Folding of Oceanic Crust Along the Davie Fracture Zone, Offshore Tanzania
Abstract
1. Introduction
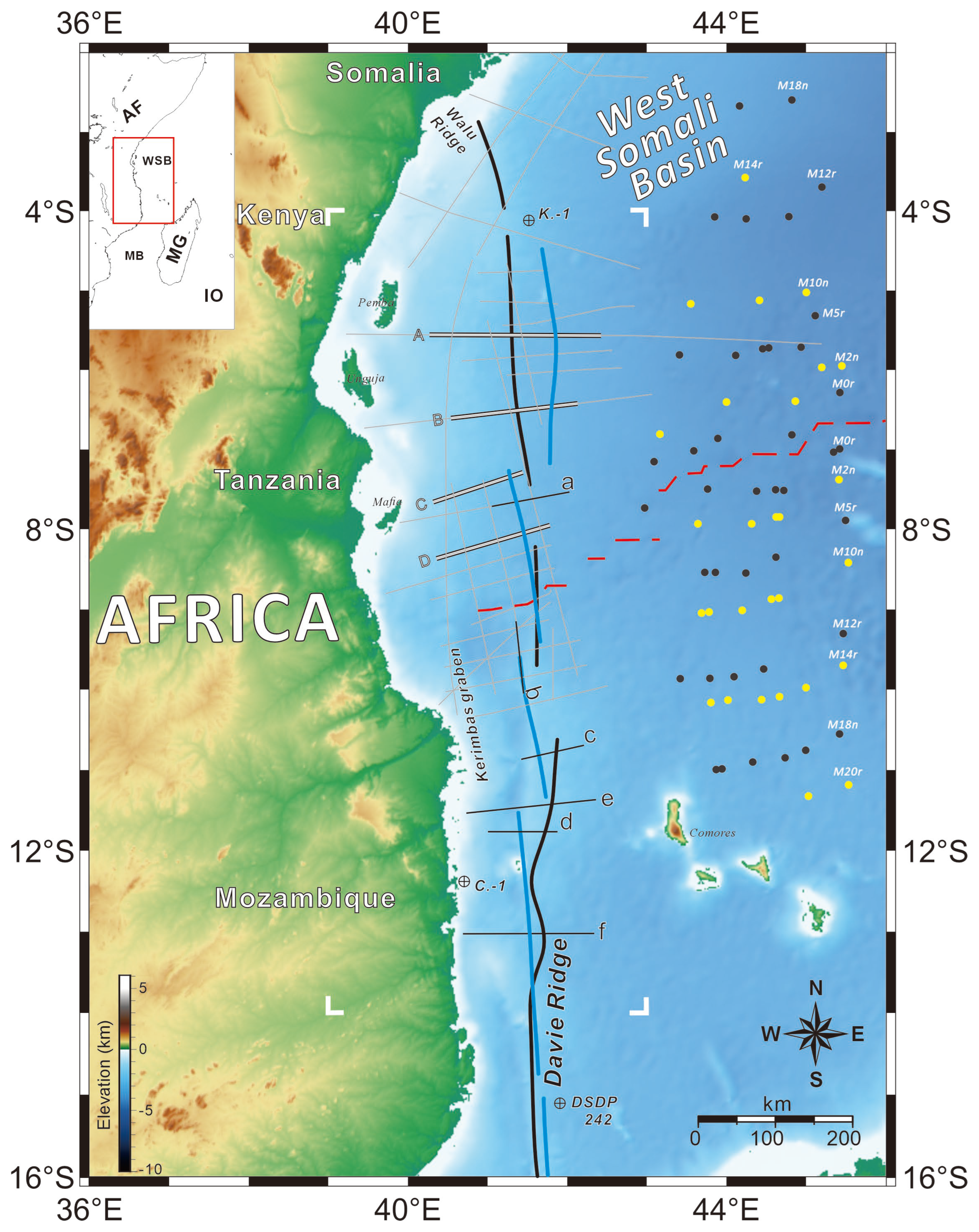
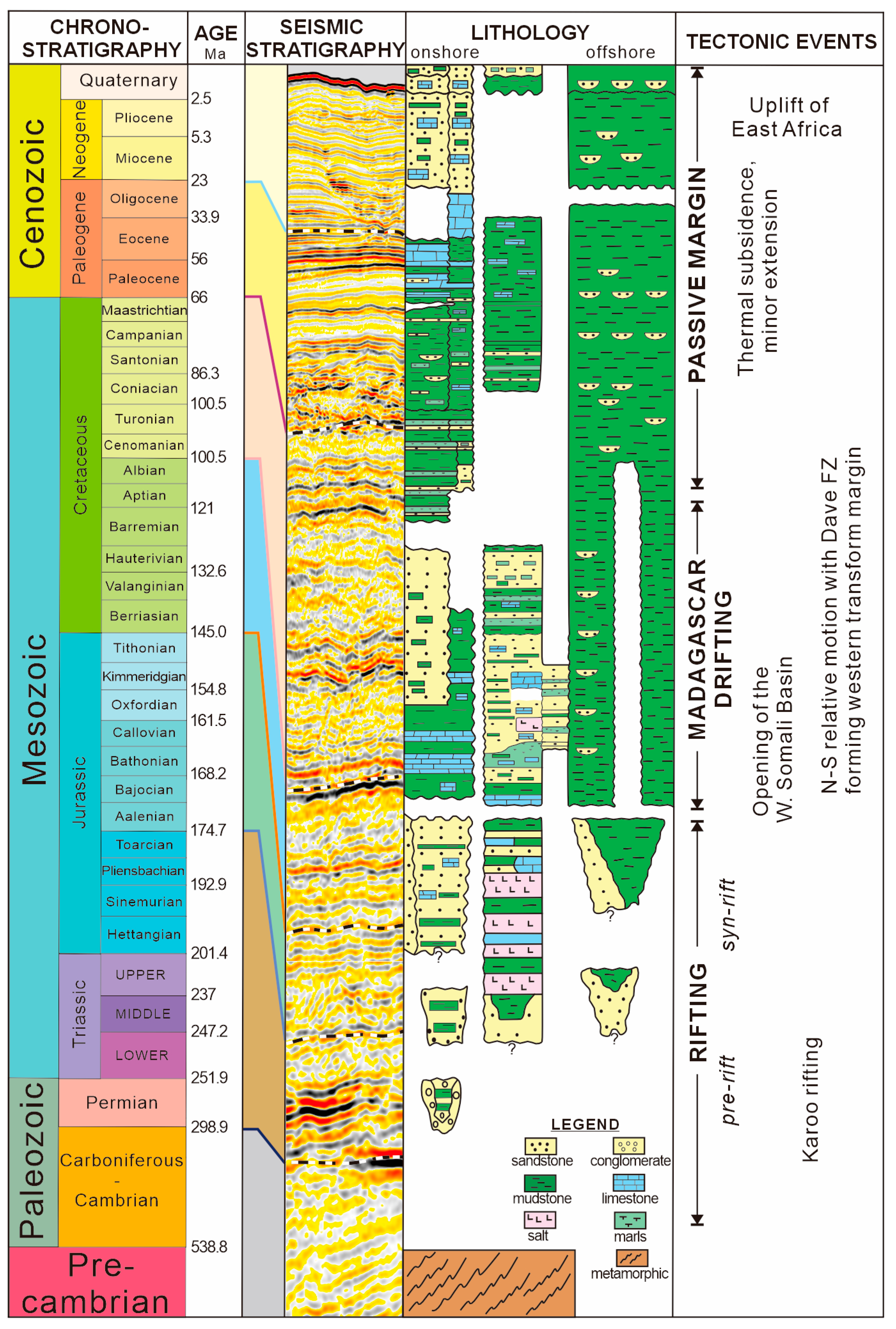
2. Geological Setting
3. Data and Methods
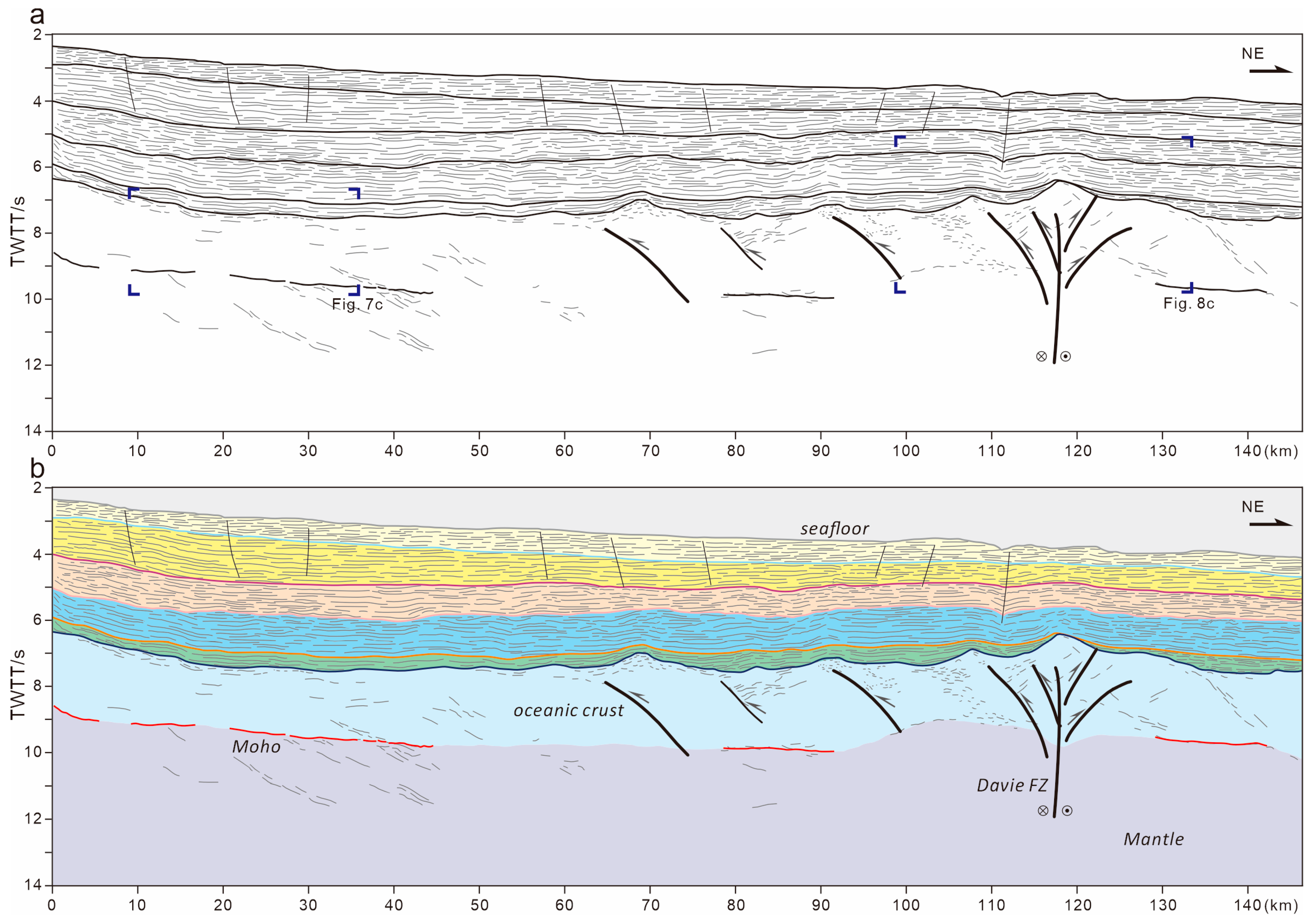
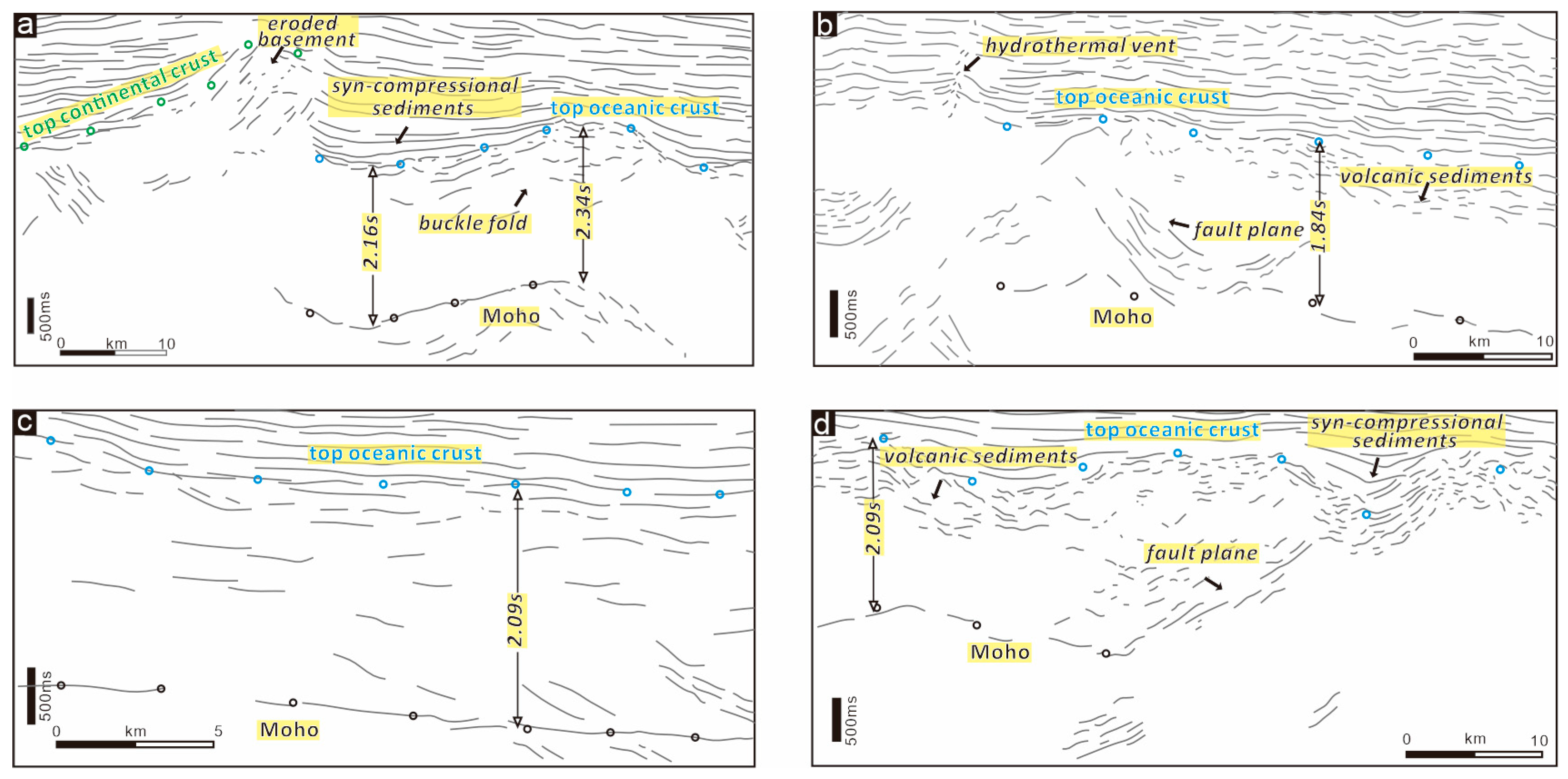
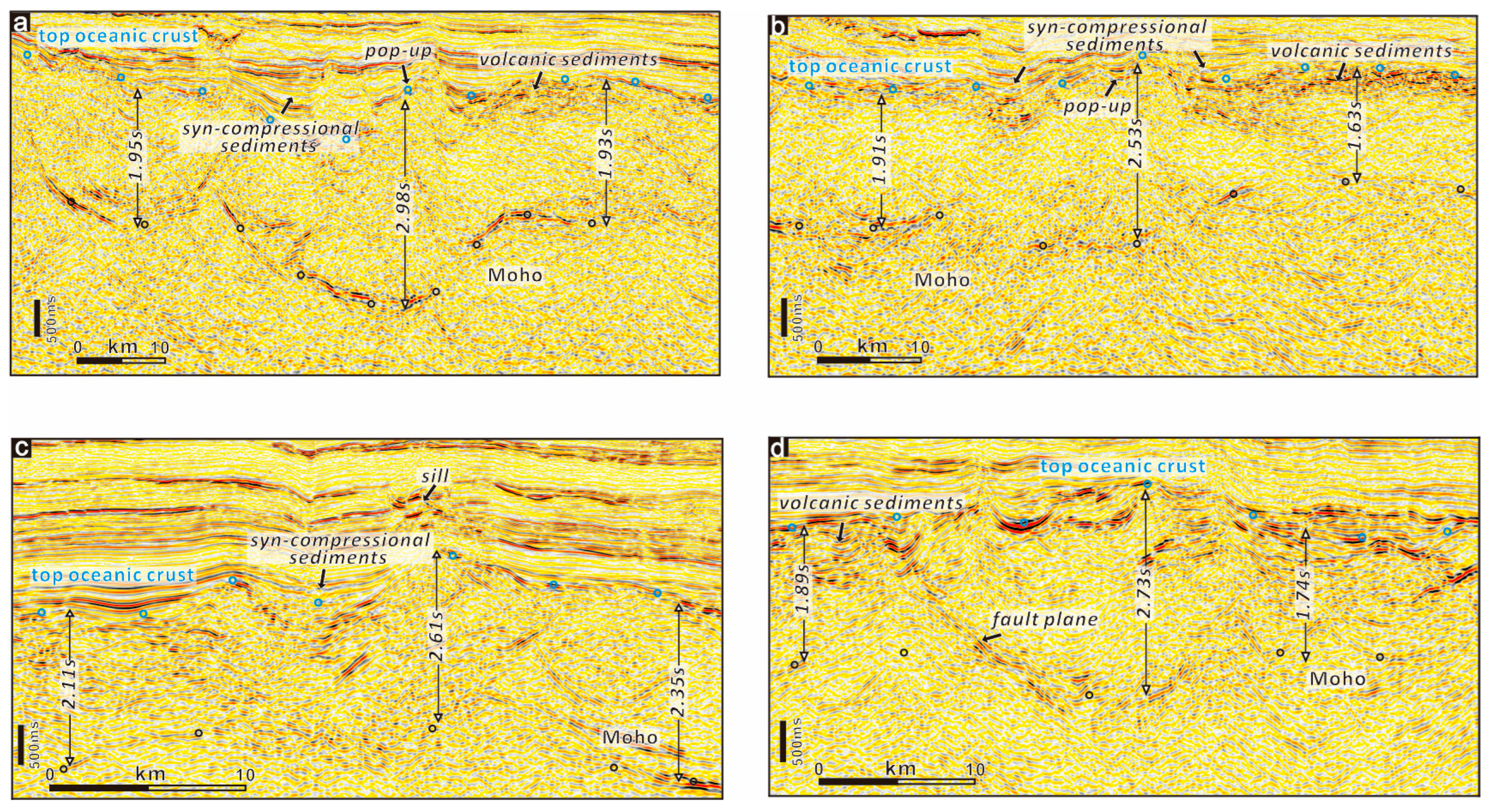
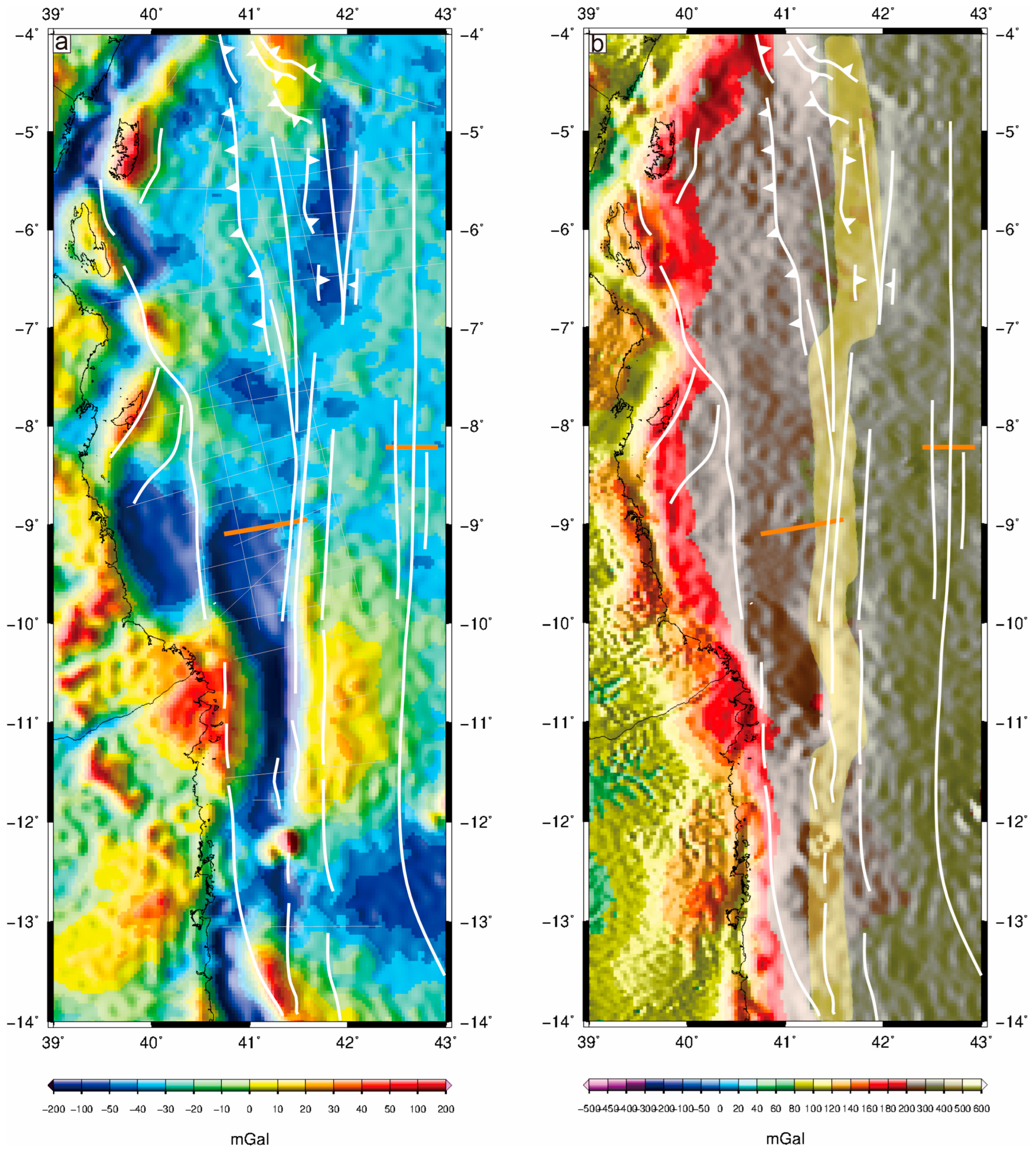
4. Results
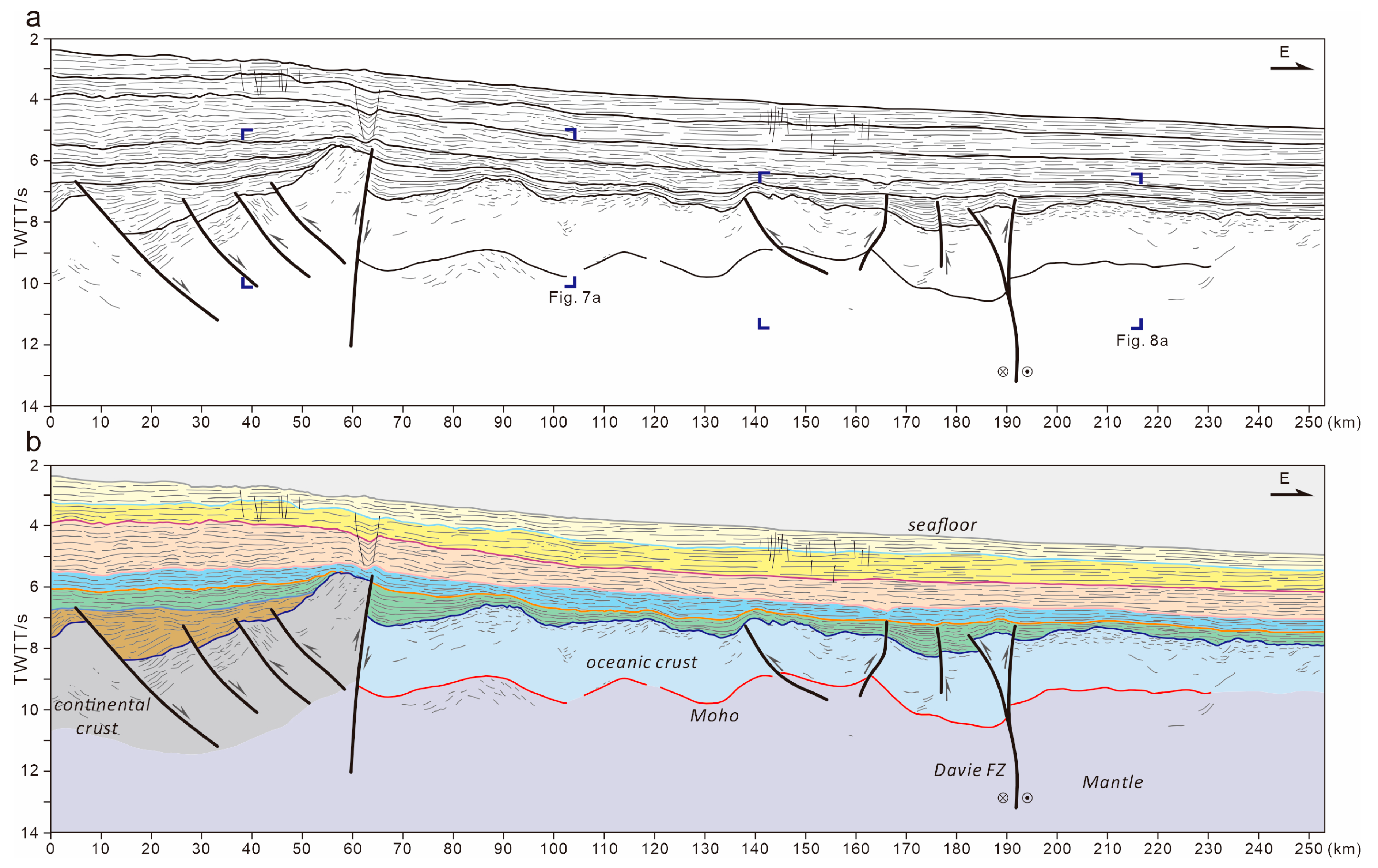
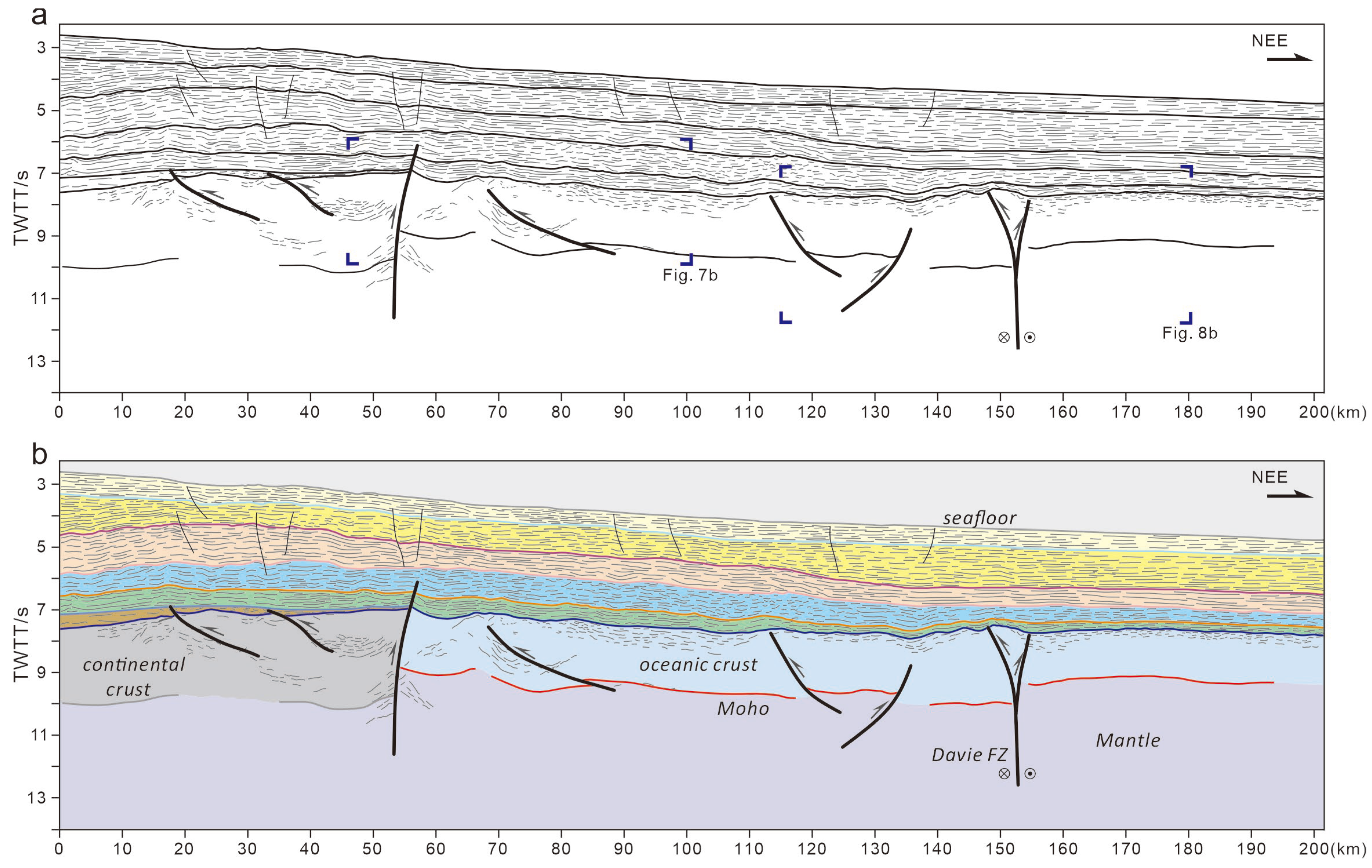
4.1. Crustal Domains
4.2. Compression Deformation in the Oceanic Domain
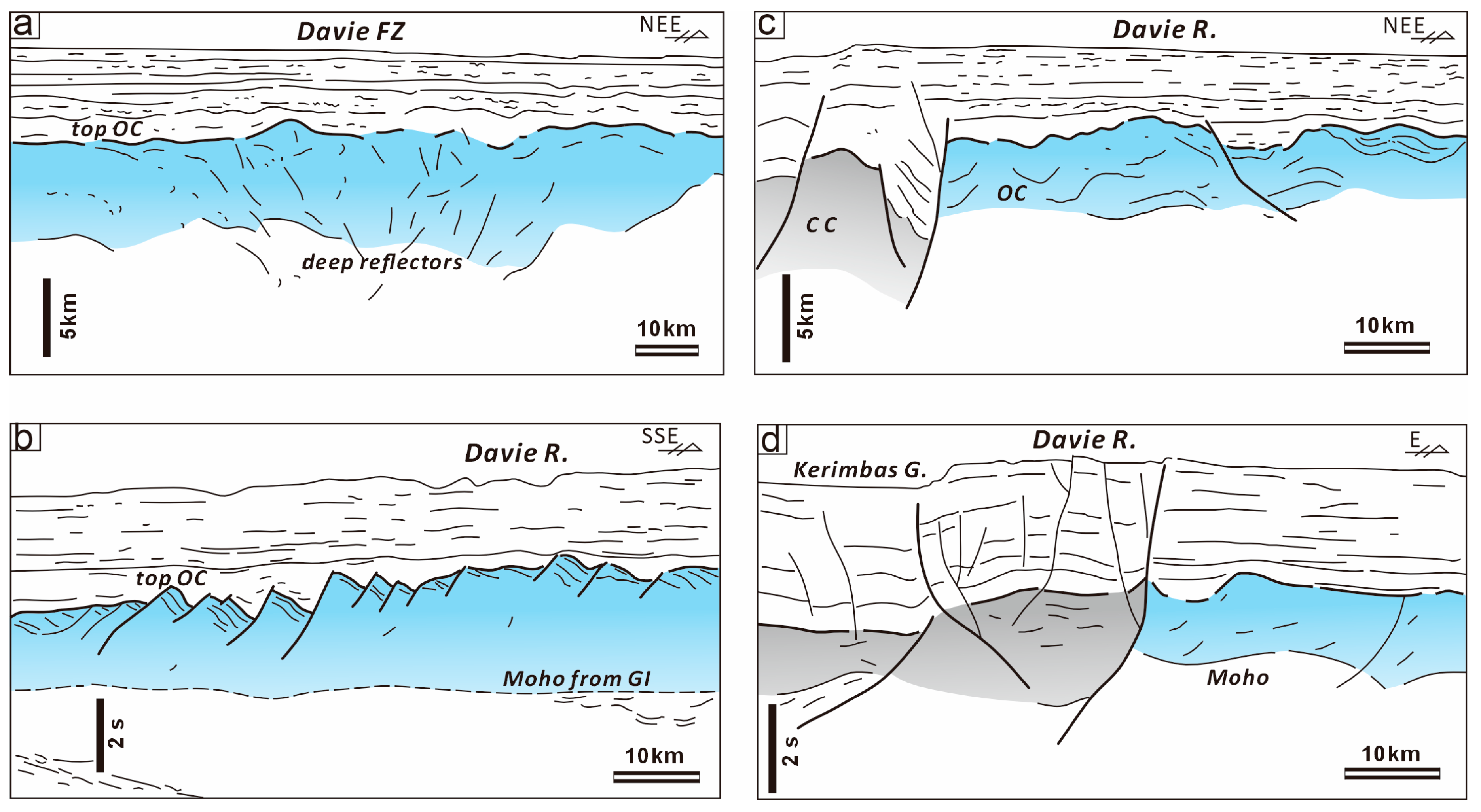
4.3. Trace of the Davie FZ
5. Discussion
5.1. Basement Architecture Along the Davie FZ
5.2. Boundary of Oceanic Deformation
5.3. Regional Tectonic Reconstruction
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- Stratigraphic architectures defined by several seismic horizons above the basement indicate a passive margin offshore Tanzania. The continental domain characterized by extended crust and seaward uplifted Moho is bordered by a landward dipping overthrust fault at the continent–ocean boundary. Seaward, a typical oceanic domain consists of volcanic sediments atop the basement and undulating Moho reflection in the deep.
- (2)
- Distinct compressive deformation characterized by crustal undulation of around 40 km wavelength occurs in the ocean domain. The thickened oceanic crust forms typical folds accompanied by thrust faults in the basement. The Davie FZ, characterized by positive flower structures with uplifted basement and deepened Moho, suggest strike-slip activity evidenced by Late Jurassic sediments onlapping onto the fold crest.
- (3)
- The Davie FZ evolved from a proto-transform fault located in Gondwana before the spreading of the West Somali Basin. During the Late Jurassic, a kinematics change shifted the spreading direction from NW–SE to N–S, resulting in a contemporaneous transpressional deformation in offshore Tanzania.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bird, D. Shear margins: Continent-ocean transform and fracture zone boundaries. Lead. Edge 2001, 20, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavier, L.L.; Manatschal, G. A mechanism to thin the continental lithosphere at magma-poor margins. Nature 2006, 440, 324–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geoffroy, L. Volcanic passive margins. Comptes Rendus Géoscience 2005, 337, 1395–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundin, E.R.; Doré, A.G.; Naliboff, J.; van Wijk, J. Utilization of continental transforms in break-up: Observations, models, and a potential link to magmatism. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2023, 524, 121–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peron-Pinvidic, G. (Ed.) Continental Rifted Margins 1: Definition and Methodology; ISTE Ltd./John Wiley and Sons Inc: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2022; ISBN 9781789450613. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, X.; Li, C.-F. Along-strike break-up variations of the continent–ocean transition zone in the northern South China Sea. J. Geol. Soc. 2024, 181, jgs2023-134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAdoo, D.C.; Sandwell, D.T. Folding of oceanic lithosphere. J. Geophys. Res. 1985, 90, 8563–8569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doré, A.G.; Lundin, E.R.; Fichler, C.; Olesen, O. Patterns of basement structure and reactivation along the NE Atlantic margin. J. Geol. Soc. 1997, 154, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doré, A.G.; Lundin, E.R. Cenozoic compressional structures on the NE Atlantic margin nature, origin and potential significance for hydrocarbon exploration. Pet. Geosci. 1996, 2, 299–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paton, D. Post-Rift Deformation of the North East and South Atlantic Margins: Are “Passive Margins” Really Passive? In Tectonics of Sedimentary Basins: Recent Advances; Busby, C., Pérez Azor, A., Eds.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 249–269. ISBN 9781444347166. [Google Scholar]
- Cloetingh, S.; Beekman, F.; Ziegler, P.A.; van Wees, J.-D.; Sokoutis, D. Post-rift compressional reactivation potential of passive margins and extensional basins. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2008, 306, 27–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bull, J.M.; Scrutton, R.A. Fault reactivation in the central Indian Ocean and the rheology of oceanic lithosphere. Nature 1990, 344, 855–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bull, J.M.; Scrutton, R.A. Seismic reflection images of intraplate deformation, central Indian Ocean, and their tectonic significance. J. Geol. Soc. 1992, 149, 955–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissel, J.K.; Anderson, R.N.; Geller, C.A. Deformation of the Indo–Australian plate. Nature 1980, 287, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briggs, S.E.; Davies, R.J.; Cartwright, J.; Morgan, R. Thrusting in oceanic crust during continental drift offshore Niger Delta, equatorial Africa. Tectonics 2009, 28, TC1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, S.R.; Beach, A.; Jackson, O.; Jackson, A. Deformation of oceanic crust in the eastern Gulf of Guinea: Role in the evolution of the Cameroon Volcanic Line and influence on the petroleum endowment of the Douala-Rio Muni Basin. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2017, 438, 7–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauter, D.; Ringenbach, J.C.; Cannat, M.; Maurin, T.; Manatschal, G.; McDermott, K.G. Intraplate Deformation of Oceanic Crust in the West Somali Basin: Insights From Long-offset Reflection Seismic Data. Tectonics 2018, 37, 588–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roche, V.; Ringenbach, J.-C. The Davie Fracture Zone: A recorder of continents drifts and kinematic changes. Tectonophysics 2022, 823, 229188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basile, C.; Loncke, L.; Roest, W.R.; Graindorge, D.; Klingelhoefer, F.; Museur, T.; Heuret, A.; Lesourd-Laux, T.; Vetel, W. Initiation of transform continental margins: The Cretaceous margins of the Demerara plateau. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2023, 524, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loncke, L.; de Lépinay, M.M.; Basile, C.; Maillard, A.; Roest, W.R.; de Clarens, P.; Patriat, M.; Gaullier, V.; Klingelhoefer, F.; Graindorge, D.; et al. Compared structure and evolution of the conjugate Demerara and Guinea transform marginal plateaus. Tectonophysics 2022, 822, 229112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graindorge, D.; Museur, T.; Klingelhoefer, F.; Roest, W.R.; Basile, C.; Loncke, L.; Sapin, F.; Heuret, A.; Perrot, J.; Marcaillou, B.; et al. Deep structure of the Demerara Plateau and its two-fold tectonic evolution: From a volcanic margin to a transform marginal plateau, insights from the Conjugate Guinea Plateau. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2023, 524, 339–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scrutton, R.A. Davie fracture zone and the movement of Madagascar. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1978, 39, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coffin, M.F.; Rabinowitz, P.D. Reconstruction of Madagascar and Africa: Evidence from the Davie Fracture Zone and Western Somali Basin. J. Geophys. Res. 1987, 92, 9385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vormann, M.; Jokat, W. Crustal variability along the rifted/sheared East African margin: A review. Geo-Mar. Lett. 2021, 41, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.O.; Moulin, M.; Aslanian, D.; de Clarens, P.; Guillocheau, F. New starting point for the Indian Ocean: Second phase of breakup for Gondwana. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2019, 191, 26–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, C.V.; Teasdale, J.P.; Mahanjane, E.S. Insight into the Eastern Margin of Africa from a new tectonic model of the Indian Ocean. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2016, 431, 299–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.K.; Lawver, L.A.; Norton, I.O.; Gahagan, L.M. New Somali Basin magnetic anomalies and a plate model for the early Indian Ocean. Gondwana Res. 2016, 34, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabinowitz, P.D.; Coffin, M.F.; Falvey, D. The Separation of Madagascar and Africa. Science 1983, 220, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, S.T.; Saha, S.; Longacre, M.; Basu, S.; Jha, R.; Mondal, T. Crustal Architecture and Nature of Continental Breakup Along a Transform Margin: New Insights From Tanzania-Mozambique Margin. Tectonics 2019, 38, 1273–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauter, D.; Unternehr, P.; Manatschal, G.; Tugend, J.; Cannat, M.; Le Quellec, P.; Kusznir, N.; Munschy, M.; Leroy, S.; Mercier de Lepinay, J.; et al. Evidence for magma entrapment below oceanic crust from deep seismic reflections in the Western Somali Basin. Geology 2016, 44, 407–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roche, V.; Ringenbach, J.-C.; Sapin, F.; Leroy, S. South and East African fracture zones: A long lifespan since the breakup of Gondwana. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2023, 524, 279–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vormann, M.; Jokat, W. The crustal structure of the Kerimbas Basin across the offshore branch of the East African Rift System. Geophys. J. Int. 2021, 226, 2073–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, E.S.; Schlich, R. DSDP Leg 25, Site 242; DSDP: College Station, TX, USA, 1974; Volume 25. [Google Scholar]
- Phethean, J.J.; Kalnins, L.M.; van Hunen, J.; Biffi, P.G.; Davies, R.J.; McCaffrey, K.J. Madagascar’s escape from Africa: A high-resolution plate reconstruction for the Western Somali Basin and implications for supercontinent dispersal. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2016, 17, 5036–5055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loncke, L.; Roest, W.R.; Klingelhoefer, F.; Basile, C.; Graindorge, D.; Heuret, A.; Marcaillou, B.; Museur, T.; Fanget, A.S.; Mercier de Lépinay, M. Transform Marginal Plateaus. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2020, 203, 102940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimke, J.; Franke, D. Gondwana breakup: No evidence for a Davie Fracture Zone offshore northern Mozambique, Tanzania and Kenya. Terra Nova 2016, 28, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabinowitz, P.D. Gravity Anomalies across the East African Continental Margin. J. Geophys. Res. 1971, 76, 7107–7117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosendahl, B.R. Architecture of Continental Rifts with Special Reference to East Africa. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 1987, 15, 445–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiger, M.; Clark, D.N.; Mette, W. Reappraisal of the timing of the breakup of Gondwana based on sedimentological and seismic evidence from the Morondava Basin, Madagascar. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2004, 38, 363–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, K.G. Karoo igneous activity, and the early stages of the break-up of Gondwanaland. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 1992, 68, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leinweber, V.T.; Jokat, W. The Jurassic history of the Africa–Antarctica corridor—new constraints from magnetic data on the conjugate continental margins. Tectonophysics 2012, 530–531, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaina, C.; Torsvik, T.H.; van Hinsbergen, D.J.; Medvedev, S.; Werner, S.C.; Labails, C. The African Plate: A history of oceanic crust accretion and subduction since the Jurassic. Tectonophysics 2013, 604, 4–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vormann, M.; Franke, D.; Jokat, W. The crustal structure of the southern Davie Ridge offshore northern Mozambique—A wide-angle seismic and potential field study. Tectonophysics 2020, 778, 228370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahanjane, E.S. The Davie Fracture Zone and adjacent basins in the offshore Mozambique Margin—A new insight for the hydrocarbon potential. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2014, 57, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coffin, M.F.; Rabinowitz, P.D.; Houtz, R.E. Crustal structure in the Western Somali Basin. Geophys. J. Int. 1986, 86, 331–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimke, J.; Franke, D.; Gaedicke, C.; Schreckenberger, B.; Schnabel, M.; Stollhofen, H.; Rose, J.; Chaheire, M. How to identify oceanic crust—Evidence for a complex break-up in the Mozambique Channel, off East Africa. Tectonophysics 2016, 693, 436–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonvalot, S.; Briais, A.; Kuhn, M.; Peyrefitte, A.; Vales, N.; Biancale, R.; Gabalda, G.; Moreaux, G.; Reinquin, F.; Sarrailh, M. World Gravity Map; Commission for the Geological Map of the World, Ed.; BGI-CGMW-CNES-IRD: Paris, France, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Christensen, N.I.; Mooney, W.D. Seismic velocity structure and composition of the continental crust: A global view. J. Geophys. Res. 1995, 100, 9761–9788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Liu, C. Three Types of Flower Structures in a Divergent-Wrench Fault Zone. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2017, 122, 10478–10497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, A.S.; Windley, B.F. The Tectonic Evolution of Central and Northern Madagascar and Its Place in the Final Assembly of Gondwana. J. Geol. 2002, 110, 325–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, C.O.; Jokat, W. The initial Gondwana break-up: A synthesis based on new potential field data of the Africa-Antarctica Corridor. Tectonophysics 2019, 750, 301–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaina, C.; van Hinsbergen, D.J.J.; Spakman, W. Tectonic interactions between India and Arabia since the Jurassic reconstructed from marine geophysics, ophiolite geology, and seismic tomography. Tectonics 2015, 34, 875–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Avraham, Z.; Hartnady, C.; Kitchin, K.A. Structure and tectonics of the Agulhas-Falkland fracture zone. Tectonophysics 1997, 282, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuck-Martin, A.; Adam, J.; Eagles, G. New plate kinematic model and tectono-stratigraphic history of the East African and West Madagascan Margins. Basin Res. 2018, 30, 1118–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadiki, N.; Godfray, G.; Msabi, M. Characterization of the accommodation zones along restraining and releasing bends from analogue modelling simulating the seagap fault, off-shore Tanzania. Pet. Res. 2021, 6, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerya, T.V. Initiation of transform faults at rifted continental margins: 3D petrological-thermomechanical modeling and comparison to the Woodlark Basin. Petrology 2013, 21, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sage, F.; Basile, C.; Mascle, J.; Pontoise, B.; Whitmarsh, R.B. Crustal structure of the continent-ocean transition off the Côte d’Ivoire-Ghana transform margin: Implications for thermal exchanges across the palaeotransform boundary. Geophys. J. Int. 2000, 143, 662–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassias, Y. Petrological and geochemical investigation of rocks from the Davie fracture zone (Mozambique Channel) and some tectonic implications. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 1992, 15, 321–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peng, X.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, Z. Folding of Oceanic Crust Along the Davie Fracture Zone, Offshore Tanzania. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 1179. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13061179
Peng X, Zhou Y, Wang L, Liu Z. Folding of Oceanic Crust Along the Davie Fracture Zone, Offshore Tanzania. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(6):1179. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13061179
Chicago/Turabian StylePeng, Xi, Yuanyuan Zhou, Li Wang, and Zhaoqian Liu. 2025. "Folding of Oceanic Crust Along the Davie Fracture Zone, Offshore Tanzania" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 6: 1179. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13061179
APA StylePeng, X., Zhou, Y., Wang, L., & Liu, Z. (2025). Folding of Oceanic Crust Along the Davie Fracture Zone, Offshore Tanzania. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(6), 1179. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13061179





