Marine Rare Earth Elements: Distribution Patterns, Enrichment Mechanisms and Microbial Interactions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. REY in Seawater
2.1. Sources and Distribution of REY in Seawater
2.2. Speciation and Fractionation of REY in Seawater
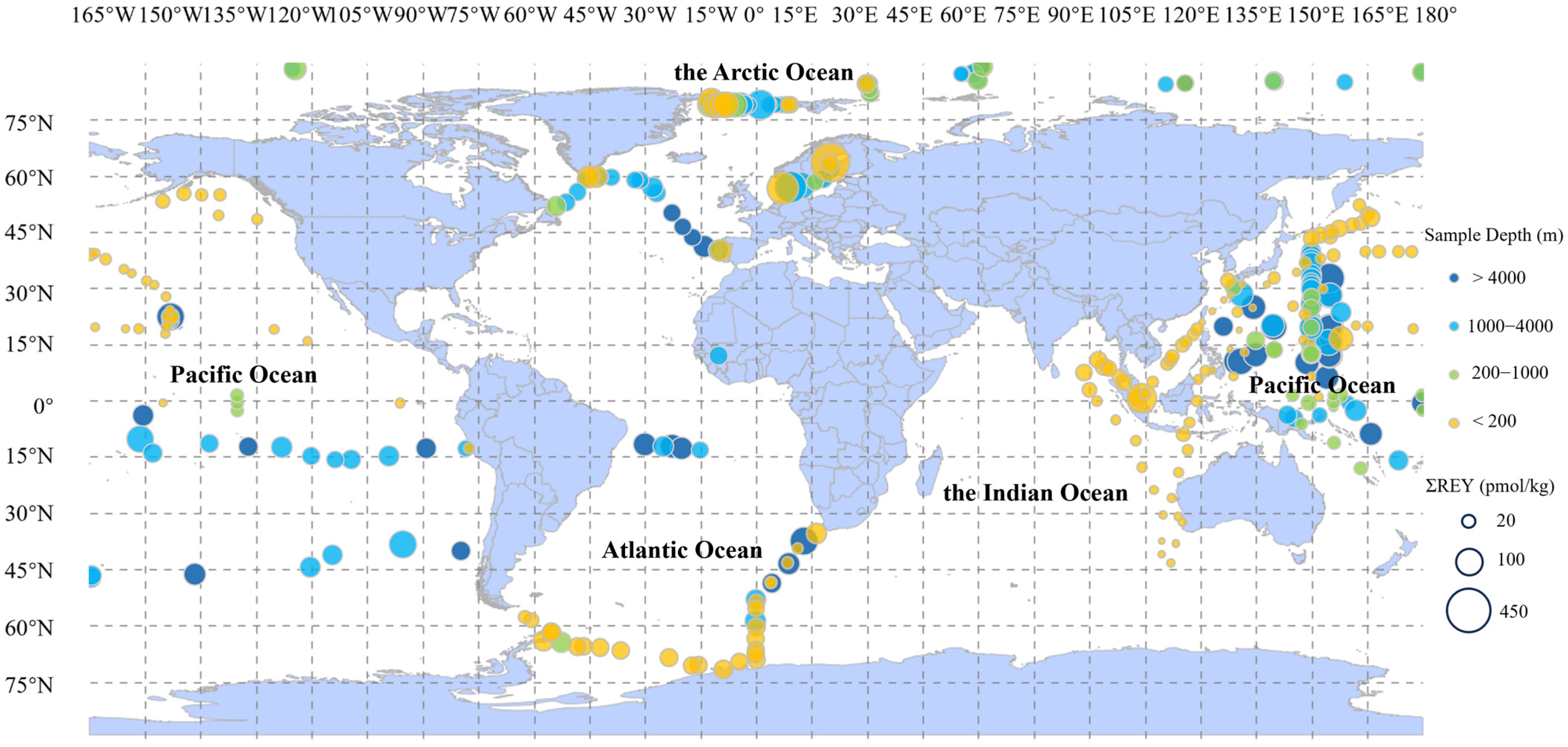
3. REY in Deep-Sea Sediments
3.1. Deep-Sea Sediments REY Sources and Distribution
3.2. REY Enrichment Process in Deep-Sea Sediments
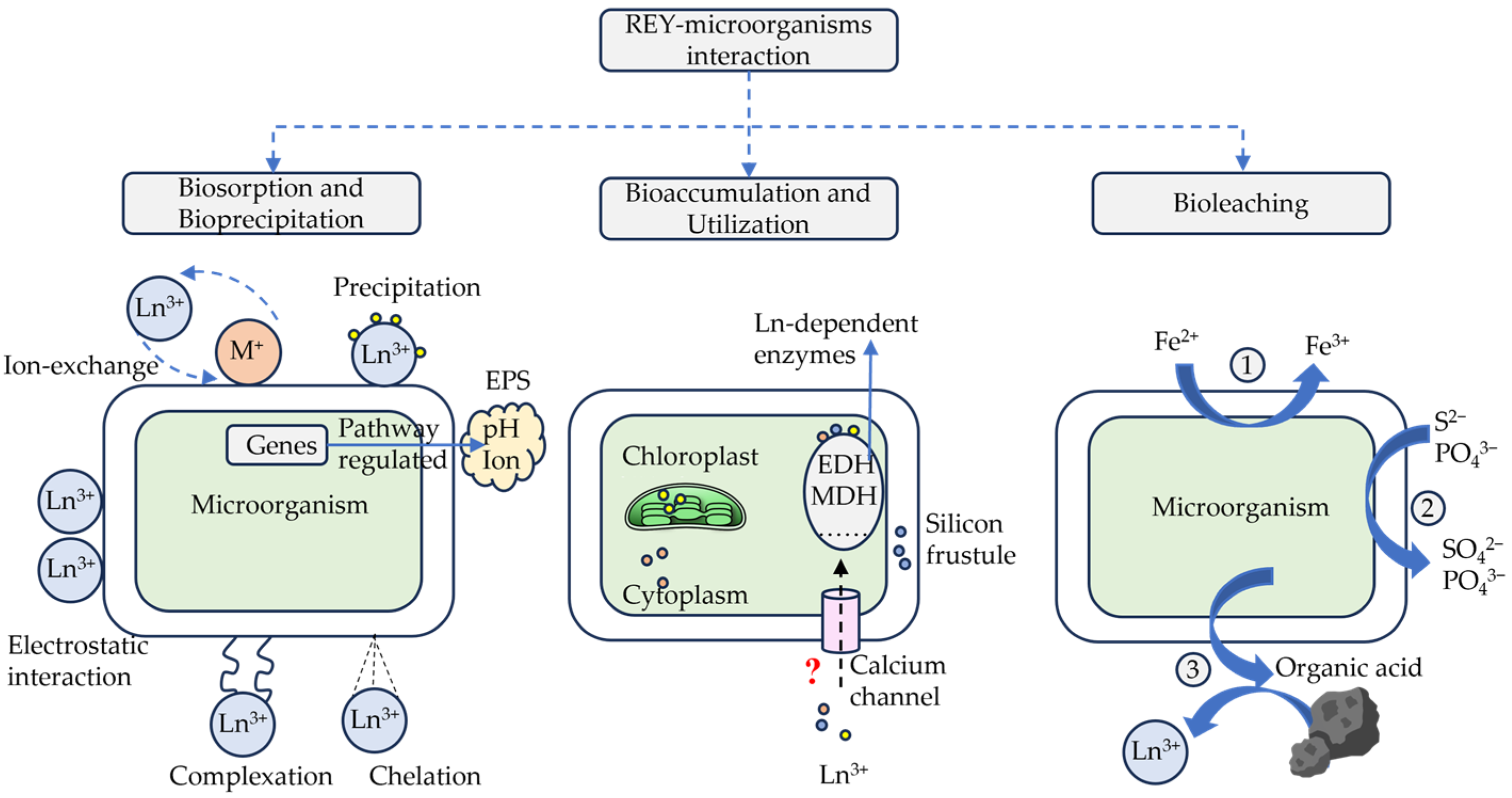
4. Microorganism–REY Interactions
4.1. REY Biosorption and Bioprecipitation
| Mechanism | Categories | Strains | Tested REY | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biosorption | F | Aspergillus flavus | Ce | [101] |
| F | Aspergillus niger | Ce | [101] | |
| F | Botryosphaeria rhodina | La, Sm | [102] | |
| F | Candida colliculosa | Nd | [103] | |
| F | Candida utilis | La, Sm, Sc, Y | [104] | |
| F | Catenulostroma chromoblastomyces | Ce, Nd, Gd, Dy | [96] | |
| F | Debaryomyces hansenii | Nd | [103] | |
| F | Fusarium sp. | Nd, Gd, Dy, Lu | [96] | |
| F | Kluyveromyces marxianus | Nd | [103] | |
| F | Pichia naganishii | La, Nd, Dy, Yb | [96] | |
| F | Pichia sp. | La, Nd, Dy, Yb | [96] | |
| F | Saccharomyces cerevisiae | La, Sm, Gd, Dy, Yb, Lu, Ce | [90,91,92,96,103,105] | |
| N | Agrobacterium sp. | La, Ce | [106] | |
| N | Caulobacter crescentus | Tb | [107] | |
| N | Escherichia coli | HREY | [87,89] | |
| N | Leisingera methylohalidivorans | HREY | [96] | |
| N | Magnetospirillum magneticum | La | [108] | |
| N | Methylobacterium extorquens * | Ln | [100,109] | |
| N | Paenisporosarcina sp. | Ce | [10] | |
| N | Phaeobacter inhibens | HREY | [96,97] | |
| N | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | La, Eu, Yb | [110] | |
| N | Pseudomonas fluorescens | Ce, Sm | [86] | |
| N | Sulfitobacter sp. | Ce | [10] | |
| P | Bacillus licheniformis | Ce | [111] | |
| P | Bacillus thuringiensis | Eu | [112] | |
| P | Jeotgalibacillus sp. | Ce | [10] | |
| Bioleaching | F | Aspergillus flavus | Ce; REY from industry wastes | [101] |
| F | Aspergillus niger | REY ore | [113,114,115,116,117] | |
| F | Aspergillus terreus | La, Ce, Nd, Pr | [118] | |
| F | Aspergillus sp. | Nd, Pm, Sm, Eu, Gd | [119] | |
| F | Candida bombicola | REY from coal fly ash | [120] | |
| F | Cryptococcus curvatus | REY from coal fly ash | [120] | |
| F | Paecilomyces sp. | La, Ce, Nd, Pr | [118,121] | |
| F | Penicillium chrysogenum | La, Ce, Y | [122] | |
| F | Penicillium tricolor | La, Ce, Nd, Sc, Y | [123] | |
| F | Penicillium sp. | REY from monazite | [124] | |
| F | Phanerochaete chrysosporium | La, Ce, Nd, Sc, Y | [120] | |
| F | Yarrowia lipolytica | La, Nd, Ce | [115] | |
| N | Acetobacter aceti | REY from monazite | [125] | |
| N | Acetobacter sp. | La, Ce, Nd, Sc, Y | [126] | |
| N | Acetobacter tropicalis | Sc | [127] | |
| N | Acidianus manzaensis | Ce, Gd, Sc, Y, | [128] | |
| N | Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans | Nd, Pm, Sm, Eu, Gd, REY from phosphogypsum | [119,129,130,131,132] | |
| N | Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans | La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Sm, Eu, Gd, Dy, Ho, Y | [133,134] | |
| N | Acidophilium multivorum | Ce, Dy, Er, Eu, Gd, Ho, La, Nd, Pr, Sm, Tb, Tm, Lu | [135] | |
| N | Aspergillus ficuum | REY from monazite | [136] | |
| N | Burkholderia thailandensis | REY from monazite | [137] | |
| N | Enterobacter aerogenes | REY from monazite | [124] | |
| N | Gluconobacter oxydans | REY ore | [138,139,140] | |
| N | Leptospirillum ferriphilum | La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Sm, Eu, Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm, Lu | [135] | |
| N | Pantoea agglomerans | REY from monazite | [124] | |
| N | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | REY from monazite; coal fly ash | [120,136] | |
| N | Pseudomonas putida | REY from monazite | [124] | |
| P | Alicyclobacillus tolerans | La, Ce, Nd | [141] | |
| P | Arthrobacter nicotianae | REY ore | [89] | |
| P | Bacillus licheniformis | Ce; REY from industry wastes | [111] | |
| P | Bacillus sp. | La, Ce, Dy, Lu | [142] | |
| P | Streptomyces sp. | La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Sm, Eu, Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm, Yb, Lu, Y | [143] |
4.2. REY Bioaccumulation and Utilization
4.3. REY Bioleaching and Degradation
5. Conclusions: Existing Challenges and Future Perspectives
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| REY | Rare earth elements and yttrium |
| LREY | Light rare earth elements |
| MREY | Middle rare earth elements |
| HREY | Heavy rare earth elements |
| MDH | Methanol dehydrogenase |
| EDH | Ethanol dehydrogenase |
| SDH | Sorbose dehydrogenase |
| GDH | Glucose dehydrogenase |
| Ln | Lanthanide |
| Ce | Cerium |
References
- Balaram, V. Rare earth elements: A review of applications, occurrence, exploration, analysis, recycling, and environmental impact. Geosci. Front. 2019, 10, 1285–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Ilton, E.S.; Wang, Z.; Rosso, K.M.; Zhang, X. Global rare earth element resources: A concise review. Appl. Geochem. 2024, 175, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piarulli, S.; Hansen, B.H.; Ciesielski, T.; Zocher, A.-L.; Malzahn, A.; Olsvik, P.A.; Sonne, C.; Nordtug, T.; Jenssen, B.M.; Booth, A.M. Sources, distribution and effects of rare earth elements in the marine environment: Current knowledge and research gaps. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 291, 118230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, Y.; Fujinaga, K.; Nakamura, K.; Takaya, Y.; Kitamura, K.; Ohta, J.; Toda, R.; Nakashima, T.; Iwamori, H. Deep-sea mud in the Pacific Ocean as a potential resource for rare-earth elements. Nat. Geosci. 2011, 4, 535–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neira, P.; Romero-Freire, A.; Basallote, M.; Qiu, H.; Cobelo-García, A.; Cánovas, C.R. Review of the concentration, bioaccumulation, and effects of lanthanides in marine systems. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 920405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatje, V.; Schijf, J.; Johannesson, K.; Andrade, R.; Caetano, M.; Brito, P.; Haley, B.; Lagarde, M.; Jeandel, C. The global biogeochemical cycle of the rare earth elements. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2024, 38, e2024GB008125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Guo, Q.; Liu, C.; He, G.; Cao, J.; Liao, J.; Liu, C.; Wang, H.; Zhou, J.; Liu, Y. Early diagenetic control on the enrichment and fractionation of rare earth elements in deep-sea sediments. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabn5466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Ren, J.; Guo, Q.; Cao, J.; Wang, H.; Liu, C. Rare earth element geochemistry characteristics of seawater and porewater from deep sea in western Pacific. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J.; Jiang, X.; He, G.; Wang, F.; Yang, T.; Luo, S.; Deng, Y.; Zhou, J.; Deng, X.; Yao, H. Enrichment and sources of REY in phosphate fractions: Constraints from the leaching of REY-rich deep-sea sediments. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2022, 335, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Cao, W.; Saren, G.; Chang, F. Study on the enrichment and mineralization of rare earth element cerium by marine bacteria. Mar. Geol. Quat. Geol. 2023, 43, 190–197. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Giese, E.C. Biosorption as green technology for the recovery and separation of rare earth elements. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 36, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lhamo, P.; Mahanty, B. Bioleaching of rare earth elements from industrial and electronic wastes: Mechanism and process efficiency. In Environmental Technologies to Treat Rare Earth Element Pollution: Principles and Engineering; Sinharoy, A., Lens, P.N.L., Eds.; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2022; pp. 207–226. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, H.; Huang, L.; Zhao, L.; Zeng, Q.; Liu, X.; Sheng, Y.; Shi, L.; Wu, G.; Jiang, H.; Li, F. A critical review of mineral–microbe interaction and co-evolution: Mechanisms and applications. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2022, 9, nwac128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akagi, T. Rare earth element (REE)–silicic acid complexes in seawater to explain the incorporation of REEs in opal and the “leftover” REEs in surface water: New interpretation of dissolved REE distribution profiles. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2013, 113, 174–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akagi, T.; Fu, F.F.; Hongo, Y.; Takahashi, K. Composition of rare earth elements in settling particles collected in the highly productive North Pacific Ocean and Bering Sea: Implications for siliceous-matter dissolution kinetics and formation of two REE-enriched phases. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2011, 75, 4857–4876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flierdt, T.V.D.; Frank, M.; Lee, D.C.; Halliday, A.N.; Reynolds, B.C.; Hein, J.R. New constraints on the sources and behavior of neodymium and hafnium in seawater from Pacific Ocean ferromanganese crusts. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2004, 68, 3827–3843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olías, M.; Cerón, J.C.; Fernández, I.; Rosa, J.D.L. Distribution of rare earth elements in an alluvial aquifer affected by acid mine drainage: The Guadiamar aquifer (SW Spain). Environ. Pollut. 2005, 135, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olías, M.; Cánovas, C.R.; Basallote, M.D.; Lozano, A. Geochemical behaviour of rare earth elements (REE) along a river reach receiving inputs of acid mine drainage. Chem. Geol. 2018, 493, 468–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sholkovitz, E.R.; Landing, W.M.; Lewis, B.L. Ocean particle chemistry: The fractionation of rare earth elements between suspended particles and seawater. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1994, 58, 1567–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hathorne, E.C.; Stichel, T.; Brück, B.; Frank, M. Rare earth element distribution in the atlantic sector of the Southern Ocean: The balance between particle scavenging and vertical supply. Mar. Chem. 2015, 177, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffett, J.W. Microbially mediated cerium oxidation in sea water. Nature 1990, 345, 421–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.Y.; Rempfer, J.; Frank, M.; Stumpf, R.; Molina-Kescher, M. Upper ocean vertical supply: A neglected primary factor controlling the distribution of neodymium concentrations of open ocean surface waters? J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2013, 118, 3887–3894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chester, R.; Jickells, T. Marine Geochemistry, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; 411p. [Google Scholar]
- Elderfield, H.R.; Upstill-Goddard, R.; Sholkovitz, E.R. The rare earth elements in rivers, estuaries, and coastal seas and their significance to the composition of ocean waters. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1990, 54, 971–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatje, V.; Bruland, K.W.; Flegal, A.R. Determination of rare earth elements after pre-concentration using NOBIAS-chelate PA-1®resin: Method development and application in the San Francisco Bay plume. Mar. Chem. 2014, 160, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Solsona, E.; Jeandel, C.; Labatut, M.; Lacan, F.; Vance, D.; Chavagnac, V.; Pradoux, C. Rare earth elements and Nd isotopes tracing water mass mixing and particle-seawater interactions in the SE Atlantic. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta J. Geochem. Soc. Meteorit. Soc. 2014, 125, 351–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vítová, M.; Mezricky, D. Microbial recovery of rare earth elements from various waste sources: A mini review with emphasis on microalgae. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 40, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrne, R.H.; Kim, K.-H. Rare earth element scavenging in seawater. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1990, 54, 2645–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrens, M.K.; Pahnke, K.; Paffrath, R.; Schnetger, B.; Brumsack, H.-J. Rare earth element distributions in the West Pacific: Trace element sources and conservative vs. non-conservative behavior. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2018, 486, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Z.; Cui, G.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Liu, Q. Dissolved rare earth elements in the Northwest Pacific: Sources, water mass tracing, and cross-shelf fluxes. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1135113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenier, M.; Jeandel, C.; Lacan, F.; Vance, D.; Venchiarutti, C.; Cros, A.; Cravatte, S. From the subtropics to the central equatorial Pacific Ocean: Neodymium isotopic composition and rare earth element concentration variations. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2013, 118, 592–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Kescher, M.; Hathorne, E.C.; Osborne, A.H.; Behrens, M.K.; Kölling, M.; Pahnke, K.; Frank, M. The influence of Basaltic Islands on the oceanic REE distribution: A case study from the Tropical South Pacific. Front. Mar. Sci. 2018, 5, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Kescher, M.; Frank, M.; Hathorne, E. South Pacific dissolved Nd isotope compositions and rare earth element distributions: Water mass mixing versus biogeochemical cycling. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2014, 127, 171–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tazoe, H.; Obata, H.; Gamo, T. Coupled isotopic systematics of surface cerium and neodymium in the Pacific Ocean. Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 2011, 12, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, A.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Z.; Ren, J.; Cai, Y.; Zhou, K.; Guo, X.; Liu, X. Spatiotemporal variation of dissolved rare earth elements in the North Pacific Subtropical Gyre: Influence of biogeochemical cycling and application in tracing deep water. Glob. Planet. Change 2025, 246, 104719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fröllje, H.; Pahnke, K.; Schnetger, B.; Brumsack, H.-J.; Dulai, H.; Fitzsimmons, J.N. Hawaiian imprint on dissolved Nd and Ra isotopes and rare earth elements in the central North Pacific: Local survey and seasonal variability. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2016, 189, 110–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hongo, Y.; Obata, H.; Sotto Alibo, D.; Nozaki, Y. Spatial variations of rare earth elements in North Pacific surface water. J. Oceanogr. 2006, 62, 441–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, Y.; Obata, H.; Doi, T.; Hongo, Y.; Gamo, T.; Takeda, S.; Tsuda, A. Rare earth elements in seawater during an iron-induced phytoplankton bloom of the western subarctic Pacific (SEEDS-II). Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2009, 56, 2839–2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haley, B.A.; Wu, Y.; Muratli, J.M.; Basak, C.; Pena, L.D.; Goldstein, S.L. Rare earth element and neodymium isotopes of the eastern US GEOTRACES Equatorial Pacific Zonal Transect (GP16). Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2021, 576, 117233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagarde, M.; Pham, V.Q.; Lherminier, P.; Belhadj, M.; Jeandel, C. Rare earth elements in the North Atlantic, part I: Non-conservative behavior reveals margin inputs and deep waters scavenging. Chem. Geol. 2024, 664, 122230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stichel, T.; Frank, M.; Rickli, J.; Hathorne, E.C.; Haley, B.A.; Jeandel, C.; Pradoux, C. Sources and input mechanisms of hafnium and neodymium in surface waters of the Atlantic sector of the Southern Ocean. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2012, 94, 22–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.-Y.; Plancherel, Y.; Saito, M.A.; Scott, P.M.; Henderson, G.M. Rare earth elements (REEs) in the tropical South Atlantic and quantitative deconvolution of their non-conservative behavior. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2016, 177, 217–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crocket, K.C.; Hill, E.; Abell, R.E.; Johnson, C.; Gary, S.F.; Brand, T.; Hathorne, E.C. Rare earth element distribution in the NE Atlantic: Evidence for benthic sources, longevity of the seawater signal, and biogeochemical cycling. Front. Mar. Sci. 2018, 5, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amakawa, H.; Alibo, D.S.; Nozaki, Y. Nd isotopic composition and REE pattern in the surface waters of the eastern Indian Ocean and its adjacent seas. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2000, 64, 1715–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paffrath, R.; Pahnke, K.; Böning, P.; Rutgers van der Loeff, M.; Valk, O.; Gdaniec, S.; Planquette, H. Seawater-Particle Interactions of Rare Earth Elements and Neodymium Isotopes in the Deep Central Arctic Ocean. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2021, 126, e2021JC017423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laukert, G.; Frank, M.; Bauch, D.; Hathorne, E.C.; Rabe, B.; von Appen, W.-J.; Wegner, C.; Zieringer, M.; Kassens, H. Ocean circulation and freshwater pathways in the Arctic Mediterranean based on a combined Nd isotope, REE and oxygen isotope section across Fram Strait. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2017, 202, 285–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takaya, Y.; Yasukawa, K.; Kawasaki, T.; Fujinaga, K.; Ohta, J.; Usui, Y.; Nakamura, K.; Kimura, J.-I.; Chang, Q.; Hamada, M. The tremendous potential of deep-sea mud as a source of rare-earth elements. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, K.; Fujinaga, K.; Yasukawa, K.; Takaya, Y.; Ohta, J.; Machida, S.; Haraguchi, S.; Kato, Y. REY-Rich Mud: A Deep-Sea Mineral Resource for Rare Earths and Yttrium. Handb. Phys. Chem. Rare Earths 2015, 46, 79–127. [Google Scholar]
- Iijima, K.; Yasukawa, K.; Fujinaga, K.; Nakamura, K.; Machida, S.; Takaya, Y.; Ohta, J.; Haraguchi, S.; Nishio, Y.; Usui, Y. Discovery of extremely REY-rich mud in the western North Pacific Ocean. Geochem. J. 2016, 50, 557–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasukawa, K.; Liu, H.; Fujinaga, K.; Machida, S.; Haraguchi, S.; Ishii, T.; Nakamura, K.; Kato, Y. Geochemistry and mineralogy of REY-rich mud in the eastern Indian Ocean. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2014, 93, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasukawa, K.; Kino, S.; Ohta, J.; Azami, K.; Tanaka, E.; Mimura, K.; Fujinaga, K.; Nakamura, K.; Kato, Y. Stratigraphic variations of Fe–Mn micronodules and implications for the formation of extremely REY-rich mud in the western North Pacific Ocean. Minerals 2021, 11, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasukawa, K.; Nakamura, K.; Fujinaga, K.; Machida, S.; Kato, Y. Rare-earth, major, and trace element geochemistry of deep-sea sediments in the Indian Ocean: Implications for the potential distribution of REY-rich mud in the Indian Ocean. Geochem. J. 2015, 49, 621–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasukawa, K.; Ohta, J.; Miyazaki, T.; Vaglarov, B.S.; Chang, Q.; Ueki, K.; Toyama, C.; Kimura, J.I.; Tanaka, E.; Nakamura, K. Statistic and Isotopic Characterization of Deep-Sea Sediments in the Western North Pacific Ocean: Implications for Genesis of the Sediment Extremely Enriched in Rare Earth Elements. Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 2019, 20, 3402–3430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.F.; Bi, D.J.; Huang, M.; Yu, M.; Luo, Y.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, J. Distribution and metallogenesis of deep-sea area rare earth elements. Geol. Bull. China 2021, 40, 195–208. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Fujinaga, K.; Yasukawa, K.; Nakamura, K.; Machida, S.; Kato, Y. Geochemistry of REY-rich mud in the Japanese Exclusive Economic Zone around Minamitorishima Island. Geochem. J. 2016, 50, 575–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Shi, X.; Huang, M.; Yu, M.; Bi, D.; Ren, X.; Yang, G.; Zhu, A. The Influence of Hydrothermal Fluids on the REY-Rich Deep-Sea Sediments in the Yupanqui Basin, Eastern South Pacific Ocean: Constraints from Bulk Sediment Geochemistry and Mineralogical Characteristics. Minerals 2020, 10, 1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wells, M.L.; Rember, R. Dissolved iron anomaly in the deep tropical–subtropical Pacific: Evidence for long-range transport of hydrothermal iron. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2015, 75, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, B.; Dong, Y.; Han, X.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Chu, F. Enrichment of smectite in the REY-rich mud of the Clarion-Clipperton Fracture Zone in the eastern Pacific and its geological significance. Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 2024, 25, e2023GC011283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koschinsky, A.; Halbach, P. Sequential leaching of marine ferromanganese precipitates: Genetic implications. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1995, 59, 5113–5132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, R.M.; Olivarez, A.M. Geochemistry of rare earth elements in Pacific hydrothermal sediments. Mar. Chem. 1988, 25, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schijf, J.; Byrne, R.H. Speciation of yttrium and the rare earth elements in seawater: Review of a 20-year analytical journey. Chem. Geol. 2021, 584, 120479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Haley, B.A.; Mix, A.C.; Abbott, A.N.; Manus, J.M.; Vance, D. Reactive-transport modeling of neodymium and its radiogenic isotope in deep-sea sediments: The roles of authigenesis, marine silicate weathering and reverse weathering. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. Lett. J. Devoted Dev. Time Earth Planet. Syst. 2022, 596, 117792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liang, X.; He, H.; Li, J.; Ma, L.; Tan, W.; Zhong, Y.; Zhu, J.; Zhou, M.-F.; Dong, H. Microorganisms accelerate REE mineralization in supergene environments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2022, 88, e00632-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.; Shi, X.; Huang, M.; Liu, J.; Yan, Q.; Yang, G.; Li, C.; Yang, B.; Zhou, T.; Bi, D.; et al. The transfer of rare earth elements during early diagenesis in REY-rich sediments: An example from the Central Indian Ocean Basin. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 136, 104269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, J.; Yasukawa, K.; Nakamura, K.; Fujinaga, K.; Iijima, K.; Kato, Y. Geological features and resource potential of deep-sea mud highly enriched in rare-earth elements in the Central Pacific Basin and the Penrhyn Basin. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 139, 104440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, D.; Shi, X.; Huang, M.; Yu, M.; Fang, X. Geochemical and mineralogical characteristics of deep-sea sediments from the western North Pacific Ocean: Constraints on the enrichment processes of rare earth elements. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 104318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, F.; He, G.; Deng, X.; Wei, Z.; Yao, H. Mechanism and influencing factors of REY enrichment in deep-sea sediments. Minerals 2021, 11, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Chen, J.; Sun, X.; Wu, Z.; Deng, Y.; Shi, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Koschinsky, A. Quantifying the controlling mineral phases of rare-earth elements in deep-sea pelagic sediments. Chem. Geol. 2022, 595, 120792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Sun, X.; Li, D.; Sa, R.; Lu, Y.; Lin, Z.; Xu, L.; Zhan, R.; Pan, Y.; Xu, H. New insights into nanostructure and geochemistry of bioapatite in REE-rich deep-sea sediments: LA-ICP-MS, TEM, and Z-contrast imaging studies. Chem. Geol. 2019, 512, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, J.; Yasukawa, K.; Machida, S.; Fujinaga, K.; Kato, Y. Geological factors responsible for REY-rich mud in the western North Pacific Ocean: Implications from mineralogy and grain size distributions. Geochem. J. 2016, 50, 591–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Shi, X.; Huang, M.; Yu, M.; Shi, M. Genesis of REY-rich deep-sea sediments in the Tiki Basin, eastern South Pacific Ocean: Evidence from geochemistry, mineralogy and isotope systematics. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 138, 104330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kon, Y.; Hoshino, M.; Sanematsu, K.; Morita, S.; Takagi, T. Geochemical Characteristics of Apatite in Heavy REE-rich Deep-Sea Mud from Minami-Torishima Area, Southeastern Japan. Resour. Geol. 2014, 64, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jing, Y.; Zhao, W. Distribution of rare earth elements and implication for Ce anomalies in the clay-sized minerals of deep-sea sediment, Western Pacific Ocean. Appl. Clay Sci. 2023, 235, 106876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Algeo, T.J.; Cao, L.; Zhao, L.; Chen, Z.Q.; Li, Z. Diagenetic uptake of rare earth elements by conodont apatite. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2016, 458, 176–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elderfield, H. The Oceans and Marine Geochemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006; Volume 6. [Google Scholar]
- Bradbury, M.H.; Baeyens, B. Sorption of Eu on Na- and Ca-montmorillonites: Experimental investigations and modelling with cation exchange and surface complexation. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2002, 66, 2325–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.C.; Shi, X.; Zhou, T.; Huang, M.; Yu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Bi, D.; Zhu, A.; Fang, X. Evaluating the contribution of hydrothermal fluids and clay minerals to the enrichment of rare earth elements and yttrium (REY) in deep-sea sediments. Ore Geol. Rev. 2023, 161, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Algeo, T.J.; Zhao, L.; Chen, Z.Q.; Cao, L.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y. Diagenetic uptake of rare earth elements by bioapatite, with an example from Lower Triassic conodonts of South China. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2015, 149, 181–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.N.; Lhr, S.; Trethewy, M. Are Clay Minerals the Primary Control on the Oceanic Rare Earth Element Budget. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hein, J.R.; Mizell, K.; Koschinsky, A.; Conrad, T.A. Deep-ocean mineral deposits as a source of critical metals for high- and green-technology applications: Comparison with land-based resources. Ore Geol. Rev. 2013, 51, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, Y.; Hayasaka, Y.; Morita, K.; Kashiwabara, T.; Nakada, R.; Marcus, M.A.; Kato, K.; Tanaka, K.; Shimizu, H. Transfer of rare earth elements (REE) from manganese oxides to phosphates during early diagenesis in pelagic sediments inferred from REE patterns, X-ray absorption spectroscopy, and chemical leaching method. Geochem. J. 2015, 49, 653–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagarde, M.; Lemaitre, N.; Planquette, H.; Grenier, M.; Jeandel, C. Particulate Rare Earth Element behavior in the North Atlantic (GEOVIDE cruise). Biogeosciences 2020, 17, 5539–5561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soli, A.L.; Byrne, R.H. Europium silicate complexation at 25 °C and 0.7 molar ionic strength. Mar. Chem. 2017, 195, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picone, N.; den Camp, H.J.O. Role of rare earth elements in methanol oxidation. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2019, 49, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalali, J.; Lebeau, T. The Role of Microorganisms in Mobilization and Phytoextraction of Rare Earth Elements: A Review. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 688430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohnuki, T.; Jiang, M.; Sakamoto, F.; Kozai, N.; Yamasaki, S.; Yu, Q.; Tanaka, K.; Utsunomiya, S.; Xia, X.; Yang, K. Sorption of trivalent cerium by a mixture of microbial cells and manganese oxides: Effect of microbial cells on the oxidation of trivalent cerium. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2015, 163, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, Y.; Châtellier, X.; Hattori, K.H.; Kato, K.; Fortin, D. Adsorption of rare earth elements onto bacterial cell walls and its implication for REE sorption onto natural microbial mats. Chem. Geol. 2005, 219, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuruta, T. Selective accumulation of light or heavy rare earth elements using gram-positive bacteria. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2006, 52, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, D.; Middleton, A.; Smith, R.; Deblonde, G.; Laudal, D.; Theaker, N.; Hsu-Kim, H.; Jiao, Y. A biosorption-based approach for selective extraction of rare earth elements from coal byproducts. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 241, 116726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Ohnuki, T.; Tanaka, K.; Kozai, N.; Kamiishi, E.; Utsunomiya, S. Post-adsorption process of Yb phosphate nano-particle formation by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2012, 93, 30–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Ohnuki, T.; Utsunomiya, S. Biomineralization of middle rare earth element samarium in yeast and bacteria systems. Geomicrobiol. J. 2018, 35, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Caprio, F.; Altimari, P.; Zanni, E.; Uccelletti, D.; Toro, L.; Pagnanelli, F. Lanthanum biosorption by different Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2016, 49, 37–42. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, S.; Pan, J.; Dong, B.; Zhou, W.; Zhou, C. Bioleaching of rare earth elements: Perspectives from mineral characteristics and microbial species. Minerals 2023, 13, 1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Wang, F.; Ma, C.; Zhang, H.; Liu, K. Microbial-driven fabrication of rare earth materials. Sci. China Mater. 2024, 67, 2376–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Zhang, X.; Chen, J.; Qian, X.; Zhong, Y.; Ma, C.; Zhang, H.; Liu, K. The construction of a microbial synthesis system for rare earth enrichment and material applications. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2303457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breuker, A.; Ritter, S.F.; Schippers, A. Biosorption of rare earth elements by different microorganisms in acidic solutions. Metals 2020, 10, 954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldeinstein, J.P.N.; Bassin, J.P. Biosorption as a Strategy for the Recovery of Rare Earth Elements. Biosorption Wastewater Contam. 2022, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dev, S.; Sachan, A.; Dehghani, F.; Ghosh, T.; Briggs, B.R.; Aggarwal, S. Mechanisms of biological recovery of rare-earth elements from industrial and electronic wastes: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 397, 124596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macaskie, L.E.; Yong, P.; Paterson-Beedle, M.; Thackray, A.C.; Marquis, P.M.; Sammons, R.L.; Nott, K.P.; Hall, L.D. A novel non line-of-sight method for coating hydroxyapatite onto the surfaces of support materials by biomineralization. J. Biotechnol. 2005, 118, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roszczenko-Jasińska, P.; Vu, H.N.; Subuyuj, G.A.; Crisostomo, R.V.; Cai, J.; Lien, N.F.; Clippard, E.J.; Ayala, E.M.; Ngo, R.T.; Yarza, F. Gene products and processes contributing to lanthanide homeostasis and methanol metabolism in Methylorubrum extorquens AM1. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sallam, A.; Amin, M.; Elaassy, I.E.; El-Feky, H.; Nada, A.; Harpy, N. Biosorption of Rare Earth Elements by Two Fungal Genera from Lower Carboniferous Carbonaceous Shales, Southwestern Sinai, Egypt. J. Appl. Environ. Biol. Sci. 2014, 4, 146–154. [Google Scholar]
- Giese, E.C.; Dekker, R.F.H.; Barbosa-Dekker, A.M. Biosorption of lanthanum and samarium by viable and autoclaved mycelium of Botryosphaeria rhodina MAMB-05. Biotechnol. Prog. 2019, 35, e2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlachou, A.; Symeopoulos, B.D.; Koutinas, A.A. A comparative study of neodymium sorption by yeast cells. Int. J. Chem. Asp. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 2009, 97, 437–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korenevsky, A.A.; Sorokin, V.V.; Karavaiko, G. Biosorption of rare earth elements. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 1998, 19, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M. Biological nano-mineralization of Ce phosphate by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Chem. Geol. 2010, 277, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuxia, X.U.; Zhang, S.; Chen, K.; Han, J.; Kun, W.U. Biosorption of La3+ and Ce3+ by Agrobacterium sp. HN1. J. Rare Earths 2011, 29, 265–270. [Google Scholar]
- Park, D.M.; Reed, D.W.; Yung, M.C.; Eslamimanesh, A.; Lencka, M.M.; Anderko, A.; Fujita, Y.; Riman, R.E.; Navrotsky, A.; Jiao, Y. Bioadsorption of Rare Earth Elements through Cell Surface Display of Lanthanide Binding Tags. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 2735–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, M.; Reinicke, B.; Wawrousek, K. Biosorption and biomagnetic recovery of La3+ by Magnetospirillum magneticum AMB-1 biomass. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 303, 122140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotruvo, J.A., Jr.; Featherston, E.R.; Mattocks, J.A.; Ho, J.V.; Laremore, T.N. Lanmodulin: A highly selective lanthanide-binding protein from a lanthanide-utilizing bacterium. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 15056–15061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Texier, A.C.; Andrès, Y.; Cloirec, P.L. Selective biosorption of lanthanide (La, Eu, Yb) ions by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, L.; Ke, Z.; Kovarik, L.; Dong, H. Resource Recovery: Adsorption and Biomineralization of Cerium by Bacillus licheniformis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 426, 127844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.; Wu, W.; Lü, J.; Chen, Z.; Li, L.; Rao, W.; Guan, X. Biosorption and extraction of europium by Bacillus thuringiensis strain. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2017, 75, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Li, S.; Wang, J.; Jiang, S.; Panchal, B.; Sun, Y. Bioleaching rare earth elements from coal fly ash by Aspergillus niger. Fuel 2023, 354, 129387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahaloo-Horeh, N.; Mousavi, S.M. A novel green strategy for biorecovery of valuable elements along with enrichment of rare earth elements from activated spent automotive catalysts using fungal metabolites. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 430, 128509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, L.; Zhou, H.; Shi, Q.; Meng, X.; Zhao, Y.; Qiu, G.; Zhang, X.; Yu, H.; He, X.; He, H. Comparative chemical and non-contact bioleaching of ion-adsorption type rare earth ore using ammonium sulfate and metabolites of Aspergillus niger and Yarrowia lipolytica to rationalise the role of organic acids for sustainable processing. Hydrometallurgy 2023, 216, 106019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, L.; Gómez-lvarez, H.; González, F.; Muoz, J. Biorecovery of rare earth elements from fluorescent lamp powder using the fungus Aspergillus niger in batch and semicontinuous systems. Miner. Eng. 2017, 75, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Wang, J.; Yu, X.; Kang, J.; Qiu, G.; Zhao, H.; Shen, L. Effective extraction of rare earth elements from ion-adsorption type rare earth ore by three bioleaching methods. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 330, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brisson, V.L.; Zhuang, W.Q.; Alvarez-Cohen, L. Bioleaching of rare earth elements from monazite sand. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2016, 113, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnett, M.J.; Palumbo-Roe, B.; Deady, E.A.; Gregory, S.P. Comparison of Three Approaches for Bioleaching of Rare Earth Elements from Bauxite. Minerals 2020, 10, 649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Liang, Y. Bioleaching of trace elements and rare earth elements from coal fly ash. Int. J. Coal Sci. Technol. 2019, 6, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, S.; Zhuang, W.Q.; Rabaey, K.; Alvarez-Cohen, L.; Hennebel, T. Concomitant Leaching and Electrochemical Extraction of Rare Earth Elements from Monazite. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 1654–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilyas, S.; Kim, H.; Srivastava, R.R. Feasibility of the Bio-Mobilization of Rare Earth Elements from Bauxite Residual Red Mud. Environ. Sci. Proc. 2021, 6, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, Y.; Lian, B. Bioleaching of rare earth and radioactive elements from red mud using Penicillium tricolor RM-10. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 136, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corbett, M.K.; Eksteen, J.J.; Xi-Zhi, N.; Watkin, E.L.J. Syntrophic effect of indigenous and inoculated microorganisms in the leaching of rare earth elements from Western Australian monazite. Res. Microbiol. 2018, 169, 558–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doyun, S.; Jiwoong, K.; Byung-Su, K.; Jinki, J.; Jae-Chun, L. Use of Phosphate Solubilizing Bacteria to Leach Rare Earth Elements from Monazite-Bearing Ore. Minerals 2015, 5, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, X.; Tian, W.; Zhang, Y. Bioleaching of Major, Rare Earth, and Radioactive Elements from Red Mud by using Indigenous Chemoheterotrophic Bacterium Acetobacter sp. Minerals 2019, 9, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiskira, K.; Lymperopoulou, T.; Tsakanika, L.-A.; Pavlopoulos, C.; Papadopoulou, K.; Ochsenkühn, K.-M.; Lyberatos, G.; Ochsenkühn-Petropoulou, M. Study of Microbial Cultures for the Bioleaching of Scandium from Alumina Industry By-Products. Metals 2021, 11, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.R.; Chen, H.R.; Nie, Z.Y.; Xia, J.L.; Li, E.P.; Fan, X.L.; Zheng, L. Extraction of Al and rare earths (Ce, Gd, Sc, Y) from red mud by aerobic and anaerobic bi-stage bioleaching. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 401, 125914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Hu, X.; Song, X.; Yang, A. Bioleaching of rare-earth elements from phosphate rock using Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 75, 1111–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, C.; Tang, Q.; Liu, S.; Kim, H.; Liu, D. A two-step bioleaching process enhanced the recovery of rare earth elements from phosphogypsum. Hydrometallurgy 2023, 221, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.M.; Vakilchap, F.; Baniasadi, M.; Mousavi, S.; Darban, A.K.; Farnaud, S. Green recovery of cerium and strontium from gold mine tailings using an adapted acidophilic bacterium in one-step bioleaching approach. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2022, 138, 104482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homayoun, F.; Hackett, M.J.; Khaleque, H.N.; Eksteen, J.J.; Kaksonen, A.H.; Watkin, E.L.J. Better together: Potential of co-culture microorganisms to enhance bioleaching of rare earth elements from monazite. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2018, 3, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.F.; Tan, F.; Lin, J.F. An integrated approach combines hydrothermal chemical and biological treatment to enhance recycle of rare metals from coal fly ash. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 395, 124640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayar, S.P.; Palmieri, M.C.; Bevilaqua, D. Sulfuric acid bioproduction and its application in rare earth extraction from phosphogypsum. Miner. Eng. 2022, 185, 107662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Balboa, C.; Martínez-Alesón García, P.; López-Rodas, V.; Costas, E.; Baselga-Cervera, B. Microbial biominers: Sequential bioleaching and biouptake of metals from electronic scraps. MicrobiologyOpen 2022, 11, e1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussien, S.S. Bioleaching of some Rare Earth Elements from Egyptian Monazite using Aspergillus ficuum and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Walailak J. Sci. Technol. 2014, 11, 809–823. [Google Scholar]
- Castro, L.; Gómez-lvarez, H.; Carmona, M.; González, F.; Muoz, J.A. Influence of biosurfactants in the recovery of REE from monazite using Burkholderia thailandensis. Hydrometallurgy 2023, 222, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, V.; Dorte, F.; Derik, W.; Harrison, S.T.L.; Athanasios, K.; Mark, D. Toward the bioleaching of bauxite residue by Gluconobacter oxydans. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2024, 135, lxae279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aston, J.E.; Thompson, V.S.; Fujita, Y.; Reed, D.W. Metabolic flux modeling of Gluconobacter oxydans enables improved production of bioleaching organic acids. Process Biochem. 2022, 122, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, A.M.; Pian, B.; Medin, S.; Reid, M.C.; Wu, M.; Gazel, E.; Barstow, B. Generation of a Gluconobacter oxydans knockout collection for improved extraction of rare earth elements. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Issayeva, A.U.; Pankiewicz, R.; Otarbekova, A.A. Bioleaching of Metals from Wastes of Phosphoric Fertilizers Production. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2020, 29, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnett, M.J.; Palumbo-Roe, B.; Gregory, S.P. Comparison of heterotrophic bioleaching and ammonium sulfate ion exchange leaching of rare earth elements from a Madagascan ion-adsorption clay. Minerals 2018, 8, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Dong, H.; Liu, Y.; Bian, L.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Huang, Y. Bioleaching of rare earth elements from bastnaesite-bearing rock by actinobacteria. Chem. Geol. 2018, 483, 544–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabochnicka-Swiatek, M.; Krzywonos, M. Potentials of Biosorption and Bioaccumulation Processes for Heavy Metal Removal. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2014, 23, 551–561. [Google Scholar]
- Macmillan, G.A.; Chételat, J.; Heath, J.P.; Mickpegak, R.; Amyot, M. Rare earth elements in freshwater, marine, and terrestrial ecosystems in the eastern Canadian Arctic. Env. Sci. Process. Impacts 2017, 19, 1336–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strady, E.; Kim, I.; Radakovitch, O.; Kim, G. Rare earth element distributions and fractionation in plankton from the northwestern Mediterranean Sea. Chemosphere 2015, 119, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, C.B.; Krsten, S.; Rsken, L.M.; Cappel, F.; Beresko, C.; Ankerhold, G.; Schnleber, A.; Geimer, S.; Ecker, D.; Wehner, S. Cyanobacterial promoted enrichment of rare earth elements europium, samarium and neodymium and intracellular europium particle formation. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 32581–32593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.M.; Bakar, N.K.A.; Bakar, A.F.A.; Ashraf, M.A. Chemical speciation and bioavailability of rare earth elements (REEs) in the ecosystem: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 22764–22789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Řezanka, T.; Kaineder, K.; Mezricky, D.; Řezanka, M.; Bišová, K.i.; Zachleder, V.; Vítová, M. The effect of lanthanides on photosynthesis, growth, and chlorophyll profile of the green alga Desmodesmus quadricauda. Photosynth. Res. 2016, 130, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, P.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Zhu, J.; Reinert, T.; Heitmann, J.; Spemann, D.; Vogt, J.; Flagmeyer, R.-H.; Butz, T. Study of metal bioaccumulation by nuclear microprobe analysis of algae fossils and living algae cells. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. At. 2000, 161, 801–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Ren, Q.G.; Mi, Y.; Shi, X.F.; Liu, B. Investigation of metal ion accumulation in Euglena gracilis by fluorescence methods. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. 2002, 189, 506–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne; Robert, H.; Patten; James, T. Assessment of Fe(III) and Eu(III) complexation by silicate in aqueous solutions. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta J. Geochem. Soc. Meteorit. Soc. 2017, 202, 361–373. [Google Scholar]
- Pałasz, A.; Czekaj, P. Toxicological and cytophysiological aspects of lanthanides action. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2000, 47, 1107–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voutsinos, M.Y.; Banfield, J.F.; McClelland, H.-L.O. Extensive and diverse lanthanide-dependent metabolism in the ocean. ISME J. 2025, 19, wraf057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reitz, Z.L.; Medema, M.H. Genome mining strategies for metallophore discovery. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2022, 77, 102757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Good, N.M.; Vu, H.N.; Suriano, C.J.; Subuyuj, G.A.; Skovran, E.; Martinez-Gomez, N.C. Pyrroloquinoline Quinone Ethanol Dehydrogenase in Methylobacterium extorquens AM1 Extends Lanthanide-Dependent Metabolism to Multicarbon Substrates. J. Bacteriol. 2016, 198, 3109–3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahn, B.; Pol, A.; Lumpe, H.; Barends, T.R.M.; Dietl, A.; Hogendoorn, C.; Opdencamp, P.H.J.M.; Daumann, P.L.J. Similar but Not the Same: First Kinetic and Structural Analyses of a Methanol Dehydrogenase Containing a Europium Ion in the Active Site. Wiley-Blackwell Online Open 2018, 19, 1147–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pol, A.; Barends, T.R.; Dietl, A.; Khadem, A.F.; Eygensteyn, J.; Jetten, M.S.; Op den Camp, H.J. Rare earth metals are essential for methanotrophic life in volcanic mudpots. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 16, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitriyanto, N.A.; Fushimi, M.; Matsunaga, M.; Pertiwiningrum, A.; Iwama, T.; Kawai, K. Molecular structure and gene analysis of Ce3+-induced methanol dehydrogenase of Bradyrhizobium sp. MAFF211645. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2011, 111, 613–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, H.; Zheng, Y.; Ludmila, C. Lanthanide-Dependent Methanol Dehydrogenases of XoxF4 and XoxF5 Clades Are Differentially Distributed Among Methylotrophic Bacteria and They Reveal Different Biochemical Properties. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1366. [Google Scholar]
- Hibi, Y.; Asai, K.; Arafuka, H.; Hamajima, M.; Iwama, T.; Kawai, K. Molecular structure of La3+-induced methanol dehydrogenase-like protein in Methylobacterium radiotolerans. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2011, 111, 547–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wehrmann, M.; Billard, P.; Martin-Meriadec, A.; Zegeye, A.; Klebensberger, J. Functional Role of Lanthanides in Enzymatic Activity and Transcriptional Regulation of Pyrroloquinoline Quinone-Dependent Alcohol Dehydrogenases in Pseudomonas putida KT2440. Mbio 2017, 8, e00570-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arienzo, M.; Ferrara, L.; Trifuoggi, M.; Toscanesi, M. Advances in the Fate of Rare Earth Elements, REE, in Transitional Environments: Coasts and Estuaries. Water 2022, 14, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Good, N.M.; Walser, O.N.; Moore, R.S.; Suriano, C.J.; Martinez-Gomez, N.C. Investigation of lanthanide-dependent methylotrophy uncovers complementary roles for alcohol dehydrogenase enzymes. Cold Spring Harb. Lab. 2018, 329011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochsner, A.M.; Hemmerle, L.; Vonderach, T.; Nüssli, R.; Bortfeld-Miller, M.; Hattendorf, B.; Vorholt, J.A. Use of rare-earth elements in the phyllosphere colonizer Methylobacterium extorquens PA1. Mol. Microbiol. 2019, 111, 1152–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soleimanifar, M.; Rodriguez-Freire, L. Biointeraction of cerium oxide and neodymium oxide nanoparticles with pure culture Methylobacterium extorquens AM1. Chemosphere 2023, 335, 139113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auerbach, R.; Bokelmann, K.; Stauber, R.; Gutfleisch, O.; Schnell, S.; Ratering, S. Critical raw materials—Advanced recycling technologies and processes: Recycling of rare earth metals out of end of life magnets by bioleaching with various bacteria as an example of an intelligent recycling strategy. Miner. Eng. 2019, 134, 104–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.; Su, Z.; Inaba, Y.; West, A.C.; Banta, S. Genetic Modification of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans for Rare-Earth Element Recovery under Acidic Conditions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 19902–19911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Wang, J.; Hu, S.; Zhang, R.; Yang, B.; Liu, Y.; Qiu, G. Efficient recovery of rare earth elements from ion-adsorption rare earth tailings: Based on the addition of pyrite calcination modification. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 356, 129767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathollahzadeh, H.; Eksteen, J.J.; Kaksonen, A.H.; Watkin, E.L.J. Role of microorganisms in bioleaching of rare earth elements from primary and secondary resources. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 1043–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keekan, K.K.; Jalondhara, J.C.; Abhilash. Extraction of Ce and Th from Monazite Using REE Tolerant Aspergillus niger. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 2017, 38, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, L.; Blázquez, M.L.; González, F.; Muoz, J.A. Bioleaching of Phosphate Minerals Using Aspergillus niger: Recovery of Copper and Rare Earth Elements. Metals 2020, 10, 978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Deep-Sea REY Metallogenic Belts | Western Pacific | Southeast Pacific | Central-Eastern Pacific | Central Indian Ocean Basin | Wharton Basin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main sediment types | Deep-sea clay (zeolite clay and oceanic clay) | Deep-sea clay (zeolite clay and oceanic clay) | Deep-sea clay (zeolite clay and oceanic clay) | Deep-sea clay (zeolite clay and oceanic clay) | Deep-sea clay (zeolite clay and oceanic clay) |
| Main mineral phases | Biogenic apatite, Fe-Mn micronodules | Biogenic apatite, Fe-Mn micronodules | Biogenic apatite, Fe-Mn micronodules | Biogenic apatite, Fe-Mn micronodules | Biogenic apatite, Fe-Mn micronodules |
| ΣREY range (10−6 μg/g) | 700–7974 | 700–2738 | 700–1732 | 700–1987 | 700–1113 |
| ΣREY average (10−6 μg/g) | 1330 | 1243 | 910 | 1120 | 815 |
| REY enrichment depth | 2–12 m (3 layers ΣREY > 2000 × 10−6) | 0–10 m | 0–64 m (multilayer) | 0–5 m | 103–122 m |
| Category | Strain | Enzyme/Protein | Interacted REY | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | Methylacidiphilum fumariolicum SolV | MDH XoxF | La3+, Ce3+, Pr3+, Nd3+, Eu3+, Lu3+ | [157,158] |
| N | Methylorubrum extorquens AM1 | EDH ExaF, MDH XoxF1, Lanmodulin | La3+, Nd3+, Ln3+ | [109,156,164,165,166] |
| N | Bradyrhizobium sp. | MDH XoxF | Ce3+ | [159] |
| N | Methylotenera mobilis JLW8 | MDH XoxF4-1/XoxF4-2 | Ce3+ | [160] |
| N | Methylomonas sp. LW13 | MDH XoxF5 | Ce3+ | [160] |
| N | Methylobacterium radiotolerans | MDH XoxF | La3+ | [161] |
| N | Pseudomonas putida | EDH PedH | La3+, Ce3+, Pr3+, Sm3+, Nd3+ | [162] |
| —— | Marine microorganism metagenome | MDH, EDH, putative SDH and GDH | LREY | [154] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, S.; Deng, Y. Marine Rare Earth Elements: Distribution Patterns, Enrichment Mechanisms and Microbial Interactions. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 1471. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13081471
Liu S, Deng Y. Marine Rare Earth Elements: Distribution Patterns, Enrichment Mechanisms and Microbial Interactions. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(8):1471. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13081471
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Shun, and Yinan Deng. 2025. "Marine Rare Earth Elements: Distribution Patterns, Enrichment Mechanisms and Microbial Interactions" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 8: 1471. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13081471
APA StyleLiu, S., & Deng, Y. (2025). Marine Rare Earth Elements: Distribution Patterns, Enrichment Mechanisms and Microbial Interactions. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(8), 1471. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13081471







