Abstract
The Oligocene Dongying Formation beach-bar system, widely distributed in the HHK Depression of the Bohai Bay Basin, constitutes a key target for mid-deep hydrocarbon exploration, though its provenance remains controversial due to complex peripheral source terrains. To address this, we developed an integrated methodology combining LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating with whole-rock rare earth element (REE) analysis, facilitating provenance studies in areas with limited drilling and heavy mineral data. Analysis of 849 high-concordance zircons (concordance >90%) from 12 samples across 5 wells revealed that Geochemical homogeneity is evidenced by strongly consistent moving-average trendlines of detrital zircon U-Pb ages among the southern/northern provenances and the central uplift zone, complemented by uniform REE patterns characterized by HREE (Gd-Lu) enrichment and LREE depletion; geochemical disparities manifest as dual dominant age peaks (500–1000 Ma and 1800–3100 Ma) in the southern provenance and central uplift samples, contrasting with three distinct peaks (65–135 Ma, 500–1000 Ma, and 1800–3100 Ma) in the northern provenance; spatial quantification via multidimensional scaling (MDS) demonstrates closer affinity between the southern provenance and central uplift (dij = 4.472) than to the northern provenance (dij = 6.708). Collectively, these results confirm a dual (north–south) provenance system for the central uplift beach-bar deposits, with the southern provenance dominant and the northern acting as a subsidiary source. This work establishes a dual-provenance beach-bar model, providing a universal theoretical and technical framework for provenance analysis in hydrocarbon exploration within analogous settings.
1. Introduction
Sediment provenance analysis serves as a critical approach for deciphering regional tectonic evolution, paleogeographic patterns, and crustal material cycling [1,2,3,4]. Current challenges in this field include the mixed superposition effects of multiple source regions, variations in source-to-sink processes under different tectonic settings, and ambiguous sediment supply—all of which significantly constrain research on the formation mechanisms of sedimentary systems [5,6,7]. In recent years, provenance studies have exhibited an interdisciplinary trend, with increasing applications of isotopic dating and geochemical element analysis [8,9]. Detrital zircon U-Pb dating has developed along various technical pathways [10]. Among these, laser ablation–inductively coupled plasma–mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS) has emerged as a rapid and cost-effective method for analyzing mineral isotopic information, making it a prevalent technique in the field of zircon U-Pb geochronology [11,12,13].
In provenance analysis, LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating effectively traces sediment source regions, thereby providing key insights into basin evolution and basin–range coupling processes [14,15,16]. Furthermore, geochemical element characteristics have been shown to possess substantial indicative value in the context of sediment provenance studies [17,18,19]. Sediments, as fundamental components of Earth’s surface environments, serve as repositories of geological information concerning the properties of the underlying rock formations, the processes of weathering, and the mechanisms of transport. This information is inscribed within their elemental composition. Moreover, distribution patterns and quantitative analyses of rare earth elements (REEs), trace elements, and related parameters (e.g., La/Yb and Ce/Eu ratios) can reveal the tectonic settings, material composition, and paleoenvironmental evolution of source regions [20,21]. REE distribution patterns, characteristic ratios (e.g., La/Yb and Ce/Eu), and isotopic compositions (e.g., Sr, Nd) have been extensively applied to discriminate provenance directions and the degree of mixing in terrigenous clastic rocks [22,23,24]. However, sediment geochemical signatures are influenced by multiple factors (e.g., diagenesis, biological activity, post-depositional alteration), which may lead to ambiguous elemental fractionation. Consequently, the employment of integrated methodologies is imperative to enhance the accuracy of provenance tracing. The combined application of LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating and geochemical element analysis provides high-precision chronological constraints and geochemical fingerprints, enabling confirmation of primary sediment sources and construction of robust sediment supply models [25,26].
The central uplift zone of the HHK Depression, Bohai Bay Basin, China (Figure 1), contains widespread, thin, and continuous Oligocene Dongying Formation beach-bar deposits—primary reservoirs for mid-deep hydrocarbon exploration [27]. However, the complex provenance systems surrounding the depression have obscured sediment sources of these deposits, leading to persistent debate regarding sandbody genesis. Existing literature remains inconclusive: some studies attribute the primary sediment source to braided river delta systems along the northern steep slope [28], while others propose dominant southern gentle-slope provenance systems [29]. A third perspective suggests bidirectional (north–south) sediment supply [30]. Notwithstanding, there are as yet unresolved knowledge gaps regarding provenance directions and supply capacity. Existing studies primarily rely on singular approaches such as stratigraphic thickness analysis [31,32], paleogeomorphic reconstruction, and sedimentary facies comparison [33,34,35]. Given the limitations of traditional provenance methods and the insufficiency of heavy mineral data, this study employs a multifaceted approach that integrates LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating with comprehensive whole-rock rare earth element (REE) distribution patterns. This multidisciplinary approach systematically analyzes detrital zircon age spectra and REE characteristics of the Dongying Formation within the HHK Depression, aiming to (1) resolve provenance ambiguities of the beach-bar system, (2) clarify source composition and temporal evolution, (3) establish a robust depositional model, and (4) provide insights for provenance studies in analogous basins.
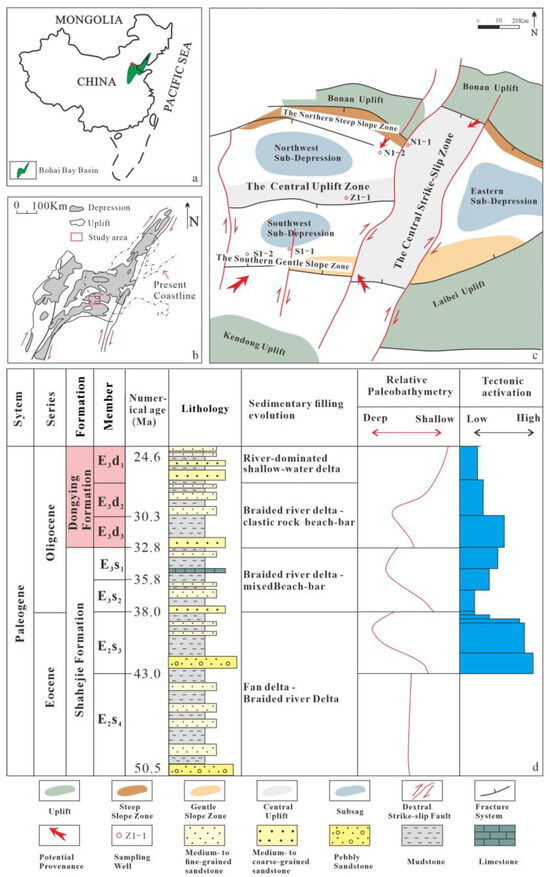
Figure 1.
Structural location and stratigraphic column of HHK Depression in the Bohai Bay Basin (revised following [20,21]; the tectonic zoning was refined based on fault distribution patterns documented in the literature to ensure its accuracy. The red box in the figure indicates the target layer). (a) Regional location of the Bohai Bay Basin; (b) location of the HHK Depression; (c) the structural division of the HHK Depression; (d) composite stratigraphic column of the Paleogene Shahejie and Dongying formations in the HHK Depression.
2. Regional Geological Setting
The HHK Depression is situated in the eastern Bohai Bay Basin, China (Figure 1a,b), and is bordered by the Bonan Uplift to the north, the Kendong Uplift to the southwest, the Laibei Uplift to the southeast, and the Miaoxi Depression to the east [36,37]. This depression, which is significant in terms of its hydrocarbon richness, is located within the Bohai Sea area (Figure 1c). The depression primarily features nearly EW-trending extensional fault systems and NNE-trending strike-slip fault systems, forming secondary structural zones including the northern steep slope zone, southern gentle slope zone, central strike-slip zone, and central uplift zone. The internal sub-sags are further subdivided into three distinct categories: the southwestern, northwestern, and eastern sub-depression (Figure 1c).
During the Paleogene rifting–subsidence stage, the Bohai Sea area exhibited a tectonic paleogeomorphology characterized by alternating horsts and grabens. Rifting in this region progressed in an episodic manner and can be subdivided into four extensional phases corresponding to the depositional periods of the Kongdian Formation: fourth member of the Shahejie Formation (E1k-E2s4), third member of the Shahejie Formation (E2s3), second–first members of the Shahejie Formation (E3s2-E3s1), and Dongying Formation (E3d). The HHK Depression preserves a relatively complete Paleogene stratigraphic succession, comprising (in ascending order) the Kongdian Formation (E1k), the fourth to the first member of the Shahejie Formation (E2s4-E3s1), and the third to the first member of the Dongying Formation (E3d3-E3d1). These formations are overlain by the Neogene Guantao (Ng) and Minghuazhen (Nm) formations and Quaternary (Q) deposits [38] (Figure 1d).
The Paleogene initial Rifting Episode I in the Bohai Bay Basin was constrained by low crustal extensional intensity and a dispersed fault depression pattern. The activity rates of basin-controlling faults were generally low (<100 m/Ma), resulting in isolated, restricted distributions of coeval deposits from the Kongdian Formation (E1k) to the fourth member of the Shahejie Formation (E2s4). In contrast, during Rifting Episodes II–III (corresponding to the third member of the Shahejie Formation, E2s3, to the Dongying Formation, E3d), enhanced fault activity (peak rates >300 m/Ma) and lacustrine basin interconnection promoted extensive coverage expansion of sedimentary systems. This led to the development of widely distributed lacustrine to deltaic systems across the entire basin [38,39,40]. Strong tectonic differential activity and significant topographic relief during the Sha-3 Member (E2s3) favored the development of fan-delta and braided-river delta systems. Reduced tectonic activity and subdued topography from the Sha-2 Member (E3s2) to the Sha-1 Member (E3s1) diminished the scale and abundance of fan deltas while increasing the prevalence of braided-river deltas [39]. The Sha-2 Member (E3s2) primarily developed braided-river delta systems with locally mixed beach-bar deposits. The Sha-1 Member (E3s1) inherited the depositional characteristics of the underlying Sha-2 Member (E3s2). However, increased water depth led to a reduction in overall delta scale, thereby shifting the system toward shore-shallow lacustrine deposition with localized beach-bar accumulations [40] (Figure 2a,c).
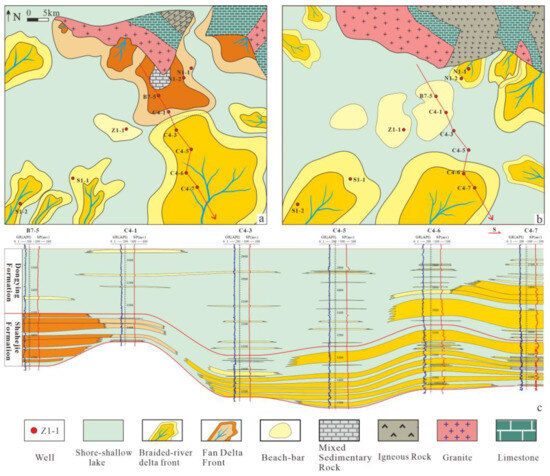
Figure 2.
Depositional system characteristics of the Shahejie and Dongying Formations (Paleogene), HHK Depression. (a) Planar distribution of the Shahejie Formation depositional systems; (b) planar distribution of the Dongying Formation depositional systems; (c) profile distribution of sandbody vertical well correlation between the Shahejie and Dongying Formations.
During the depositional phase of the Dong-3 Member (E3d3), the region experienced fault reactivation and large-scale lacustrine transgression triggered by tectonic activity. These processes resulted in the formation of thick mudstones interbedded with thin sandstones/siltstones, as well as localized braided-river deltas and beach-bar deposits [30]. The Dong-2 Member (E3d2) witnessed attenuated basin subsidence, a shallowing paleo-water depth, and accelerated delta progradation, accompanied by intensified lake-wave reworking. This resulted in expanded beach-bar development, forming braided-river delta–beach-bar depositional systems [41,42]. Late Dongying Formation deposition was accompanied by weakened depression subsidence and rapid delta progradation, leading to lake-basin shrinkage and the dominance of shallow-water deltaic environments [43]. This study focuses on the braided-river delta–beach-bar system of the Dong-3 to Dong-2 Members (E3d3 to E3d2) (Figure 2b,c).
3. Materials and Methods
Samples were collected from Paleogene Dongying Formation sandstones in boreholes within the HHK Depression. Twelve sandstone samples were obtained from five wells: Z1-1, N1-1, N1-2, S1-1, and S1-2 (Figure 1c), yielding 1243 analytical points, of which 849 were valid (concordance >90%), representing a validity rate of 68.3% (Table 1; Supplementary Tables S1–S5). Details of the obtained samples are as follows (Figure 3):

Table 1.
LA-ICP-MS dating sample statistics of detrital zircons from the Dongying Formation in the HHK Depression (detailed data are shown in Tables S1–S5).
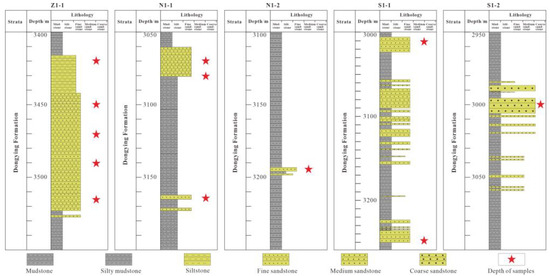
Figure 3.
Lithological histogram of boreholes, physical core photographs, and sampling locations.
Z1-1 well: Core depths 3420 m, 3450 m, 3470 m, 3490 m, and 3515 m; lithology: siltstone–fine sandstone.
N1-1 well: Core depths 3070 m, 3080 m, 3165 m; lithology: fine sandstone.
N1-2 well: Core depth 3190 m; lithology: siltstone–fine sandstone.
S1-1 well: Core depths 3010 m, 3250 m; lithology: fine sandstone.
S1-2 well: Core depth 3000 m; lithology: medium–coarse sandstone.
Zircon separation, mount preparation, and analyses were conducted at the Bohai Laboratory Center, CNOOC Engineering Technology Branch, under controlled conditions (23 ± 2 °C; 35–50% humidity). Key instrumentation included a laser ablation system (LSX-213 G2+; Serial: 51801) and an inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometer (Agilent 7800; Serial: SG19253814). For U-Pb dating, zircon domains with clear zoning and no fractures or inclusions were targeted. Laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS) was performed using a 30-μm beam diameter. Detrital zircons with 90–100% concordance were assigned 207Pb-based (207Pb/206Pb) corrected ages, while discordant data (<90%) were excluded [44,45,46].
For data processing, external standardization used Plesovice zircon for U-Pb ratio correction (instrumental mass bias), and trace element calibration employed 91,500 zircon along with NIST610-614 glass standards. Isotope and element calculations were performed using the ICP-MS-Data-Cal and Excel 2010 modules, while Isoplot 3.0 was used to generate concordia plots, age probability density functions, and weighted mean ages, following international microbeam U-Pb geochronology standards.
For REE analysis, concentrations were quantified via ICP-MS [47,48] following laser ablation and aerosol nebulization. Normalization used the North American Shale Composite (NASC) for LaN/YbN, δEu, and δCe [47,48,49] (Table 2), which was prioritized over chondrite normalization due to its suitability in hydrocarbon exploration contexts (as opposed to optimization for magmatic differentiation or mantle evolution studies).

Table 2.
REE concentrations (ppm) of detrital rocks from the Dongying Formation in the HHK Depression (REE patterns normalized to NASC).
4. Results
4.1. LA-ICP-MS Zircon Age Characteristics
Statistical analysis of zircon samples (Table 1; Supplementary Tables S1–S5) revealed zircon counts per well as follows: Z1-1 (118), N1-1 (377), N1-2 (101), S1-1 (139), and S1-2 (56). The Concordia diagram for detrital zircon U-Pb ages from the Dongying Formation in the HHK Depression demonstrates that the majority of analytical points plot on or near the concordia curve (concordance > 90%; Figure 4), indicating closed U-Pb isotopic systems with minimal post-crystallization U/Pb mobility.
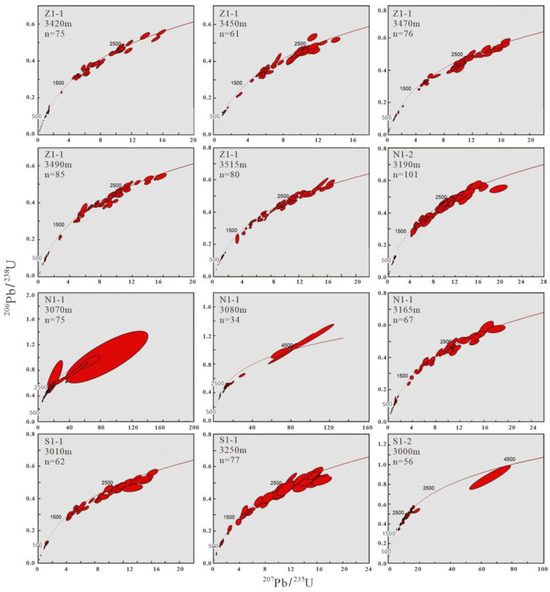
Figure 4.
Concordia diagram of detrital zircon U-Pb ages (concordance > 90%) from Dongying Formation samples in the HHK Depression.
Detrital zircon U-Pb ages range from 65 to 3500 Ma, exhibiting three dominant age peaks: 65–135 Ma, 500–1000 Ma, and 1800–3100 Ma (weighted mean ages: 137.3 Ma, 689 Ma, and 2339 Ma, respectively). Age distribution histograms (0–3500 Ma) and stratigraphic column charts (Mesozoic, Paleozoic, Neoproterozoic, Mesoproterozoic/Paleoproterozoic/Neoarchean), along with moving average trend lines, were constructed for the northern and southern source areas as well as the central uplift zone (Table 3; Figure 5).

Table 3.
Statistical summary of U-Pb geochronology for detrital zircons from the Dongying Formation, HHK Depression.
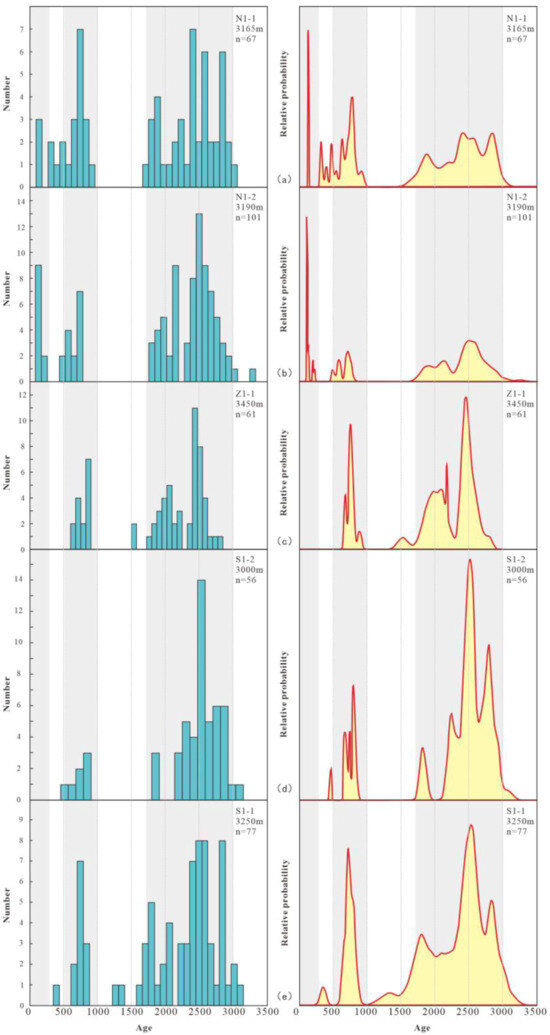
Figure 5.
Detrital zircon U-Pb ages obtained from samples of the Dongying Formation samples in the HHK Depression. (a) Samples from Well N1-1. (b) Samples from Well N1-2. (c) Samples from Well Z1-1. (d) Samples from Well S1-2. (e) Samples from Well S1-1.
The relative proportions of zircon ages in the Mesoproterozoic–Neoarchean range are 63% in the central uplift zone, 69% in the southern source area, and 71% in the northern source area. For the Neoproterozoic, the proportions are 20% (central), 18% (south), and 21% (north). Paleozoic zircon populations account for 9% in both the central and southern zones, but only 3% in the north. Mesozoic zircons make up 8% of the central uplift assemblage, 3% of the southern, and 5% of the northern. The moving average trends reveal generally consistent zircon evolution across all wells. However, age spectra (Figure 6) show distinct differences: the N1-1 and N1-2 wells in the north display prominent triple age peaks, while Z1-1, S1-1, and S1-2, representing the central uplift and southern areas, exhibit only dual peaks (500–1000 Ma and 1800–3100 Ma), with the 65–135 Ma peak being relatively weak.
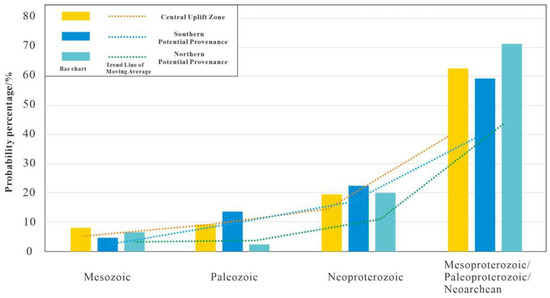
Figure 6.
Histogram and moving average trendline of zircon age distribution.
4.2. Whole-Rock REE Abundance Analysis
Fifteen Dongying Formation sandstone samples exhibit high total rare earth element (ΣREE) concentrations, ranging from 616.36 to 1535.31 ppm, and significant light-to-heavy REE fractionation (LREE/HREE = 0.05–0.13; Table 2, Figure 7). North American Shale Composite (NASC)-normalized REE patterns show the following features: Extreme La depletion and Yb enrichment (LaN/YbN = 0.0002–0.0048; mean 0.0011); HREE enrichment (Gd-Lu) with left-leaning patterns (Figure 7); negative Eu anomalies (δEu = 0.43–0.61; mean 0.54); positive Ce anomalies (δCe = 1.69–13.99; mean 6.07) [50,51,52].
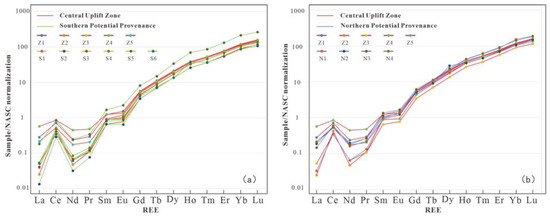
Figure 7.
NASC-normalized REE distribution patterns of the Dongying Formation in the HHK Depression: (a) southern potential provenance and central uplift zone; (b) northern potential provenance and central uplift zone.
Statistical analysis of rare earth element (REE) data reveals significant negative Eu anomalies and positive Ce anomalies. During magmatic differentiation, Eu2+ preferentially partitions into the melt phase due to its geochemical affinity, resulting in Eu depletion within residual solid phases and subsequent magmatic rocks. The relatively consistent δEu values (mean = 0.54) indicate magmatic processes exert dominant control. However, post-magmatic hydrothermal alteration may further modify Eu distribution. Hydrothermally mediated selective dissolution–reprecipitation reactions can remobilize Eu, potentially exacerbating observed Eu depletion in samples [50,51,52].
The broad range of positive Ce anomalies (δCe = 1.69–13.99) reflects multifactorial controls wherein reducing conditions are essential for stabilizing Ce3+, as kinetic hindrance under anoxic/suboxic environments suppresses oxidation of Ce3+ to insoluble Ce4+. This enables persistent aqueous residence and preferential enrichment of Ce3+, thereby generating positive Ce anomalies, while organic matter or specific reductants in sedimentary systems may further enhance Ce3+ stability through complexation reactions to elevate δCe values. Concurrently, the influx of Ce-enriched hydrothermal fluids substantially enhances sedimentary Ce concentrations, with fluid–rock interactions during hydrothermal events facilitating Ce mobilization and precipitation that further enriches Ce within the sedimentary record. These coupled processes—including redox stabilization, hydrothermal influx, and reactive transport—collectively govern the observed broad δCe variability [53,54].
5. Discussion
5.1. Provenance Analysis
Detrital zircon age spectra, histograms, and relative probability curves reveal consistent evolutionary trends with localized variations across the three studied regions (Figure 5). The northern potential source area exhibits three distinct age peaks (65–135 Ma, 500–1000 Ma, 1800–3100 Ma), whereas the central uplift zone and southern potential source area show only two prominent peaks (500–1000 Ma, 1800–3100 Ma), with a weakly developed 65–135 Ma peak. This pattern suggests an altered or diminished sediment supply from the northern source area.
The aforementioned study analyzed sediment supply characteristics from northern and southern potential provenances based on feature similarity, preliminarily revealing a bidirectional (north–south) provenance supply system for the Paleogene Dongying Formation beach-bar system in the HHK Depression. Notably, zircon signatures from the southern provenance exhibit closer affinity with those of the central uplift zone, indicating its dominance within the provenance framework.
To further elucidate supply disparities between these provenances, multidimensional scaling (MDS) was employed to transform detrital zircon age spectra into three-dimensional spatial coordinates [55]. This approach quantifies sediment kinship through spatial distances governed by the core equation:
dij—The Bray–Curtis dissimilarity between samples;
yi—3D projection coordinates.
The 3D MDS plot and associated distance matrix quantification demonstrate that the central uplift zone derives sediment bidirectionally from southern and northern provenances, with closer spatial proximity to the southern provenance (dij = 4.472) versus greater separation from the northern provenance (dij = 6.708). This spatial metric confirms the southern provenance as the dominant sediment source, while the northern provenance provides subsidiary inputs (Table 4, Figure 8).

Table 4.
Distance matrix of three-dimensional MDS diagram for zircon U-Pb ages of the Dongying Formation, HHK Depression.
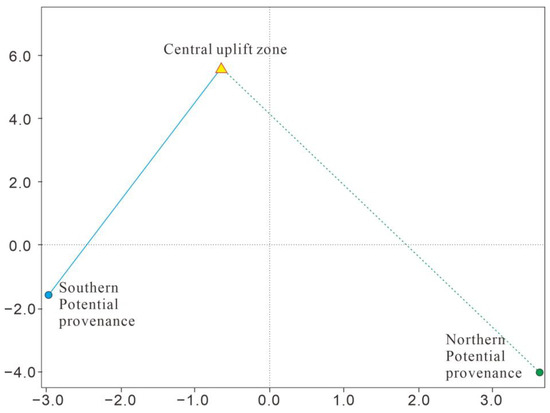
Figure 8.
Three-dimensional MDS diagram of zircon U-Pb age in HHK Depression. The axes are dissimilarities measured between samples.
Comparative analysis of whole-rock rare earth element (REE) patterns from the southern potential provenance, northern potential provenance, and central uplift zone in the Dongying Formation of the HHK Depression reveals consistent heavy rare earth element (HREE, Gd-Lu) enrichment and left-leaning curve characteristics in both southern-central (Figure 7a) and northern-central (Figure 7b) profiles [56,57]. This uniformity indicates identical REE distribution modes across all three domains.
Integrated assessment of detrital zircon age distributions, whole-rock REE patterns, and multidimensional scaling (MDS) analysis demonstrates (1) feature homogeneity: moving-average trendlines of detrital zircon U-Pb ages and REE distribution patterns exhibit strong consistency among the southern/northern provenances and central uplift zone; (2) local disparities: zircon spectra from both the southern provenance and central uplift zone display two dominant age peaks, while the northern provenance exhibits three distinct age peaks; (3) MDS spatial quantification: The 3D MDS distance matrix of zircon U-Pb age spectra demonstrates closer spatial proximity between the southern provenance and central uplift zone (dij = 4.472), whereas the northern provenance shows greater separation (dij = 6.708). Synthesizing this evidence, the beach-bar system in the central uplift zone of the HHK Depression derives from a bidirectional (north–south) sediment supply system. Critically, the southern provenance serves as the dominant sediment source, with the northern provenance providing subsidiary inputs.
5.2. Depositional Model
Building upon the established provenance framework and integrating sedimentary environments with tectonic evolution characteristics of the Paleogene HHK Depression [58,59], a dual-provenance-controlled sandbody distribution model has been developed for the Dongying Formation beach-bar system. The Kendong Uplift (south) and Bonan Uplift (north) functioned as regional sediment sources governing delta development along the southern gentle slope and northern steep slope zones, respectively. During Dongying Formation deposition, the basin underwent rift-depression transition, forming braided-river delta–lacustrine systems under the influence of southern (Kendong Uplift) and northern (Bonan Uplift) source-to-sink systems, with beach-bar systems developing in the central uplift zone (Figure 2).
Sands from braided-river deltas along the southern gentle slope and northern steep slope were reworked by lake waves and alongshore currents [60,61,62,63]. These sediments were subsequently redeposited in the central uplift zone—an ‘intra-depression low uplift’ area with attenuated wave energy—forming extensive beach-bar complexes [64,65]. This study confirms the southern provenance as the predominant sediment source, with the southern-slope braided-river delta constituting the primary origin for the central uplift beach-bar system. Conversely, the northern provenance provided subsidiary inputs, with the northern steep-slope delta making relatively minor contributions (Figure 9).
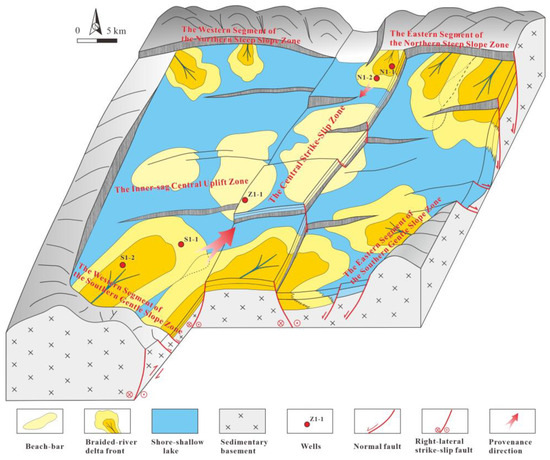
Figure 9.
Structural and depositional system map showing well location distribution in the HHK Depression.
6. Conclusions
(1) The detrital zircon U-Pb age moving average trends of the northern and southern potential provenances and the central uplift belt in the Paleogene Dongying Formation of the HHK Depression are consistent. Whole-rock rare earth element (REE) patterns across all three areas are uniform, characterized by heavy rare earth element (HREE: Gd-Lu) enrichment and a left-leaning REE distribution curve. Detrital zircon age spectra reveal three significant peaks (65–135 Ma, 500–1000 Ma, 1800–3100 Ma) in the northern provenance, whereas the central uplift belt and southern provenance exhibit only two dominant peaks (500–1000 Ma, 1800–3100 Ma) with a weak Mesozoic peak. Multidimensional scaling (MDS) spatial quantification of zircon U-Pb dating indicates significantly closer spatial affinity between the central uplift zone and southern provenance (dij = 4.472) than with the northern provenance (dij = 6.708).
(2) Integrated LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating and whole-rock REE analyses reveal consistent overall variation patterns among the southern/northern provenances and the central uplift belt. This confirms a dual-provenance system (northern and southern) for the bar-beach system in the central uplift belt of the HHK Sag. Detrital zircon age comparative analysis further indicates differential sediment supply capacities: the southern provenance functions as the primary sediment source, while the northern provenance constitutes a secondary contributor.
(3) A “dual-provenance differential supply model” for the bar-beach system has been established. Under an intra-depression low-uplift tectonic setting, the Kendong Uplift (south) and Bonan Uplift (north) control the development of gentle-slope braided river deltas and steep-slope fan deltas, respectively. Lacustrine waves and coastal currents rework delta-front sands, which are subsequently redeposited in the weak hydrodynamic zone of the central low-uplift belt to form the bar-beach system. This model provides a theoretical basis for predicting deeply buried bar-beach systems and has significant implications for hydrocarbon exploration in similar faulted basins.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/jmse13071331/s1, Table S1: Zircon LA-ICP-MS U-Pb Age Data of Well Z1-1; Table S2: Zircon LA-ICP-MS U-Pb Age Data of Well N1-1; Table S3: Zircon LA-ICP-MS U-Pb Age Data of Well N1-2; Table S4:Zircon LA-ICP-MS U-Pb Age Data of Well S1-1; Table S5: Zircon LA-ICP-MS U-Pb Age Data of Well S1-2.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.W. and Y.H.; methodology, H.L. and J.W.; software, T.G., D.G., B.F. and X.H.; validation, Q.C., T.G., D.G., X.H. and Z.Z.; formal analysis, Z.Z. and Q.C.; investigation, T.G., D.G., X.H. and Q.C.; resources, H.L., B.F. and Z.Z.; data curation, H.L., Z.Z. and B.F.; writing—original draft preparation, J.W.; writing—review and editing, J.W. and Y.H.; visualization, Y.H., H.L., Q.C. and Z.Z.; supervision, Y.H., H.L., Q.C. and J.W.; project administration, T.G., D.G. and X.H.; funding acquisition, T.G., D.G. and X.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant numbers 42272115 and 42272113 and the National Key Technologies R&D Program of China during the 14th Five-Year Plan Period, grant number CCL2022TJT0NST1867).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author(s).
Acknowledgments
We would like to extend our gratitude to CNOOC (China) Tianjin Branch Bohai Petroleum Research Institute for their invaluable administrative and technical support, which facilitated the completion of this study. Additionally, we appreciate the kind donations of experimental materials provided by the School of Geosciences, Yangtze University, without which the research would not have been possible.
Conflicts of Interest
Author T.G., D.G., X.H. were employed by the company China National Offshore Oilfield Corporation Limited-Tianjin. Author B.F. was employed by the Changqing Division, China Petroleum Logging Co. Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Kosler, J.; Fonneland, H.; Sylvester, P.; Tubrett, M.; Pedersen, R.B. U-Pb dating of detrital zircons for sediment provenance studies-a comparison of laser ablation ICPMS and SIMS techniques. Chem. Geol. 2002, 182, 605–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Yu, X.; Li, S. Multiple sediment source infill in a low-accommodation basin: Implications for the late Paleozoic sediment routing system in the southeastern Ordos Basin. Geol. Mag. 2023, 160, 1649–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seminara, S.; Pease, V.; Toro, J.; Omma, J. Provenance studies and basin evolution: Insight from the Yukon-Koyukuk Basin, Alaska. Sedimentology 2024, 72, 666–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Liu, S.; Zhu, Q.; Liu, B.; Zeng, Z.; Li, S. Provenance Analysis of the Lower Jurassic Dongdaohaizi depression and Sediment Provenance Response Characteristics. Acta Sedimentol. Sin. 2025; ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Zhu, X.; Colombera, L.; McArthur, A.; Mountney, N.P.; Zhu, S.; Jin, L.; Shen, T.; Yang, H.; Chen, H.; et al. Sediment provenance and dispersal in the early Eocene Dongying Depression, Bohai Bay Basin, Eastern China: Evidence from detrital zircon geochronology, geochemistry and petrology. Sediment. Geol. 2023, 454, 106453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, R.; Zhu, W.; Zheng, B.; Wu, H.; He, J.; Zhu, X. Early Pan-African magmatism in the Tarim Craton: Insights from zircon U–Pb–Lu–Hf isotope and geochemistry of granitoids in the Korla area, NW China. Precambrian Res. 2012, 212, 117–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golosov, V.; Navas, A.; Castillo, A.; Mavlyudov, B.; Kharchenko, S.; Lizaga, I.; Gaspar, L.; Dercon, G. Sediment source analysis in the korabelny stream catchment, King George Island, maritime Antarctica: Geomorphological survey, fingerprinting and delivery rate assessment. Geomorphology 2024, 461, 109312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, R.F.S.; de Oliveira, D.C.; Marangoanha, B.; Galarza, M.A.; Santos, M.R. Geochemistry, zircon U-Pb geochronology and Lu-Hf isotopes of the Manda Saia granite: Petrological affinity and magma source of evolved A-type granites from the Carajás province, southeastern Amazonian craton, Brazil. LITHOS 2023, 462–463, 107412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, M.; Verma, S.K.; Armstrong-Altrin, J.S.; Ramos-Vazquez, M.A.; Mishra, S.; Oliveira, E.P.; González-Partida, E.; Hernández-Mendoza, H.; Malviya, V.P. Identification of source terranes of beach sediments from the NW Gulf of Mexico, Atlantic ocean: Constraints from geochemistry and U-Pb detrital zircon geochronology. J. South Am. Earth Sci. 2025, 158, 105496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q. Multi-method-constrained tracing of complex provenance: A case study of thesequence from the Paleogene Kongdian Formation to the lower submember of the 4th member of the Shahejie Formation in the Dongying depression. Oil Gas Geol. 2025, 46, 599–616. [Google Scholar]
- Skovitina, T.M.; Kotov, A.B.; Lopatin, D.V.; Kovach, V.P.; Buchnev, I.N.; Adamskaya, E.V.; Bobrovskaya, O.V. Sources of Late Cenozoic Deposits from the Aeolian “Sands” Massif in the Chara Basin of the Baikal Rift Zone: First Results of U-Th-Pb (LA-ICP-MS)-Geochronological Study of Detrital Zircon. Dokl. Earth Sci. 2023, 510, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Q.; Guo, L.; Xie, Y.; Sun, L.; Chi, Y.; Liu, H.; Wei, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wu, P. U-Pb age characteristics and geological significance of the detrital zircon in the sediments of the Songhua River, Jilin Province. Acta Geol. Sin. 2025. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Shen, A.; Hu, A.; Hao, Y.; Zhao, J. LA-ICP-MS U-Pb Age, Clumped and Stable Isotope Constraints on the Origin of Middle Permian Coarse-Crystalline Dolomite Reservoirs in Northwest Sichuan Basin, Southwest China. Acta Geol. Sin. 2020, 94, 1312–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonev, N.; Filipov, P.; Vladinova, T.; Stoylkova, T.; Georgieva, H.; Georgiev, S.; Kiselinov, H.; Macheva, L. U-Pb Zircon Age Constraints on the Paleozoic Sedimentation, Magmatism and Metamorphism of the Sredogriv Metamorphics, Western Balkan Zone, NW Bulgaria. Geosciences 2025, 15, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garza, H.K.; Catlos, E.J.; Lapen, T.J.; Clarke, J.A.; Brookfield, M.E. New U-Pb constraints and geochemistry of the East Kirkton Quarry, Scotland: Implications for early tetrapod evolution in the Carboniferous. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0321714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeasmin, R.; Abdullah, R.; Hossain, M.S.; Ao, S.; Khan, M.S.H.; Sayem, A.S.M.; Xiao, W.; Zhang, P.; Zoarder, A.; Tithi, T.J. Petrography, geochemistry and detrital zircon U-Pb dating of the Pliocene-Pleistocene Dupi Tila Formation from the Lalmai Anticline, Bengal Basin: Regional tectonic implications. Geol. J. 2024, 59, 1239–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roigé, M.; Gómez-Gras, D.; Stockli, D.F.; Teixell, A.; Boya, S.; Poyatos-Moré, M. Recycling effects in detrital zircon U-Pb signatures in a foreland basin: Identifying the multicyclic sediment sources of the Eocene-Miocene Jaca basin (southern Pyrenees, Spain). Sediment. Geol. 2023, 456, 106500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappell, M.; Rojas, H.; Andros, C.; Acree, A.; Slowey, Y.M.; Young, C.; Fowler, P.; Lotufo, E.; Rowland, W.; Wynter, M.; et al. Geochemical exploration of rare earth element resources in highland karstic bauxite deposits in the Sierra de Bahoruco, Pedernales Province, Southwestern Dominican Republic. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0315147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagasawa, M.; Shimizu, Y.; Yamaguchi, A.; Tokunaga, K.; Mukai, H.; Aoyagi, N.; Mei, H.; Takahashi, Y. Interpretation of vertical migration and enrichment processes of rare earth elements (REEs) in ion-adsorption-type mineralization in Japan based on REE speciation analyses. Chem. Geol. 2024, 670, 122431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernst, D.M.; Vogt, J.; Bau, M.; Mues, M. Polynomial modelling of high-quality yet incomplete rare earth element data sets and a holistic assessment of REE anomalies. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 5360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Qian, G.; Xu, C.; Gao, Y. Sandstone Distribution and Reservoir Characteristics of Shahejie Formation in Huangheko depression, Bohai Bay Basin. Earth Sci. 2023, 48, 3068–3080. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, X.; Wang, Q.; Xie, T.; Zhao, M.; Feng, C. Paleogene provenance and its control on high-quality reservoir in the northern margin of HHK Depression. Lithol. Reserv. 2020, 32, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Sun, M.; Huang, J.; Huang, Y.; Liang, X.; Zhu, J. Distribution and Fractionation of Rare Earth Elements (REE) in the Ion Adsorption-type REE Deposit (IAD) at Maofeng Mountain, Guangzhou, China. Clays Clay Miner. 2023, 71, 340–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keita, I.; Tsuyoshi, I.; Mihoko, H. REE-Th-U and Nd isotope systematics of monazites in magnetite- and ilmenite-series granitic rocks of the Japan arc: Implications for its use as a tracer of magma evolution and detrital provenance. Chem. Geol. 2017, 484, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awan, R.S.; Liu, B.; Li, H.; Gul, S.A.M.A.; Zhao, L.; Khan, A. Unlocking paleolatitudinal secrets of the early Cretaceous by rare earth element imprints: Implications for seawater chemistry, depositional environments, and paleoclimate in the Talhar Shale, Lower Indus Basin, Pakistan. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2025, 671, 112985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skublov, S.G.; Gawad, A.E.A.; Levashova, E.V.; Ghoneim, M.M. U-Pb geochronology, REE and trace element geochemistry of zircon from El Fereyid monzogranite, south Eastern Desert, Egypt. J. Mineral. Petrol. Sci. 2021, 116, 220–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, C.; Song, F.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Q. Architectural characteristics of beach-bar reservoirs in the lower submember of the 2nd member of the Paleogene Dongying Formation in block SC7, Huanghekou Sag, Bohai Bay Basin. Oil Gas Geol. 2024, 45, 486–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, H.; Shen, X.; Liu, X.; Tang, X. LA-ICP-MS In-situ Zircon U-Pb Dating and its Application in Zircon Geochronology of the Jianchuan Syenite in Western Yunnan. Geotecton. Metallog. 2021, 45, 822–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Han, J.; Zhao, J.; You, D. LA-ICP-MS U-Pb geochronology of calcites reveals multiphase tectonic activities and associated fluid flow in Western Shunbei area, NW China. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2025, 68, 1180–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Hu, Z.; Shi, P.; Dai, L.; Li, S.; Li, F.; Wang, Z.; Hu, Z. Meso-Cenozoic tectonic evolution and geomorphologic restoration of the west section of Bonan low uplift, Bohai Bay basin. Acta Geol. Sin. 2025, 99, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, X.; Niu, C.; Liu, H.; Huang, J. Growth of strike-slip zone in the southern Bohai Bay Basin and its significances for hydrocarbon accumulation. Oil Gas Geol. 2019, 40, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhu, X.; Shi, R.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Q.; Zhu, Z.; Yan, Z. Provenance transformation and sedimentary response of ramp facies in downfaulted basins: A case study on the Paleogene source-to-sink system in Lixian slope, Raoyang depression, Bohai Bay Basin. Oil Gas Geol. 2023, 44, 689–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, L.; Xu, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhu, W. Control of Neotectonic movements on the ultimate hydrocarbon accumulation in shallow formations in bulge and slope-subdepression areas in Bohai Sea. China Pet. Explor. 2024, 29, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Fan, A. Palaeotopography Controls on Types and Distribution of Sedimentary Systems: A Case Study from the Second Member of the Eastern Sub-depression in HHK. J. Sichuan Norm. Univ. Nat. Sci. 2022, 45, 270–279. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Wang, F.; Chen, R. Paleoclimate, provenance, and tectonic setting of the First Member of the Paleogene Shahejie Formation in the southern slope of HHK Depression. Mar. Geol. Front. 2023, 39, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Kra, K.L.; Qiu, L.; Yang, B.; Dong, D.; Wang, Y.; Khan, D. Impact of sedimentation and diagenesis on deeply buried sandy conglomerate reservoirs quality in nearshore sublacustrine fan: A case study of lower Member of the Eocene Shahejie Formation in Dongying Sag, Bohai Bay Basin (East China). Sediment. Geol. 2023, 444, 106317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, X.; Niu, C.; Liu, H.; Wei, W. Constraints by Tectonic Slope-break Zones on the Depositional Systems in Eogene in the depression of the Yellow River Estuary. Geol. Rev. 2014, 60, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Hou, X.; Guan, D.; Huang, X.; Xy, W.; Shi, W.; Liu, R.; Li, H. Elements geochemical characteristics and sedimentary paleoenvironmental significance of the Paleogene in the central depression of the Huanghekou depression, Bohai Bay Basin. J. Yangtze Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2025. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Lin, G.; Guo, Y.; Pang, X. Mobility of Paleogene Basion-controlling Faults in the Bozhong sag and depositional responses. Mar. Geol. Quat. Geol. 2016, 36, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, Z. Diachronous characteristics and genetic mechanism of the Paleogene tectonic transition in Bohai Bay basin: A case study of the southwest Bohai Sea and Jiyang Depression. J. Cent. South Univ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 53, 1095–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, X.; Wang, D.; Cheng, Y. Evolution and reservoir characteristics of the “Chengbei-Kendong” structural transfer zone in the Bohai Bay Basin. Oil Gas Geol. 2022, 43, 1321–1333+1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Lü, D.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, M. The Fault System and Its Tectonophysics Simulation in the Eastern Huanghekou Sag in Bohai Bay Basin. Earth Sci. 2021, 46, 2391–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Qi, P.; Niu, Y. Mesozoic tectonic evolution and dynamic mechanisms of the northern Bozhong depression of the Bohai Bay Basin, eastern China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2024, 273, 106254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.; Xie, X.; Xu, C.; Du, X.; Du, X.; Song, Z. Sedimentary features and their controls in a mixed siliciclastic-carbonate system in a shallow lake area: An example from the BZ-X block in the Huanghekou depression, Bohai Bay Basin, Eastern China. Geol. J. 2018, 54, 2016–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Li, C.; Guo, C.; Yue, H. Geomorphology of channel sandbodies in fluvially dominated shallow water delta front: Taking the Lower Member of the Minghuazhen Formation in BZ34 Oilfield of the Huanghekou depression, Bohai Bay Basin as an example. Mar. Geol. Front. 2024, 40, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzoul, B.; Uchman, A.; Adaci, M.; Tabol, P.W.; Krzemińska, E. Provenance of the Numidian Formation deposits (Oligo-Miocene) in northern Algeria: Insights from sandstone petrography, palaeocurrent data, geochemistry, and zircon geochronology. Sediment. Geol. 2025, 477, 106808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, P.A.A.; Pimentel, M.M.; Hauser, N.; Moya, M.C. U-Pb LA-ICP-MS geochronology of detrital zircon grains from low-grade metasedimentary rocks (Neoproterozoic—Cambrian) of the Mojotoro Range, northwest Argentina. J. South Am. Earth Sci. 2014, 49, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahak, S.K.; Dasgupta, S.; Prabhakar, N.; Banerjee, S. Paleozoic to Mesozoic paleotectonic reconstructions of Gondwana assembly: Insights from petrography, heavy mineral chemistry and detrital U-Th-total Pb monazite geochronology of sandstones in the Pranhita-Godavari Basin (SE India). Mar. Pet. Geol. 2024, 166, 106914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adánez-Sanjuán, P.; Llamas-Borrajo, J.F.; García-Cortés, Á.; Locutura-Rupérez, J. Study of rare earth elements in overbank sediments under the influence of different geochemical-lithological environments. J. Iber. Geol. 2021, 47, 551–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creason, C.G.; Justman, D.; Rose, K.; Montross, S.; Bean, A.; Mark Moser, M.; Wingo, P.; Sabbatino, M.; Thomas, R.B. A Geo-Data Science Method for Assessing Unconventional Rare-Earth Element Resources in Sedimentary Systems. Nat. Resour. Res. 2023, 32, 855–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuleshov, V.N.; Bychkov, A.Y.; Sviridov, L.I. Specific Features of the Rare Earth Element Distribution in Rocks and Ores of the Porozhinsk Manganese Deposit (Yenisei Ridge, Krasnoyarsk Region). Lithol. Miner. Resour. 2022, 57, 299–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esha, R.; Debajyoti, P. Major and Trace Element Characteristics of the Average Indian Post-Archean Shale: Implications for Provenance, Weathering, and Depositional Environment. ACS Earth Space Chem. 2021, 5, 1114–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, N.; Xu, W.; Zuo, Y.; Chang, J.; Liu, C. Evolution of Meso-Cenozoic thermal structure and thermal- rheological structure of the lithosphere in the Bohai Bay Basin, eastern North China Craton. Earth Sci. Front. 2017, 24, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Liu, J.; Jiao, Y.; Liu, H.; Li, W.; Yu, Z. Coupling of Cenozoic Magmatism and Fault Activity in the Bohai Bay Basin and Subei Basin. Geotecton. Metallog. 2024, 1, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; He, Y.; Peng, W.; Zhang, L.; Huang, H.; Du, X.; Zhang, C.; Yang, Y. Provenance analysis of beach bar deposits during the Eocene periodin Jianghan Basin and their response to paleoclimate: Evidence fromdetrital zircon U-Pb ages. Acta Geosci. Sin. 2024, 12, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, L.; Li, W.; Li, P. Detrital zircon U-Pb dating of the Late Cretaceous aeolian sandstones from the Tangbian Formation in the Yiyang area of Jiangxi Province and its provenance significanceg. Geol. Bull. China 2019, 38, 667–679. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Z.; Farahbakhsh, E.; Müller, R.D.; Zuo, R. Multivariate statistical analysis and bespoke deviation network modeling for geochemical anomaly detection of rare earth elements. Appl. Geochem. 2024, 174, 106146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slukovskii, Z.I.; Dauvalter, V.A.; Shelekhova, T.S. Anomalies of rare earth elements and heavy metals/metalloids in modern sediments of small lakes in the north of Karelia (Arctic): Geology and technogenesis influence. Environ. Earth Sci. 2025, 84, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Shields, G.A. Early diagenetic mobilization of rare earth elements and implications for the Ce anomaly as a redox proxy. Chem. Geol. 2023, 635, 121619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federica, M.; Andrea, S.; Tiziana, T.; Grazia, G.M.; Daniele, D.; Chiara, M.; Mirko, P.; Antonella, P.; Michela, S. Silica-supported pyrolyzed lignin for solid-phase extraction of rare earth elements from fresh and sea waters followed by ICP-MS detection. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 7635–7643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.; Zhang, K.; Davranche, M.; Dia, A.; Dutruch, L.; Vantelon, D.; Marsac, R. Facet-Dependent Adsorption of Rare Earth Elements (REEs) and Actinides onto Goethite: REE Pattern Variability and Cerium Anomaly. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 21729–21739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avellaneda-Jiménez, D.S. Relating steep REE patterns in modern volcanism and the development of an amphibole-rich middle to lower crust at the Colombian magmatic arc: A geochemical and receiver functions approach. J. South Am. Earth Sci. 2023, 130, 104597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, W.; Tang, Y.-T.; Wang, S.; Cao, Y.; Chen, Z.; Xie, C.; Liu, C.; Guo, M.; Qiu, R. Effects of in situ leaching on the origin and migration of rare earth elements in aqueous systems of South China: Insights based on REE patterns, and Ce and Eu anomalies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 435, 128959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, X.; Song, Z.; Zhou, X. Volcanic activity and its effect on the hydrocarbon accumulation conditions in the southeastern margin of HHK Depression. J. Northeast Pet. Univ. 2016, 40, 45–53+6–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Yang, X. Volcanic Eruption Phases and 3-D Characterization of Volcanic Rocks in BZ34-9 Block of HHK Depression, Bohai Bay Basin. Earth Sci. 2014, 39, 1309–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).