Abstract
Based on the experience gained worldwide from potential solutions to the fouling problem of fisheries and aquaculture infrastructure, we attempted to design, construct and test the antifouling efficiency of a new hybrid filament created from non-laminated copper wire braided with synthetic fibers made of Dyneema. The design involved the creation of a hybrid twine substituting a percentage of the synthetic fibers with 0.1–0.15 mm diameter copper wire at 5%, 10%, 20% and 40% levels. There is limited information in the international literature for comparison with our results, since there has never been any attempt to create such a hybrid net. The results showed that for the 6 mm mesh, the maximum openness obtained after the 8-month experimental period was 8.72%, with Cu wire substitution at 35%. For the 12 mm mesh, these values were 27.07% at 26%, and for the 20 mm mesh, they were 33.68% at 28%. A conservative average independent from mesh size to achieve optimum openness in the long term is 30 ± 4.73% Cu wire substitution. In addition, we found that both the mesh size (mm) and the copper substitution percentage affected the fouling process during the experimental period, which lasted 8 months.
1. Introduction
The prevention of antifouling, either completely or at least the delay of the process, is crucial for net cage-based aquaculture. Antifouling increases the cost of production, increases the workload of the farm staff and reduces the life of essential infrastructure of the farms, such as the nets, the cages, the ropes and the mooring system. Historically, antifouling actions have been reported since before 2000 BC, when ancient mariners covered the lower parts of their boats with copper tiles, showing a good understanding of the biocide capacity of this metal [1,2]. Most antifouling technology upgrades and experiences originate from the shipping sector, for which antifouling is a major issue that leads to increased vessel weight, limits speed capabilities and may increase fuel consumption by 40% [3].
Marine biofouling can be defined as the undesirable accumulation of micro-organisms, algae and animals on underwater structures. The fouling process according to [3] is divided into five stages: surface adsorption, immobilization, consolidation and micro- and macrofouling. During the first three phases, a polymeric biofilm matrix is formed by bacteria and other micro-organisms, which serves both as a new surface around the submerged structure and a source of nourishment for other micro- and macro-organisms. Despite the characteristics of modern materials which are used in aquatic environments (for example, steel), biofouling has always been a reason for material failure, limiting the lifespan and service of these materials [3]. Although interest in the fouling process stems mainly from its harmful effects on man-made structures such as nets, ropes and boats, the process can also occur on the surfaces of living marine organisms (a phenomenon named “epibiosis”) and can cause problems in the aquaculture of sedentary organisms such as shellfish. Biofouling organisms can be roughly divided into microfouling (such as bacteria and diatoms) and macrofouling (such as macroalgae, shellfish, tubeworms and Bryozoa) types, which form a community on submerged structures [4].
Initially the typical antifouling materials were coatings based on copper, mercury and tin (TBT). Later, due to national and international policies and environmental concerns, other environmentally friendly coatings were developed. Those were tin free or made from nanomaterials and other substances, such as alkali silicate agents, capsaicin agents (from pepper plants) as well as electrodeposited substances for the metal surfaces (nickel- or silver-based substances and similar) [5,6,7,8]. Especially for aquaculture purposes, the most effective developed coating is made of a water-soluble solution based on Cu, and this is the current standard. In addition to the chemical approaches to various coatings, there has been significant research on the net material and, in particular, the design and use of copper alloy nets [9] but not always with good results in relation to Cu leaching [10]. Furthermore, experience has shown that copper alloy nets are very expensive and extremely difficult for farm staff to handle. In view of the possibility that the EU will proactively ban this material from being used in aquaculture [11] due to the potential for Cu leaching in the environment [8] and contamination of both cultivated organisms and other locally occurring aquatic organisms, thus reaching the consumer, a large amount of research has recently focused on the development of environmentally friendly solutions based on copper oxide [12,13,14,15]. Moreover, the EU has introduced the Biocidal Products Regulation (BPR) [15], which established a method of assessment for whether a commercial coating product should be considered as hazardous to the environment based on its leaching potential. Cu2O leaching rates are proportional to salinity, and therefore there may be issues with marine aquaculture [16].
The common synthetic thread, which is used to create aquaculture nets in Greece, has a denier value of 220/8 and is composed of more than 1600 fibers (with a size of 0.1 mm or less). The first-stage yarns are created using special machines stacked with dozens of fiber spools, which are automatically twisted together to form the initial thread. The threads are then twisted (in groups of three) to create the final strand, which is then braided to create the knotless aquaculture nets. The main material for these filaments is made of nylon or of Dyneema in recently manufactured nets. Dyneema, an ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE; www.dyneema.com; URL accessed on 12 August 2021) product, is advertised as the world’s strongest fiber and exhibits some advantages over nylon and the other commonly used synthetic fibers when used for aquaculture nets, such as increased rigidity, increased durability in stretching and friction and a smoother surface, which reduces its vulnerability to fouling by benthic organisms. Moreover, Dyneema filaments exhibit smaller diameter than nylon filaments and have superior rigidity and durability. The benefits of these specifications are that the volume and weight of Dyneema nets are smaller, making their handling, transportation and storage easier, and these nets exhibit higher rigidity and durability than similar nets made of nylon. In addition, macrofouling settlement and growth are affected by the material. It has been reported that aluminum, carbon steel and bronze are more susceptible to biofouling than some non-metallic substrata, such as glass fiber, polyethylene, polyamide and rubber [17].
Considering the above previous research work, we aim to examine and compare the antifouling properties of a variety of different Dyneema nets in relation to the period until the complete fouling of the net and in relation to the mesh size. Preliminary results analyzed during the experimental process were promising [18]. The objectives of this new design were to increase the thread durability (especially in the case of gilthead seabream culture, which is known for creating holes in the net), reduce the use of antifouling paints by exploiting the antimicrobial characteristics of copper alloys and preserve similar handling of the hybrid net to nets made only of synthetic filaments. The experimental setup we followed includes a series of two nets treated with commercial antifouling: one with a nanomaterial (copper-free) coating and the other with a commercial antifouling paint based on Cu oxides. In addition, we used four Dyneema nets, in which 5%, 10%, 20% and 40% of the synthetic fibers were replaced by pure copper wire (0.1–0.15 mm, suitable for transformers without any coating), and finally, we used a control net made from Dyneema fibers without any treatment. In addition, each net was produced with mesh sizes of 6, 12 and 20 mm (a total of 21 different nets and an equal number of frames).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Net Material
A series of 21 different nets was constructed. There were 7 different types based on the antifouling methods used multiplied by 3 different mesh sizes 6, 12 and 20 mm. The nets were made of Dyneema fibers. The experimental setup is summarized in Table 1.

Table 1.
Specifications of the nets studied.
Standard Cu2O-based coating was procured from the market without modification. It is a red-colored water-soluble coating known for its very good antifouling properties (AquaNet Mediterranean®, Steen-Hansen, Hylkje, Norway) and widely used in Greece. The copper-free coating was also procured from the market, specifically for aquaculture nets (ECONEA®, Janssen PMP, Beerse, Belgium).
The hybrid net threads were made by combining and threading together commercial Dyneema fibers and pure copper non-laminated wire with a diameter of 0.1–0.15 mm commonly used to make transformers and induction coils for the electronic and electrical sectors. In total, 5%, 10%, 20% and 40% of the Dyneema fibers within each type of hybrid 220/8 thread were replaced. The 220/8 thread is composed of a total of around 1600 fibers, and based on this, the copper wire requirement for 4–40% replacement was calculated. The hybrid threads and the net pieces for the frames were produced at the net factory of DIOPAS S.A. (Nea Michaniona, North Greece; https://diopas.com/).
2.2. The Testing Platform
A series of rectangular frames were constructed from welded copper pipe with a diameter of 15 mm. The dimensions of each frame were 2 × 2 m. A piece of aquaculture net (hexagonal mesh, braided and knotless) was attached to each frame. All frames were immersed within a cage fish farm area and suspended from cage frames under the cage side corridors (Figure 1). A total of 42 frames were used for a duplicate experiment. The frames were always kept vertical in the water to simulate the sides of the actual net pens. Photographs were always taken from the same area of the frame.
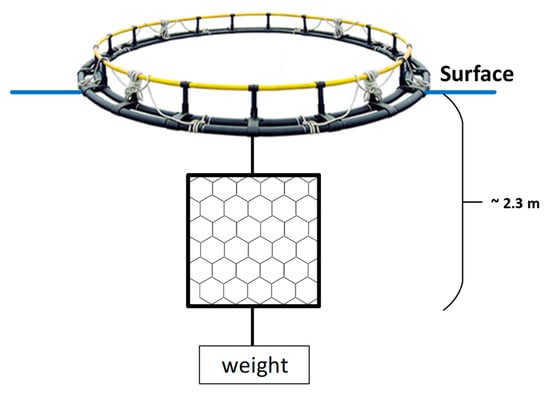
Figure 1.
Testing platform (not to scale).
2.3. Experimental Site
The nets were left immersed in seawater within the eutrophic environment of an operational fish farm (total annual licensed tonnage: 350 tn of European sea bass, Dicentrarchus labrax, and Gilthead seabream, Sparus aurata, with a complete production cycle of 16 months and final marketable size of fish ~400 g) located in the area of Sagiada (North Greece; Figure 2) for 7.95 months (242 days; from 1 October 2022 to 31 May 2023).
Figure 2.
Location of the experiments.
The basic physical characteristics of the surface waters in the study area were as follows: temperature: 17–29 °C; salinity: 20–37‰; 7.5–11 mg/L.
2.4. Data Collection and Analysis
The frames were taken out from the water periodically (every 10–15 days depending on the weather and the workload of the farm staff). Each frame was photographed at least 3 times in 3 different parts of the frame. The frames were photographed immediately after being removed from the water (while wet), and they were immersed again immediately after in at the same location and at the same depth. All photographs were analyzed using ImageJ image analysis software (v. 1.53s; https://imagej.net/ij/; URL accessed on 12 April 2022) in order to determine the percentage of mesh openness (see Figure 3)
where the total area includes the mesh area and the threads.
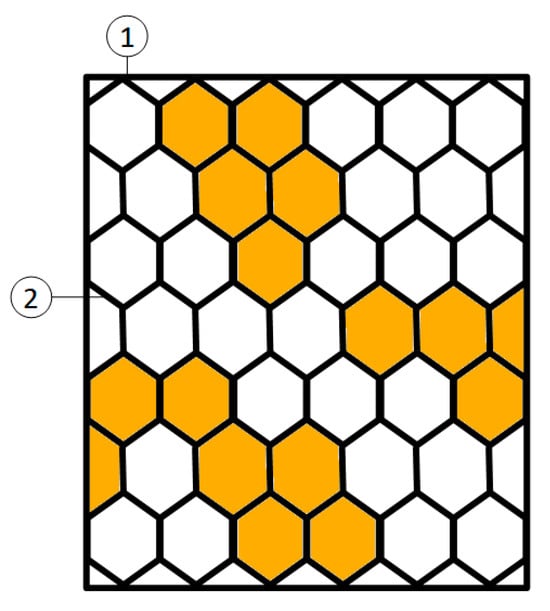
Figure 3.
A general scheme of image analysis considerations during data collection on a frame (point 1). The clogged mesh area is considered as the sum of the brown areas (in cm2 and expressed as the percentage of the open meshes over the total mesh area in the photograph) clogged by fouling and encrustations and the areas covered by the mesh itself (point 2).
2.5. Statistical Analyses
Statistical analysis was performed using JAMOVI (v. 2.3.18; https://www.jamovi.org; URL accessed on 10 November 2022) software, the PAST (v. 2.03; https://www.nhm.uio.no/english/research/resources/past/; URL accessed on 12 April 2020) ecological analysis software and the Orange Data Mining Platform. Regressions were performed using the software CurveExpert (v. 2.6.5; https://www.curveexpert.net/; URL accessed on 30 August 2018). Regression between parameters was based on the 2nd-order polynomial model and on multiple linear regressions whenever appropriate. The equations are accompanied in the text with the correlation coefficient (r2) and the probability (P). Maximization of the 2nd-order equations was carried out using the SIMPLEX linear programming algorithm.
3. Results
The results are illustrated in Figure 4, Figure 5 and Figure 6. In most cases, the time series profiles of openness percentage show a short period of stability at 95–100%, lasting from a few days to a month, during which minimal or no macroencrustations are observed. This period is characterized by the development of the biofilm, which later forms the basis for the other macrobenthic organisms. From this point on, a period of steady decrease in the opening percentage is observed due to macrobenthic encrustations that contaminate the surfaces of the nets.
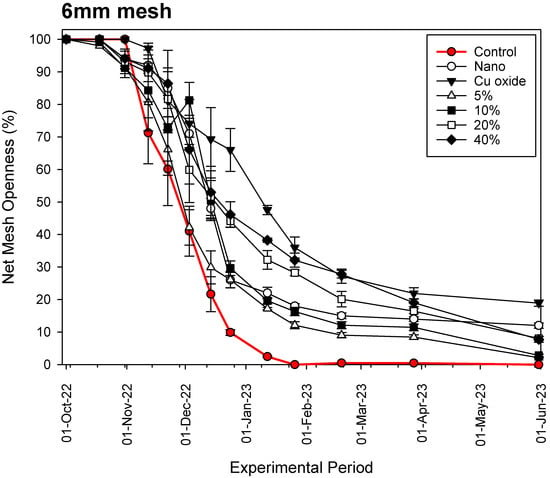
Figure 4.
Fouling process of the various nets examined on a 6 mm mesh net.
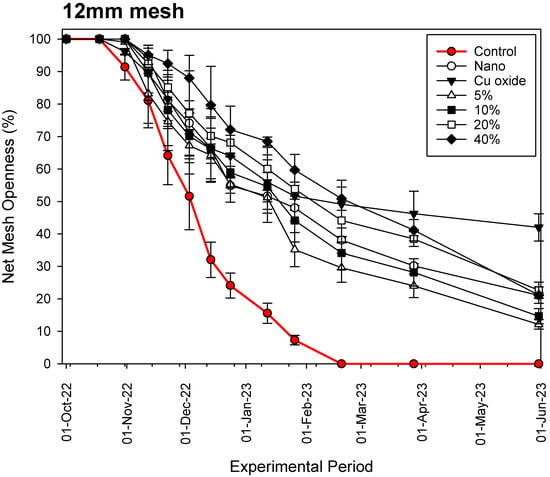
Figure 5.
Fouling process of the various nets examined on a 12 mm mesh net.
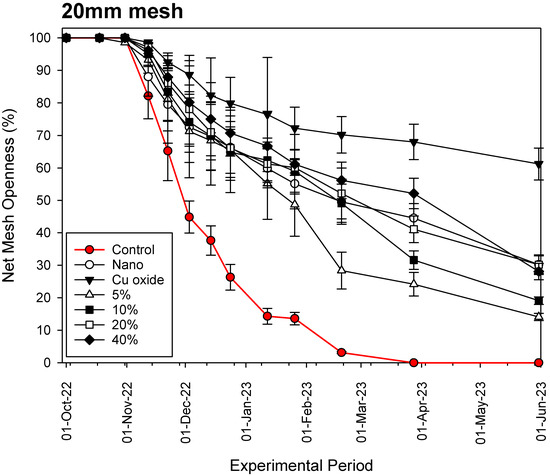
Figure 6.
Fouling process of the various nets examined on a 20 mm mesh net.
Our results show that, in all cases and throughout the experimental period, the commercial copper-based coating (Cu-oxide paint) is the most effective antifouling material for aquaculture nets, reaching openness values of 18.91 ± 0.95%, 42.01 ± 6.73% and 61.22 ± 4.90% for the 6 mm, 12 mm and 20 mm mesh nets, respectively, after 8 months of constant immersion in seawater. Our hybrid nets with Cu wire substitution percentage below 20% are not as effective as the rest. The data show that in all cases, fouling progression follows an exponential decay function with several stable periods of time, during which it is observed that fouling organisms could detach from the nets due to their weight and as a result of water movement through the net mesh.
The growth begins on the braided side of the mesh of the net, then spreads across the net opening, creating more support for other benthic organisms. Although the general trend in openness percentage is negative (Figure 4, Figure 5 and Figure 6), the rate of decline appears to gradually decrease towards the end of the experimental period. This is for two reasons: (a) the competition between organisms for space, which increases with increasing diversity and biomass, and (b) we observe macrobenthic organisms breaking away from the Dyneema twine. Dyneema has a far smoother surface than standard fibers used for aquaculture nets, reducing the ability to bind macrobenthos. Fish farmers also report that the movement of the net due to waves and currents allows some of the encrustation to be dislodged.
Comparison of the openness percentage by the end of the experimental period of 242 days for all types of nets examined in this study showed two groupings: the first includes the 5% and 10% nets, and the second includes the nano-coated (copper-free) net and the 20% and 40% nets (Figure 7). A more detailed analysis based on clustering provides detailed proof of this result (Figure 8). Moreover, the analysis showed close similarities between the 5% and 10% and 20% and 40% net pairs. On a higher level, the nano-coated (copper-free) nets cluster with the 20% and 40% nets, while the control and the Cu oxide-coated nets are significantly dissimilar from all the rest.
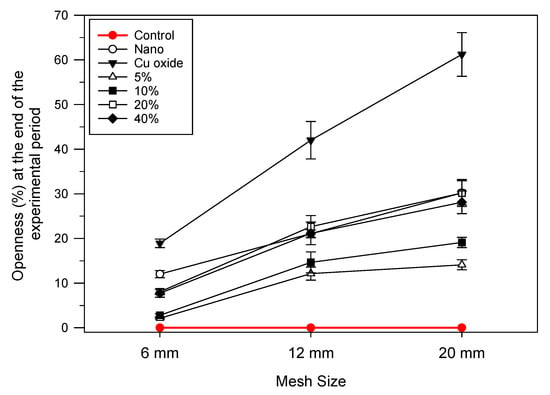
Figure 7.
Relationship between the mesh size, the Cu wire substitution percentage and the percentage of openness of the nets by the end of the experimental period.
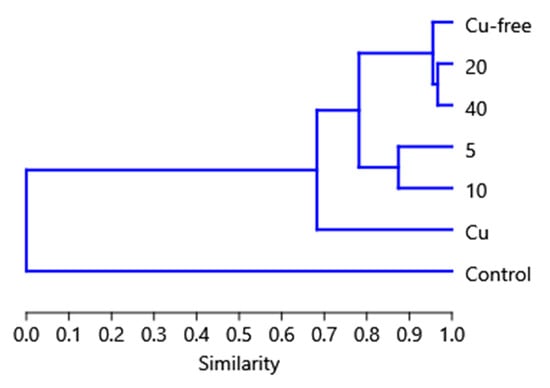
Figure 8.
Bray–Curtis clustering of the results based on the mesh size (values 6, 12 and 20 mm), the Cu wire substitution percentage (values 0, 5, 10, 20 and 40%) and the openness of the nets (%) by the end of the experiment (where Cu-free: the nanomaterial-coated (copper-free) net; Cu: net with the commercial Cu2O coating).
Regression analysis based on the second-order polynomial and maximization between the level of substitution of the Dyneema fibers with Cu wire (5–40%) and the final openness percentage (%) achieved by the end of the experimental period showed an overall statistically significant regression:
Openness (%) = 0.350·[Cu-wire, %] + 0.622·[Mesh, mm], r2 = 0.919, p < 0.05
Using the log(10) values of all variables, the above model becomes the following:
log(Openness,%) = 0.985·(log Cu-wire)−0.018·(Log[Mesh]), r2 = 0.993, p = 0
The coefficients of the log transformed model indicate that the important parameter that affects openness (%) is the Cu wire (%) substitution level, while the mesh effect is insignificant. The relationship between openness (%) and Cu wire (%) substitution for each mesh size studied separately also showed a statistically significant relationship, which follows the second-order polynomial model:
6 mm: Openness (%) = 0.494·(Cu-wire, %) − 0.007·(Cu)2, r2 = 0.967, std. error = ±1.05%
12 mm: Openness (%) = 2.055·(Cu-wire, %) − 0.039·(Cu)2, r2 = 0.966, std. error = ±2.79%
20 mm: Openness (%) = 2.407·(Cu-wire, %) − 0.043·(Cu)2, r2 = 0.991, std. error = ±1.93%
Maximization of the above equations showed that for the 6 mm mesh, the maximum openness obtained after the 8-month experimental period was 8.72% with Cu wire substitution at 35%. For the 12 mm mesh, these values were 27.07% at 26%, and for the 20 mm mesh, they were 33.68% at 28%. A conservative average independent from mesh size to achieve optimum openness in the long term is 30 ± 4.73% Cu wire substitution.
The results presented herein also show that small mesh nets tend to clog more quickly than larger mesh nets because the surface area of the net per unit area is larger and polluting organisms have more space to become lodged (Figure 4, Figure 5 and Figure 6). The analysis of the relationship between mesh size (in mm), Cu wire substitution percentage (%) and the time period until 50% of the net is not covered by fouling (in days) gave the following model:
where, the mesh takes the values 6, 12 and 20 mm and the Cu wire substitution percentage takes the values 0, 5, 10, 20 and 40%.
Time(days) = 21.75 + 3.92·[Mesh, mm] + 1.77·[Cu-wire %], r2 = 0.873, p < 0.05
ANOVA results showed that both the mesh and the Cu wire percentage affect the model, i.e., the days until 50% coverage of the net. In particular, the model also showed that the average time period from the point of immersion in seawater until the first observation of fouling organisms is around 21 ± 14 days.
Clustering analysis performed on the data based on the Bray–Curtis dissimilarity index (data used: mesh size, Cu wire levels in % and final openness in %) proves in a statistical manner using the observations in Figure 7 that the final openness (%) values can be categorized into four groups: (a) the control net group, (b) the nano-coated (copper-free) net and the 20 and 40% Cu wire (%) substitution nets, (c) the 5 and 10% Cu wire (%) substitution nets and (d) the Cu2O-based commercial coating (Figure 8).
4. Discussion
The fouling of aquaculture infrastructure immersed in water by macro- and microbenthic organisms (ranging from microbes to crustaceans and shellfish) has always been a major issue affecting the performance of the equipment (for example, net drag [19]; function, form and durability [20,21,22]; increased competition with cultivated species [23] and the harboring of pathogens responsible for disease outbreaks [24]). The fouling process has been described in detail in several reports and papers (for example, see [25]; Figure 2 [26,27]). In general, fouling species in marine shellfish and finfish culture belong to the groups of Chordata, Turbellaria, Annelida, Algae, Porifera, Mollusca, Cnidaria and Arthropoda [28,29], of which algae contribute the most to the foulant biomass [30]. In view of climate change and the issue of abrupt and high-intensity weather phenomena along the coastal zone, any issue which reduces the durability of aquaculture facilities can lead to damage and very high financial losses [20]. Conservative estimates indicate that the economic costs of fouling are as high as 5–10% of production costs or globally around USD 1.5 and 3 billion annually [23]. Indicatively, the direct costs of antifouling per species can be as high as 0.03–0.12 USD/kg for salmon, 30% of the final market price for scallops and 20% for oysters. Fouling increases the weight of the facilities (nets, ropes, buoys, mooring systems, etc.) and covers the meshes, disrupting the local hydrology patterns and the water exchange within the net pens. Most antifouling technology has been developed in the merchant marine sector in order to minimize the effects of fouling on vessel hulls, with estimates showing an increase in resistance and required power by approximately 20%, while the capacity of the ships has also increased, resulting in them becoming vectors of pathogens between continents and locations [31,32]. This kind of fouling substantially alters hull hydrodynamics and increases friction and fuel consumption [16]. It has also been estimated that the antifouling cost for salmon in Norway could be as high as USD 420–490,000 per production cycle, though this does not seem realistic [33]. The cost of fouling on mussel culture in Scotland was estimated at EUR 450,000–750,000 per year for farmers [34]. The same authors report that antifouling costs for a medium-sized salmon farm in UK are around EUR 120,000 per year for the net handling and reapplication of coatings.
A “gray” area is the absence of uniformity of the regulatory limits for heavy metals that can be used in coatings in terms of their concentration in fish tissues. For example, there are no limits in EU regulations related to the maximum levels of copper in foodstuffs (EC 629/2008, L.173 and EU 2023/915). According to a recent publication [35], only the FAO (and FAO/WHO) and UK Food Standard Committee have adopted maximum regulatory limits of 30 and 20 ppm or mg/kg in fish samples, respectively. On the other hand, there are set limits for chromium (Cr), cadmium (Cd) and lead (Pb) in the EU regulations. There are also limits for magnesium (Mn), iron (Fe) and nickel (Ni) in the FAO and FAO/WHO guidelines [35]. The Scottish Environment Protection Agency has set maximum limits for the sediment within the Allowable Zone of Effect (25 m around the cages; Sediment Quality Criteria, SQC) of 410 mg/g for zinc and 270 mg/for copper [36]. Finally, according to [37], the water quality guidelines of British Columbia have established a maximum limit of 3 μg Cu/L (as total copper), while the Alaska Department of Environmental Conservation/US EPA (2007) established an acute average maximum limit of 4.8 μg Cu/L.
Currently there are three main approaches to antifouling prevention (usually in combination): (a) chemical-induced limitation of the biofoulant’s attachment on surfaces, (b) use of chemicals to kill the biofoulants and (c) the mechanical removal of the biofouling from the surfaces [38]. The most popular antifouling method is the use of coatings, which include various biocides in order to stop or prolong the fouling process. The importance of these coatings lies in the simplicity and cost of their application, which is almost double the cost of TBT coatings, which have been banned since 2008. Considering examples from the shipping industry, most of the coatings on hard surfaces (such as a ship’s hull) that are allowed to be used for antifouling can have a lifespan of 3–5 years [3].
Taking these approaches into consideration, we addressed the issue of designing a hybrid thread composed of Dyneema filaments (0.1–0.2 mm) and pure non-insulated copper wire with a diameter of 0.1–0.15 mm (similar to those used to make transformers and coils). We tested the antifouling efficiency of nets made of this thread (braided, knotless) for a long time period with constant immersion in seawater using the percentage of Dyneema filament replacement in the thread (5, 10, 20 and 40%) as a factor, and in addition we compared those four nets with nets treated with a commercial copper-free nanocoating and a common copper-based antifouling coating. Our results showed that, in all cases and throughout the experimental period, the copper oxide-based coating is the most effective antifouling material for aquaculture nets [39,40], reaching openness values of 18.91 ± 0.95%, 42.01 ± 6.73% and 61.22 ± 4.90% for the 6 mm, 12 mm and 20 mm mesh nets after 8 months of constant immersion in seawater. Hybrid nets below 20% are not as effective as the rest. The data showed that in all cases, fouling progression followed an exponential decay function with several stable periods of time, during which it was observed that fouling organisms could detach from the nets due to their weight and the water movement (currents, waves) through the nets.
Experiments have shown that nanomaterial coatings have low antifouling potential unless they contain copper or other commonly used metal oxides such as titanium oxide [41]. The use of nanomaterial coating in a similar series of experiments lasting 7 months showed a final obstruction percentage of 14%, while the value for the control net was 24.66% and similar to the results reported by [12]. However, this paper [12] did not provide information on the mesh of the net. The reported value of 14% after 7 months is within the values found in this study of 14%, 21% and 30% for 6, 12 and 20 mm meshes after 8 months. Copper-nanomaterial-based coatings are not only known to prevent fouling with the included biocides and their gradual release, but also, through surface preparation before coating, they also can affect the adhesion of the fouling organisms [34,42]. In general, it has been shown that the application of nanomaterial coatings is a complicated process which starts with the chemical preparation of the surface in order to allow the attachment and stabilization of the coating. This procedure involves the use of chemicals (for example, silane [41]). Our results showed that the nanomaterial approach is inferior to the use of hybrid nets and copper coatings (see also [40,43]. This can be considered as an added benefit of the use of nanomaterial coatings should copper and other biocides be banned in the near future [44]. An important disadvantage of these coatings seems to be their fast degradation in the marine environment and the need for re-application after a period of several months (6–7 months according to [42]). Tralopyril, which was used in this study, is a pyrrole, i.e., a synthetic organohalogen compound, and it can be considered as an endocrine disruptor and is used as an insecticide and as an antifouling biocide. Since tralopyril works by disabling mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation, it is a broad-spectrum antifoulant. However, some businesses also combine tralopyril with copper or zinc pyrithione as the latter may be more effective against the growth of algae [45]. At this time, no maximum residue levels (MRLs) have been established for tralopyril, though there are reports that some residues are measurable in the muscle of fish such as salmon [45] and turbot [46] as well as shellfish [47,48], even after short-term exposure. The approval of tralopyril as an antifouling product by the European Commission made it clear how crucial it is to carefully consider the risks, exposure and efficacy related to any application-covered uses when evaluating a product. It is critical to reduce emissions and losses in the environment and to collect any waste or losses that contain tralopyril for reuse or disposal. It is necessary to verify whether existing minimal risk levels for products that may leave residues in food or feed should be modified or whether new ones should be established. In order to ensure that the applicable minimal risk levels are not exceeded, any necessary risk mitigation measures should also be implemented [45].
The use of copper alloy nets instead of nylon or polyamide, etc., has also been proposed the last 10 years, and several designs have been studied [49,50] worldwide (Chile, Australia, Scotland, China, Turkey, Greece, USA, etc.) for a variety of species such as salmon, trout, gilthead seabream, European sea bass, cod, and cobia [37]. Despite the obvious disadvantages of high weight and handling difficulties, as well as the frame needed for carrying this weight in water [49], the copper surface acts as a potent biocide for any fouling organisms. In addition, the material prevents rips in the mesh, which can allow escapes from the farms and the opposite, negative results from attacks by predators [50]. The biocide capabilities eliminate the need for coatings or other antifouling applications. It should be noted that even though these nets are known in the market as copper alloy nets, they contain significant amounts of zinc, composing with copper 89.18% of the material (65–71.5% Cu and 27.4–35% Zn) [9,51]. A seven-month experiment with gilthead seabream in copper alloy nets, in comparison with nylon nets, showed improved weight gain by almost 25% (in weight percentage in relation to the control nylon net) and almost 11.6% in specific growth rate (in relation to the control nylon net) for the fish reared in the copper alloy nets [9]. Finally, the Food Conversion Ratio was found to be lower for the fish reared in the copper alloy nets in relation to the others reared in the nylon nets (1.48 and 2.09 g feed/g weight, respectively) [9]. In addition to these benefits, certain risks in their use are recognized, such as the possibility of creating metal-resistant micro-organisms due to their constant immersion in water and the fact that metal is leached out into the environment [52]. Even though there is a general understanding that due to the manufacture of the copper alloy nets from copper/zinc (2–3 mm in diameter) they have minimal handling requirements and almost an infinite life cycle, according to [37], these cages have 6–8 years of life expectancy or less (4 years according to [51]) and also require cleaning in situ 1–2 times per year [37]. A similar approach was recently reported and involves the use of other metals—such as stainless steel—which have very low toxicity in relation to copper or copper/zinc but also have a very small life cycle due to high corrosion and biofouling potential. The durability of these materials against water can be increased using nanoporous films of neutral metals, such as tungsten oxide films, which are applied through electrodeposition [6]. Their main mode of action is that the coating significantly reduces the potential of the surface to allow fouling.
Finally, the mechanical approach has also been applied in European aquaculture in three main ways, often in combination: on site using scrapers and pressurized water, net removal and cleaning on shore either using washing machines or air drying [34]. The benefit of this approach is that chemicals are not used, and it is more environmentally friendly than the other approaches. However, mechanical scraping of the nets reduces their lifespan and increases production costs. In addition, it has been reported that the effects of on-site cleaning on gill’s integrity and health status are much more detrimental because fouling particles are detached from the net, and a thick cloud of debris is produced [43].
Copper leaching experiments have shown that the most important period after the immersion of the metal in the water is the first 1 month. Experiments with copper alloy nets showed that leaching to the environment starts from 630 μg/cm2/day (day 1) and stabilizes at levels around 1.4–6.9 μg/cm2/day, whereas when leaching from antifouling copper coatings (data from shipping), this value can be as much as 30 μg/cm2/day according to a review of eight commercial hard and polishing Cu2O shipping coatings [16]. In a similar way, leaching from nylon nets with copper antifouling paint starts from 250 μg/cm2/day (day 1) and stabilizes below 0.5 μg/cm2/day as reported in [51]. According to experimental findings regarding their toxicity, copper alloys do not present a significant environmental risk, even though subsequent LCA analysis showed that loading of copper for a period over four years, results in copper release to the environment of an estimated 282 kg and 35 kg per net pen for a copper alloy and nylon with an antifouling coating net, respectively [51]. In comparison to a recreational boat (LOA 12 m, beam 4 m painted with copper–epoxy hull coat), the leaching process may produce 4.3 kg of copper during a 3- year life cycle assessment [51,53]. Experiments with copper nanomaterials (polyaniline) showed that leaching starts from day 1 at 158–160 μg/L and stabilizes at 17–19 μg/L after 8 days of cultivation of pig-face seabream (Lethrinus lentjan; [12]).
Even though we did not perform toxicity tests for copper residuals in water and fish, in all cases that we know of, the use of copper as an antifoulant has not caused problems with the quality of consumer products from aquaculture (tissue concentration) with regard to the existing limits [43,54,55], and therefore we speculate that our approach is environmentally and product-friendly within the current limits. Experimental results on the comparison of leaching and toxicity from copper alloy nets and nylon nets treated with copper antifouling paint showed that, according to [37], copper is an essential micronutrient for the metabolism of plants and animals and is also used in fish food and in dietary supplements. Therefore, it should also be considered that the leaching of copper from these nets (hybrids studied here and the copper alloy nets as well) can be beneficial for the environment (also considering the currents and waves, which disperse all pollutants, [51]) as long as the concentration levels do not exceed toxic limits. Furthermore, the chemical changes expected due to climate change (increase in temperature and acidity) also need to be factored into the studies of metal leaching. Finally, the rates of retention of copper in the bodies of fish is another factor which needs to be examined, considering that it has also been shown that after a period of 2–3 weeks, copper is released from the body, reaching 12–19% of the initial value in the body muscle (100% at day 0; [56]).
The usefulness of pure copper alloy nets or hybrid synthetic Cu wire nets, as in this case, can be limited by their corrosion in seawater. Measurements reported by the Copper Development Association indicate a loss of 0.02 mm/y. This allows the estimation of complete corrosion of the wire used in this study (0.1–0.15 mm in diameter) after 60 to 90 months. Some manufacturers of pure copper alloy nets indicate a lifespan of more than 60 months (for example, Qingdao Waysail Ocean Technology Co., Ltd, Qingdao City, China; https://www.qdwaysail.com/fishing-net-copper-alloy-net.html; URL accessed on 13 December 2024). Similar results showing a corrosion rate of 13.9 μm/y (0.014 mm/y) following a 12-month exposure to natural seawater were reported by [57] for pure Cu wire. Conventional synthetic nets (nylon, polyethylene, polypropylene and mixtures), in comparison, also show a high loss of tensile strength by 52% after 3 years of use [58] due to the effects of seawater and UV radiation at low depths. In a review, it was reported that polyamide loses 80% of its strength after 4 years, while nylon nets exhibit an overall lifespan of 4–6 years (48–72 months) [59]. It should be noted that such lifespan estimates are indicative, since, as we discussed above, handling can reduce the lifespan of the net significantly (for example, sun drying instead of washing or the use of mechanical antifouling methods instead of washing).
5. Conclusions
Our analysis and experiments, which are presented here, demonstrate that our method, which substitutes copper-based coatings with a thread made of Dyneema filaments and uncoated copper wire of the same diameter, offers an alternative antifouling solution for aquaculture nets. Although the results unequivocally demonstrate that the conventional copper-based coatings currently in use exhibit the best antifouling properties, our method produces intriguing results in the context of a potential EU ban on the use of copper-based coatings. Furthermore, our method makes it possible to build aquaculture nets that are comparable to the synthetic nets currently in use in terms of material flexibility and handling using the equipment already present in a typical fish farm (such as cranes, warehouse space and suitability for cleaning in a net washer). Additionally, adding copper wire to the thread makes the net more rigid against water movement and currents and increases its resistance to bites from certain fish, like the gilthead seabream.
Our results and the existing literature on the subject clearly identify two issues: at first, the Cu-based solutions show the best antifouling performance for aquaculture nets, and secondly, research is still ongoing, since actual solutions with similar performance have not been produced yet. The possibility of a ban on Cu coatings on an EU level will force fish farmers to utilize other existing commercial methods that have limited antifouling performance, which will directly affect the production cost (workload of staff, more frequent use of materials, reduction in the life cycle of the nets, etc.). Also, the literature shows that more attention should be paid to solutions that do not significantly change the characteristics of the nets (flexibility, easy handling using the machinery of an average farm, easy application, low/minimal copper leaching). Finally, it is obvious that further research is required to establish the relation between the copper wire surface and diameter, since the surface is linearly related to the copper ions available for antifouling performance.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.C.; methodology, A.C. and E.C.; validation, A.C., E.C. and D.K.; formal analysis and manuscript revision, A.C. and D.K.; investigation, D.K. and B.G.; resources, A.C.; data curation, D.K. and B.G.; writing—original draft preparation, A.C., E.C., D.K. and B.G.; writing—review and editing, A.C.; visualization, D.K.; supervision, A.C.; project administration, A.C.; funding acquisition, A.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The data of this paper were collected within the frame of the project entitled “COPPERNET- Design and Construction of New Thread Types for Fishing and Aquaculture Use” (Contract 5021805; 2019–2023) co-funded by the European Union (EMFF fund) and the Ministry of Agriculture Development and Food (Greece) and coordinated by Dr Alexis J. Conides, Research Director of the Institute for Marine Biological Resources and Inland Waters of the Hellenic Centre for Marine Research (Greece) and main author here.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the anonymous reviewers of the journal for their very thorough revision and targeted comments, which helped us to revise and increase the quality of the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Papafillipou, C. Legislation and Application of Ecological Coatings for Ships. Bachelor’s Thesis, Macedonia Merchant Marine Academy of Greece, Nea Michaniona, Greece, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Selim, M.S.; Shenashen, M.A.; El-Safty, S.A.; Higazy, S.A.; Selim, M.M.; Isago, H.; Elmarakbi, A. Recent progress in marine foul-release polymeric nanocomposite coatings. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2017, 87, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abioye, O.P.; Loto, C.A.; Fayomi, O.S.I. Evaluation of anti-biofouling progresses in marine application. J. Bio Tribo Corros. 2019, 5, 1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellio, C.; Yebra, D. Advances in Marine Antifouling Coatings and Technologies; Woodhead Publishing in Materials; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, M.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, L.; Wang, J. The application of Ag@PPy composite coating in the cathodic polarization antifouling. Mater. Lett. 2018, 230, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesler, A.B.; Kim, P.; Kolle, S.; Howell, C.; Ahanotu, O.; Aizenberg, J. Extremely durable biofouling-resistant metallic surfaces based on electrodeposited nanoporous tungstite films on steel. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.; Barrios, C.A.; Cutright, T.; Zhang Newby, B. Evaluation of toxicity of capsaicin and zosteric acid and their potential application as antifoulants. Environ. Toxicol. 2005, 20, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciriminna, R.; Bright, F.V.; Pagliaro, M. Ecofriendly antifouling marine coatings. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yigit, M.; Celikkol, B.; Ozalp, B.; Bulut, M.; Dwyer, R.L.; Yilmaz, S.; Maita, M.; Buyukates, Y. Comparison of copper alloy mesh with conventional nylon nets in offshore cage farming of Gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata). Aquac. Stud. 2018, 18, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalantzi, I.; Zeri, C.; Catsiki, V.-A.; Tsangaris, C.; Strogyloudi, E.; Kaberi, H.; Vergopoulos, N.; Tsapakis, M. Assessment of the use of copper alloy aquaculture nets: Potential impacts on the marine environment and on the farmed fish. Aquaculture 2016, 465, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Plassche, E.; Van der Aa, E. Harmonisation of Environmental Emission Scenarios; An Emission Scenario Document for Antifouling Products in OECD Countries. Environmental Emission Scenario Document; Contract No. B4-3040/2002/348010/MAR/C3, Final Report 9M2892.01; European Commission, DG-Environment: Brussels, Belgium, 2004; 194p. [Google Scholar]
- Ashraf, P.M.; Lekshmi, N.M.; Chinnadurai, S.; Anjitha, S.; Archana, M.; Vineeth, K.; Chirayil, M.; Sandhya, K.M.; Gop, A.P. Impact assessment of biofouling resistant nano copper oxide–polyaniline coating on aquaculture cage nets. Aquac. Fish. 2023, 8, 538–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurioglu, A.G.; Esteves, A.; De With, G. Non-toxic, non-biocide-release antifouling coatings based on molecular structure design for marine applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 6547–6570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashwitha, A.; Thamizharasan, K.; Roshini, S.; Snega Priya, P.; Bhuvaneswari, S.; Sankari, D. Biofouling-bioadhesion of micro-organisms and its prevention: A Review. Int. J. Eng. Res. Rev. 2018, 6, 11–21. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Regulation (EU) No 528/2012 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 22 May 2012 concerning the making available on the market and use of biocidal products. In Official Journal of the European Union OJ L 167; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2012; 123p. [Google Scholar]
- Lagerström, M.; Ytreberg, E.; Wiklund, A.-K.E.; Granhag, L. Antifouling paints leach copper in excess—Study of metal release rates and efficacy along a salinity gradient. Water Res. 2020, 186, 116383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinagre, P.A.; Simas, T.; Cruz, E.; Pinori, E.; Svenson, J. Marine Biofouling: A European Database for the Marine Renewable Energy Sector. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conides, A.; Kallias, I.; Cotou, E.; Georgiou, P.; Gialamas, I.; Klaoudatos, D. Preliminary Results on the Antifouling Potential of Copper Wire and Dyneema® Fiber Combined Twines for Aquaculture Net Cages. WSEAS Trans. Environ. Dev. 2023, 19, 607–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swift, M.R.; Fredriksson, D.W.; Unrein, A.; Fullerton, B.; Patursson, O.; Baldwin, K. Drag force acting on biofouled net panels. Aquac. Eng. 2006, 35, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannister, J.; Sievers, M.; Bush, F.; Bloecher, N. Biofouling in marine aquaculture: A review of recent research and developments. Biofouling 2019, 35, 631–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gansel, L.C.; Plew, D.R.; Endresen, P.C.; Olsen, A.I.; Misimi, E.; Guenther, J.; Jensen, Ø. Drag of clean and fouled net panels—Measurements and parameterization of fouling. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lader, P.; Dempster, T.; Fredheim, A.; Jensen, Ø. Current induced net deformations in full-scale sea-cages for Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Aquac. Eng. 2008, 38, 52–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitridge, I.; Dempster, T.; Guenther, J.; de Nys, R. The impact and control of biofouling in marine aquaculture: A review. Biofouling 2012, 28, 649–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, R.J.; Luu, H.A.; Chen, D.Z.; Holmes, C.F.; Kent, M.L.; Le Blanc, M.; Taylor, F.; Williams, D.E. Chemical and biological evidence links microcystins to salmon ‘netpen liver disease’. Toxicon 1993, 31, 1315–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, S.; Wang, J.; Chen, H.; Chen, D. Progress of marine biofouling and antifouling technologies. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2011, 56, 598–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dürr, S.; Thomason, J. Biofouling, 1st ed.; Blackwell Publishing Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Railkin, A.I. Marine Biofouling: Colonization Processes and Defenses; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- IMO. Common Hull Fouling Invasive Species. Available online: https://www.imo.org/en/ourwork/environment/pages/common-hull-fouling-invasive-species.aspx (accessed on 12 December 2022).
- Jackson, L. Marine biofouling and invasive species; guidelines for prevention and management. In Global Invasive Species Program; UNEP Regional Seas Programm: Nairobi, Kenya, 2008; 68p. [Google Scholar]
- García-Bueno, N.; Marín, A. Ecological management of biomass and metal bioaccumulation in fish-cage nettings: Influence of antifouling paint and fiber manufacture. Aquaculture 2021, 544, 737142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bressy, C.; Lejars, M. Marine Fouling: An Overview. J. Ocean. Technol. 2014, 9, 19–28. [Google Scholar]
- California State Lands Commission. Biofouling Management Regulations to Minimize the Transfer of Nonindigenous Species from Vessels Arriving at California Ports: California Code of Regulations, title 2, section 2298.1 et seq. In Marine Invasive Species Program; California State Lands Commission: Sacramento, CA, USA, 2017; p. 25. [Google Scholar]
- Blöcher, N.; Floerl, O. Towards cost-effective biofouling management in salmon aquaculture: A strategic outlook. Rev. Aquac. 2021, 13, 783–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willemsen, P. Biofouling in European aquaculture: Is there an easy solution? In Aquaculture Europe 2005; European Aquaculture Society: Trondheim, Norway, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Younis, E.M.; Abdel-Warith, A.-W.A.; Al-Asgah, N.A.; Elthebite, S.A.; Mostafizur Rahman, M. Nutritional value and bioaccumulation of heavy metals in muscle tissues of five commercially important marine fish species from the Red Sea. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 1860–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dean, R.J.; Shimmield, T.M.; Black, K.D. Copper, zinc and cadmium in marine cage fish farm sediments: An extensive survey. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 145, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, H.E.; Gace, L.; Dwyer, R.L.; Santore, R.C.; McGree, J.; Smith, D.S. Field testing of copper alloy cages in British Columbia: Comparison of measured copper to ambient water quality criteria. In Farming Our Waters—Agrifood Innovations; Aquaculture Association of Canada: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Blöcher, N.; Floerl, O. Efficacy testing of novel antifouling coatings for pen nets in aquaculture: How good are alternatives to traditional copper coatings? Aquaculture 2020, 519, 734936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rejeki, S.; Susilowati, T.; Aryati, R.W. Application of copper oxide paints as prevention for macrofouling attachment on a marine floating net cage. J. Coast. Dev. 2010, 13, 166–178. [Google Scholar]
- Blöcher, N. Biofouling in the Norwegian Salmon Farming Industry. Ph.D. Thesis, Norwegian University of Science and Technology, Trondheim, Norway, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ashraf, P.; Anjana, C.; Lekshmi, N.M. Photocatalytic mediated marine biofouling inhibition using nano CuO: TiO2-carbon dot embedded on organo silane surface modified polyethylene aquaculture cage nets. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2024, 193, 105856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, P.M.; Edwin, L. Nano copper oxide incorporated polyethylene glycol hydrogel: An efficient antifouling coating for cage fishing net. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2016, 115, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comas, J.; Parra, D.; Balasch, J.C.; Tort, L. Effects of fouling management and net coating strategies on reared gilthead sea bream juveniles. Animals 2021, 11, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, I.; Pangule, R.C.; Kane, R.S. Antifouling coatings: Recent developments in the design of surfaces that prevent fouling by proteins, bacteria, and marine organisms. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 690–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grøsvik, E.; Kristiansen, D.E.; Ali, A. Analysis of uptake of tralopyril and transformation products in salmon exposed to tralopyril coated net pen. In Rapport Fra Havforskningen 2024-43; Havforsknings Instituttet: Bergen, Norway, 2024; 24p. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Li, P.; He, S.; Xing, S.; Cao, Z.; Cao, X.; Wang, X.; Li, Z.-H. Effects of short-term exposure to tralopyril on physiological indexes and endocrine function in turbot (Scophthalmus maximus). Aquat. Toxicol. 2022, 245, 106118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Li, P.; He, S.; Xing, S.; Cao, Z.; Cao, X.; Liu, B.; Li, Z.-H. Effects of tralopyril on histological, biochemical and molecular impacts in Pacific oyster, Crassostrea gigas. Chemosphere 2022, 289, 133157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, I.B.; Groh, K.J.; Stadnicka-Michalak, J.; Schönenberger, R.; Beiras, R.; Barroso, C.M.; Langford, K.H.; Thomas, K.V.; Suter, M.J.-F. Tralopyril bioconcentration and effects on the gill proteome of the Mediterranean mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Aquat. Toxicol. 2016, 177, 198–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drach, A.; Tsukrov, I.; DeCew, J.; Celikkol, B. Engineering procedures for design and analysis of submersible fish cages with copper netting for exposed marine environment. Aquac. Eng. 2016, 70, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayer, N.; Martin, S.; Dwyer, R.L.; Gace, L.; Laurin, L. Environmental performance of copper-alloy Net-pens: Life cycle assessment of Atlantic salmon grow-out in copper-alloy and nylon net-pens. Aquaculture 2016, 453, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earley, P.J.; Swope, B.L.; Colvin, M.A.; Rosen, G.; Wang, P.-F.; Carilli, J.; Rivera-Duarte, I. Estimates of environmental loading from copper alloy materials. Biofouling 2020, 36, 276–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berillis, P.; Mente, E.; Kormas, K.A. The Use of Copper Alloy in Aquaculture Fish Net Pens: Mechanical, Economic and Environmental Advantages. J. Fish. Sci. 2017, 11, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earley, P.J.; Swope, B.L.; Barbeau, K.; Bundy, R.; McDonald, J.A.; Rivera-Duarte, I. Life cycle contributions of copper from vessel painting and maintenance activities. Biofouling 2014, 30, 51–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, C.K.; Austin Hew, T.Y.; Nulit, R.; Syazwan, W.M.; Okamura, H.; Horie, Y.; Ong, M.C.; Ismail, M.S.; Kumar, K.; Zakaly, H.M.H.; et al. Copper in Commercial Marine Fish: From Biomonitoring to the ESG (Environment, Social, and Governance) Method. Pollutants 2024, 4, 117–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotou, E.; Henry, M.; Zeri, C.; Rigos, G.; Torreblanca, A.; Catsiki, V.-A. Short-term exposure of the European sea bass Dicentrarchus labrax to copper-based antifouling treated nets: Copper bioavailability and biomarkers responses. Chemosphere 2012, 89, 1091–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Zhang, W.; Du, S.; Green, I.; Tan, Q.; Zhang, L. Developmental patterns of copper bioaccumulation in a marine fish model Oryzias melastigma. Aquat. Toxicol. 2016, 170, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drach, A.; Tsukrov, I.; DeCew, J.; Aufrecht, J.; Grohbauer, A.; Hofmann, U. Field studies of corrosion behaviour of copper alloys in natural seawater. Corros. Sci. 2013, 76, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagnotta, L. Sustainable Netting Materials for Marine and Agricultural Applications: A Perspective on Polymeric and Composite Developments. Polymers 2025, 17, 1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardia, F.; Lovatelli, A. Aquaculture operations in floating HDPE cages: A field handbook. In FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Technical Papervol. 593. FAO; Ministry of Agriculture of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia: Rome, Italy, 2015. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
