Biosynthesis and Bioactivity of Melanin from the Deep-Sea Hydrothermal Vent Yeast Hortaea werneckii Mo34
Abstract
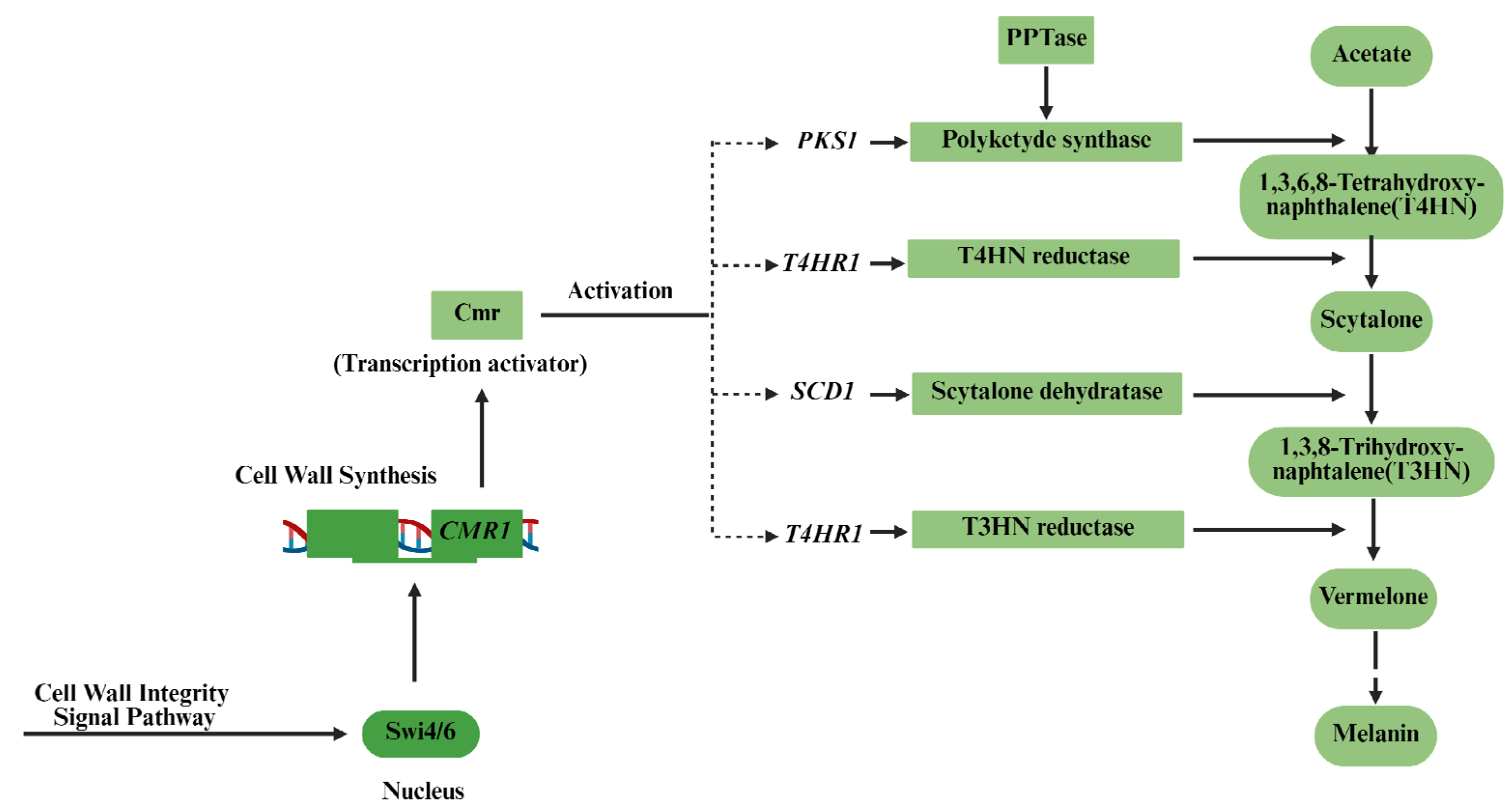
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Microbial Strains, Media and Plasmids
2.2. Construction of the Recombinant Plasmids Carrying the Native NR-PKS Gene and the Native CMR1 Gene Cloned from the Genomic DNA of H. werneckii Mo34
2.3. Total RNA Extraction and cDNA Obtainment
2.4. Construction of the Expression Vectors Carrying Coding Sequences (CDSs) of PKS1-2 Genes and CMR1-2 Genes
2.5. Transformation and Isolation of the Transformants
2.6. Confirmation of the Inserted NAT Gene in the Transformants
2.7. Extraction and Quantitative Determination of Melanin
2.8. Determination of the Transcriptional Levels of the Relevant Genes for Melanin Biosynthesis
2.9. Melanin Production by H. werneckii Mo34, Extraction and Purification of Melanin
2.10. Solubility of the Purified Melanin
2.11. Fourier-Transform Infrared Analysis of the Purified Melanin
2.12. Determination of the Fe2+-Chelating Ability of the Purified Melanin
2.13. Measurement of Superoxide-Radical Scavenging Activity
2.14. Assay of 1,1-Diphenyl-2-picryl-hydrazyl (DPPH) Radical-Scavenging Activity
2.15. Assay of Antibacterial Activity of the Purified Melanin
2.16. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
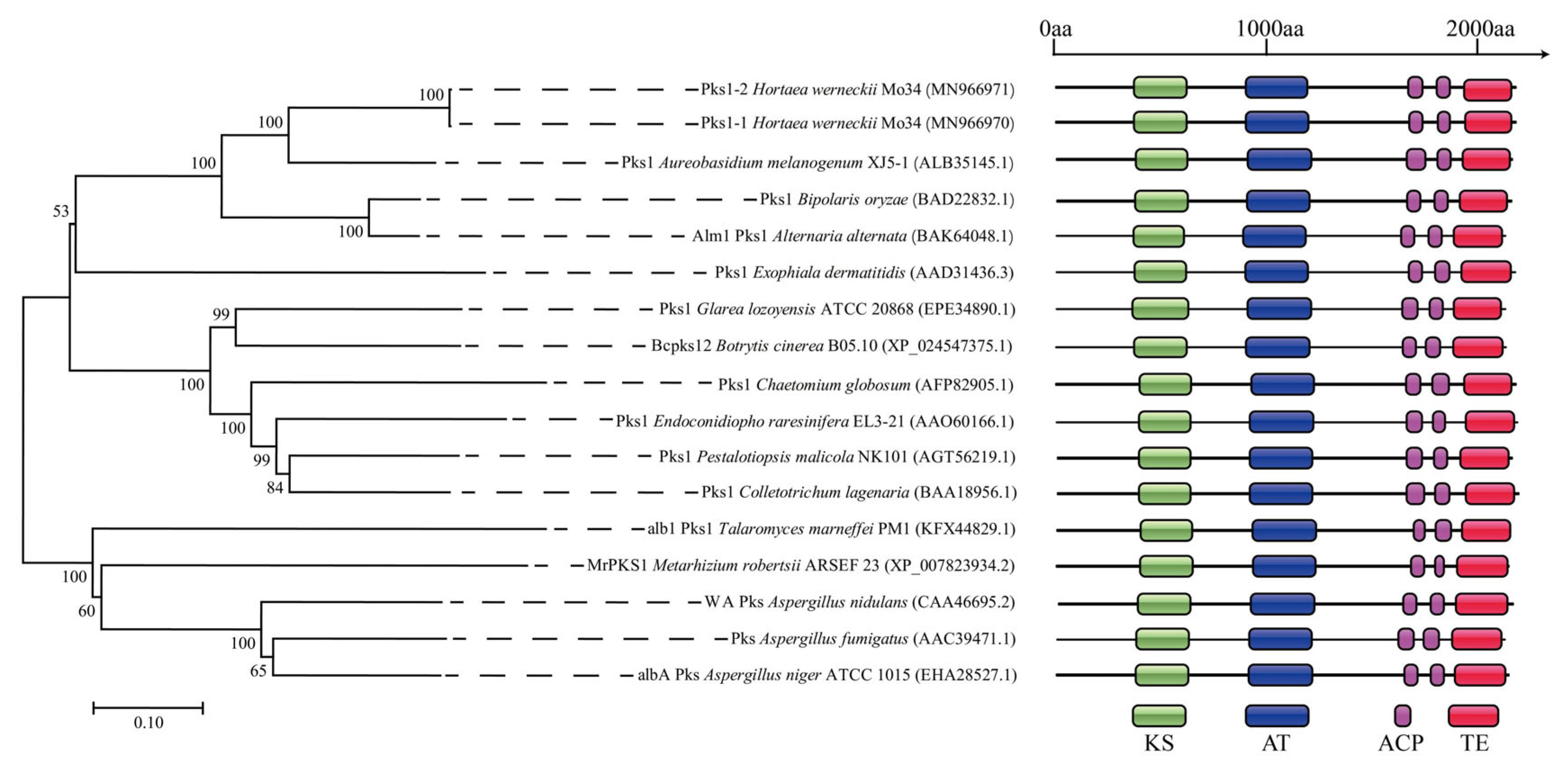
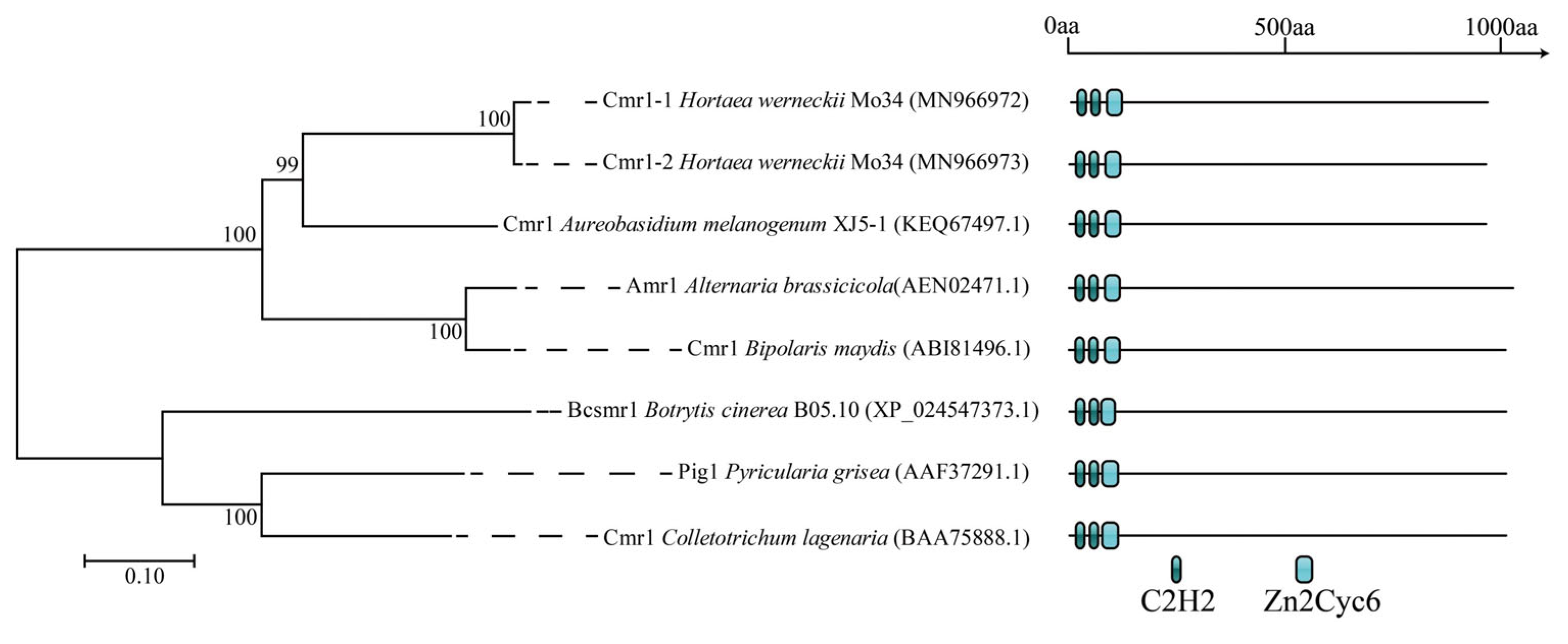
3.1. Characterization of the PKS1-1, PKS1-2, CMR1-1, and CMR1-2 Genes from H. werneckii Mo34
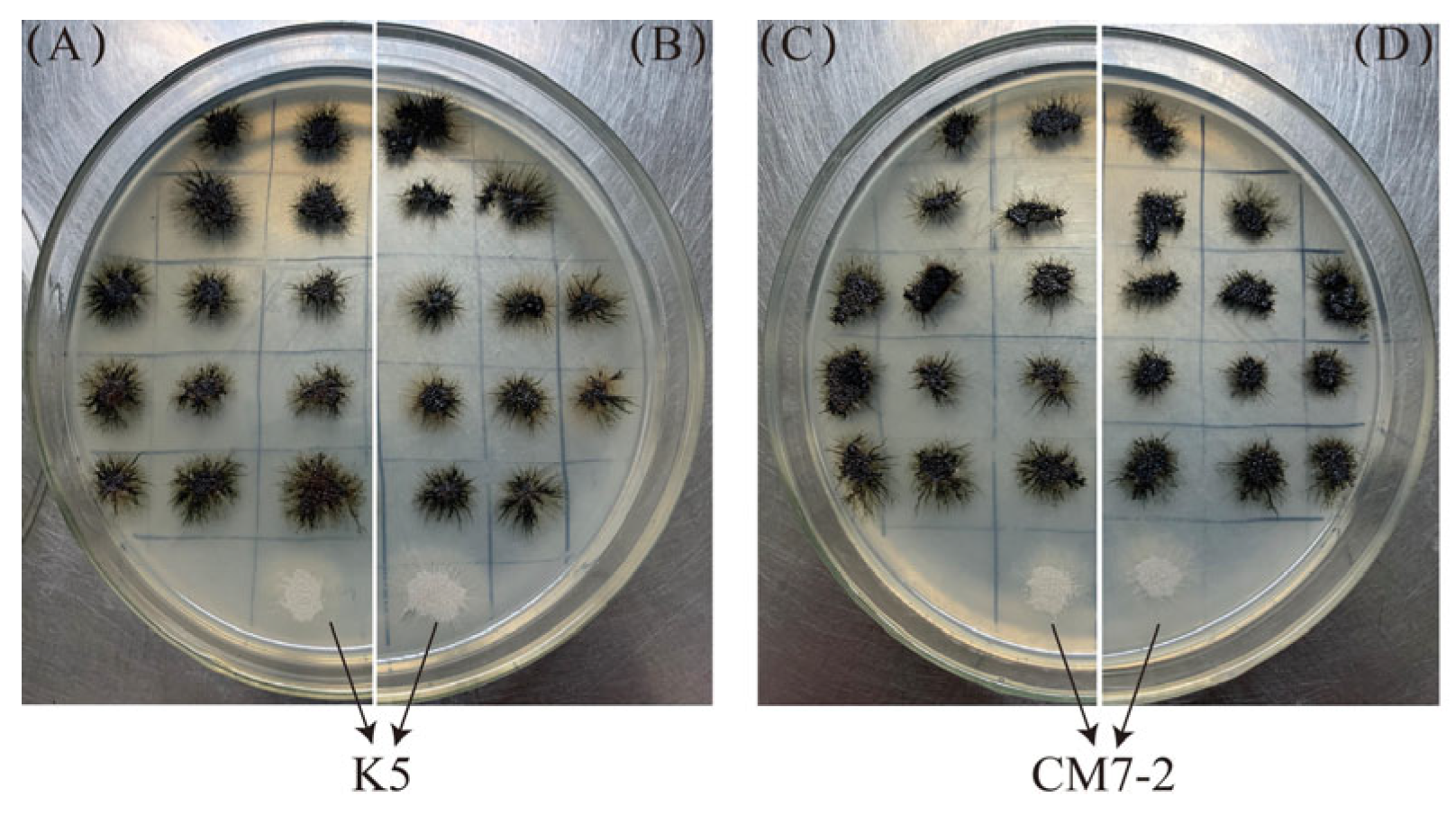
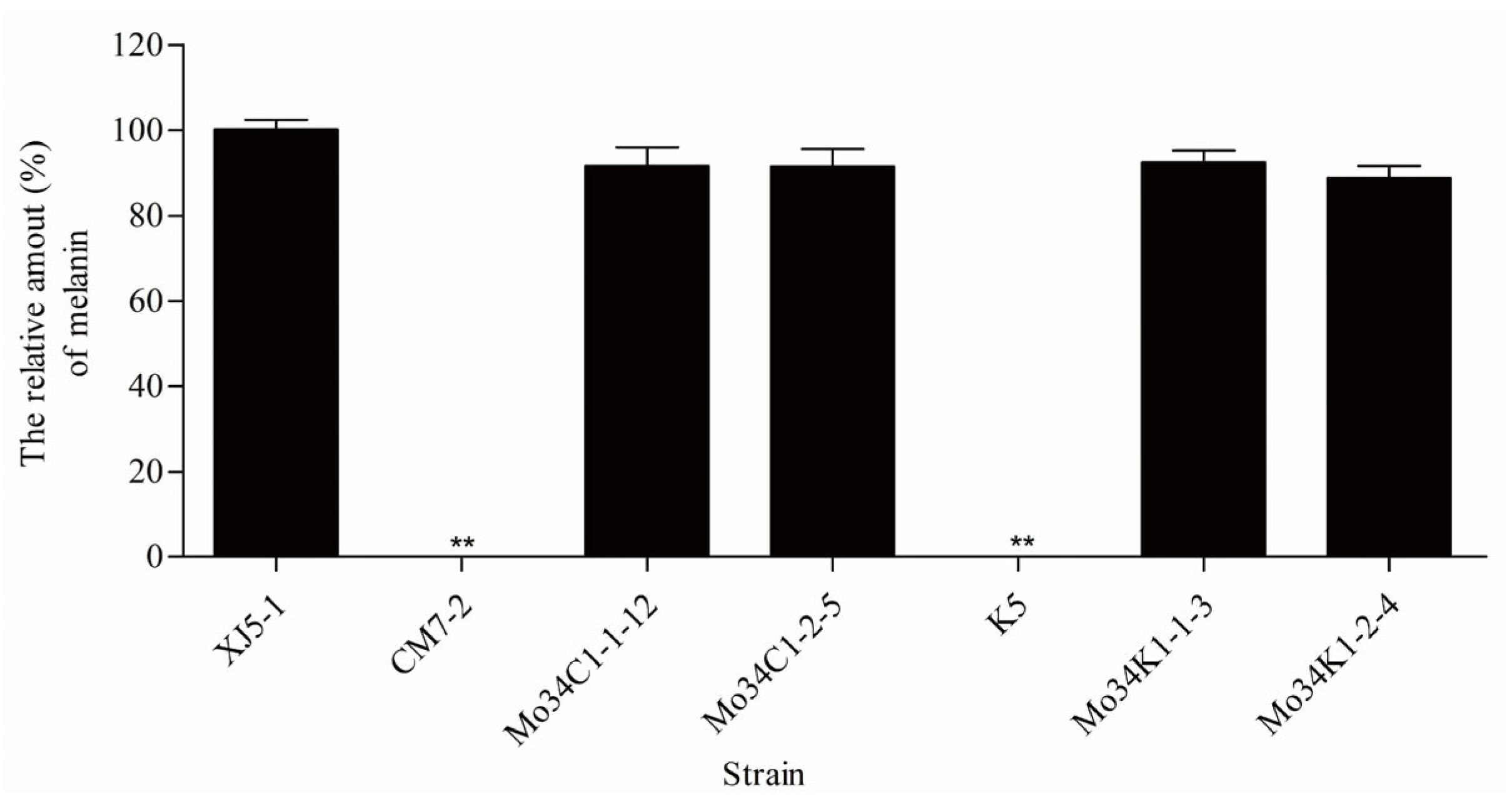
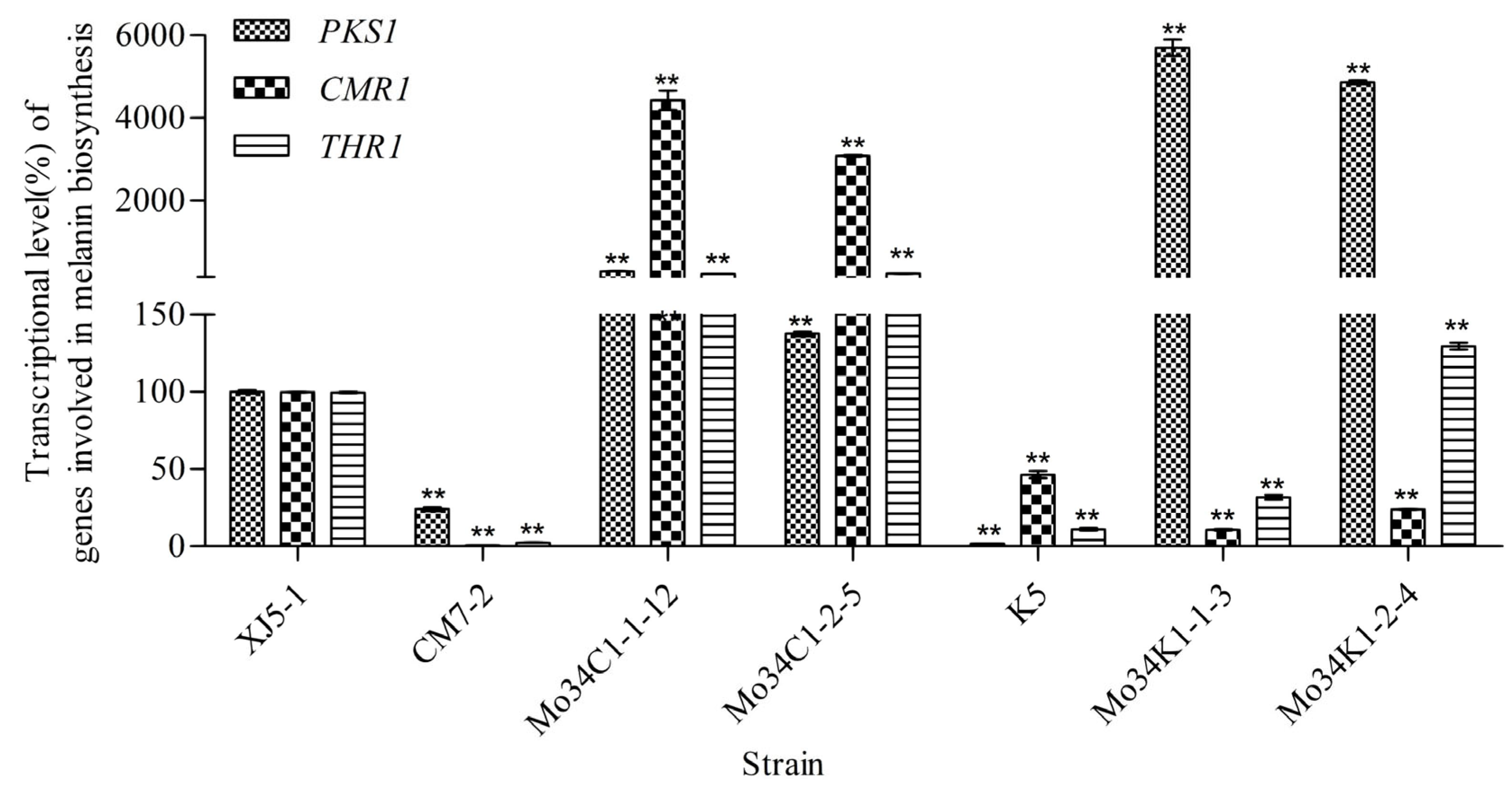
3.2. Expression of the PKS1-1, PKS1-2, CMR1-1, and CMR1-2 Genes from H. werneckii Mo34 in the Albino Mutants of A. melanogenum XJ5-1
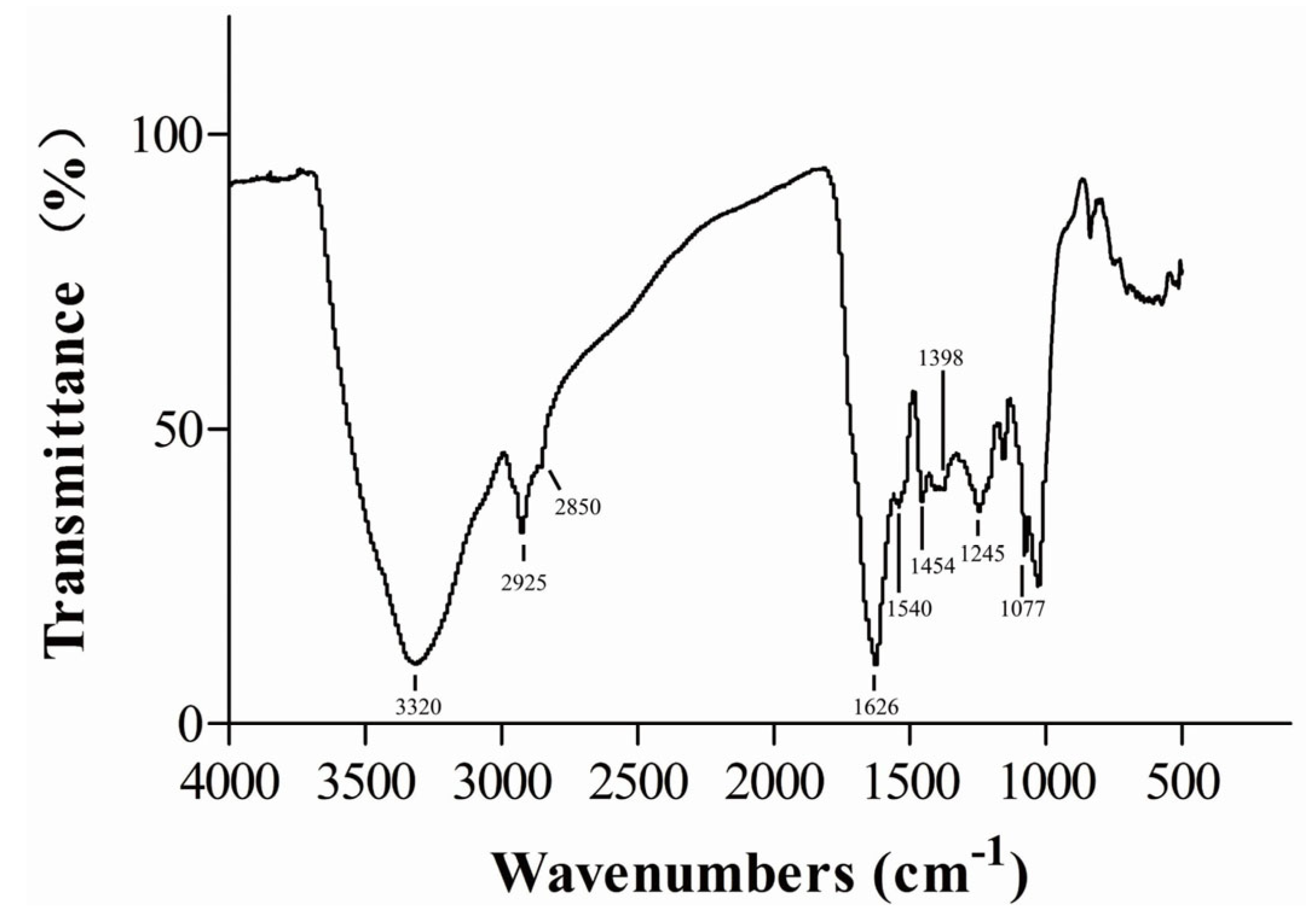
3.3. Chemical and Physical Properties of Melanin Produced by H. werneckii Mo34
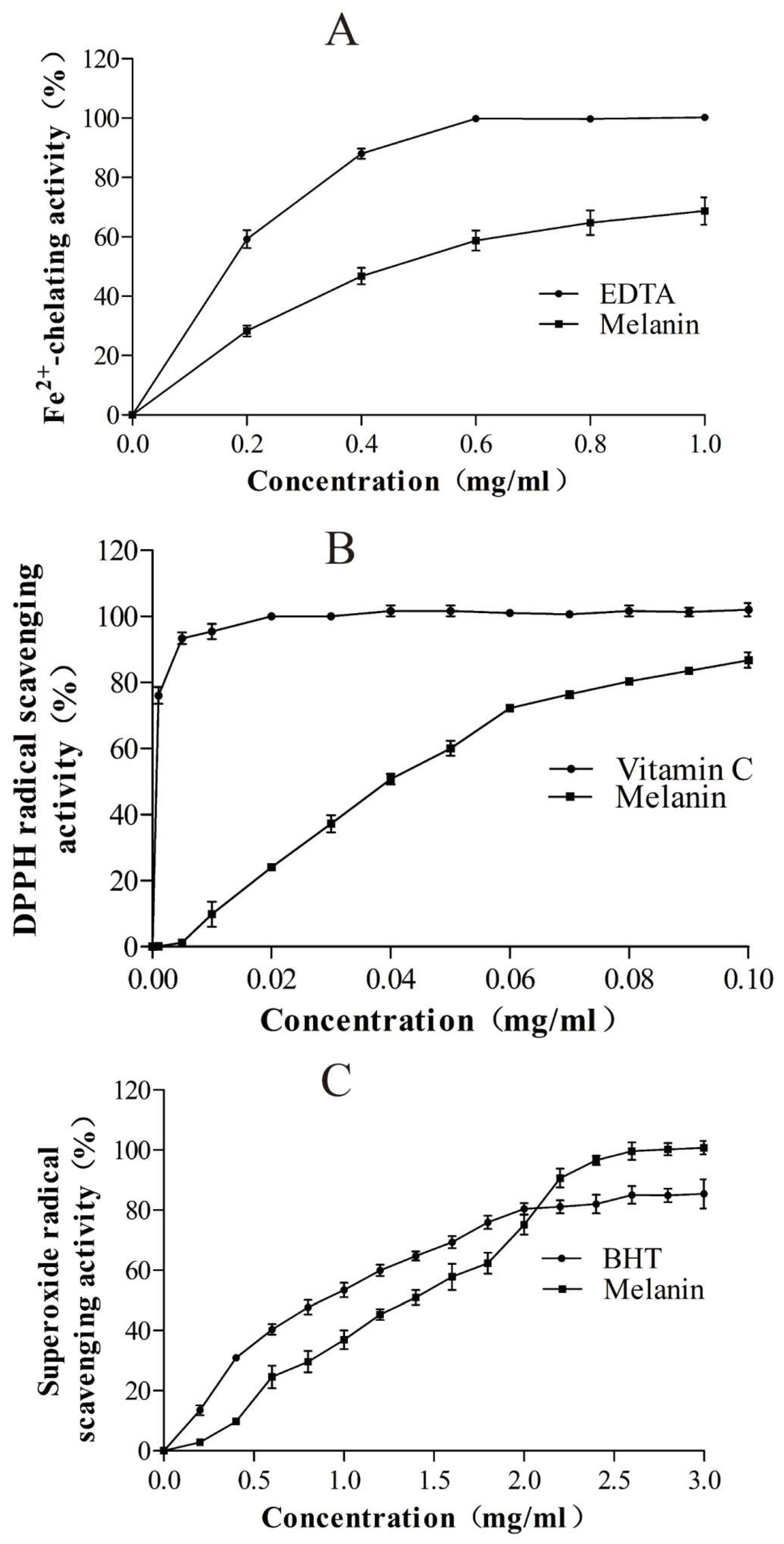
3.4. Bioactivity of the Purified Melanin
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mitchison-Field, L.M.Y.; JVargas-Muniz, J.M.; Stormo, B.M.; Lew, D.J.; Field, C.M.; Gladfelter, A.S. Unconventional cell division cycles from marine derived yeasts. Curr. Biol. 2019, 29, 3439–3456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenassi, M.; Gostincar, C.; Jackman, S.; Turk, M.; Sadowsk, I.; Nislo, C.; Jones, S.; Biro, I.; Gunde-Cimerman, N.; Plemenitas, A. Whole genome duplication and enrichment of metal cation transporters revealed by De Novo genome sequencing of extremely halotolerant black yeast Hortaea werneckii. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romeo, O.; Marchetta, A.; Giosa, D.; Giuffrè, L.; Urzì, C.; De Leo, F. Whole genome sequencing and comparative genome analysis of the halotolerant deep sea black yeast Hortaea werneckii. Life 2020, 10, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, M.; Zhang, K.; Hu, J.; Huang, X.; Fan, G.; Grossart, H.P.; Luo, Z. Complete genome sequencing of Hortaea werneckii M-3 for identifying polyester polyurethane degrading enzymes. Mar. Genom. 2024, 75, 101111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochereau, B.; Le Strat, Y.; Ji, Q.; Pawtowski, A.; Delage Amélie Weill, L.; Mazéas, L.; Hervé, C.; Burgaud, G.; Gunde-Cimerman, N.; François Pouchus, Y.; et al. Heterologous expression and biochemical characterization of a new chloroperoxidase isolated from the deep-sea hydrothermal vent black yeast Hortaea werneckii UBOCC-A-208029. Mar. Biotechnol. 2023, 25, 519–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gostinčar, C.; Gunde-Cimerman, N. Black yeasts in hypersaline conditions. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 108, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayis, A.; Hassan, S.W.M.; Ghanem, K.M.; Khairy, H. Optimization of melanin pigment production from the halotolerant black yeast Hortaea werneckii AS1 isolated from solar salter in Alexandria. BMC Microbiol. 2022, 22, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salah El-Din Hodhod, M.; Zakaria Gaafar, A.; Alshameri, A.; Qahtan, A.A.; Abdulrahman Noor, A.; Abdel-Wahab, M. Molecular characterization and bioactive potential of newly identified strains of the extremophilic black yeast Hortaea werneckii isolated from red sea mangrove. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2020, 34, 1288–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Chi, Z.; Liu, G.L.; Hu, Z.; Zhao, S.Z.; Chi, Z.M. Melanin biosynthesis in the desert-derived Aureobasidium melanogenum XJ5-1 is controlled mainly by the CWI signal pathway via a transcriptional activator Cmr1. Curr. Genet. 2020, 66, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Z.; Wei, X.; Ge, N.; Jiang, H.; Liu, G.L.; Chi, Z.M. NsdD, a GATA-type transcription factor is involved in regulation and biosynthesis of macromolecules melanin, pullulan, and polymalate in Aureobasidium melanogenum. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 268, 131820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgaud, G.; Arzur, D.; Durand, L.; Cambon-Bonavita, M.A.; Barbie, G. Marine culturable yeasts in deep-sea hydrothermal vents: Species richness and association with fauna. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2010, 73, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, Z.; Wang, X.X.; Ma, Z.C.; Buzdar, M.A.; Chi, Z.M. The unique role of siderophore in marine-derived Aureobasidium pullulans HN6.2. Biometals 2012, 25, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.L.; Wang, D.S.; Wang, L.F.; Zhao, S.F.; Chi, Z.M. Mig1 is involved in mycelial formation and expression of the genes encoding extracellular enzymes in Saccharomycopsis fibuligera A11. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2011, 48, 904–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.C.; Liu, N.N.; Chi, Z.; Liu, G.L.; Chi, Z.M. Genetic modification of the marine-isolated yeast Aureobasidium melanogenum P16 for efficient pullulan production from inulin. Mar. Biotechnol. 2015, 17, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, W.; Lowman, D.; Puthumana, J.; Kuriakose, R.; Bright Singh, I.S.; Philip, R. Biocompatible melanin from the marine black yeast Hortaea werneckii R23 with antioxidant and photoprotection property. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2024, 55, 3171–3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogej, T.; Wheeler, M.H.; Lanisnik Rizner, T.; Gunde-Cimerman, N. Evidence for 1,8-dihydroxynaphthalene melanin in three halophilic black yeasts grown under saline and non-saline conditions. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2004, 232, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beld, J.; Sonnenschein, E.C.; Vickery, R.V.; Noel, J.P.; Burkart, M.D. The phosphopantetheinyl transferases: Catalysis of a post-translational modification crucial for life. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2014, 31, 61–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, G.; Takano, T.K.Y.; Sweigard, J.; Sweigard, J.; Farrall, L.; Furusawa, I.; Horino, O.; Kubo, Y. Novel fungal transcriptional activators, Cmr1p of Colletotrichum lagenarium and Pig1p of Magnaporthe grisea, contain Cys2His2 zinc finger and Zn(II)2Cys6 binuclear cluster DNA-binding motifs and regulate transcription. Mol. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 940–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, N.; Ramasamy, S. Genetic validation and spectroscopic detailing of DHN-melanin extracted from an environmental fungus. Biochem. Biophy. Rep. 2017, 12, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryanarayanan, T.S.; Ravishankar, J.P.; Venkatesan, G.; Murali, T.S. Characterization of the melanin pigment of a cosmopolitan fungal endophyte. Mycol. Res. 2004, 108, 974–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Hu, W.; Ma, K. Physicochemical properties and antioxidant activities of melanin and fractions from Auricularia auricula fruiting bodies. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2015, 24, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Li, Y. Metal ions driven production, characterization and bioactivity of extracellular melanin from Streptomyces sp. ZL-24. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 123, 521–530. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Li, J.; Yang, L. Antibacterial activity and a membrane damage mechanism of Lachnum YM30 melanin against Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Staphylococcus aureus. Food Control 2017, 73, 1445–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minasyan, E.; Aghajanyan, A.; Karapetyan, K.; Khachaturyan, N.; Hovhannisyan, G.; Yeghyan, K.; Tsatury, A. Antimicrobial activity of melanin isolated from wine waste. Indian J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 64, 1528–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Strain | Concentrations (mg/mL) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 | 0.15 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 1.0 | 2.0 | 3.0 | |
| S. saureus (G+) | +++ | ++ | + | - | - | - | - | - |
| B. subtilis (G+) | +++ | ++ | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| P. putida (G−) | +++ | ++ | + | + | + | - | - | - |
| V. harveyi (G−) | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | ++ | + |
| V. anguillarum (G−) | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | ++ | + |
| P. aeruginosa (G−) | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | ++ | ++ |
| A. baumannii (G−) | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | ++ |
| E. cloacae (G−) | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | ++ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.-J.; Chi, Z.-M. Biosynthesis and Bioactivity of Melanin from the Deep-Sea Hydrothermal Vent Yeast Hortaea werneckii Mo34. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 1004. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13061004
Li H-J, Chi Z-M. Biosynthesis and Bioactivity of Melanin from the Deep-Sea Hydrothermal Vent Yeast Hortaea werneckii Mo34. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(6):1004. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13061004
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Hui-Juan, and Zhen-Ming Chi. 2025. "Biosynthesis and Bioactivity of Melanin from the Deep-Sea Hydrothermal Vent Yeast Hortaea werneckii Mo34" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 6: 1004. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13061004
APA StyleLi, H.-J., & Chi, Z.-M. (2025). Biosynthesis and Bioactivity of Melanin from the Deep-Sea Hydrothermal Vent Yeast Hortaea werneckii Mo34. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(6), 1004. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13061004






