Multimodal Underwater Sensing of Octocoral Populations and Anthropogenic Impacts in a Conservation-Priority Area (NE Aegean Sea, Greece)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
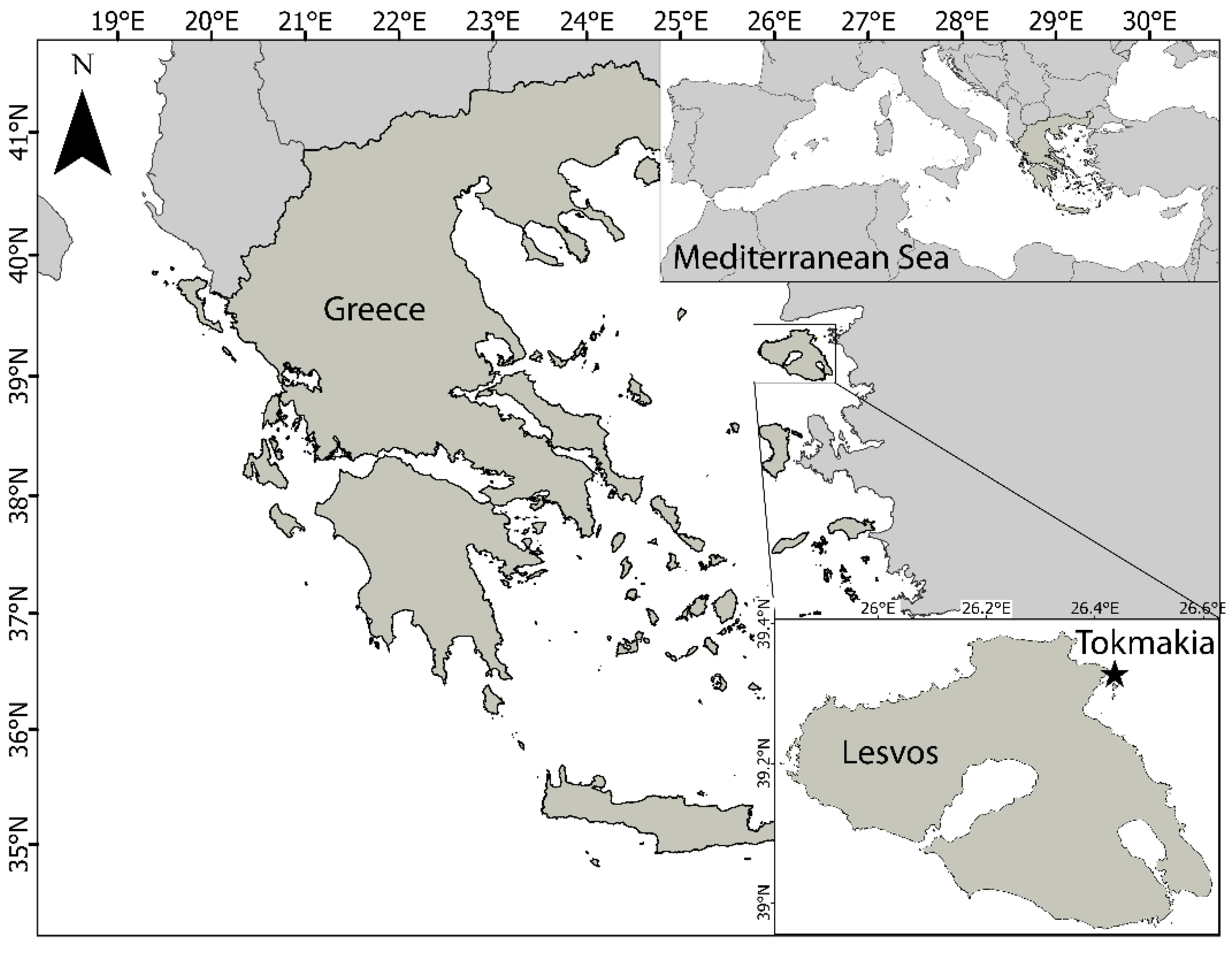
2.1. Study Area
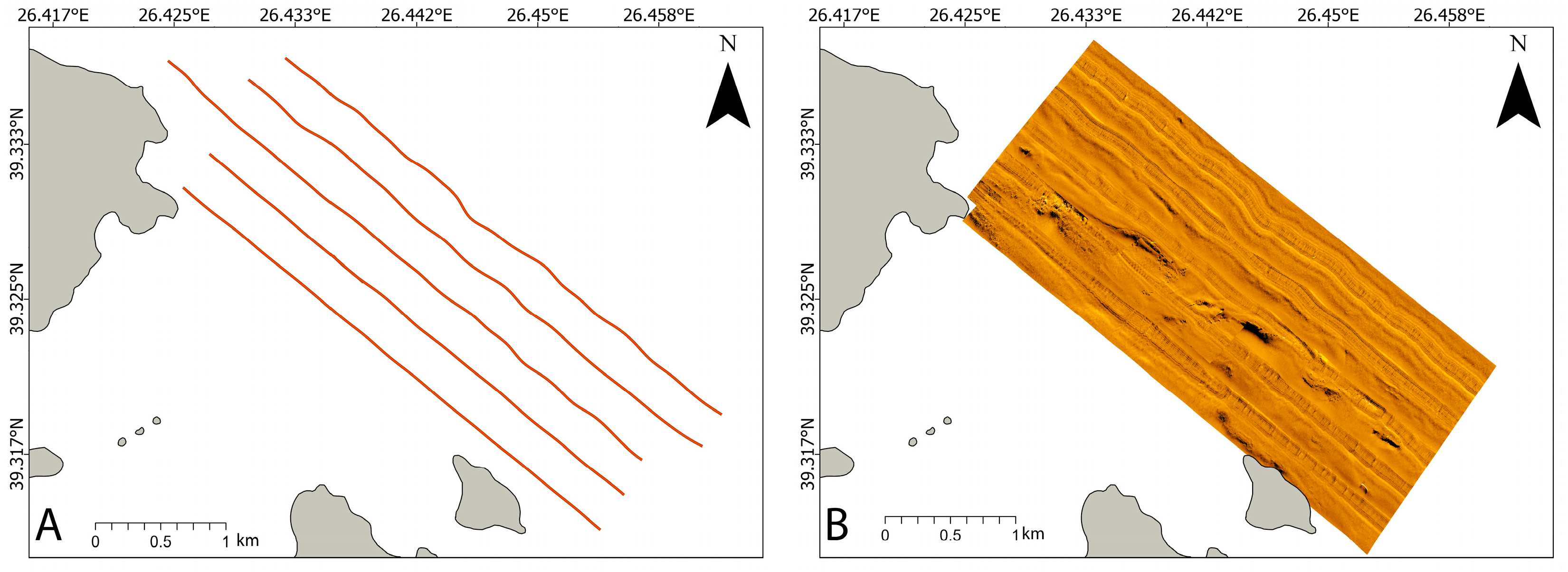
2.2. Seabed Mapping
2.3. Marine Litter and Gorgonian Population Assessment
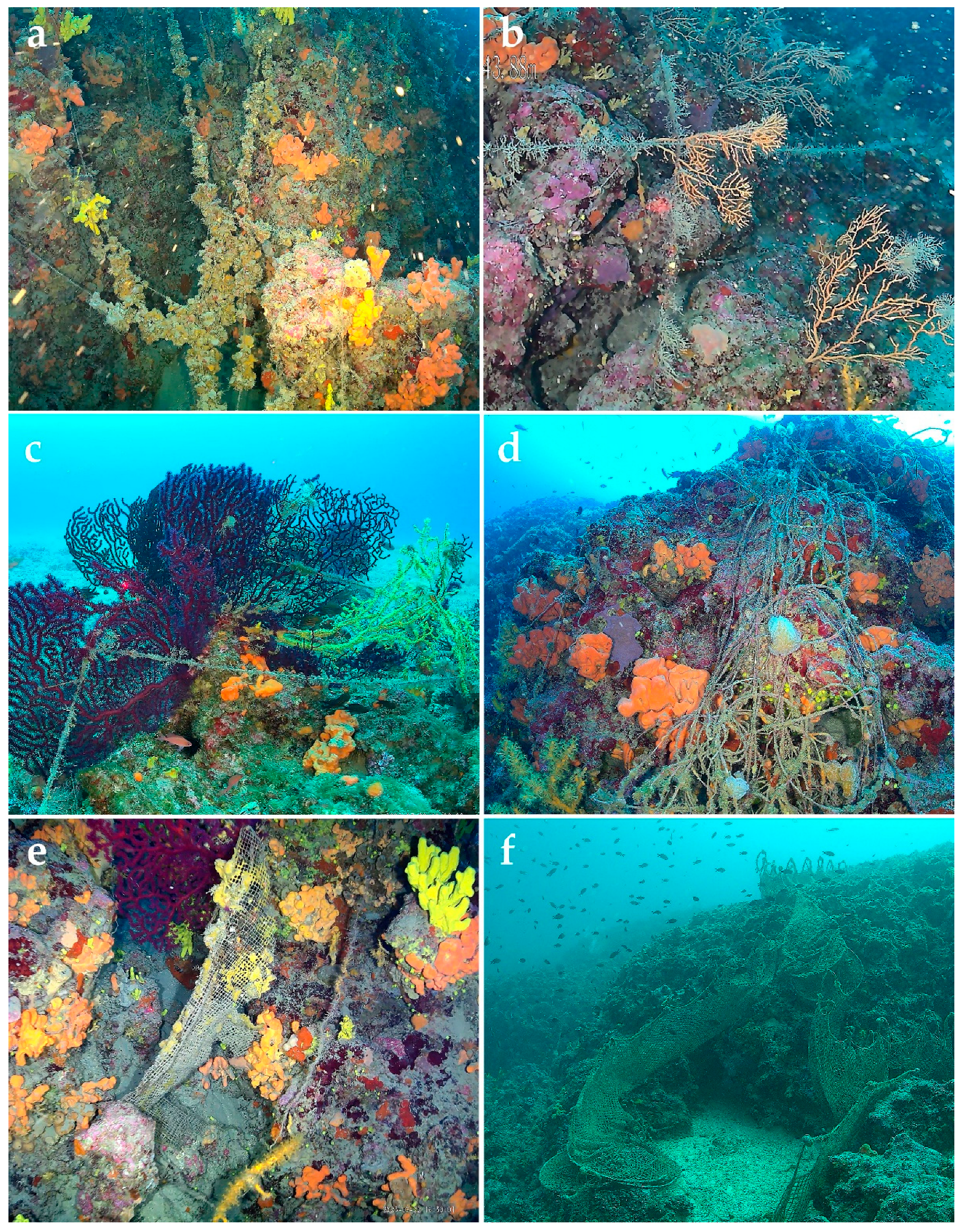
2.3.1. Marine Litter
2.3.2. Gorgonian Population Density
2.3.3. Population Structure and Health Status
3. Results
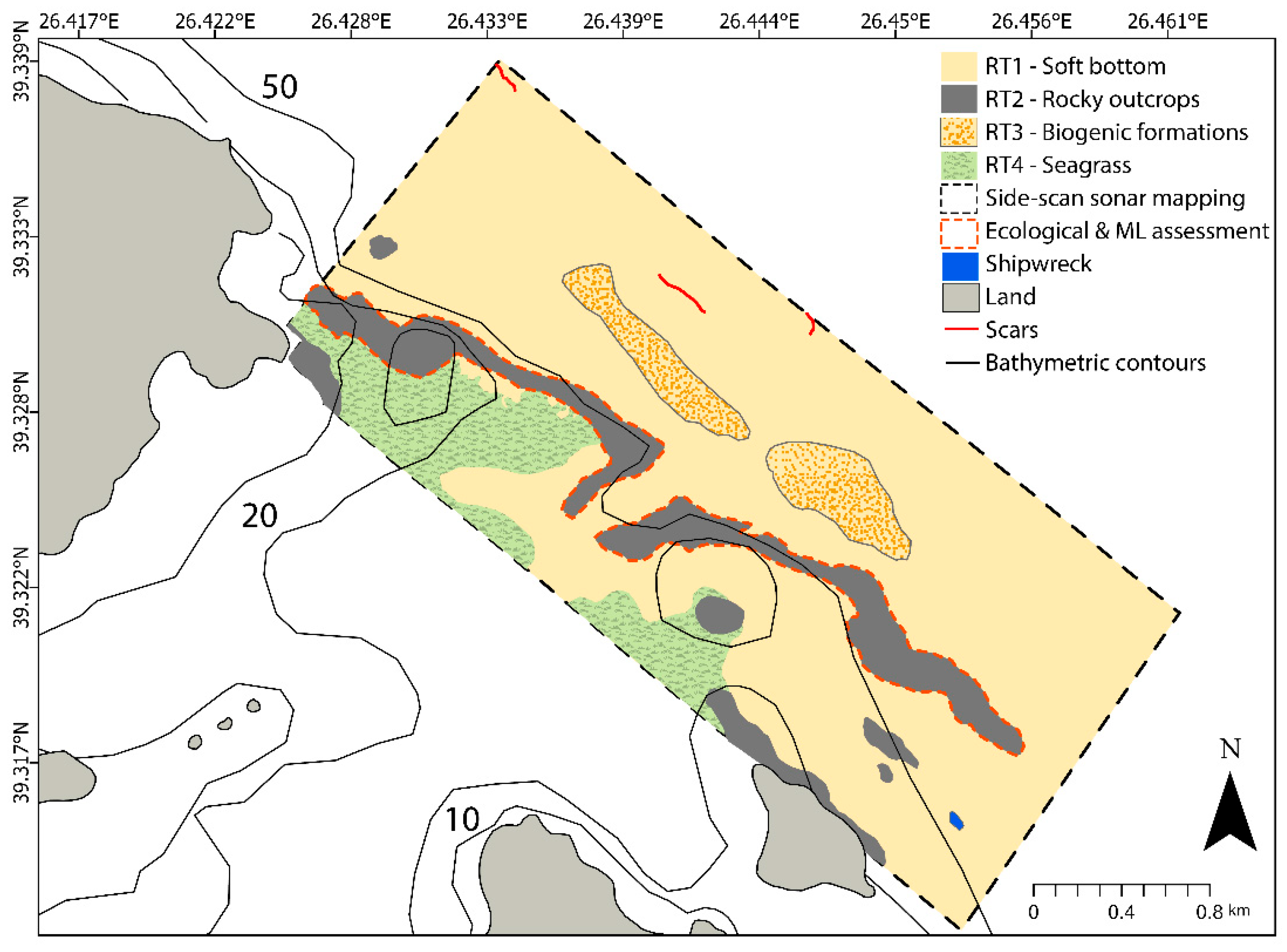
3.1. Results on Seabed Mapping
3.2. Results on Marine Litter and Gorgonian Population Assessment
3.2.1. Results on Marine Litter
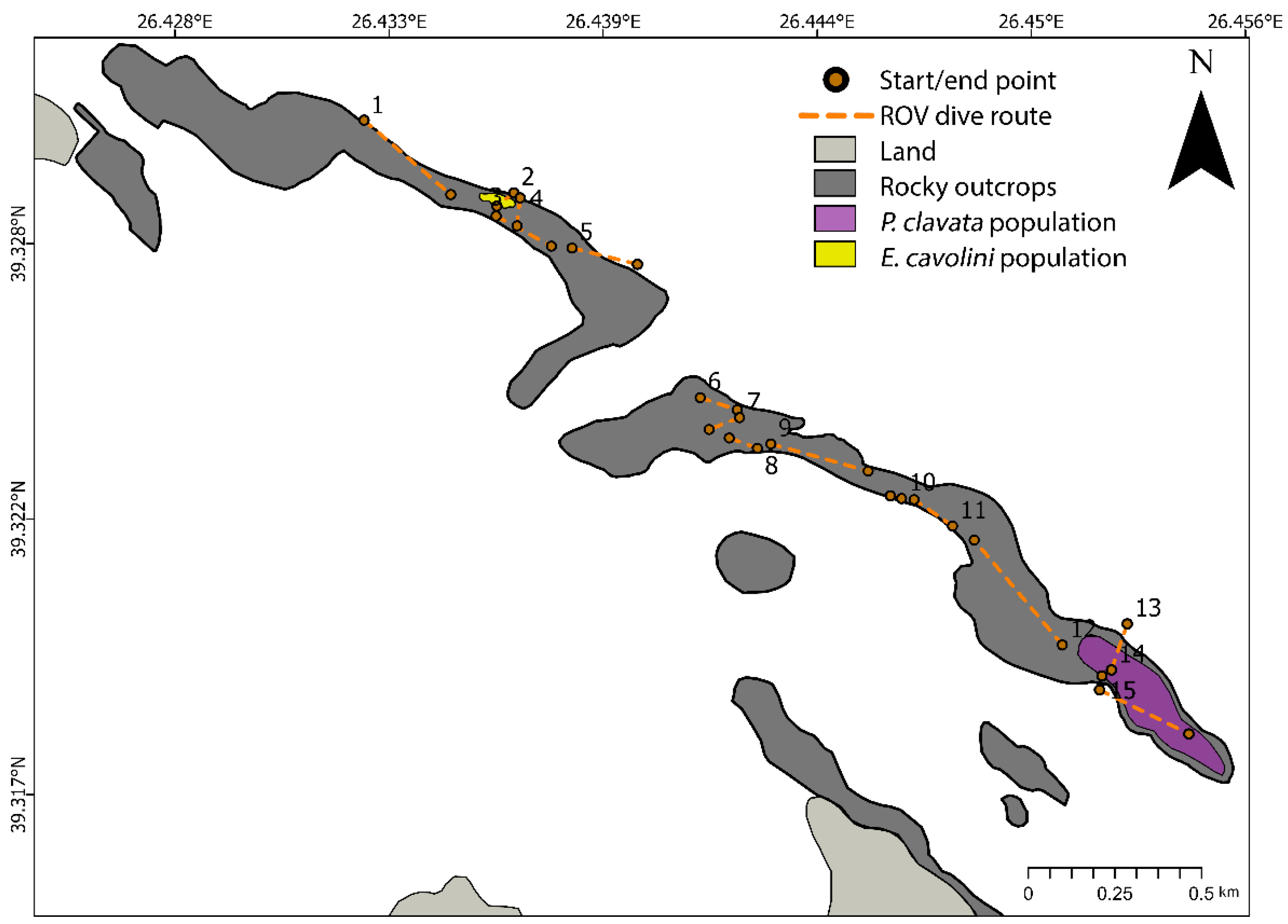
3.2.2. Results on Gorgonian Population Density
3.2.3. Results on Population Structure and Health Status
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AIC | Akaike Information Criterion |
| CI | Confidence Interval |
| CV | Coefficient of Variation |
| HNHS | Hellenic Navy Hydrographic Service |
| MCDS | Multiple-Covariate Distance Sampling |
| ML | Marine Litter |
| MSFD | Marine Strategy Framework Directive |
| ROV | Remotely Operated Vehicles |
| RT | Reflectivity Types |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| SE | Standard Error |
| SSS | Side-Scan Sonar |
References
- Ballesteros, E. Mediterranean coralligenous assemblages: A synthesis of present knowledge. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. Annu. Rev. 2006, 44, 123–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNEP-MAP-RAC/SPA. Action Plan for the Conservation of the Coralligenous and Other Calcareous Bio-Concretions in the Mediterranean Sea; RAC/SPA: Tunis, Tunisia, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Cerrano, C.; Bavestrello, G.; Bianchi, C.N.; Calcinai, B.; Cattaneo-Vietti, R.; Morri, C.; Sarà, M. The role of sponge bioerosion in the Mediterranean coralligenous accretion. In Mediterranean Ecosystems: Structures and Processes; Faranda, F.M., Guglielmo, L., Spezie, G., Eds.; Springer: Milano, Italy, 2001; pp. 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laborel, J. Le concrétionnement algal “coralligène” et son importance géomorphologique en Méditerranée. Rec. Trav. Stn. Mar. Endoume Bull. 1961, 23, 37–60. [Google Scholar]
- Pérès, J.M.; Picard, J. Nouveau manuel de bionomie benthique de la Méditerranée. Rec. Trav. Stat. Mar. Endoume 1964, 31, 5–137. [Google Scholar]
- Boudouresque, C.F. Marine biodiversity in the Mediterranean: Status of species, populations and communities. Sci. Rep. Port-Cros Natl. Park 2004, 20, 97–146. [Google Scholar]
- Coll, M.; Piroddi, C.; Steenbeek, J.; Kaschner, K.; Ben Rais Lasram, F.; Aguzzi, J.; Ballesteros, E.; Bianchi, C.N.; Corbera, J.; Dailianis, T.; et al. The biodiversity of the Mediterranean Sea: Estimates, patterns, and threats. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orejas, C.; Carreiro-Silva, M.; Mohn, C.; Reimer, J.D.; Samaai, T.; Allcock, A.L.; Rossi, S. Marine Animal Forests of the World: Definition and characteristics. Res. Ideas Outcomes 2022, 8, e96274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerrano, C.; Danovaro, R.; Gambi, C.; Pusceddu, A.; Riva, A.; Schiaparelli, S. Gold coral (Savalia savaglia) and gorgonian forests enhance benthic biodiversity and ecosystem functioning in the mesophotic zone. Biodivers. Conserv. 2010, 19, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, S.; Cúrdia, J.; Pereira, F.; Guerra-García, J.M.; Santos, M.N.; Cunha, M.R. Biodiversity patterns of epifaunal assemblages associated with the gorgonians Eunicella gazella and Leptogorgia lusitanica in response to host, space and time. J. Sea Res. 2014, 85, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cúrdia, J.; Carvalho, S.; Pereira, F.; Guerra-García, J.M.; Santos, M.N.; Cunha, M.R. Diversity and abundance of invertebrate epifaunal assemblages associated with gorgonians are driven by colony attributes. Coral Reefs 2015, 34, 611–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbera, G.; Dominguez-Carrió, C.; Grange, L.; Ambroso, S.; Corbera, J.; Gili, J.-M. The role of arborescent octocorals as ecosystem engineers in shaping the diversity and composition of shelf-dwelling benthic assemblages. Mar. Biol. 2025, 172, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, S.; Bramanti, L.; Gori, A.; Orejas, C. (Eds.) Marine Animal Forests: The Ecology of Benthic Biodiversity Hotspots; Springer International Publishing AG: Cham, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linares, C.; Doak, D.F.; Coma, R.; Dıáz, D.; Zabala, M. Life history and viability of a long-lived marine invertebrate: The octocoral Paramuricea clavate. Ecology 2007, 88, 918–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, S.; Bramanti, L.; Horta, P.; Allcock, L.; Carreiro-Silva, M.; Coppari, M.; Denis, V.; Hadjioannou, L.; Isla, E.; Jimenez, C.; et al. Protecting global marine animal forests. Science 2022, 376, 929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, L.; Vega Fernández, T.; Necci, F.; Grelaud, M.; Ziveri, P.; Gerovasileiou, V.; Rossi, S. Can Marine Animal Forests benefit from existing conservation measures? A systematic approach towards the identification of protected sessile benthic species in the Mediterranean Sea. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2025, 26, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Directorate-General for Environment (European Commission); Rodwell, J.R.; García Criado, M.; Gubbay, S.; Borg, J.; Otero, M.; Janssen, J.A.M.; Haynes, T.; Beal, S.; Nieto, A.; et al. European Red List of Habitats. Part 1, Marine Habitats; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2016; ISBN 978-92-79-61586-3. [Google Scholar]
- Otero, M.M.; Numa, C.; Bo, M.; Orejas, C.; Garrabou, J.; Cerrano, C.; Kružic, P.; Antoniadou, C.; Aguilar, R.; Kipson, S.; et al. Overview of the Conservation Status of Mediterranean Anthozoans; IUCN: Malaga, Spain, 2017; 73p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloret, J. Human health benefits supplied by Mediterranean marine biodiversity. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 60, 1640–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salomidi, M.; Katsanevakis, S.; Borja, A.; Braeckman, U.; Damalas, D.; Galparsoro, I.; Mifsud, R.; Mirto, S.; Pascual, M.; Pipitone, C.; et al. Assessment of goods and services, vulnerability, and conservation status of European seabed biotopes: A stepping stone towards ecosystem-based marine spatial management. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2012, 13, 49–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tribot, A.S.; Mouquet, N.; Villéger, S.; Raymond, M.; Hoff, F.; Boissery, P.; Holon, F.; Deter, J. Taxonomic and functional diversity increase the aesthetic value of coralligenous reefs. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thierry de Ville d’Avray, L.; Ami, D.; Chenuil, A.; David, R.; Féral, J.-P. Application of the ecosystem service concept at a small-scale: The cases of coralligenous habitats in the North-western Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 138, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrabou, J.; Gómez-Gras, D.; Medrano, A.; Cerrano, C.; Ponti, M.; Schlegel, R.; Bensoussan, N.; Turicchia, E.; Sini, M.; Gerovasileiou, V.; et al. Marine heatwaves drive recurrent mass mortalities in the Mediterranean Sea. Glob. Change Biol. 2022, 28, 5708–5725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karachle, P.K.; Dimarchopoulou, D.; Tsikliras, A.C. Is shore-based recreational fishing in Greece an unregulated activity that increases catch uncertainty? Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2020, 36, 101273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sini, M.; Katsanevakis, S.; Koukourouvli, N.; Gerovasileiou, V.; Dailianis, T.; Buhl Mortensen, L.; Damalas, D.; Dendrinos, P.; Dimas, X.; Frantzis, A.; et al. Assembling ecological pieces to reconstruct the conservation puzzle of the Aegean Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilman, E.; Musyl, M.; Suuronen, P.; Chaloupka, M.; Gorgin, S.; Wilson, J.; Kuczenski, B. Highest risk abandoned, lost and discarded fishing gear. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macfadyen, G.; Huntington, T.; Cappell, R. Abandoned, Lost or Otherwise Discarded Fishing Gear; UNEP Regional Seas Reports and Studies No. 185; FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Technical Paper No. 523; UNEP/FAO: Rome, Italy, 2009; 115p, Available online: https://www.fao.org/4/i0620e/i0620e00.htm (accessed on 1 September 2025).
- Galgani, F.; Hanke, G.; Werner, S.; De Vrees, L. Marine litter within the European Marine Strategy Framework Directive. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2013, 70, 1055–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angiolillo, M.; di Lorenzo, B.; Farcomeni, A.; Bo, M.; Bavestrello, G.; Santangelo, G.; Cau, A.; Mastascusa, V.; Sacco, F.; Canese, S. Distribution and assessment of marine debris in the deep Tyrrhenian Sea (NW Mediterranean Sea, Italy). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 92, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enrichetti, F.; Bava, S.; Bavestrello, G.; Betti, F.; Lanteri, L.; Bo, M. Artisanal fishing impact on deep coralligenous animal forests: A Mediterranean case study of marine vulnerability. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2019, 177, 112–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, M.; Bava, S.; Canese, S.; Angiolillo, M.; Cattaneo-Vietti, R.; Bavestrello, G. Fishing impact on deep Mediterranean rocky habitats as revealed by ROV investigation. Biol. Conserv. 2014, 171, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enrichetti, F.; Bavestrello, G.; Betti, F.; Findi, F.; Tregrosso, A.; Bo, M. Fate of lost fishing gears: Experimental evidence of biofouling colonization patterns from the northwestern Mediterranean Sea. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 268, 115746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betti, F.; Bavestrello, G.; Bo, M.; Ravanetti, G.; Enrichetti, F.; Coppari, M.; Cappanera, V.; Venturini, S.; Cattaneo-Vietti, R. Evidences of fishing impact on the coastal gorgonian forests inside the Portofino MPA (NW Mediterranean Sea). Ocean Coast. Manag. 2020, 187, 105105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angiolillo, M.; Fortibuoni, T. Impacts of marine litter on Mediterranean reef systems: From shallow to deep waters. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 581966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavestrello, G.; Cerrano, C.; Zanzi, D.; Cattaneo-Vietti, R. Damage by fishing activities to the gorgonian coral Paramuricea clavata in the Ligurian Sea. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 1997, 7, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiappone, M.; Dienes, H.; Swanson, D.W.; Miller, S.L. Impacts of lost fishing gear on coral reef sessile invertebrates in the Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary. Biol. Conserv. 2005, 121, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrabou, J.; Sala, E.; Arcas, A.; Zabala, M. The impact of diving on rocky sublittoral communities: A case study of a bryozoan population. Conserv. Biol. 1998, 12, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coma, R.; Pola, E.; Ribes, M.; Zabala, M. Long-term assessment of the patterns of mortality of a temperate octocoral in protected and unprotected areas: A contribution to conservation and management needs. Ecol. Appl. 2004, 14, 1466–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linares, C.; Zabala, M.; Garrabou, J.; Coma, R.; Diaz, D.; Hereu, B.; Dantart, L. Assessing the impact of diving in coralligenous communities: The usefulness of demographic studies of red gorgonian populations. Sci. Rep. Port-Cros Natl. Park 2010, 24, 161–184. [Google Scholar]
- Linares, C.; Bianchimani, O.; Torrents, O.; Marschal, C.; Drap, P.; Garrabou, J. Marine protected areas and the conservation of long-lived invertebrates: The Mediterranean red coral. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2010, 402, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cebrian, E.; Linares, C.; Marschal, C.; Garrabou, J. Exploring the effects of invasive algae on the persistence of gorgonian populations. Biol. Invasions 2012, 14, 2647–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piazzi, L.; Gennaro, P.; Balata, D. Threats to macroalgal coralligenous assemblages in the Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 2623–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNEP/MAP. Action Plan for the Conservation of the Coralligenous and Other Calcareous Bio-Concretions in the Mediterranean Sea; UNEP/MAP: Athens, Greece, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Tsirintanis, K.; Azzurro, E.; Crocetta, F.; Dimiza, M.; Froglia, C.; Gerovasileiou, V.; Langeneck, J.; Mancinelli, G.; Rosso, A.; Stern, N.; et al. Bioinvasion impacts on biodiversity, ecosystem services, and human health in the Mediterranean Sea. Aquat. Invasions 2022, 17, 308–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Gras, D.; Linares, C.; Dornelas, M.; Madin, J.S.; Brambilla, V.; Ledoux, J.-B.; López-Sendino, P.; Bensoussan, N.; Garrabou, J. Climate change transforms the functional identity of Mediterranean coralligenous assemblages. Ecol. Lett. 2021, 24, 1038–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlot, J.; Galobart, C.; Gómez-Gras, D.; Santamaría, J.; Golo, R.; Sini, M.; Cebrian, E.; Gerovasileiou, V.; Ponti, M.; Turicchia, E.; et al. Vulnerability of benthic trait diversity across the Mediterranean Sea following mass mortality events. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, S. The destruction of the ‘animal forests’ in the oceans: Towards an oversimplification of the benthic ecosystems. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2013, 84, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapata-Ramírez, P.A.; Scaradozzi, D.; Sorbi, L.; Palma, M.; Pantaleo, U.; Ponti, M.; Cerrano, C. Innovative study methods for the Mediterranean coralligenous habitats. Adv. Oceanogr. Limnol. 2013, 4, 102–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Camillo, C.G.; Ponti, M.; Storari, A.; Scarpa, C.; Roveta, C.; Pulido Mantas, T.; Coppari, M.; Cerrano, C. Review of the indexes to assess the ecological quality of coralligenous reefs: Towards a unified approach. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1252969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astruch, P.; Boudouresque, C.F.; Cabral, M.; Schohn, T.; Ballesteros, E.; Bellan-Santini, D.; Belloni, B.; Bianchi, C.N.; Cassetti, O.; Chevaldonné, P.; et al. An ecosystem-based index for Mediterranean coralligenous reefs: A protocol to assess the quality of a complex key habitat. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2025, 220, 118375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgiadis, M.; Papatheodorou, G.; Tzanatos, E.; Geraga, M.; Ramfos, A.; Koutsikopoulos, C.; Ferentinos, G. Coralligène formations in the eastern Mediterranean Sea: Morphology, distribution, mapping and relation to fisheries in the southern Aegean Sea (Greece) based on high-resolution acoustics. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2009, 368, 44–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracchi, V.; Basso, D.; Marchese, F.; Corselli, C.; Savini, A. Coralligenous morphotypes on subhorizontal substrate: A new categorization. Cont. Shelf Res. 2017, 144, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimas, X.; Fakiris, E.; Christodoulou, D.; Georgiou, N.; Geraga, M.; Papathanasiou, V.; Orfanidis, S.; Kotomatas, S.; Papatheodorou, G. Marine priority habitat mapping in a Mediterranean conservation area (Gyaros, South Aegean) through multi-platform marine remote sensing techniques. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 953462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giakoumi, S.; Sini, M.; Gerovasileiou, V.; Mazor, T.; Beher, J.; Possingham, H.P.; Abdulla, A.; Çinar, M.E.; Dendrinos, P.; Gucu, A.C.; et al. Ecoregion-based conservation planning in the Mediterranean: Dealing with large-scale heterogeneity. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, C.S.; Giannoulaki, M.; De Leo, F.; Scardi, M.; Salomidi, M.; Knittweis, L.; Pace, M.L.; Garofalo, G.; Gristina, M.; Ballesteros, E.; et al. Coralligenous and maërl habitats: Predictive modelling to identify their spatial distributions across the Mediterranean Sea. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, S.B.; Pizarro, O.R.; Jakuba, M.V.; Johnson, C.R.; Barrett, N.S.; Babcock, R.C.; Kendrick, G.A.; Steinberg, P.D.; Heyward, A.J.; Doherty, P.J.; et al. Monitoring of benthic reference sites: Using an autonomous underwater vehicle. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2012, 19, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, S.D.; Mahon, I.; Marzloff, M.P.; Pizarro, O.; Johnson, C.R.; Williams, S.B. Stereo-imaging AUV detects trends in sea urchin abundance on deep overgrazed reefs. Adv. Oceanogr. Limnol. Methods 2016, 14, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benoist, N.M.A.; Morris, K.J.; Bett, B.J.; Durden, J.M.; Huvenne, V.A.I.; Le Bas, T.P.; Wynn, R.B.; Ware, S.J.; Ruhl, H.A. Monitoring mosaic biotopes in a marine conservation zone by autonomous underwater vehicle. Conserv. Biol. 2016, 33, 1178–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.J.; Smith, S.J.; Lawton, P.; Anderson, J.T. Benthic habitat mapping: A review of progress towards improved understanding of the spatial ecology of the seafloor using acoustic techniques. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2011, 92, 502–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochrane, G.R.; Lafferty, K.D. Use of acoustic classification of sidescan sonar data for mapping benthic habitat in the Northern Channel Islands, California. Cont. Shelf Res. 2002, 22, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sward, D.; Monk, J.; Barrett, N. A systematic review of remotely operated vehicle surveys for visually assessing fish assemblages. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierdomenico, M.; Bonifazi, A.; Argenti, L.; Ingrassia, M.; Casalbore, D.; Aguzzi, L.; Viaggiu, E.; Le Foche, M.; Chiocci, F.L. Geomorphological characterization, spatial distribution and environmental status assessment of coralligenous reefs along the Latium continental shelf. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 131, 108219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sini, M.; Kipson, S.; Linares, C.; Koutsoubas, D.; Garrabou, J. The yellow gorgonian Eunicella cavolini: Demography and disturbance levels across the Mediterranean Sea. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sini, M.; Garrabou, J.; Trygonis, V.; Koutsoubas, D. Coralligenous formations dominated by Eunicella cavolini (Koch, 1887) in the NE Mediterranean: Biodiversity and structure. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2019, 20, 174–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoutsoglou, E.; Hasiotis, T.; Kyriakoudi, D.; Velegrakis, A.; Lowag, J. Puzzling micro-relief (mounds) of a soft-bottomed, semi-enclosed shallow marine environment. Geo-Mar. Lett. 2018, 38, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanke, G.; Galgani, F.; Werner, S.; Oosterbaan, L.; Nilsson, P.; Fleet, D.; Kinsey, S.; Thompson, R.C.; Van Franeker, J.A.; Vlachogianni, T.; et al. Guidance on Monitoring of Marine Litter in European Seas; EUR 26113; JRC83985; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An Open-Source Platform for Biological-Image Analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckland, S.; Anderson, D.; Burnham, K.; Laake, J.; Borchers, D.; Thomas, L. Introduction to Distance Sampling: Estimating Abundance of Biological Populations; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, L.; Buckland, S.T.; Rexstad, E.A.; Laake, J.L.; Strindberg, S.; Hedley, S.L.; Bishop, J.R.; Marques, T.A.; Burnham, K.P. Distance software: Design and analysis of distance sampling surveys for estimating population size. J. Appl. Ecol. 2010, 47, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, T.A.; Thomas, L.; Fancy, S.G.; Buckland, S.T. Improving estimates of bird density using multiple-covariate distance sampling. Auk 2007, 124, 1229–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akaike, H. Information theory as an extension of the maximum likelihood principle. In Proceedings of the Second International Symposium on Information Theory; Petrov, B.N., Csaki, F., Eds.; Akademiai Kiado: Budapest, Hungary, 1973; pp. 267–281. [Google Scholar]
- Burnham, K.P.; Anderson, D.R. Model Selection and Inference: A Practical Information-Theoretic Approach, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrabou, J.; Kipson, S.; Kaleb, S.; Kruzic, P.; Jaklin, A.; Ante, Z.; Rajkovic, Z.; Rodic, P.; Jelic, K.; Zupan, D. (Eds.) UNEP-MAP-RAC/SPA. Monitoring Protocol for Reefs—Coralligenous Community; RAC/SPA—MedMPAnet Project: Tunis, Tunisia, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Linares, C.; Coma, R.; Garrabou, J.; Díaz, D.; Zabala, M. Size Distribution, Density and Disturbance in Two Mediterranean Gorgonians: Paramuricea clavata and Eunicella singularis. J. Appl. Ecol. 2008, 45, 688–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrabou, J.; Coma, R.; Benssoussan, N.; Bally, M.; Chevaldonné, P.; Cigliano, M.; Diaz, D.; Harmelin, J.G.; Gambi, M.C.; Kersting, D.K.; et al. Mass mortality in NW Mediterranean rocky benthic communities: Effects of the 2003 heat wave. Glob. Change Biol. 2009, 15, 1090–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linares, C.; Coma, R.; Diaz, D.; Zabala, M.; Hereu, B.; Dantart, L. Immediate and delayed effects of a mass mortality event on gorgonian population dynamics and benthic community structure in the NW Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2005, 305, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lioupa, V.; Petsimeris, I.; Karsiotis, P.; Papavasileiou, F.; Poulos, A.; Andreadis, O.; Manoutsoglou, E.; Hasiotis, T. Sensing underwater landscape off coastal cities: Implications for better management strategies. In Proceedings of the Eleventh International Conference on Remote Sensing and Geoinformation of the Environment (RSCy2025), Paphos, Cyprus, 17–19 March 2025; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Turicchia, E.; Abbiati, M.; Ponti, M. Mediterranean Gorgonians Fighting. Mar. Biodivers. 2020, 50, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iborra, L.; Leduc, M.; Fullgrabe, L.; Cuny, P.; Gobert, S. Temporal Trends of Two Iconic Mediterranean Gorgonians (Paramuricea clavata and Eunicella cavolini) in the Climate Change Context. J. Sea Res. 2022, 186, 102241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chimienti, G.; Maiorca, M.; Digenis, M.; Poursanidis, D. Conservation status of upper-mesophotic octocoral habitats at Sporades Archipelago (Aegean Sea). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 190, 114868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tignat-Perrier, R.; van de Water, J.A.J.M.; Guillemain, D.; Aurelle, D.; Allemand, D.; Ferrier-Pagès, C. The effect of thermal stress on the physiology and bacterial communities of two key Mediterranean gorgonians. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2022, 88, e02340-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blouet, S.; Bramanti, L.; Guizien, K. Ecological niche modelling of five gorgonian species within the shallow rocky habitat of the French Mediterranean coast. Vie Milieu/Life Environ. 2024, 7, 1–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figuerola-Ferrando, L.; Amblas, D.; Matos, F.L.; Zentner, Y.; Garrabou, J.; Linares, C. Modelling the distribution of key Mediterranean gorgonians: An ensemble approach to unravel broad-scale patterns and guide conservation efforts. J. Biogeogr. 2025, 52, 392–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, M.; Canese, S.; Spaggiari, C.; Pusceddu, A.; Bertolino, M.; Angiolillo, M.; Giusti, M.; Loreto, M.F.; Salvati, E.; Greco, S.; et al. Deep coral oases in the south Tyrrhenian Sea. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshioka, P.M. Size-specific life history pattern of a shallow-water gorgonian. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1994, 184, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cupido, R.; Cocito, S.; Barsanti, M.; Sgorbini, S.; Peirano, A.; Santangelo, G. Unexpected long-term population dynamics in a canopy-forming gorgonian coral following mass mortality. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2009, 394, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Previati, M.; Scinto, A.; Cerrano, C.; Osinga, R. Oxygen consumption in Mediterranean octocorals under different temperatures. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2010, 390, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerrano, C.; Bavestrello, G.; Bianchi, C.N.; Cattaneo-Vietti, R.; Bava, S.; Morganti, C.; Morri, C.; Picco, P.; Sara, G.; Schiaparelli, S.; et al. A catastrophic mass-mortality episode of gorgonians and other organisms in the Ligurian Sea (North-Western Mediterranean), summer 1999. Ecol. Lett. 2000, 3, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambi, M.C.; Barbieri, F.; Singorelli, S.; Saggiomo, V. Mortality events along the Campania coast (Tyrrhenian Sea) in summers 2008 and 2009 and relation to thermal conditions. Biol. Mar. Mediterr. 2010, 17, 126–127. [Google Scholar]
- Consoli, P.; Romeo, T.; Angiolillo, M.; Canese, S.; Esposito, V.; Salvati, E.; Scotti, G.; Andaloro, F.; Tunesi, L. Marine litter from fishery activities in the Western Mediterranean Sea: The impact of entanglement on marine animal forests. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 249, 472–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobsen, N.; Roveta, C.; Pulido Mantas, T.; Coppari, M.; Di Camillo, C.; Calcinai, B.; Cerrano, C. Assessment of octocoral-dominated benthic assemblages along a mesophotic gradient, with a focus on the impact of lost fishing gears. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2024, 34, e4248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Dios, A.; De la Torriente, A.; González-Irusta, R.; Aguilar, R.; Serrano, A.; Foglini, F.; Lo Iacono, C. Assessing marine litter on the VMEs of el Seco de los Olivos (W Mediterranean Sea). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2025, 215, 117802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, G.; Sanna, G.; Arrostuto, N.; Fois, N.; Sechi, C.; Tomassetti, P.; Lomiri, S. The grim fate of a Paramuricea clavata (Risso, 1827) forest off Asinara Island (northwest Sardinia, Italy). Mar. Biodivers. 2024, 54, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, C.; Resaikos, V. Chasing Ghosts: Evidence-Based Management of Abandoned Fishing Gear in the Eastern Mediterranean. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaida, T.C.; Binnerts, B.; Bos, O. Semi-automated classification of Side-Scan Sonar data for mapping Sabellaria spinulosa reefs in the Brown Bank, Dutch Continental Shelf. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Meng, J.; Zhang, H.; Yan, J. A new method for acquisition of high-resolution seabed topography by matching seabed classification images. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
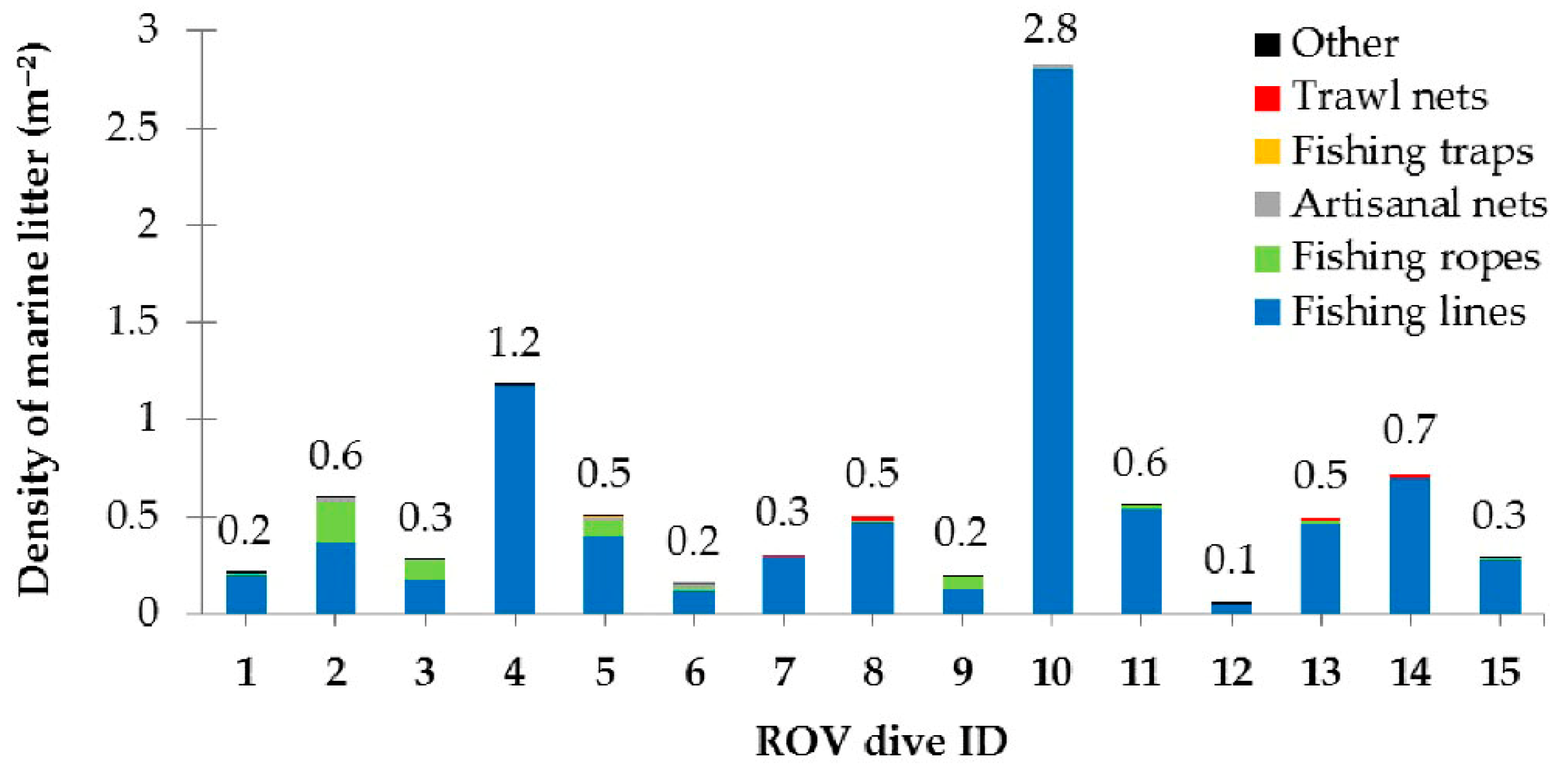
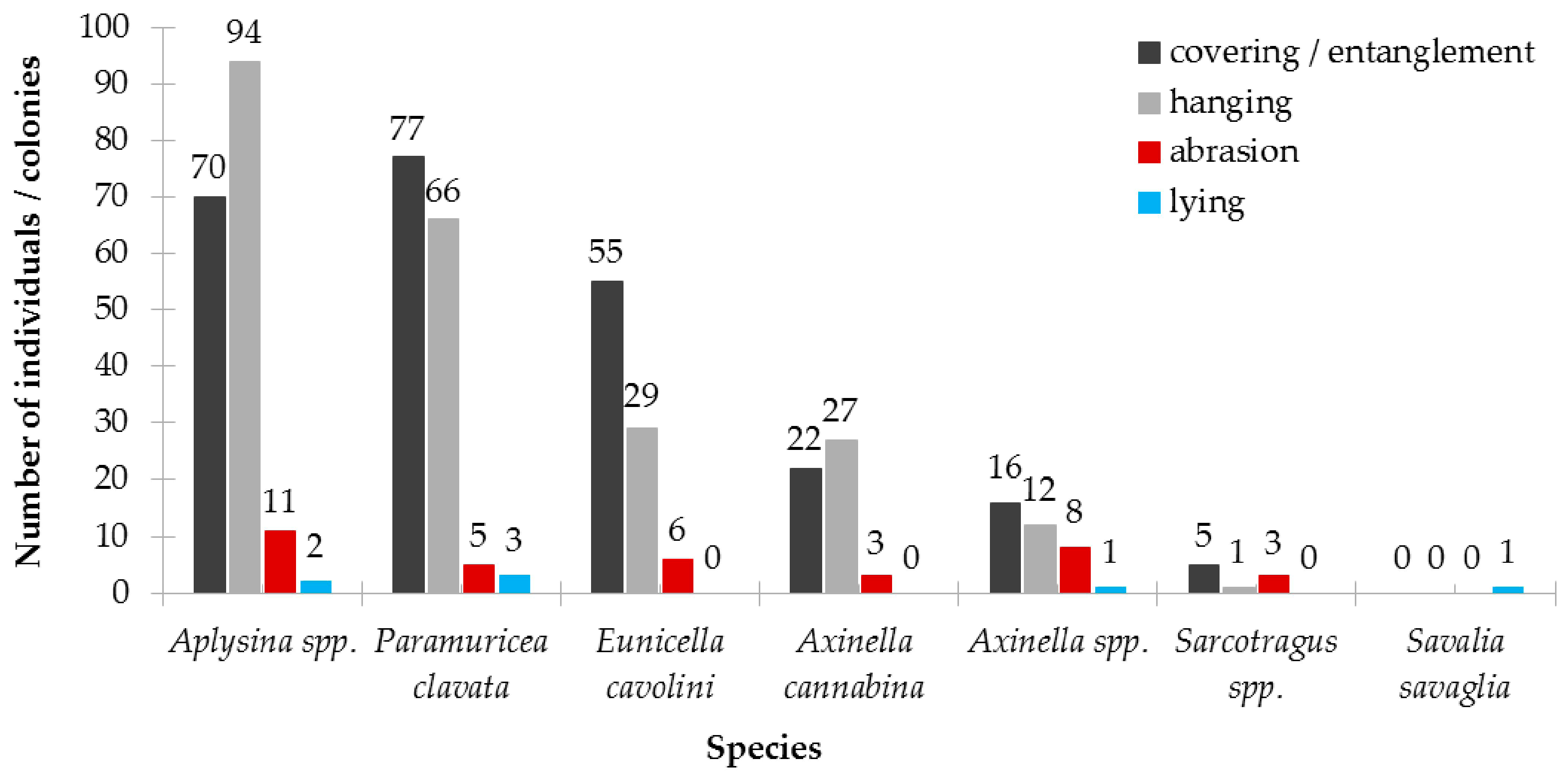
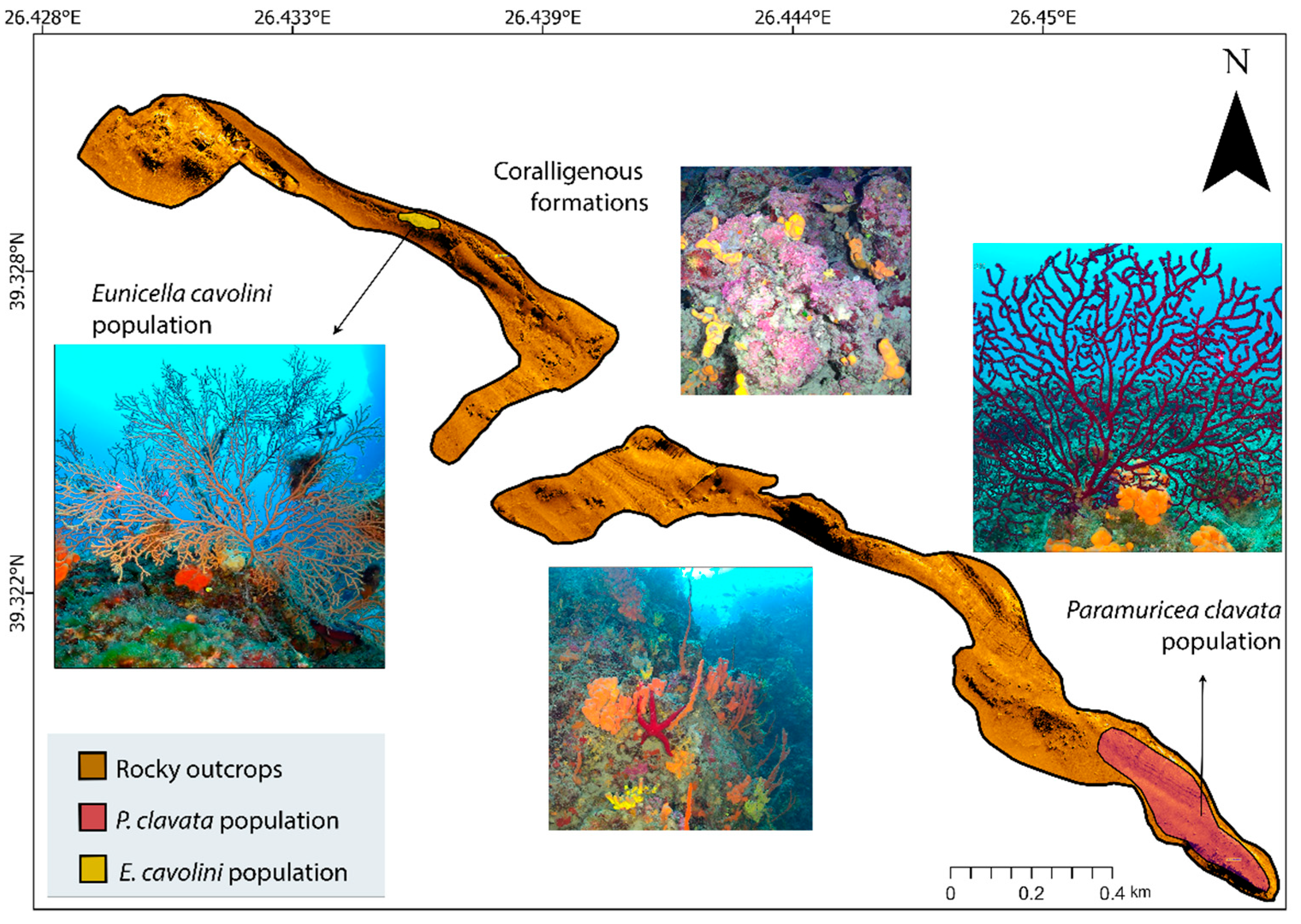
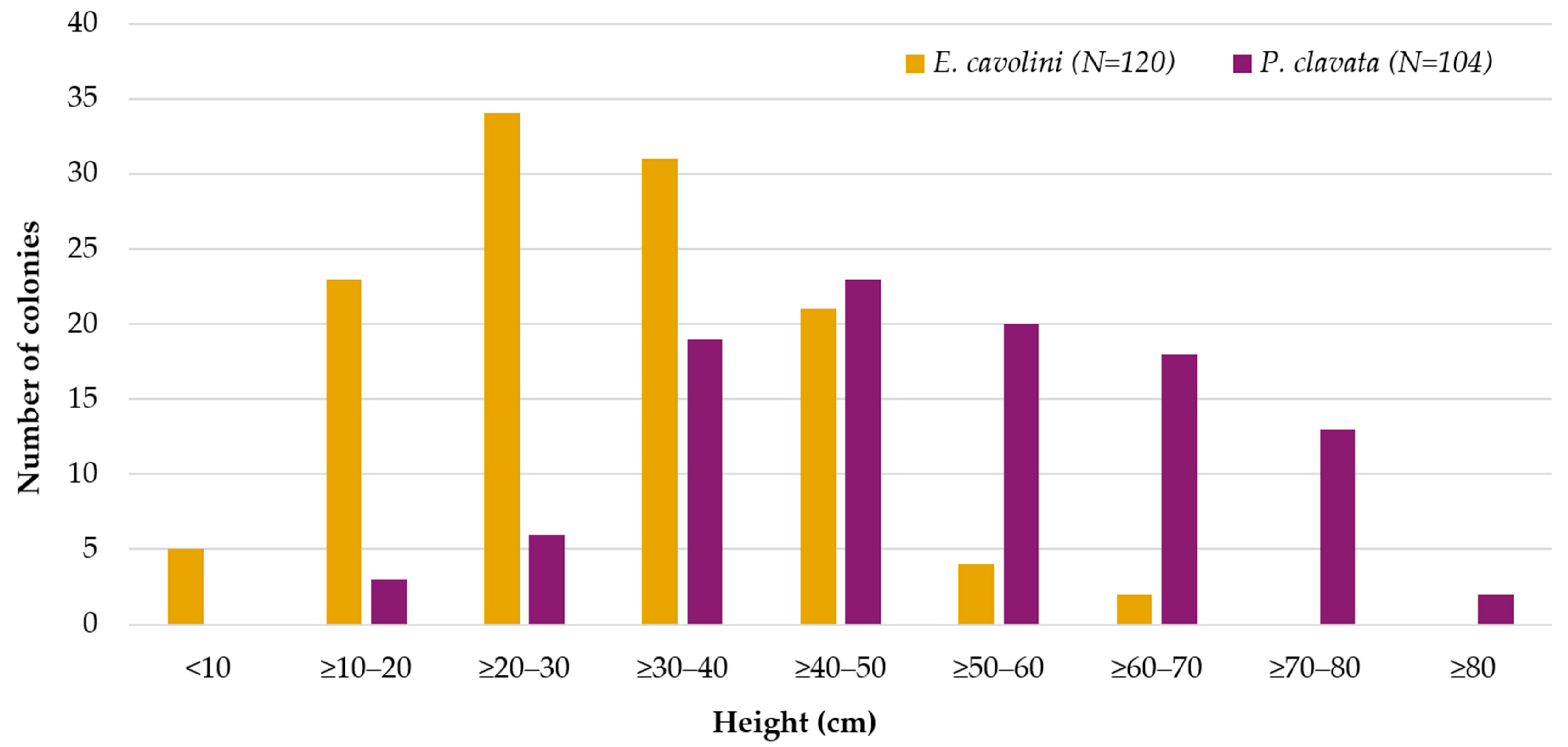
| Type | Depth Range (m) | N | ML Interaction with Substrate | ML Fouling Stage | Removal Feasibility (%) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Covering/Entangled | Abrasion | Hanging | Lying | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 0 | <50 | >50–90 | 100 | |||
| Fishing lines | 20–59 | 1435 | 507 | 30 | 736 | 162 | 3 | 86 | 424 | 922 | 190 | 422 | 485 | 338 |
| Fishing ropes | 20–59 | 151 | 26 | 0 | 46 | 79 | 0 | 22 | 86 | 43 | 11 | 53 | 25 | 62 |
| Artisanal nets | 41–57 | 12 | 3 | 0 | 5 | 4 | 0 | 5 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 2 | 0 | 5 |
| Fishing traps | 31–47 | 9 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 9 |
| Trawl nets | 39–52 | 8 | 4 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 6 |
| Anchors | 38–48 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Plastic bottle | 44–53 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| Plastic bag | 58 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Ceramic jar | 33 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Glove | 56 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Metal ring | 48.5 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Tube | 35 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Total | 1626 | |||||||||||||
| Species | N | Depth Range (m) | Height | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | Max | Mean | SD | g1 | SEg1 | Sig g1 | g2 | SEg2 | Sig g2 | |||
| E. cavolini | 120 | 30–45 | 4.3 | 65.5 | 29.7 | 12.5 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 1.4 | −0.0 | 0.4 | −0.0 |
| P. clavata | 104 | 45–56 | 10.3 | 86.9 | 50.6 | 16.3 | −0.1 | 0.3 | −0.5 | −0.4 | 0.5 | −0.8 |
| Species | N | Proportion of Uninjured, Injured and Dead Colonies According to the Proportion of Injured Surface Area (%) | Proportion of Colonies per Type of Injury (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [0–10%) | [10–99%) | 100% | A | B | C | ||
| E. cavolini | 120 | 83 | 17 | 1 | 0 | 38.1 | 61.9 |
| P. clavata | 104 | 84 | 13 | 4 | 0 | 35.3 | 64.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sini, M.; Pistevos, J.C.A.; Bosmali, A.; Manoliou, A.; Nikolaou, A.; Pitarra, G.; Petsimeris, I.T.; Andreadis, O.; Hasiotis, T.; Mazaris, A.D.; et al. Multimodal Underwater Sensing of Octocoral Populations and Anthropogenic Impacts in a Conservation-Priority Area (NE Aegean Sea, Greece). J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 2237. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13122237
Sini M, Pistevos JCA, Bosmali A, Manoliou A, Nikolaou A, Pitarra G, Petsimeris IT, Andreadis O, Hasiotis T, Mazaris AD, et al. Multimodal Underwater Sensing of Octocoral Populations and Anthropogenic Impacts in a Conservation-Priority Area (NE Aegean Sea, Greece). Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(12):2237. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13122237
Chicago/Turabian StyleSini, Maria, Jennifer C. A. Pistevos, Angeliki Bosmali, Artemis Manoliou, Athanasios Nikolaou, Giulia Pitarra, Ivan T. Petsimeris, Olympos Andreadis, Thomas Hasiotis, Antonios D. Mazaris, and et al. 2025. "Multimodal Underwater Sensing of Octocoral Populations and Anthropogenic Impacts in a Conservation-Priority Area (NE Aegean Sea, Greece)" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 12: 2237. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13122237
APA StyleSini, M., Pistevos, J. C. A., Bosmali, A., Manoliou, A., Nikolaou, A., Pitarra, G., Petsimeris, I. T., Andreadis, O., Hasiotis, T., Mazaris, A. D., & Katsanevakis, S. (2025). Multimodal Underwater Sensing of Octocoral Populations and Anthropogenic Impacts in a Conservation-Priority Area (NE Aegean Sea, Greece). Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(12), 2237. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13122237







