CFD-Based Parameter Calibration and Design of Subwater In Situ Cultivation Chambers Toward Well-Mixing Status but No Sediment Resuspension
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Fluid Models and Simulation Strategies
2.1. Transient Tracer Simulation Based on Steady MRF Flow
2.2. Multiphase Flow Model
2.3. Standard Turbulence Model
2.4. Verification of Simulation Method Based on GÖTEBORG 1 Model
2.4.1. Establishment of the Simulation Model of GÖTEBORG 1
2.4.2. Simulation Verification of Calibration Method
2.5. Simulation Model Establishment
2.6. Cabin Parameter Calculation and Calibration
3. Experimental Environment
3.1. Experimental Preparation
3.2. Mixing Time and Stirred Flow Field Experiment
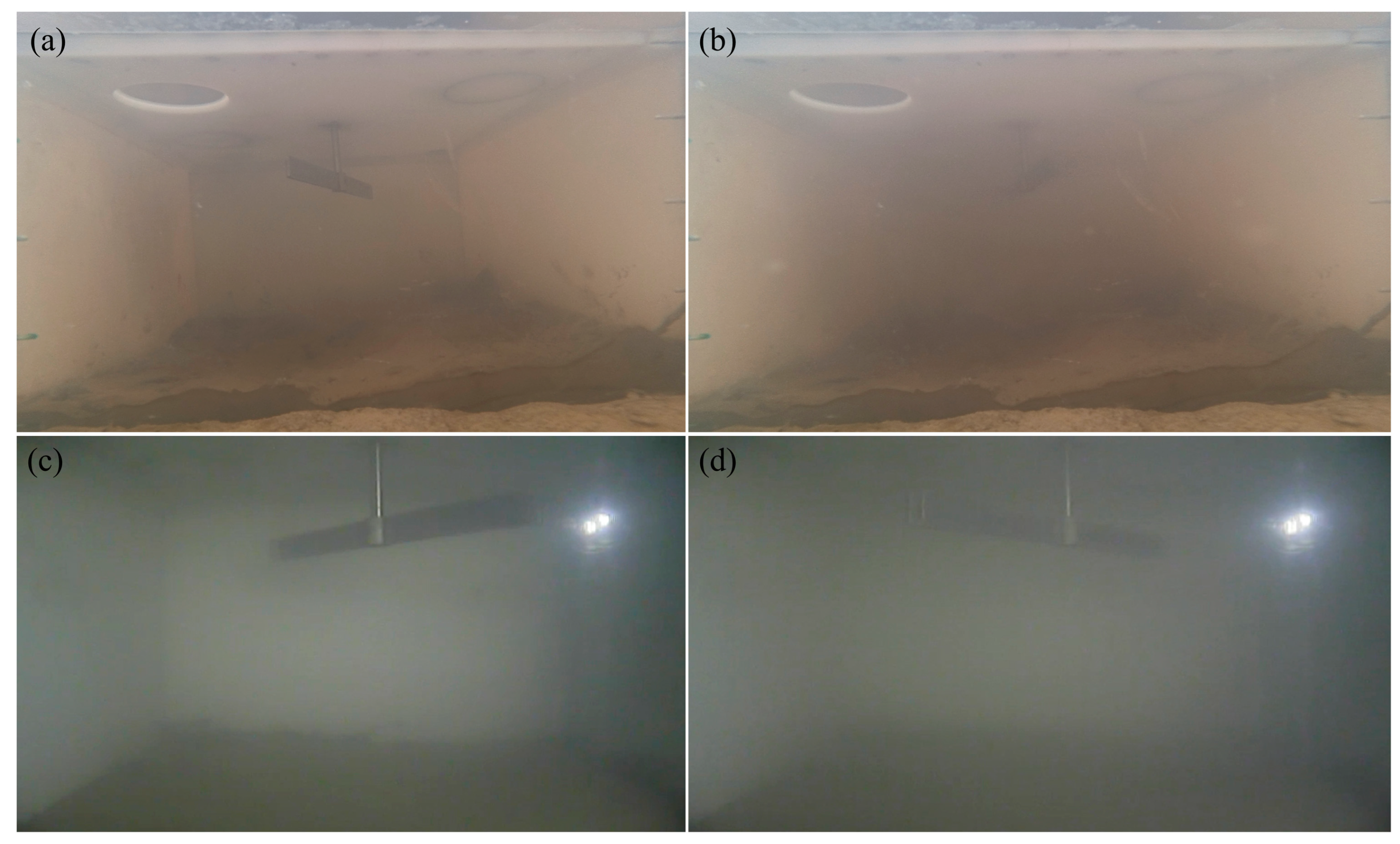
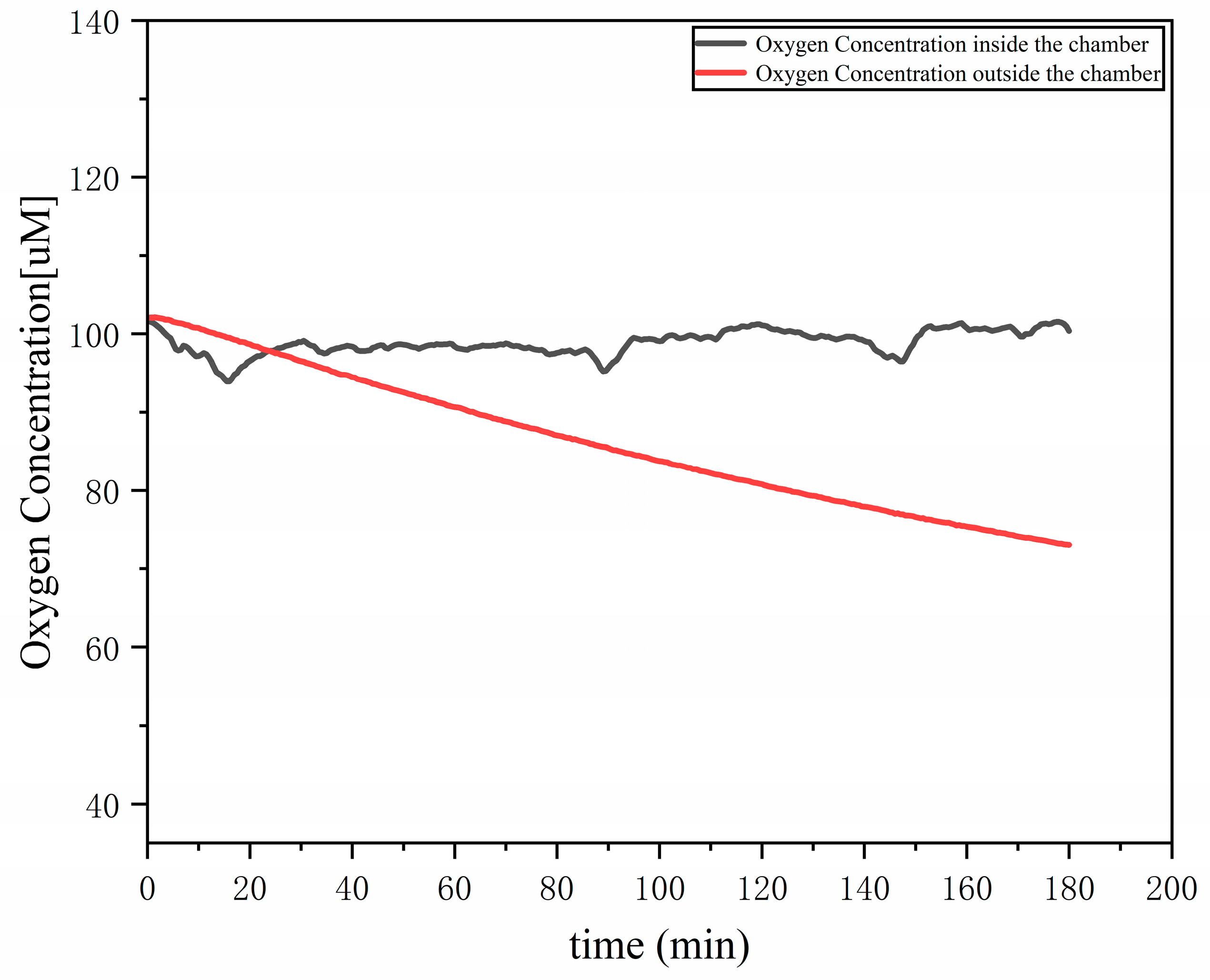
3.3. Dissolved Oxygen and Resuspension Experiment
4. Discussion of the Results from Numerical Simulation and Model Testing
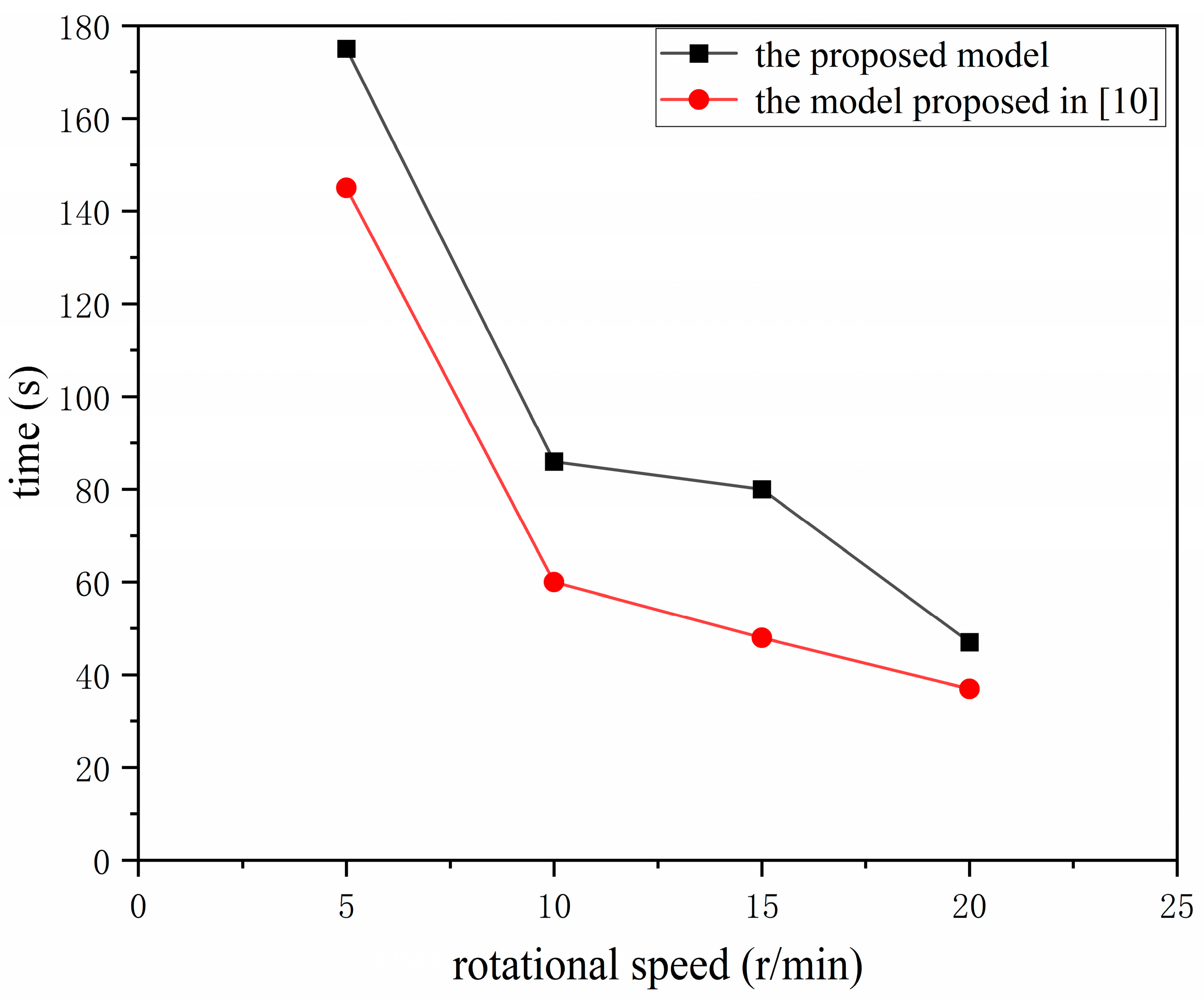
4.1. Comparison of the Complete Mixing Time
4.2. Oxidation Consumption and Resuspension
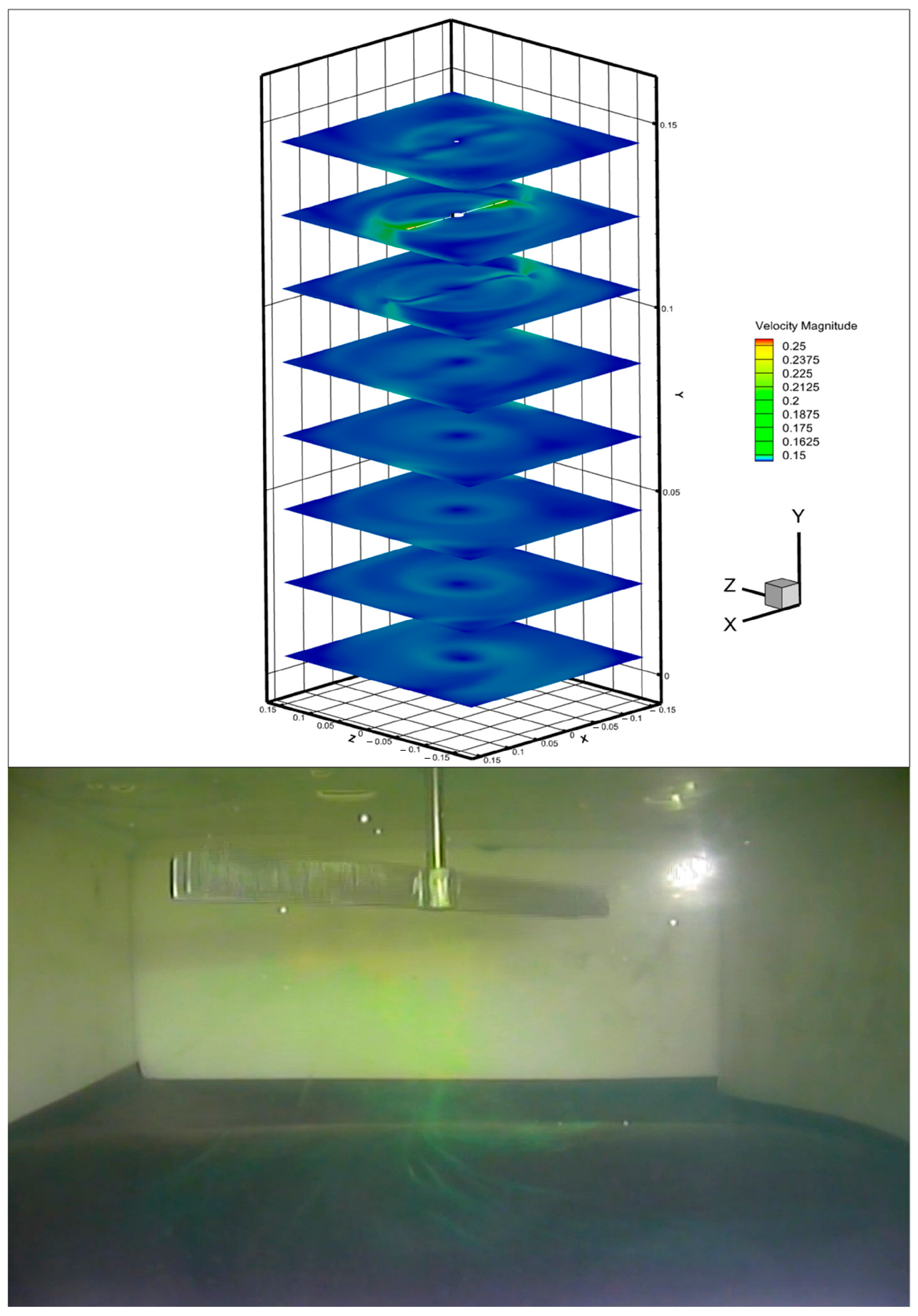
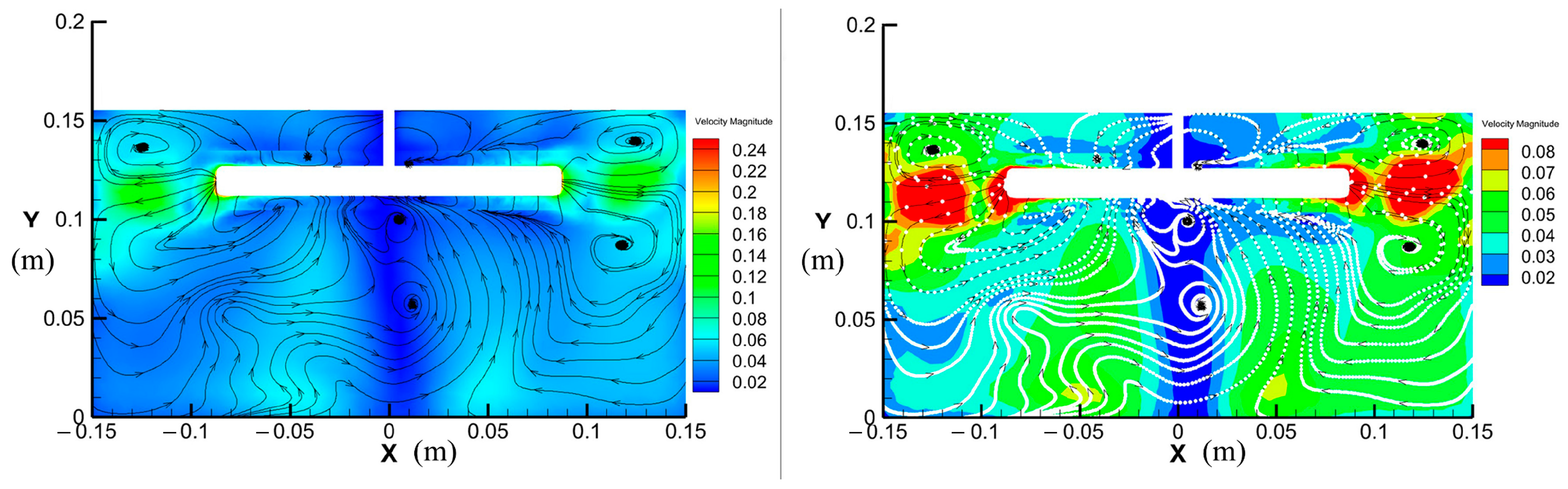
4.3. Analysis of Flow Field Characteristics Inside the Cultivation Chamber
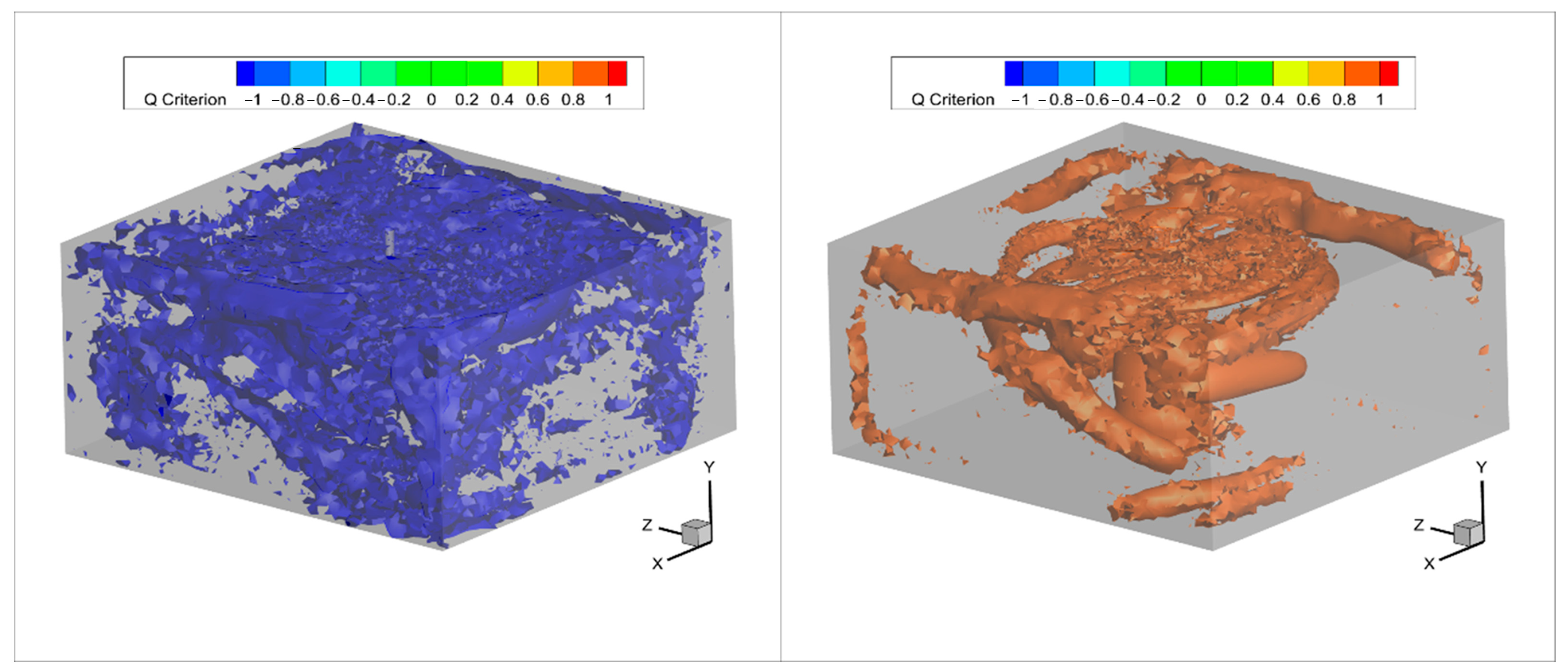
4.4. Evolution of Vortex Structure and Flow Field Stability During the Stirring Process
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Donis, D.; McGinnis, D.F.; Holtappels, M.; Felden, J.; Wenzhoefer, F. Assessing benthic oxygen fluxes in oligotrophic deep sea sediments (HAUSGARTEN observatory). Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2016, 111, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Kim, S.-H.; Min, W.-G.; Choi, D.M.; Lee, E.K.; Kim, K.-T.; An, S.-U.; Baek, J.-W.; Lee, W.-C.; Park, C.H. In-Situ Estimates of Net Ecosystem Metabolisms in the Rocky Habitats of Dokdo Islets in the East Sea of Korea. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, D.; Chen, J.; Wang, H.; Peng, X.; Zhou, P.; He, W. Development of a Hadal Microbial In Situ Multi-Stage Filtering and Preserving Device. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, Z.-M.; Li, J.; He, L.-S.; Cui, G.-J.; Li, W.-L.; Chen, J.; Xin, Y.-Z.; Cai, D.-S.; Zhang, A.-Q. Hadal water sampling by in situ microbial filtration and fixation (ISMIFF) apparatus. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2019, 144, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garel, M.; Bonin, P.; Martini, S.; Guasco, S.; Roumagnac, M.; Bhairy, N.; Armougom, F.; Tamburini, C. Pressure-retaining sampler and high-pressure systems to study deep-sea microbes under in situ conditions. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kononets, M.; Tengberg, A.; Nilsson, M.; Ekeroth, N.; Hylén, A.; Robertson, E.K.; Van De Velde, S.; Bonaglia, S.; Rütting, T.; Blomqvist, S. In situ incubations with the Gothenburg benthic chamber landers: Applications and quality control. J. Mar. Syst. 2021, 214, 103475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broman, E.; Olsson, M.; Maciute, A.; Donald, D.; Humborg, C.; Norkko, A.; Jilbert, T.; Bonaglia, S.; Nascimento, F.J. Biotic interactions between benthic infauna and aerobic methanotrophs mediate methane fluxes from coastal sediments. ISME J. 2024, 18, wrae013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.T.; Yu, X.S.; Li, X.; Shun, J.; Zhang, X.D.; Zhang, S.W.; Wang, X.N.; Li, F.Z.; Cao, R.X.; Xu, C.L. Benvir: A in situ Deep-sea observation system for Benthic environmental monitoring. High Technol. Lett. 2015, 25, 54–60. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.C. Benthic Flux Chamber of Self-Adaptive Stirring. Master’s Thesis, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Tengberg, A.; Hall, P.O.; Andersson, U.; Lindén, B.; Styrenius, O.; Boland, G.; De Bovee, F.; Carlsson, B.; Ceradini, S.; Devol, A. Intercalibration of benthic flux chambers: II. Hydrodynamic characterization and flux comparisons of 14 different designs. Mar. Chem. 2005, 94, 147–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khedr, A.; Castellani, F. Critical issues in the moving reference frame CFD simulation of small horizontal axis wind turbines. Energy Convers. Manag. X 2024, 22, 100551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rave, K.; Hermes, M.; Wirz, D.; Hundshagen, M.; Friebel, A.; von Harbou, E.; Bart, H.-J.; Skoda, R. Experiments and fully transient coupled CFD-PBM 3D flow simulations of disperse liquid-liquid flow in a baffled stirred tank. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2022, 253, 117518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddadi, M.; Hosseini, S.; Rashtchian, D.; Olazar, M. Comparative analysis of different static mixers performance by CFD technique: An innovative mixer. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2020, 28, 672–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, M.; Shan, H.; Zhang, S.; Guo, L.; Liu, X.; Jia, Y. Resuspension of sediments along the bottom boundary layer: A review. Mar. Geol. Quat. Geol. 2016, 36, 177–188. [Google Scholar]
- De La Concha-Gómez, A.; Ramírez-Muñoz, J.; Márquez-Baños, V.; Haro, C.; Alonso-Gómez, A. Effect of the rotating reference frame size for simulating a mixing straight-blade impeller in a baffled stirred tank. Rev. Mex. De Ing. Química 2019, 18, 1143–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, A.; LaRoche, R.D.; Wang, M.-H.; Calabrese, R.V. Sliding mesh simulation of laminar flow in stirred reactors. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 1997, 75, 42–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, A.; Rossi, R.; Cottini, C.; Benassi, A. CFD simulation of a Rushton turbine stirred-tank using open-source software with critical evaluation of MRF-based rotation modeling. Meccanica 2024, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coroneo, M.; Montante, G.; Paglianti, A.; Magelli, F. CFD prediction of fluid flow and mixing in stirred tanks: Numerical issues about the RANS simulations. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2011, 35, 1959–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Feng, X.; Mao, Z.-S.; Yang, C. Numerical simulation of reactive mixing process in a stirred reactor with the DQMOM-IEM model. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 360, 1177–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouketou, F.N.; Kolesnikov, A. Modelling and simulation of multiphase flow applicable to processes in oil and gas industry. Chem. Prod. Process Model. 2019, 14, 20170066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozzetti, G.; Peters, B. A multiscale DEM-VOF method for the simulation of three-phase flows. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2018, 99, 186–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wu, W.; Miao, Q.; Wu, J. Research on the Overall Design and Water Entry Simulation of Cross-Media Unmanned Underwater Vehicles. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Zhao, X. Investigation of water-water interface in dam break flow with a wet bed. J. Hydrol. 2017, 548, 104–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaini, A.; Mescher, A.; Agar, D.W. Hydrodynamic studies of liquid–liquid slug flows in circular microchannels. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2011, 66, 1168–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, L.; Liu, Z.; Hu, C.Y. Comparison of differences in simulating nearshore currents with different turbulence models. China Harb. Eng. 2022, 42, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Speziale, C.G.; Thangam, S. Analysis of an RNG based turbulence model for separated flows. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 1992, 30, 1379–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.-H.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Luo, Y.; Fan, H. Unsteady prediction of cavitating flow around a three dimensional hydrofoil by using a modified RNG k-ε model. Ocean Eng. 2018, 158, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J. Full flow field computation of mixing in baffled stirred vessels. Trans. Inst. Chem. Eng. 1993, 71, 342–344. [Google Scholar]
- Yapici, K.; Karasozen, B.; Schäfer, M.; Uludag, Y. Numerical investigation of the effect of the Rushton type turbine design factors on agitated tank flow characteristics. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2008, 47, 1340–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, M.S.; Khalid, M.H.; Badar, A.W.; Saeed, M.; Asim, T. Parametric analysis using cfd to study the impact of geometric and numerical modeling on the performance of a small scale horizontal axis wind turbine. Energies 2022, 15, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, M.; Yaraghi, A.; Ein-Mozaffari, F.; Lohi, A. The effect of impeller configurations on particle mixing in an agitated paddle mixer. Powder Technol. 2018, 332, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biggs, R. Mixing rates in stirred tanks. AIChE J. 1963, 9, 636–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jongen, T. Characterization of batch mixers using numerical flow simulations. AIChE J. 2000, 46, 2140–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Wu, C.; Liang, J.; Lei, Y.; Yang, B. Study on shear properties of six kinds of conventional agitator. Huaxue Gongcheng/Chem. Eng. China 2017, 45, 68–73. [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui, M.S.; Fonn, E.; Kvamsdal, T.; Rasheed, A. Finite-volume high-fidelity simulation combined with finite-element-based reduced-order modeling of incompressible flow problems. Energies 2019, 12, 1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
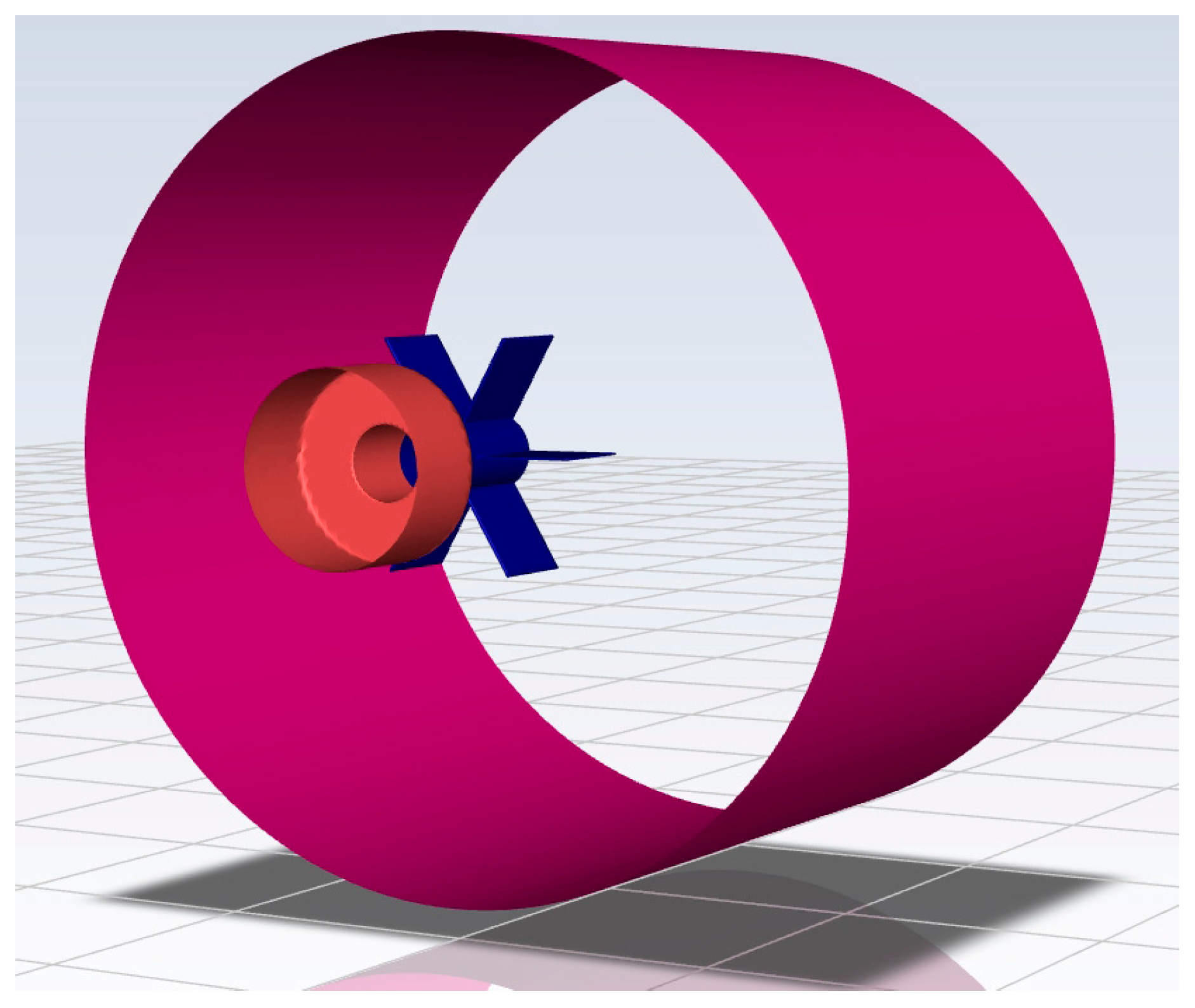

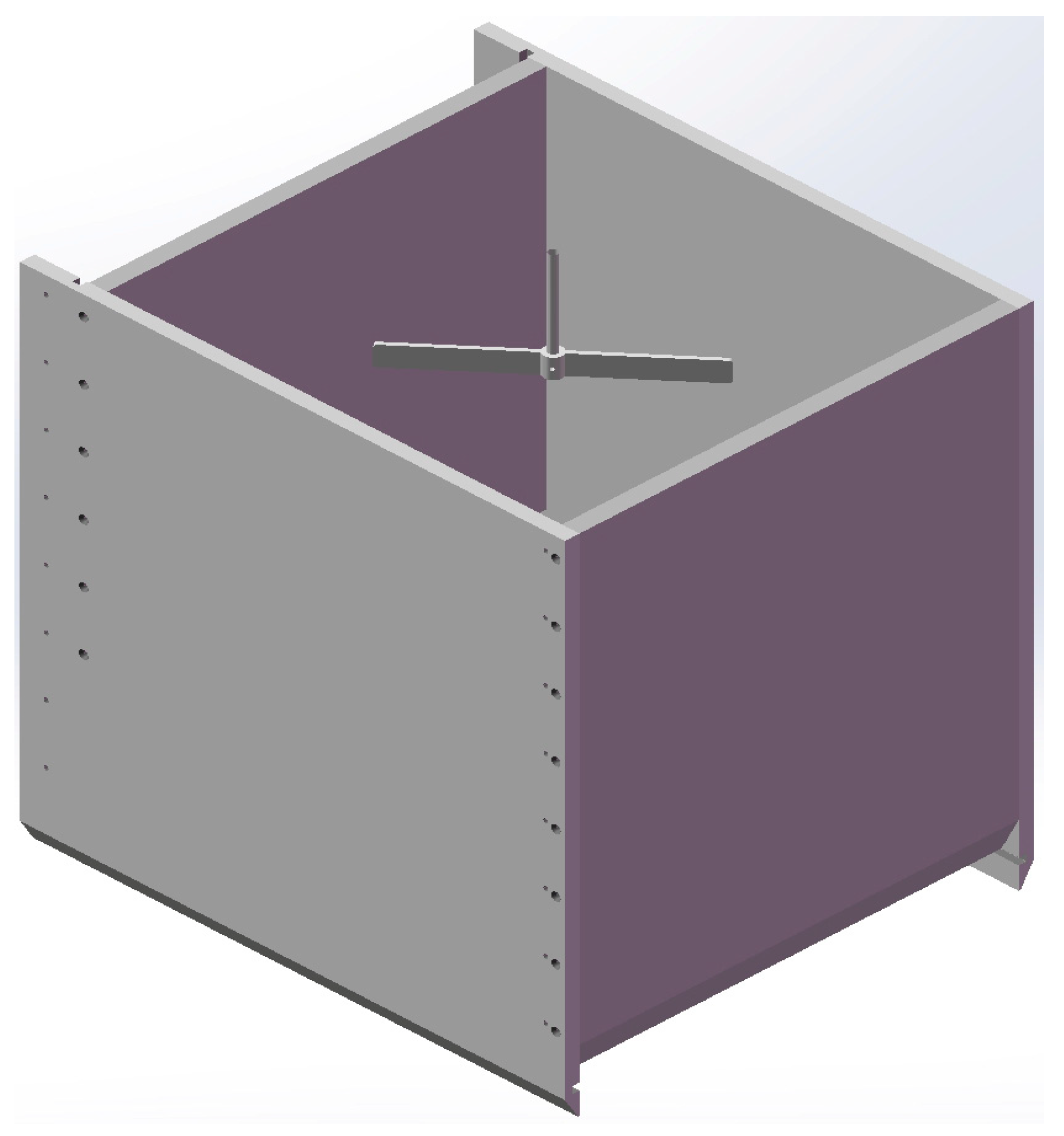
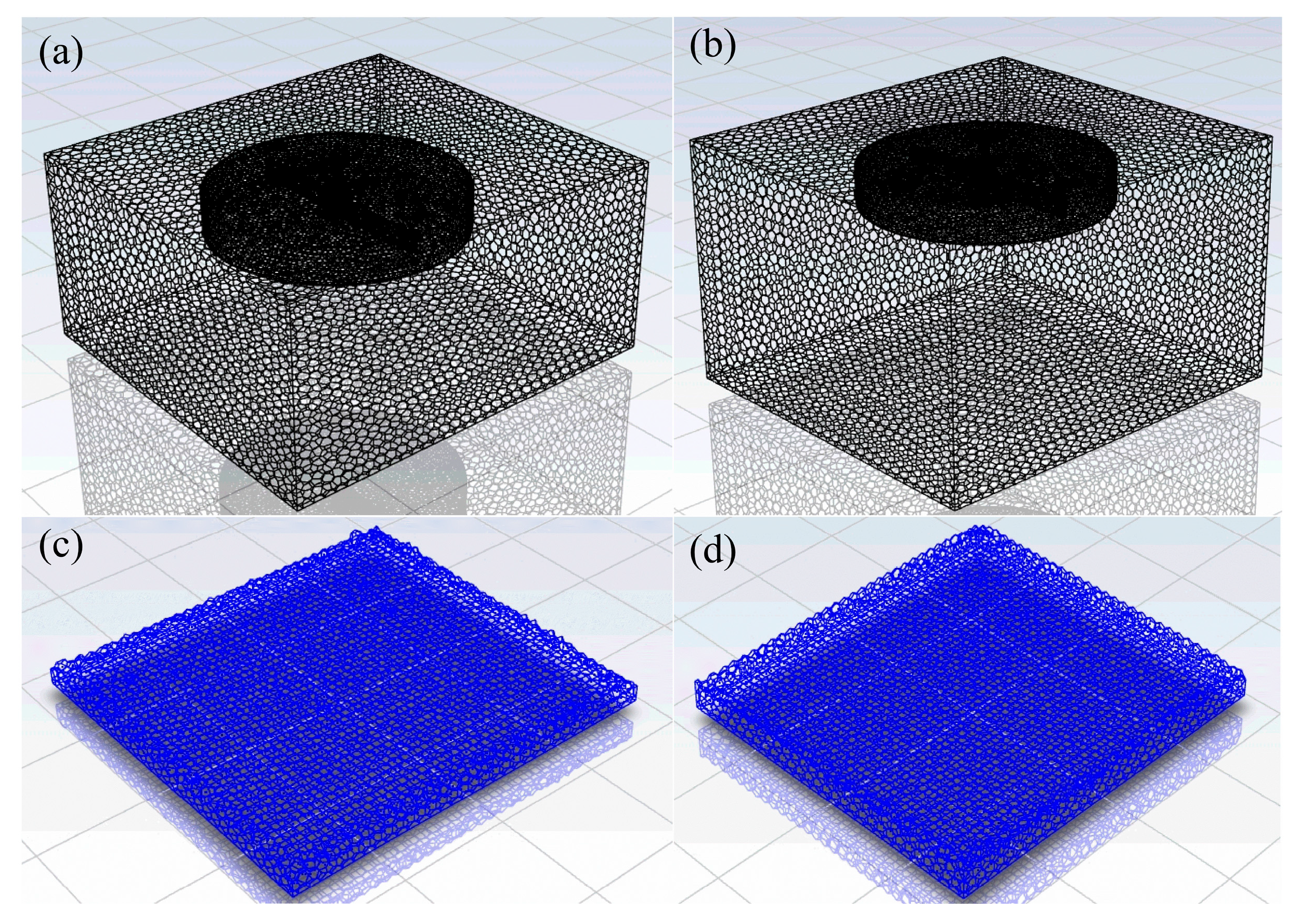
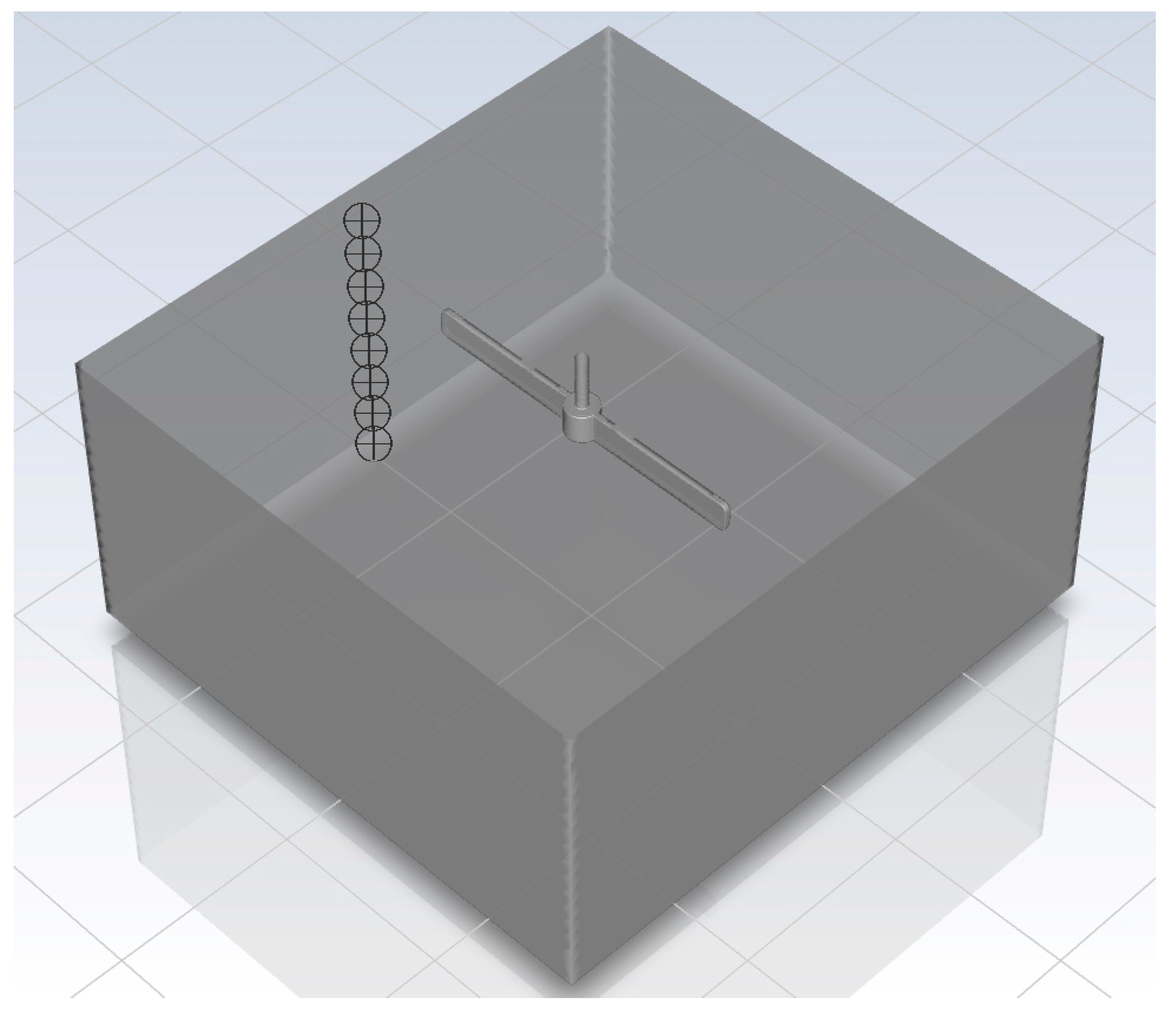


| Parameters | Actual Size | Model |
|---|---|---|
| size (λ) | 1 | 1:5 |
| height (mm) | 1000 | 200 |
| diameter (mm) | 750 | 150 |
| shaft length (mm) | 270 | 54 |
| shaft axis | eccentric | eccentric |
| blade | evenly distributed six blades | evenly distributed six blades |
| Density (kg/m3) | ) | Model Height (mm) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| water | 998.2 | 0.001003 | 450 |
| tracer | 998.2 | 0.001003 | 50 |
| Length | Width | Height | Circumference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 205 mm sediment calculation domain | 323 | 300 | 205 | |
| 155 mm sediment calculation domain | 323 | 300 | 155 | |
| stirring paddle rotation domain (mm) | 30 | 0 | 1276 |
| Setting Name | Specific Option or Value |
|---|---|
| turbulence model | RNG K-epsilon |
| multi-phase flow model | VOF |
| energy model | Off |
| computational model | MRF |
| meshing method | poly-hexcore |
| species model | species transport |
| surface tension coefficient | 0.073 N/m |
| time step | 0.01 s |
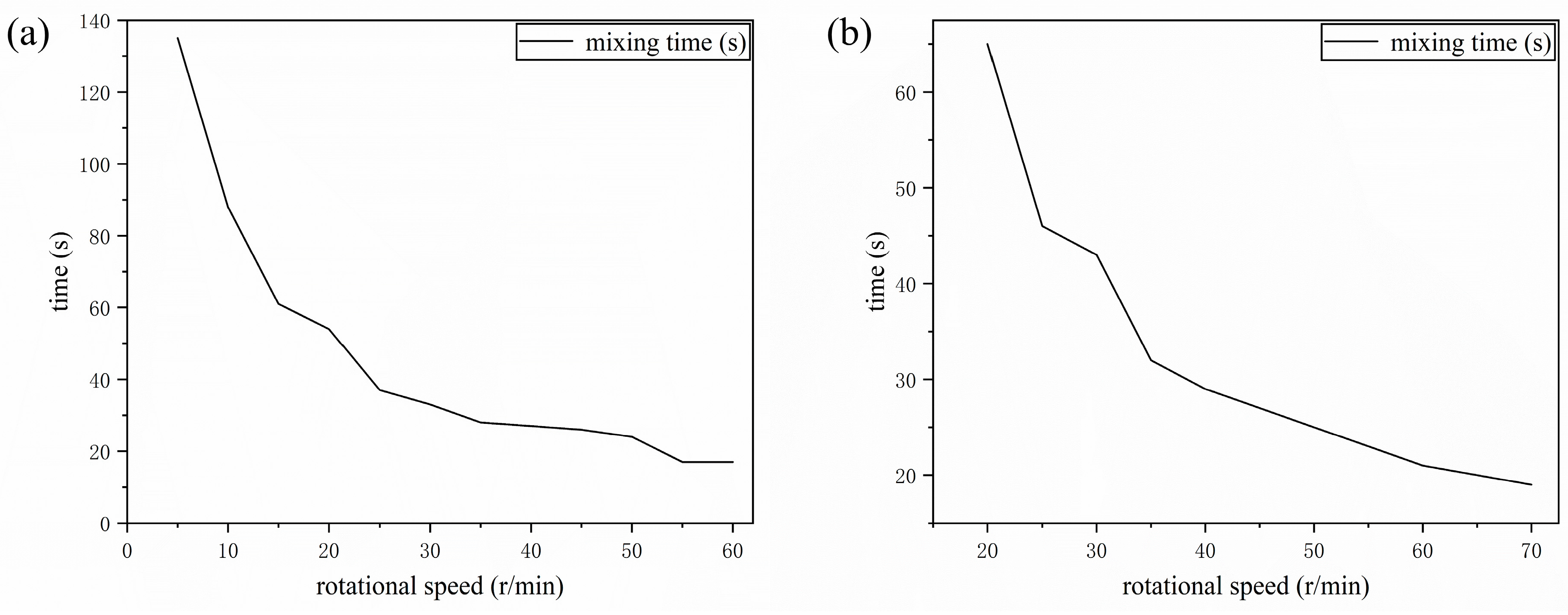
| rotational speed of the model with an overlying water height of 155 mm | 5~60 r/min |
| rotational speed of the model with an overlying water height of 205 mm | 0~70 r/min |
| Sediment Depth (mm) | Stirrer Speed (r/min) | Experimental Full Mixing Time (s) | Simulation Full Mixing Time (s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 155 | 20 | 60–64 | 65 |
| 155 | 25 | 42–46 | 46 |
| 155 | 30 | 40–44 | 43 |
| 155 | 35 | 33–34 | 32 |
| 155 | 40 | 28–30 | 29 |
| 155 | 45 | 25–27 | 27 |
| 155 | 50 | - | 25 |
| 155 | 55 | - | 23 |
| 155 | 60 | - | 21 |
| 155 | 65 | - | 20 |
| 155 | 70 | - | 19 |
| 205 | 5 | - | 135 |
| 205 | 10 | - | 88 |
| 205 | 15 | 63–67 | 61 |
| 205 | 20 | 50–54 | 54 |
| 205 | 25 | 37–39 | 37 |
| 205 | 30 | 31–33 | 33 |
| 205 | 35 | 27–29 | 28 |
| 205 | 40 | 28–30 | 27 |
| 205 | 45 | - | 26 |
| 205 | 50 | - | 24 |
| 205 | 55 | - | 17 |
| 205 | 60 | - | 17 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, L.; Luo, M.; Gong, S.; Han, Z.; Liu, W.; Pan, B. CFD-Based Parameter Calibration and Design of Subwater In Situ Cultivation Chambers Toward Well-Mixing Status but No Sediment Resuspension. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 1290. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13071290
Zhang L, Luo M, Gong S, Han Z, Liu W, Pan B. CFD-Based Parameter Calibration and Design of Subwater In Situ Cultivation Chambers Toward Well-Mixing Status but No Sediment Resuspension. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(7):1290. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13071290
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Liwen, Min Luo, Shanggui Gong, Zhiyang Han, Weihan Liu, and Binbin Pan. 2025. "CFD-Based Parameter Calibration and Design of Subwater In Situ Cultivation Chambers Toward Well-Mixing Status but No Sediment Resuspension" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 7: 1290. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13071290
APA StyleZhang, L., Luo, M., Gong, S., Han, Z., Liu, W., & Pan, B. (2025). CFD-Based Parameter Calibration and Design of Subwater In Situ Cultivation Chambers Toward Well-Mixing Status but No Sediment Resuspension. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(7), 1290. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13071290





