Seasonal Self-Purification Process of Nutrients Entering Coastal Water from Land-Based Sources in Tieshan Bay, China: Insights from Incubation Experiments
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
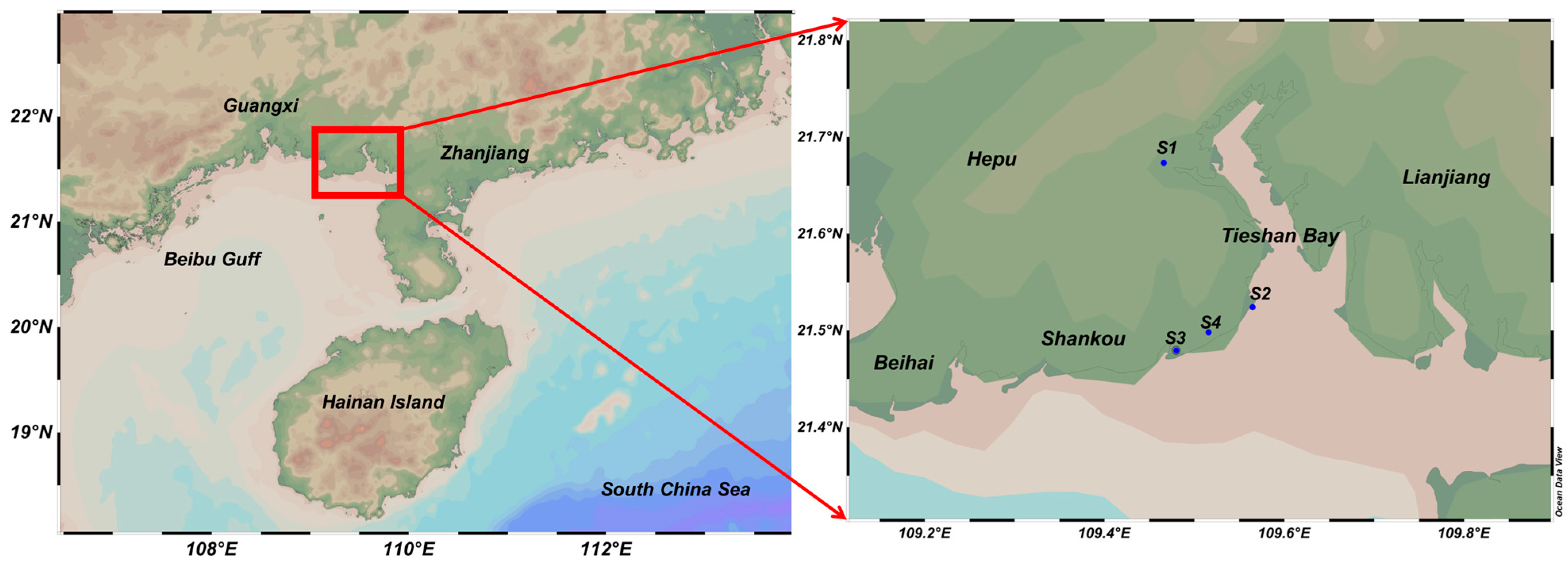
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Experimental Design of Ecological Incubation and Field Monitoring
2.3. Statistical Method
3. Results
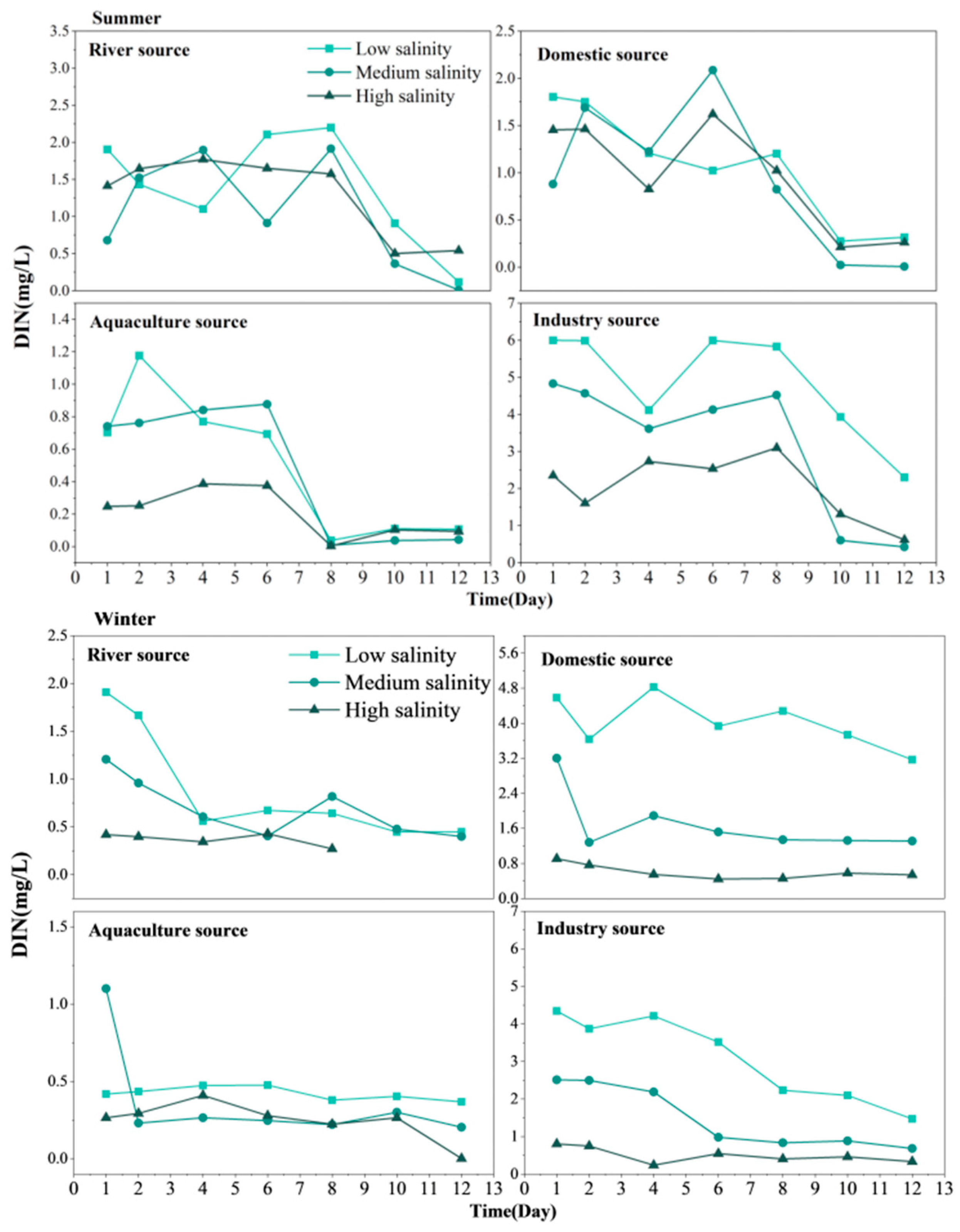
3.1. Dynamics of Environmental Factors During Ecological Incubation Experiments
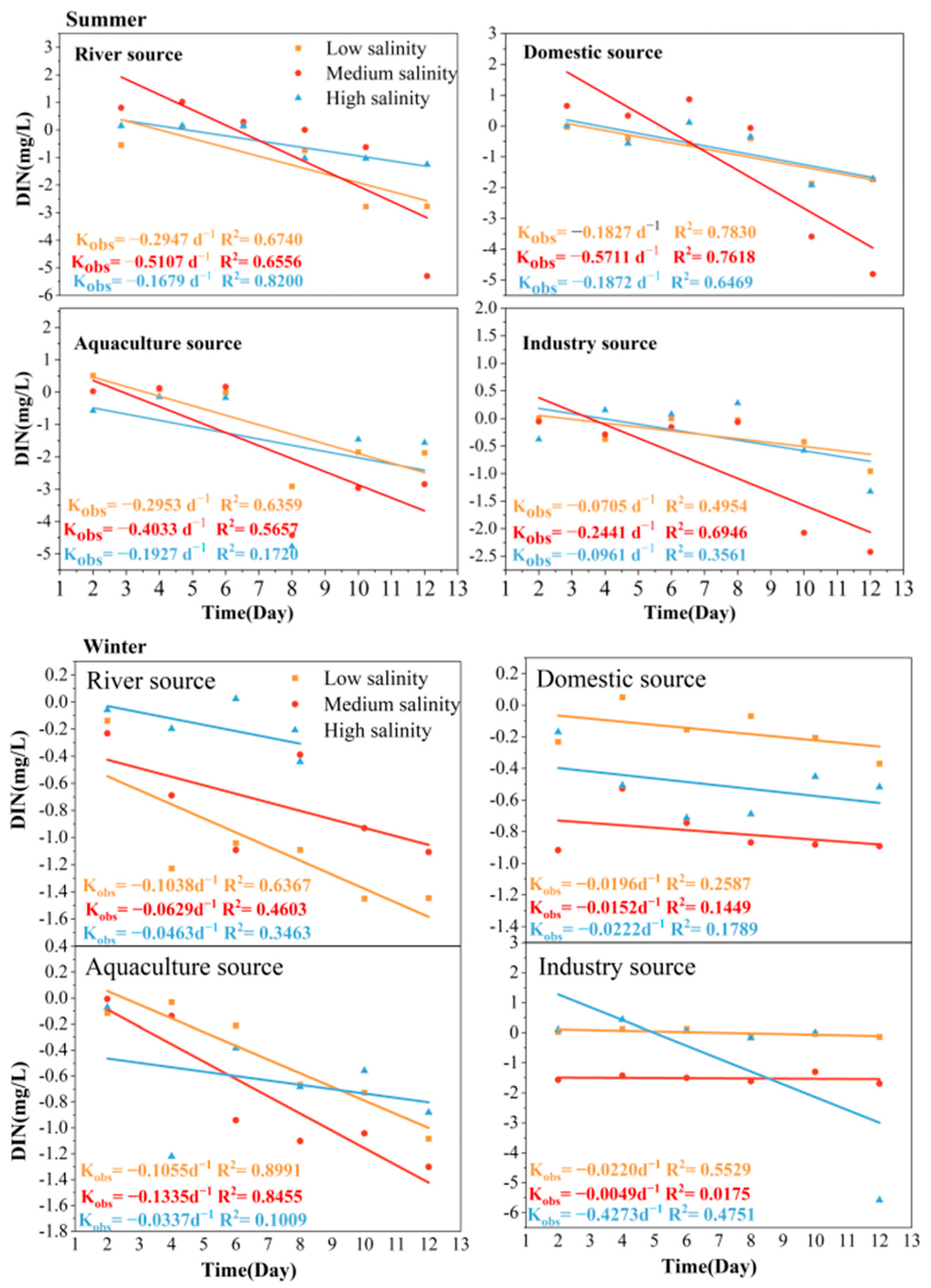
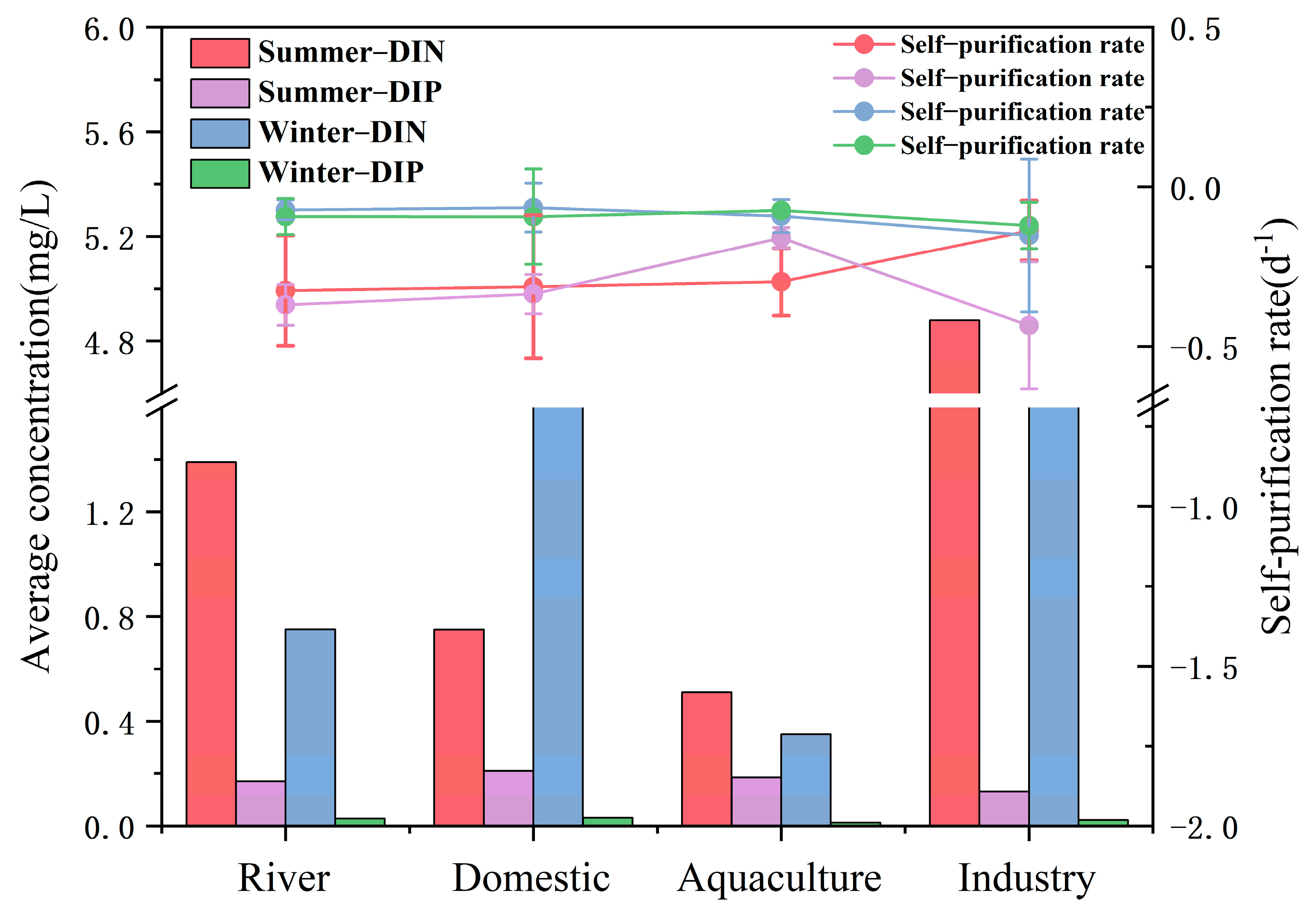
3.2. Self-Purification Process of Land-Based Sources of DIN in Seawater in TSB
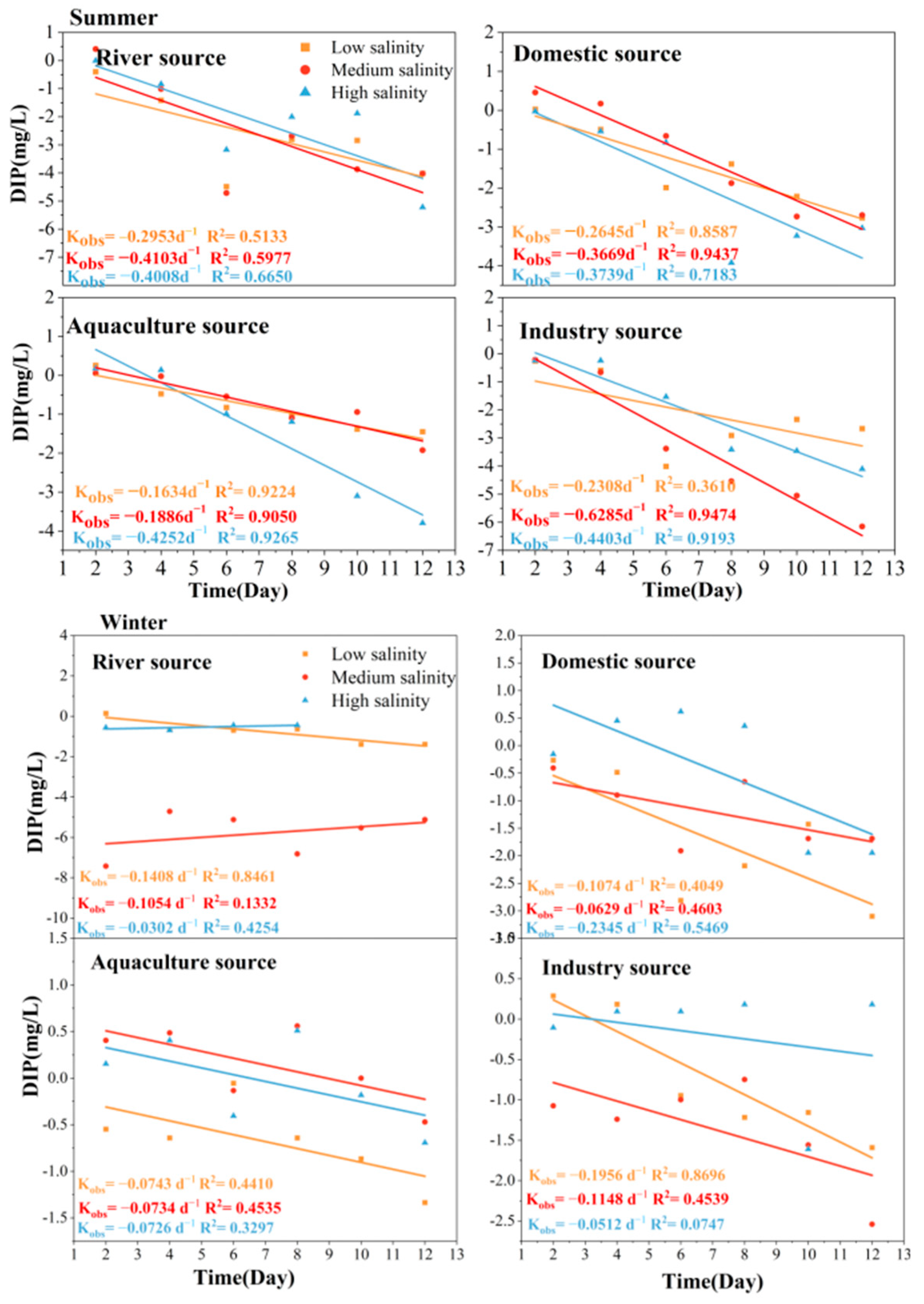
3.3. Self-Purification Process of TSB Land-Based DIP in Seawater
3.4. Self-Purification Process of DSi from Land-Based Sources in TSB in Seawater
3.5. Chl-a Variations in Different Sources of Nutrients Input to TSB
4. Discussion
4.1. Critical Control Factors for Self-Purification Rate Process of Different Sources of Nutrients in TSB
4.2. First-Order Kinetic Self-Purification Rate Processes of DIN, DIP, and DSi at Different Salinity in TSB
4.3. Treatment Options for Different Sources of Pollution
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yong, D.; Tang, X.-X.; Zhen, Y.; You, W. Effect of nutrients structure on primary production in offshore of Shandong Province. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2011, 30, 177–181. [Google Scholar]
- Tromme, G.; Poxleitner, M.; Lorenz, P.; Bitzilekis, B.; Gogaladze, A.; Stibor, H. Altered food-web dynamics under increased nitrogen load in phosphorus deficient lakes. Aquat. Sci. 2017, 79, 1009–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Long, H.; Li, Z.; Chen, R.; Peng, D.; Zhang, J. Effects of typhoon events on coastal hydrology, nutrients, and algal bloom dynamics: Insights from continuous observation and machine learning in semi-enclosed Zhanjiang Bay, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 924, 171676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.H.; Lin, Y.L.; Wang, Y.; Lan, W.L. Assessment of the Eutrophication Level of the Marine Environment and Its Effect on Phytoplankton Chlorophyll a in Qinzhou Bay. Mar. Dev. Manag. 2021, 37, 67–74. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Peng, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J.Y.; Zhao, H. Long-Term Harmful Algal Blooms and Nutrients Patterns Affected by Climate Change and Anthropogenic Pressures in the Zhanjiang Bay, China. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 849819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Xu, J.L.; Zhang, J.B.; Li, J.X.; Luo, X.Q. Spatiotemporal dissolved silicate variation, sources, and behavior in the eutrophic Zhanjiang Bay, China. Water 2020, 12, 3586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.L.; Li, Y.; Chen, Z.P.; Li, R.M.; Chen, H.R.; Mu, J.L. Spatiotemporal distributions of nutrients and their potential influencingfactors in Sansha bay. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2023, 42, 440–448. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, W.L.; Li, T.S.; Han, L.J. Distribution and seasonal variation of nutrition in the adjacent waters of Tieshangang bay in Guangxi. Mar. Sci. 2014, 38, 63–69. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, S.; Zhang, P.; Ou, S.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; Zhang, J. Spatiotemporal nutrient patterns, composition, and implications for eutrophication mitigation in the Pearl River Estuary, China. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2022, 266, 107749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.H. Temporal and spatial nutrient variations in inshore waters of Xiamen and eutrophication assessment. J. Appl. Oceanogr. 2023, 42, 75–84. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, R.G.; Follows, M.J. Physical Transport of Nutrients and the Maintenance of Biological Production; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003; pp. 19–51. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, X.P.; Wu, M.; Liu, X.; Lei, F.; He, X.L. Investigation and Analysis of Water Quality Pollution in BeibuGulf of Guangxi. Guangxi Sci. 2022, 29, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Ping, L.; Hailian, M.; Zhao, G.J. Current Condition and Assessment of Inshore Water Quality in Guangxi. Bull. Sci. Technol. 2018, 7, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, X.M.; Tong, W.P.; Lai, T.H.; He, B.M. The changing characteristics of biogenic elements and their influencing factors in Tieshangang Port. Trans. Oceanol. Limnol. 2001, 4, 23–27. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, W.L.; Peng, X.Y. Characteristics of nutrient changes in Tieshan Harbor from 2003 to 2010. Guangxi Sci. 2011, 18, 380–384. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, D.; Kang, Z.; Yang, B.; Dan, S.F.; Zhong, Q. Compositions and spatio-temporal distributions of different nitrogen species and lability of dissolved organic nitrogen from the Dafengjiang River to the Sanniang Bay, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 156, 111205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.H.; Li, X.L.; Han, G. Studies on the environmental capacity of the Dapeng Bay, Part I: Numerical study of water self-purification. China Environ. Sci. 2011, 31, 2031–2038. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, X.; Zhang, C. Offshore Resources and Current Situation in Guangxi Coast; Ocean Press Beijing: Beijing, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, X.M.; Fan, H.Q.; He, B.M.; Cao, Q.X.; Li, Z. Nutritional level and component characteristic of water in mangrove area of Tieshan Bay. J. Trop. Oceanogr. 2013, 32, 1009–5470. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.H.; Chen, S.L.; Gu, G.C. Tidal types andcharacteristics of theharbors along the Guangxicoast. Oceanogr. Res. 2010, 28, 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Pei, M.F.; Hu, J.T.; Gao, J.S.; Li, T. Study on the response of water exchange capacity to reclamation and monsoon in Tieshan Port, Guangxi. Mar. Lake Bull. 2019, 6, 34–40. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Wu, S.; Xu, M.; Luo, X.; Peng, X.; Ren, C.; Zhang, J. Spatiotemporal Nutrient Patterns, Stoichiometry, and Eutrophication Assessment in the Tieshan Bay Coastal Water, China. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.M.; Wei, X.M.; Fan, H.Q.; Cao, X.Q. Spatio-temporal change ofinorganic nitrogen contentand the evaluation ofeutrophication in thesurface seawaters ofmangrove areas in Guangxibays. J. Appl. Oceanogr. 2014, 33, 140–148. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.J.W. Analysis of Nitrogen and Phosphorus Pollution in Shenzhen Bay over the Past 40 Years. Water 2024, 16, 3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, M.A.; Goepfert, T.J.; Ritt, J.T. Some thoughts on the concept of colimitation: Three definitions and the importance of bioavailability. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2008, 53, 276–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, G.M.; Young, J.L.; Aanderud, Z.T.; Jones, E.F.; Bratsman, S.; Daniels, J.; Malmfeldt, M.P.; Baker, M.A.; Abbott, B.W.; Daly, S. Nutrient limitation and seasonality associated with phytoplankton communities and cyanotoxin production in a large, hypereutrophic lake. Harmful Algae 2025, 143, 102809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dongwei, H.; Zhijian, H.; Shenzheng, Z.; Jian, L.; Dongdong, W.; Xisha, D.; Shaoping, W.; Zhili, H.; Jianguo, H. Environmental Factors Shape Water Microbial Community Structure and Function in Shrimp Cultural Enclosure Ecosystems. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2359. [Google Scholar]
- Moneta, A.; Veuger, B.; van Rijswijk, P.; Meysman, F.; Soetaert, K.; Middelburg, J.J. Dissolved inorganic and organic nitrogen uptake in the coastal North Sea: A seasonal study. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2014, 147, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, P.A.; Kirchman, D. Utilization of inorganic and organic nitrogen by bacteria in marine systems. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1986, 31, 998–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, L.; Yin, K.; Lü, Y.; Yang, Y.; Huang, X. Spatial and Seasonal Variations of Nutrients in Sediment Profiles and Their Sediment-Water Fluxes in the Pearl River Estuary, Southern China. J. Earth Science. 2014, 25, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.H.; Yuan, X.C.; Huo, W.Y.; Yin, K.D. Distribution of chlorophyll a and primary productivity in the Yangtze estuary neighborhood. J. Oceanogr. 2004, 26, 143–150. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Wei, W.; Gao, Z.H.; Wang, D.; Yang, Y.; Ma, Y. Study of the nutrient distribution and its influence factorsin the Qinzhou Bay. Mar. Bull. 2013, 32, 481–487. [Google Scholar]
- Gunnars, A.; Blomqvist, S.; Johansson, P.; Andersson, C. Formation of Fe(III) oxyhydroxide colloids in freshwater and brackish seawater, with incorporation of phosphate and calcium. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2002, 66, 745–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.F.; Li, X.Y.; Zhang, W.L.; Zhang, J.L. Spatial and temporal distribution of silicate and chlorophyll a in the coastal waters with picophytoplankton algal bloom. Ecol. Sci. 2013, 32, 509–513. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, K.M.; Chen, B.J.; Yuan, Y.X.; Xin, F.Y. Preliminary study of nitrogen-phosphorous nutrients affecting the population composition of phytoplankton diatom in seawater. J. Appl. Ecol. 2000, 11, 445–448. [Google Scholar]
- Bin, Y.; Huai-Yi, F.; Li-Li, X.U.; Qiu-Ping, Z.; Shu-Shi, L. Spatio-temporal variation characteristics and driving factors of water pollution in Qinzhou bay. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2017, 36, 877–883. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.S.; Yang, G.P.; Gao, X.X.; Wei, Y.; He, Z. Variation of volatile haloearbon concentrations in the ineubation experiments with the addition of nutrients in the western Pacific Ocean. China Environ. Sci. 2019, 39, 4313–4320. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Zhang, P.; Xu, F.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, J. Seasonal nutrients variation, eutrophication pattern, and Chlorophyll a response adjacent to Guangdong coastal water, China. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1236609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.W.; Ju, Y.R.; Chen, C.F.; Dong, C.D. Evaluation of organic pollution and eutrophication status of Kaohsiung Harbor, Taiwan. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2016, 113, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.; Huang, T.; Huang, H. Phytoplankton Community Response to Environmental Factors along a Salinity Gradient in a Seagoing River, Tianjin, China. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloern, J. Turbidity as a control on phytoplankton biomass and productivity in estuaries. Cont. Shelf Res. 1987, 7, 1367–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geeraert, N.; Archana, A.; Xu, M.; Kao, S.; Baker, D.; Thibodeau, B. Investigating the link between Pearl River-induced eutrophication and hypoxia in Hong Kong shallow coastal waters. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 772, 145007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nana, P.A.; Seth, R.E.; Tamko, N.A.N.; Ossomba, V.R.O.; Bricheux, G.; Metsopkeng, C.S.; Nola, M.; Sime-Ngando, T. Tidal effect on the dispersion of fecal pollution indicator bacteria and associated health risks along the Kribi beaches (Southern Atlantic coast, Cameroon). Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2023, 60, 102831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Qu, L.; Huang, B.G.; Li, Q.; You, Q.M. Status and evaluation on nutrients for the adjacent sea water of the YellowRiver estuary in autumn of 2014. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2016, 35, 732–738. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Zou, D.; Gao, K. Impacts of increased atmospheric CO2 concentration on photosynthesis and growth of micro-and macro-algae. Sci. China Ser. C Life Sci. 2008, 51, 1144–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Huang, X.; Liu, Y.; Guan, M.; Tian, Y. Hydrological conditions can change the effects of major nutrients and dissolved organic matter on phytoplankton community dynamics in a eutrophic river. J. Hydrol. 2024, 628, 130503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackay, E.B.; Feuchtmayr, H.; De Ville, M.M.; Thackeray, S.J.; Callaghan, N.; Marshall, M.; Rhodes, G.; Yates, C.A.; Johnes, P.J.; Maberly, S.C. Dissolved organic nutrient uptake by riverine phytoplankton varies along a gradient of nutrient enrichment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 722, 137837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, D.L.; Brock, M.A.; Rees, G.N.; Baldwin, D.S. Effects of Increasing Salinity on Freshwater Ecosystems in Australia. Aust. J. Bot. 2003, 51, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Wei, M. The characteristics of the bionomical environment in Qinzhou Bay and the relationship between the characteristics and the self-purifying conditions of the water body. Mar. Sci. Bull./Haiyang Tongbao 2004, 23, 50–54. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, Z.; Tan, Y.; Ma, Y.; Huang, L.; Wang, S. Effects of surface current patterns on spatial variations of phytoplankton community and environmental factors in Sunda shelf. Cont. Shelf Res. 2014, 82, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharathi, M.D.; Sarma, V.V.S.S.; Ramaneswari, K. Intra-annual variations in phytoplankton biomass and its composition in the tropical estuary: Inuence of river discharge. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 129, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muylaert, K.; Sabbe, K.; Vyverman, W. Changes in phytoplankton diversity and community composition along the salinity gradient of the Schelde estuary (Belgium/The Netherlands). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2009, 82, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montagna, P.A.; Kalke, R.D. The effect of freshwater inflow on meiofaunal and macrofaunal populations in the Guadalupe and Nueces Estuaries, Texas. Estuaries 1992, 15, 307–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquemot, L.; Kalenitchenko, D.; Matthes, L.; Lovejoy, C. Protist communities along freshwater–marine transition zones in Hudson Bay (Canada). Elem. Sci. Anthr. 2021, 9, 00111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orchard, E.D.; Ammerman, J.W.; Lomas, M.W.; Dyhrman, S. Dissolved inorganic and organic phosphorus uptake in Trichodesmium and the microbial community: The importance of phosphorus ester in the Sargasso Sea. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2010, 55, 1390–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragueneau, O.; De Blas, V.E.; Treguer, P.; Queguiner, B. Phytoplankton dynamics in relation to biogeochemical cycle of silicon in a coastal ecosystem of Western Europe. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1994, 106, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Z. Phytoplankton, dissolved oxygen and nutrient patterns along a eutrophic river-estuary continuum: Observation and modeling. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 261, 110233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Guo, X.; Gao, H.; Gao, J.; Shi, J.; Yu, X.; Wu, Z. Seasonal variations of nutrient concentrations and their ratios in the central Bohai Sea. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 799, 149416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendriks, A.T.; Langeveld, J.G. Rethinking wastewater treatment plant effluent standards: Nutrient reduction or nutrient control? Engl. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 4735–4737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Hall, N.S.; Peierls, B.L.; Rossignol, K.L. Evolving paradigms and challenges in estuarine and coastal eutrophication dynamics in a culturally and climatically stressed world. Estuaries Coasts 2014, 37, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Xia, Y.; Ti, C.; Shan, J.; Wu, Y.; Yan, X. Thirty years of experience in water pollution control in Taihu Lake: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 914, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurtsbaugh, W.A.; Paerl, H.W.; Dodds, W.K.J. Nutrients, eutrophication and harmful algal blooms along the freshwater to marine continuum. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Water 2019, 6, e1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeppesen, E.; Meerhoff, M.; Davidson, T.; Trolle, D.; Sondergaard, M.; Lauridsen, T.; Nielsen, A. Climate change impacts on lakes: An integrated ecological perspective based on a multi-faceted approach, with special focus on shallow lakes. J. Limnol. 2014, 73, 88–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezentseva, I.V.; Sovga, E.E.; Khmara, T.V. Self-purification capacity of Sevastopol Bay ecosystems in relation to inorganic forms of nitrogen and phosphorus from 2012 to 2020. Ecol. Saf. Coast. Shelf Zones Sea 2023, 4, 101–115. [Google Scholar]
- Mokhtar, Z.; Kenway, S.; Mat Nashir, I. Challenges for Compliance with Industrial Effluent Regulations—An Industry Perspective. Challenges 2024, 16, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

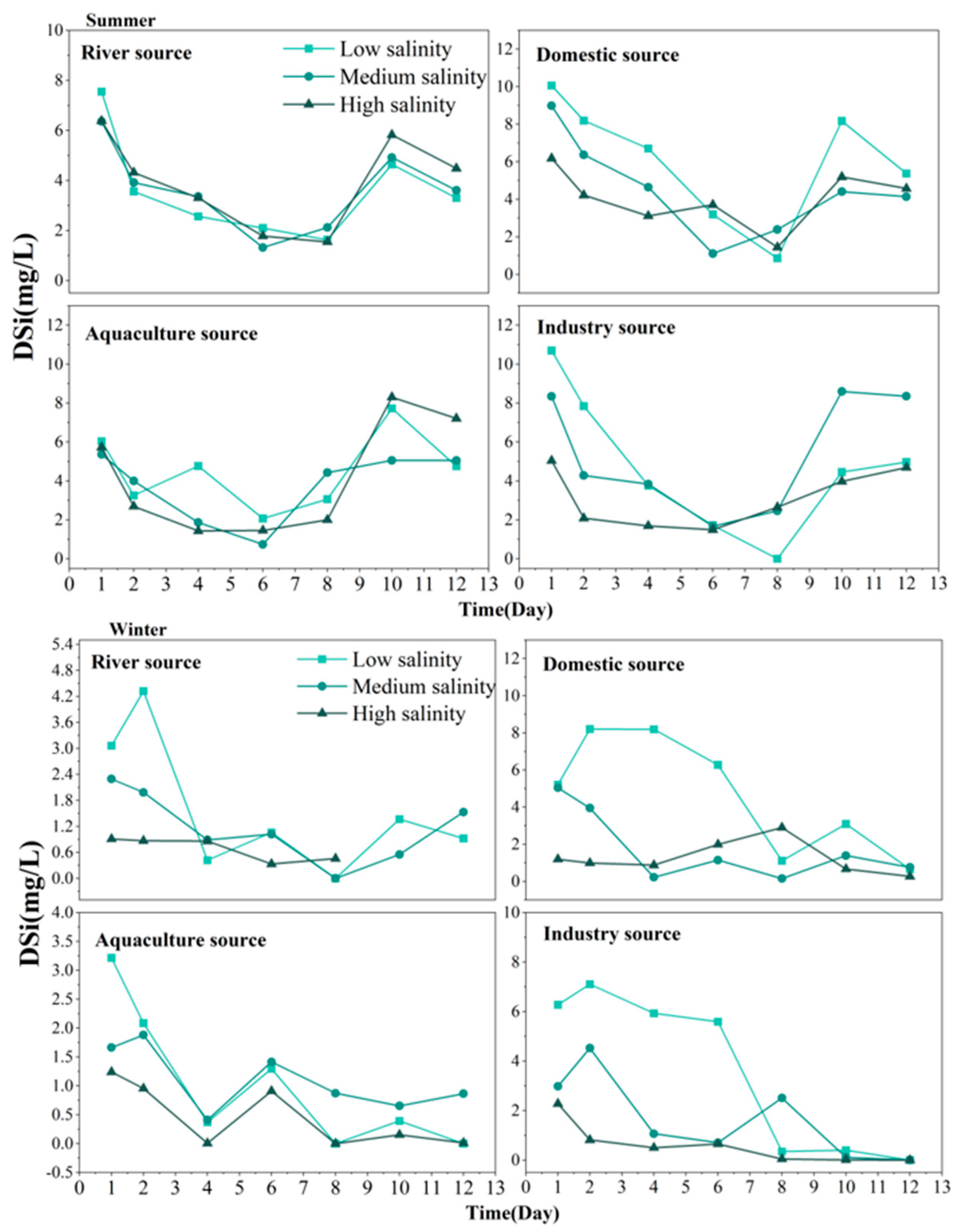
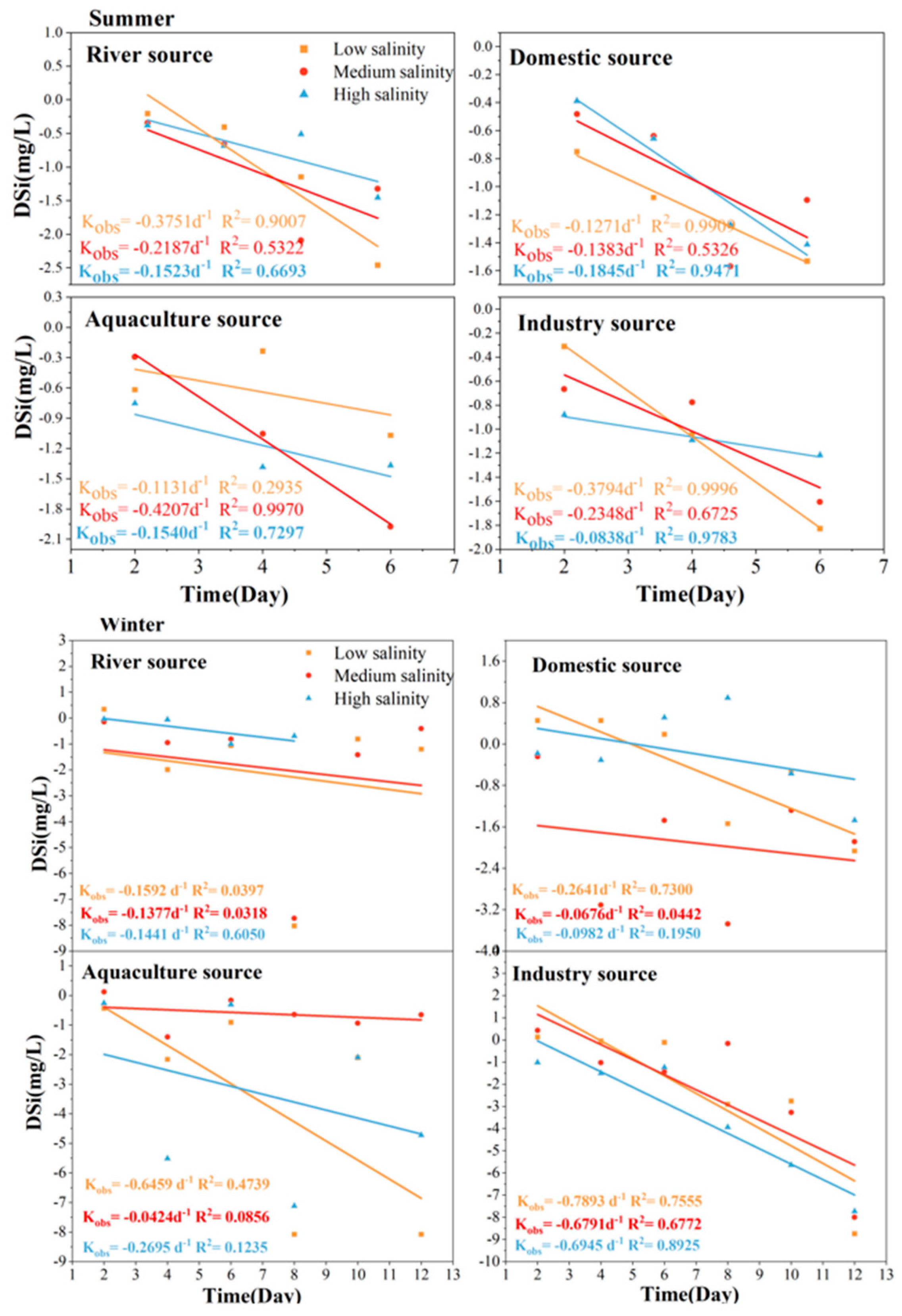
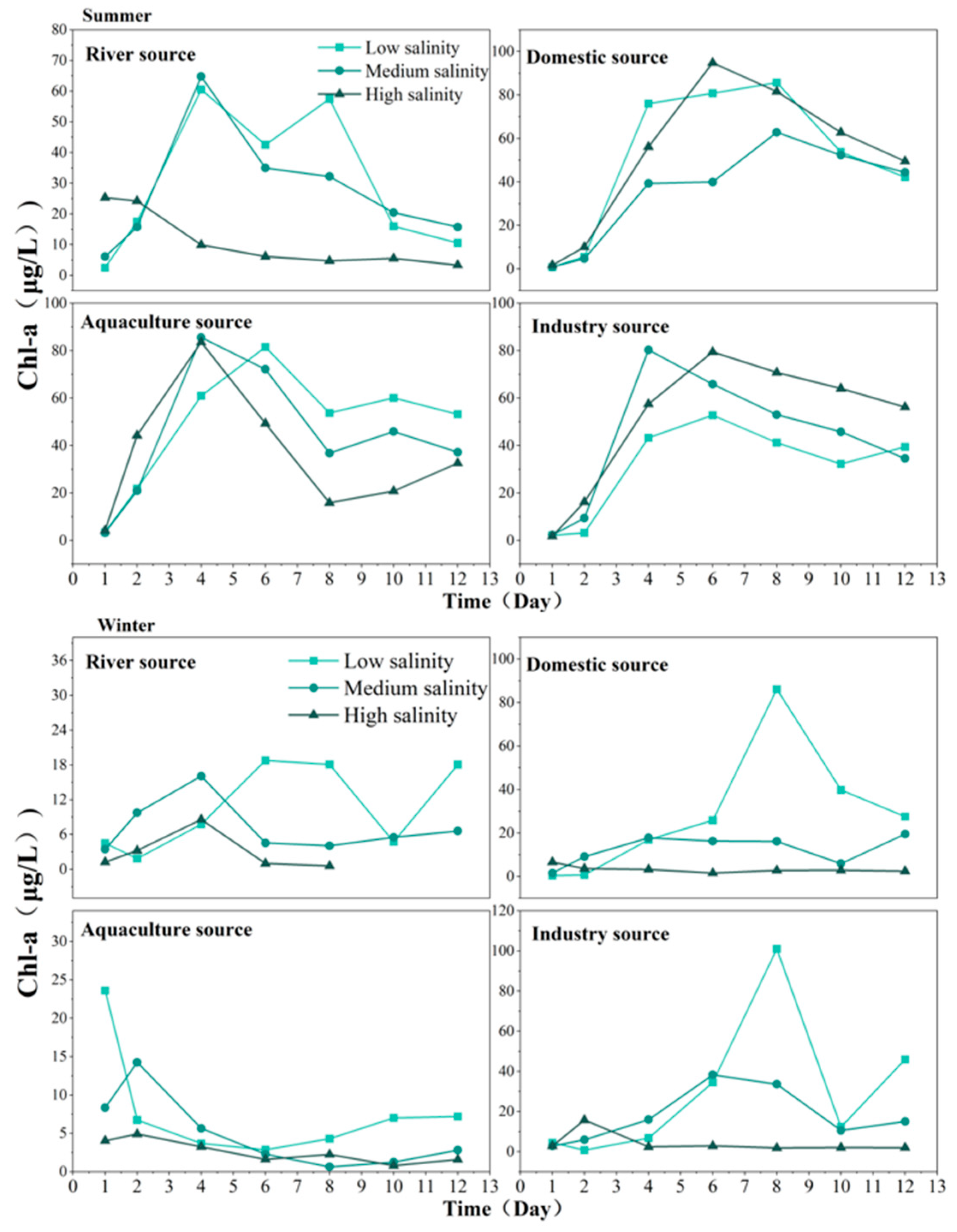


| River Sources | Domestic Sources | Aquaculture Sources | Industrial Sources | Mixed Sea Water | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature (°C) | 31.2 | 32.5 | 31.5 | 41.8 | 30.9 |
| Salinity (PSU) | 0.5 | 0.8 | 28.8 | 6.3 | 27 |
| DO (mg/L) | 7.06 | 6.76 | 6.62 | 5.1 | 6.3 |
| pH | 7.8 | 8.09 | 8.16 | 7.3 | 7.66 |
| Turbidity (NTU) | 4.93 | 2.01 | 5.88 | 65.3 | 2.87 |
| Station | Estuaries and Outfalls from Land-Based Sources | Longitudes/°E | Latitude/°N | Different Sources |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | Fozi river | 109.4658 | 21.6733 | River sources |
| S2 | Guangxi Beihai City, Tieshan Port District sewage treatment plant | 109.5648 | 21.5243 | Domestic sources |
| S3 | TSB Zhengang Aquaculture | 109.4798 | 21.4794 | Aquaculture sources |
| S4 | Sinopec Beihai Refining & Chemical company | 109.5158 | 21.4981 | Industrial sources |
| Different Sources of Pollution | Salinity Settings After Mixing with Seawater (PSU) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| River sources | 10 | 18 | 25 |
| Domestic sources | 10 | 18 | 25 |
| Aquaculture sources | 20 | 23 | 25 |
| Industrial sources | 10 | 18 | 25 |
| Different Sources of Pollution | Mixed Salinity | Temperature (°C) | DO (mg/L) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| River source | Low salinity | 30.59 ± 1.15 | 7.88 ± 1.01 | 8.87 ± 1.03 |
| Medium salinity | 30.83 ± 1.45 | 7.80 ± 2.15 | 8.82 ± 1.02 | |
| High salinity | 31.01 ± 1.66 | 8.40 ± 4.40 | 8.86 ± 1.07 | |
| Domestic source | Low salinity | 31.04 ± 2.26 | 8.80 ± 3.00 | 8.92 ± 1.19 |
| Medium salinity | 30.79 ± 2.50 | 8.42 ± 3.23 | 8.78 ± 0.98 | |
| High salinity | 30.91 ± 1.91 | 8.93 ± 3.53 | 8.83 ± 1.07 | |
| Aquaculture source | Low salinity | 31.06 ± 2.26 | 8.64 ± 3.34 | 8.82 ± 1.15 |
| Medium salinity | 31.31 ± 2.50 | 8.31 ± 4.00 | 8.74 ± 1.14 | |
| High salinity | 31.17 ± 1.90 | 8.70 ± 2.97 | 8.65 ± 0.83 | |
| Industrial source | Low salinity | 31.07 ± 2.43 | 6.79 ± 1.80 | 8.73 ± 1.45 |
| Medium salinity | 31.09 ± 1.56 | 8.55 ± 3.06 | 8.79 ± 1.07 | |
| High salinity | 31.14 ± 1.91 | 8.19 ± 2.17 | 8.75 ± 1.04 |
| Different Sources of Pollution | Mixed Salinity | Temperature (°C) | DO (mg/L) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| River source | Low salinity | 21.61 ± 1.18 | 8.54 ± 1.60 | 8.34 ± 0.72 |
| Medium salinity | 21.4 ± 1.64 | 7.77 ± 1.07 | 7.80 ± 0.53 | |
| High salinity | 20.93 ± 0.95 | 8.33 ± 0.661 | 7.77 ± 0.19 | |
| Domestic sources | Low salinity | 21.49 ± 1.06 | 9.55 ± 1.49 | 8.59 ± 1.02 |
| Medium salinity | 21.32 ± 1.07 | 8.05 ± 1.82 | 8.29 ± 0.56 | |
| High salinity | 21.28 ± 1.06 | 7.23 ± 0.89 | 8.08 ± 0.26 | |
| Aquaculture sources | Low salinity | 21.20 ± 0.95 | 7.61 ± 0.96 | 7.96 ± 0.27 |
| Medium salinity | 21.20 ± 0.96 | 7.86 ± 21.06 | 8.05 ± 0.32 | |
| High salinity | 21.23 ± 0.98 | 7.73 ± 0.61 | 7.79 ± 0.19 | |
| Industrial source | Low salinity | 21.15 ± 0.92 | 8.97 ± 1.73 | 8.53 ± 0.54 |
| Medium salinity | 21.21 ± 0.95 | 7.85 ± 1.91 | 8.16 ± 0.33 | |
| High salinity | 21.37 ± 1.22 | 7.54 ± 1.01 | 7.85 ± 0.15 |
| Different Sources of Pollution | Average DIN Self-Purification (d−1) | Average DIP Self-Purification (d−1) | Average DSi Self-Purification (d−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Summer | |||
| River source | −0.3244 ± 0.17 | −0.3688 ± 0.06 | −0.1499 ± 0.03 |
| Domestic source | −0.3122 ± 0.22 | −0.3351 ± 0.06 | −0.2487 ± 0.11 |
| Aquaculture source | −0.2971 ± 0.11 | −0.1591 ± 0.03 | −0.2293 ± 0.17 |
| Industry source | −0.1369 ± 0.09 | −0.4332 ± 0.20 | −0.2327 ± 0.15 |
| Winter | |||
| River source | −0.0717 ± 0.03 | −0.0921 ± 0.06 | −0.1470 ± 0.01 |
| Domestic source | −0.0646 ± 0.08 | −0.0930 ± 0.15 | −0.1433 ± 0.11 |
| Aquaculture source | −0.0909 ± 0.05 | −0.0734 ± 0.00 | −0.3193 ± 0.31 |
| Industry source | −0.1541 ± 0.24 | −0.1205 ± 0.07 | −0.7109 ± 0.06 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, F.; Zhang, P.; He, Y.; Long, H.; Zhang, J.; Lu, D.; Ren, C. Seasonal Self-Purification Process of Nutrients Entering Coastal Water from Land-Based Sources in Tieshan Bay, China: Insights from Incubation Experiments. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 1133. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13061133
Xu F, Zhang P, He Y, Long H, Zhang J, Lu D, Ren C. Seasonal Self-Purification Process of Nutrients Entering Coastal Water from Land-Based Sources in Tieshan Bay, China: Insights from Incubation Experiments. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(6):1133. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13061133
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Fang, Peng Zhang, Yingxian He, Huizi Long, Jibiao Zhang, Dongliang Lu, and Chaoxing Ren. 2025. "Seasonal Self-Purification Process of Nutrients Entering Coastal Water from Land-Based Sources in Tieshan Bay, China: Insights from Incubation Experiments" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 6: 1133. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13061133
APA StyleXu, F., Zhang, P., He, Y., Long, H., Zhang, J., Lu, D., & Ren, C. (2025). Seasonal Self-Purification Process of Nutrients Entering Coastal Water from Land-Based Sources in Tieshan Bay, China: Insights from Incubation Experiments. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(6), 1133. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13061133





