Intelligent Diagnosis of Ship Propulsion Motor Bearings Based on Dynamic Class Weights
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Bearing Fault Test
3. Fault Diagnosis Model Migration Performance Analysis
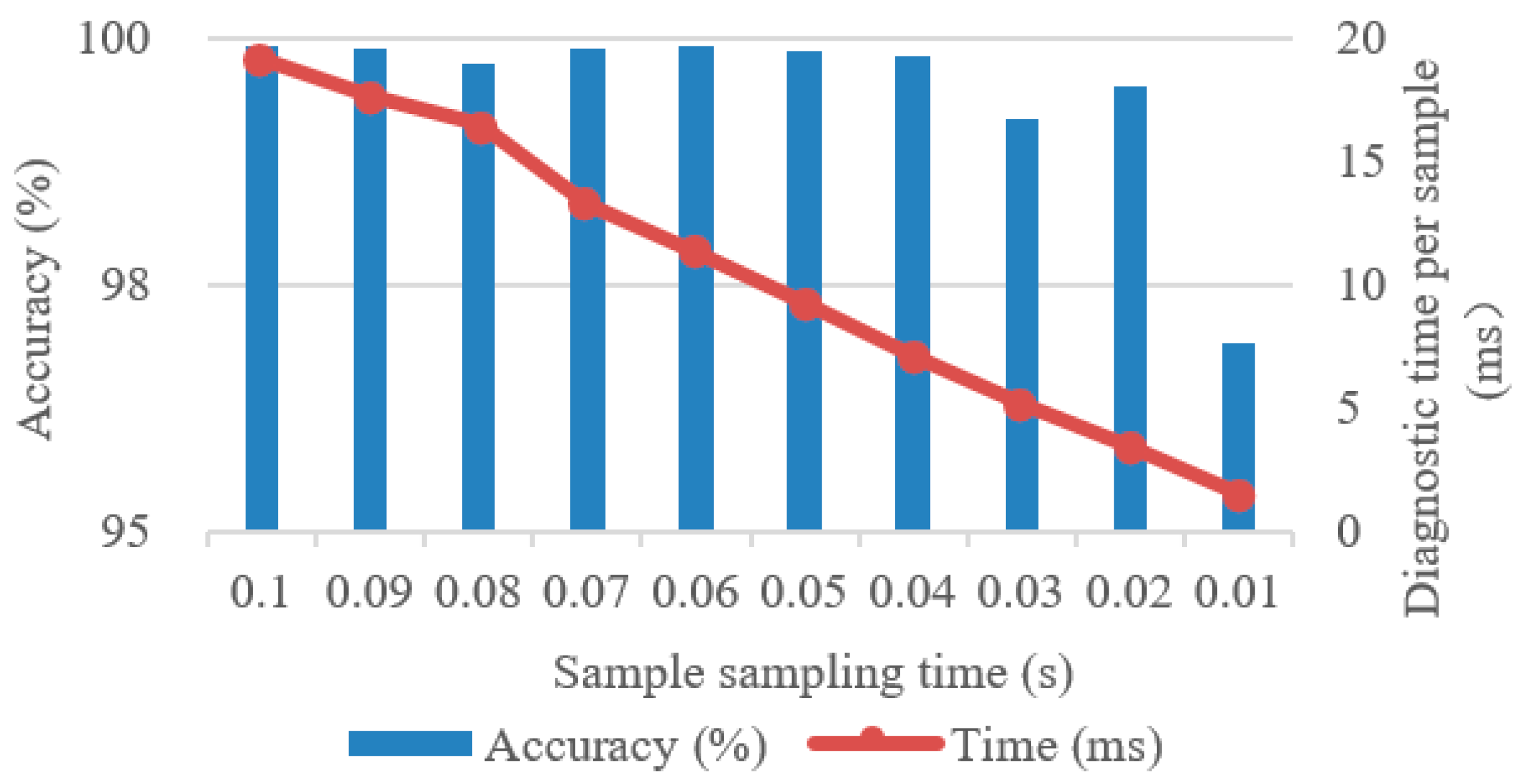
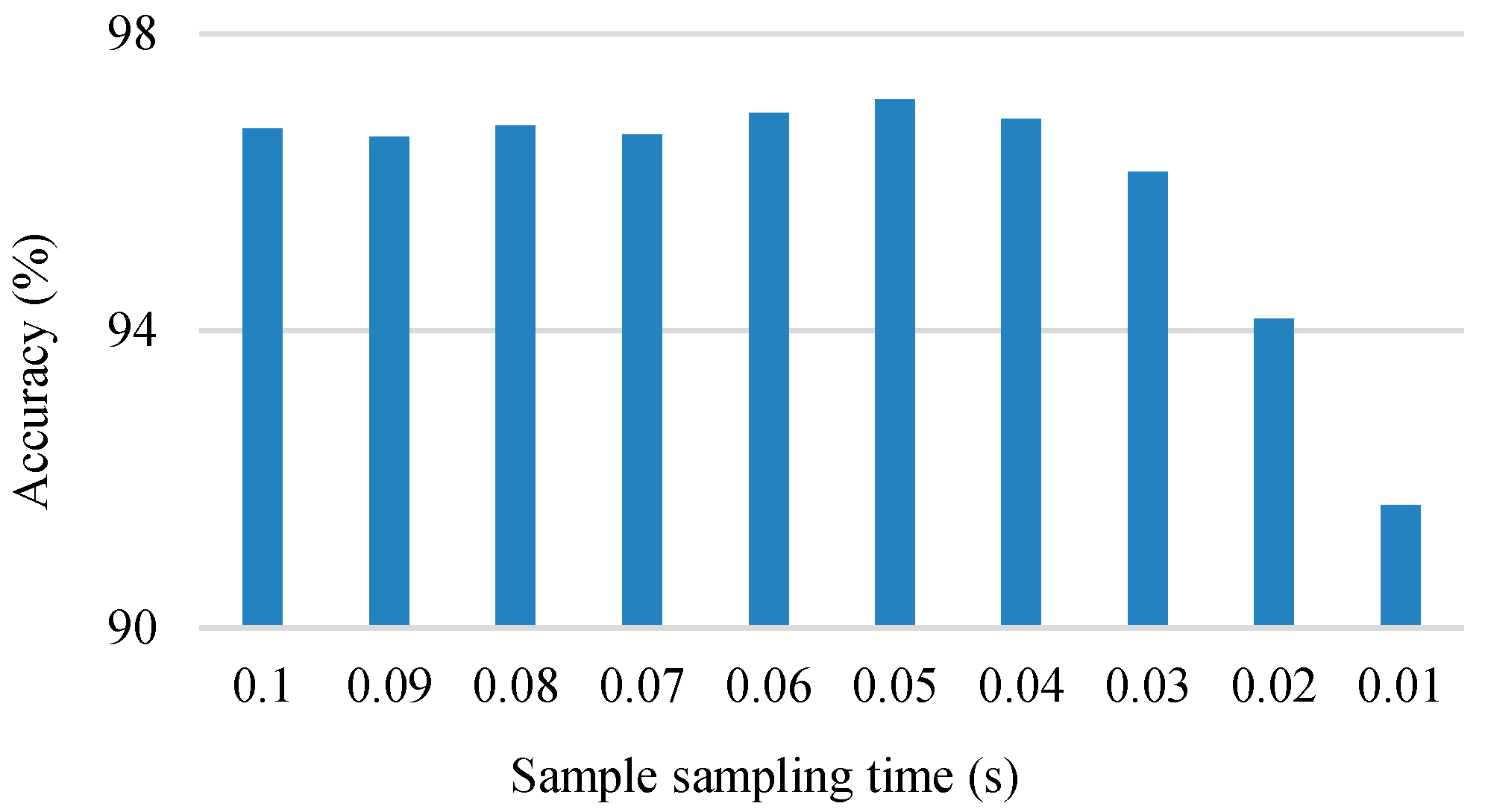
3.1. Impact Analysis of Sample Duration
3.2. Generalisation Performance Test
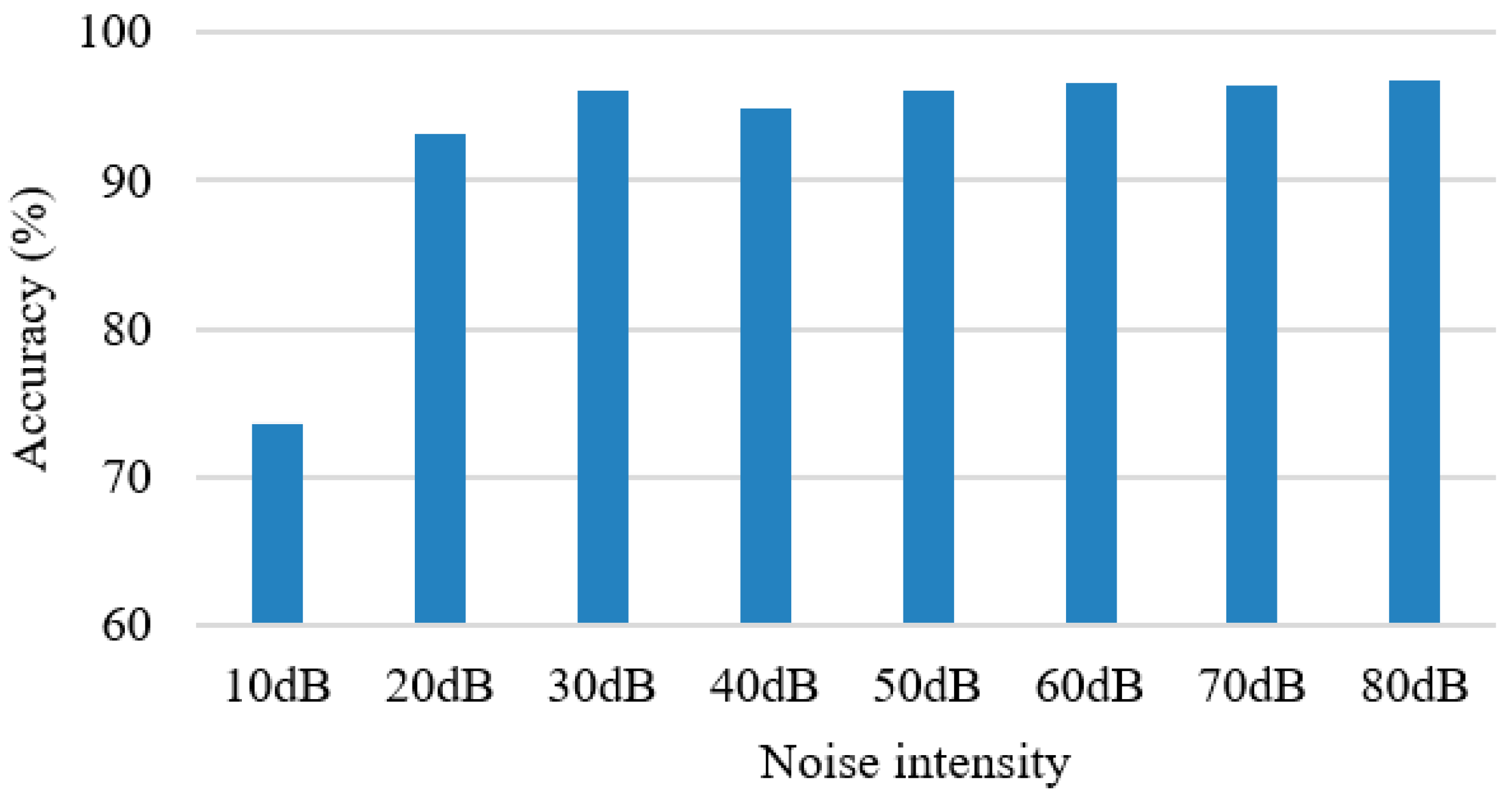
3.3. Anti-Noise Test
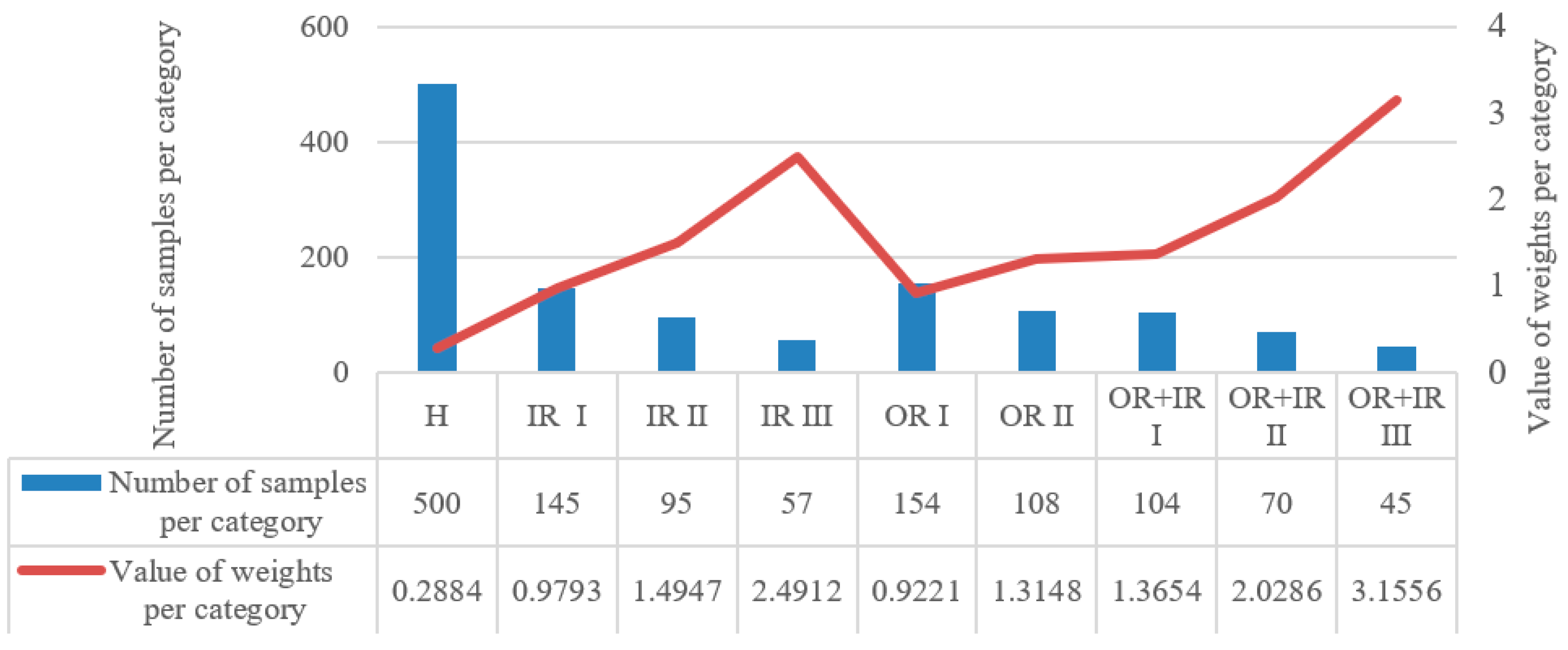
4. Data Imbalance Test for Traditional Class Weights
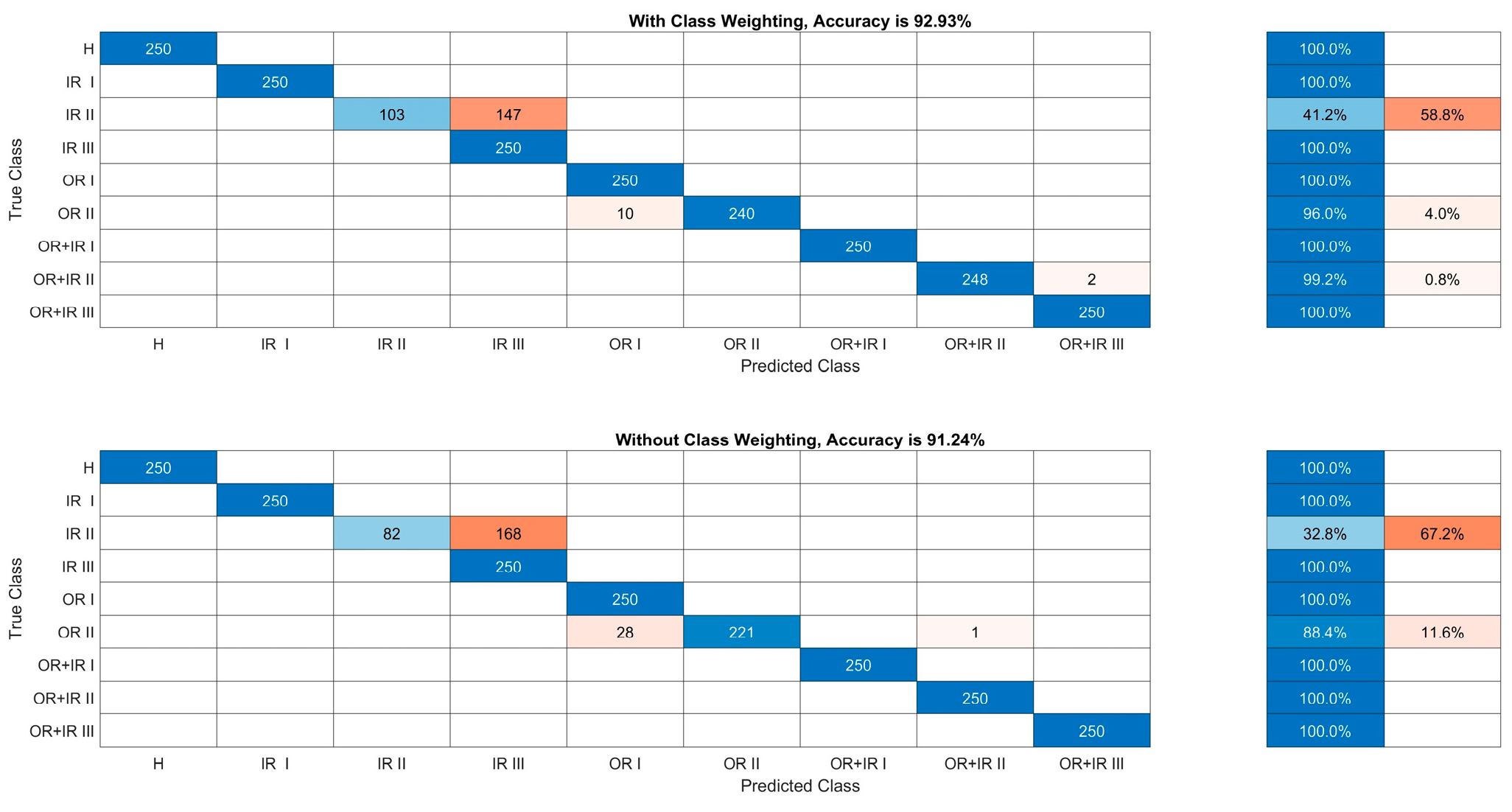
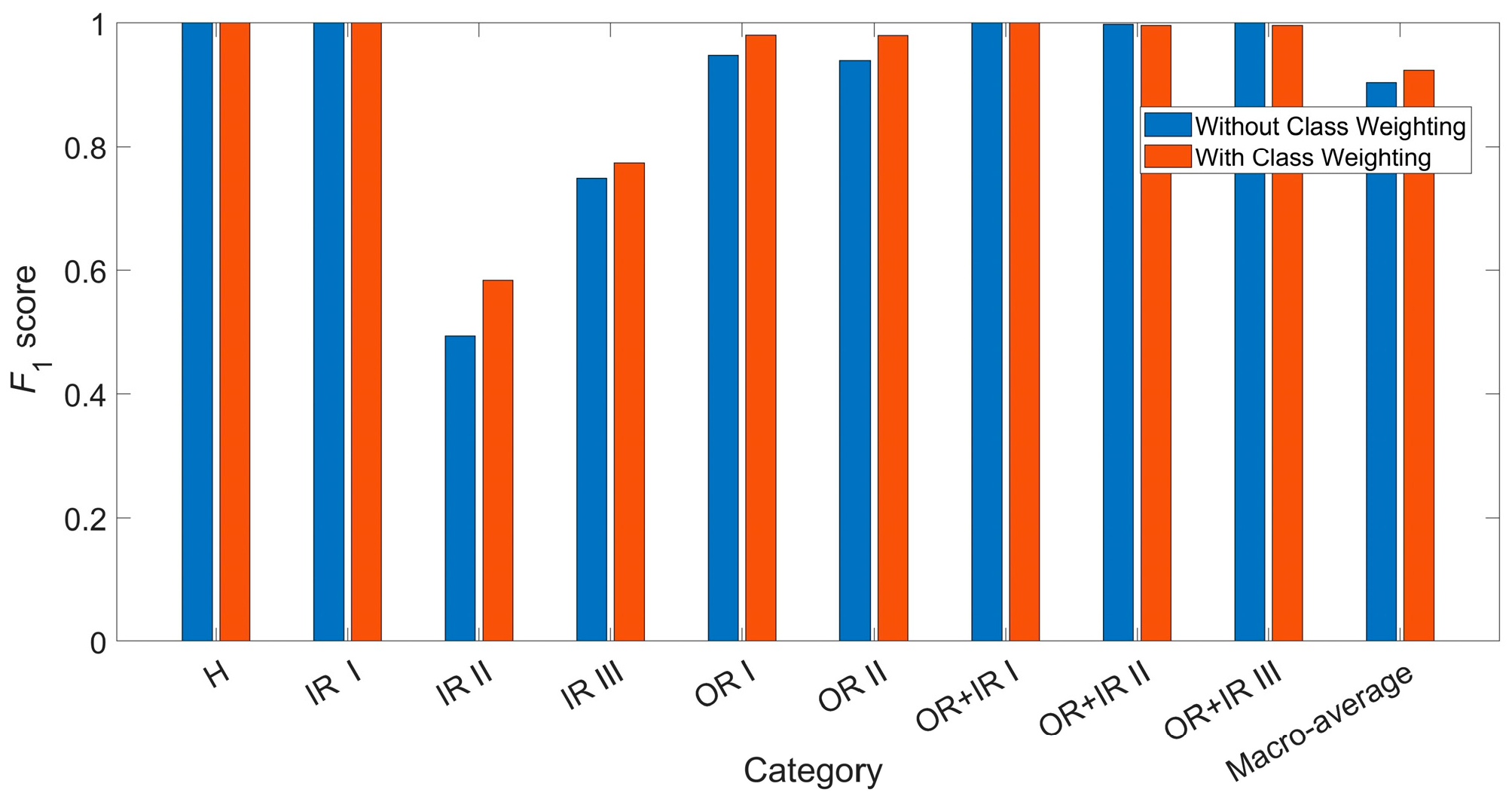
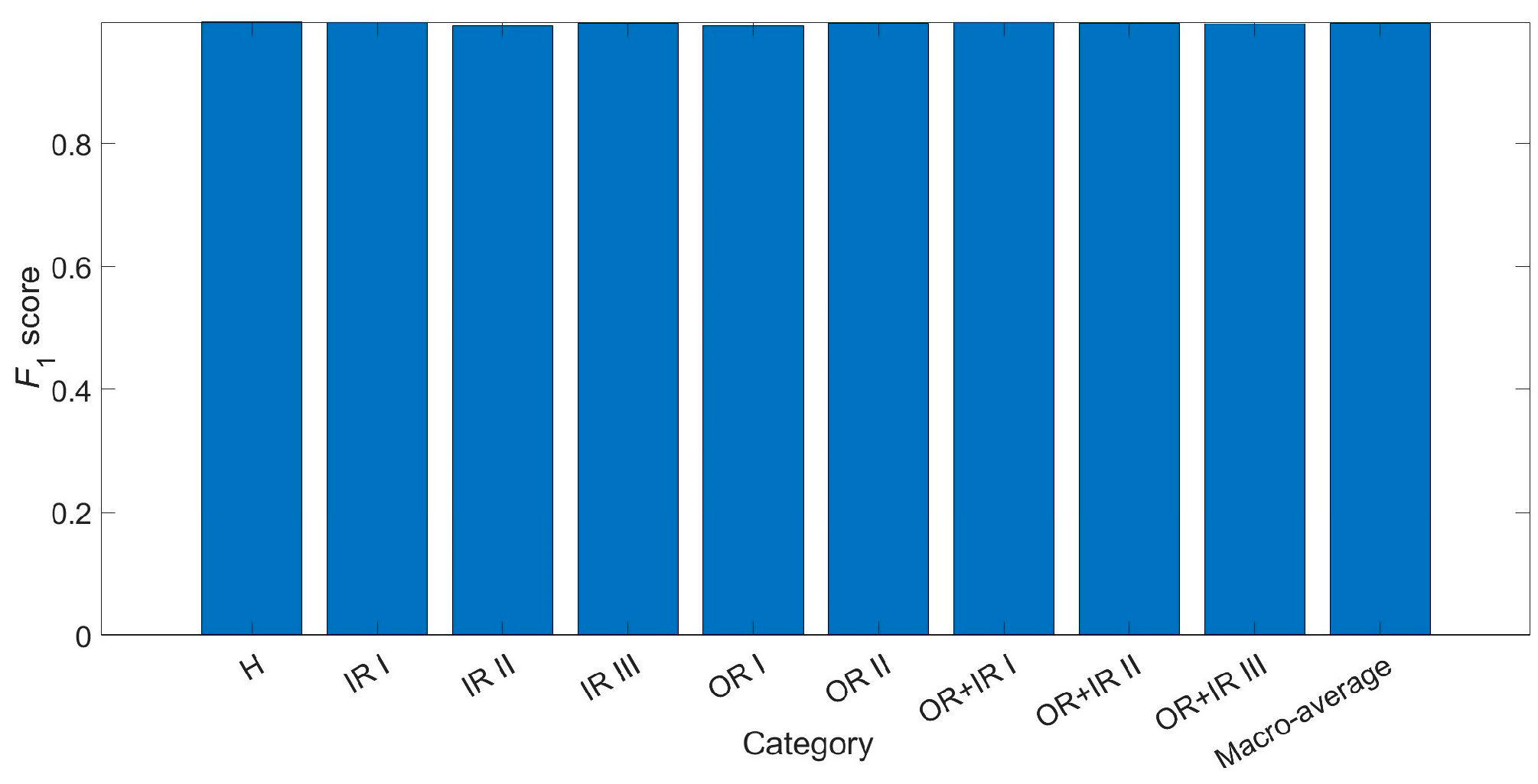
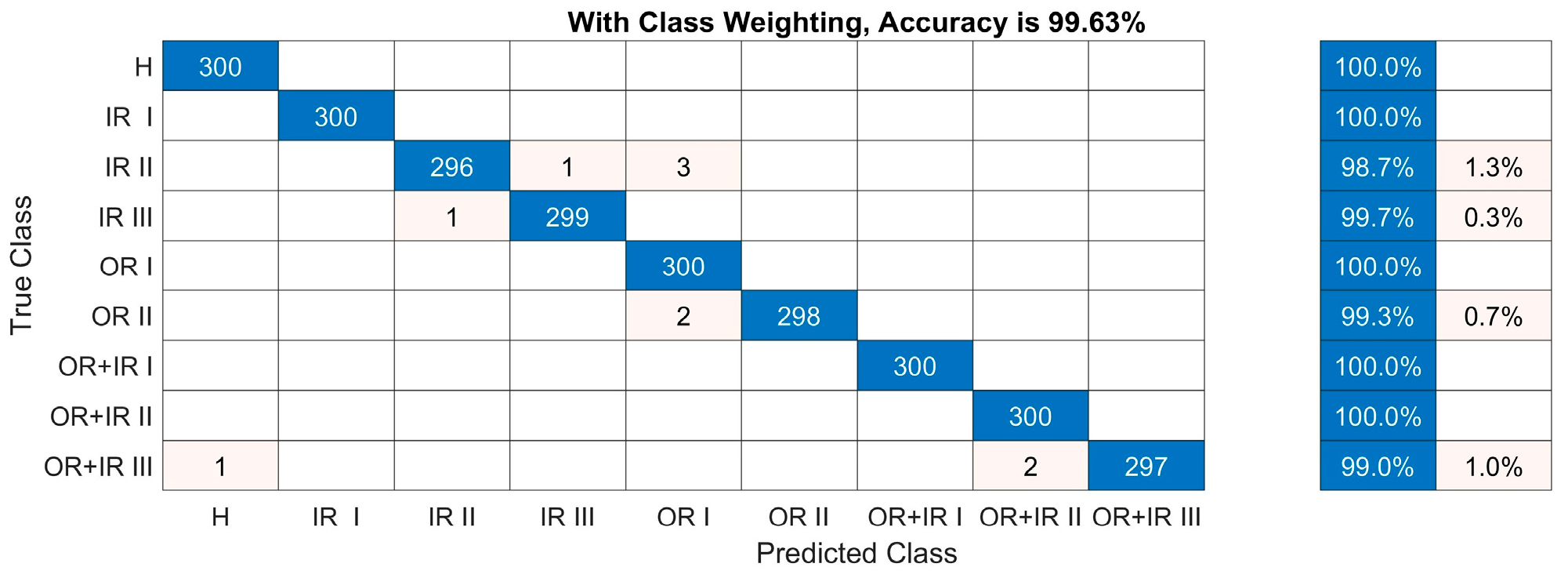
4.1. Test Analyses
4.2. Generalisation Performance Test
5. Data Imbalance Test for Dynamic Class Weights
5.1. Dynamic Class Weights
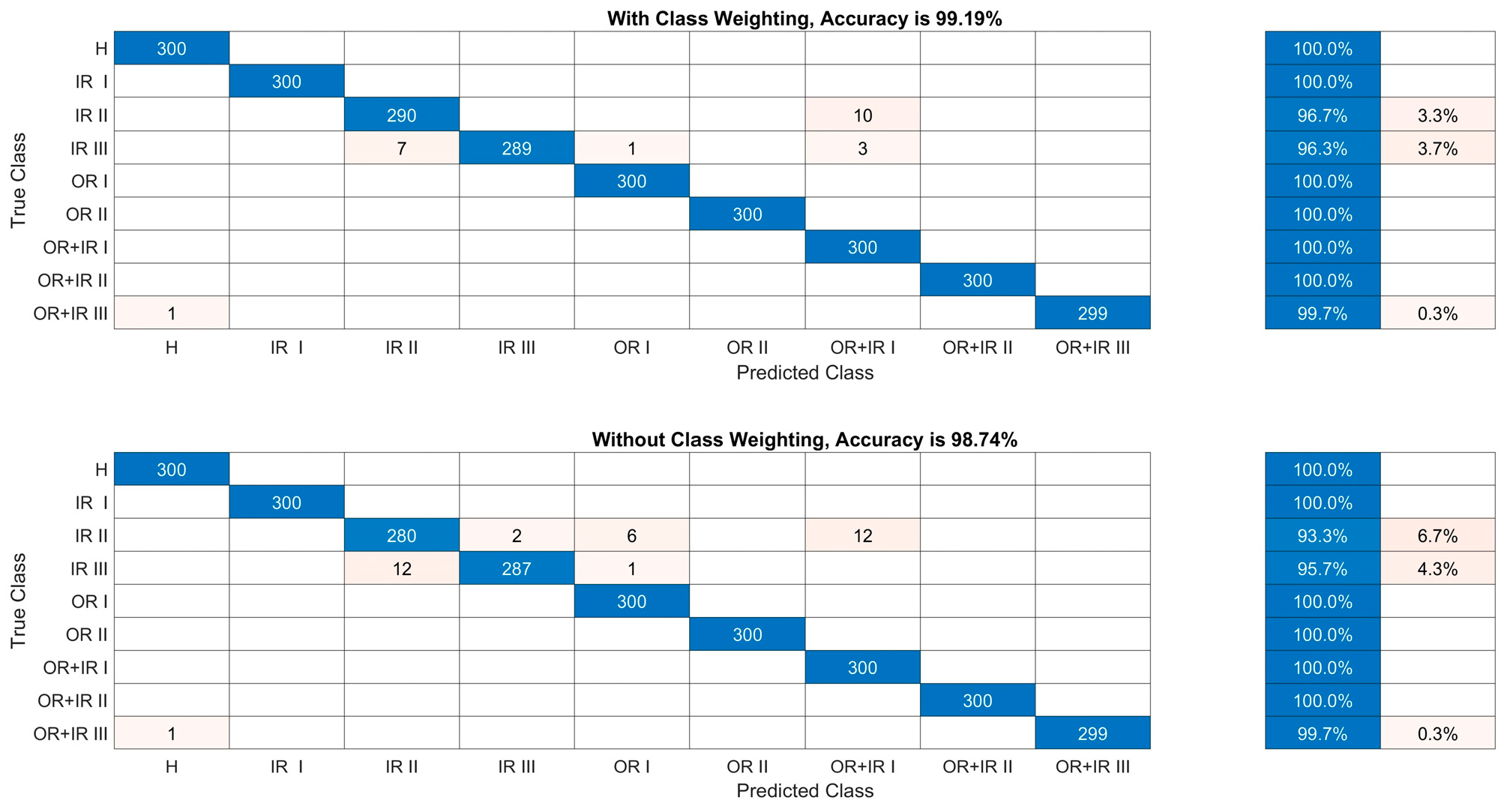
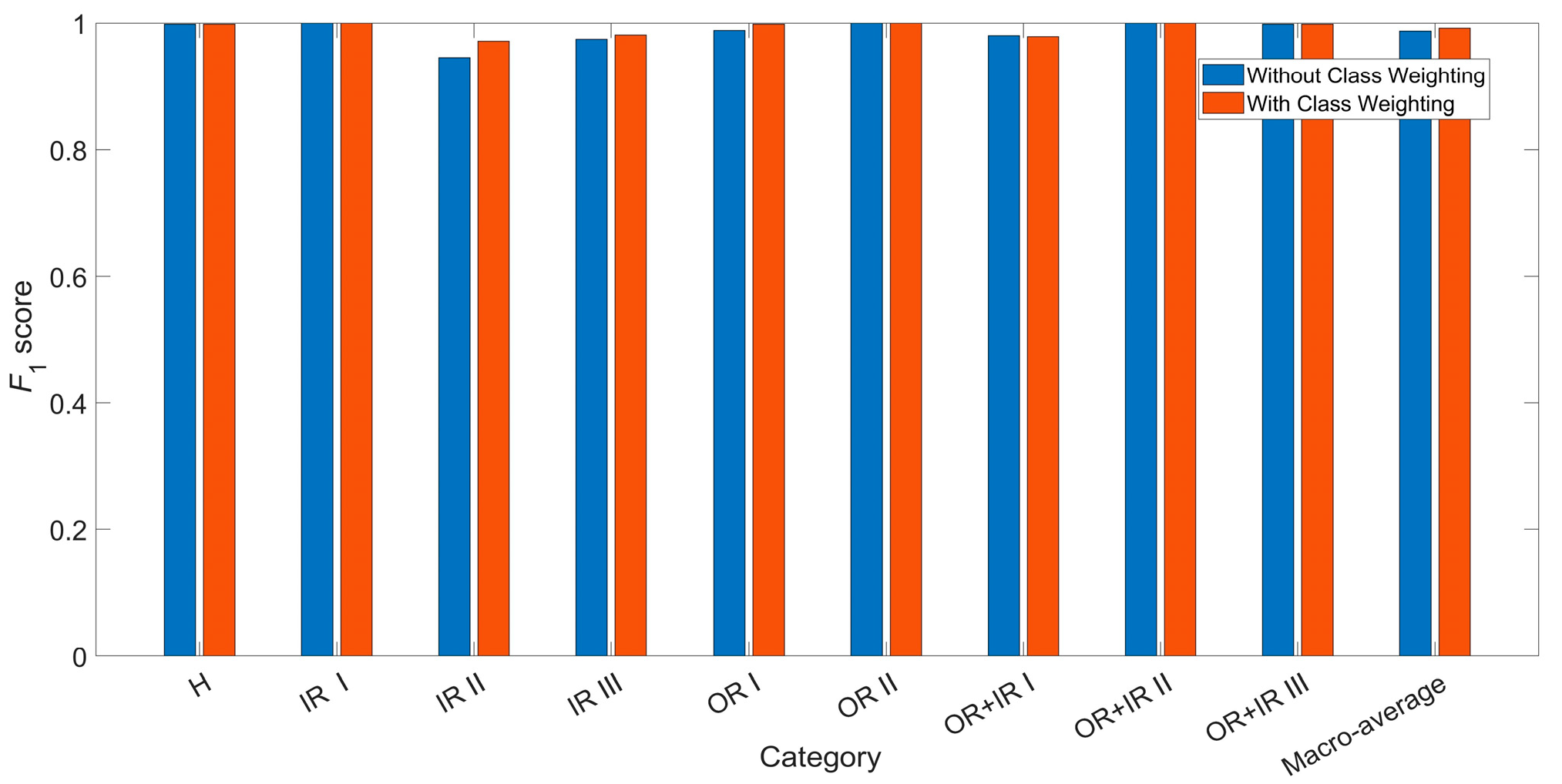
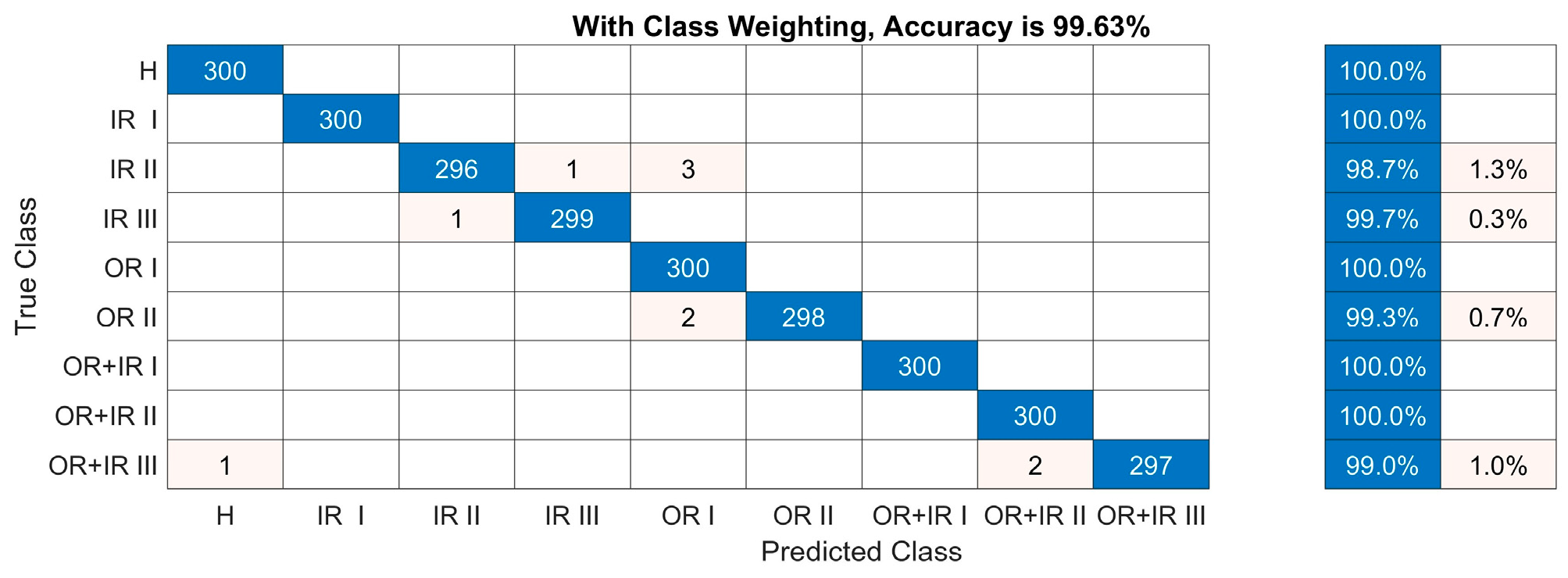
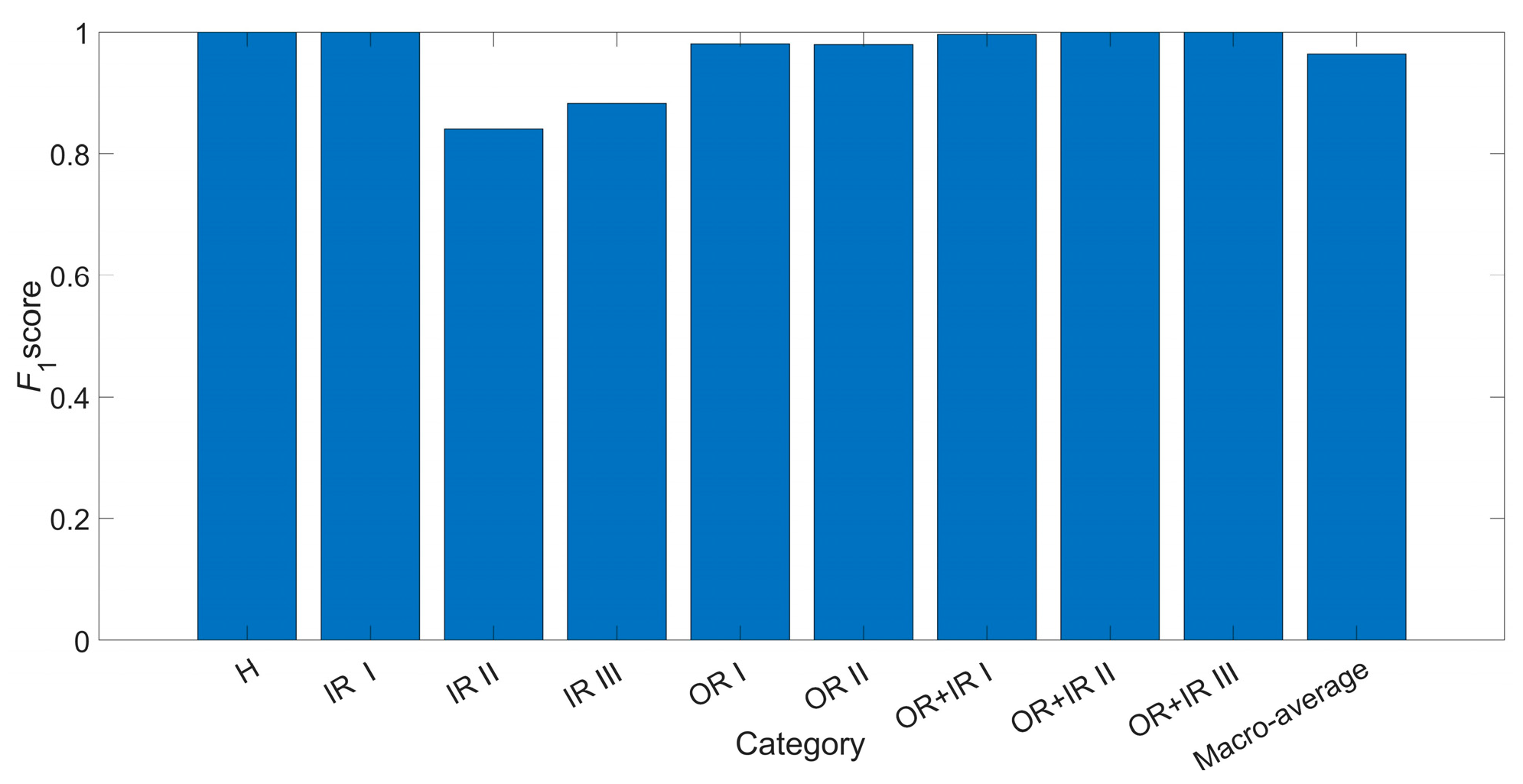
5.2. Test Analyses
5.3. Generalisation Test
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Orlowska-Kowalska, T.; Wolkiewicz, M.; Pietrzak, P.; Skowron, M.; Ewert, P.; Tarchala, G.; Krzysztofiak, M.; Kowalski, C.T. Fault Diagnosis and Fault-Tolerant Control of PMSM Drives–State of the Art and Future Challenges. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 59979–60024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, S.; Wang, B.; Habetler, T.G. Deep Learning Algorithms for Bearing Fault Diagnostics—A Comprehensive Review. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 29857–29881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Xu, Q.; Jia, M. Improved shuffled frog leaping algorithm-based BP neural network and its application in bearing early fault diagnosis. Neural Comput. Appl. 2016, 27, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad-Alikhani, A.; Nahid-Mobarakeh, B.; Hsieh, M.F. One-Dimensional LSTM-Regulated Deep Residual Network for Data-Driven Fault Detection in Electric Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2024, 71, 3083–3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verstraete, D.; Ferrada, A.; Droguett, E.L.; Meruane, V.; Modarres, M. Deep Learning Enabled Fault Diagnosis Using Time-Frequency Image Analysis of Rolling Element Bearings. Shoc. Vib. 2017, 2017, 5067651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayas, S.; Ayas, M.S. A novel bearing fault diagnosis method using deep residual learning network. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2022, 81, 22407–22423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deveci, B.U.; Celtikoglu, M.; Albayrak, O.; Unal, P.; Kirci, P. Transfer Learning Enabled Bearing Fault Detection Methods Based on Image Representations of Single-Dimensional Signals. Inf. Syst. Front. 2024, 26, 1345–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Kim, Y.-H.; Choo, J. Intelligent fault detection using raw vibration signals via dilated convolutional neural networks. J. Supercomput. 2020, 76, 8086–8100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Mao, J.; Zhao, M. Rolling Bearing Fault Diagnosis Method Based on Attention CNN and BiLSTM Network. Neural Process. Lett. 2023, 55, 3377–3410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cao, G. A multiscale convolution neural network for bearing fault diagnosis based on frequency division denoising under complex noise conditions. Complex Intell. Syst. 2023, 9, 4263–4285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Horn, G.; Mac Aodha, O.; Song, Y.; Cui, Y.; Sun, C.; Shepard, A.; Adam, H.; Perona, P.; Belongie, S. The inaturalist species classification and detection dataset. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 8769–8778. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, A.; Dollar, P.; Girshick, R. Lvis: A dataset for large vocabulary instance segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 5356–5364. [Google Scholar]
- Bansal, M.A.; Sharma, D.R.; Kathuria, D.M. A systematic review on data scarcity problem in deep learning: Solution and applications. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 2022, 54, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, D.; Girshick, R.; Ramanathan, V.; He, K.; Paluri, M.; Li, Y.; Bharambe, A.; Van Der Maaten, L. Exploring the limits of weakly supervised pretraining. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 181–196. [Google Scholar]
- Mikolov, T.; Sutskever, I.; Chen, K.; Corrado, G.S.; Dean, J. Distributed representations of words and phrases and their compositionality. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 26, Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 5–10 December 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, B.; Ma, H.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, X. BWLM: A Balanced Weight Learning Mechanism for Long-Tailed Image Recognition. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lessmeier, C.; Kimotho, J.K.; Zimmer, D.; Sextro, W. Condition monitoring of bearing damage in electromechanical drive systems by using motor current signals of electric motors: A benchmark data set for data-driven classification. In Proceedings of the PHM Society European Conference, Bilbao, Spain, 5–8 July 2016; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Li, X.; Ding, Q. Deep residual learning-based fault diagnosis method for rotating machinery. ISA Trans. 2019, 95, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.; Liao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Li, W. Deep Decoupling Convolutional Neural Network for Intelligent Compound Fault Diagnosis. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 1848–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; He, Q. Energy-Fluctuated Multiscale Feature Learning with Deep ConvNet for Intelligent Spindle Bearing Fault Diagnosis. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2017, 66, 1926–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Yao, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Xu, Y.; Li, C.; Jiang, H. Dual-Core Denoised Synchrosqueezing Wavelet Transform for Gear Fault Detection. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 3521611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, W.A.; Randall, R.B. Rolling element bearing diagnostics using the Case Western Reserve University data: A benchmark study. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2015, 64–65, 100–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Jiao, Y.; Zhang, X. A Fault Diagnosis Method of Rotor System Based on Parallel Convolutional Neural Network Architecture with Attention Mechanism. J. Signal Process. Syst. 2023, 95, 965–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, G.; Hu, Y. Inter-turn short circuit and demagnetization fault diagnosis of ship PMSM based on multiscale residual dilated CNN and BiLSTM. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2024, 35, 046105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
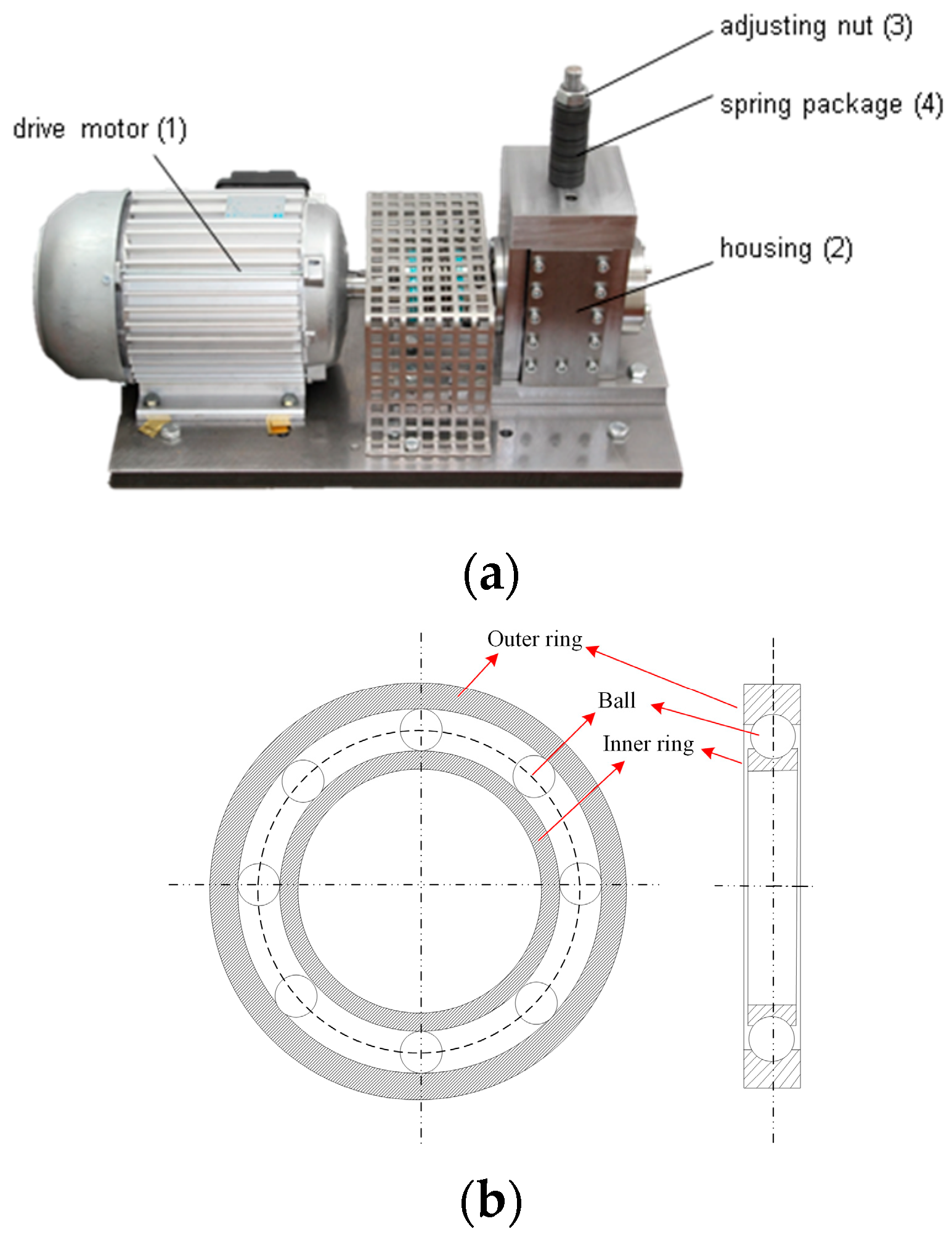
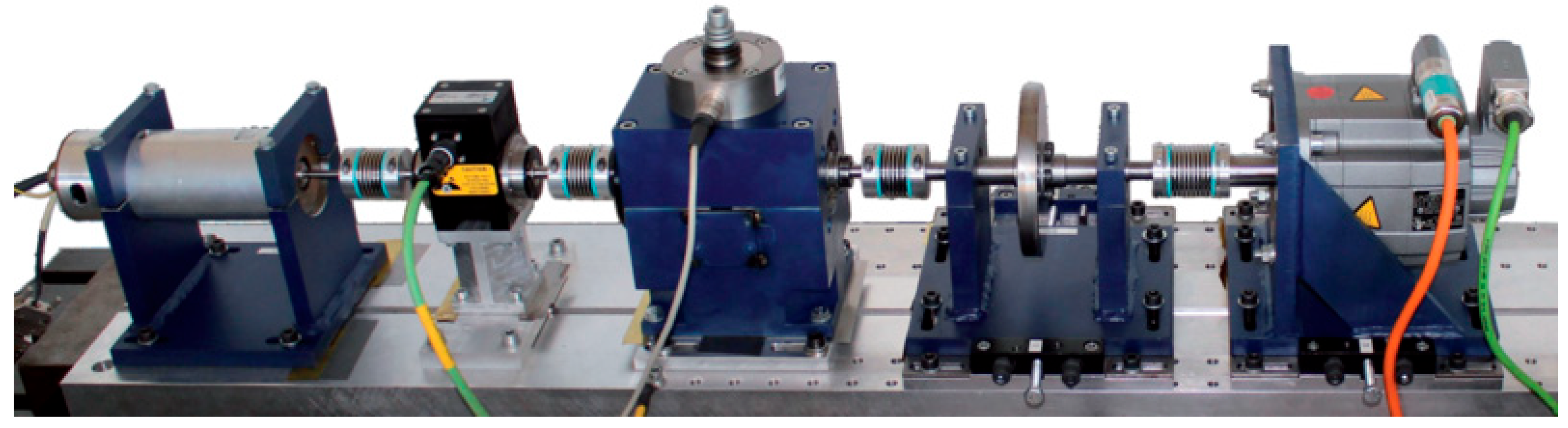
| Damage Level | Percentage of Damage Length to Pitch Circumference | Corresponding Damage Range of Test Bearing |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0~2% | ≤2 mm |
| 2 | 2~5% | >2 mm |
| 3 | 5~15% | >4.5 mm |
| 4 | 15~35% | >13.5 mm |
| 5 | >35% | >31.5 mm |
| Test Operation Condition | Speed (r/min) | Load Torque (Nm) | Radial Force (N) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1500 | 0.7 | 1000 |
| 2 | 900 | 0.7 | 1000 |
| 3 | 1500 | 0.1 | 1000 |
| 4 | 1500 | 0.7 | 400 |
| Status | Damage Level | Code |
|---|---|---|
| Health | H | |
| Inner ring damage | 1 | IR I |
| 2 | IR II | |
| 3 | IR III | |
| Outer ring damage | 1 | OR I |
| 2 | OR II | |
| Damage to both inner and outer rings | 1 | IR + OR I |
| 2 | IR + OR II | |
| 3 | IR + OR III |
| Fault Type | Training Samples | Validation Samples | Test Sample | Status Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Health | 525 | 225 | 250 | H |
| Inner ring level 1 | 525 | 225 | 250 | IR I |
| Inner ring level 2 | 525 | 225 | 250 | IR II |
| Inner ring level 3 | 525 | 225 | 250 | IR III |
| Outer ring level 1 | 525 | 225 | 250 | OR I |
| Outer ring level 2 | 525 | 225 | 250 | OR II |
| Compound fault level 1 | 525 | 225 | 250 | IR + OR I |
| Compound fault level 2 | 525 | 225 | 250 | IR + OR II |
| Compound fault level 3 | 525 | 225 | 250 | IR + OR III |
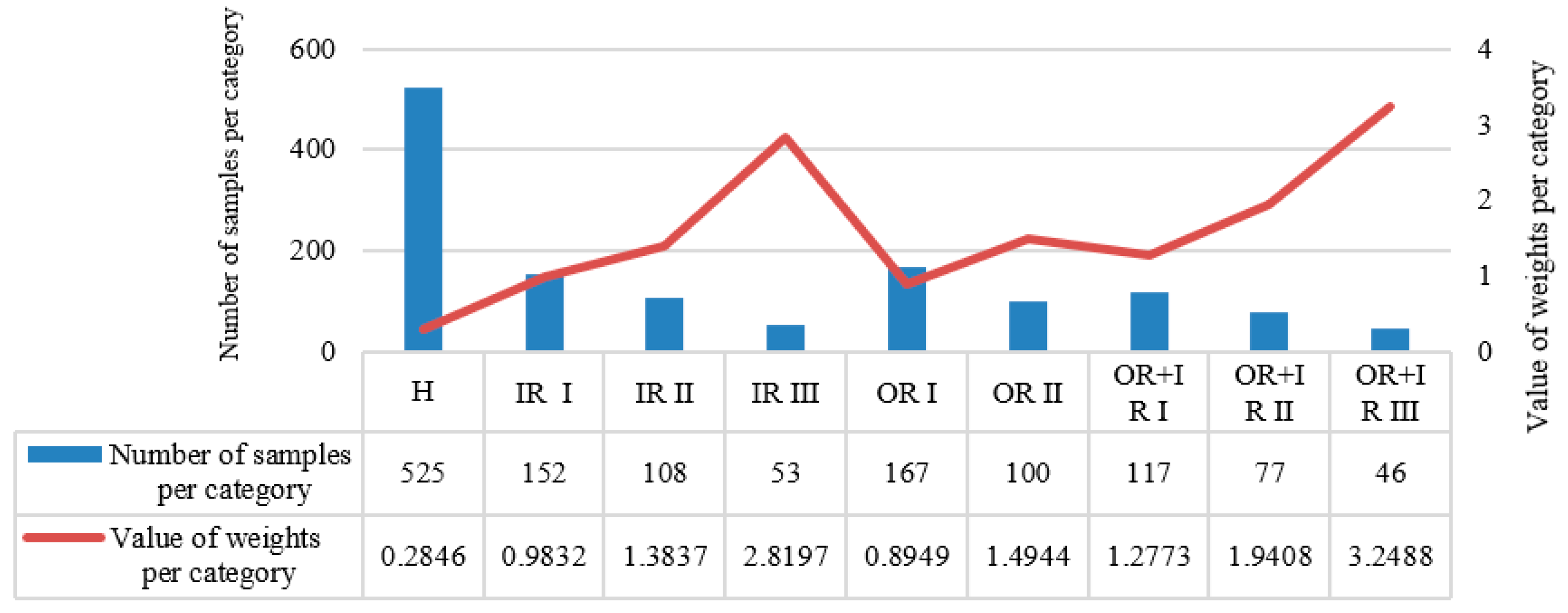
| Fault Type | Training Samples | Percentage Range (%) | Unbalanced Sample Intervals | Status Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Health | 500 | 100 | 500 | H |
| Inner ring level 1 | 500 | 20~30 | 100~150 | IR I |
| Inner ring level 2 | 500 | 10~20 | 50~100 | IR II |
| Inner ring level 3 | 500 | 5~10 | 25~50 | IR III |
| Outer ring level 1 | 500 | 20~30 | 100~150 | OR I |
| Outer ring level 2 | 500 | 10~20 | 50~100 | OR II |
| Compound fault level 1 | 500 | 15~20 | 75~100 | IR + OR I |
| Compound fault level 2 | 500 | 10~15 | 50~75 | IR + OR II |
| Compound fault level 3 | 500 | 5~10 | 25~50 | IR + OR III |
| Fault Type | Training Samples | Percentage Range (%) | Unbalanced Sample Intervals | Status Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Health | 525 | 100 | 525 | H |
| Inner ring level 1 | 525 | 20~30 | 105~158 | IR I |
| Inner ring level 2 | 525 | 10~20 | 53~105 | IR II |
| Inner ring level 3 | 525 | 5~10 | 26~53 | IR III |
| Outer ring level 1 | 525 | 20~30 | 105~158 | OR I |
| Outer ring level 2 | 525 | 10~20 | 53~105 | OR II |
| Compound fault level 1 | 525 | 15~20 | 79~105 | IR + OR I |
| Compound fault level 2 | 525 | 10~15 | 53~79 | IR + OR II |
| Compound fault level 3 | 525 | 5~10 | 26~53 | IR + OR III |
| Iteration Period | Items | Health | Inner Ring Level 1 | Inner Ring Level 2 | Inner Ring Level 3 | Outer Ring Level 1 | Outer Ring Level 2 | Compound Fault Level 1 | Compound Fault Level 2 | Compound Fault Level 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Number of class samples | 500 | 163 | 97 | 44 | 149 | 97 | 104 | 74 | 56 |
| Initial class weights | 0.29 | 0.95 | 1.44 | 2.80 | 0.94 | 1.32 | 1.37 | 1.97 | 2.47 | |
| 10 | F1 scores | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.72 | 0.76 | 0.97 | 0.99 | 0.95 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Updated category weights | 0.29 | 0.95 | 1.92 | 3.25 | 0.98 | 1.36 | 1.42 | 1.97 | 2.48 | |
| 20 | F1 scores | 1.00 | 0.99 | 0.83 | 0.74 | 0.99 | 0.98 | 0.93 | 0.99 | 0.99 |
| Updated category weights | 0.29 | 0.96 | 2.34 | 3.85 | 0.98 | 1.38 | 1.51 | 1.98 | 2.47 | |
| 30 | F1 scores | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.95 | 0.88 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Updated category weights | 0.29 | 0.96 | 2.71 | 4.66 | 1.01 | 1.38 | 1.53 | 1.98 | 2.47 | |
| 40 | F1 scores | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Updated category weights | 0.29 | 0.96 | 2.73 | 4.68 | 1.02 | 1.39 | 1.53 | 1.98 | 2.48 |
| Iteration Period | Items | Health | Inner Ring Level 1 | Inner Ring Level 2 | Inner Ring Level 3 | Outer Ring Level 1 | Outer Ring Level 2 | Compound Fault Level 1 | Compound Fault Level 2 | Compound Fault Level 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Number of class samples | 525 | 146 | 110 | 45 | 166 | 111 | 117 | 74 | 52 |
| Initial class weights | 0.29 | 1.02 | 1.35 | 3.32 | 0.90 | 1.35 | 1.28 | 2.02 | 2.88 | |
| 10 | F1 scores | 0.99 | 1.00 | 0.68 | 0.87 | 0.92 | 0.98 | 0.90 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Updated category weights | 0.29 | 1.03 | 1.99 | 3.82 | 0.97 | 1.37 | 1.42 | 2.02 | 2.89 | |
| 20 | F1 scores | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 0.98 | 0.92 | 0.94 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Updated category weights | 0.29 | 1.03 | 1.99 | 3.87 | 1.06 | 1.46 | 1.42 | 2.02 | 2.89 | |
| 30 | F1 scores | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Updated category weights | 0.29 | 1.03 | 2.01 | 3.89 | 1.06 | 1.46 | 1.42 | 2.02 | 2.90 | |
| 40 | F1 scores | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Updated category weights | 0.29 | 1.03 | 2.03 | 3.90 | 1.06 | 1.46 | 1.44 | 2.02 | 2.91 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, G.; Wang, X.; Liu, K.; Kang, J.; Yi, X. Intelligent Diagnosis of Ship Propulsion Motor Bearings Based on Dynamic Class Weights. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 2204. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13112204
Yan G, Wang X, Liu K, Kang J, Yi X. Intelligent Diagnosis of Ship Propulsion Motor Bearings Based on Dynamic Class Weights. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(11):2204. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13112204
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Guohua, Xiaoding Wang, Kai Liu, Jingran Kang, and Xinhua Yi. 2025. "Intelligent Diagnosis of Ship Propulsion Motor Bearings Based on Dynamic Class Weights" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 11: 2204. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13112204
APA StyleYan, G., Wang, X., Liu, K., Kang, J., & Yi, X. (2025). Intelligent Diagnosis of Ship Propulsion Motor Bearings Based on Dynamic Class Weights. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(11), 2204. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13112204






