Vertical Deformation Extraction Using Joint Track SBAS-InSAR Along Coastal California, USA
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
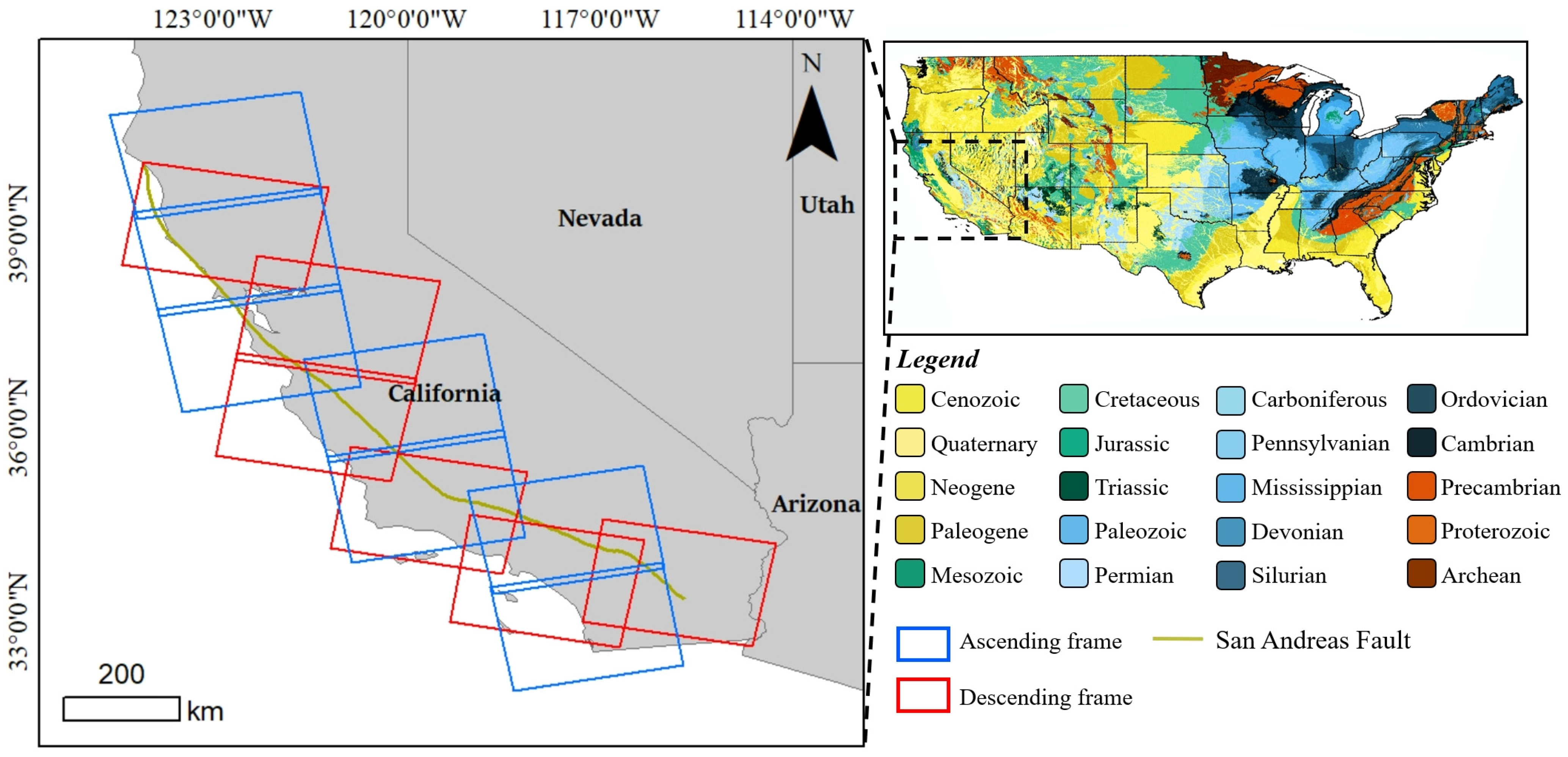
2.1. Study Area and Data
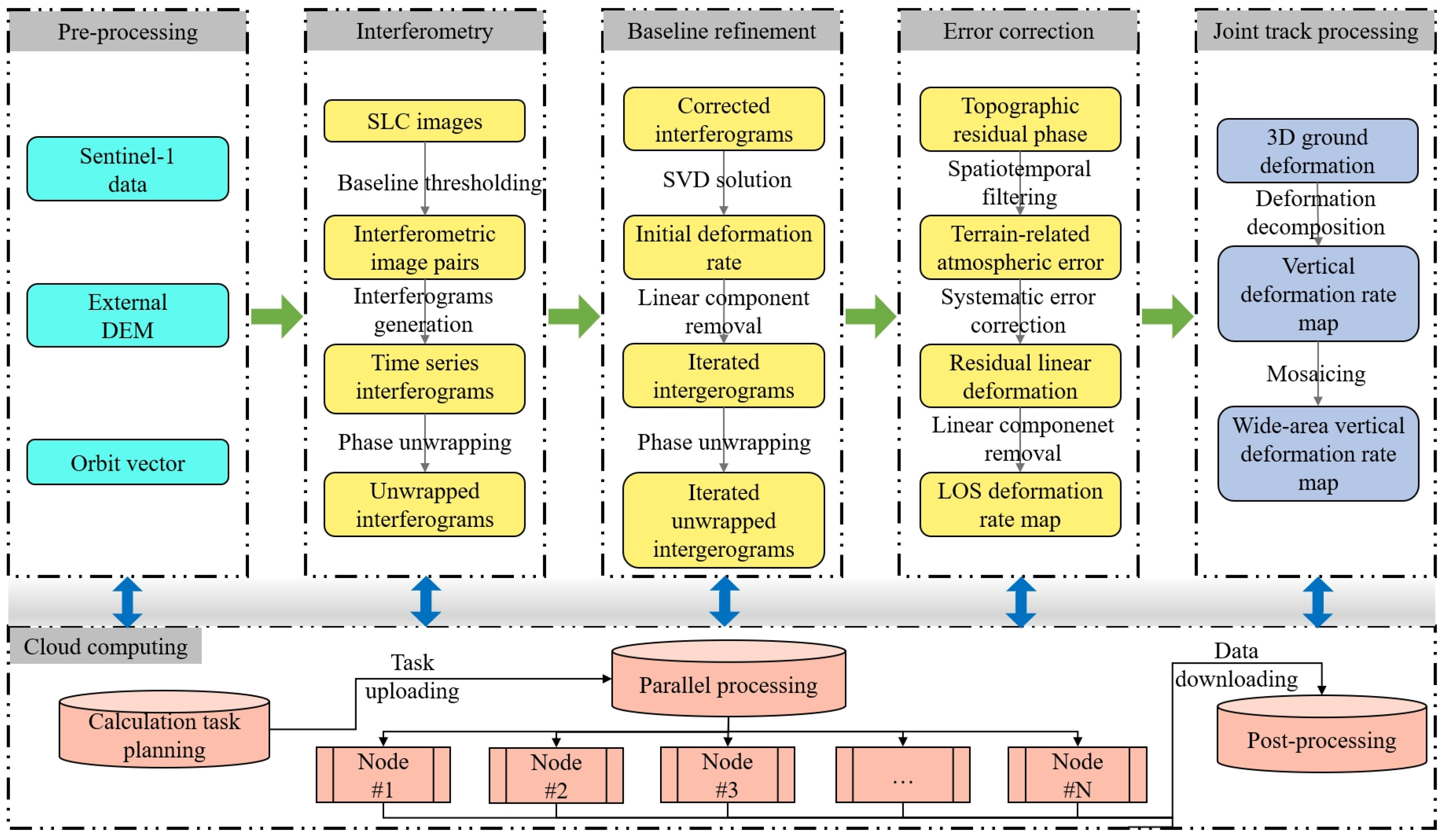
2.2. Methods
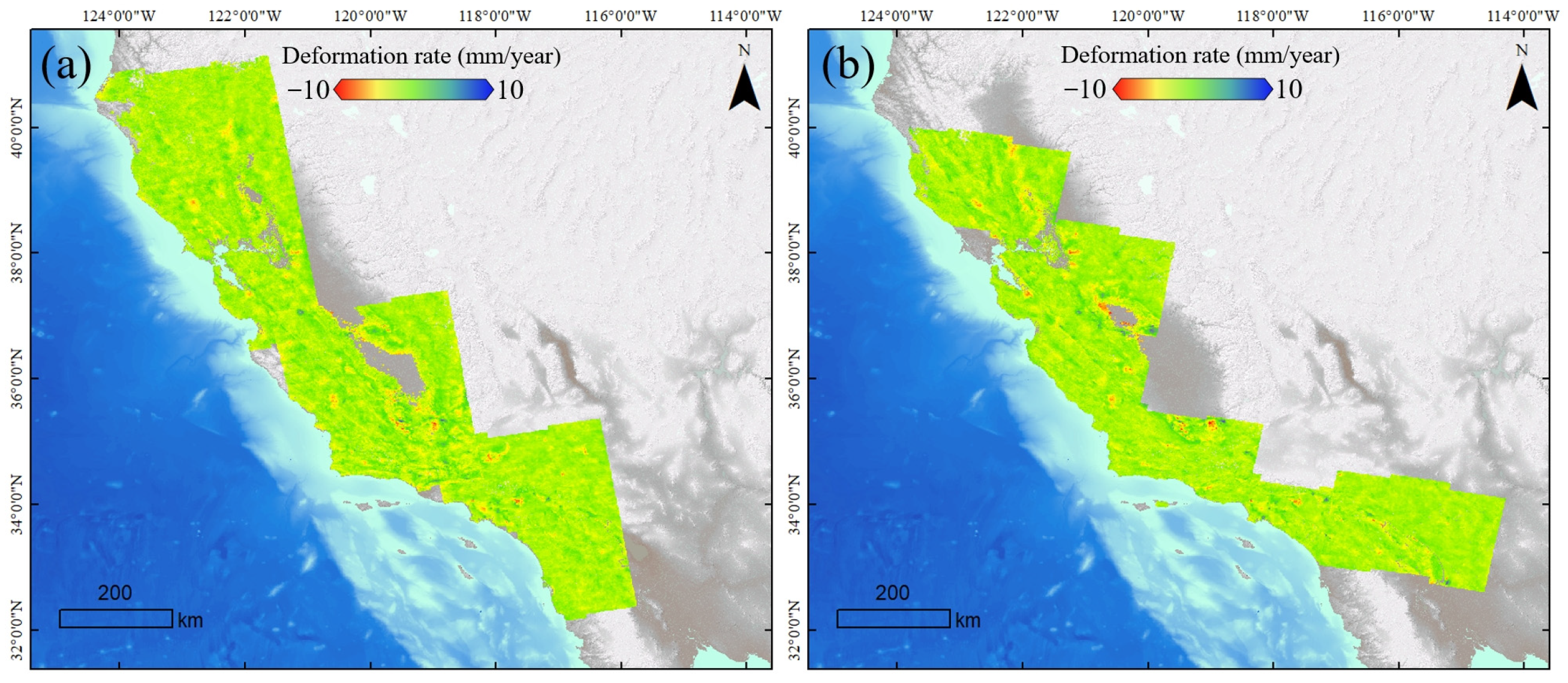
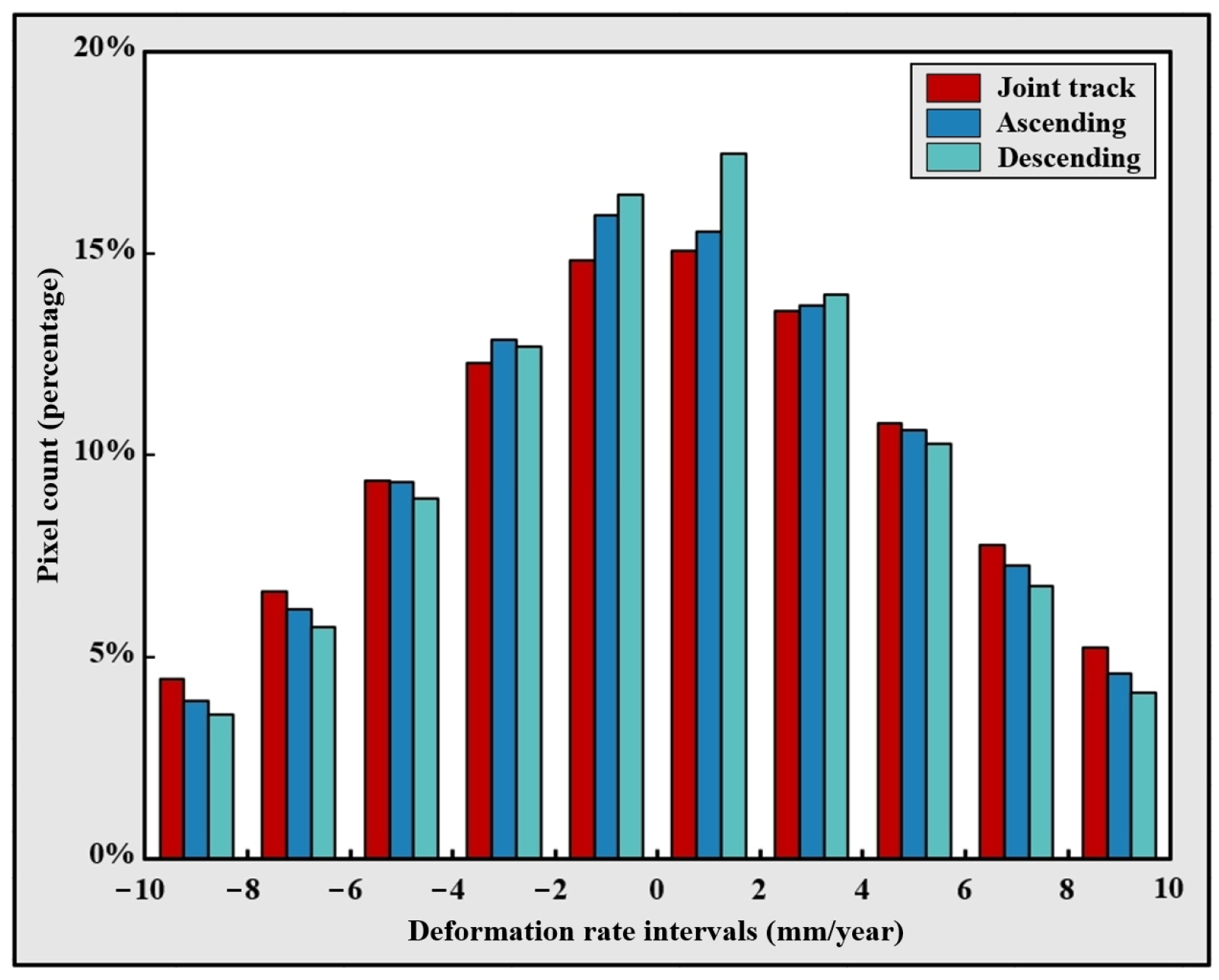
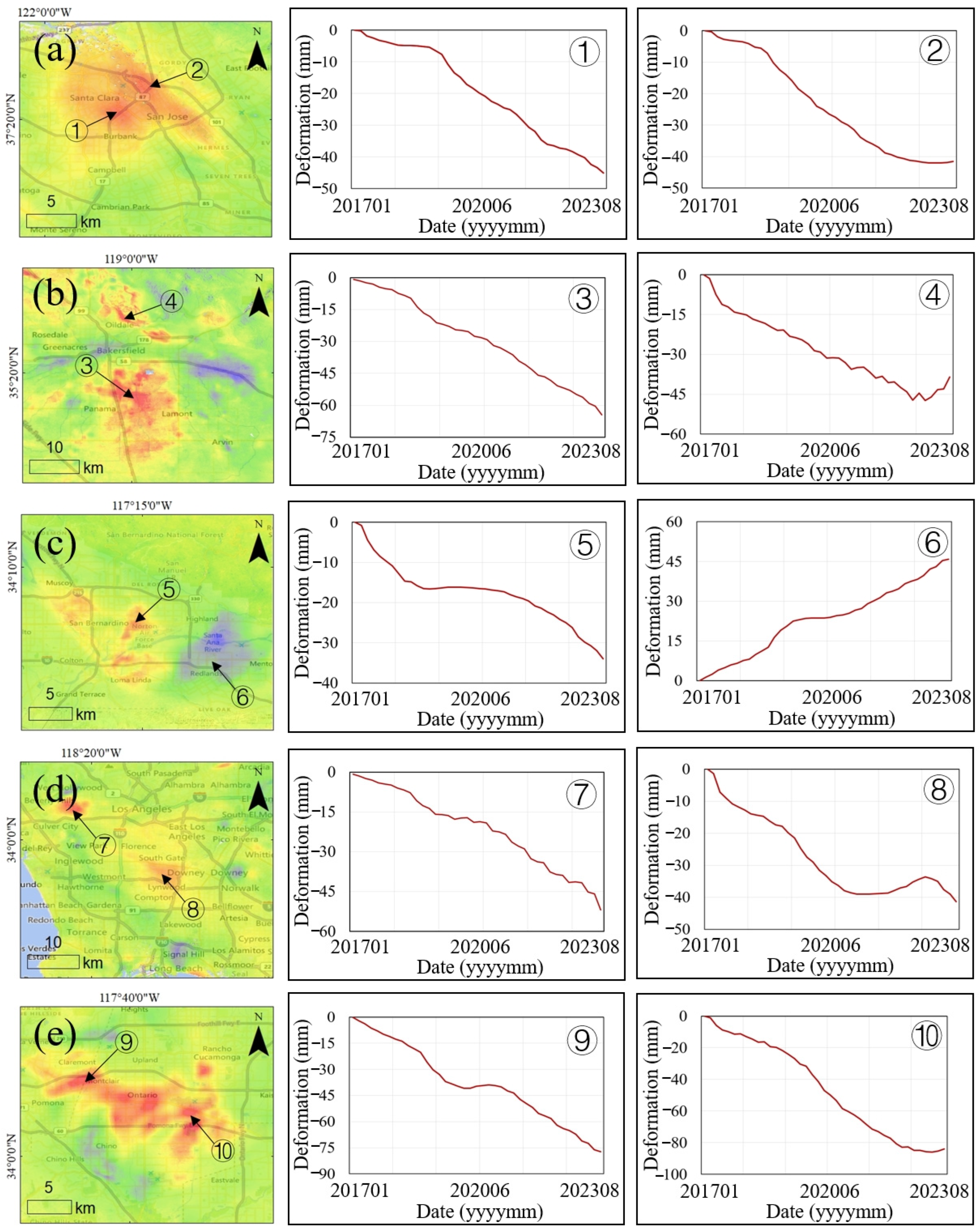
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Herrera-García, G.; Ezquerro, P.; Tomás, R.; Béjar-Pizarro, M.; López-Vinielles, J.; Rossi, M.; Mateos, R.M.; Carreón-Freyre, D.; Lambert, J.; Teatini, P.; et al. Mapping the global threat of land subsidence. Science 2021, 371, 34–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adebisi, N.; Balogun, A.-L.; Min, T.H.; Tella, A. Advances in estimating Sea Level Rise: A review of tide gauge, satellite altimetry and spatial data science approaches. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2021, 208, 105632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, C.; Lindsey, E.O.; Chin, S.T.; McCaughey, J.W.; Bekaert, D.; Nguyen, M.; Hua, H.; Manipon, G.; Karim, M.; Horton, B.P.; et al. Sea-level rise from land subsidence in major coastal cities. Nat. Sustain. 2022, 5, 1049–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haer, T.; Kalnay, E.; Kearney, M.; Moll, H. Relative sea-level rise and the conterminous United States: Consequences of potential land inundation in terms of population at risk and GDP loss. Glob. Environ. Change 2013, 23, 1627–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellazzi, P.; Martel, R.; Rivera, A.; Huang, J.; Pavlic, G.; Calderhead, A.I.; Chaussard, E.; Garfias, J.; Salas, J. Groundwater depletion in Central Mexico: Use of GRACE and InSAR to support water resources management. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 528, 5985–6003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, G.; Schmid, W.; Castellazzi, P. Understanding the Spatial Variability of the Relationship between InSAR-Derived Deformation and Groundwater Level Using Machine Learning. Geosciences 2023, 13, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andriolo, U.; Gonçalves, G. Is coastal erosion a source of marine litter pollution? Evidence of coastal dunes being a reservoir of plastics. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 174, 113307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, J.H.; Spencer, K.L. Potential contamination of the coastal zone by eroding historic landfills. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 146, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirzaei, M.; Bürgmann, R. Global climate change and local land subsidence exacerbate inundation risk to the San Francisco Bay Area. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaap9234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweet, W.V.; Hamlington, B.D.; Kopp, R.E.; Weaver, C.P.; Barnard, P.L.; Bekaert, D.; Brooks, W.; Craghan, M.; Dusek, G.; Frederikse, T.; et al. Global and Regional Sea Level Rise Scenarios for the United States: Updated Mean Projections and Extreme Water Level Probabilities along U.S. Coastlines; NOAA Technical Report NOS 01; National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wöppelmann, G.; Marcos, M. Vertical land motion as a key to understanding sea level change and variability. Rev. Geophys. 2016, 54, 64–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackwell, E.; Shirzaei, M.; Ojha, C.; Werth, S. Tracking California’s sinking coast from space: Implications for relative sea-level rise. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaba4551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Min, X.; Ye, T.; Li, X.; Hu, X. Monitoring the subsidence at different periods in high underground water level coal mine areas using differential interferometric synthetic aperture radar (D-InSAR). Geocarto Int. 2023, 38, 2215730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osmanoğlu, B.; Sunar, F.; Wdowinski, S.; Cabral-Cano, E. Time series analysis of InSAR data: Methods and trends. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 115, 90–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Soldato, M.; Confuorto, P.; Bianchini, S.; Sbarra, P.; Casagli, N. Review of Works Combining GNSS and InSAR in Europe. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Li, Z.; Ding, X.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, L.; Sun, Q. Resolving three-dimensional surface displacements from InSAR measurements: A review. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2014, 133, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talledo, D.A.; Miano, A.; Bonano, M.; Di Carlo, F.; Lanari, R.; Manunta, M.; Meda, A.; Mele, A.; Prota, A.; Saetta, A.; et al. Satellite radar interferometry: Potential and limitations for structural assessment and monitoring. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 46, 103756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, J. Shifting ground. Science 2021, 371, 876–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, T.J.; Parsons, B.; England, P.C.; Fielding, E.J. InSAR Observations of Low Slip Rates on the Major Faults of Western Tibet. Science 2004, 305, 236–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biggs, J.; Wright, T.J. How satellite InSAR has grown from opportunistic science to routine monitoring over the last decade. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drougkas, A.; Verstrynge, E.; Van Balen, K.; Shimoni, M.; Croonenborghs, T.; Hayen, R.; Declercq, P.-Y. Country-scale InSAR monitoring for settlement and uplift damage calculation in architectural heritage structures. Struct. Health Monit. 2021, 20, 2317–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teodosio, B.; Wasantha, P.L.P.; Yaghoubi, E.; Guerrieri, M.; Fragomeni, S.; van Staden, R.C. Monitoring of geohazards using differential interferometric satellite aperture radar in Australia. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2022, 43, 3769–3802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casagli, N.; Intrieri, E.; Tofani, V.; Gigli, G.; Raspini, F. Landslide detection, monitoring and prediction with remote-sensing techniques. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2023, 4, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cigna, F.; Tapete, D. Present-day land subsidence rates, surface faulting hazard and risk in Mexico City with 2014–2020 Sentinel-1 IW InSAR. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 253, 112161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasowski, J.; Bovenga, F. Investigating landslides and unstable slopes with satellite Multi Temporal Interferometry: Current issues and future perspectives. Eng. Geol. 2014, 174, 103–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulsoom, I.; Hua, W.; Hussain, S.; Chen, Q.; Khan, G.; Shihao, D. SBAS-InSAR based validated landslide susceptibility mapping along the Karakoram Highway: A case study of Gilgit-Baltistan, Pakistan. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 3344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, K.; Deng, J.; Xu, Q.; Li, Z.; Shi, X.; Hancock, C.; Wen, N.; Zhang, L.; Zhuo, G. Interpretation and sensitivity analysis of the InSAR line of sight displacements in landslide measurements. GIScience Remote Sens. 2022, 59, 1226–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohenhen, L.O.; Shirzaei, M.; Ojha, C.; Sherpa, S.F.; Nicholls, R.J. Disappearing cities on US coasts. Nature 2024, 627, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simms, A.; Reynolds, L.C.; Bentz, M.; Roman, A.; Rockwell, T.; Peters, R. Tectonic Subsidence of California Estuaries Increases Forecasts of Relative Sea-Level Rise. Estuaries Coasts 2016, 39, 1571–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsey, E.O.; Natsuaki, R.; Xu, X.; Shimada, M.; Hashimoto, M.; Melgar, D.; Sandwell, D.T. Line-of-sight displacement from ALOS-2 interferometry: Mw 7.8 Gorkha Earthquake and Mw 7.3 aftershock. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 6655–6661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, N.; Zhang, X.-N.; Wei, T.; Chen, Y.-F.; Zha, J.-F. Full parameters inversion model for mining subsidence prediction using simulated annealing based on single line of sight D-InSAR. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuhrmann, T.; Garthwaite, M.C. Resolving Three-Dimensional Surface Motion with InSAR: Constraints from Multi-Geometry Data Fusion. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Hu, J.; Li, Z.; Ma, Z.; Wu, L.; Jiang, W.; Feng, G.; Zhu, J. Complete three-dimensional coseismic displacements due to the 2021 Maduo earthquake in Qinghai Province, China from Sentinel-1 and ALOS-2 SAR images. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2022, 65, 687–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardino, P.; Fornaro, G.; Lanari, R.; Sansosti, E. A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline differential SAR interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2375–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, G.; Chen, Z.; Cui, H.; Zheng, Y.; Xu, Z.; Li, Q. Surface deformation extraction from small baseline subset synthetic aperture radar interferometry (SBAS-InSAR) using coherence-optimized baseline combinations. GIScience Remote Sens. 2022, 59, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunjun, Z.; Fattahi, H.; Amelung, F. Small baseline InSAR time series analysis: Unwrapping error correction and noise reduction. Comput. Geosci. 2019, 133, 104331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepe, A.; Euillades, L.D.; Manunta, M.; Lanari, R. New Advances of the Extended Minimum Cost Flow Phase Unwrapping Algorithm for SBAS-DInSAR Analysis at Full Spatial Resolution. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 4062–4079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Tile Identifier | Acquisition Dates 1 | Direction | Total Acquisitions | Tile Identifier | Acquisition Dates 1 | Direction | Total Acquisitions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P35F117 | 201701–202308 | Ascending | 163 | P42F467 | 201701–202308 | Descending | 188 |
| P35F122 | 163 | P42F472 | 188 | ||||
| P35F127 | 163 | P71F480 | 189 | ||||
| P64F103 | 176 | P115F462 | 190 | ||||
| P64F108 | 177 | P144F476 | 199 | ||||
| P137F108 | 182 | P173F480 | 188 | ||||
| P137F113 | 182 |
| Parameter | Ascending Track | Descending Track | Joint Track | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Detected Points | 229,198,008 | 186,641,213 | 277,808,906 | |
| Point Density (points/km2) | 879 | 716 | 1066 | |
| Velocity (mm/year) | Minimum | −24.79 | −27.71 | −25.49 |
| Maximum | 24.53 | 28.16 | 28.43 | |
| Average | −0.10 | −0.11 | −0.11 | |
| Std | 0.93 | 0.89 | 0.82 | |
| Cumulative Displacement (mm) | Minimum | −140.31 | 155.17 | 142.74 |
| Maximum | 137.36 | 157.69 | 159.20 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.; Lu, F.; Qi, P.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, S.; Song, W.; Ma, T. Vertical Deformation Extraction Using Joint Track SBAS-InSAR Along Coastal California, USA. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 761. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13040761
Wang S, Lu F, Qi P, Zhang M, Zhang Z, Wang S, Song W, Ma T. Vertical Deformation Extraction Using Joint Track SBAS-InSAR Along Coastal California, USA. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(4):761. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13040761
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Shunyao, Fengxian Lu, Pengcheng Qi, Miao Zhang, Ziyue Zhang, Shunying Wang, Wenkai Song, and Taofeng Ma. 2025. "Vertical Deformation Extraction Using Joint Track SBAS-InSAR Along Coastal California, USA" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 4: 761. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13040761
APA StyleWang, S., Lu, F., Qi, P., Zhang, M., Zhang, Z., Wang, S., Song, W., & Ma, T. (2025). Vertical Deformation Extraction Using Joint Track SBAS-InSAR Along Coastal California, USA. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(4), 761. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13040761






