and protecting the marine environment, maritime transport plays an indispensable role. Against this backdrop, this study aims to develop a machine learning-based prediction model for ship detention risk under Port State Control (PSC), utilizing the Random Forest algorithm, with a focus on the PSC inspections and detentions at the Port of Singapore. The goal is to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of ship safety management.
As the main artery of global economic activity, shipping has immeasurable value in facilitating international trade and maintaining global market stability. However, as maritime transport volumes continue to rise, the risk of ship-related accidents also increases, threatening the safety of crews and cargo and potentially causing irreversible damage to the marine environment. Therefore, enhancing ship safety and reducing transport risks have become critical research topics in the maritime domain.
PSC, as an internationally recognized maritime safety and environmental protection measure, aims to reduce maritime accidents and environmental pollution by inspecting ships in port for compliance with international standards. However, given the wide variety of vessels and the complexity of shipping activities, port states face many challenges in conducting effective inspections. Therefore, developing a model that can accurately predict the risk of ship detention has significant practical value for improving inspection efficiency and guiding shipping companies to enhance ship management.
According to the ‘Review of Maritime Transport 2022’ report published by the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) [1], even under the impact of the Russia-Ukraine war and COVID-19, Asia remained the largest maritime cargo handling center in the world. This study uses ship inspection data from the Tokyo Memorandum of Understanding (Tokyo MoU) as its analytical basis and focuses on the Port of Singapore. Located in a key geographical position in Asia, Singapore is one of the busiest ports in East and Southeast Asia. Its location makes it a critical hub for international trade, resulting in a high demand for ship inspections. Moreover, the port benefits from a relatively robust legal framework and a well-developed port management system, making its inspection practices more representative. With advanced port facilities and inspection technologies—including equipment and personnel training—these developments significantly influence inspection efficiency and accuracy, making Singapore a valuable reference point for studying ship inspections.
This study conducts an in-depth analysis of the Port of Singapore, using ship inspection data from the implementation of the New Inspection Regime (NIR) under the Tokyo MoU starting in 2014 through to 2022. By applying the Random Forest algorithm to build a prediction model, this research not only predicts the risk of ship detention but also explores the various factors influencing ship safety. Through the application of machine learning techniques, this study aims to provide new analytical approaches and strategic recommendations for maritime safety management, enhance the safety and reliability of maritime transport, offer decision-making support for shipping companies, port authorities, and policymakers, and promote a data-driven decision-making model in the maritime industry. Additionally, the findings of this study can serve as a reference for other global shipping centers, contributing to the improvement of international maritime safety standards and fostering the sustainable development of the global shipping industry.
2. Literature Review
In recent years, to enhance ship safety management and the effectiveness of Port State Control (PSC) inspections, many scholars have conducted in-depth studies on the key factors influencing ship detention and inspection outcomes. These studies, ranging from traditional statistical models to modern data mining and machine learning techniques, have progressively revealed the significance of both static and dynamic factors—such as ship age, type, flag, and inspection history—in predicting ship inspections and detention risks. The following is a review of relevant literature, summarizing the analytical methods and key findings of previous studies, as well as how emerging data-driven approaches have been applied to PSC inspections and detention risk prediction in practice.
Cariou et al. [2] explored PSC inspection databases and confirmed that ship age is a critical focus of inspections and an important factor leading to detention. In a subsequent study, they further analyzed the main causes of ship detentions and found that up to 40% were related to aging ships. Cariou and Wolff [3] used quantile regression to analyze the relationship between specific ship types and deficiency items. Knapp and Franses [4], using PSC inspection and ship casualty databases, built a logistic regression model to predict casualty probabilities based on detailed ship information, classification societies, owner details, flag, and PSC inspection frequency, identifying major factors contributing to ship casualties and providing insights to improve PSC inspection efficiency. Knapp and Velden [5] compared the inspection focuses of various PSC regimes and found that Paris MoU member states place particular emphasis on deficiencies in ship stability, structure, and safety equipment.
Fan et al. [6] integrated a binary logistic model and a linear model to explain ship inspection rates, finding that the likelihood of being selected for inspection is related not only to past inspection records but also to certain predefined priority conditions, with ship age being the most significant factor. Hanninen and Kujala [7] employed Bayesian network models based on PSC inspection data to identify the interrelationships among deficiencies and between deficiencies and maritime accidents. Their results indicated that ship type, PSC inspection category, and the number of structural deficiencies are key explanatory factors for maritime incidents and potential safety risks. Tsou [8] applied association rule mining from big data analytics to analyze the deficiency items of detained ships in the Tokyo MoU detention database, identifying common features accompanying detentions to guide Port State Control Officers (PSCO) and ship managers in inspection preparation and priority setting.
Developing accurate prediction models for ship detention based on a ship’s generic factors and inspection history prior to inspection is challenging due to the highly imbalanced nature of the data. To address this, Yan et al. [9] developed a balanced random forest (BRF) classification model using 1600 inspection records from the Port of Hong Kong over 3 years. Numerical experiments showed that the proposed BRF model correctly identified 81.25% of all detained ships in a separate test set of 400 records. Demirci and Cicek [10] developed a decision support system to improve the effectiveness of ship inspections by proposing an Intelligent Ship Inspection Analytics (I-SIA) model, based on the Knowledge Discovery in Database (KDD) process and utilizing fuzzy c-means clustering and Apriori algorithms. Yang et al. [11] enhanced inspection policy efficiency and reduced detention duration by developing a data-driven Bayesian network model using an improved machine learning methodology. Their model identified deficiency types that significantly impact detention duration, uncovered interdependencies between these types, and clarified major and abnormal deficiency types across different port states. Wang et al. [12] proposed a transfer learning–enhanced Extreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost) model that innovatively incorporates sample similarity calculations to adapt the model to the unique characteristics of the target port. This novel model integrates relevant data from other ports, improving predictive performance under specific port conditions, utilizing PSC inspection records from ports within the Tokyo MoU and focusing on the Port of Singapore.
In summary, the literature shows that factors such as ship age, type, flag, and inspection history play critical roles in predicting inspection and detention risks. Both traditional statistical methods and recent machine learning techniques have demonstrated their effectiveness. However, these studies also face challenges such as data imbalance, lack of interpretability, and results that are too dispersed to be actionable. To address these issues, this study proposes an integrated machine learning approach that effectively overcomes data imbalance, enhances the reasonableness and focus of predictions, and provides more precise and actionable decision support for PSC inspection practices.
3. Methodology
This study predicts and evaluates the risk of ship detention under Singapore’s Port State Control (PSC) using the Random Forest algorithm. Random Forest is an ensemble learning method based on decision trees, which improves overall model accuracy and stability by building multiple decision trees and aggregating their predictions. The principles and mechanisms of Random Forest employed in this study are described as follows:
3.1. Principles of the Random Forest Algorithm
Random Forest is an ensemble learning algorithm that combines multiple decision trees to enhance prediction accuracy and stability [13]. During the construction of decision trees, several key formulas are used to build the model and evaluate node purity:
(1) Gini Impurity: Gini Impurity measures the degree of class heterogeneity within a node, where a lower value indicates purer data in the node. The Gini Impurity is calculated as:
where pi is the proportion of class i in the node, and n is the total number of classes. For binary classification, the formula simplifies to:
Where p and 1 − p represent the proportions of the two classes.
(2) Information Gain: Information gain is often used to select the best splitting feature in a decision tree. It is defined as the difference between the parent node’s purity and the weighted average purity of the child nodes after the split:
where Giniparent is the Gini impurity of the parent node, Ginileft and Giniright are the impurities of the left and right child nodes, Nleft and Nright are the sample sizes of the child nodes, and N is the total sample size of the parent node.
These formulas guide the tree construction by evaluating the effectiveness of each split and selecting the optimal feature accordingly.
(3) Introducing Randomness: Random Forest builds multiple decision trees by repeatedly sampling from the original dataset (Bootstrap Aggregating). Each tree is trained on a bootstrap sample, meaning the same sample may appear multiple times in one tree’s training data and not at all in another. Furthermore, during the tree-building process, Random Forest randomly selects a subset of features at each split rather than considering all features, increasing tree diversity and improving the overall model’s generalization ability.
(4) Decision and Prediction: For classification problems, Random Forest predicts based on the majority voting principle:
Y = mode{T1(x), T2(x),…, Tn(x)}
Through a majority voting approach, particularly for binary classification problems, the probability values of different classes can be calculated, and the class with the higher probability is selected as the predicted output. This not only provides the classification result but also indicates the confidence level of the prediction.
For regression problems, the prediction is the average of all tree outputs.
(5) Feature Importance Evaluation: One way Random Forest evaluates feature importance is by measuring the reduction in Gini impurity contributed by each feature:
where ΔGini(Fj,Ti) is the reduction in Gini impurity when feature Fj is used for splitting in the decision tree Ti. This indicator quantifies each feature’s contribution to node purity improvement across all trees, helping explain the model’s decisions and providing practical insights for managing influential factors.
Overall, Random Forest, as a robust ensemble learning method, enhances model generalization and prediction accuracy through bootstrap sampling and random feature selection while effectively reducing overfitting. Additionally, its built-in feature importance evaluation mechanism helps identify key factors influencing predictions, providing valuable support for decision-making. Therefore, this study adopts Random Forest as the core method to predict and assess ship detention risk under Singapore’s PSC, leveraging existing data features and improving the interpretability and rationality of results, thereby supporting the optimization of PSC inspection strategies with a scientific basis.
3.2. Research Steps
Before conducting this study, I designed a series of comprehensive steps to ensure the rigor and effectiveness of the methodology. These steps, spanning from preliminary data processing to final interpretation of results, are crucial to the reliability and practical value of the findings. Our goal was to develop a model capable of effectively predicting ship detention risk, thereby providing valuable insights for maritime safety management. The specific steps of our study are as follows:
- (1)
- Data Preprocessing:
Data Cleaning: Handle missing values and outliers to ensure data accuracy and completeness.
Feature Selection: Select features relevant to ship detention risk based on domain knowledge, such as ship age, flag state, and historical detention records.
Data Transformation: Encode categorical variables and standardize or normalize numerical variables.
- (2)
- Random Forest Model Construction:
Build the Random Forest model by setting parameters such as the number of decision trees, maximum tree depth, and minimum samples required for node splitting. Use cross-validation to select optimal parameter settings and ensure good generalization ability of the model.
- (3)
- Model Training and Validation:
Split the dataset into training and test sets. Train the model on the training set and evaluate its predictive performance on the test set using metrics such as accuracy, recall, and F1-score.
- (4)
- Feature Importance Analysis:
Use the feature importance evaluation function (Formula (6)) of the Random Forest algorithm to identify which factors play critical roles in predicting ship detention.
- (5)
- Result Interpretation and Application:
Based on the model’s predictions, provide insights and interpretations regarding ship detention risk. Propose data-driven recommendations for ship safety management to guide port authorities and ship operators.
- (6)
- Model Optimization and Iteration:
Make necessary adjustments and refinements based on model performance and external feedback to improve accuracy and reliability.
Through this methodology, I aim to develop a model that can effectively predict ship detention risk while deriving valuable insights and strategies for improving maritime safety management.
4. Big Data Analysis of PSC Ship Inspection Data
4.1. Data Source
The data used in this study comes from the Port State Control (PSC) inspection results database at the Port of Singapore, within the Tokyo Memorandum of Understanding (Tokyo MoU) region, covering the period from 2014 to 2022. This dataset comprises 10,736 records and contains 16 different data fields (Table 1). These data support research in ship risk assessment, maritime safety analysis, and the evaluation of ships’ compliance with international maritime regulations. Below is an overview of these key fields:

Table 1.
Overview of Tokyo MoU database fields.
4.2. Preprocessing of Imbalanced Data
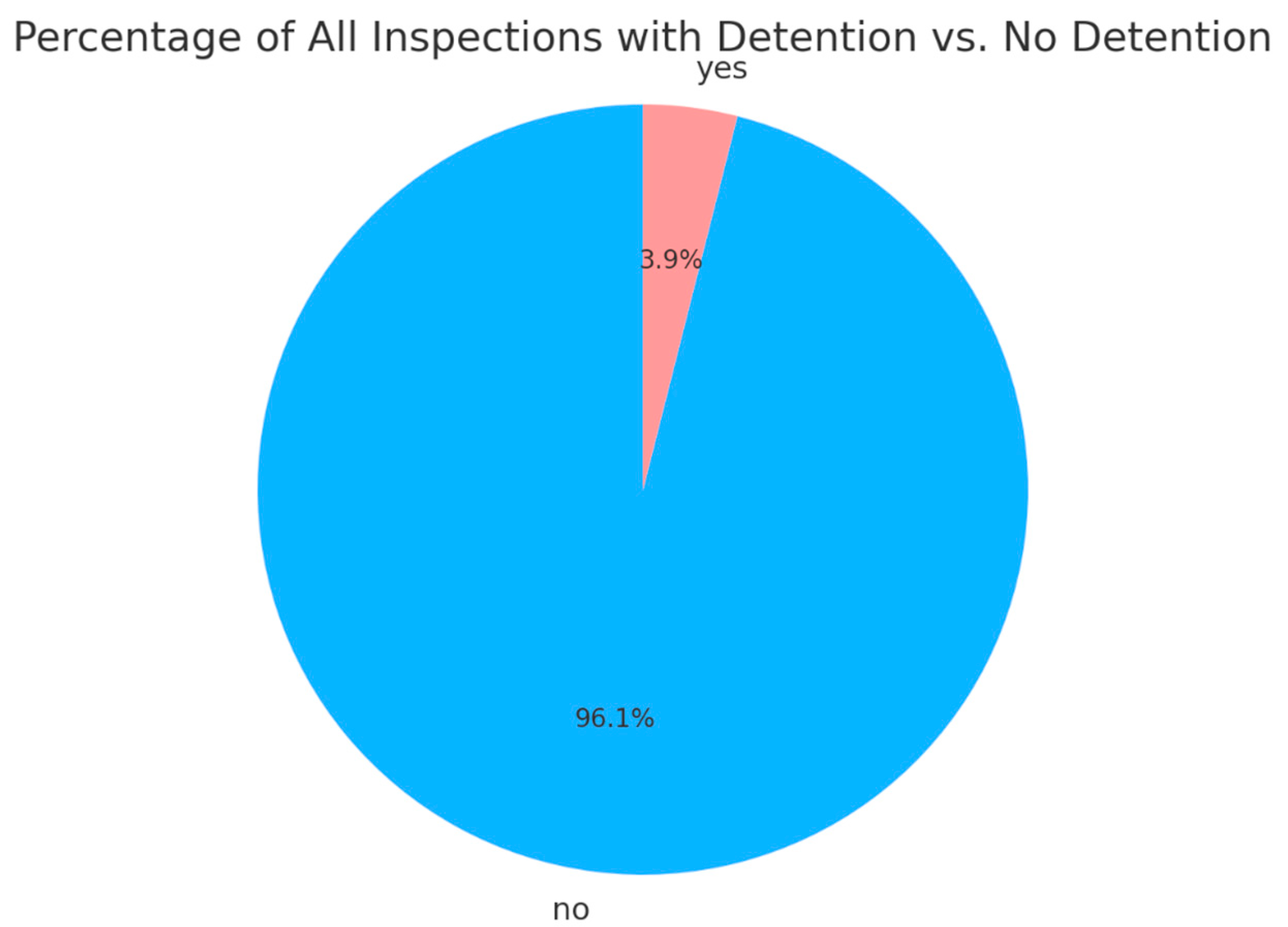
Considering the highly imbalanced nature of the original dataset regarding “whether detained,” a strategic adjustment of the prediction target was made in this study. In the original data (Figure 1), non-detained instances accounted for 96.1%, while detained instances were only 3.9%, making it likely that the model would overlook the minority class during training.
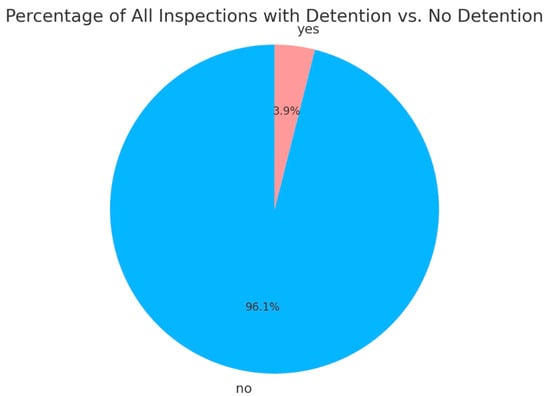
Figure 1.
Detention rate at Port of Singapore under Tokyo MoU (2014–2022). (Source: Tokyo MoU website and compiled by this study).
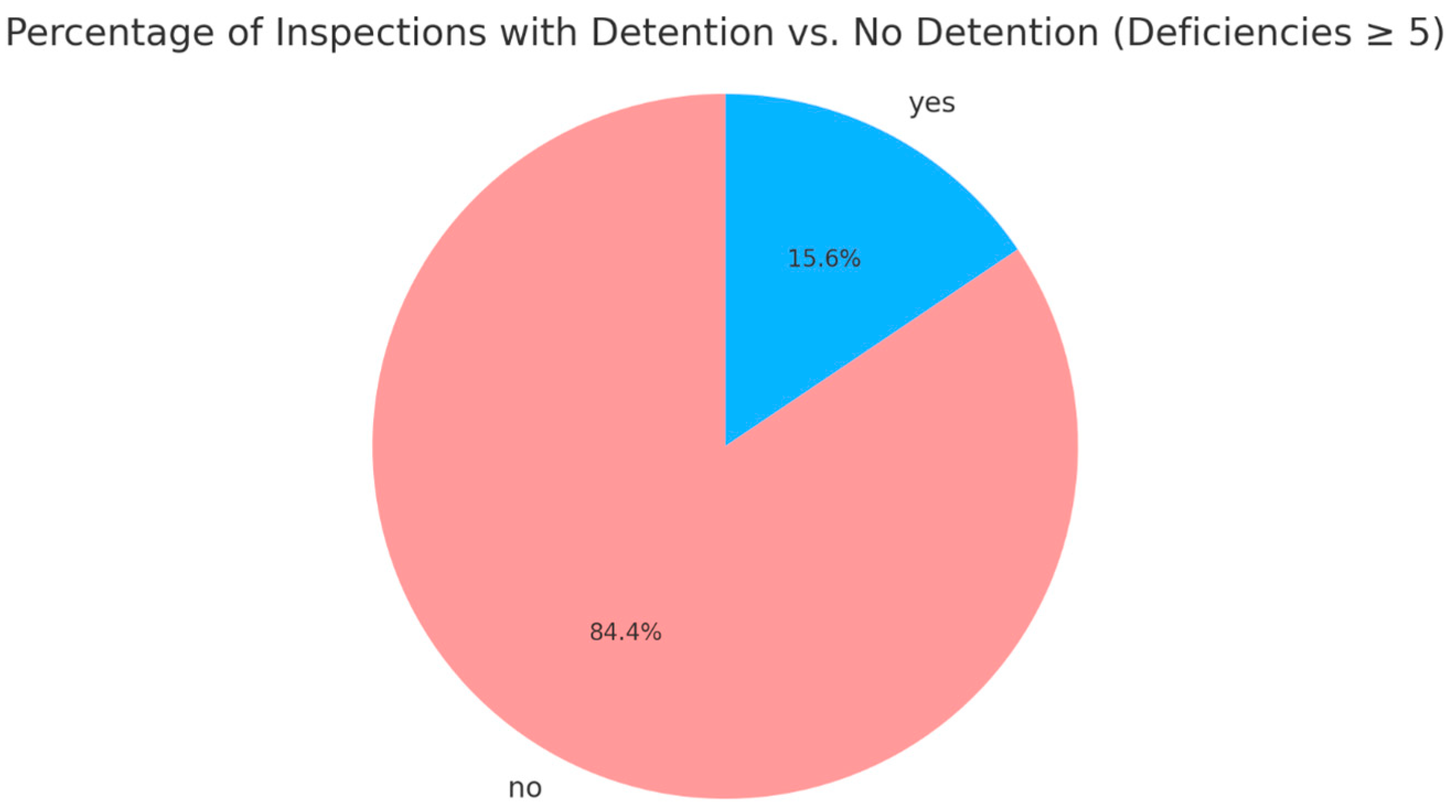
To mitigate this, the prediction target was changed to “inspection results with deficiencies ≥ 5,” where the proportion of detained versus non-detained instances was 15.6% to 84.4% (Figure 2), achieving a relatively more balanced distribution.
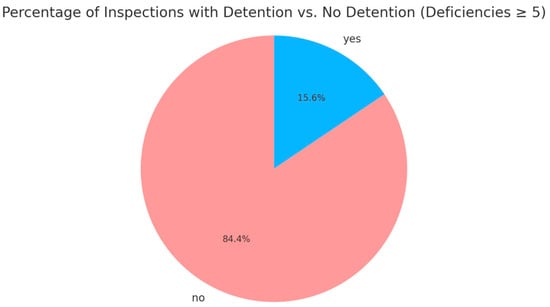
Figure 2.
Inspections with deficiencies <5 vs. ≥5 at Port of Singapore under Tokyo MoU (2014–2022). (Source: Tokyo MoU website and compiled by this study).
This adjustment was based on several considerations:
First, deficiencies represent a directly observable quantitative indicator with significant predictive value for detention risk. Second, setting the threshold at ≥5 deficiencies captures potential high-risk ships while maintaining class balance and reducing bias during model prediction. Finally, this approach improves the ability to identify potentially high-risk ships, providing more accurate decision support for actual maritime safety supervision and risk management. Another key reason for choosing the “≥5 deficiencies” threshold is its consistency with the Tokyo MoU’s quantitative ship risk rules. According to Tokyo MoU regulations, if a ship records more than 5 deficiencies during each inspection over the past 36 months, its risk score increases by 1 point for each such inspection, and ships reaching a total of 4 points are classified as high-risk. This rule reflects the potential impact of deficiency numbers on the ship’s overall safety status. Therefore, applying this threshold aligns the study with internationally recognized ship risk assessment standards, enhancing the practical relevance of the findings. Through this adjustment of the prediction target, this study aims to improve the model’s predictive accuracy and generalization capability with a more balanced data distribution, ensuring effective identification of high-risk ships in practice and improving overall safety management efficiency.
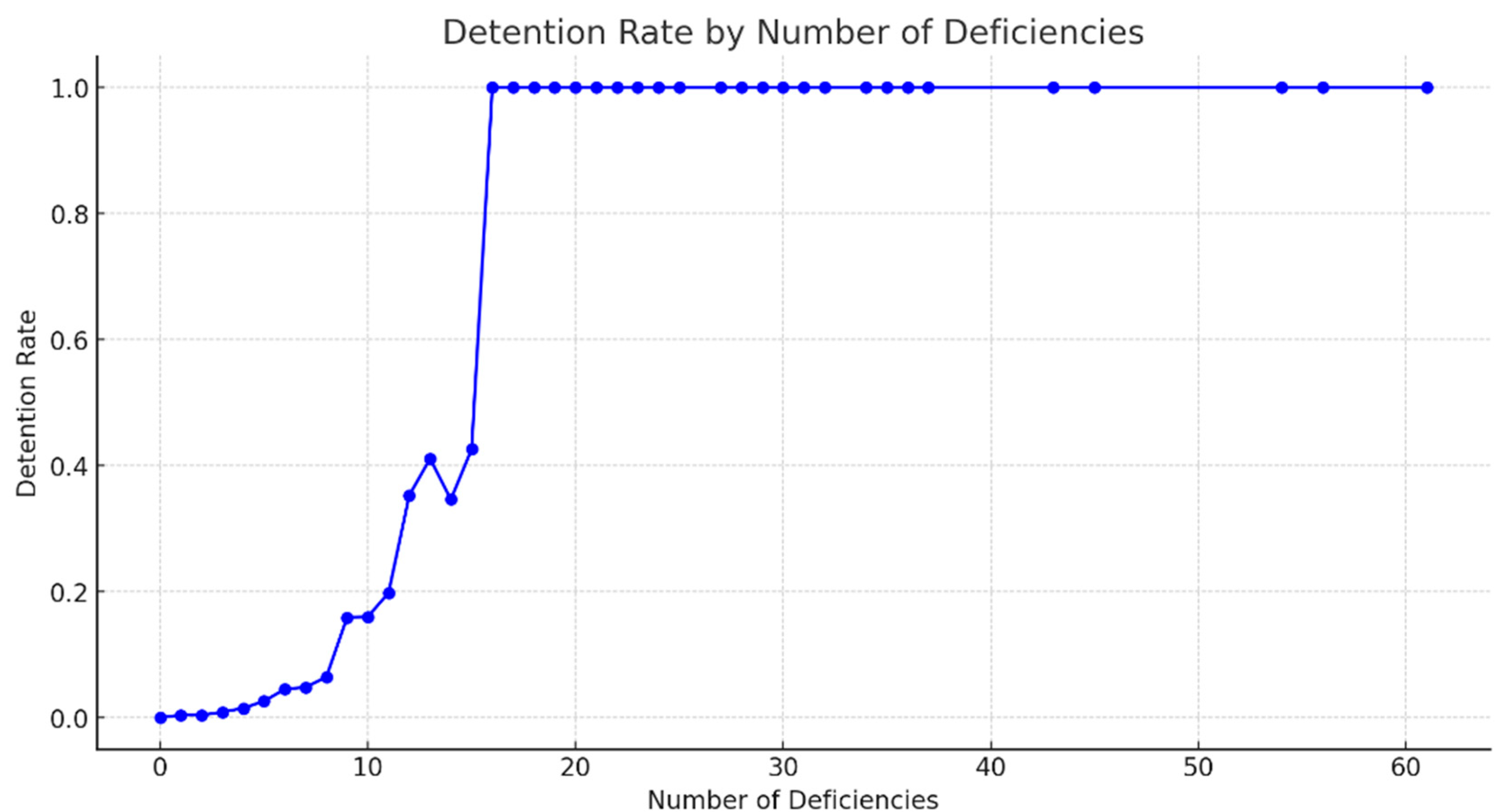
Figure 3 shows a line chart of average detention rates across different deficiency count ranges. The results indicate that as the number of deficiencies increases, the likelihood of detention rises correspondingly. Linear regression analysis between deficiency counts and detention rate yielded:
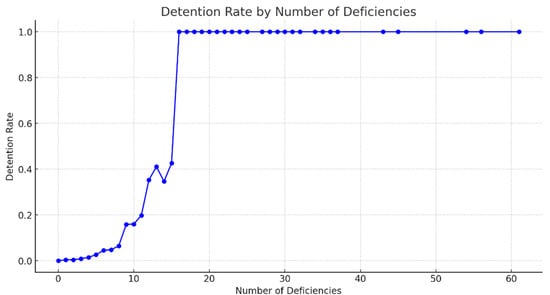
Figure 3.
Relationship between deficiency counts and detention rate at Port of Singapore under Tokyo MoU (2014–2022). (Source: Tokyo MoU website and compiled by this study).
Slope: 0.0215—implying that each additional deficiency increases the detention rate by approximately 2.15%, indicating a strong positive association.
R-squared: 0.5887—meaning about 58.87% of the variance in detention rate is explained by deficiency counts, indicating moderate-to-high explanatory power.
p-value: 7.71 × 10−9—Highly significant, indicating that I am very confident the slope is not zero, i.e., there is a significant linear relationship between the number of deficiencies and the detention rate.
As the number of deficiencies increases, the likelihood of a vessel being detained indeed rises. The data show that when the number of deficiencies increases from 8 to 9, the detention rate rises from approximately 15.88% to 16.00%, which is a small increase, but subsequent increases become more pronounced. When the number of deficiencies increases from 10 to 11, the detention rate jumps significantly from about 19.80% to 35.29%, a very large leap. When the number of deficiencies rises from 14 to 15, the detention rate surges from approximately 42.59% to 100%, the most significant increase observed. Preliminary data analysis indicates that especially when the number of deficiencies reaches 10 or more, the increase in detention rate becomes much more pronounced, and at 15 deficiencies, detention of the vessel is almost guaranteed. Therefore, it can be interpreted that once the number of deficiencies exceeds 5, the detention rate gradually increases, and after surpassing 10, the increase becomes even more substantial.
4.3. Data Cleaning
Data cleaning is a critical step in the analysis process, significantly enhancing accuracy and efficiency by producing a more focused and actionable dataset:
- Improving Data Quality:
Through removing erroneous data, imputing missing values, and standardizing data formats, the quality of the dataset improves. High-quality data reduce analytical errors and ensure the reliability of findings. For example, removing unnecessary personal identifiers (like IMO number and ship name) helps avoid privacy issues and focuses analysis on more meaningful variables.
- Simplifying Data Structure:
In the updated dataset, irrelevant or redundant fields (such as call sign and MMSI) were removed, making the dataset more concise. This simplification improves data processing efficiency and reduces memory requirements during analysis.
- Enhancing Data Focus:
New fields, such as Operating Years and Target Deficiencies, were introduced to align directly with the research objectives. Converting “Date keel laid” to the ship’s operational age (Operating Years) and creating a binary variable (Target Deficiencies) for inspections with ≥5 deficiencies enable more targeted statistical analysis and modeling. This focus ensures the analyses directly address the research questions, improving both relevance and practicality.
- Data Standardization or Normalization:
Ensuring all data adhere to consistent formats and standards is crucial, especially for longitudinal or cross-sectional comparisons. Standardized data facilitate integration and analysis of long-term trends and patterns.
Through these data cleaning measures, the final dataset was consolidated into eight distinct fields (Table 2). The updated dataset not only offers higher-quality and more focused data but also provides a solid foundation for further data analysis and decision support.

Table 2.
Overview of refined Tokyo MoU database fields.
4.4. Feature Selection
The feature selection process in the Random Forest involves first training a Random Forest model, during which the algorithm automatically calculates the importance of each feature. After model training, importance scores for each feature are obtained (as described by Formula (6)). These scores reflect each feature’s contribution to model performance when used as a split point in the decision trees. Based on the feature importance scores, the most significant features are retained. This is usually done by setting a threshold—for example, selecting the top-ranked features or those cumulatively contributing to a certain percentage of importance. The selected subset of features is then used to retrain the model. This can improve training speed and predictive performance while helping to avoid overfitting. Finally, the model trained on the reduced feature set is evaluated to ensure that feature selection does not adversely impact its predictive ability.
- Step 1: Setting the Importance Threshold
In this study, I chose the top 7 most important features based on their calculated importance. The initial feature selection included the following:
- 1.
- Flag: The ship’s flag state or country of registration, which reflects its legal and regulatory environment.
- 2.
- Ship risk profile at the time of inspection: The ship’s assessed risk level at the time of inspection, indicating its potential deficiencies and safety status.
- 3.
- Classification: The classification society certifying the ship, directly associated with its compliance and safety standards.
- 4.
- Type: The type or category of the ship, providing insights into its design, usage, and risk characteristics.
- 5.
- Tonnage: The ship’s gross tonnage, an important indicator of size and cargo capacity, relevant for evaluating structural and operational characteristics.
- 6.
- Company: The ship’s owner or operator, reflecting the management practices and maintenance standards.
- 7.
- Operating Years: The number of years the ship has been in operation, indicating aging and potential operational stability issues.
- Step 2: Analyzing Important Features
Feature importance scores were calculated based on each feature’s average contribution to reducing impurity in the model.
- Step 3: Retraining the Model with Selected Features
After identifying the important features, the Random Forest model was retrained using this feature subset. This step tests the effectiveness of the selected features, potentially improving training speed and prediction performance.
- Step 4: Performance Evaluation
The model trained with the reduced feature set was then evaluated to ensure that its predictive performance was not degraded. In this study, the prediction target was Target Deficiencies (i.e., whether the inspected ship had ≥ 5 deficiencies).
4.5. Model Training and Validation
In the field of data-driven research, machine learning has proven itself to be a powerful tool for risk assessment. This technology effectively identifies key risk factors from historical inspection records and uses them to predict and model ship inspection outcomes. The training of the machine learning model is particularly critical in risk assessment, as it directly affects the accuracy and reliability of the results.
One of the main challenges faced in this study was the extreme imbalance in the original dataset regarding the “detained or not” variable. Such an imbalance could introduce bias during model training and adversely impact the final risk assessment results. To address this issue, and based on preliminary data analysis, I strategically adjusted the prediction target to “deficiencies ≥ 5.” This threshold was chosen to mitigate classification problems caused by the highly imbalanced data. In addition, to further improve the model’s generalization ability and prevent overfitting, I applied an oversampling technique to adjust the proportion of the target classes to approximately 50:50. This method not only enhanced the model’s learning of the minority class but also ensured balanced representation of both classes during training, thereby improving predictive accuracy on unseen data.
During the model training and testing process, 80% of the data was used as the training set to build and tune the model, while the remaining 20% served as the test set to evaluate model performance and generalization ability. This split helped us more effectively validate the model’s reliability and validity in practical applications.
Through the application of these comprehensive strategies, the model was expected to more accurately identify high-risk ships and provide strong support and guidance during actual inspections. To effectively evaluate the model’s performance, I conducted an analysis of the confusion matrix, a key tool for assessing the effectiveness of classification models. The confusion matrix provides an intuitive way to understand the model’s real-world performance, particularly its ability to distinguish between different classes—correctly identifying ships as high-risk or low-risk. In the confusion matrix, each row represents the actual class, and each column represents the predicted class. This clearly shows the number of true positives (TP), false positives (FP), true negatives (TN), and false negatives (FN).
From these values, I calculated the following metrics to further evaluate the model’s performance:
Accuracy: The proportion of correct predictions (both positive and negative) over the total predictions.
Precision: The proportion of true positives among all instances predicted as positive.
Recall: The proportion of true positives among all actual positive instances.
F1 Score: The harmonic mean of precision and recall, providing a single metric to evaluate overall model effectiveness.
While no universally accepted standard exists for interpreting specific F1-score ranges, this study adopts commonly used empirical thresholds to categorize model performance (e.g., poor, fair, good, excellent) for practical evaluation purposes, following the general guidance on F1-score interpretation as described by [14,15].
The F1 performance evaluation ranges and overfitting considerations are as follows:
Poor: F1 score between 0% and 50%. The model likely suffers from high bias (underfitting), failing to learn general patterns of the data, and may also reflect overfitting to the training data with poor generalization to new data.
Fair: F1 score between 50% and 70%. The model demonstrates basic predictive capability but may perform overly well on the training set and insufficiently on the test set, indicating mild overfitting.
Good: F1 score between 70% and 85%. This range indicates good generalization ability with low risk of overfitting. The model’s performance is relatively consistent between training and test sets, achieving reliable and stable predictions.
Excellent: F1 score between 85% and 100%. The model performs exceptionally well, suggesting high accuracy and good generalization. However, there is reasonable suspicion of overfitting because the model may have fit the training data—including its noise and outliers—too perfectly, which may not exist in new, unseen data. While excellent performance is desirable, caution is still required to ensure the model has not overfitted.
5. Results and Validation
5.1. Discussion of Results
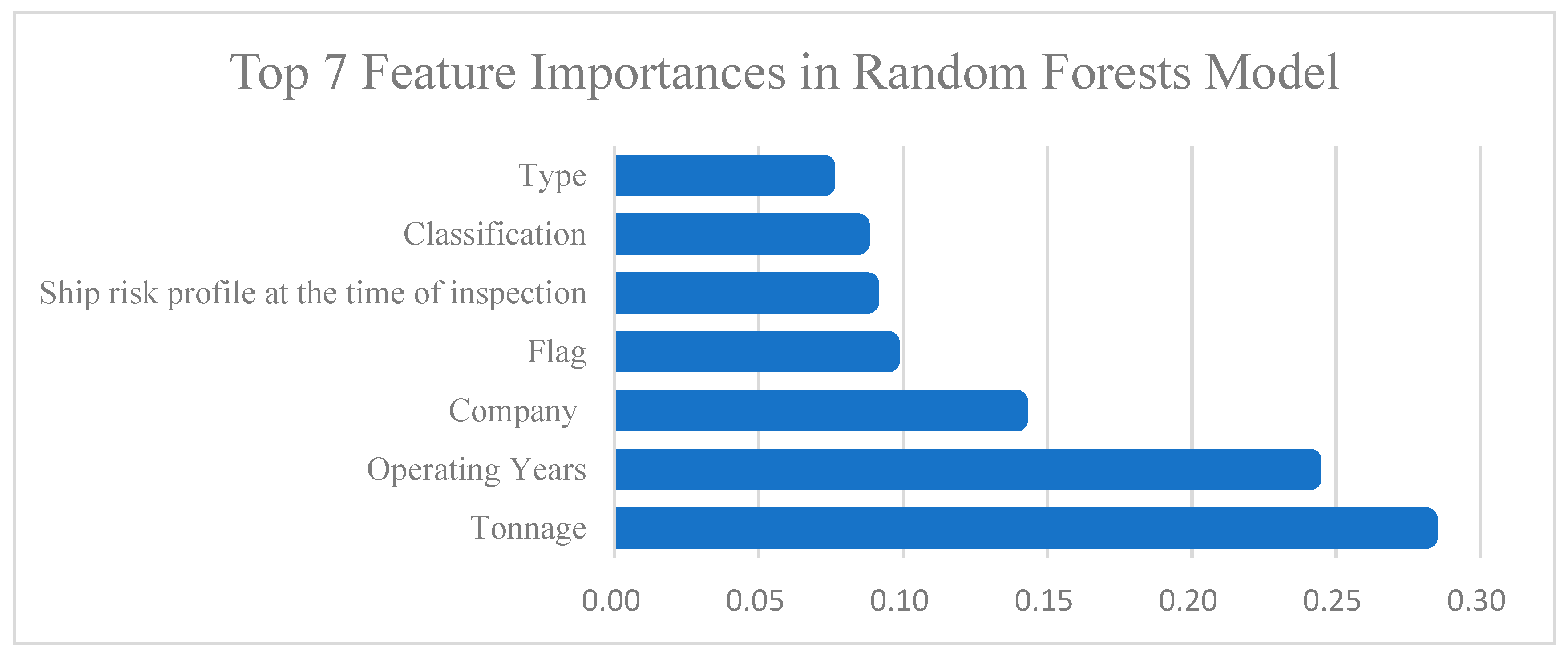
Figure 4 shows the top seven features in terms of importance in the Random Forest model. These importance scores were calculated based on the formula 6 which sums each feature’s contributions to node purity across all decision trees as its overall importance indicator.
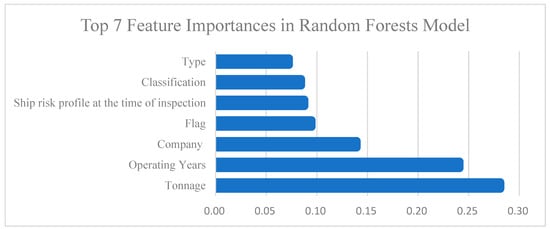
Figure 4.
Top 7 important features in the Random Forest model.
The results indicate that Tonnage (gross tonnage) and Operating Years (operating age) are the two most influential factors affecting the model’s predictions, contributing approximately 0.29 and 0.25, respectively—significantly higher than the other features. Next are Company (management company) and Flag (flag state), with importance scores ranging between 0.10 and 0.15, suggesting that both the managing company and the flag state also have considerable value in assessing ship risk. In contrast, Ship risk profile at the time of inspection, Classification (classification society), and Type (ship type) have relatively lower influence, with contributions all below 0.10.
This suggests that ship size (tonnage), operational age, and management background are key risk indicators influencing PSC inspection outcomes and should be prioritized as primary screening criteria.
However, when using the Random Forest model to predict a ship’s target deficiencies, I typically obtain a binary classification result: the ship is classified as “1” (deficiencies ≥ 5) or “0” (deficiencies < 5). In reality, even if two ships are both classified as “1” (deficiencies ≥ 5), there may still be inherent differences in their risk levels. This is because the Random Forest model does not merely predict the binary target, but also provides the probability associated with each prediction—that is, the model’s confidence that the ship belongs to the “1” category.
For example, if one ship is classified as “1” (deficiencies ≥ 5) with a probability of 85%, while another ship is also classified as “1” but with a probability of 70%, this indicates that although both ships are predicted to have at least five deficiencies, the model is more confident about the first ship. In other words, the first ship may present a higher degree of risk compared to the second. Therefore, when assessing ship risk, in addition to the binary classification result, it is also important to consider the probability value of each prediction for a more comprehensive evaluation of the ship’s risk level.
Thus, by obtaining the probability value of each prediction during the Random Forest modeling process, it is possible to more accurately identify the true risk level of ships. Compared to a decision tree model, the complexity of Random Forest may make it less straightforward to visualize as a tree diagram, which can make understanding the model’s internal workings more challenging. In this context, the predicted probability values provided by Random Forest offer decision-makers a more intuitive and user-friendly way to interpret the model’s output. This approach not only increases the transparency of the model but also enhances decision-makers’ confidence in the risk assessment.
To ensure the stability of the initial model, cross-validation—a technique for evaluating model performance—was applied to minimize result bias caused by data splitting and to provide an estimate of model stability. Here, 5-fold cross-validation was used, where the complete dataset was evenly divided into five parts (called “folds”); in each iteration, one fold was used as the test set while the other four served as the training set, rotating through all folds. The results are presented below (Table 3), illustrated with the confusion matrix and evaluation metrics.

Table 3.
Confusion matrix of the Random Forest model.
Accuracy: 81.75%.
This indicates that 81.75% of all predictions were correct.
(514 + 541)/(514 + 131 + 111 + 541) = 81.75%
Precision: 80.49%.
Among all ships predicted to have ≥5 deficiencies, 80.49% were actually correct.
541/(541 + 111) = 80.49%
Recall: 83.01%.
Among all ships that actually had ≥5 deficiencies, 83.01% were correctly identified by the model.
541/(541 + 131) = 83.01%
F1 Score: 81.73%.
The harmonic mean of precision and recall reflects a balanced performance between the two.
From the confusion matrix and performance metrics shown in Table 3, it can be seen that the Random Forest model developed in this study performs well in predicting the number of ship inspection deficiencies using the threshold of 5. The model achieved an overall accuracy of 81.75%, with precision and recall reaching 80.49% and 83.01%, respectively, indicating that the model balances prediction correctness and completeness. The F1 score of 81.73% further demonstrates that the model achieves a good balance between precision and recall.
The confusion matrix results show that the model is capable of correctly predicting the majority of ships with deficiencies above or below 5, with a relatively low proportion of misclassifications. Overall, the Random Forest model proposed in this study exhibits stable and reliable predictive ability and holds practical value in assisting Port State Control authorities in prioritizing high-risk ships for inspection, thereby making better use of limited inspection resources.
5.2. Case Validation
Table 4 presents 6 cases extracted from the Tokyo MoU database, used to validate the model:

Table 4.
Extracted data from the Tokyo MoU inspection database for case validation.
- (1)
- Case Validation 1
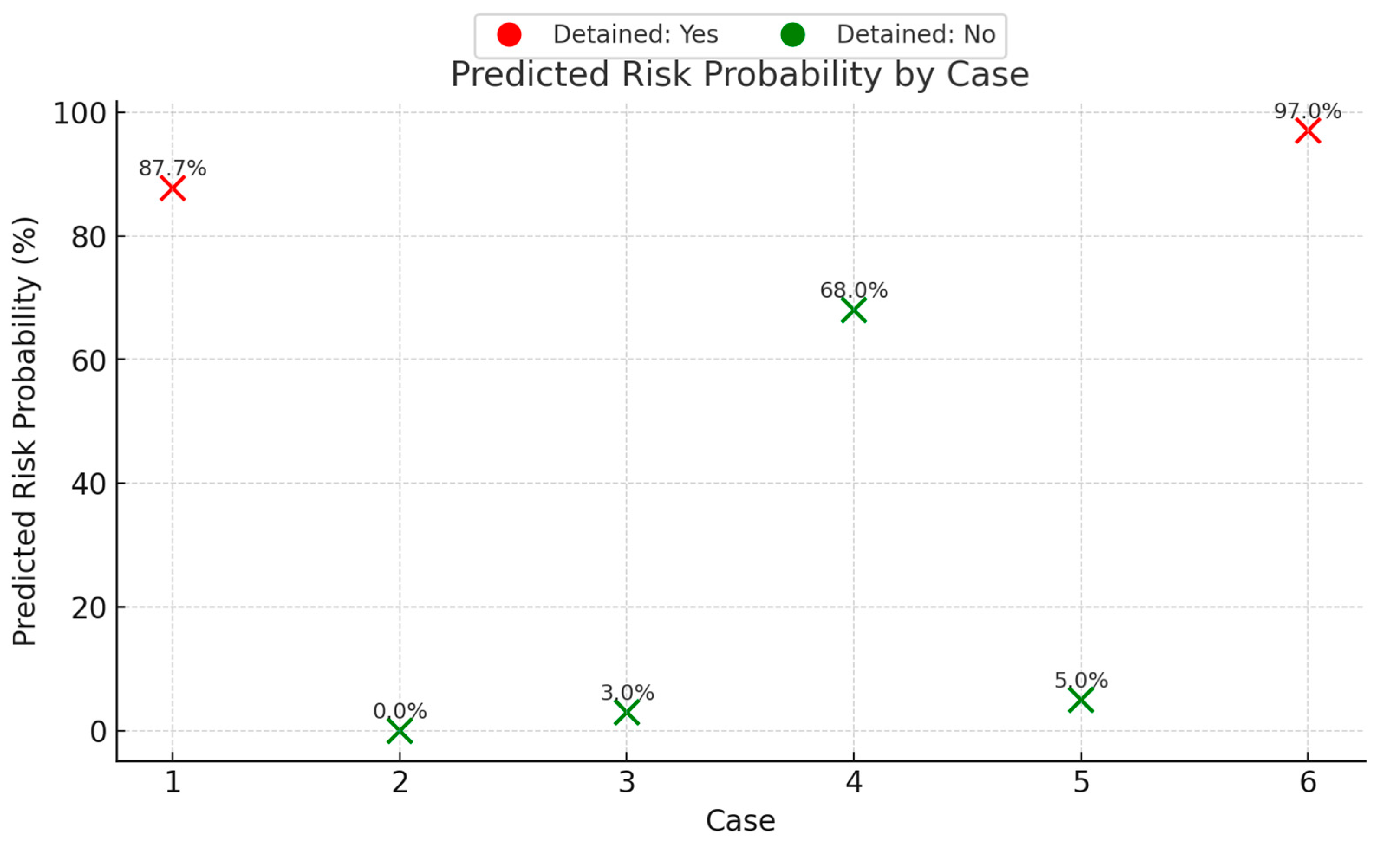
This vessel flies the flag of the Marshall Islands and is classified by the Korean Register of Shipping. It is a combined oil/chemical tanker with a gross tonnage of 11,761, managed by SONGA Ship Management. At the time of inspection, it was rated as a low-risk ship. According to the Tokyo MoU, the vessel was inspected at the Port of Singapore after 13 years of operation. The risk prediction model developed in this study estimated an 87.7% probability of having ≥5 deficiencies during inspection. The actual inspection revealed 12 deficiencies, and the vessel was detained by port authorities due to safety issues.
- (2)
- Case Validation 2
This vessel flies the flag of Belgium and is classified by Lloyd’s Register. It is an oil tanker with a gross tonnage of 8148, managed by EURONAV. At the time of inspection, it was rated as a low-risk ship. According to the Tokyo MoU, the vessel was inspected at the Port of Singapore after 13 years of operation. The risk prediction model indicated a 0.0% probability of having ≥5 deficiencies. The actual inspection found no deficiencies, and the vessel was not detained.
- (3)
- Case Validation 3
This vessel flies the flag of Liberia and is classified by DNV (Det Norske Veritas). It is a container ship with a gross tonnage of 47,952, managed by Yang Ming Marine Transport. At the time of inspection, it was rated as a standard-risk ship. According to the Tokyo MoU, the vessel was inspected at the Port of Singapore after 8 years of operation. The risk prediction model estimated a 3.0% probability of having ≥5 deficiencies. The actual inspection revealed no deficiencies, and the vessel was not detained.
- (4)
- Case Validation 4
This vessel flies the flag of Liberia and is classified by ClassNK (Nippon Kaiji Kyokai). It is a bulk carrier with a gross tonnage of 92,993, managed by KLAN GEMI YONETIMI. At the time of inspection, it was rated as a standard-risk ship. According to the Tokyo MoU, the vessel was inspected at the Port of Singapore after 18 years of operation. The risk prediction model estimated a 68.0% probability of having ≥5 deficiencies. The actual inspection revealed 8 deficiencies, but the vessel was not detained.
- (5)
- Case Validation 5
This vessel flies the flag of China and is classified by the China Classification Society. It is a container ship with a gross tonnage of 66,433, managed by Shanghai Ocean Shipping Company. At the time of inspection, it was rated as a high-risk ship. According to the Tokyo MoU, the vessel was inspected at the Port of Singapore after 19 years of operation. The risk prediction model estimated a 5.0% probability of having ≥5 deficiencies. The actual inspection found no deficiencies, and the vessel was not detained.
- (6)
- Case Validation 6
This vessel flies the flag of the United Kingdom and is classified by the American Bureau of Shipping. It is a container ship with a gross tonnage of 76,067, managed by Evergreen Marine Corporation. At the time of inspection, it was rated as a high-risk ship. According to the Tokyo MoU, the vessel was inspected at the Port of Singapore after 20 years of operation. The risk prediction model estimated a 97.0% probability of having ≥5 deficiencies. The actual inspection revealed 22 deficiencies, and the vessel was detained by port authorities due to safety issues.
5.3. Insights from Case Validation
The case validation results provide valuable insights into the predictive capability and practical implications of the proposed Random Forest model (Figure 5). Among the six validation cases, the model demonstrated strong performance in identifying high-risk vessels. For instance, Cases 1 and 6, which were both detained and exhibited high numbers of deficiencies (12 and 22, respectively), received high predicted risk probabilities of 87.7% and 97.0%, respectively. This suggests that the model effectively captured the key risk patterns associated with severe deficiencies and detention events.
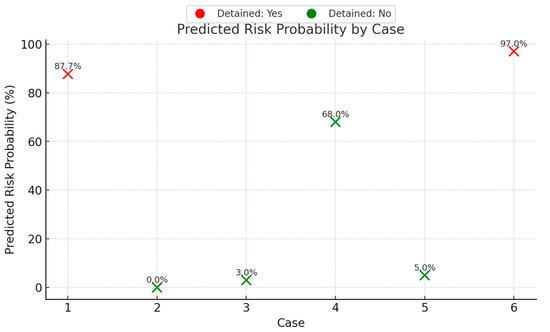
Figure 5.
Predicted risk probability by case.
Furthermore, for low-risk and standard-risk vessels (Cases 2, 3, 4, and 5), the model predicted low-risk probabilities (ranging from 0% to 68%), and these vessels were not detained in practice, aligning with the model’s prediction trend. Case 4, however, highlights an interesting observation: despite the predicted risk of 68% and having eight deficiencies, the vessel was not detained. This suggests that in practice, detention decisions may depend on additional factors beyond the number of deficiencies, such as the severity or type of deficiencies, and the feasibility of on-site rectification.
Notably, the model’s output of risk probabilities, rather than a simple binary classification, allows port authorities to prioritize inspections based on a continuous risk scale. For example, two vessels classified as high risk (“≥5 deficiencies”) still exhibited different levels of predicted probability (e.g., 87.7% vs. 68%), which can guide more nuanced decision-making and resource allocation.
In summary, the model demonstrated high sensitivity in identifying truly high-risk vessels while maintaining specificity for low-risk ones. It also provided interpretable risk scores that can support inspection prioritization. These findings confirm the model’s potential as an effective decision support tool in Port State Control practices while underscoring the need to integrate professional judgment for borderline cases.
6. Conclusions and Recommendations
In modern maritime transport, the regulatory role of port states is crucial, especially for international trade hub ports such as Singapore. As the number and size of ships continue to grow, traditional inspection methods relying on human experience are no longer sufficient to meet the demands of efficient and precise safety management. This study introduced advanced machine learning techniques and developed a risk assessment model based on historical inspection data and multidimensional ship operational indicators, providing port authorities with a more scientific decision-making tool.
This study applied Random Forest and Decision Tree models to analyze and validate ship inspection data from the Port of Singapore (within the Tokyo MoU region). The results show that the model effectively identifies high-risk ships from among thousands of inbound vessels, significantly improving the targeting and efficiency of inspections. The Random Forest model performed well, achieving an accuracy of 81.75%, precision of 80.49%, recall of 83.01%, and an F1 score of 81.73%. This demonstrates excellent predictive and generalization ability. Compared to simple decision trees or human judgment, it better captures the complex interactions between features and effectively reduces the risk of overfitting.
The application of this model enables port authorities to anticipate the risk status of ships before arrival, allocate inspection orders and resources more rationally, and focus scrutiny on high-risk vessels. This improves the efficiency and transparency of port safety management and reduces the incidence of safety incidents. Additionally, the risk assessment results help shipowners complete necessary maintenance and repairs before entering the port, enhancing seaworthiness and avoiding detentions; it also provides clearer safety guidance for crew members, encouraging self-checks and improving professional skills.
In summary, this study demonstrates the practicality and potential of machine learning techniques in PSC inspections. It not only improves existing inspection systems but also facilitates scientific resource allocation and enhances inspection efficiency, contributing significantly to compliance with international standards, maritime safety, and the effectiveness of ship management and supervision. In the future, the model’s scope and granularity can be further expanded to provide stronger data support and decision-making references for global maritime safety management.
For future research, creating interaction or derived features can help uncover hidden patterns in the data and enhance predictive capability. For example, combining features such as tonnage and operating years, or flag and ship type, as new composite features, or calculating aggregated features such as the average ship age per company, can enable the model to more comprehensively understand the relationships between variables.
To further improve the model’s generalization and applicability, future studies could integrate data from other major global ports to capture the operational characteristics and risk differences of ships across regions. In addition, developing a dynamic risk assessment model that incorporates real-time shipping and monitoring data is also an important direction. Such a model could continuously update the risk status of ships, improve the timeliness and accuracy of risk assessment, and respond more effectively to unexpected situations that may arise during ship operations.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Science and Technology Council, Taiwan, under grant number 111-2410-H-992-027. The APC was also funded under the same grant.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are openly available in the Tokyo Memorandum of Understanding (Tokyo MoU). [Tokyo Memorandum of Understanding (Tokyo MoU)] [https://apcis.tmou.org/public/, accessed on 29 July 2025].
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD). Review of Maritime Transport 2022; United Nation Publications: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 105–107. [Google Scholar]
- Cariou, P.; Mejia, M.Q.; Wolff, F.-C. Evidence on target factors used for port state control inspections. Mar. Policy 2009, 33, 847–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cariou, P.; Wolff, F.-C. Identifying substandard vessels through Port State Control inspections: A new methodology for Concentrated Inspection Campaigns. Mar. Policy 2015, 60, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapp, S.; Franses, P.H. Econometric analysis on the effect of port state control inspections on the probability of casualty—Can targeting of substandard ships for inspections be improved? Mar. Policy 2007, 31, 550–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapp, S.; Velden, M.v.d. Visualization of differences in treatment of safety inspections across Port State Control regimes: A case for increased harmonization efforts. Transp. Rev. 2009, 29, 499–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Luo, M.; Yin, J. Flag choice and Port State Control inspections—Empirical evidence using a simultaneous model. Transp. Policy 2014, 35, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hänninen, M.; Kujala, P. Bayesian network modeling of Port State Control inspection findings and ship accident involvement. Expert Syst. Appl. 2014, 41, 1632–1646. [Google Scholar]
- Tsou, M.C. Big data analysis of port state control ship detention database. J. Mar. Eng. Technol. 2019, 18, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Wang, S.; Peng, C. An Artificial Intelligence Model Considering Data Imbalance for Ship Selection in Port State Control Based on Detention Probabilities. J. Comput. Sci. 2021, 48, 101257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirci, S.M.E.; Cicek, K. Intelligent ship inspection analytics: Ship deficiency data mining for port state control. Ocean. Eng. 2023, 278, 114232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Yu, Q.; Yang, Z.; Wan, C. A data-driven Bayesian model for evaluating the duration of detention of ships in PSC inspections. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2024, 181, 103371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhang, M.; Gong, F.; Wang, S.; Yan, R. Improving port state control through a transfer learning-enhanced XGBoost model. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2025, 253, 110558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, D.M.W. Evaluation: From precision, recall and F-measure to ROC, informedness, markedness and correlation. J. Mach. Learn. Technol. 2011, 2, 37–63. [Google Scholar]
- Futurense. F1 Score in Machine Learning: All You Need To Know in 2025. 2025. Available online: https://futurense.com/uni-blog/f1-score-machine-learning (accessed on 20 June 2025).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).