Microplastics in Nearshore and Subtidal Sediments in the Salish Sea: Implications for Marine Habitats and Exposure
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
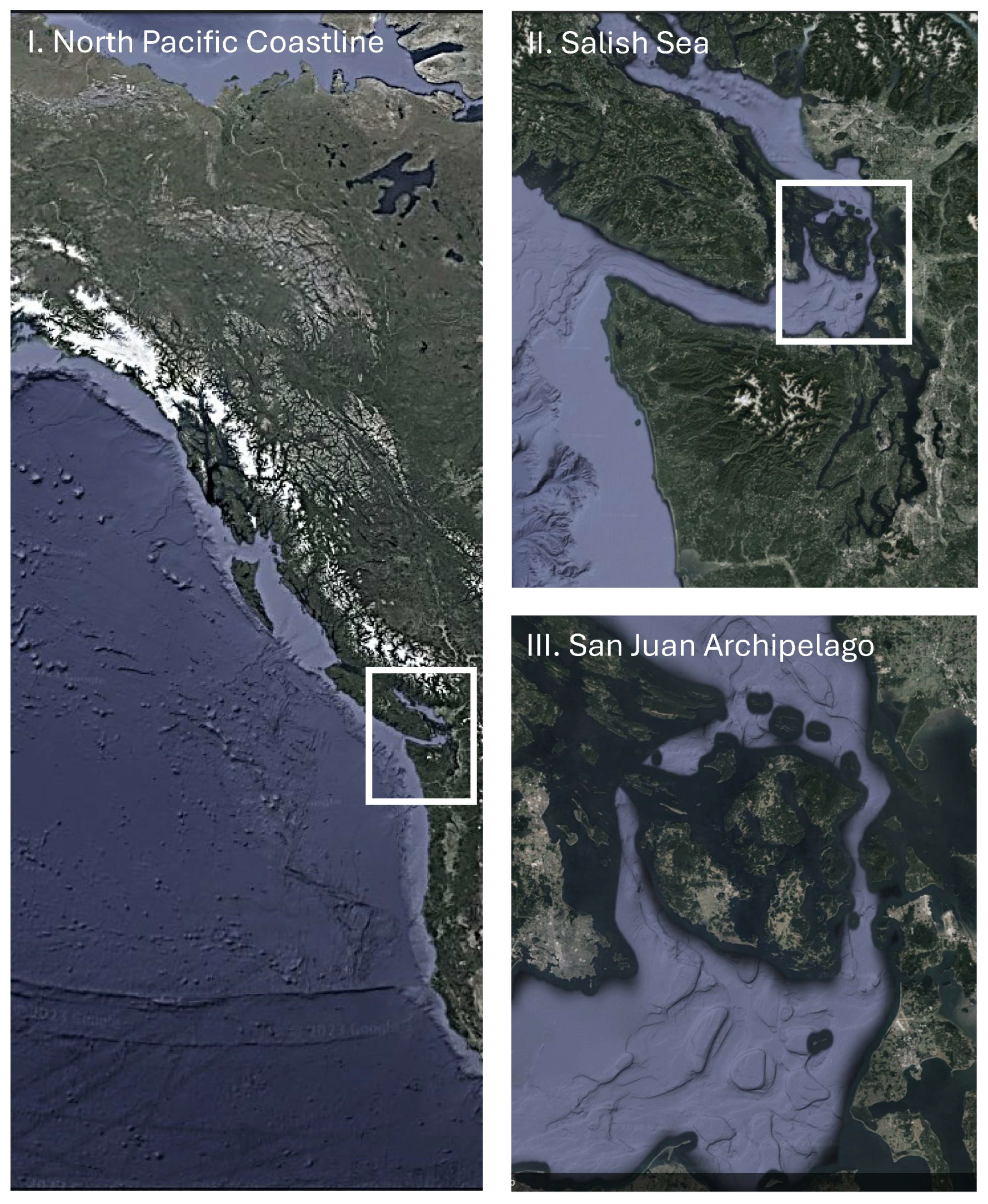
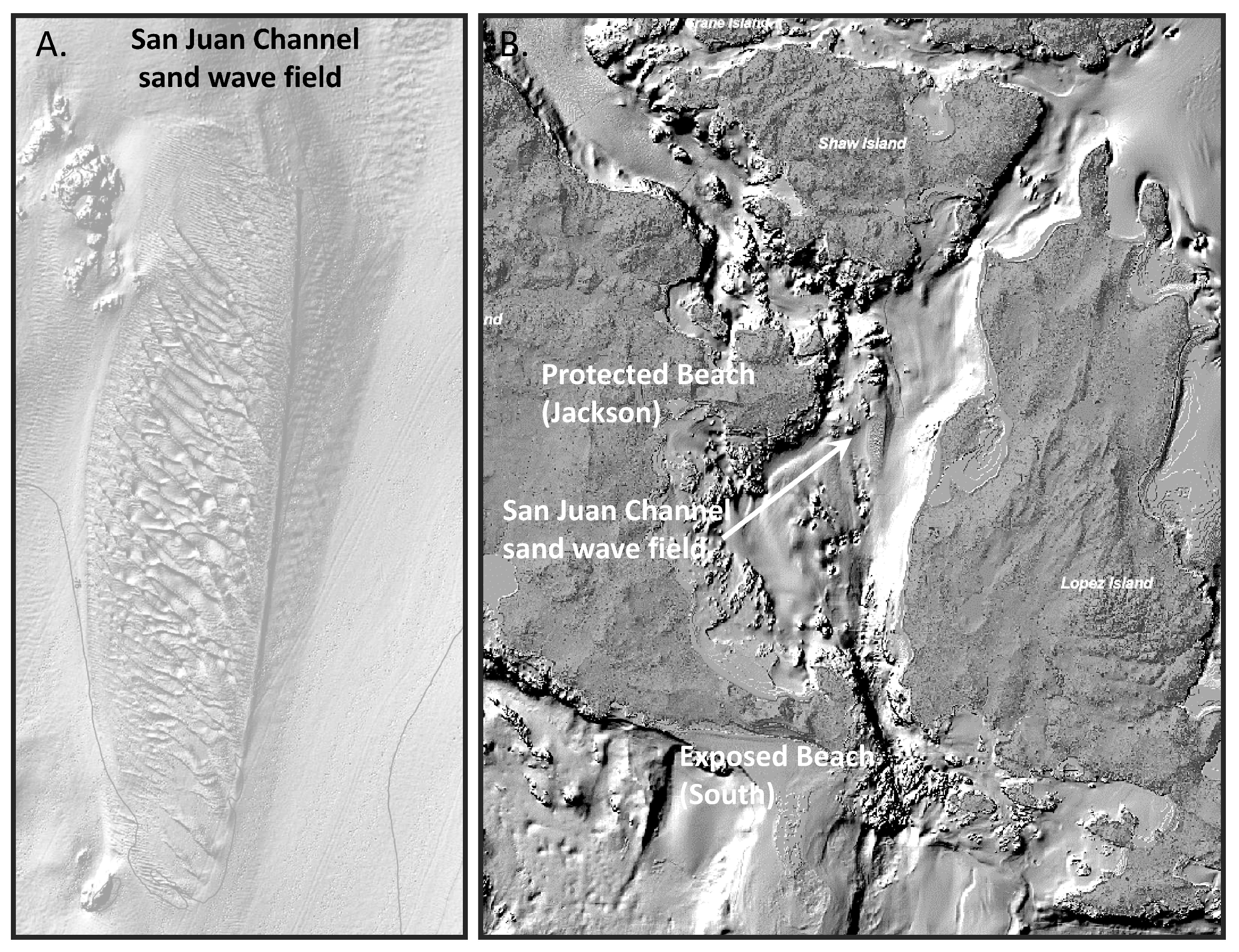
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Sediment Sampling
2.3. Sediment Processing for Microplastics
2.4. Microscope Examination and Classification and Gravimetric Analysis
2.5. Classification of Shorelines and Oceanographic Attributes
2.6. Statistical Analysis and Models
3. Results
3.1. Microplastics in Various Sites
3.2. Types of Microplastics
3.3. Size Distribution of Microplastics
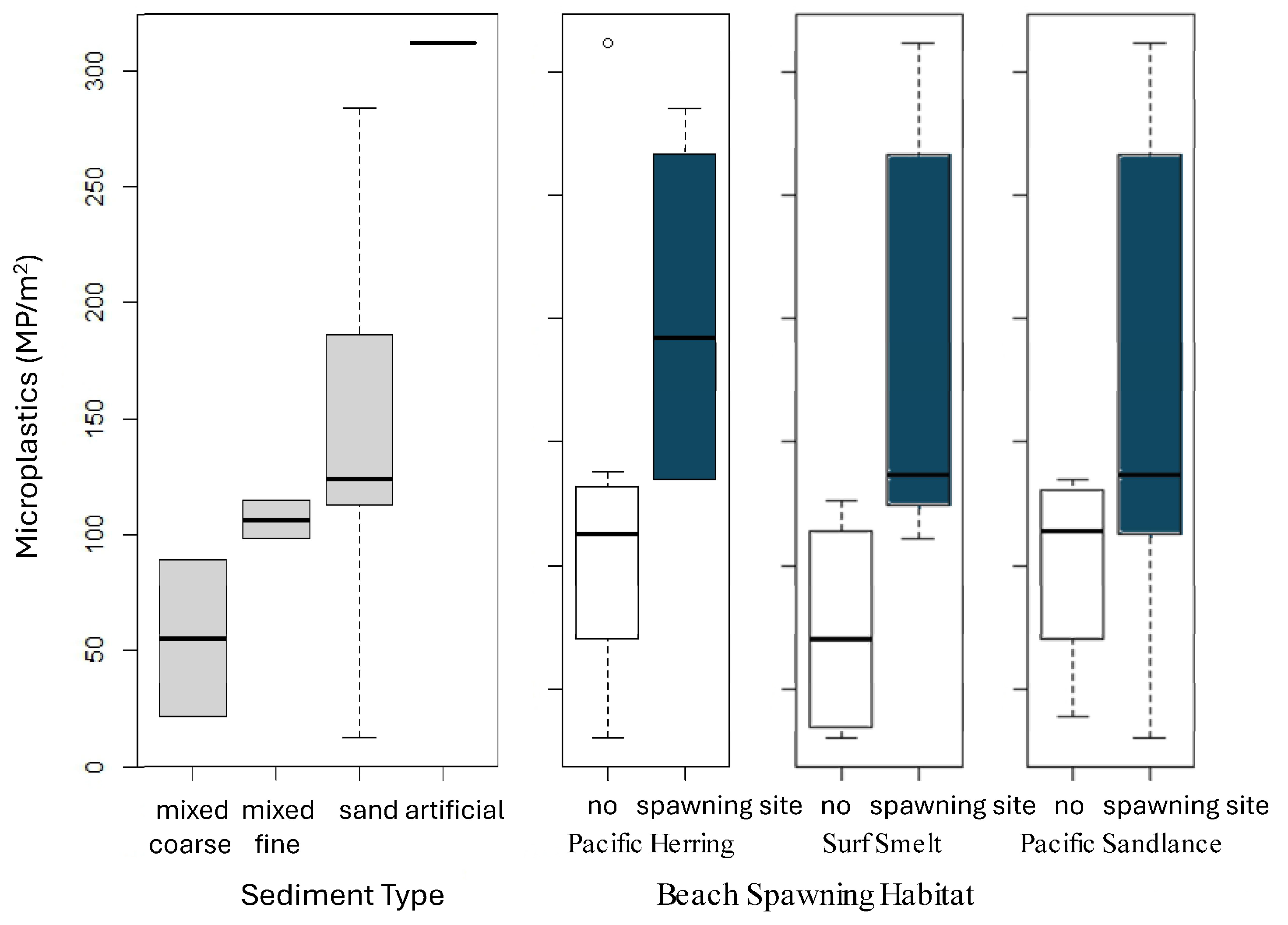
3.4. Analyses of Site-Specific Wave Exposure and Sediment Type
3.5. Microplastics at Beach Sites Confirmed as Spawning Habitats for Forage Fish
3.6. Model of Microplastic Loads as a Function of Site Attributes (Oceanography and Sediments)
4. Discussion
4.1. Relative Abundance of Microplastics
4.2. Microplastic Types and Size Classification
4.3. Comparison to Microplastics in Sediments Elsewhere in the Salish Sea
4.4. Comparison to Other Analyses of Sediment Loads in Beaches and Subtidal Bedforms
4.5. Sources and Transport of Microplastics
4.5.1. Sources
4.5.2. Movement and Transport in Pelagic Environment
4.5.3. Patterns in Deposition and Relative Abundance in Marine Habitats
4.5.4. Deposition and Movement in Beaches
4.5.5. Deposition and Movement in Subtidal Sediments
4.6. Microplastics in Critical Fish Habitats
4.7. Implications for Marine Life
4.8. Methodological Approach and Limitations
4.9. Suggestions for Future Research
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

References
- Andrady, A.L. Microplastics in the marine environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 1596–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foekema, E.M.; De Gruijter, C.; Mergia, M.T.; van Franeker, J.A.; Murk, A.J.; Koelmans, A.A. Plastic in North Sea fish. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 8818–8824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kukulka, T.; Proskurowski, G.; Morét-Ferguson, S.; Meyer, D.W.; Law, K.L. The effect of wind mixing on the vertical distribution of buoyant plastic debris. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, 7601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H. Transport of microplastics in coastal seas. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2017, 199, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, C.J. Synthetic polymers in the marine environment: A rapidly increasing, long-term threat. Environ. Res. 2008, 108, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodall, L.C.; Gwinnett, C.; Packer, M.; Thompson, R.C.; Robinson, L.F.; Paterson, G.L.J. Using a forensic science approach to minimize environmental contamination and to identify microfibres in marine sediments. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 95, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koelmans, A.A.; Kooi, M.; Law, K.L.; Van Sebille, E. All is not lost: Deriving a top-down mass budget of plastic at sea. Environ. Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 114028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everaert, G.; Van Cauwenberghe, L.; De Rijcke, M.; Koelmans, A.A.; Mees, J.; Vandegehuchte, M.; Janssen, C.R. Risk assessment of microplastics in the ocean: Modelling approach and first conclusions. Environ. Poll. 2018, 242, 1930–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desforges, J.W.; Galbraith, M.; Dangerfield, N.; Ross, P.S. Widespread distribution of microplastics in subsurface seawater in the NE Pacific Ocean. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 79, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, D.K.; Galgani, F.; Thompson, R.C.; Barlaz, M. Accumulation and fragmentation of plastic debris in global environments. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 1985–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, M.A.; Crump, P.; Niven, S.J.; Teuten, E.; Tonkin, A.; Galloway, T.; Thompson, R. Accumulation of microplastic on shorelines worldwide: Sources and sinks. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 9175–9179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, M.J.; Watson, W.; Bowlin, N.M.; Sheavly, S.B. Plastic particles in coastal pelagic ecosystems of the Northeast Pacific Ocean. Mar. Environ. Res. 2011, 71, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Sebille, E.; Aliani, S.; Law, K.L.; Maximenko, N.; Alsina, J.; Bagaev, A. The physical oceanography of the transport of floating marine debris. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 023003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanjer, A.R.; Liedtke, T.L.; Conn, K.E.; Weiland, L.K.; Black, R.W.; Godfrey, N. Evidence for rapid gut clearance of microplastic polyester fibers fed to Chinook salmon: A tank study. Environ Poll. 2020, 265, 115083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, H.G.; Baker, M.R.; Aschoff, J. A dynamic bedforms habitat for the forage fish Pacific sand lance, San Juan Islands, WA USA. In Seafloor Geomorphology as Benthic Habitat. GeoHab Atlas of Seafloor Geomorphic Features and Benthic Habitats; Harris, P.T., Ed.; Elsevier Science: Oxford, UK, 2020; p. 1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aschoff, J.; Baker, M.R.; Greene, H.G. Subtidal Pacific Sand Lance Habitat and Salmon Foraging. A Research Effort into Subtidal Pacific Sand Lance Habitat and Salmon Foraging in the San Juan Archipelago. ESRI Online. 2023. Available online: https://storymaps.arcgis.com/stories/2fe14a29ad854454a983cfa6c0facb7f (accessed on 1 May 2025).
- Sutherland, D.A.; MacCready, P.; Banas, N.S.; Smedstad, L.F. A model study of the Salish Sea estuarine circulation. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2011, 41, 1125–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacCready, P.; McCabe, R.M.; Siedlecki, S.A.; Lorenz, M.; Giddings, S.N.; Bos, J.; Albertson, S.; Banas, N.S.; Garnier, S. Estuarine circulation, mixing, and residence times in the Salish Sea. J. Geophys. Res. 2021, 126, e2020JC016738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NOAA Estuaries. NOAA National Ocean Service Education. 2004. Available online: https://oceanservice.noaa.gov/education/tutorial_estuaries/est05_circulation.html (accessed on 1 November 2018).
- Nelson, J. Coastal Water Estuaries—Classification by Water Mixing. 2007. Available online: http://www.iupui.edu/~g115/mod14/lecture03.html (accessed on 1 May 2025).
- Therriault, T.W.; Schweigert, J.F. Biological overview and trends in pelagic forage fish abundance in the Salish Sea (Strait of Georgia, British Columbia). Mar. Ornithol. 2009, 37, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liedtke, T.; Gibson, C.; Lowry, D.; Fagergren, D. Conservation and Ecology of Marine Forage Fishes—Proceedings of a Research Symposium, September 2012: U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 2013-1035; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2013; 24p. [Google Scholar]
- Quinn, T.J.; Armstrong, J.L.; Baker, M.R.; Heifetz, J.; Witherell, D. Assessing and Managing Data-Limited Fish Stocks. Proceedings of the Wakefield Symposium. Alaska Sea Grant Publication AK-SG-16-01. 2016. Available online: https://seagrant.uaf.edu/bookstore/pubs/AK-SG-16-01.html (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- Konar, M.; Qiu, S.; Tougher, B.; Vause, J.; Tlusty, M.; Fitzsimmons, K.; Barrows, R.; Cao, L. Illustrating the hidden economic, social and ecological values of global forage fish resources. Res. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 151, 104456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huard, J.; Hemming, V.; Baker, M.R.; Hipfner, M.J.; Davoren, G.K.; Koval, B.A.; Dionne, P.; Lowry, D.; Monks, R.; Nicholas, G.; et al. Assessment of population trajectory and threats for Pacific sand lance in the Salish Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 11, 1445215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, N.V.; White, M.A.V.; Tavera, J.; O’Hara, P.D.; Baker, M.R.; Bertram, D.F.; Summers, A.; Fifield, D.A.; Juanes, F. Noise results in lower energy density in an important forage fish—The Pacific sand lance, Ammodytes personatus. Mar. Poll. Bull. 2025, 123, 117664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalan, I.A.; Bowlin, N.; Baker, M.R.; Berg, F.; Bertrand, A.; Brazier, A.; Brochier, T.; Del Favero, J.M.; Garrido, S.; Gherardi, D.F.M.; et al. Worldwide appraisal of knowledge gaps in the space usage of small pelagic fish—Highlights across stock uncertainties and research priorities. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquacult. 2025, 1–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, M.R.; Smeltz, T.S.; Williams, K.; Greufe, C.; Chapman, J.; Ewing, M.; Glassy, J.; Hasegawa, E.; Cieri, K.; Matson, S.; et al. Diel vertical migration in a pelagic forage fish—Pacific sand lance—Associated with benthic substrates. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2023, 80, 1758–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, C.L.; Hrynyk, D.; Barrie, J.V.; Schweigert, J. Identifying subtidal burying habitat of Pacific sand lance (Ammodytes hexapterus) in the Strait of Georgia, British Columbia, Canada. Prog. Oceanogr. 2013, 115, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, M.R.; Matta, M.E.; Beaulieu, M.; Parris, N.; Huber, S.; Graham, O.J.; Pham, T.; Sisson, N.B.; Heller, C.P.; Witt, A.; et al. Intra-seasonal and inter-annual patterns in the demographics of sand lance and response to environmental drivers in the North Pacific. Mar. Ecol. Progr. Ser. 2019, 617, 221–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, M.R.; Greene, H.G.; Aschoff, J.; Aitoro, E.; Bates, E.; Hesselroth, D.; Johnson, K.; Mather, B.; Sealover, N. Atlas of Pacific sand lance benthic habitat—Application of multibeam acoustics and directed sampling to identify viable subtidal substrates. Mar. Environ. Res. 2024, 202, 106778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, G.H.; Baker, M.R.; Aschoff, J.; Pacunski, R. Hazards evaluation of a valuable vulnerable sand-wave field forage fish habitat in the marginal central Salish Sea using a submersible. Oceanologia 2021, 65, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huard, J.R.; Proudfoot, B.; Rooper, C.N.; Martin, T.G.; Robinson, C.L. Intertidal beach habitat suitability model for Pacific sand lance (Ammodytes personatus) in the Salish Sea, Canada. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2022, 79, 1681–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Good, T.P.; Pearson, S.F.; Hodum, P.; Boyd, D.; Anulacion, B.F.; Ylitalo, G.M. Persistent organic pollutants in forage fish prey of rhinoceros auklets breeding in Puget Sound and the northern California Current. Mar. Poll. Bull. 2014, 86, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conn, K.E.; Liedtkeb, T.L.; Takesuec, R.K.; Dinicola, R.S. Legacy and current-use toxic contaminants in Pacific sand lance (Ammodytes personatus) from Puget Sound, Washington, USA. Mar. Poll. Bull. 2020, 158, 111287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, J.M.; Pearson, W.H.; Anderson, J.W. Sediment preferences and oil contamination in the Pacific sand lance Ammodytes hexapterus. Mar. Biol. 1984, 83, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, W. Microplastic Fibres in Pacific Sand Lance (Ammodytes personatus) Burying Habitats in the Strait of Georgia, British Columbia, Canada. Master’s Thesis, Simon Fraser University, Burnaby, BC, Canada, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hipfner, J.M.; Galbraith, M.; Tucker, S.; Studholme, K.R.; Domalik, A.D.; Pearson, S.F.; Good, T.P.; Ross, P.S.; Hodum, P. Two forage fishes as potential conduits for the vertical transfer of microfibres in Northeastern Pacific Ocean food webs. Environ. Poll. 2018, 239, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selden, K.R.; Baker, M.R. Influence of marine habitat on microplastic prevalence in forage fish and salmon in the Salish Sea. Mar. Poll. Bull. 2023, 197, 115748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacCready, P.; Geyer, W.R. Estuarine exchange flow in the Salish Sea. J. Geophys. Res. 2024, 129, e2023JC020369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, M.R.; Williams, K.; Greene, G.H.; Aschoff, J.; Greufe, C.; Lopes, H.; Towler, R. Use of manned submersible and autonomous stereo-camera array to assess forage fish and associated subtidal habitat. Fish. Res. 2021, 243, 106067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sisson, N.; Baker, M.R. Feeding ecology of Pacific sand lance in the San Juan Archipelago. Mar. Coast. Fish. 2017, 9, 612–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banas, N.S.; Conway-Cranos, L.; Sutherland, D.A.; MacCready, P.; Kiffney, P.; Plummer, M. Patterns in river influence and connectivity among subbasins of Puget Sound. Estuar. Coasts 2015, 38, 735–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bale, A.J.; Kenny, A.J. Sediment analysis and seabed characterisation. In Methods for the Study of Marine Benthos, 3rd ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 43–86. [Google Scholar]
- Blott, S.J.; Pye, K. GRADISTAT: A grain size distribution and statistics package for the analysis of unconsolidated sediments. Earth Surf. Proc. Landf. 2001, 26, 1237–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folk, R.L. A review of grain-size parameters. Sedimentology 1966, 6, 73–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo-Ruz, V.; Gutow, L.; Thompson, R.C.; Thiel, M. Microplastics in the marine environment: A review of the methods used for identification and quantification. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 3060–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masura, J.; Foster, G.; Arthur, C. Laboratory methods for the analysis of microplastics in the marine environment: Recommendations for quantifying synthetic particles in waters and sediments. In NOAA Technical Memorandum NOS-OR&R-48; NOAA Marine Debris Program: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, J.M.; Rodríguez, Y.; Blasco-Monleon, S.; Porter, A.; Lewis, C.; Pham, C.K. Microplastic in the stomachs of open-ocean and deep-sea fishes of the North-East Atlantic. Environ. Poll. 2020, 265, 115060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, N.B.; Hüffer, T.; Thompson, R.C.; Hassellöv, P.; Verschoor, A.; Daugaard, A.E.; Rist, S.; Karlsson, T.; Brennholt, N.; Cole, M.; et al. Are we speaking the same language? Recommendations for a definition and categorization framework for plastic debris. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 1039–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bermúdez, J.R.; Swarzenski, P.W. A microplastic size classification scheme aligned with universal plankton survey methods. MethodsX 2021, 8, 101516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devriese, L.I.; van der Meulen, M.D.; Maes, T.; Bekaert, K.; Paul-Pont, I.; Frère, L.; Robbens, J.; Vethaak, A.D. Microplastic contamination in brown shrimp from coastal waters of the Southern North Sea and Channel area. Mar. Poll. Bull. 2015, 98, 17987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lusher, A.L.; Welden, N.A.; Sobral, P.; Cole, M. Sampling, isolating and identifying microplastics ingested by fish and invertebrates. Anal. Meth. 2017, 9, 1346–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckingham, B.; Apintiloaiei, A.; Moore, C.; Brandes, J. Hot or not: Systematic review and laboratory evaluation of the hot needle test for microplastic identification. Micropl. Nanopl. 2023, 3, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dethier, M.N. A Marine and Estuarine Habitat Classification System; Washington State Department of Natural Resources: Olympia, WA, USA, 1990; p. 60. [Google Scholar]
- Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R. Generalized Additive Models. Statist. Sci. 1986, 1, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, S.N. A simple test for random effects in regression models. Biometrika 2013, 100, 1005–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, S. Mixed GAM Computation Vehicle with Automatic Smoothness Estimation. 2023. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/mgcv/mgcv.pdf (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- Black, R.W.; Barnes, A.; Elliot, C.; Lanksbury, J. Nearshore Sediment Monitoring for the STORMWATER Action Monitoring (SAM) Program, Puget Sound, Western Washington (No. 2018-5076); U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Collicutt, B.; Juanes, F.; Dudas, S.E. Microplastics in juvenile Chinook salmon and their nearshore environments on the east coast of Vancouver Island. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 244, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, W.; Robinson, C.; Kohfeld, K.; Pellatt, M.; Bertram, D. Extent of Microplastics in Pacific Sand Lance Burying Habitat in the Salish Sea. Salish Sea Ecosystem Conference. 2020. Available online: https://cedar.wwu.edu/ssec/2018ssec/allsessions/422/ (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- Esiukova, E. Plastic pollution on the Baltic beaches of Kaliningrad region, Russia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 114, 1072–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chubarenko, I.; Esiukovaa, E.; Khatmullinaa, L.; Lobchuka, O.; Gravea, A.; Kilesob, A.; Hasel, M. From macro to micro, from patchy to uniform: Analyzing plastic contamination along and across a sandy tide-less coast. Mar. Poll. Bull. 2020, 156, 111198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esiukova, E.; Zobkov, M.; Chubarenko, I. Data on microplastic contamination of the Baltic Sea bottom sediment samples in 2015–2016. Data Brief 2020, 28, 104887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozdnyakov, S.R.; Ivanova, E.V.; Guzeva, A.V.; Shalunova, E.P.; Martinson, K.D.; Tikhonova, D.A. Studying the concentration of microplastic particles in water, bottom sediments and subsoils in the coastal area of the Neva Bay, the Gulf of Finland. Water Res. 2020, 47, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zobkov, M.; Esiukova, E. Microplastics in Baltic bottom sediments: Quantification procedures and first results. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 114, 724–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esiukova, E.E.; Chubarenko, I.P. Microplastics in the water column, bottom sediments, and beach sands of the southeastern Baltic Sea: Concentrations, particle distributions by size and shape. Reg. Ecol. 2019, 2, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haseler, M.; Schernewski, G.; Balciunas, A.; Sabaliauskaite, V. Monitoring methods for large micro- and meso-litter and applications at Baltic beaches. J. Coast. Conserv. 2018, 22, 27–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagaev, A.; Esiukova, E.; Litvinyuk, D.; Chubarenko, I.; Veerasingam, S.; Venkatachalapathy, R.; Verzhevskaya, L. Investigations of plastic contamination of seawater, marine and coastal sediments in the Russian seas: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 32264–32281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leslie, H.A.; Brandsma, S.H.; Van Velzen, M.J.M.; Vethaak, A.D. Microplastics en route: Field measurements in the Dutch river delta and Amsterdam canals, wastewater treatment plants, North Sea sediments and biota. Environ. Int. 2017, 101, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, T.; Van der Meulen, M.D.; Devriese, L.I.; Leslie, H.A.; Huvet, A.; Frère, L.; Robbens, J.; Vethaak, A.D. Microplastics baseline surveys at the water surface and in sediments of the North-East Atlantic. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avio, C.G.; Gorbi, S.; Regoli, F. Plastics and microplastics in the oceans: From emerging pollutants to emerged threat. Mar. Environ. Res. 2017, 128, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, M.R.; Greene, H.G.; Aschoff, J.; Hoge, M.; Aitoro, E.; Childers, S.; Liu, J.; Newton, J.A. Bathymetric profile and sediment composition of a dynamic subtidal bedform habitat for Pacific sand lance. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025; in press. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, P.T. The fate of microplastic in marine sedimentary environments: A review and synthesis. Mar. Poll. Bull. 2020, 158, 111398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolte, A.; Forster, S.; Gerdts, G.; Schubert, H. Microplastic concentrations in beach sediments along the German Baltic coast. Mar. Poll. Bull. 2015, 99, 216–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugwu, K.; Herrera, A.; Gómez, M. Microplastics in marine biota—A review. Mar. Poll. Bull. 2021, 169, 112540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singdahl-Larsen, C. Accumulation of Microplastic in Fjord Sediments-The Bunnefjord, Inner Oslofjord, Norway. Master’s Thesis, University of Oslo, Oslo, Norway, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ballent, A.; Purser, A.; de Jesus Mendes, P.; Pando, S.; Thomsen, L. Physical transport properties of marine microplastic pollution. Biogeosci. Discuss. 2012, 9, 18755–18798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Census Bureau. King County, Washington; 2017. Available online: https://data.census.gov/ (accessed on 1 May 2025).
- Mahara, N.; Alava, J.J.; Kowal, M.; Grant, E.; Boldt, J.L.; Kwong, L.E.; Hunt, B.P.V. Assessing size-based exposure to microplastic particles and ingestion pathways in zooplankton and herring in a coastal pelagic ecosystem of British Columbia, Canada. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2022, 683, 139–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Wang, T.; Chen, B.; Booth, A.M.; Liu, S.; Wang, R.; Zhu, L.; Zhao, X.; Qu, K.; Xia, B. Factors influencing the occurrence and distribution of microplastics in coastal sediments: From source to sink. J. Hazard. Mat. 2021, 410, 124982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Booth, A.M.; Sørensen, L. Microplastic fate and impacts in the environment. In Handbook of Microplastics in the Environment; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 757–779. [Google Scholar]
- Browne, M.A.; Galloway, T.S.; Thompson, R.C. Spatial patterns of plastic debris along estuarine shorelines. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 3404–3409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Cauwenberghe, L.; Devriese, L.; Galgani, F.; Robbens, J.; Janssen, C.R. Microplastics in sediments: A review of techniques, occurrence and effects. Mar. Environ. Res. 2015, 111, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eo, S.; Hong, S.H.; Song, Y.K.; Lee, J.; Lee, J.; Shim, W.J. Abundance, composition, and distribution of microplastics larger than 20 μm in sand beaches of South Korea. Environ. Poll. 2018, 238, 894–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; O’Connor, D.; Wang, L.; Wu, W.M.; Luo, J.; Hou, D. Microplastics in urban runoff: Global occurrence and fate. Water Res. 2022, 225, 119129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chubarenko, I.; Bagaiev, A.; Zobkov, M.; Esiukova, E. On some physical and dynamical properties of microplastic particles in marine environment. Mar. Poll. Bull. 2016, 108, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chubarenko, I.P.; Esiukova, E.E.; Bagaev, A.V.; Bagaeva, M.A.; Grave, A.N. Three dimensional distribution of anthropogenic microparticles in the body of sandy beaches of a non-tidal sea and its oceanographic causes. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 628–629, 1340–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claessens, M.; Meester, S.; De Landuyt, L.; Van Clerck, K.; De Janssen, C.R. Occurrence and distribution of microplastics in marine sediments along the Belgian coast. Mar. Poll. Bull. 2011, 62, 2199–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, T.S.; Cole, M.; Lewis, C. Interactions of microplastic debris throughout the marine ecosystem. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 1, 0116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Napper, I.E.; Parker-Jurd, F.N.F.; Wright, S.L.; Thompson, R.C. Examining the release of synthetic microfibres to the environment via two major pathways: Atmospheric deposition and treated wastewater effluent. Sci. Tot. Environ. 2023, 857, 159317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.F.; Ju, Y.R.; Lim, Y.C.; Chen, C.W.; Dong, C.D. Seasonal variation of diversity, weathering, and inventory of microplastics in coast and harbor sediments. Sci. Tot. Environ. 2021, 781, 146610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isobe, A.; Kubo, K.; Tamura, Y.; Kako, S.; Nakashima, E.; Fujii, N. Selective transport of microplastics and mesoplastics by drifting in coastal waters. Mar. Poll. Bull. 2014, 89, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auta, H.S.; Emenike, C.U.; Fauziah, S.H. Distribution and importance of microplastics in the marine environment: A review of the sources, fate, effects, and potential solutions. Environ. Int. 2017, 102, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillman, R.A. Ecological Consequences of Marine Debris: Understanding Large-Scale Species Transport on Tsunami Debris and Research Priorities in Oregon. Master Thesis, Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR, USA, 2018. Available online: https://ir.library.oregonstate.edu/ (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- Morales-Caselles, C.; Viejo, J.; Martí, E.; González-Fernández, D.; Pragnell-Raasch, H.; González-Gordillo, J.I.; Montero, E.; Arroyo, G.M.; Hanke, G.; Salvo, V.S.; et al. An inshore–offshore sorting system revealed from global classification of ocean litter. Nat. Sustain. 2021, 4, 484–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, W.; Murphy, A. Plastic in Surface Waters of the Inside Passage and Beaches of the Salish Sea in Washington State. Mar. Poll. Bull. 2015, 97, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Peng, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, K.; Bao, S. Occurrence of microplastics in the beach sand of the Chinese inner sea: The Bohai Sea. Environ. Poll. 2016, 214, 722–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.C.; Olsen, Y.; Mitchell, R.P.; Davis, A.; Rowland, S.J.; John, A.W.G.; McGonigle, D.; Russell, A.E. Lost at sea: Where is all the plastic? Science 2004, 304, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, S.D.; Sinclair, M.; Levi, C.J.; Reeves, S.E.; Edgar, G.J. Ubiquity of microplastics in coastal seafloor sediments. Mar. Poll. Bull. 2017, 121, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enders, K.; Käppler, A.; Biniasch, O.; Feldens, P.; Stollberg, N.; Lange, X.; Fischer, D.; Eichhorn, K.J.; Pollehne, F.; Oberbeckmann, S.; et al. Tracing microplastics in aquatic environments based on sediment analogies. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.R.; Cole, M.; Lindeque, P.K.; Fileman, E.; Blackford, J.; Lewis, C.; Lenton, T.M.; Galloway, T.S. Marine microplastic debris: A targeted plan for understanding and quantifying interactions with marine life. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2016, 14, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, T.; Robinson, C. Re-use of shallow sediment patches by Pacific sand lance (Ammodytes hexapterus), in Barkley Sound, British Columbia, Canada. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2011, 92, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, M.R.; De Robertis, A.; Levine, R.; Cooper, D.; Farley, E. Spatial distribution of Arctic sand lance in the Chukchi Sea related to the physical environment. Deep-Sea Res. II 2022, 206, 105213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, S. Trophic Transfer of Microplastics in the Marine Food Web. 2017. Available online: https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.2.30917.96489 (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- Wright, S.L.; Thompson, R.C.; Galloway, T.S. The physical impacts of microplastics on marine organisms: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 178, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teuten, E.L.; Saquing, J.M.; Knappe, D.R.U.; Barlaz, M.A.; Jonsson, S.; Bjorn, A.; Rowland, S.J.; Thompson, R.C.; Galloway, T.S.; Yamashita, R.; et al. Transport and release of chemicals from plastics to the environment and to wildlife. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2009, 364, 2027–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, M.R.; Gobush, K.S.; Vynne, C.H. Review of factors influencing stress hormones in fish and wildlife. J. Conserv. Nat. 2013, 21, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, G.; Ye, X.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, Y.; Han, Y.; Lu, L.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, H. Multigenerational toxic effects in Daphnia pulex are induced by environmental concentrations of tire wear particle leachate. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 486, 136977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matta, M.E.; Baker, M.R. Age and growth of Pacific sand lance (Ammodytes personatus) at the latitudinal extremes of the Gulf of Alaska large marine ecosystem. Northwest Nat. 2020, 101, 34–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhukova, K.A.; Baker, M.R. Gonadal maturation and maturity staging of the Pacific Sand Lance. J. Ichthyol. 2022, 62, 921–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thain, J.E.; Vethaak, A.D.; Hylland, K. Contaminants in marine ecosystems: Developing an integrated indicator framework using biological-effect techniques. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2008, 65, 1508–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piva, F.; Ciaprini, F.; Onorati, F.; Benedetti, M.; Fattorini, D.; Ausili, A.; Regoli, F. Assessing sediment hazard through a weight of evidence approach with bioindicator organisms: A practical model to elaborate data from sediment chemistry, bioavailability, biomarkers and ecotoxicological bioassays. Chemosphere 2011, 83, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okwuosa, O.B.; Eyo, J.E.; Omovwohwovie, E.E. Role of fish as bioindicators: A Review. Iconic Res. Eng. J. 2019, 2, 1456–8880. [Google Scholar]
- Recabarren-Villalón, T.; Ronda, A.C.; Oliva, A.L.; Cazorla, A.L.; Marcovecchio, J.E.; Arias, A.H. Seasonal distribution pattern and bioaccumulation of Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in four bioindicator coastal fishes of Argentina. Environ. Poll. 2021, 291, 118125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunther, K.; Baker, M.R.; Aydin, K. Using predator diets to inform forage fish distributions and assess responses to climate variability in the eastern Bering Sea. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2024, 741, 71–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grüss, A.; Thorson, J.T.; Carroll, G.; Ng, E.L.; Holsman, K.K.; Aydin, K.; Kotwicki, S.; Morzaria-Luna, H.N.; Ainsworth, C.H.; Thompson, K.A. Spatio-temporal analyses of marine predator diets from data-rich and data-limited systems. Fish Fish. 2020, 21, 718–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steins, N.A.; Baker, M.R.; Brooks, K.; Mackinson, S.; Stephenson, R.L. Co-creating knowledge with fishers: Challenges and lessons learned for integrating fisher knowledge contributions into marine science. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1338271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, M.R.; Steins, N.A.; Pastoors, M.A.; Neuenfeldt, S.; de Boer, A.; Haasnoot, D.; Madsen, S.; Muller, J.; Post, K.; Sparrevohn, C.R.; et al. A new era for science-industry collaboration—A view towards to the future. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1144181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soursou, V.; Campo, J.; Picó, Y. A critical review of the novel analytical methods for the determination of microplastics in sand and sediment samples. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 166, 117190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, M.A.; Gaga, E.O.; Gedik, K. How can contamination be prevented during laboratory analysis of atmospheric samples for microplastics? Environ. Monit. Assess. 2024, 196, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawson, A.L.; Santana, M.F.; Nelis, J.L.; Motti, C.A. Taking control of microplastics data: A comparison of control and blank data correction methods. J. Hazardous Mat. 2023, 443, 130218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noonan, M.J.; Grechi, N.; Mills, C.L.; de Ferraz, M. Microplastics analytics: Why we should not underestimate the importance of blank controls. Microplastics Nanoplastics 2023, 3, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cashman, M.A.; Ho, K.T.; Boving, T.B.; Russo, S.; Robinson, S.; Burgess, R.M. Comparison of microplastic isolation and extraction procedures from marine sediments. Mar. Poll. Bull. 2020, 159, 111507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, J.; Sobral, P. Plastic marine debris on the Portuguese coastline: A matter of size? Mar. Poll. Bull. 2011, 62, 2649–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, V.; Elsner, N.O.; Brenke, N.; Schwabe, E.; Brandt, A. Plastic pollution of the Kuril-Kamchatka trench area (NW pacific). Deep Sea Res. II 2015, 111, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, C.J.; Moore, S.L.; Leecaster, M.K.; Weisberg, S.B. A comparison of plastic and plankton in the North Pacific Central Gyre. Mar. Poll. Bull. 2001, 42, 1297–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, S.; Majeed, L.R.; Mehta, N.; Radu, T.; Martín-Fabiani, I.; Bhat, M.A. Microplastics in terrestrial ecosystems: Sources, transport, fate, mitigation, and remediation strategies. Euro-Mediterr. J. Environ. Integr. 2025, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, M.R.; Palsson, W.; Zimmermann, M.; Rooper, C.N. Model of trawlable area using benthic terrain and oceanographic variables—Informing survey bias and benthic habitat in the Gulf of Alaska. Fish. Oceanogr. 2019, 28, 629–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, M.R.; Schindler, D.E.; Holtgrieve, G.W.; St Louis, V.L. Bioaccumulation and transport of contaminants: Salmon as vectors of mercury. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 8840–8846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Site | MP/kg DW | MP/m2 | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Research Sites—Salish Sea, Pacific Ocean | |||
| San Juan Archipelago Protected Beach | 134.8 | 16.77 | ** |
| San Juan Archipelago Exposed Beach | 45.4 | 12.33 | ** |
| San Juan Channel sand wavefield | 43.6 | 9.01 | ** |
| Puget Sound, Howarth Beach | 312 | ** | |
| Puget Sound, Carkeek Park | 285 | ** | |
| Puget Sound, Alki Beach | 249 | ** | |
| Puget Sound, Dash Point State Park | 138 | ** | |
| Puget Sound, Discovery Park | 135 | ** | |
| Puget Sound, Golden Gardens Park | 135 | ** | |
| Puget Sound, Elliot Bay Marina | 126 | ** | |
| Puget Sound, Picnic Point | 114 | ** | |
| Puget Sound, Tolmie State Park | 111 | ** | |
| Puget Sound, Shine Tidelands State Park | 102 | ** | |
| Puget Sound, Edmonds Marina | 39 | ** | |
| Puget Sound, Mukilteo | 30 | ** | |
| Reference Sites—Northeastern Pacific Ocean | |||
| Puget Sound, Salish Sea, Pacific Ocean | 150.0 | [59] | |
| Puget Sound, Salish Sea, Pacific Ocean | 60.2 | [60] | |
| Coastal British Columbia, Pacific Ocean | max = 9200 | [9] | |
| Strait of Georgia, Salish Sea Pacific Ocean | 30–230 | [61] | |
| Reference Sites—Northeastern Atlantic Ocean | |||
| Baltic Sea, Atlantic Ocean | 1.3−36 | 370−7330 | [62] |
| Baltic Sea, Atlantic Ocean | 3235 | [63] | |
| Baltic Sea, Atlantic Ocean | 2–572 | [64] | |
| Baltic Sea, Atlantic Ocean | 100–1000 | [65] | |
| Baltic Sea, Atlantic Ocean | 34–10,179 | [66,67] | |
| Reference Sites—Global Oceans | |||
| Worldwide, Multiple Oceans | 115 | 3155 | [68] |
| Worldwide, Multiple Oceans | 1.3–10,179 | 1–336,000 | [69] |
| Worldwide, Multiple Oceans | 1–2000 | [70,71] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Eshom-Arzadon, F.K.; Conway, K.; Masura, J.; Baker, M.R. Microplastics in Nearshore and Subtidal Sediments in the Salish Sea: Implications for Marine Habitats and Exposure. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 1441. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13081441
Eshom-Arzadon FK, Conway K, Masura J, Baker MR. Microplastics in Nearshore and Subtidal Sediments in the Salish Sea: Implications for Marine Habitats and Exposure. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(8):1441. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13081441
Chicago/Turabian StyleEshom-Arzadon, Frances K., Kaitlyn Conway, Julie Masura, and Matthew R. Baker. 2025. "Microplastics in Nearshore and Subtidal Sediments in the Salish Sea: Implications for Marine Habitats and Exposure" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 8: 1441. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13081441
APA StyleEshom-Arzadon, F. K., Conway, K., Masura, J., & Baker, M. R. (2025). Microplastics in Nearshore and Subtidal Sediments in the Salish Sea: Implications for Marine Habitats and Exposure. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(8), 1441. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13081441





