Bathymetric Profile and Sediment Composition of a Dynamic Subtidal Bedform Habitat for Pacific Sand Lance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
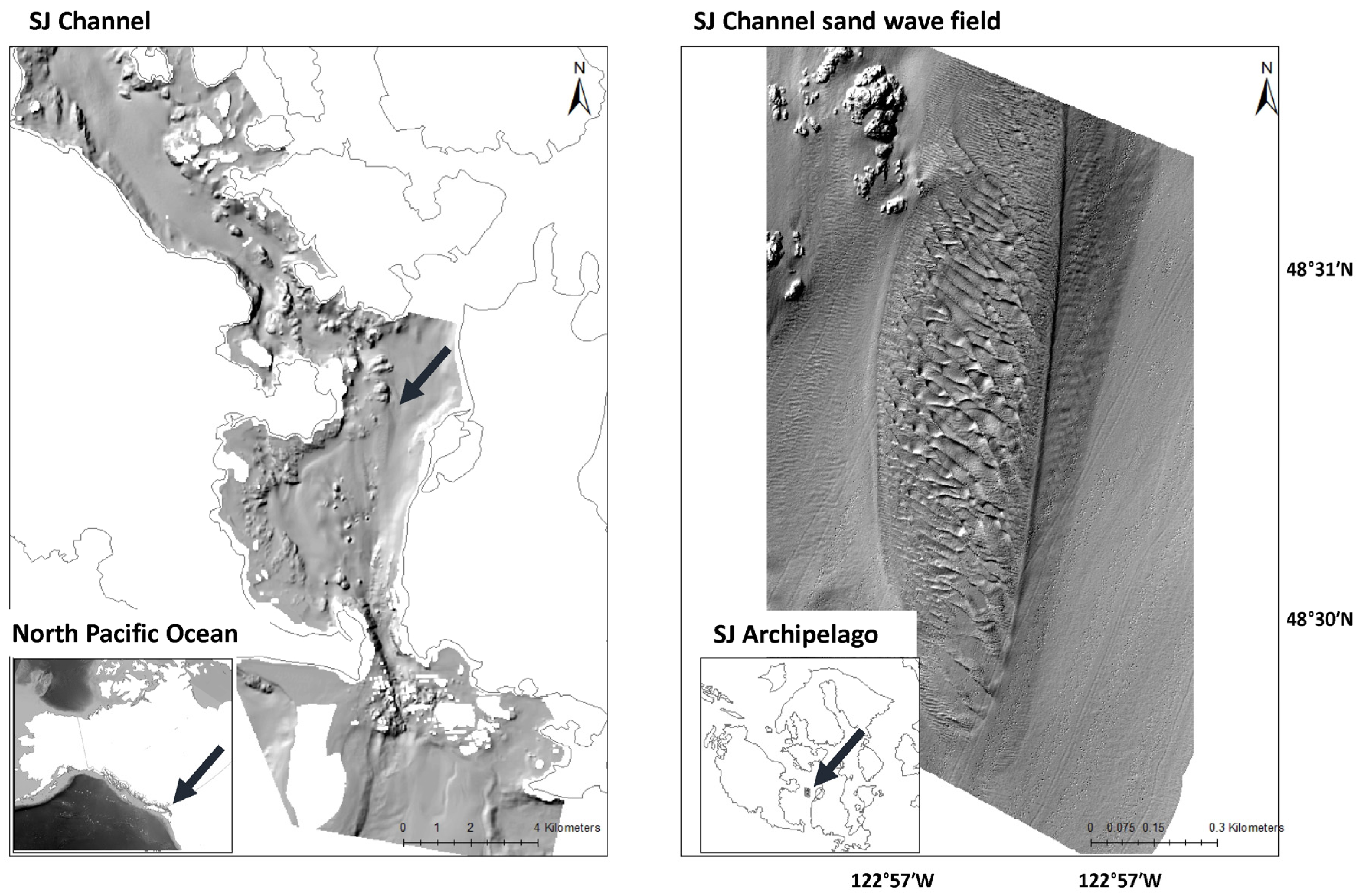
2.1. Sample Site—San Juan Channel Sand Wave Field
2.2. Multibeam Bathymetric Echosounder Survey Data and Imaging
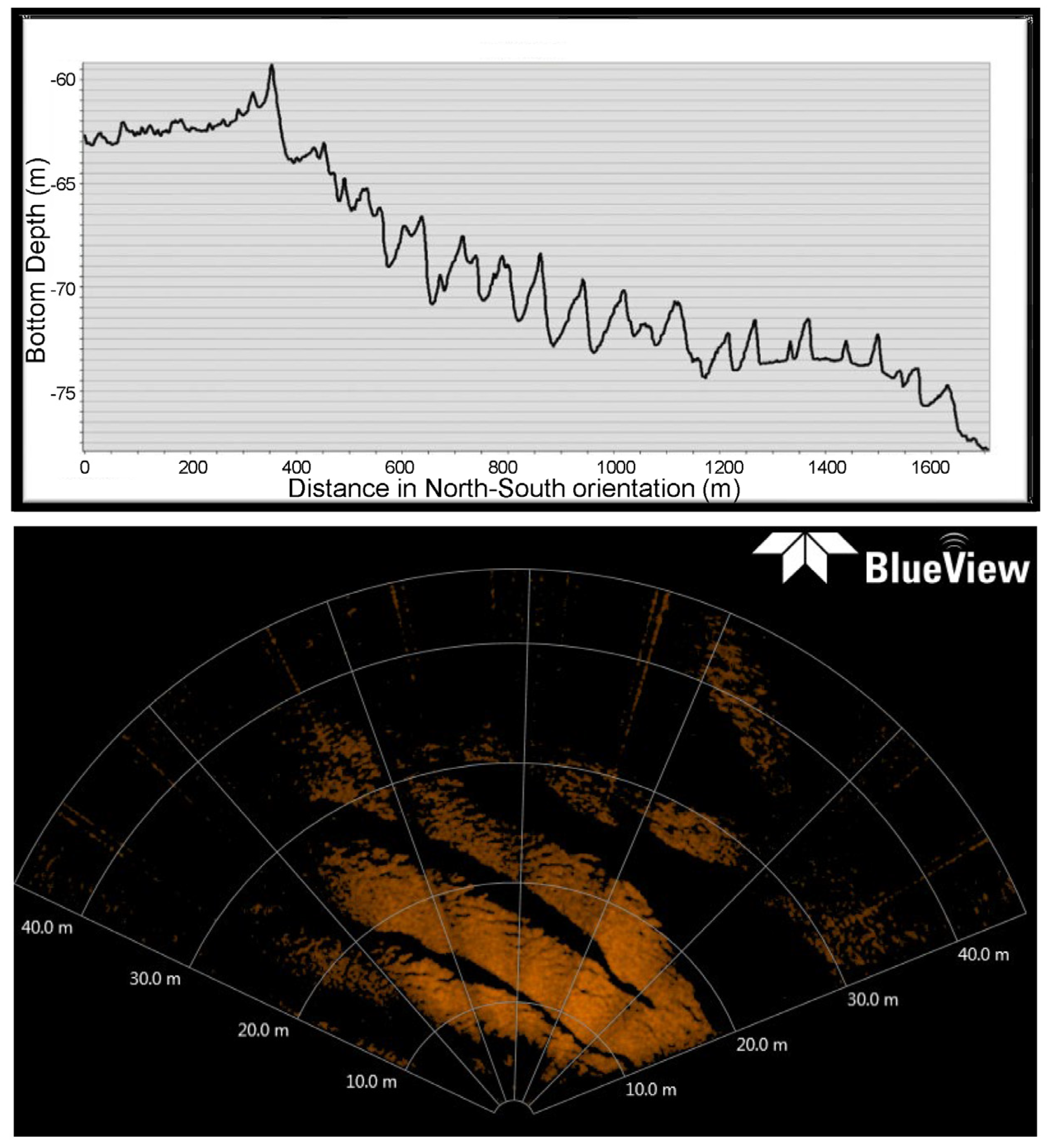
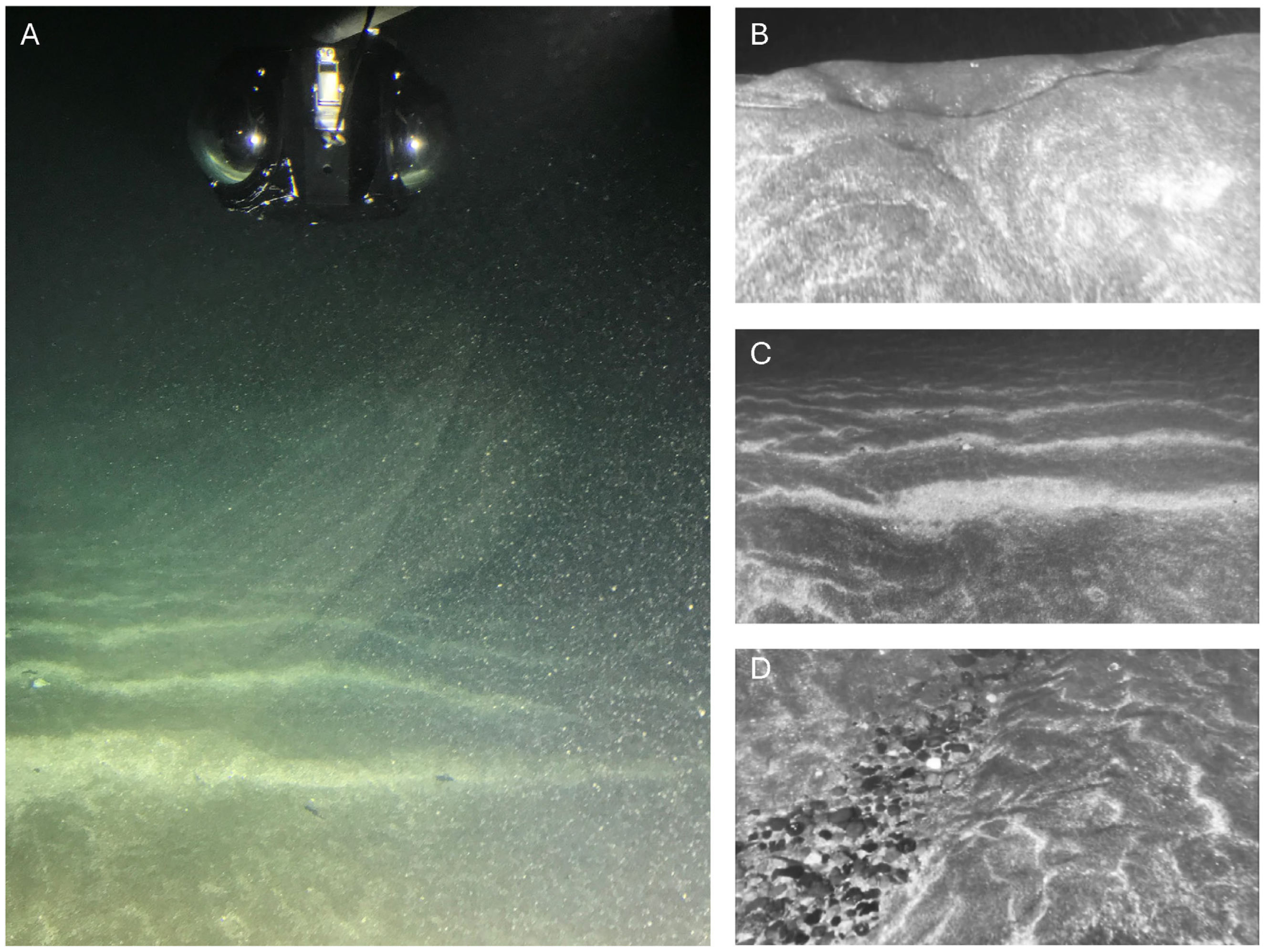
2.3. Submersible Surveys and Sonar Images
2.4. Sediment Collection
2.5. Sediment Processing
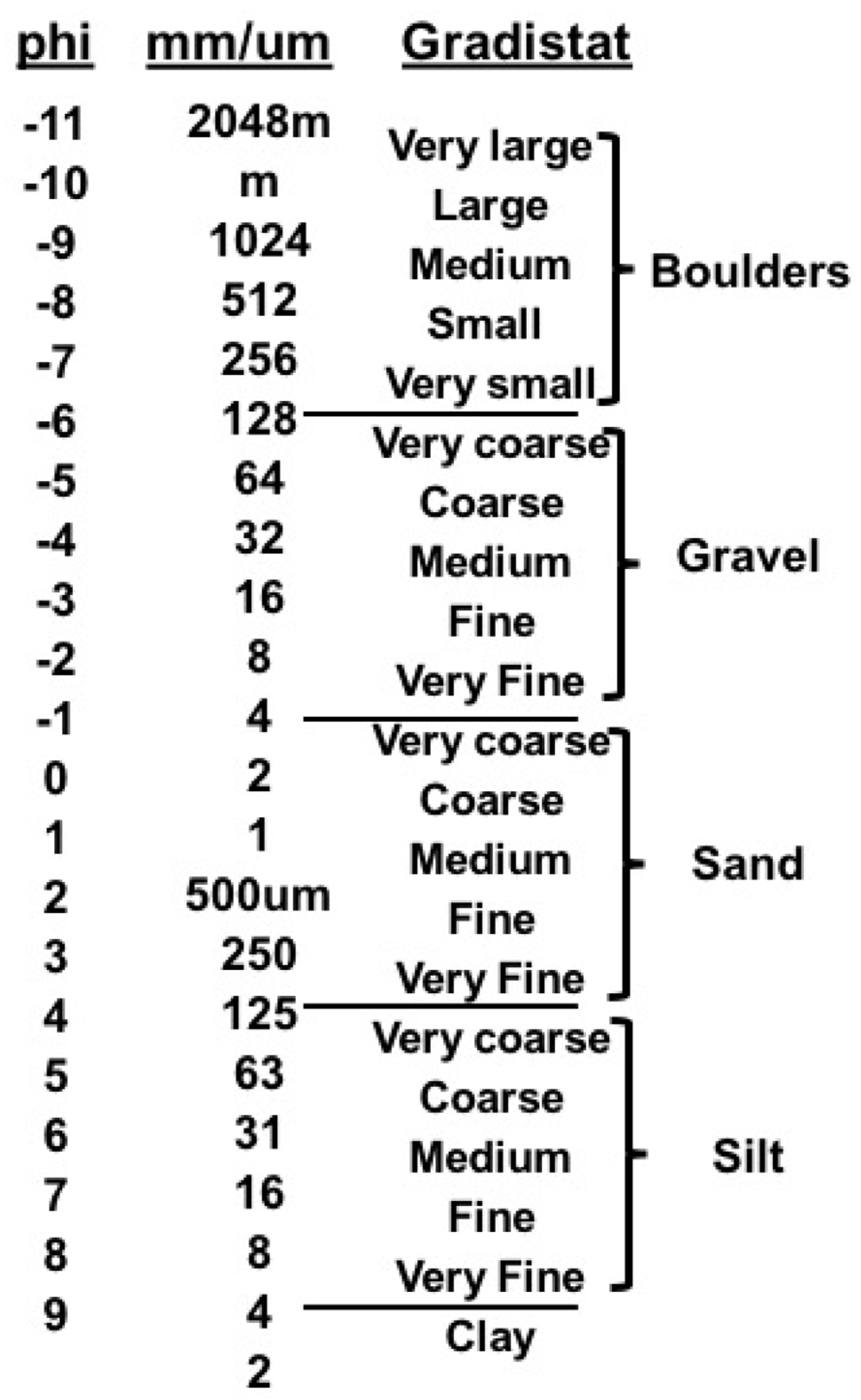
2.6. Sediment Analytics—Grain Size Analysis and Statistics
2.7. Physical Oceanography–Oxygen Profiles
2.8. Geographic Information Systems and Data Visualization
3. Results
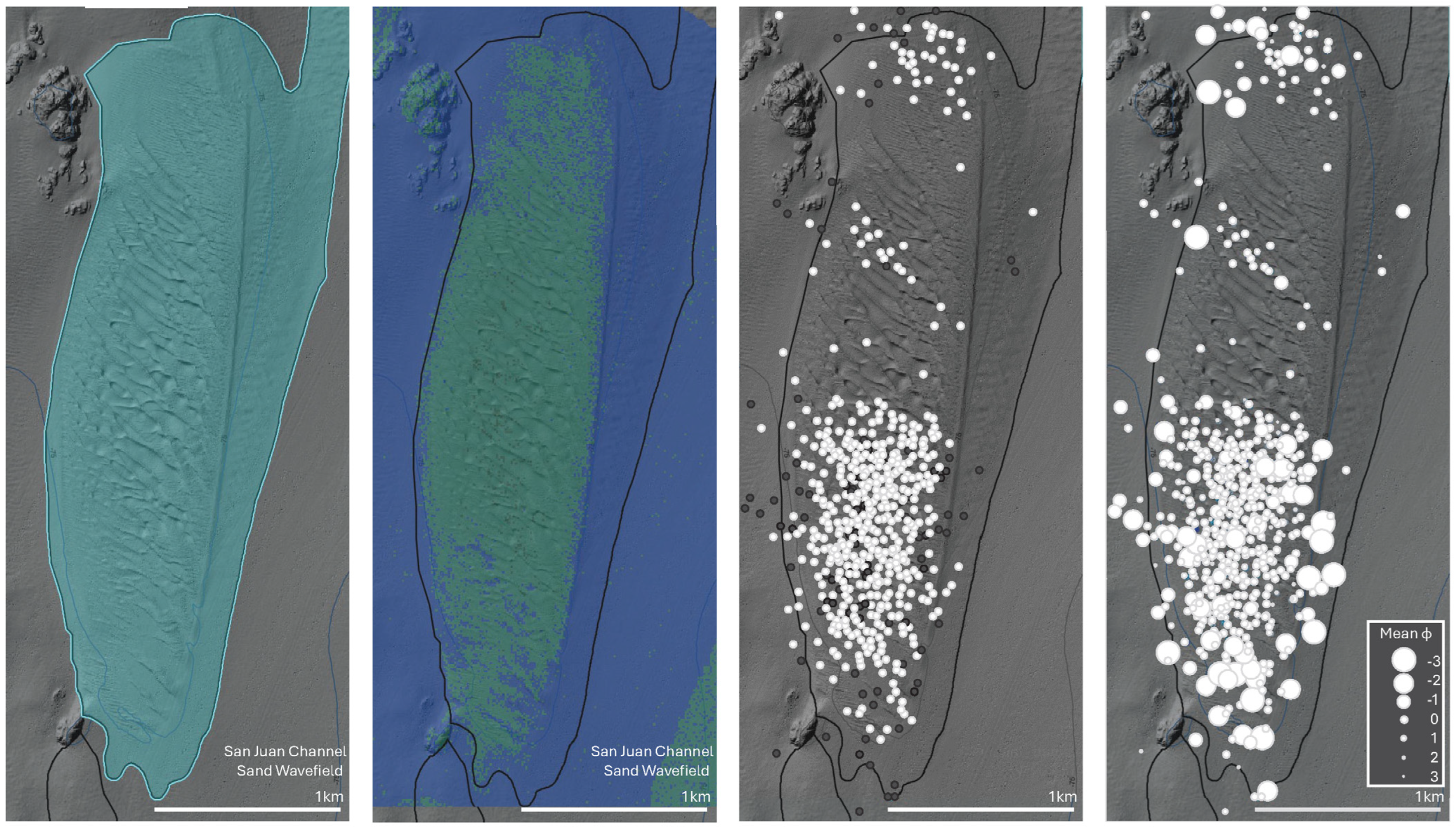
3.1. San Juan Channel Sand Wave Field Attributes
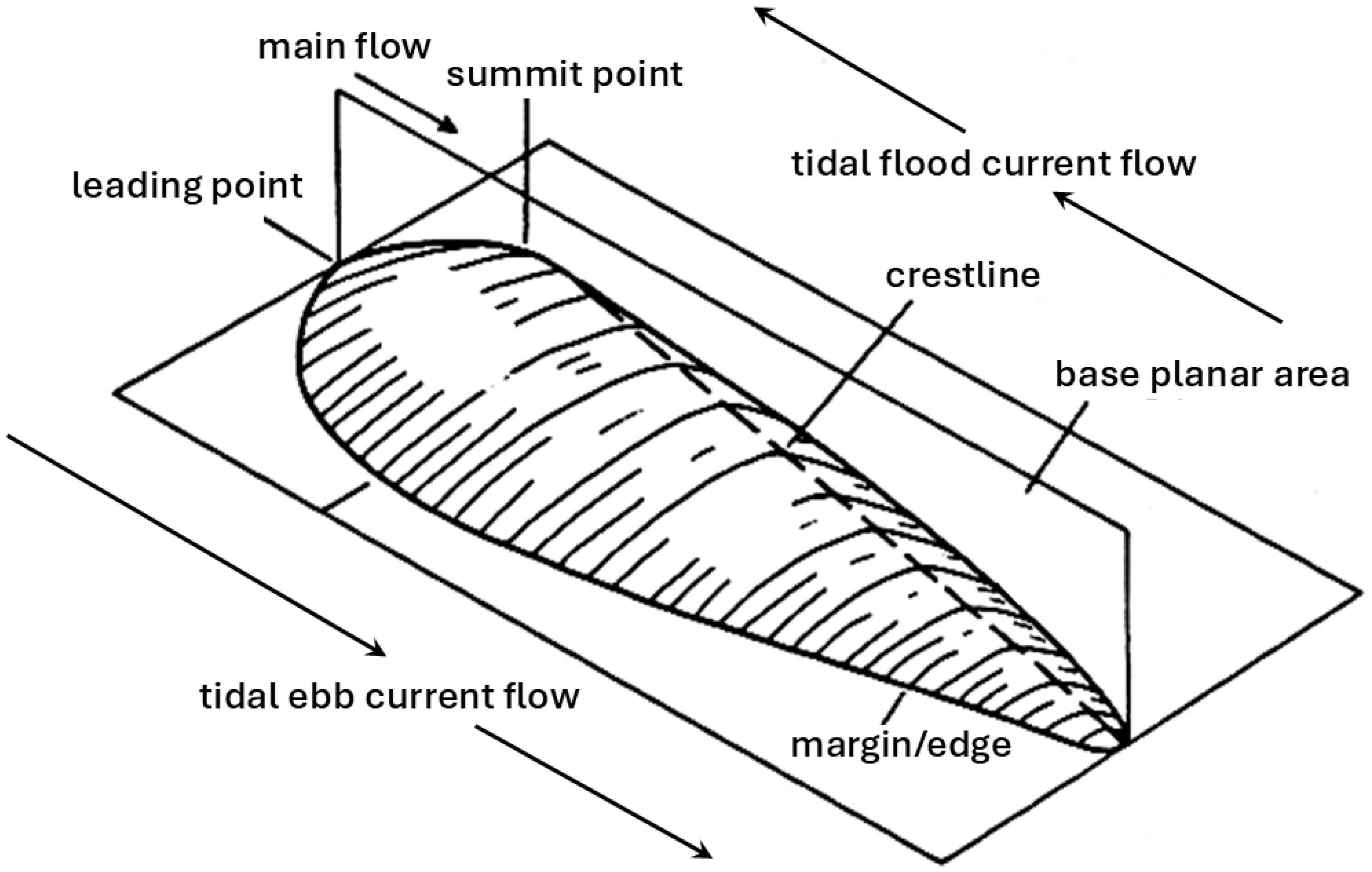
3.2. Sand Wave Field Morphology and Geometry
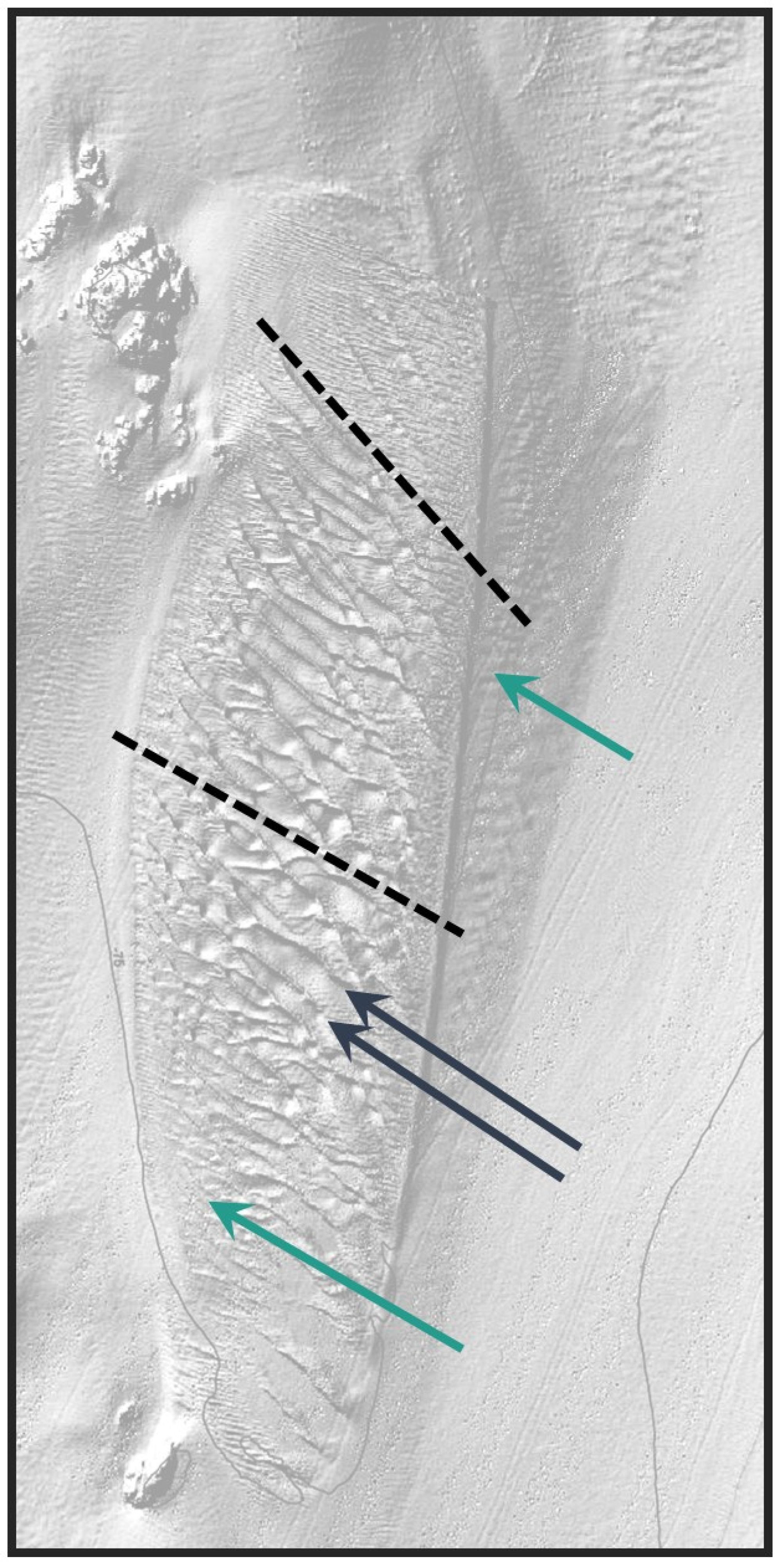
3.3. Bathymetric Profile and Sonar Imagery
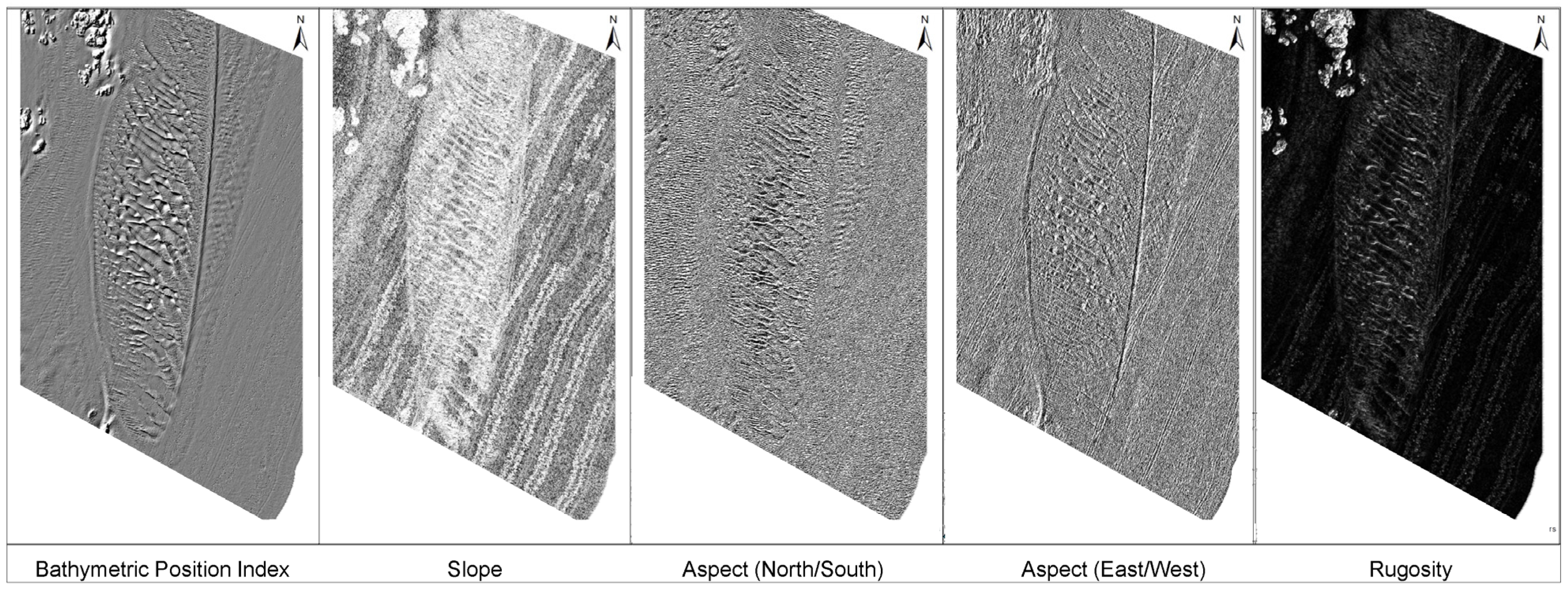
3.4. Derived Benthic Terrain Metrics
3.5. Sand Wave Composition and Structure
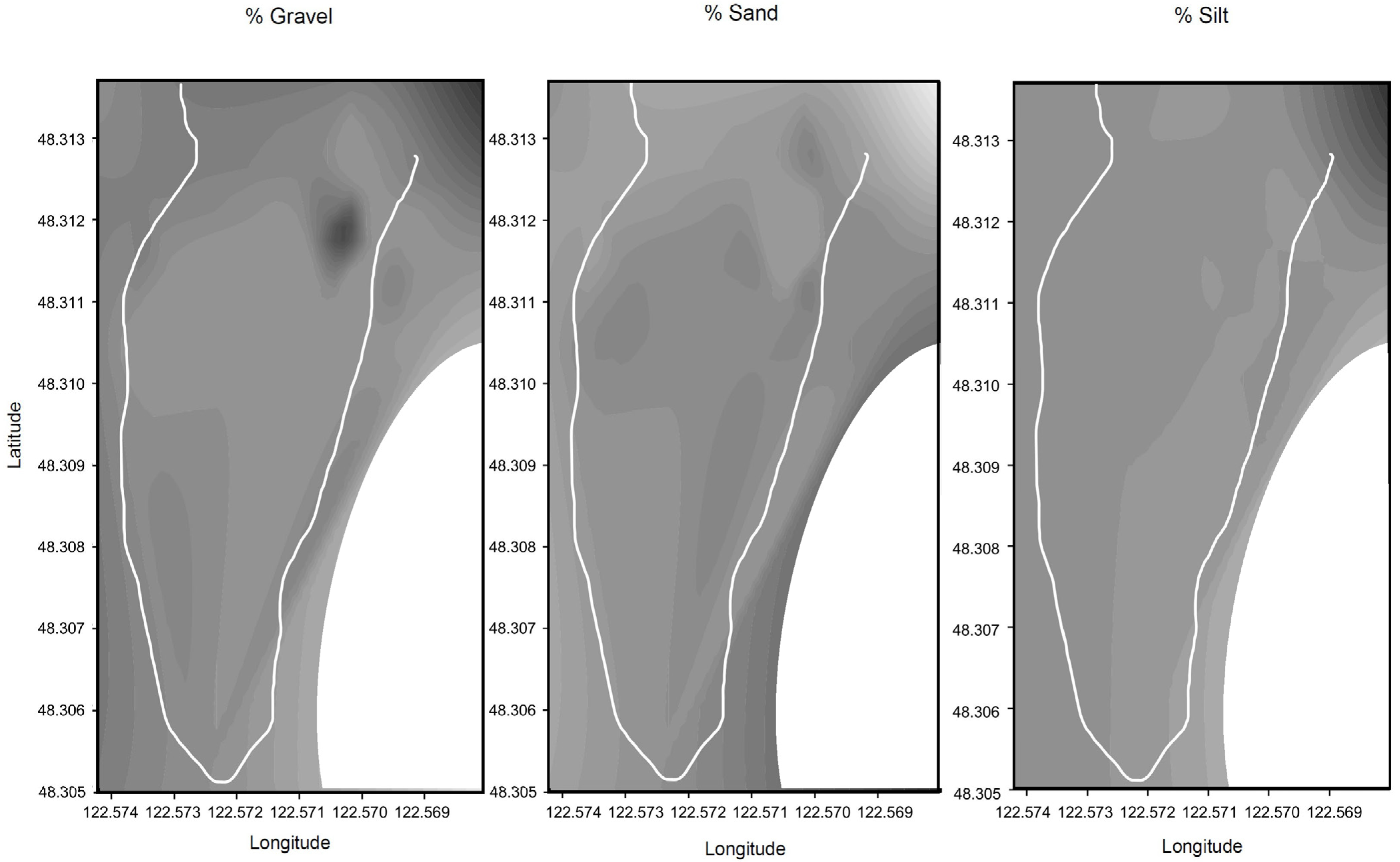
3.6. Sediment Composition and Distribution Within the SJC Sand Wave Field
3.7. Bedform Topography and Definition—Bathymetric Structure of the SJC Sand Wave Field
3.8. Physical Oceanography—Oxygen Levels in the Water Column
4. Discussion
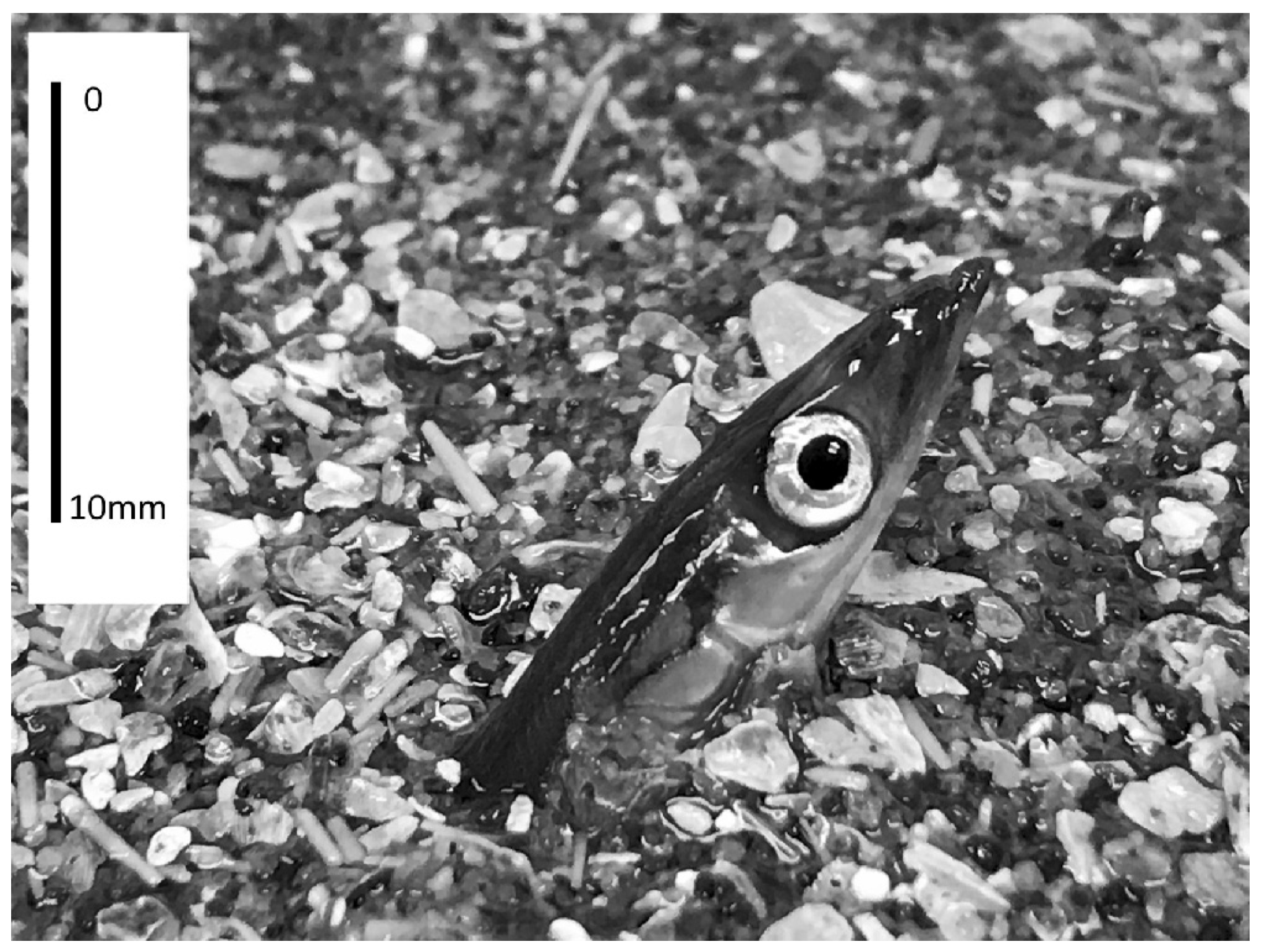
4.1. Essential Fish Habitat—Sand Wave Fields as Sand Lance Habitat
4.2. Attributes of SJC Sand Wave Field Sediments and Bedform Morphology
4.3. Physical Oceanographic Dynamics and Oxygen
4.4. Limitations
4.5. Implications for Research Results and Avenues for Future Exploration
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

References
- Allen, J.R.L. The Nature and Origin of Bedform Hierarchies. Sedimentology 1968, 10, 161–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynn, R.B.; Stow, D.A.V. Classification and Characterisation of Deep-Water Sediment Waves. Mar. Geol. 2002, 192, 7–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USGS Thesaurus. United States Geological Survey. Coastal and Marine Ecological Classification. 2025. Available online: https://apps.usgs.gov/thesaurus/ (accessed on 1 May 2025).
- Rodrigues, S.; Hernandez-Molina, F.J.; Fonnesu, M.; Miramontes, E.; Rebesco, M.; Campbell, D.C. A New Classification System for Mixed (Turbidite–Contourite) Depositional Systems: Examples, Conceptual Models and Diagnostic Criteria for Modern and Ancient Records. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2022, 230, 104030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, A.; Bigford, T.E.; Leathery, S.; Hill, R.L.; Bickers, K. Ecosystem Approaches to Fishery Management through Essential Fish Habitat. Bull. Mar. Sci. 2000, 66, 535–542. [Google Scholar]
- Levin, P.S.; Stunz, G.W. Habitat Triage for Exploited Fishes: Can We Identify Essential “Essential Fish Habitat”? Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2005, 64, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, T.J.; Armstrong, J.L.; Baker, M.R.; Heifetz, J.; Witherell, D. Assessing and Managing Data-Limited Fish Stocks. In Lowell Wakefield Fisheries Symposium; Alaska Sea Grant Publication: Anchorage, AK, USA, 2016; Available online: https://seagrant.uaf.edu/bookstore/pubs/AK-SG-16-01.html (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- Baker, M.R.; Siddon, E. Fishes and Invertebrates. In Marine Ecosystems of the North Pacific Ocean 2009–2016: Synthesis Report; Chandler, P.C., Yoo, S., Eds.; PICES Special Publication 7, North Pacific Marine Science Organization: Victoria, BC, Canada, 2021; pp. 46–61. ISBN 978-1-927797-42-6. Available online: https://meetings.pices.int/publications/special-publications/NPESR/2021/PICES_SP7_NPESR3_2021_SM_FNL.pdf (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- Peck, M.A.; Catalán, I.A.; Rykaczewski, R.R.; Takasuka, A.; Garrido, S.; Asch, R.G.; Baker, M.R.; Bowlin, N.M.; Boldt, J.; Brodeur, R.D.; et al. Advancing Ecological Understanding and Sustainable Management of Small Pelagic Fish. Fish Fish. 2025; in press. [Google Scholar]
- Catalan, I.A.; Bowlin, N.; Baker, M.R.; Berg, F.; Bertrand, A.; Brazier, A.; Brochier, T.; Del Favero, J.M.; Garrido, S.; Gherardi, D.F.M. Worldwide Appraisal of Knowledge Gaps in the Space Usage of Small Pelagic Fish—Highlights across Stock Uncertainties and Research Priorities. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquacult. 2025, 1–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, I.; Hazen, E.L.; Wildermuth, R.; Koenigstein, S.; Hill-Cruz, M.; Pierre-Yves, H.; Muhling, B. The Devil’s in the Details of Using Species Distribution Models to Inform Multispecies and Ecosystem Models. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2025; in press. [Google Scholar]
- Gunther, K.; Baker, M.R.; Aydin, K. Using Predator Diets to Infer Forage Fish Distribution and Assess Responses to Climate Variability in the Eastern Bering Sea. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2024, 741, 71–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovellini, A.; Punt, A.E.; Bryan, M.D.; Kaplan, I.C.; Dorn, M.W.; Aydin, K.; Fulton, E.A.; Alglave, B.; Baker, M.R.; Carroll, G.; et al. Linking Climate Stressors to Ecological Processes in Ecosystem Models—A Case Study from the Gulf of Alaska. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2024, 82, fsae002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auster, P.J.; Stewart, L.L. Species Profiles: Life Histories and Environmental Requirements of Coastal Fishes and Invertebrates (North Atlantic): Sand Lance. Ammodytes spp.; Connecticut University: Groton, MA, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Robards, M.D.; Anthony, J.A.; Rose, G.A.; Piatt, J.F. Changes in Proximate Composition and Somatic Energy Content for Pacific Sand Lance (Ammodytes hexapterus) from Kachemak Bay, Alaska Relative to Maturity and Season. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1999, 242, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bizzarro, J.J.; Peterson, A.N.; Blaine, J.M.; Balaban, J.P.; Greene, H.G.; Summers, A.P. Burrowing Behavior, Habitat, and Functional Morphology of the Pacific Sand Lance (Ammodytes personatus). Fish. Bull. 2016, 114, 445–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, M.R.; Greene, H.G.; Aschoff, J.; Aitoro Bates, E.; Hesselroth, D.; Johnson, K.; Mather, B.; Sealover, N. Atlas of Benthic Habitat for Sand Lance—Application of Multibeam Acoustics and Directed Sampling to Identify Viable Subtidal Substrates. Mar. Environ. Res. 2024, 202, 106778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haynes, T.B.; Robinson, C.K.; Dearden, P. Modelling Nearshore Intertidal Habitat Use of Young-Of-The-Year Pacific Sand Lance (Ammodytes hexapterus) in Barkley Sound, British Columbia, Canada. Environ. Biol. Fish. 2008, 83, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrie, J.V.; Conway, K.W.; Picard, K.; Greene, H.G. Large-Scale Sedimentary Bedforms and Sediment Dynamics on a Glaciated Tectonic Continental Shelf: Examples from the Pacific Margin of Canada. Cont. Shelf Res. 2009, 29, 796–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aschoff, J.; Greene, H.G.; Baker, M.R. Pacific Sand Lance in the Central Salish Sea: StoryMap. ArcGIS StoryMaps. 2020. Available online: https://storymaps.arcgis.com/stories/9bac8e095b014cee98877e86393d5537 (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- Greene, H.G.; Aschoff, J. Oil Spill Assessment Maps of the Central Salish Sea–Marine Seafloor & Coastal Habitats of Concern–A Tool for Oil Spill Mitigation within the San Juan Archipelago, Washington State, USA. Cont. Shelf Res. 2023, 253, 104880. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, M.R.; Williams, K.; Greene, H.G.; Aschoff, J.; Greufe, C.; Lopes, H.; Towler, R. Use of Manned Submersible and Autonomous Stereo-Camera Array to Assess Forage Fish and Associated Subtidal Habitat. Fish. Res. 2021, 243, 106067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goff, J.A.; Mayer, L.A.; Traykovski, P.; Buynevich, I.; Wilkens, R.; Raymond, R.; Glang, G.; Evans, R.L.; Olson, H.; Jenkins, C. Detailed Investigation of Sorted Bedforms, or Rippled Scour Depressions, within the Martha’s Vineyard Coastal Observatory, Massachusetts. Cont. Shelf Res. 2005, 25, 461–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, K.T.; Elmore, P.A. A Review of Heterogeneous Sediments in Coastal Environments. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2008, 89, 116–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auster, P.J.; Malatesta, R.J.; Langton, R.W.; Watting, L.; Valentine, P.C.; Donaldson, C.L.S.; Langton, E.W.; Shepard, A.N.; Babb, W.G. The Impacts of Mobile Fishing Gear on Seafloor Habitats in the Gulf of Maine (Northwest Atlantic): Implications for Conservation of Fish Populations. Rev. Fish. Sci. 1996, 4, 185–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snelgrove, V.R. Getting to the Bottom of Marine Biodiversity: Sedimentary Habitats. BioScience 1999, 49, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerstner, C.L.; Webb, P.W. The Station-Holding Performance of the Plaice Pleuronectes platessa on Artificial Substratum Ripples. Can. J. Zool. 1998, 76, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoner, A.W.; Titgen, R.H. Biological Structures and Bottom Type Influence Habitat Choices Made by Alaska Flatfishes. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2003, 292, 43–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, M.R.; Palsson, W.; Zimmermann, M.; Rooper, C.N. Model of Trawlable Area Using Benthic Terrain and Oceanographic Variables—Informing Survey Bias and Benthic Habitat in the Gulf of Alaska. Fish. Oceanogr. 2019, 28, 629–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valavanis, V.D.; Pierce, G.J.; Zuur, A.F.; Palialexis, A.; Saveliev, A.; Katara, I.; Wang, J. Modelling of Essential Fish Habitat Based on Remote Sensing, Spatial Analysis and GIS. In Essential Fish Habitat Mapping in the Mediterranean; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2008; pp. 5–20. ISBN 978-1-4020-9140-7. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, M.R.; Hollowed, A.B. Delineating Ecological Regions in Marine Systems: Integrating Physical Structure and Community Composition to Inform Spatial Management in the Eastern Bering Sea. Deep Sea Res. II 2014, 109, 215–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, A.; Sigler, M.; Baker, M.R.; Hendrix, N.; Tyler, B. Physical Oceanographic Conditions Drive Patterns in Seasonal Core Habitat among Marine Top Predators in the San Juan Archipelago. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, N.P.; Henriksen, O.; Lundberg, P.; Baker, M.R.; Brodin, T.; van Deurs, M. A Systematic Review of the Ecological Roles, Functions and Services Provided for Fish by North Sea Sand- and Gravel-Bank Ecosystems. 2025. Available online: https://osf.io/7c9sb (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- Greene, H.G.; Cacchione, D.A.; Hampton, M.A. Characteristics and Dynamics of a Large Sub-Tidal Sand Wave Field—Habitat for Pacific Sand Lance (Ammodytes personatus), Salish Sea, Washington, USA. Geosciences 2017, 7, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, H.G.; Baker, M.; Aschoff, J. A Dynamic Bedforms Habitat for the Forage Fish Pacific Sand Lance, San Juan Islands, WA, USA. In Seafloor Geomorphology as Benthic Habitat, 2nd ed.; Harris, P.T., Baker, E.K., Eds.; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; p. 1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, H.G.; Baker, M.R.; Aschoff, J.; Pacunski, R. Hazards Evaluation of a Valuable Vulnerable Sand-Wave Field Forage Fish Habitat in the Marginal Central Salish Sea Using a Submersible. Oceanologia 2021, 65, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sisson, N.; Baker, M.R. Feeding Ecology of Pacific Sand Lance in the San Juan Archipelago. Mar. Coast. Fish. 2017, 9, 612–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, M.R.; Matta, M.E.; Beaulieu, M.; Parris, N.; Huber, S.; Graham, O.J.; Pham, T.; Sisson, N.B.; Heller, C.P.; Witt, A. Intra-Seasonal and Inter-Annual Patterns in the Demographics of Sand Lance and Response to Environmental Drivers in the North Pacific. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2019, 617–618, 221–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Høines, Å.S.; Bergstad, O.A. Density of Wintering Sand Eel in the Sand Recorded by Grab Catches. Fish. Res. 2001, 49, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wentworth, C.K. A Scale of Grade and Class Terms for Clastic Sediments. J. Geol. 1922, 30, 377–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, S.J.; Arsenault, M.A.; Buczkowski, B.J.; Reid, J.A.; Flocks, J.G.; Kulp, M.A.; Penland, S.; Jenkins, C.J. Surficial Sediment Character of the Louisiana Offshore Continental Shelf Region: A GIS Compilation. U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 2006–1195. 2006. Available online: https://pubs.usgs.gov/of/2006/1195/index.htm (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- Blott, S.J.; Pye, K. GRADISTAT: A Grain Size Distribution and Statistics Package for the Analysis of Unconsolidated Sediments. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2001, 26, 1237–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeeman, S.; Fortier, B. Sediment Grain Size Analysis. In BIO350 Oceanography; University of New England: Armidale, NSW, Australia, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Alin, S.R.; Newton, J.A.; Feely, R.A.; Curry, B.; Greeley, d.; Herndon, J.; Warner, M. A decade-long cruise time-series (2008–2018) of physical and biogeochemical conditions in the southern Salish Sea, North America. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2024, 16, 837–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenness, J.S. DEM Surface Tools. 2014. Available online: https://www.jennessent.com/arcgis/surface_area.htm (accessed on 1 November 2024).
- Wright, D.J.; Lundblad, E.R.; Larkin, E.M.; Rinehart, R.W.; Murphy, J.; Cary-Kothera, L.; Draganov, K. ArcGIS Benthic Terrain Modeler. NOAA Coastal Services Center and Oregon State University. 2005. Available online: https://maps.csc.noaa.gov/digitalcoast/tools/btm (accessed on 1 November 2024).
- Wright, D.J.; Pendleton, M.; Boulware, J.; Walbridge, S.; Gerlt, B.; Eslinger, D.; Huntley, E. ArcGIS Benthic Terrain Modeler (BTM), v. 3.0; Environmental Systems Research Institute, NOAA Coastal Services Center, Massachusetts Office of Coastal Zone Management: Wood Hole, MA, USA. 2012; Available online: https://www.arcgis.com/index.html (accessed on 1 November 2024).
- Southard, J.B. Representation of Bed Configurations in Depth-Velocity-Size Diagrams. J. Sediment. Petrol. 1971, 41, 903–915. [Google Scholar]
- Orr, J.W.; Wildes, S.; Kai, Y.; Raring, N.; Nakabo, T.; Katugin, O.; Guyon, J. Systematics of North Pacific Sand Lances of the Genus Ammodytes Based on Molecular and Morphological Evidence, with the Description of a New Species from Japan. Fish. Bull. 2015, 113, 129–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, P.J.; Jensen, H.; Tuck, I. The Influence of Sediment Type on the Distribution of the Lesser Sandeel, Ammodytes marinus. J. Sea Res. 2000, 44, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horkan, E.; Baker, M.R. Experimental Trials Provide Insight to Potential Climate Impacts on Condition and Over-Winter Survival in Pacific Sand Lance, Ammodytes personatus. Behav. Process. 2025, 226, 105169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, S.M.; Davoren, G.K. Habitat Characteristics and Diel Patterns of Sand Lance (Ammodytes spp.) in Coastal Newfoundland. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2024, 107, 443–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhukova, K.A.; Baker, M.R. Gonadal Maturation and Maturity Staging of the Pacific Sand Lance (Ammodytes personatus). J. Ichthyol. 2022, 62, 921–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, M.R.; Smeltz, T.S.; Williams, K.; Greufe, C.; Chapman, J.; Ewing, M.; Glassy, J.; Hasegawa, E.; Cieri, K.; Matson, S. Diel Vertical Migration in a Pelagic Forage Fish—Pacific Sand Lance (Ammodytes personatus) Associated with Benthic Substrates. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2023, 80, 1758–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokranov, A.M. Distribution and Some Biological Features of the Pacific Sand Lance (Ammodytes hexapterus) in Waters off Kamchatka in the Sea of Okhotsk. J. Ichthyol. 2007, 47, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, T.B.; Robinson, C.L. Re-Use of Shallow Sediment Patches by Pacific Sand Lance (Ammodytes hexapterus) in Barkley Sound, British Columbia, Canada. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2011, 92, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, A.; Iwasaki, N.; Shibata, J.Y.; Tomiyama, T.; Sakai, Y. The Burrowing Sand Lance Ammodytes japonicus (Teleostei, Ammodytidae) Prefers Benthic Sediments of Low Shear Strength. J. Ethol. 2019, 37, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butterworth-Heinemann. Principles and Processes of Sediment Transport. In Waves, Tides, and Shallow Water Processes; Academic: London, UK, 1999; pp. 96–124. [Google Scholar]
- Faugères, J.C.; Stow, D.A.; Imbert, P.; Viana, A. Seismic Features Diagnostic of Contourite Drifts. Mar. Geol. 1999, 162, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashley, G.M. Classification of Large-Scale Sub-Aqueous Bedforms: A New Look at an Old Problem. J. Sediment. Petrol. 1990, 60, 160–172. [Google Scholar]
- Dalrymple, R.W.; Knight, R.J.; Lambiase, J.J. Bedforms and Their Hydraulic Stability Relationships in a Tidal Environment, Bay of Fundy, Canada. Nature 1978, 275, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banas, N.; Bricker, J.; Carter, G.; Gerdes, F.; Martin, W.; Nelson, E.; Ross, T.; Scansen, B.; Simons, R.; Wells, M. Flow, Stratification, and Mixing in San Juan Channel. In Coastal and Estuarine Geophysical Fluid Dynamics; University of Washington, School of Oceanography: Seattle, WA, USA, 1999; pp. 1–89. [Google Scholar]
- MacCready, P.; Geyer, W.R. Estuarine Exchange Flow in the Salish Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2024, 129, e2023JC020369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faugères, J.C.; Mulder, T. Contour Currents and Contourite Drifts. In Developments in Sedimentology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; Volume 63, pp. 149–214. [Google Scholar]
- Barrie, J.V.; Greene, H.G.; Conway, K.W.; Picard, K. Inland Tidal Sea of the Northeastern Pacific. In Seafloor Geomorphology as Benthic Habitat: Geohab Atlas of Seafloor Geomorphic Features and Benthic Habitats; Harris, P.T., Baker, E.K., Eds.; Elsevier Insights: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 623–634. [Google Scholar]
- Bograd, S.; Castro, C.; Di Lorenzo, E.; Palacios, D.; Bailey, H.; Gilly, W.F.; Chavez, F. Oxygen Declines and the Shoaling of the Hypoxic Boundary in the California Current. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L12607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pörtner, H.O.; Lannig, G. Oxygen and Capacity Limited Thermal Tolerance. In Fish Physiology; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2009; Volume 27, pp. 143–191. [Google Scholar]
- Parker-Stetter, S.L.; Horne, J.K.; Langness, M.M. The Influence of Midwater Hypoxia on Nekton Vertical Migration. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2009, 66, 1296–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Moss, S.A.; McFarland, W.N. The Influence of Dissolved Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide on Fish Schooling Behavior. Mar. Biol. 1970, 5, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekau, W.; Auel, H.; Pörtner, H.-O.; Gilbert, D. Impacts of Hypoxia on the Structure and Processes in Pelagic Communities (Zooplankton, Macro-Invertebrates and Fish). Biogeosciences 2010, 7, 1669–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaquer-Sunyer, R.; Duarte, C.M. Thresholds of Hypoxia for Marine Biodiversity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 15452–15457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. Ambient Aquatic Life Water Quality Criteria for Dissolved Oxygen (Saltwater): Cape Cod to Cape Hatteras; EPA-822-R-00-012; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, D.; Poucher, S.; Coiro, L.L. Determination of Lethal Dissolved Oxygen Levels for Selected Marine and Estuarine Fishes, Crustaceans, and a Bivalve. Mar. Biol. 2002, 140, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dommasnes, A.; Rey, F.; Røttingen, I. Reduced Oxygen Concentrations in Herring Wintering Areas. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 1994, 51, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrens, J.W.; Steffensen, J.F. The Effect of Hypoxia on Behavioural and Physiological Aspects of Lesser Sandeel, Ammodytes tobianus (Linnaeus, 1785). Mar. Biol. 2007, 150, 1365–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrens, J.W.; Ærtebjerg, G.; Petersen, J.K.; Carstensen, J. Oxygen Deficiency Impacts on Burying Habitats for Lesser Sandeel, Ammodytes tobianus, in the Inner Danish Waters. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2009, 66, 883–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrens, J.W.; Petersen, J.K.; Ærtebjerg, G.; Steffensen, J.F. Influence of Moderate and Severe Hypoxia on the Diurnal Activity Pattern of Lesser Sandeel Ammodytes tobianus. J. Fish Biol. 2010, 77, 538–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helly, J.J.; Levin, L.A. Global Distribution of Naturally Occurring Marine Hypoxia on Continental Margins. Deep Sea Res. I 2004, 51, 1159–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, R.J. Overview of Hypoxia around the World. J. Environ. Qual. 2001, 30, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forster, S.; Huettel, M.; Ziebis, W. Impact of Boundary Layer Flow Velocity on Oxygen Utilisation in Coastal Sediments. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1996, 143, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrens, J.W.; Stahl, H.J.; Steffensen, J.F.; Glud, R.N. Oxygen Dynamics Around Buried Lesser Sandeels Ammodytes tobianus (Linnaeus 1785): Mode of Ventilation and Oxygen Requirements. J. Exp. Biol. 2007, 210, 1006–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, C.L.; Hrynyk, D.; Barrie, J.V.; Schweigert, J. Identifying Subtidal Burying Habitat of Pacific Sand Lance (Ammodytes hexapterus) in the Strait of Georgia, British Columbia, Canada. Prog. Oceanogr. 2013, 115, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrand, W.D.; Gotthardt, T.A.; Howlin, S.; Robards, M.D. Habitat Selection Models for Pacific Sand Lance (Ammodytes hexapterus) in Prince William Sound, Alaska. Northwest. Nat. 2005, 86, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murase, H.; Nagashima, H.; Yonezaki, S.; Matsukura, R.; Kitakado, T. Application of a Generalized Additive Model (GAM) to Reveal Relationships between Environmental Factors and Distributions of Pelagic Fish and Krill: A Case Study in Sendai Bay, Japan. Fish. Sci. 2009, 75, 1213–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boldt, J.; Baker, M.R.; Bernal, M.; Somarakis, S. SPF Workshop on Methods and Techniques for Sampling and Assessing Small Pelagic Fish Populations. In 2017 Inter-Sessional Science Board Meeting: A Note from the New Science Board Chair; PICES Press: Sidney, BC, Canada, 2017; Volume 25, p. 16. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, M.R.; Boldt, J.; McGowan, D.; Takasuka, A.; Takahashi, M. Improved Detection and Understanding of Factors Affecting Changes in North Pacific Forage Communities and Implications to Ecosystems. PICES Press 2024, 32, 23–25. [Google Scholar]
- Huard, J.; Hemming, V.; Baker, M.R.; Hipfner, M.J.; Davoren, G.K.; Koval, B.A.; Dionne, P.; Lowry, D.; Monks, R.; Nicholas, G.; et al. Assessment of Population Trajectory and Threats for Pacific Sand Lance in the Salish Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 11, 1445215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selden, K.R.; Baker, M.R. Spatial Analysis of Microplastics in Forage Fish and Salmon in the Southern Salish Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 193, 115748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, N.V.; White, M.A.V.; Tavera, J.J.; O’Hara, P.D.; Baker, M.R.; Bertram, D.F.; Summers, A.; Fifield, D.A.; Juanes, F. Noise Results in Lower Energy Density in an Important Forage Fish—The Pacific Sand Lance. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2025, 213, 117664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sethi, S.A.; Murphy, R.D.; Baker, M.R.; Kroska, A.; Hilborn, R.; Harris, B.P. Seeking Solutions: Challenges and Opportunities for Operationalizing Bottom-Towed Fisheries Sustainability. Fish Fish. in prep..
- Holland, G.J.; Greenstreet, S.P.R.; Gibb, I.M.; Fraser, H.M.; Robertson, M.R. Identifying Sandeel Ammodytes marinus Sediment Habitat Preferences in the Marine Environment. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2005, 303, 269–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenstreet, S.P.R.; Holland, G.J.; Guirey, E.J.; Armstrong, E.; Fraser, H.M.; Gibb, I.M. Combining Hydroacoustic Seabed Survey and Grab Sampling Techniques to Assess Local Sandeel Population Abundance. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2010, 67, 971–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanda, M. Relationship between the Habitat of Sand Lance and the Sandy Bottom in the Seto Inland Sea. In Marine Coastal Environment; Hirano, T., Ed.; Fuji Techno System: Tokyo, Japan, 1998; pp. 348–355. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, M.R.; De Robertis, A.; Levine, R.; Cooper, D.; Farley, E. Spatial Distribution of Arctic Sand Lance in the Chukchi Sea Related to the Physical Environment. Deep Sea Res. II 2022, 206, 105213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baker, M.R.; Greene, H.G.; Aschoff, J.; Hoge, M.; Aitoro, E.; Childers, S.; Liu, J.; Newton, J.A. Bathymetric Profile and Sediment Composition of a Dynamic Subtidal Bedform Habitat for Pacific Sand Lance. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 1469. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13081469
Baker MR, Greene HG, Aschoff J, Hoge M, Aitoro E, Childers S, Liu J, Newton JA. Bathymetric Profile and Sediment Composition of a Dynamic Subtidal Bedform Habitat for Pacific Sand Lance. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(8):1469. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13081469
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaker, Matthew R., H. G. Greene, John Aschoff, Michelle Hoge, Elisa Aitoro, Shaila Childers, Junzhe Liu, and Jan A. Newton. 2025. "Bathymetric Profile and Sediment Composition of a Dynamic Subtidal Bedform Habitat for Pacific Sand Lance" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 8: 1469. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13081469
APA StyleBaker, M. R., Greene, H. G., Aschoff, J., Hoge, M., Aitoro, E., Childers, S., Liu, J., & Newton, J. A. (2025). Bathymetric Profile and Sediment Composition of a Dynamic Subtidal Bedform Habitat for Pacific Sand Lance. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(8), 1469. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13081469






