A Semi-Analytical Method to Design a Dynamic Vibration Absorber for Coupled Plate Structures of Offshore Platforms
Abstract
1. Introduction
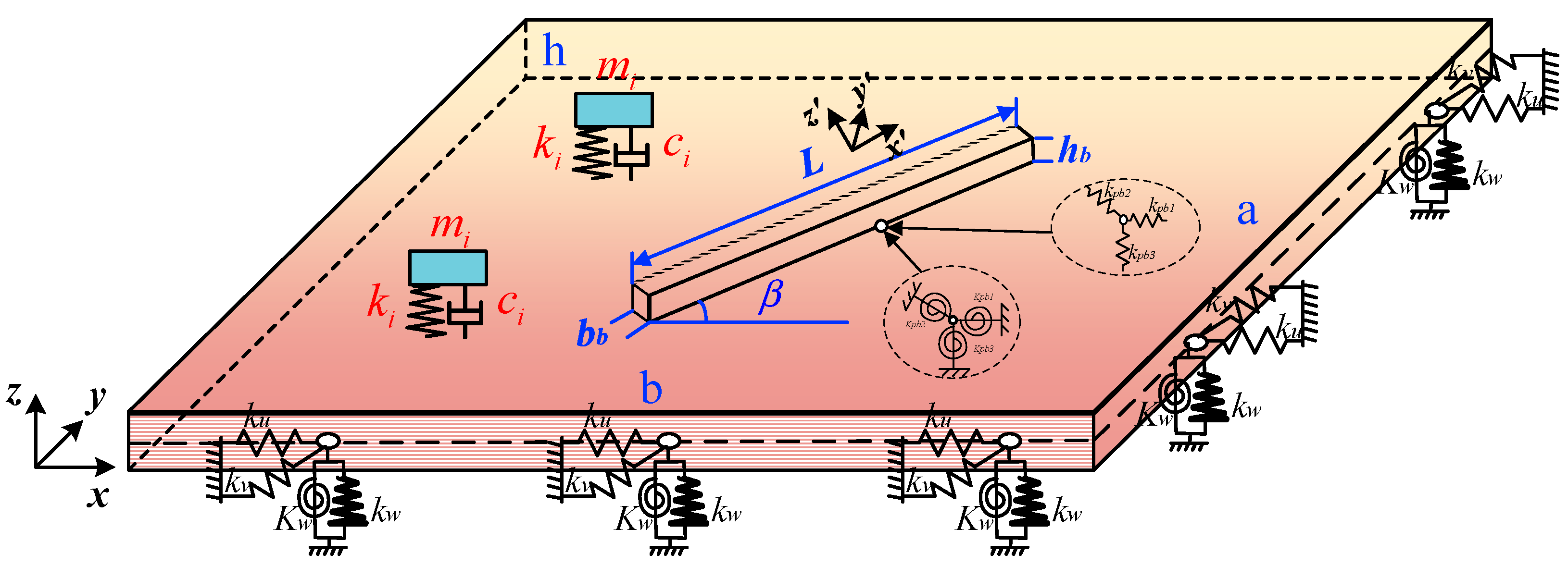
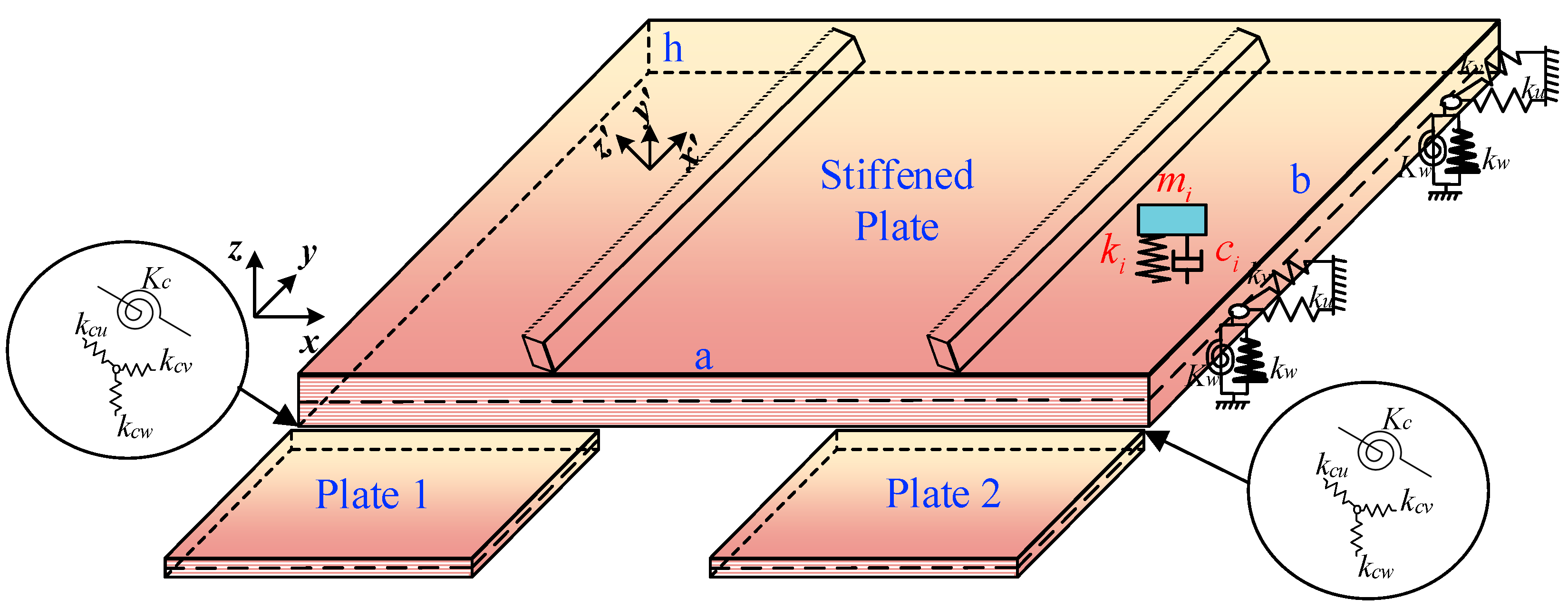
2. Mathematical Model of Coupled Plate Structures and DVA
2.1. Establishment of Energy Formula
2.2. Design of Parameters of DVA of Coupled Plate Structures
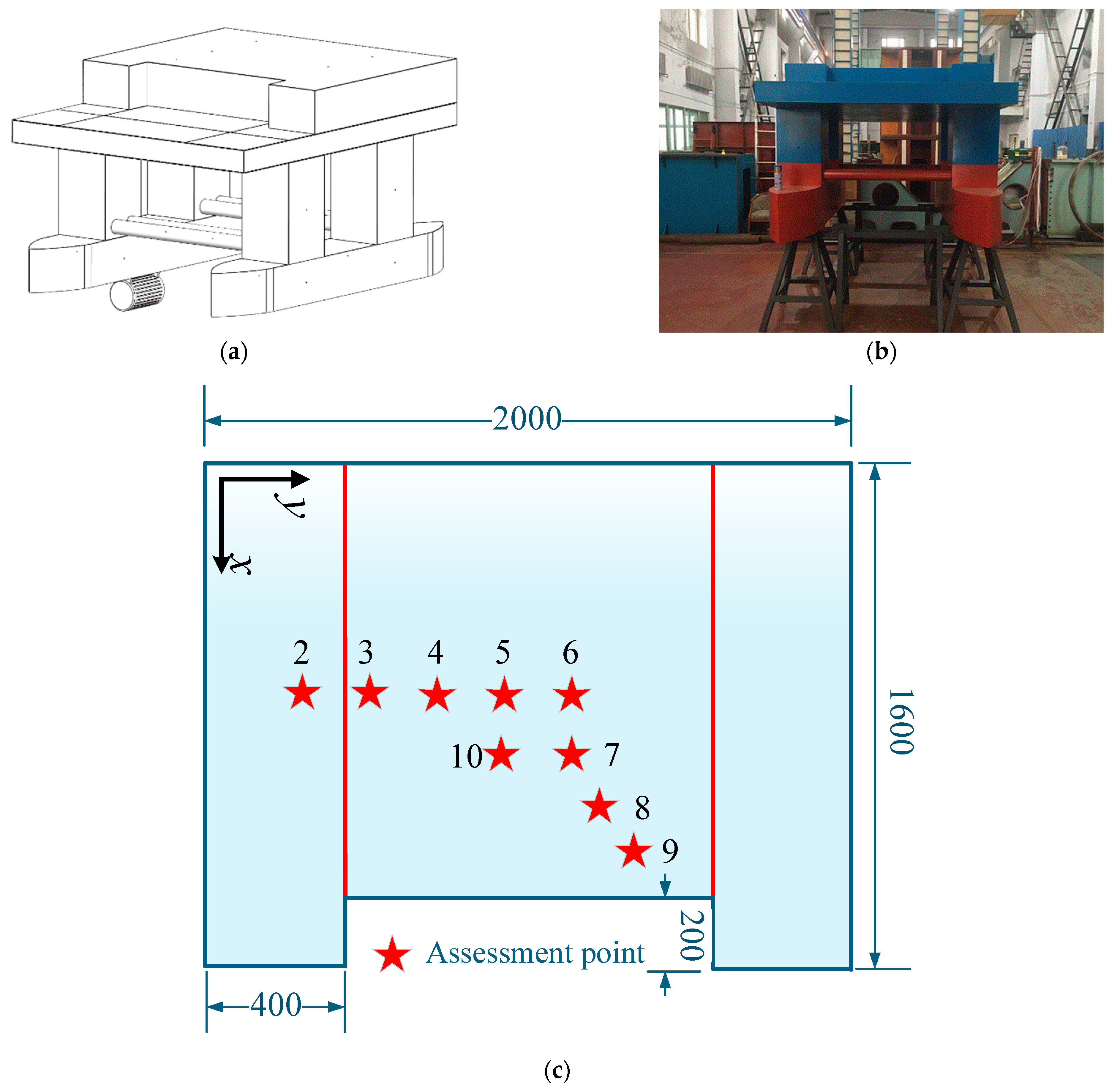
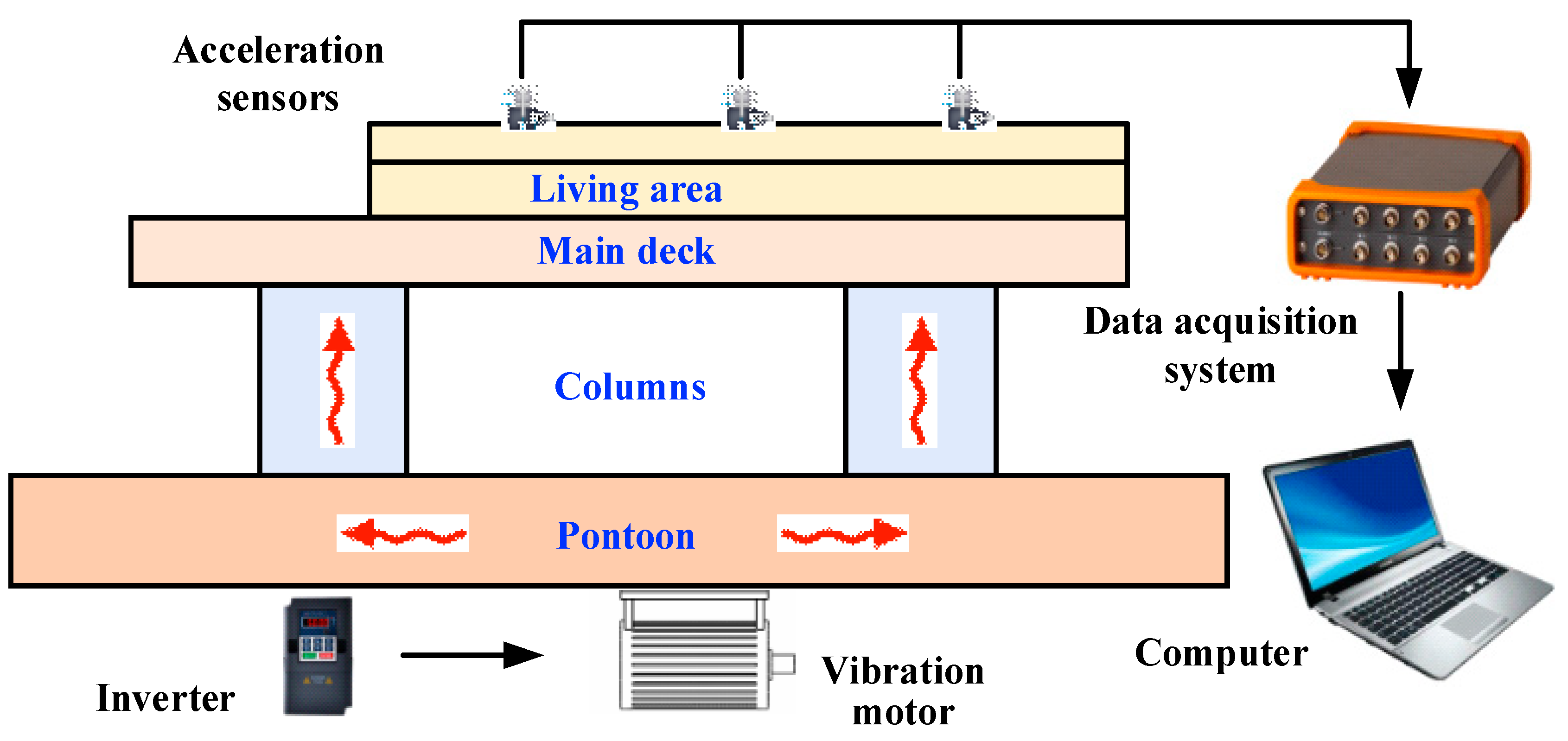
3. Experiment Verification
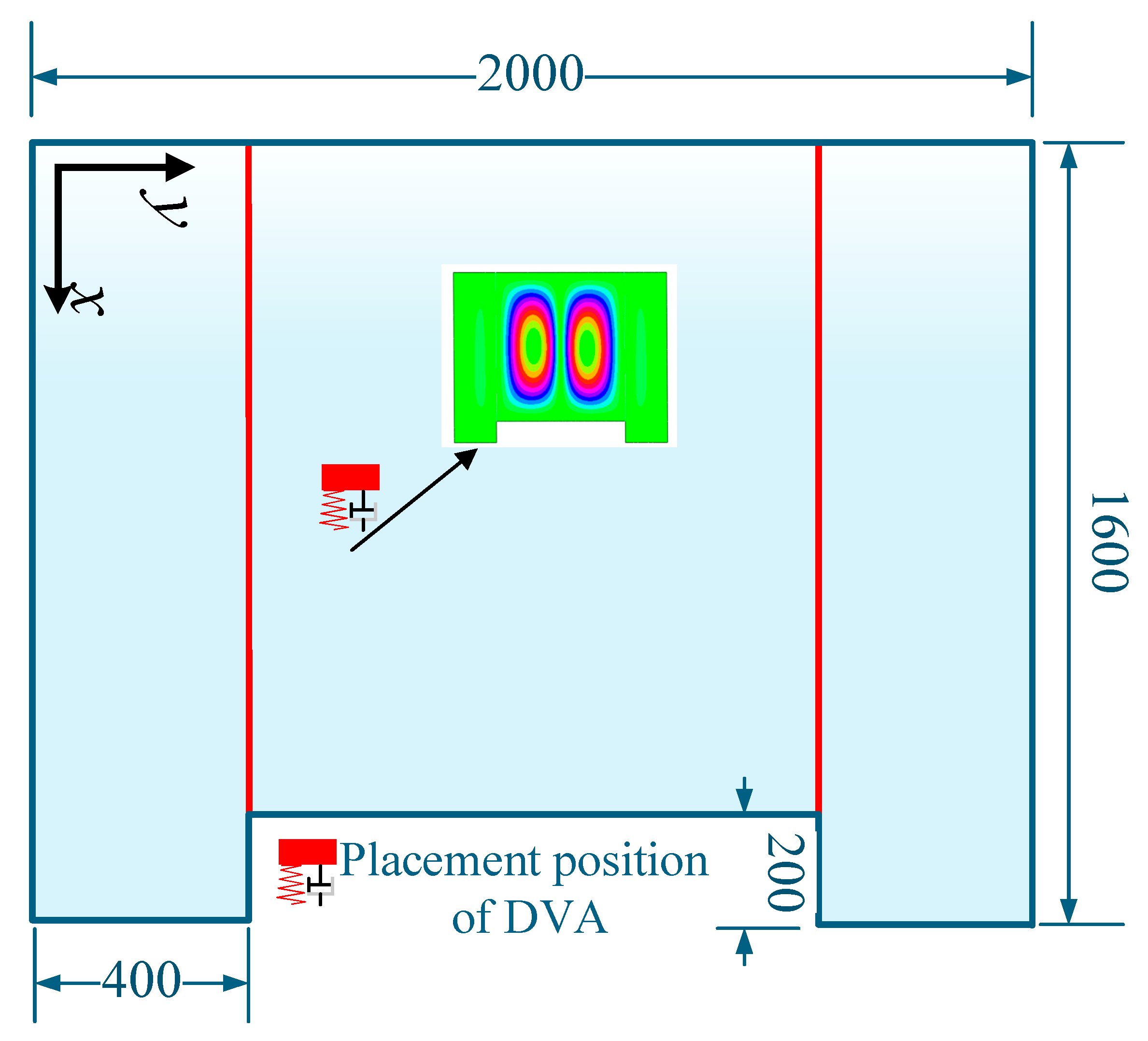
3.1. The Description of the Experiment Model
3.2. Design of DVA of the Coupled Plate Structure
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- A mathematical model of the partial resonance area was established. The experiment’s measurements of the modal shape and natural frequency accord well with the mathematical model’s computation findings, demonstrating the viability of the suggested mathematical model.
- (2)
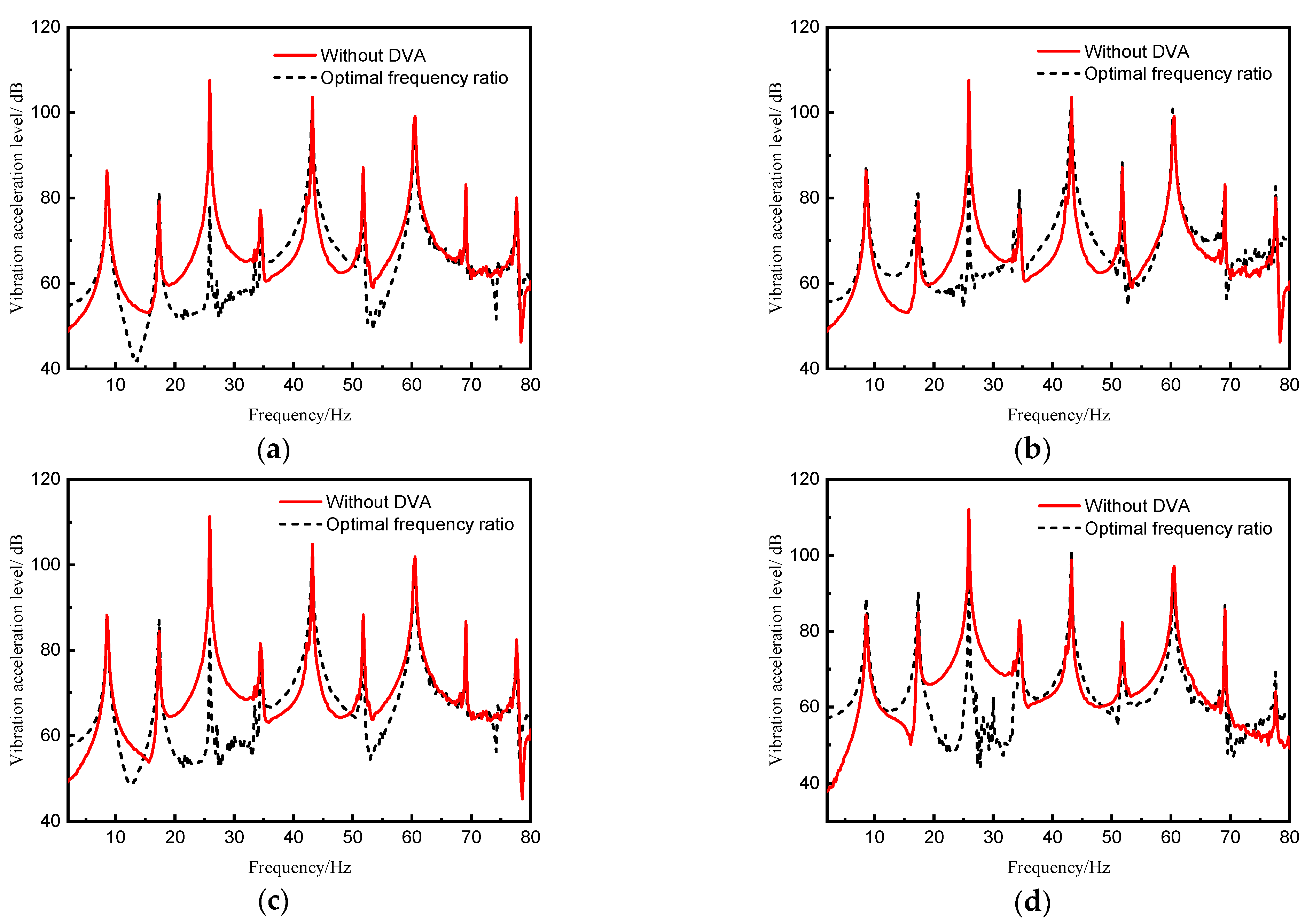
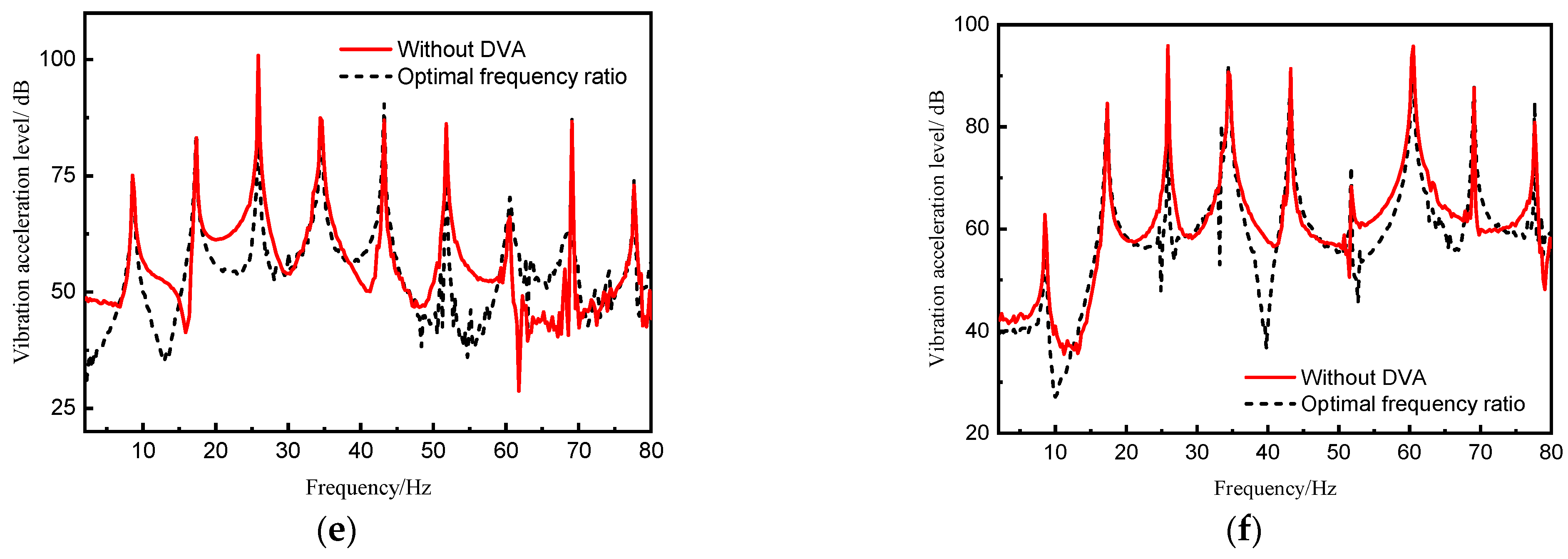
- The validity of fast determination of parameters of DVA of partial resonance area is also verified by the experiment. When the frequency ratio is optimal, the vibration control effect of the line spectrum to be controlled is the best. New peaks emerge near the target control frequency for each assessment point, these new peaks are significantly low and thus can be considered negligible.
- (3)
- A typical assessment point response under excitation load reveals the magnitude of the response of the checkpoint at the line spectrum frequency is closely related to the distance between the checkpoint and the corresponding mode wave belly.
- (4)
- As the distance between the assessment points and the DVA location increases, the effectiveness of vibration absorption decreases.
- (5)
- The method proposed in this study will be used to design and study new types of dynamic vibration-absorbing equipment in the future, and with the application of composite materials in marine equipment gradually, this method can also be extended to realize spectrum vibration control of composite materials.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Asiri, S.A.; AL-Zahrani, Y.Z. Theoretical analysis of mechanical vibration for offshore platform structures. World J. Mech. 2014, 4, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.-L.; Han, Q.-L.; Zhang, X.-M. Recent advances in vibration control of offshore platforms. Nonlinear Dyn. 2017, 89, 755–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lu, Z.; Yan, X.; Liu, Z.; Tang, L. Measurement and modelling of the vibration induced by working equipment on an offshore platform. Ocean Eng. 2021, 219, 108354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Wu, Z.H.; Cui, C.Y.; Yao, R.Q. Mitigation of Ice-Induced Vibration of Offshore Platform Based on Gated Recurrent Neural Network. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Pang, F.; Tang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, H. Vibration isolation characteristics of a novel composite flexible vibration-damping foundation. J. Vib. Control 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Pan, J.; Lin, T.R. Vibration of rectangular plates stiffened by orthogonal beams. J. Sound. Vib. 2021, 513, 116424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Vescovini, R.; Jansen, E.L. A semi-analytical framework for nonlinear vibration analysis of variable stiffness plates. Compos. Struct. 2021, 269, 113954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brubak, L.; Hellesland, J.; Hareide, O.J. Vibration analysis of plates with arbitrary stiffener arrangements using a semi-analytical approach. In Proceedings of the MARINE V: V International Conference on Computational Methods in Marine Engineering, Hamburg, Germany, 29–31 May, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Castro, S.G.; Donadon, M.V. Assembly of semi-analytical models to address linear buckling and vibration of stiffened composite panels with debonding defect. Compos. Struct. 2017, 160, 232–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.J.; He, X.C.; Chen, W.; Liang, N.; Peng, L.X. Meshless simulation and experimental study on forced vibration of rectangular stiffened plate. J. Sound. Vib. 2022, 518, 116602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Pang, F.Z.; Li, H.C.; Jia, D. A semi-analytical method for the dynamic characteristics of stiffened plate with general boundary conditions. Thin-Walled Struct. 2022, 178, 109513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, P.R.; Barik, M. Free Vibration Analysis of Stiffened Plates. J. Vib. Eng. Technol. 2020, 8, 869–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.G.; Zhou, Q.W.; Zhou, L.; Zhu, L.; Guo, K.L. Flexural wave band gaps and vibration attenuation characteristics in periodic bi-directionally orthogonal stiffened plates. Ocean Eng. 2019, 178, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Xie, F.; Qin, B.; Zhong, R.; Yu, H. Dynamics and power flow control of irregular elastic coupled plate systems: Precise modeling and experimental validation. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2020, 185, 105760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.; Zhu, G.; Liu, X. Plates’ parameters influence on the power transmission in an L-shaped plate system. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Mechatronics and Control (ICMC), Jinzhou, China, 3–5 July 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Guo, F.; Xu, D. Modeling and flexural vibration analysis of a double-thin-plate coupling system connected by nonlinear elements. Nonlinear Dyn. 2024, 112, 11851–11867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahapatra, K.; Panigrahi, S.K. Effect of general coupling conditions on the vibration and power flow characteristics of a two-plate built-up plate structure. Mech. Based Des. Struct. Mach. 2021, 49, 841–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.H.; Sanchez, J.; Benaroya, H.; Wang, J.F.; Xue, K. Free Vibration Analysis of Moderately Thick Coupled Plates with Elastic Boundary Conditions and Point Supports. Int. J. Struct. Stab. Dyn. 2019, 19, 1950150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamedani, S.J.; Khedmati, M.R.; Azkat, S. Vibration analysis of stiffened plates using finite element method. Lat. Am. J. Solids Struct. 2012, 9, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Kennedy, D. Energy flow analysis of mid-frequency vibration of coupled plate structures with a hybrid analytical wave and finite element model. Compos. Struct. 2016, 175, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, B.P. A hybrid analytical and finite element method for mid-frequency vibration analysis of plate structures with discontinuities. Int. J. Struct. Stab. Dyn. 2017, 17, 1750052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Kapania, R.K.; Dong, C.Y. Vibration and buckling analysis of curvilinearly stiffened plates using finite element method. AIAA J. 2015, 53, 1319–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Som, A.; Das, D. Seismic vibration control of offshore jacket platforms using decentralized sliding mode algorithm. Ocean Eng. 2018, 152, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmati, A.; Oterkus, E. Semi-Active Structural Control of Offshore Wind Turbines Considering Damage Development. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2018, 6, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandasamy, R.; Cui, F.; Townsend, N.; Foo, C.C.; Guo, J.; Shenoi, A.; Xiong, Y. A review of vibration control methods for marine offshore structures. Ocean Eng. 2016, 127, 279–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.-L.; Han, Q.-L.; Zhang, X.-M.; Tang, G.-Y. Active Control of Offshore Steel Jacket Platforms; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, S.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, J.; Meng, K.; Wang, M.; Pu, H.; Peng, Y.; Luo, J.; Xie, S. A tunable quasi-zero stiffness isolator based on a linear electromagnetic spring. J. Sound Vib. 2020, 482, 115449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enferadi, M.H.; Ghasemi, M.R.; Shabakhty, N. Wave-induced vibration control of offshore jacket platforms through SMA dampers. Appl. Ocean. Res. 2019, 90, 101848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghassempour, M.; Failla, G.; Arena, F. Vibration mitigation in offshore wind turbines via tuned mass damper. Eng. Struct. 2019, 183, 610–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.-D.; Xu, F.-H.; Chen, X. Vibration suppression on a platform by using vibration isolation and mitigation devices. Nonlinear Dyn. 2016, 83, 1341–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yue, Q.; Zhang, D. Ice-induced non-structure vibration reduction of jacket platforms with isolation cone system. Ocean Eng. 2013, 70, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, D.; Zhu, Z.; Xu, K.; Li, Y.; Liu, G. Vibration control of jacket offshore platform through magnetorheological elastomer (MRE) based isolation system. Appl. Ocean Res. 2021, 114, 102779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampitsis, A.; Kapasakalis, K.; Via-Estrem, L. An integrated FEA-CFD simulation of offshore wind turbines with vibration control systems. Eng. Struct. 2022, 254, 113859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, D. Ice-Induced Vibration Reduction on a Mooring Dolphin Platform Using an Isolation Cone System. J. Cold Reg. Eng. 2023, 37, 05023002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golafshani, A.A.; Gholizad, A. Friction damper for vibration control in offshore steel jacket platforms. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2009, 65, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, K.; Jangid, R. Passive control of offshore jacket platforms. Ocean Eng. 2005, 32, 1933–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh Le, L.; Van Nguyen, D.; Chang, S.; Kim, D.; Cho, S.G.; Nguyen, D.D. Vibration control of jacket offshore wind turbine subjected to earthquake excitations by using friction damper. J. Struct. Integr. Maint. 2019, 4, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, J.; Long, X.; Li, Q.; Xiao, Y. Vibration control of steel jacket offshore platform structures with damping isolation systems. Eng. Struct. 2007, 29, 1525–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Huang, S.; Huang, C.; Liu, R.; Ouyang, F. Passive control of jacket–type offshore wind turbine vibrations by single and multiple tuned mass dampers. Mar. Struct. 2021, 77, 102938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, V.N.; Basu, B. Passive control of floating offshore wind turbine nacelle and spar vibrations by multiple tuned mass dampers. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2015, 22, 152–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, M.Z.; Li, Z.; Sun, Y. Load mitigation for a barge-type floating offshore wind turbine via inerter-based passive structural control. Eng. Struct. 2018, 177, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Jahangiri, V. Bi-directional vibration control of offshore wind turbines using a 3D pendulum tuned mass damper. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2018, 105, 338–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, M.R.; Shabakhty, N.; Enferadi, M.H. Vibration control of offshore jacket platforms through shape memory alloy pounding tuned mass damper (SMA-PTMD). Ocean Eng. 2019, 191, 106348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Li, W.L.; Jin, G.; Yang, T.; Liu, Z. An analytical method for the in-plane vibration analysis of rectangular plates with elastically restrained edges. J. Sound. Vib. 2007, 306, 908–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, Q.; Deng, X.; Choe, K.; Zhong, R.; Shuai, C. Free vibrations of functionally graded porous rectangular plate with uniform elastic boundary conditions. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 168, 106–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Zou, T.; Pang, F.; Hu, C.; Ma, Y.; Li, H. Design method for distributed dynamic vibration absorbers of stiffened plate under different boundary constraints. Thin-Walled Struct. 2023, 185, 110494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Tang, Y.; Zou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Pang, F.; Jia, F.; Ma, Y.; Wang, S. The low frequency multi-linear spectrum vibration control study of cylindrical shell through a semi-analytical method. Thin-Walled Struct. 2023, 196, 111521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Liu, W.; Gao, P.X.; Ding, Y.J. An Analytical Dynamic Model for Vibration Suppression of a Multi-Span Continuous Bridge by Tuned Mass Dampers. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhu, X.; Li, T.; Yin, C.; Li, Q.; Chen, R. A Unified Solution for Free Vibration Analysis of Beam-Plate-Shell Combined Structures with General Boundary Conditions. Int. J. Struct. Stab. Dyn. 2022, 22, 2250080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

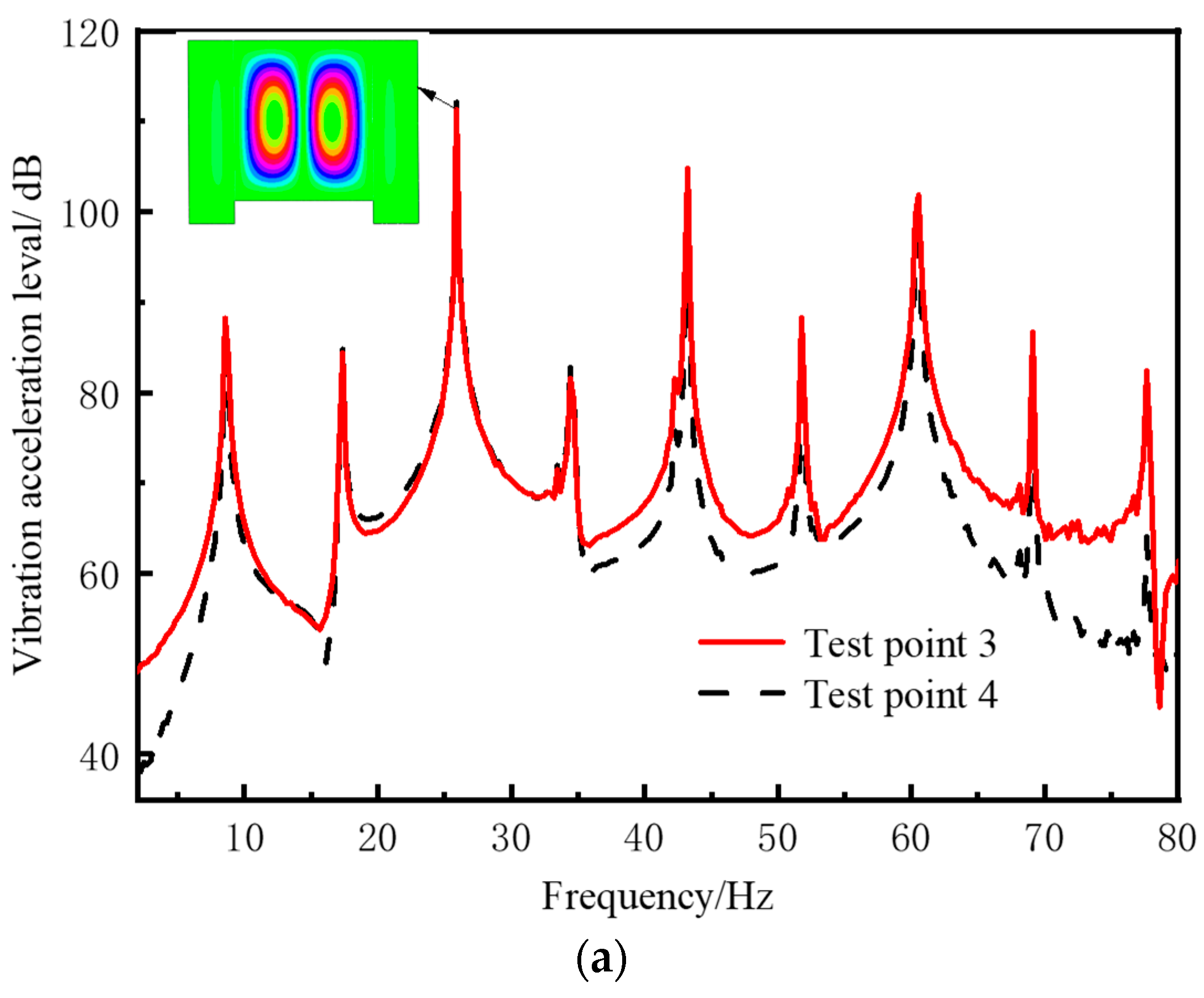
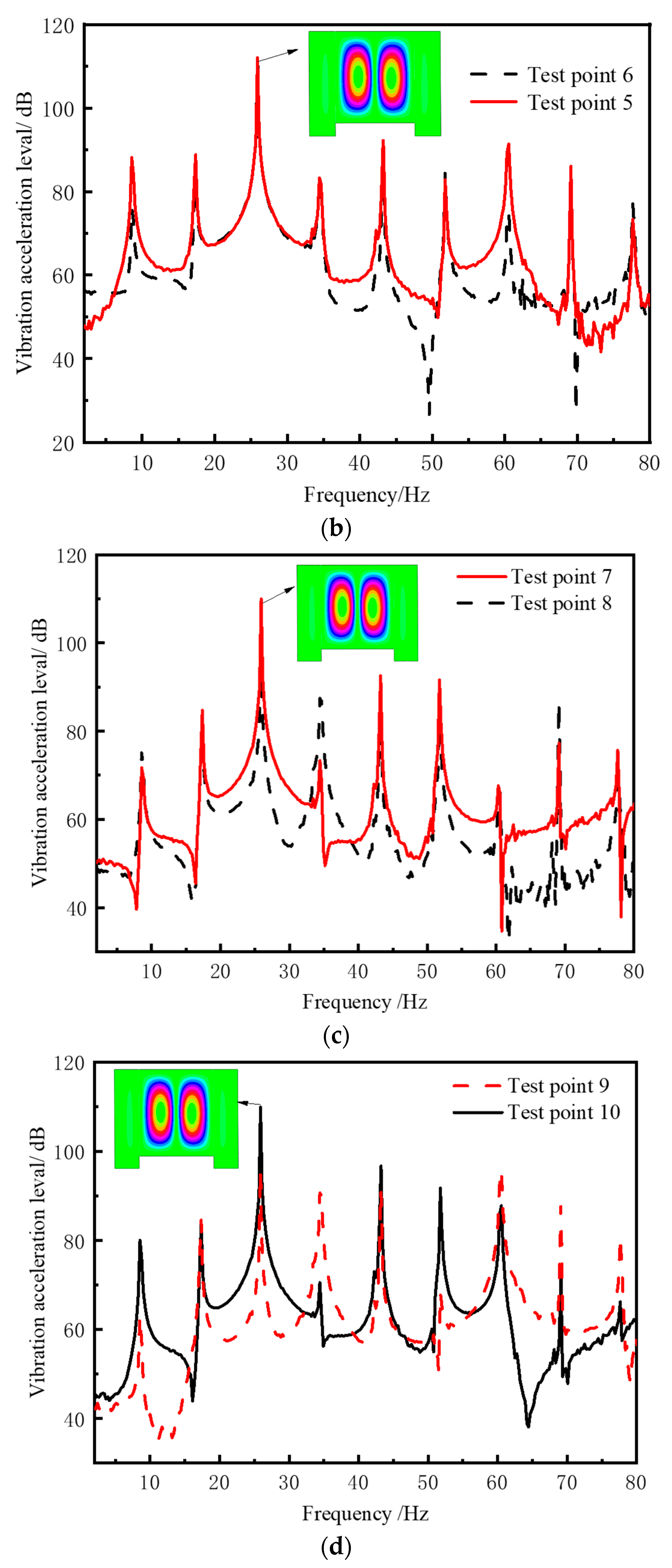

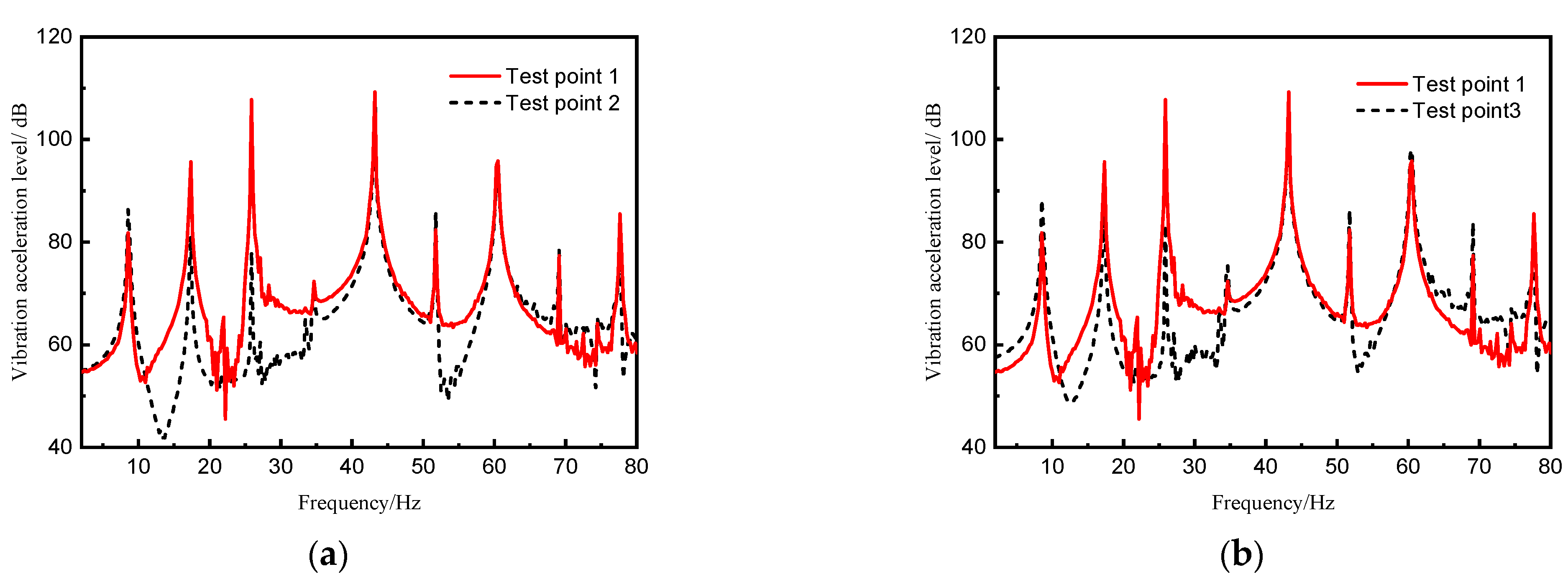
| Solution Method | The First-Order Equivalent Mass (kg) | The Second-Order Equivalent Mass (kg) | The Third-OrderEquivalent Mass (kg) | Computational Time (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Current method | 1154.7 | 1624.2 | 1105.3 | 13 |
| FEM (S4R,10,100) | 1155.4 | 1624.1 | 1105.1 | 45 |
| Name | Number | Model | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acceleration sensors | 11 | DH1A111E | Sensitivity: 100 mV/g |
| Force transducers | 1 | CL-YD-312 A | Sensitivity: 4 pC/N |
| Vibration motor | 1 | MVE500/3 | Speed: 3000 rpm |
| Inverter | 1 | SAKO/SK680 | Power: 2.2 kw |
| Data acquisition system | 1 | DH5929N | Sampling rate: 20 kHz |
| Method of Calculation | Equivalent Mass (kg) | Computational Time (s) |
|---|---|---|
| Current method | 4.99 | 21 |
| FEM (S4R,15,000) | 4.95 | 220 |
| Mode Number | Mass Ratio | Frequency Ratio | Mass (kg) | Frequency of DVA (Hz) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Third | 0.1 | 0.95 | 0.5 | 24.3 |
| Assessment Point Number | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Without DVA | 107.6 | 107.6 | 111.3 | 112.1 | 112 | 109.9 | 100.8 | 95.8 |
| Optimal frequency ratio (0.95) | 78.2 | 93.1 | 83.4 | 92.5 | 93.9 | 71.6 | 92.7 | 85.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Du, Y.; Jia, F.; Tang, Y.; Zheng, J.; Zou, Y.; Ma, Y. A Semi-Analytical Method to Design a Dynamic Vibration Absorber for Coupled Plate Structures of Offshore Platforms. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 283. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13020283
Du Y, Jia F, Tang Y, Zheng J, Zou Y, Ma Y. A Semi-Analytical Method to Design a Dynamic Vibration Absorber for Coupled Plate Structures of Offshore Platforms. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(2):283. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13020283
Chicago/Turabian StyleDu, Yuan, Fuxin Jia, Yang Tang, Jiajun Zheng, Yucheng Zou, and Yong Ma. 2025. "A Semi-Analytical Method to Design a Dynamic Vibration Absorber for Coupled Plate Structures of Offshore Platforms" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 2: 283. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13020283
APA StyleDu, Y., Jia, F., Tang, Y., Zheng, J., Zou, Y., & Ma, Y. (2025). A Semi-Analytical Method to Design a Dynamic Vibration Absorber for Coupled Plate Structures of Offshore Platforms. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(2), 283. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13020283






