Unveiling the Environmental Drivers of Pelagia noctiluca Outbreaks: A Decadal Study Along the Mediterranean Coastline of Morocco, Algeria and Tunisia
Abstract
1. Introduction
Pelagia noctiluca
2. Materials and Methods
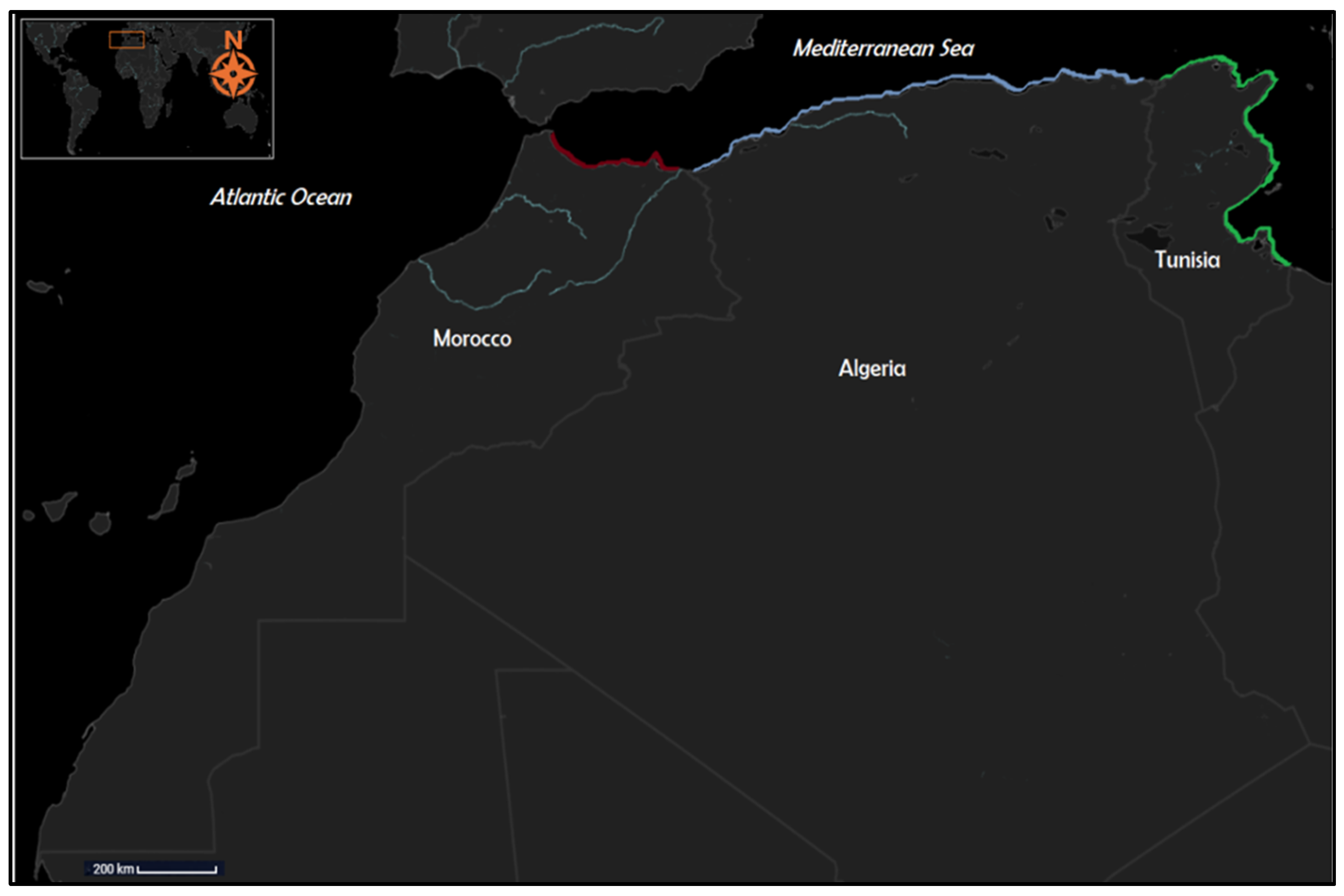
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Data Processing and Analysis
- ➢
- Data Standardization:
- Xi is the value of the variable at each data point,
- μ is the mean of the variable,
- σ is the standard deviation of the variable.
- ➢
- Correlation Analysis:
- Xi and Yi are the values of the two variables being compared,
- and are the means of the variables X and Y, respectively,
- n is the number of data points.
- ➢
- Temporal Pattern Analysis:
- B(t) is the bloom size at time t,
- β0 is the intercept,
- βj are the coefficients for each environmental variable Ej(t),
- εt is the error term.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Pelagia noctiluca Outbreaks in the Southern Mediterranean Coastline
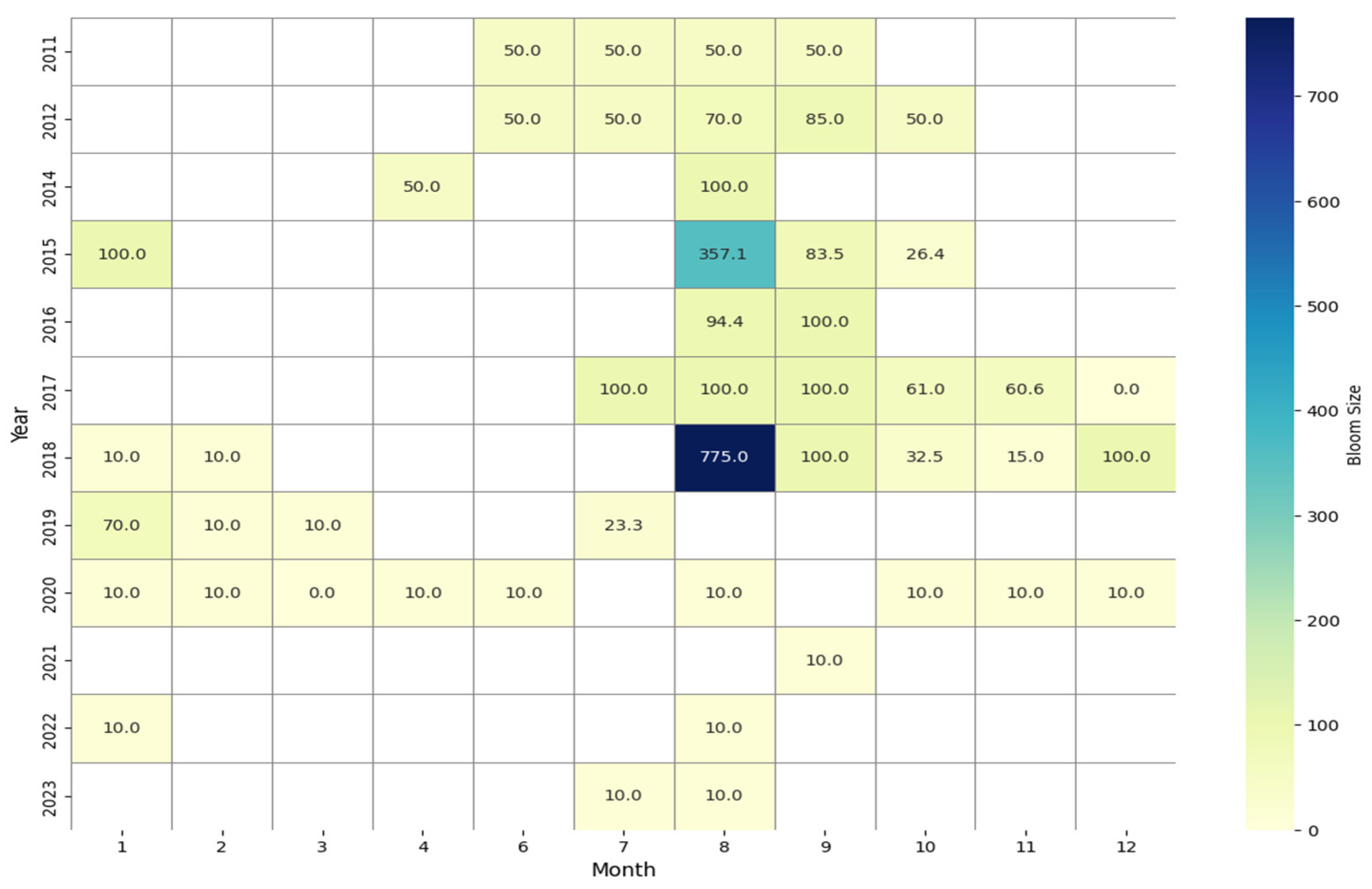
- Temporal patterns of Pelagia noctiluca blooms in the Moroccan Mediterranean coastline
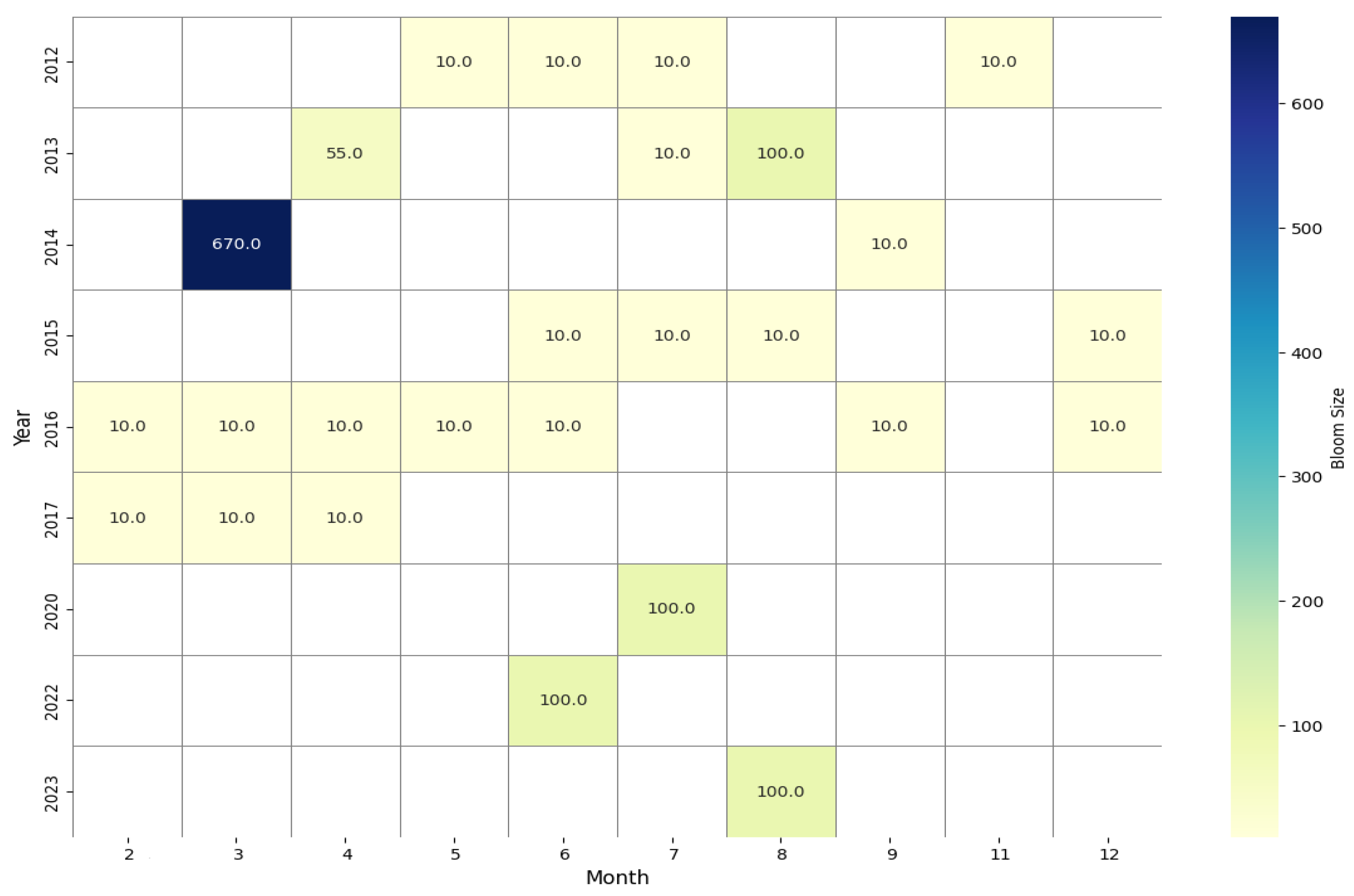
- Temporal patterns of Pelagia noctiluca blooms in the Algerian Mediterranean coastline
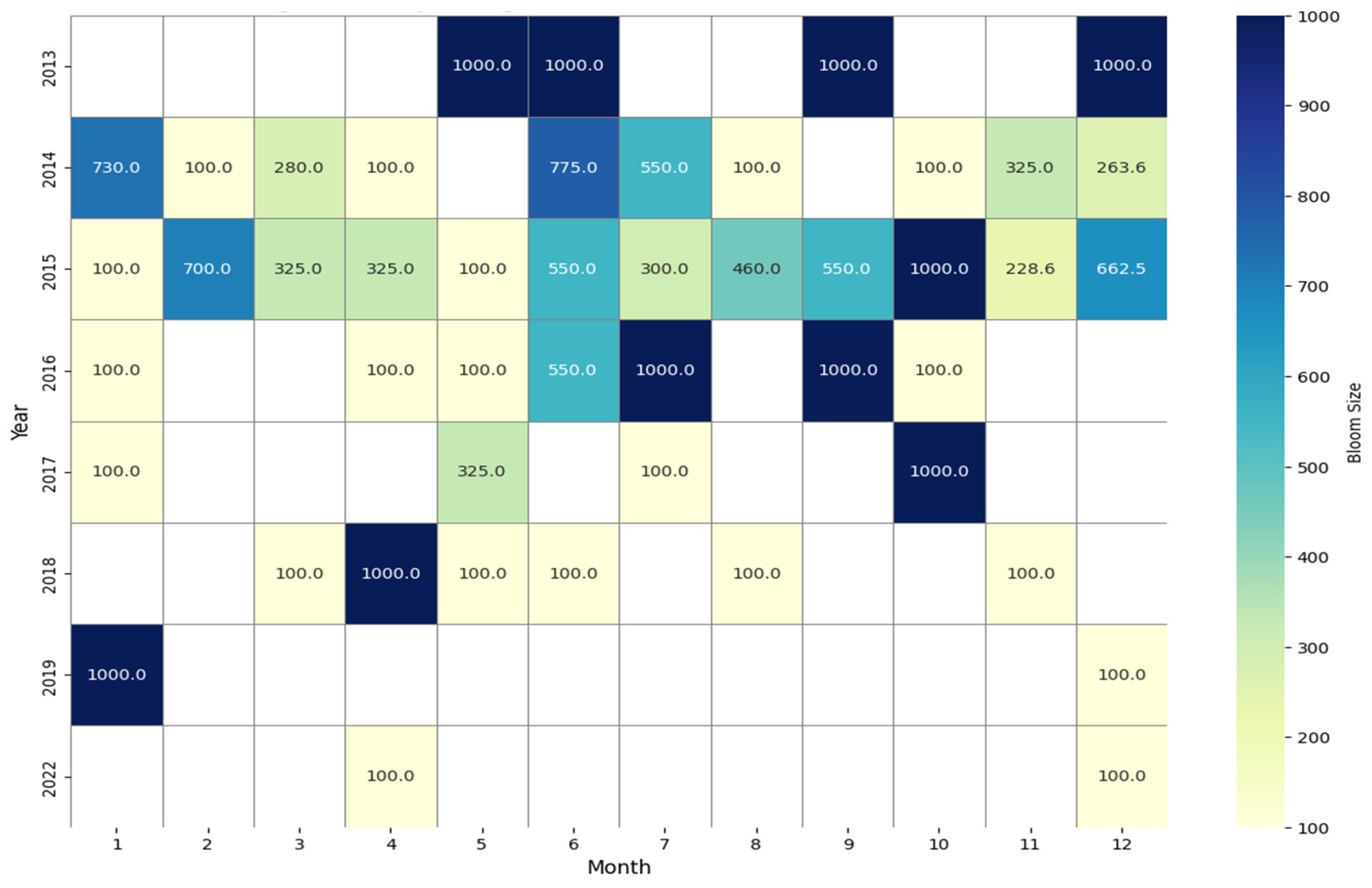
- Temporal patterns of Pelagia noctiluca blooms in the Tunisian Mediterranean coastline
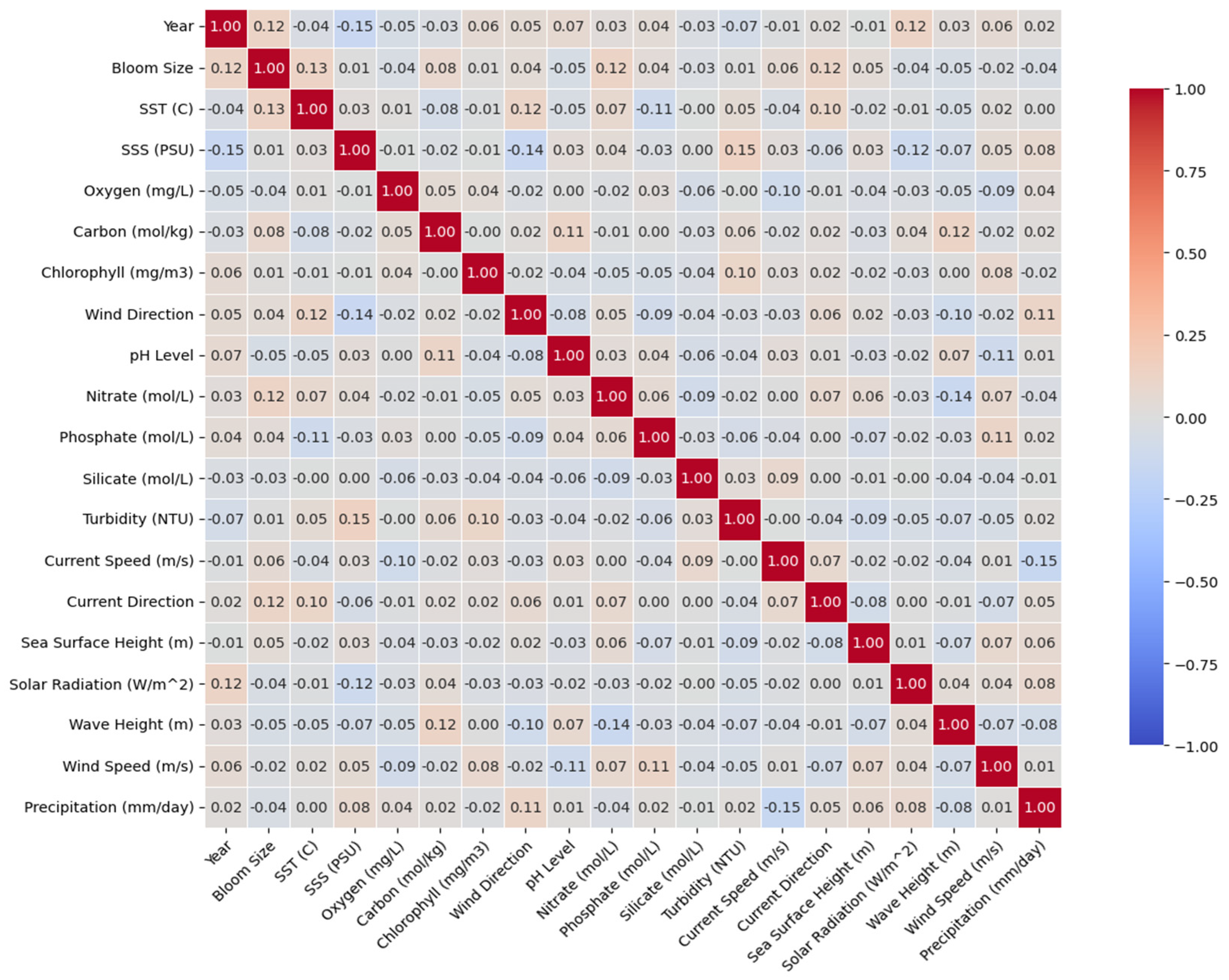
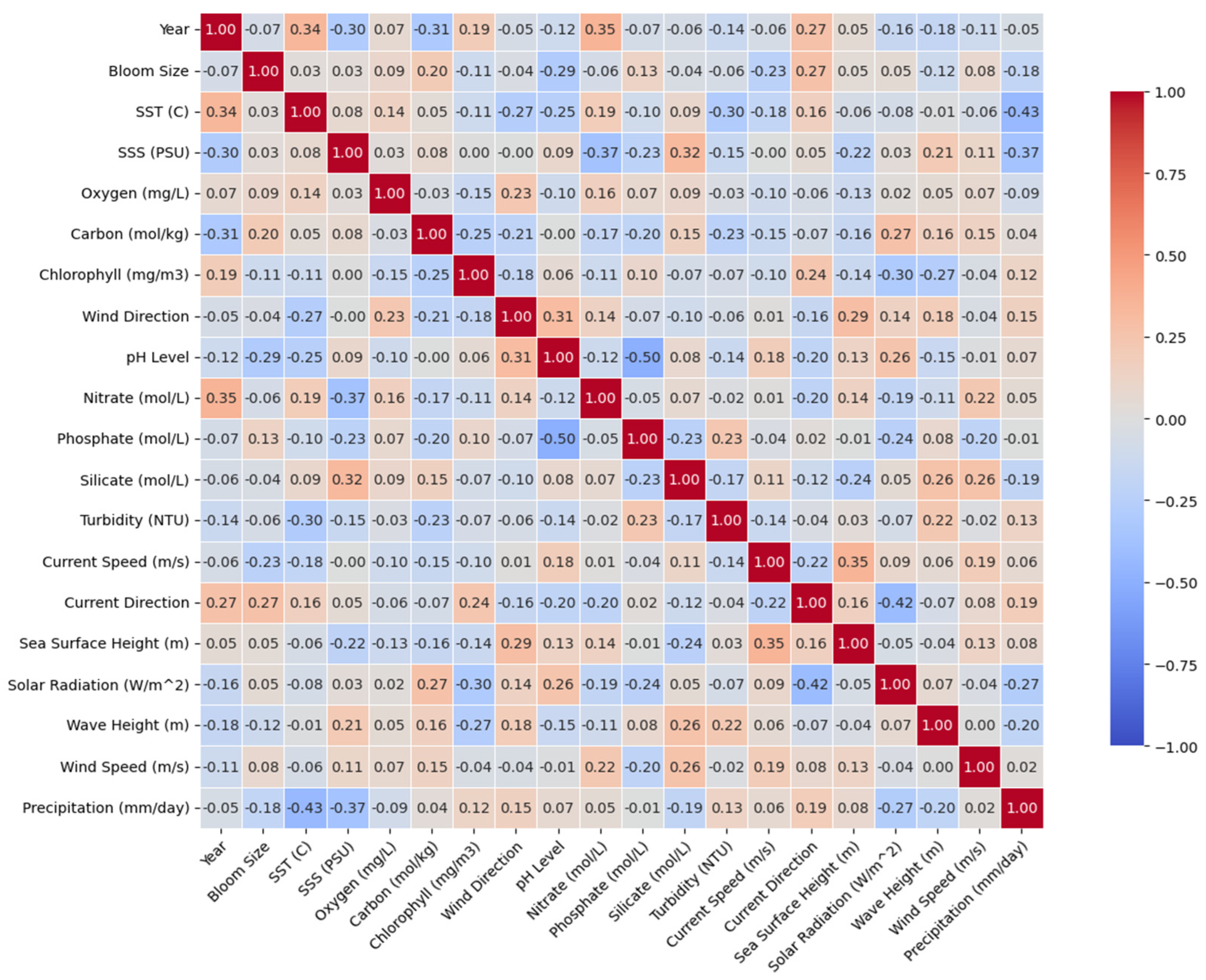
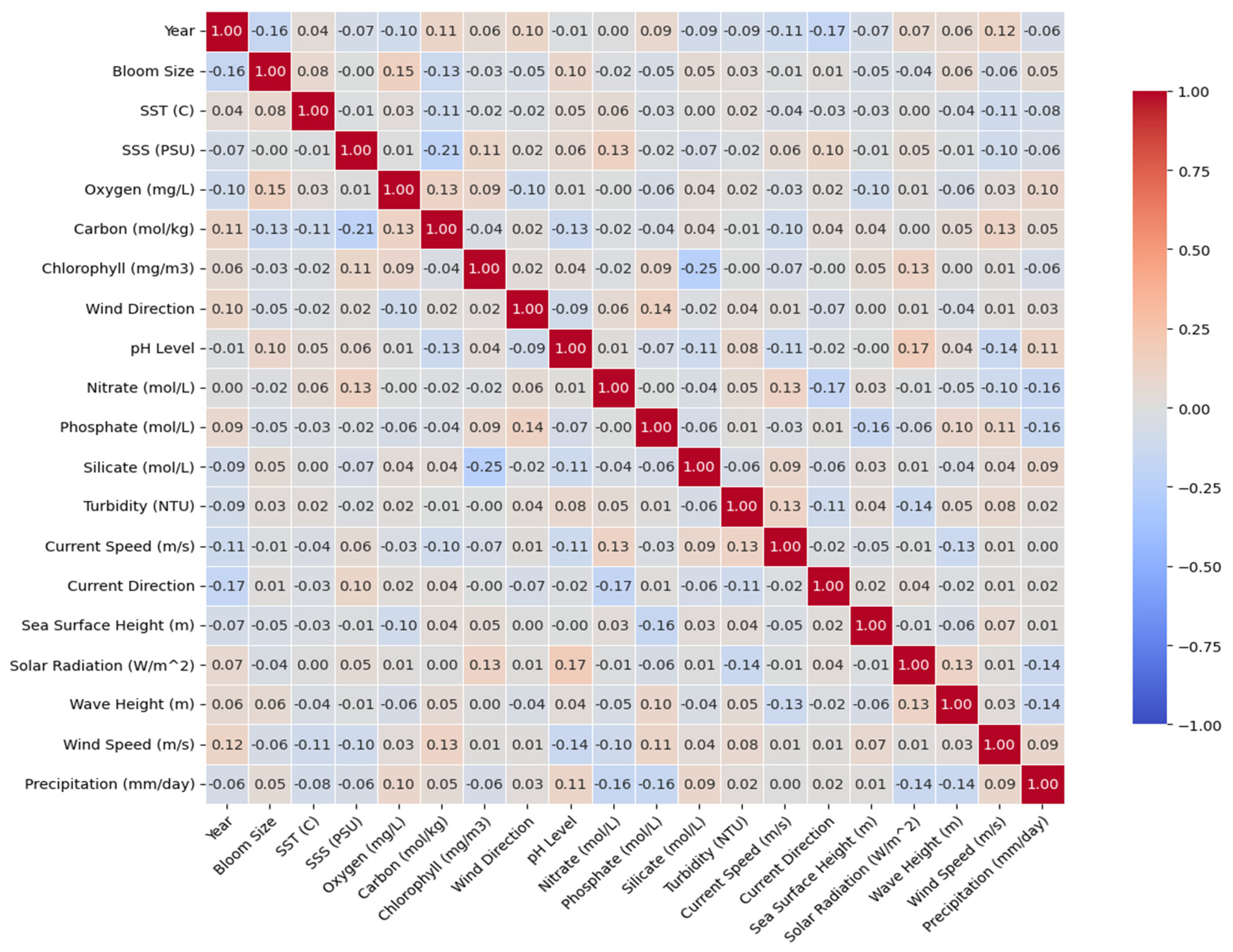
3.2. Correlation Between Environmental Variables and Bloom Intensity
- Correlation between environmental variables and bloom intensity along the Moroccan Mediterranean coast
- Correlation between environmental variables and bloom intensity along the Algerian Mediterranean coast
- Correlation between environmental variables and bloom intensity along the Tunisian Mediterranean coast
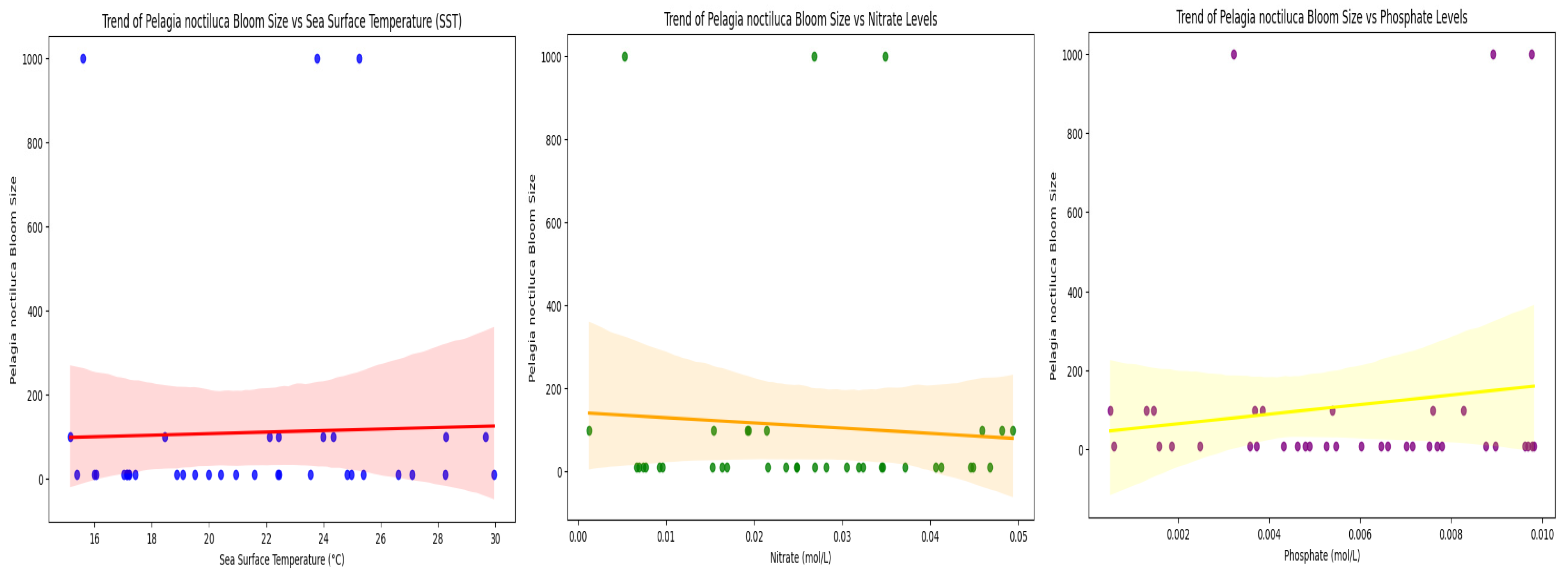
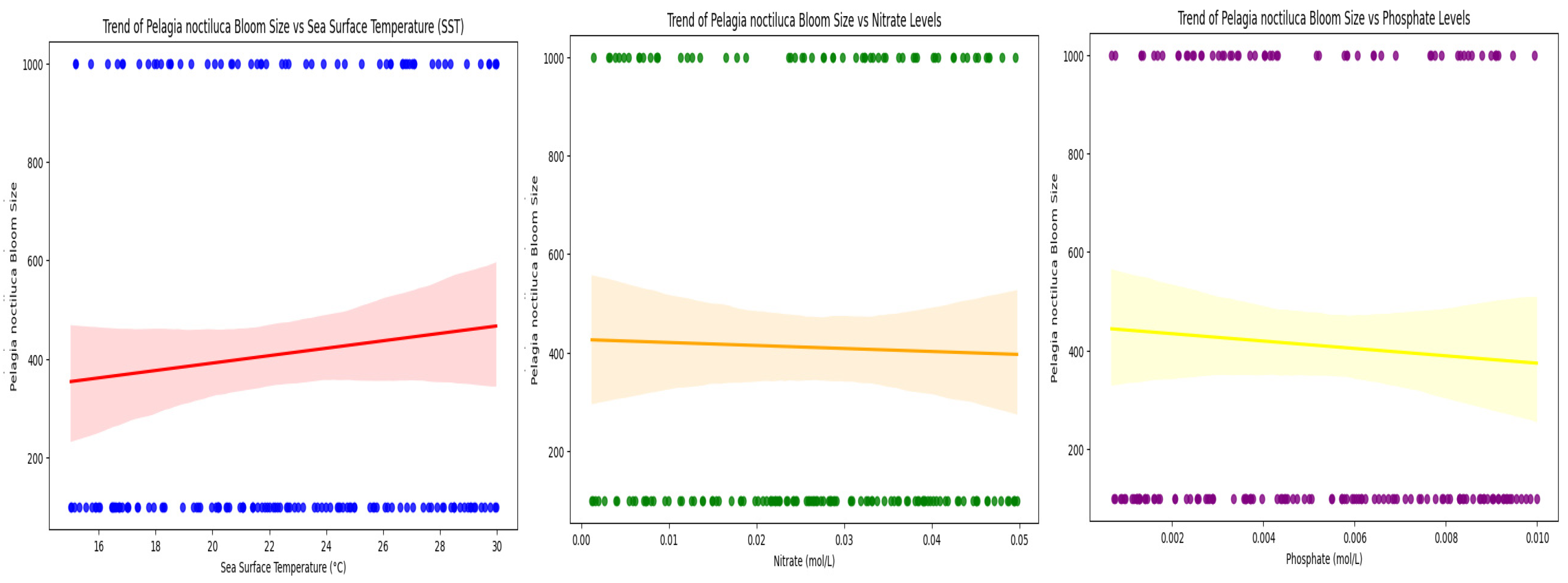
3.3. Temporal Trends in Bloom Intensity Relative to Environmental Variables
- Temporal trends in bloom intensity relative to environmental variables along the Moroccan Mediterranean coast
- Temporal trends in bloom intensity relative to environmental variables along the Algerian Mediterranean coast
- Temporal trends in bloom intensity relative to environmental variables along the Tunisian Mediterranean coast
3.4. Interannual Variability and Environmental Influences on Pelagia noctiluca Bloom Patterns in the Mediterranean
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Licandro, P.; Conway, D.V.P.; Daly Yahia, M.N.; Fernandez De Puelles, M.L.; Gasparini, S.; Hecq, J.H.; Tranter, P.; Kirby, R.R. A blooming jellyfish in the northeast Atlantic and Mediterranean. Biol. Lett. 2010, 6, 688–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, J.; Prieto, L.; Astorga, D. A model for temperature control of jellyfish (Cotylorhiza tuberculata) outbreaks: A causal analysis in a Mediterranean coastal lagoon. Ecol. Model. 2012, 233, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Fuente Roselló, A.; Perles Roselló, M.J.; Cantarero Prados, F.J. A Predictive Analysis of Beach Susceptibility to Jellyfish Arrivals in Costa del Sol. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortune, N.A. A Short Guide to Using Python for Data Analysis in Experimental Physics. Authorea, 2021; preprints. Available online: https://www.authorea.com/users/18589/articles/304710-a-short-guide-to-using-python-for-data-analysis-in-experimental-physics?commit=338281975198a5f5599acd5c0cb0535a1155bea5 (accessed on 26 February 2024).
- Ottmann, D.; Álvarez-Berastegui, D.; Prieto, L.; Balbín, R.; Alemany, F.; Fiksen, Ø.; Gordoa, A.; Reglero, P. Abundance of Pelagia noctiluca early life stages in the western Mediterranean Sea scales with surface chlorophyll. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2021, 658, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millot, C.; Taupier-Letage, I. Additional evidence of LIW entrainment across the Algerian subbasin by mesoscale eddies and not by a permanent westward flow. Prog. Oceanogr. 2005, 66, 231–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, A.P.; Bastian, T.; Haberlin, D.; Stokes, D.; Lyashevska, O.; Brophy, D.; Lawton, C.; Doyle, T. Regular widespread aggregations of the oceanic jellyfish Pelagia noctiluca in the northeast Atlantic over 11 years. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2024, 303, 108805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, J.; Uye, S.; Lo, W. Anthropogenic causes of jellyfish blooms and their direct consequences for humans: A review. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2007, 350, 153–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bejaoui, S.; Bouziz, M.; Ghribi, F.; Chetoui, I.; Cafsi, M.E. Assessment of the biochemical and nutritional values of Venerupis decussata from Tunisian lagoons submitted to different anthropogenic ranks. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 1734–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aouititen, M.; Bekkali, R.; Nachit, D.; Luan, X.; Mrhraoui, M. Predicting Jellyfish Strandings in the Moroccan North-West Mediter-Ranean Coastline. Eur. Sci. J. 2019, 15, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khames, Y.G.E.; Hafferssas, A.; Kherchouche-Ait Ouadour, A. Distribution and species composition of planktonic cnidarians in the Algerian coastal waters (SW Mediterranean Sea). Acta Adriat. 2024, 65, 33–49. [Google Scholar]
- Béjaoui, B.; Ben Ismail, S.; Othmani, A.; Ben Abdallah-Ben Hadj Hamida, O.; Chevalier, C.; Feki-Sahnoun, W.; Harzallah, A.; Hamida, N.B.H.; Bouaziz, R.; Dahech, S.; et al. Synthesis review of the Gulf of Gabes (eastern Mediterranean Sea, Tunisia): Morphological, climatic, physical oceanographic, biogeochemical and fisheries features. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2019, 219, 395–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, K.; Mattmüller, R.; Algueró-Muñiz, M.; Meunier, C.; Alvarez-Fernandez, S.; Boersma, M.; Morais, P.; Teodósio, M. Winter river discharge may affect summer estuarine jellyfish blooms. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2018, 591, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aouititen, M.; Ravibhanu, A.; Ang, S.C.; Mouanda, D.C.M.; Luan, X. New records of two jellyfish species Rhizostoma luteum (Quoy and Gaimard 1827) and Cotylorhiza tuberculata (Macri 1778) in the Moroccan northwest Mediterranean coast. Discov. Life 2024, 54, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canepa, A.; Fuentes, V.; Sabatés, A.; Piraino, S.; Boero, F.; Gili, J.M. Pelagia noctiluca in the Mediterranean Sea. In Jellyfish Blooms; Pitt, K.A., Lucas, C.H., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 237–266. Available online: https://link.springer.com/10.1007/978-94-007-7015-7_11 (accessed on 1 September 2024).
- Lucas, C.H.; Dawson, M.N. What Are Jellyfishes and Thaliaceans and Why Do They Bloom? In Jellyfish Blooms; Pitt, K.A., Lucas, C.H., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 9–44. Available online: https://link.springer.com/10.1007/978-94-007-7015-7_2 (accessed on 20 September 2024).
- Milisenda, G.; Rossi, S.; Vizzini, S.; Fuentes, V.L.; Purcell, J.E.; Tilves, U.; Piraino, S. Seasonal variability of diet and trophic level of the gelatinous predator Pelagia noctiluca (Scyphozoa). Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milisenda, G.; Martinez-Quintana, A.; Fuentes, V.; Bosch-Belmar, M.; Aglieri, G.; Boero, F.; Piraino, S. Reproductive and bloom patterns of Pelagia noctiluca in the Strait of Messina, Italy. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2018, 201, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor-Prieto, M.; Bahamon, N.; Sabatés, A.; Canepa, A.; Gili, J.M.; Carreton, M.; Company, J.B. Spatial heterogeneity of Pelagia noctiluca ephyrae linked to water masses in the Western Mediterranean. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0249756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kherchouche, A.; Hafferssas, A. Species composition and distribution of Medusae (Cnidaria: Medusozoa) in the Algerian coast between 2°e and 7°e (SW Mediterranean Sea). Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2019, 21, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mghili, B.; Analla, M.; Aksissou, M. Temporal Dynamics of Jellyfish Pelagia noctiluca Stranded on the Mediterranean Coast of Morocco. Turk. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2020, 21, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, J.E. Climate effects on formation of jellyfish and ctenophore blooms: A review. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. 2005, 85, 461–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, J.J. Connectivity between island Marine Protected Areas and the mainland. Biol. Conserv. 2008, 141, 2807–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onderka, M. Correlations between several environmental factors affecting the bloom events of cyanobacteria in Liptovska Mara reservoir (Slovakia)—A simple regression model. Ecol. Model. 2007, 209, 412–416. [Google Scholar]
- Calvo, E.; Simó, R.; Coma, R.; Ribes, M.; Pascual, J.; Sabatés, A.; Gili, J.M.; Pelejero, C. Effects of climate change on Mediterranean marine ecosystems: The case of the Catalan Sea. Clim. Res. 2011, 50, 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- Báez, J.C.; Pennino, M.G.; Albo-Puigserver, M.; Coll, M.; Giraldez, A.; Bellido, J.M. Effects of environmental conditions and jellyfish blooms on small pelagic fish and fisheries from the Western Mediterranean Sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2022, 264, 107699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaspers, C.; Bezio, N.; Hinrichsen, H.-H. Diversity and Physiological Tolerance of Native and Invasive Jellyfish/Ctenophores along the Extreme Salinity Gradient of the Baltic Sea. Diversity 2021, 13, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, C.; Koseff, J.; Lucas, L.; Cloern, J.; Schoellhamer, D. Effects of spatial and temporal variability of turbidity on phytoplankton blooms. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2003, 254, 111–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, L.; Astorga, D.; Navarro, G.; Ruiz, J. Environmental Control of Phase Transition and Polyp Survival of a Massive-Outbreaker Jellyfish. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13793. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y. Impact, Responses and Future Prediction of Climate Change on the Phenology of Jellyfish. Theor. Nat. Sci. 2023, 3, 658–665. [Google Scholar]
- Mghili, B.; Analla, M.; Aksissou, M. Medusae (Scyphozoa and hydrozoa) from the Moroccan Mediterranean coast: Abundance and spatiotemporal dynamics and their economic impact. Aquat. Ecol. 2022, 56, 213–226. [Google Scholar]
- Purcell, J.E.; Malej, A.; Benović, A. Potential links of jellyfish to eutrophication and fisheries. In Coastal and Estuarine Studies [Internet]; Malone, T.C., Malej, A., Harding, L.W., Smodlaka, N., Turner, R.E., Eds.; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 1999; pp. 241–263. Available online: http://www.agu.org/books/ce/v055/CE055p0241/CE055p0241.shtml (accessed on 5 April 2024).
- Hassen, M.B.; Hamza, A.; Drira, Z.; Zouari, A.; Akrout, F.; Messaoudi, S.; Aleya, L.; Ayadi, H. Phytoplankton-pigment signatures and their relationship to spring–summer stratification in the Gulf of Gabes. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2009, 83, 296–306. [Google Scholar]
- Condon, R.H.; Graham, W.M.; Duarte, C.M.; Pitt, K.A.; Lucas, C.H.; Haddock, S.H.D.; Sutherland, K.R.; Robinson, K.L.; Dawson, M.N.; Decker, M.B.; et al. Questioning the Rise of Gelatinous Zooplankton in the World’s Oceans. BioScience 2012, 62, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabatés, A.; Pagès, F.; Atienza, D.; Fuentes, V.; Purcell, J.E.; Gili, J.M. Planktonic cnidarian distribution and feeding of Pela-gia noctiluca in the NW Mediterranean Sea. In Jellyfish Blooms: New Problems and Solutions; Purcell, J.E., Angel, D.L., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 153–165. Available online: http://link.springer.com/10.1007/978-90-481-9541-1_12 (accessed on 1 September 2024).
- Lu, Y.; Lucas, C.; Loveridge, A. Transgenerational acclimation influences asexual reproduction in Aurelia aurita jellyfish polyps in response to temperature. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2020, 656, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly Yahia, M.N.; Kéfi-Daly Yahia, O.; Gueroun, S.; Aissi, M.; Deidun, A.; Fuentes, V.; Piraino, S. The invasive tropical scyphozoan Rhopilema nomadica Galil, 1990 reaches the Tunisian coast of the Mediterranean Sea. BioInvasions Rec. 2013, 2, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Ismail, S.; Sammari, C.; Gasparini, G.P.; Béranger, K.; Brahim, M.; Aleya, L. Water masses exchanged through the Channel of Sicily: Evidence for the presence of new water masses on the Tunisian side of the channel. Deep. Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2012, 63, 65–81. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, M.; Zhu, Y.; Hu, X.; Zhu, B.; Lyu, S.; Yinglan, A.; Wang, G. Assembly mechanism and stability of zooplankton communities affected by China’s south-to-north water diversion project. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 365, 121497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Mo, Q.; Kuo, Y.M.; Su, Y.; Zhong, Y. Hydrochemical controls on reservoir nutrient and phytoplankton dynamics under storms. Sci. Total. Environ. 2018, 619–620, 301–310. [Google Scholar]
- Pitt, K.A.; Welsh, D.T.; Condon, R.H. Influence of jellyfish blooms on carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus cycling and plankton pro-duction. Hydrobiologia 2009, 616, 133–149. [Google Scholar]
- Benyoub, B.; Mghili, B.; Hasni, S.; Asmae, A. First Inventory of the Biodiversity, Abundance, and Distribution of Jellyfish (Cnidaria) in Relation to Depth in the Bay of Al Hoceima, North Coast of Morocco, the Mediterranean Sea. Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish. 2023, 27, 897–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Union-Copernicus Marine Service. Global Ocean Biogeochemistry Analysis and Forecast; Mercator Ocean International: Toulouse, France, 2019; Available online: https://data.marine.copernicus.eu/product/GLOBAL_ANALYSISFORECAST_BGC_001_028/description (accessed on 5 May 2024).
- Arhonditsis, G.; Brett, M.T.; Frodge, J. Environmental Control and Limnological Impacts of a Large Recurrent Spring Bloom in Lake Washington, USA. Environ. Manag. 2003, 31, 603–618. [Google Scholar]
- Hallegraeff, G.M. Ocean climate change, phytoplankton community responses, and harmful algal blooms: A formidable predictive chalenge. J. Phycol. 2010, 46, 220–235. [Google Scholar]
- Sebastián, M.; Ortega-Retuerta, E.; Gómez-Consarnau, L.; Zamanillo, M.; Álvarez, M.; Arístegui, J.; Gasol, J.M. Environmental gradients and physical barriers drive the basin-wide spatial structuring of Mediterranean Sea and adjacent eastern Atlantic Ocean prokaryotic communities. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2021, 66, 4077–4095. [Google Scholar]
- Boudouresque, C.F. Marine Biodiversity—Warming vs. Biological Invasions and overfishing in the Mediterranean Sea: Take care, ‘One Train can hide another’. MOJ Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2017, 2, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gueroun, S.K.M.; Piraino, S.; KÉfi-Daly Yahia, O.; Daly Yahia, M.N. Jellyfish diversity, trends and patterns in Southwestern Mediterranean Sea: A citizen science and field monitoring alliance. J. Plankton Res. 2022, 44, 819–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribera d’Alcalà, M.; Conversano, F.; Corato, F.; Licandro, P.; Mangoni, O.; Marino, D.; Mazzocchi, M.G.; Modigh, M.; Montresor, M.; Nardella, M.; et al. Seasonal patterns in plankton communities in a pluriannual time series at a coastal Mediterranean site (Gulf of Naples): An attempt to discern recurrences and trends. Sci. Mar. 2004, 68, 65–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marambio, M.; Canepa, A.; Lòpez, L.; Gauci, A.A.; Gueroun, S.K.M.; Zampardi, S.; Boero, F.; Yahia, O.K.-D.; Yahia, M.N.D.; Fuentes, V.; et al. Unfolding Jellyfish Bloom Dynamics along the Mediterranean Basin by Transnational Citizen Science Initiatives. Diversity 2021, 13, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brotz, L.; Cheung, W.W.L.; Kleisner, K.; Pakhomov, E.; Pauly, D. Increasing jellyfish populations: Trends in Large Marine Ecosystems. In Jellyfish Blooms IV; Purcell, J., Mianzan, H., Frost, J.R., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 3–20. Available online: https://link.springer.com/10.1007/978-94-007-5316-7_2 (accessed on 1 September 2024).
- Béranger, K.; Mortier, L.; Crépon, M. Seasonal variability of water transport through the Straits of Gibraltar, Sicily and Corsica, derived from a high-resolution model of the Mediterranean circulation. Prog. Oceanogr. 2005, 66, 341–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, G.; Wirtz, K.W. Interannual variability of alongshore spring bloom dynamics in a coastal sea caused by the differential influence of hydrodynamics and light climate. Biogeosciences 2010, 7, 371–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holst, S. Effects of climate warming on strobilation and ephyra production of North Sea scyphozoan jellyfish. Hydrobiologia 2012, 690, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergamasco, A.; Cucco, A.; Guglielmo, L.; Minutoli, R.; Quattrocchi, G.; Guglielmo, R.; Palumbo, F.; Pansera, M.; Zagami, G.; Vodopivec, M.; et al. Observing and modeling long-term persistence of P. noctiluca in coupled complementary marine systems (Southern Tyrrhenian Sea and Messina Strait). Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinero, J.C.; Ibanez, F.; Nival, P.; Buecher, E.; Souissi, S. North Atlantic climate and northwestern Mediterranean plankton varia-bility. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2005, 50, 1213–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellido, J.J.; Báez, J.C.; Souviron-Priego, L.; Ferri-Yañez, F.; Salas, C.; López, J.A.; Real, R. Atmospheric indices allow anticipating the incidence of jellyfish coastal swarms. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2020, 21, 289–297. [Google Scholar]
- Leoni, V.; Bonnet, D.; Ramírez-Romero, E.; Molinero, J.C. Biogeography and phenology of the jellyfish Rhizostoma pulmo (Cnidaria: Scyphozoa) in southern European seas. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2021, 30, 622–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreano, D. Data and Dynamics Driven Approaches for Modelling and Forecasting the Red Sea Chlorophyll [Internet]. KAUST Research Repository. 2017. Available online: https://repository.kaust.edu.sa/handle/10754/623753 (accessed on 3 July 2024).
- Bastian, T.; Stokes, D.; Kelleher, J.E.; Hays, G.C.; Davenport, J.; Doyle, T.K. Fisheries bycatch data provide insights into the distribution of the mauve stinger (Pelagia noctiluca) around Ireland. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2011, 68, 436–443. [Google Scholar]
- Accoroni, S.; Tartaglione, L.; Dello Iacovo, E.; Pichierri, S.; Marini, M.; Campanelli, A.; Dell’Aversano, C.; Totti, C. Influence of environmental factors on the toxin production of Ostreopsis cf. ovata during bloom events. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 123, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rahi, J.E.; Weeber, M.P.; Serafy, G.E. Modelling the effect of behavior on the distribution of the jellyfish Mauve stinger (Pelagia noctiluca) in the Balearic Sea using an individual-based model. Ecol. Model. 2020, 433, 109230. [Google Scholar]
- Riisgård, H.; Goldstein, J. Jellyfish and Ctenophores in Limfjorden (Denmark)—Mini-Review, with Recent New Observations. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2014, 2, 593–615. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Z.; Fang, W.; Yu, Z.; Chen, X.; Su, Z.; Yu, W.; Lin, H. Key environmental parameters and numerical prediction model of jellyfish bloom in Qingchuan Bay Nuclear Power Plant, China. Mar. Environ. Res. 2024, 202, 106786. [Google Scholar]
- Hays, G.C.; Ferreira, L.C.; Sequeira, A.M.; Meekan, M.G.; Duarte, C.M.; Bailey, H.; Bailleul, F.; Bowen, W.D.; Caley, M.J.; Costa, D.; et al. Key Questions in Marine Megafauna Movement Ecology. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2016, 31, 463–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hays, G.C.; Bailey, H.; Bograd, S.J.; Bowen, W.D.; Campagna, C.; Carmichael, R.H.; Casale, P.; Chiaradia, A.; Costa, D.P.; Cuevas, E.; et al. Translating Marine Animal Tracking Data into Conservation Policy and Management. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2019, 34, 459–473. [Google Scholar]
- Berline, L.; Zakardjian, B.; Molcard, A.; Ourmières, Y.; Guihou, K. Modeling jellyfish Pelagia noctiluca transport and stranding in the Ligurian Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 70, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, C.; Selkoe, K.A.; Watson, J.; Siegel, D.A.; Zacherl, D.C.; Toonen, R.J. Ocean currents help explain population genetic structure. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2010, 277, 1685–1694. [Google Scholar]
- Ciuffardi, T.; Lo Bue, N.; Raiteri, G.; Marullo, S.; Artale, V. New Insights into Tyrrhenian Sea Warming and Heat Penetration through Long-Term Expendable Bathythermograph Data. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, S.; Pansera, M.; Granata, A.; Guglielmo, L. Interannual variability, growth, reproduction and feeding of Pelagia noctiluca (Cnidaria: Scyphozoa) in the Straits of Messina (Central Mediterranean Sea): Linkages with temperature and diet. J. Mar. Syst. 2013, 111–112, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frolova, A.; Miglietta, M.P. Insights on Bloom Forming Jellyfish (Class: Scyphozoa) in the Gulf of Mexico: Environmental Tolerance Ranges and Limits Suggest Differences in Habitat Preference and Resistance to Climate Change Among Congeners. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinder, V.A.; Popovich, C.A.; Molinero, J.C.; Marcovecchio, J. Phytoplankton summer bloom dynamics in the Bahía Blanca Estuary in relation to changing environmental conditions. Cont. Shelf Res. 2013, 52, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Ishizaka, J.; Yamaguchi, H.; Siswanto, E.; Wang, S. Relationships of interannual variability in SST and phytoplankton blooms with giant jellyfish (Nemopilema nomurai) outbreaks in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea. J. Oceanogr. 2013, 69, 511–526. [Google Scholar]
- Hari Praved, P.; Morandini, A.C.; Maronna, M.M.; Suhaana, M.N.; Jima, M.; Aneesh, B.P.; Nandan, S.B.; Jayachandran, P.R. Report of Mauve Stinger Pelagia cf. noc-tiluca (Cnidaria: Scyphozoa) Bloom from Northeastern Arabian Sea (NEAS). Thalassas 2021, 37, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffers, V.F.; Godley, B.J. Satellite tracking in sea turtles: How do we find our way to the conservation dividends? Biol. Conserv. 2016, 199, 172–184. [Google Scholar]
- West, E.J.; Pitt, K.A.; Welsh, D.T.; Koop, K.; Rissik, D. Top-down and bottom-up influences of jellyfish on primary productivity and planktonic assemblages. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2009, 54, 2058–2071. [Google Scholar]
- Tilves, U.; Fuentes, V.; Milisenda, G.; Parrish, C.; Vizzini, S.; Sabatés, A. Trophic interactions of the jellyfish Pelagia noctiluca in the NW Mediterranean: Evidence from stable isotope signatures and fatty acid composition. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2018, 591, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariottini, G.L.; Giacco, E.; Pane, L. The Mauve Stinger Pelagia noctiluca (Forsskål, 1775). Distribution, Ecology, Toxicity and Epi-demiology of Stings. Mar. Drugs 2008, 6, 496–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addessi, L. Human Disturbance and Long-Term Changes on a Rocky Intertidal Community. Ecol. Appl. 1994, 4, 786–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Sun, S.; Jin, X.; Li, C. Associations of large jellyfish distributions with temperature and salinity in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea. In Jellyfish Blooms IV; Purcell, J., Mianzan, H., Frost, J.R., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 81–96. Available online: https://link.springer.com/10.1007/978-94-007-5316-7_7 (accessed on 1 September 2024).


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aouititen, M.; Magabandi Mouanda, D.C.; Luan, X. Unveiling the Environmental Drivers of Pelagia noctiluca Outbreaks: A Decadal Study Along the Mediterranean Coastline of Morocco, Algeria and Tunisia. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 642. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13040642
Aouititen M, Magabandi Mouanda DC, Luan X. Unveiling the Environmental Drivers of Pelagia noctiluca Outbreaks: A Decadal Study Along the Mediterranean Coastline of Morocco, Algeria and Tunisia. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(4):642. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13040642
Chicago/Turabian StyleAouititen, Majda, Dorel Cevan Magabandi Mouanda, and Xiaofeng Luan. 2025. "Unveiling the Environmental Drivers of Pelagia noctiluca Outbreaks: A Decadal Study Along the Mediterranean Coastline of Morocco, Algeria and Tunisia" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 4: 642. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13040642
APA StyleAouititen, M., Magabandi Mouanda, D. C., & Luan, X. (2025). Unveiling the Environmental Drivers of Pelagia noctiluca Outbreaks: A Decadal Study Along the Mediterranean Coastline of Morocco, Algeria and Tunisia. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(4), 642. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13040642






