A Study on Energy Loss and Transient Flow Characteristics of a Large Volute Centrifugal Pump During Power-Off Process Under Cavitation Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Numerical Model
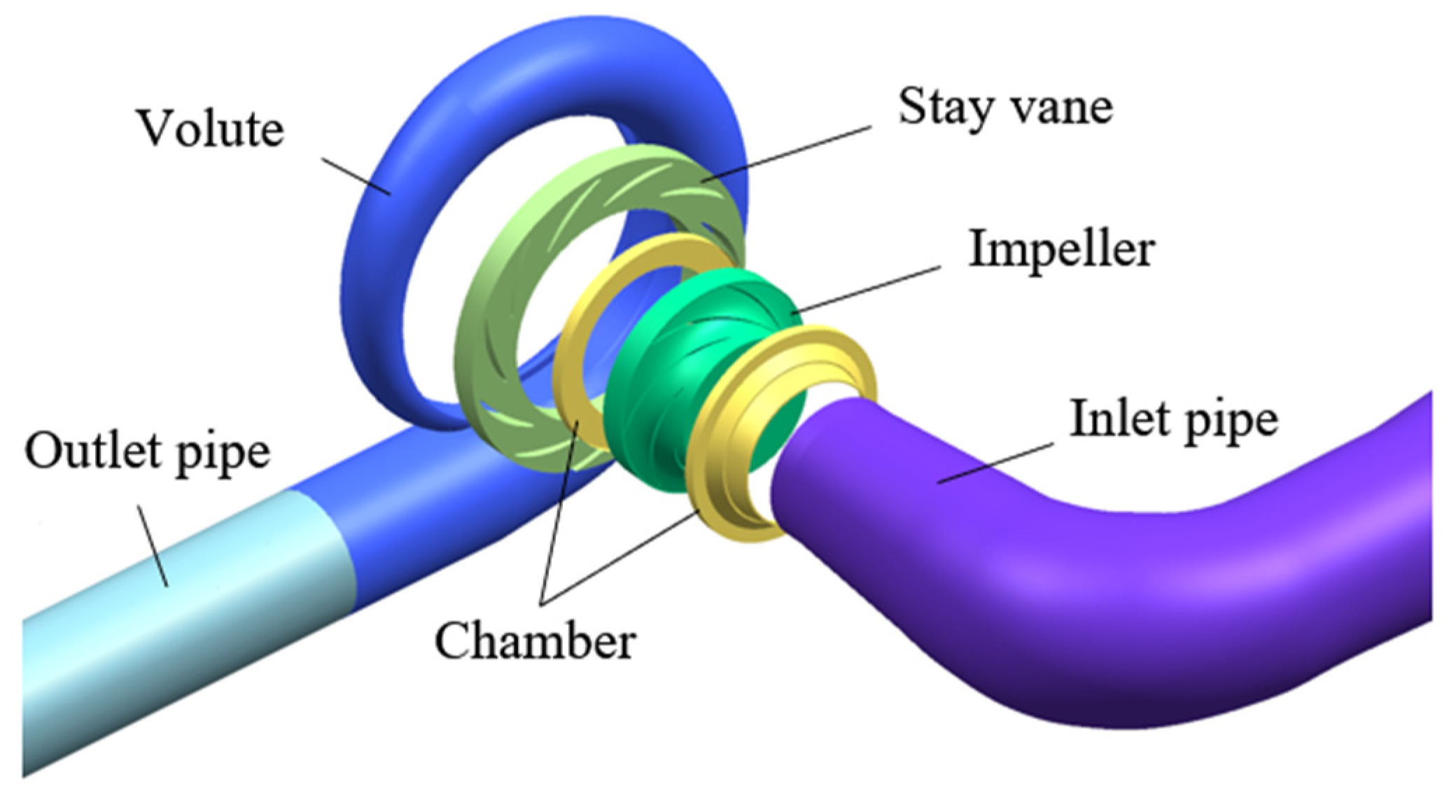
2.1. Calculation Model of LVCP
2.2. Governing Equations of Mixture Model
2.3. Cavitation Model
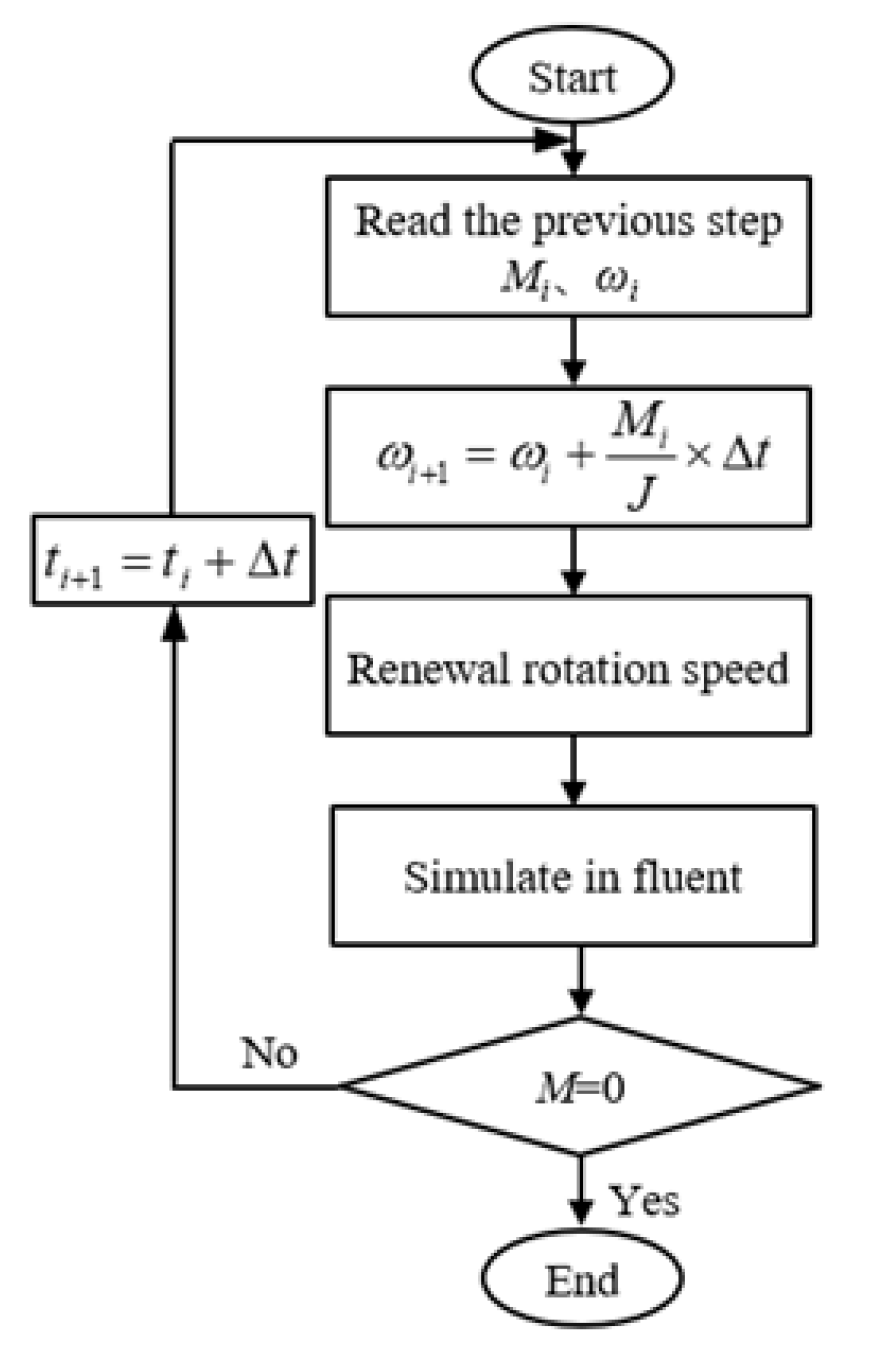
2.4. Numerical Schemes and Boundary Conditions
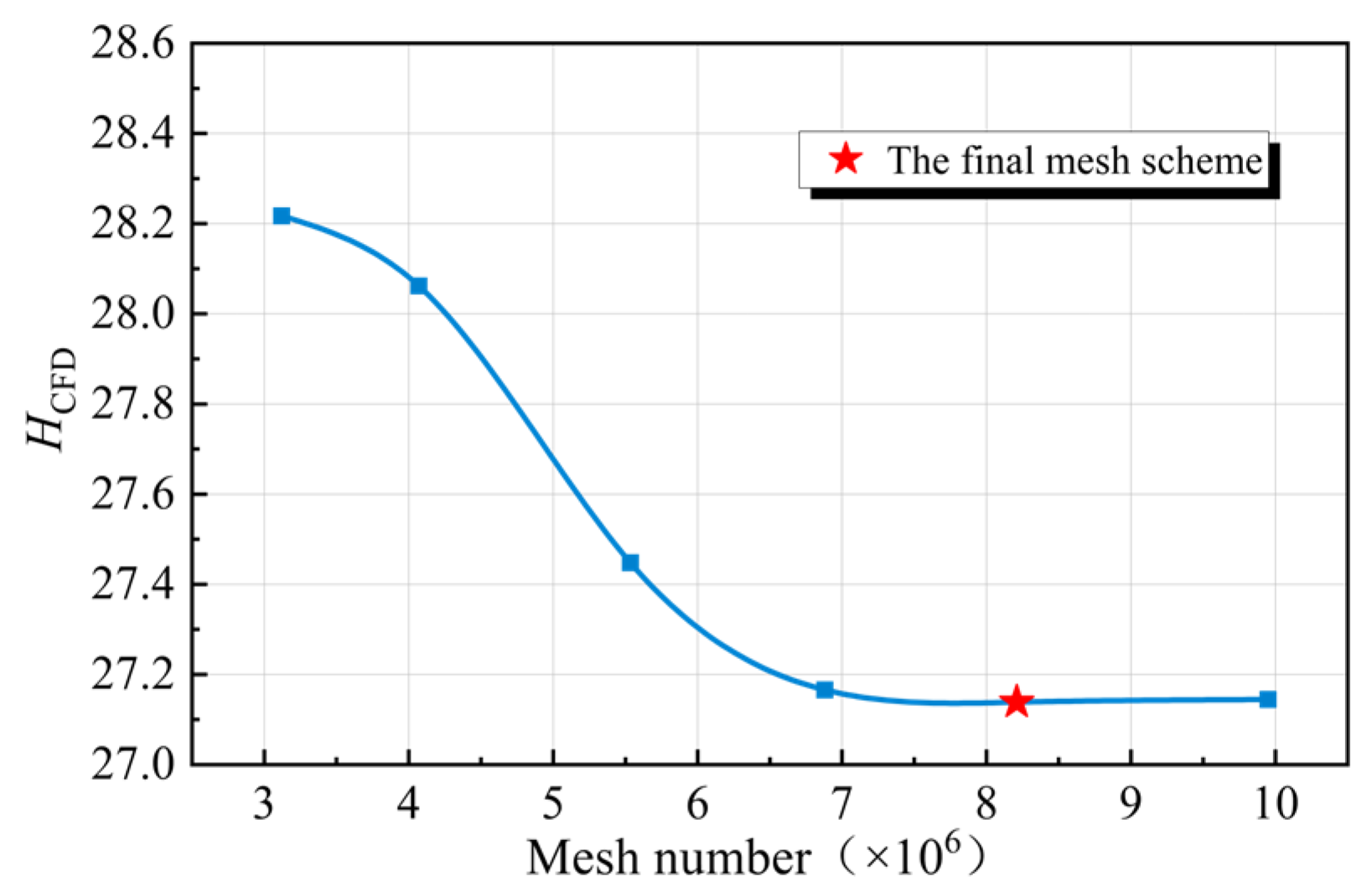
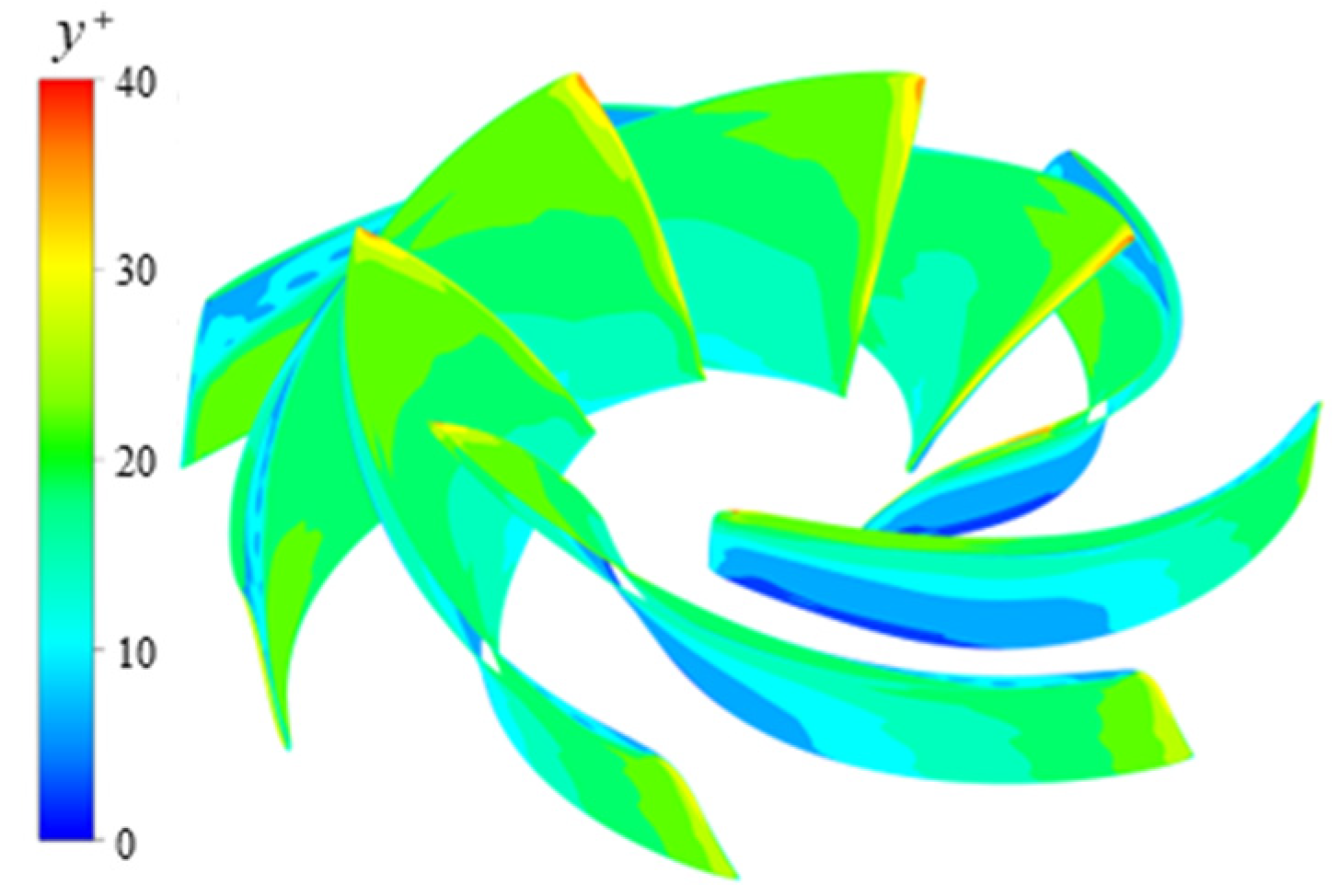
2.5. Mesh Generation and Uncertainty Verification
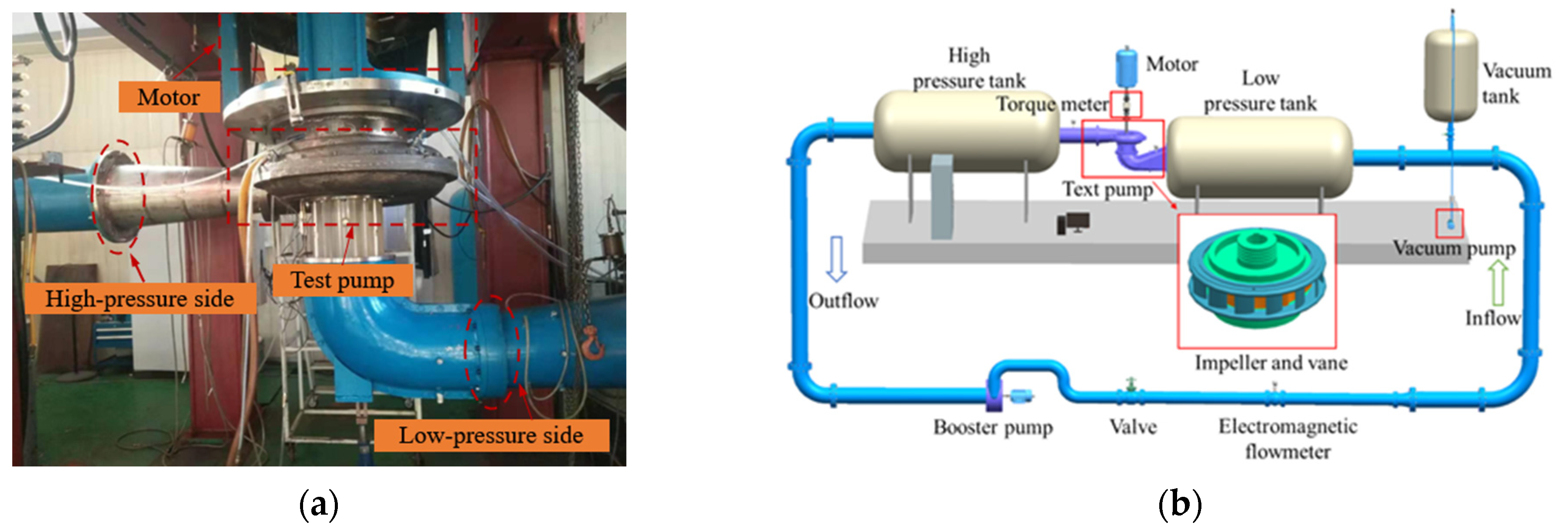
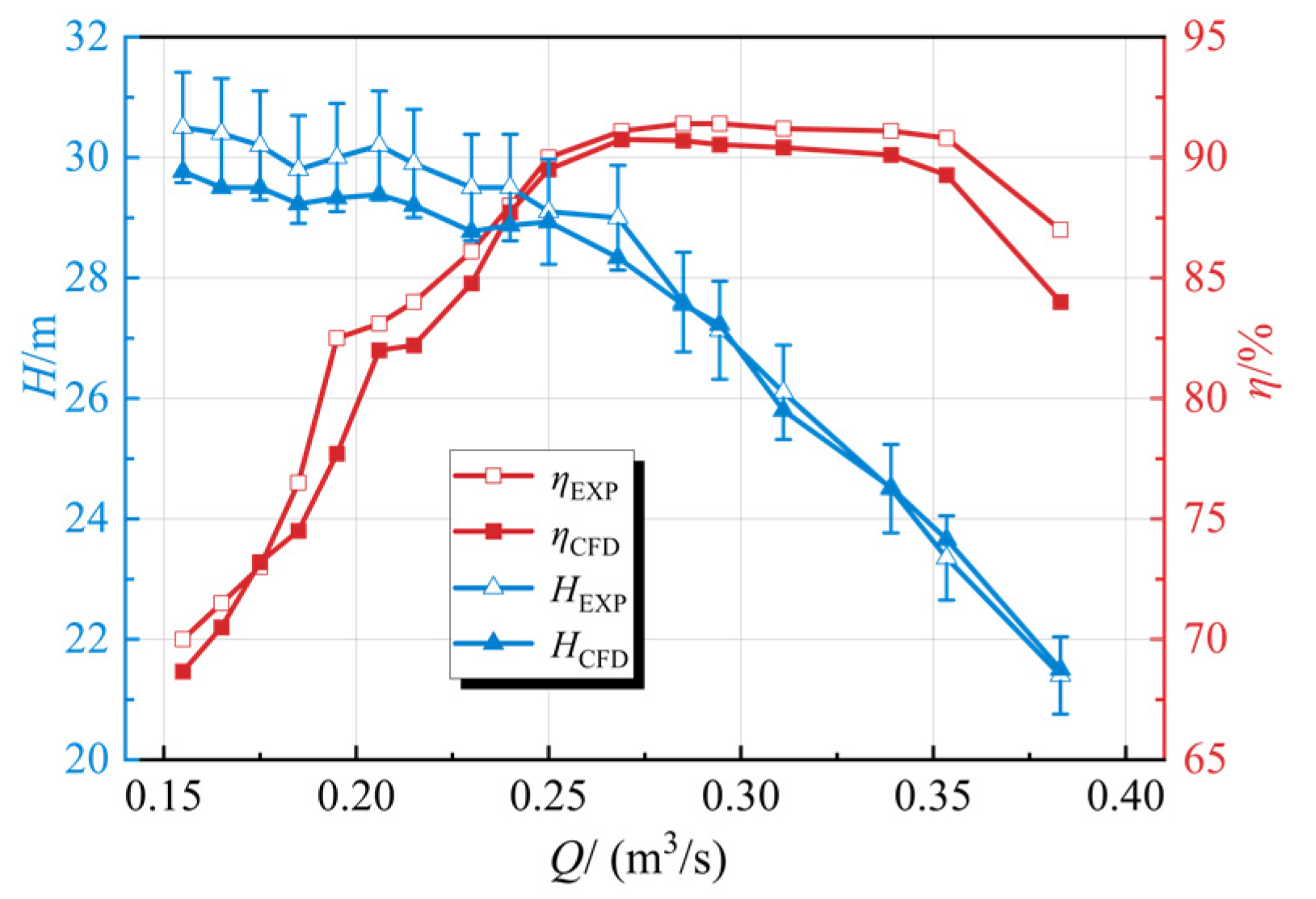
3. Experimental Verification
4. Results and Discussion
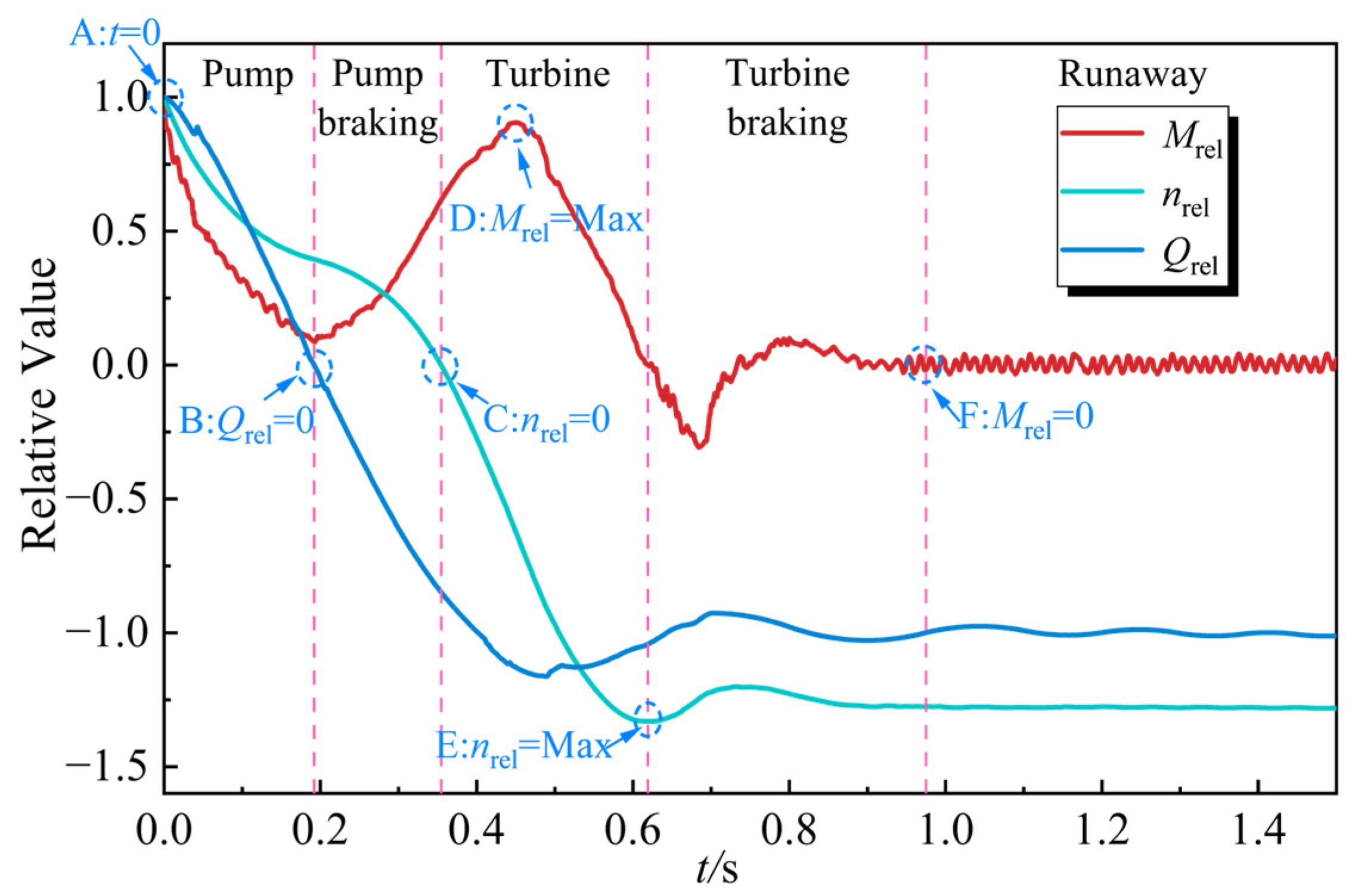
4.1. Analysis of External Performance Characteristics During Shutdown Process
4.2. Analysis of Unsteady Characteristics of Cavitation Evolution
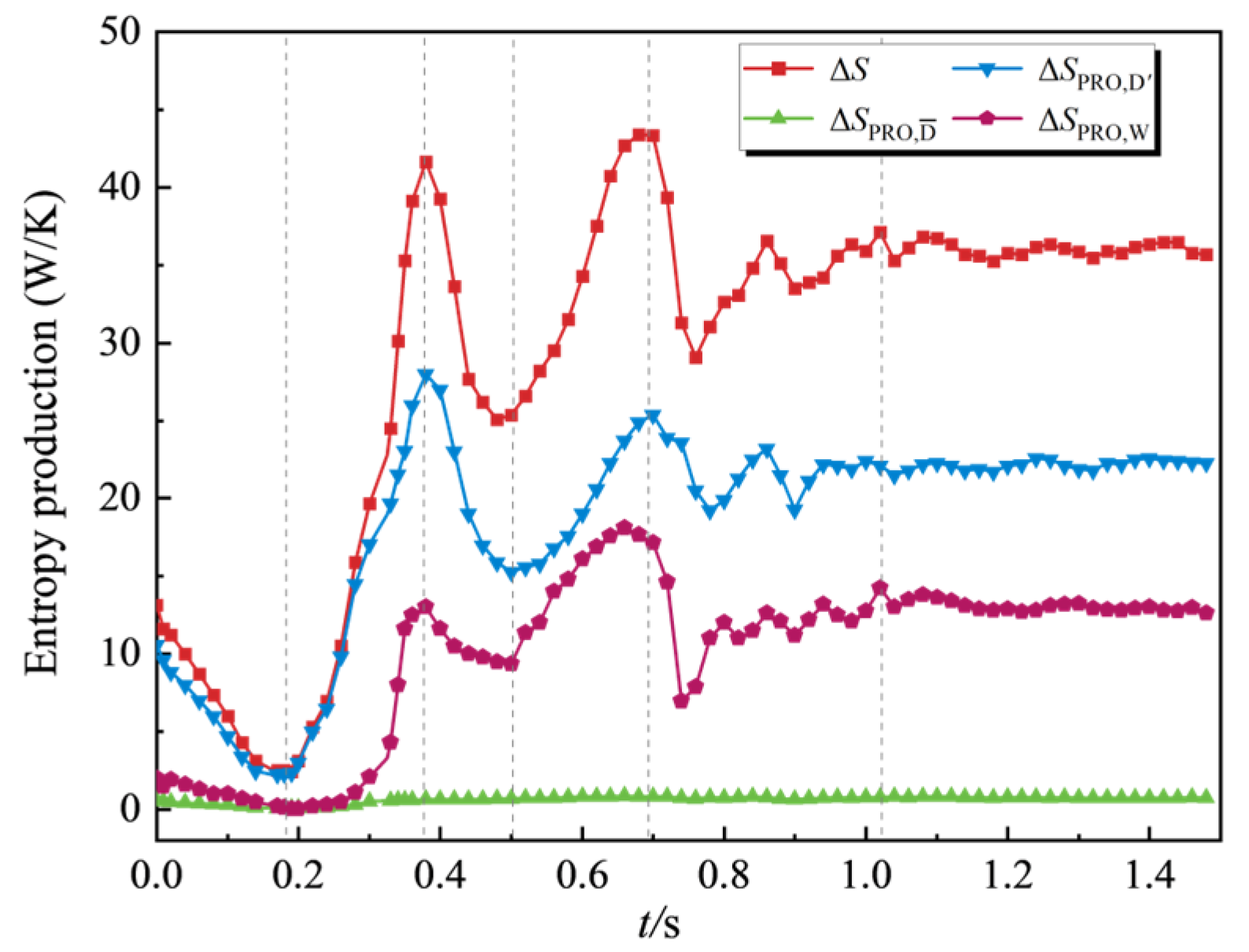
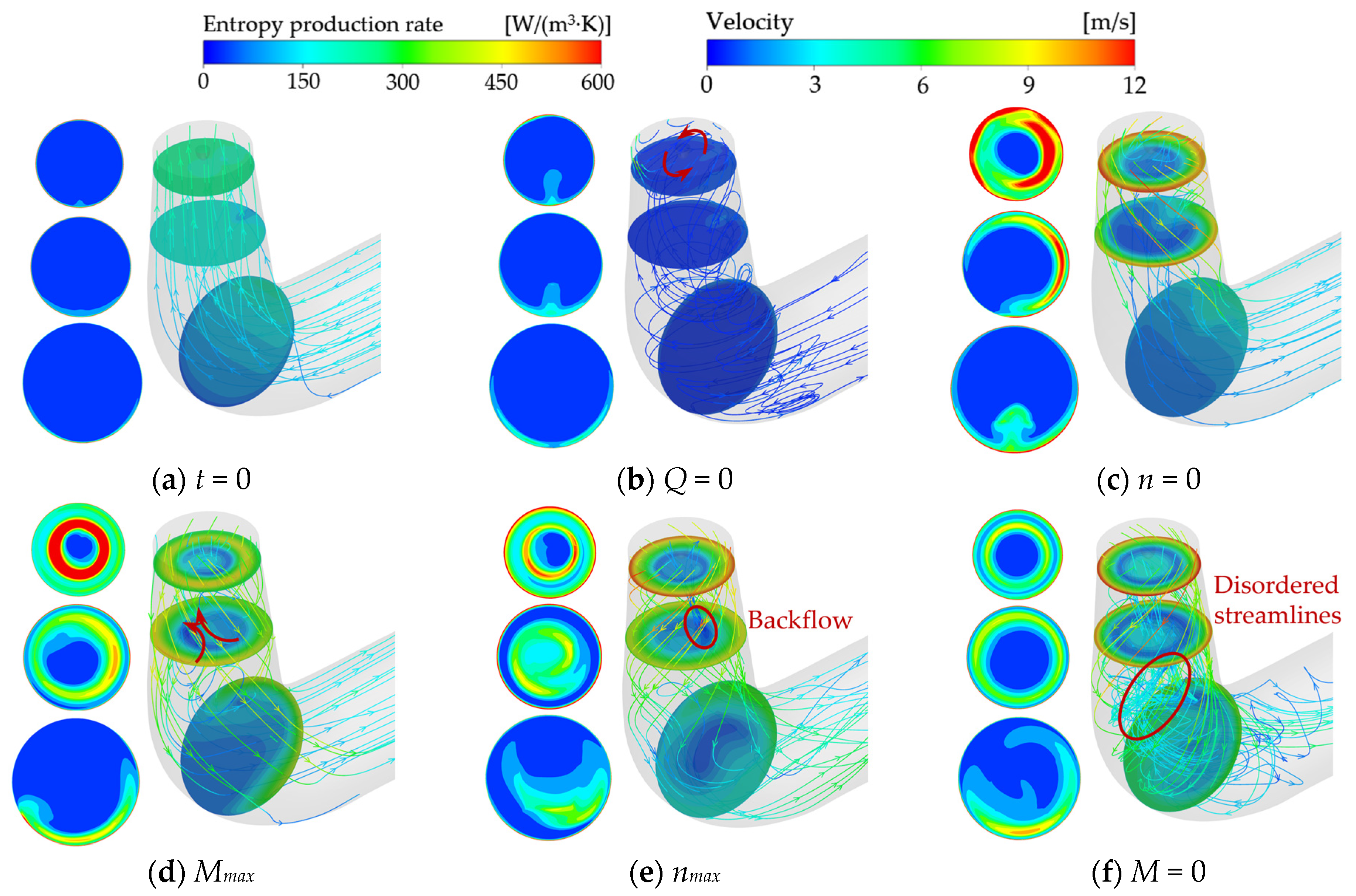
4.3. Transient Energy Loss Characteristics
4.3.1. Entropy Production Theory
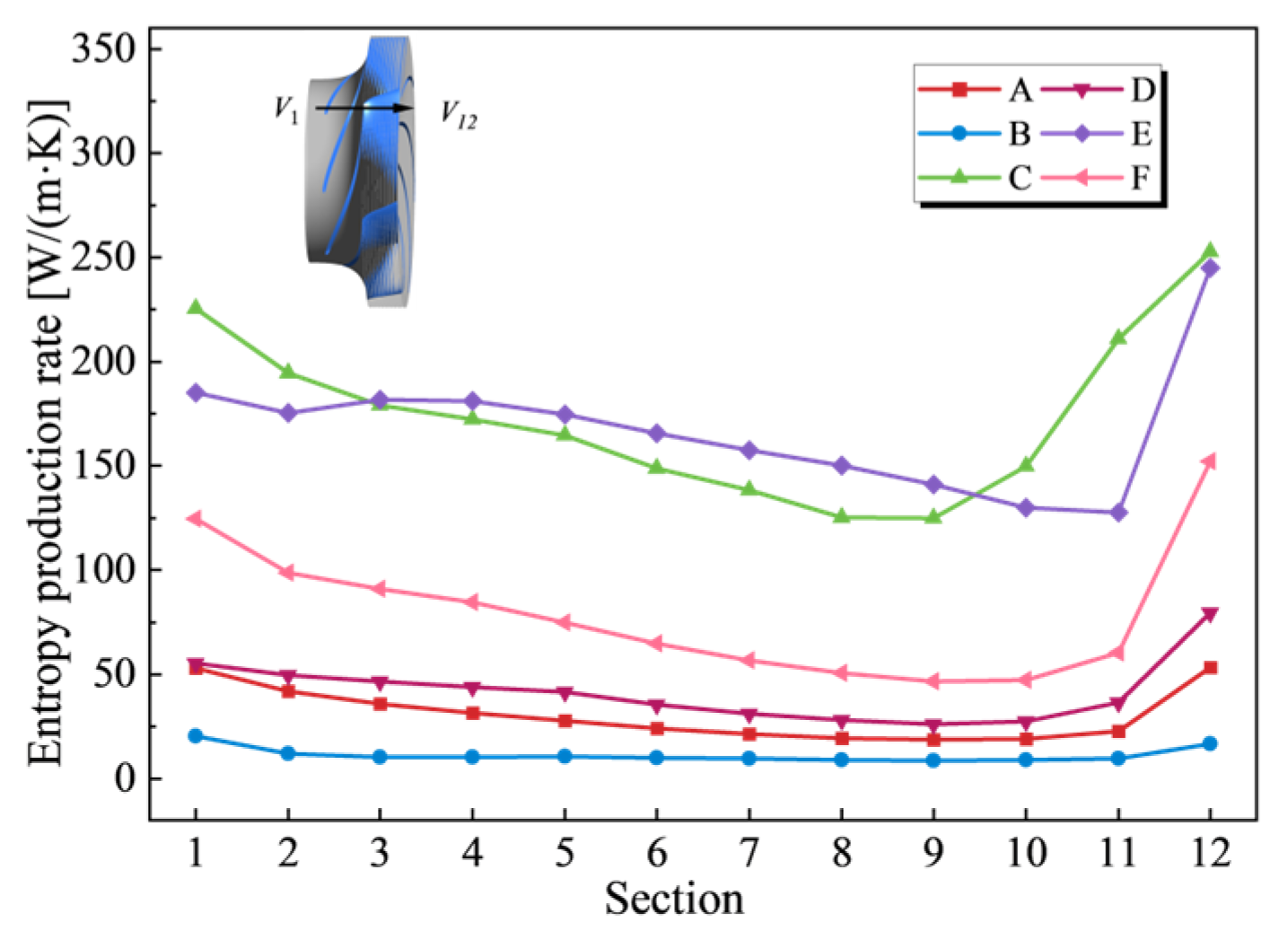
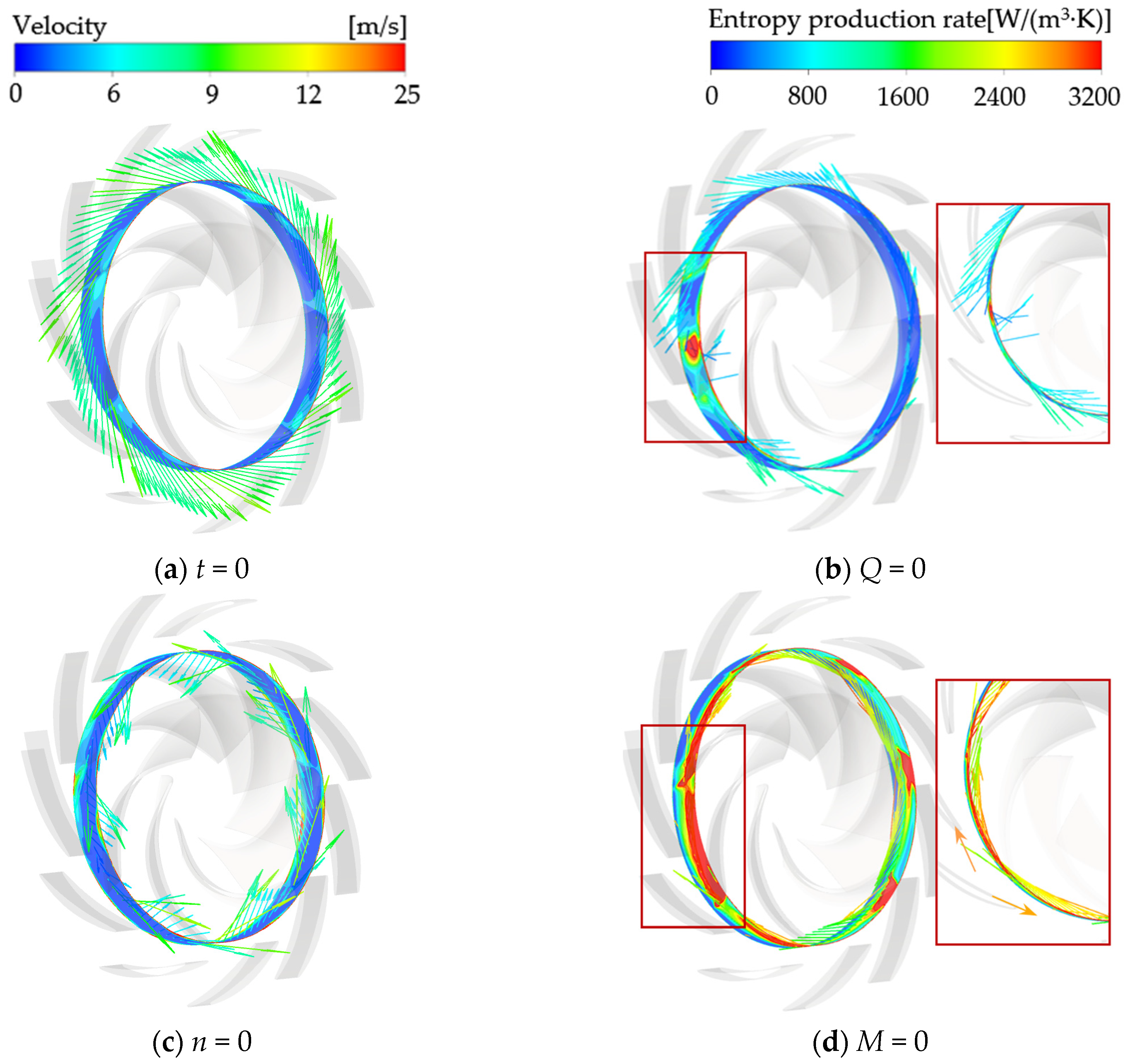
4.3.2. Characteristics of Entropy Production Distribution
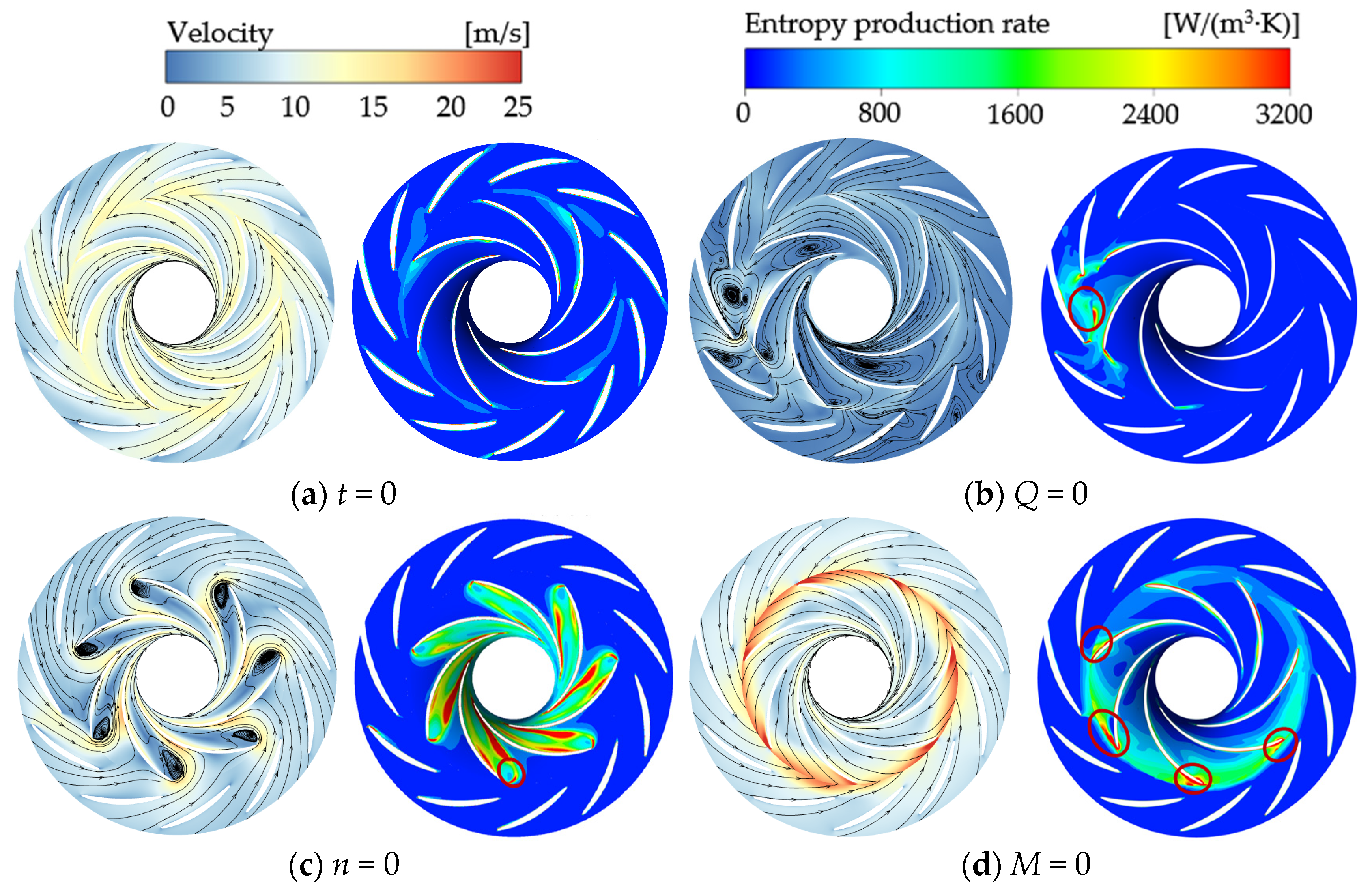
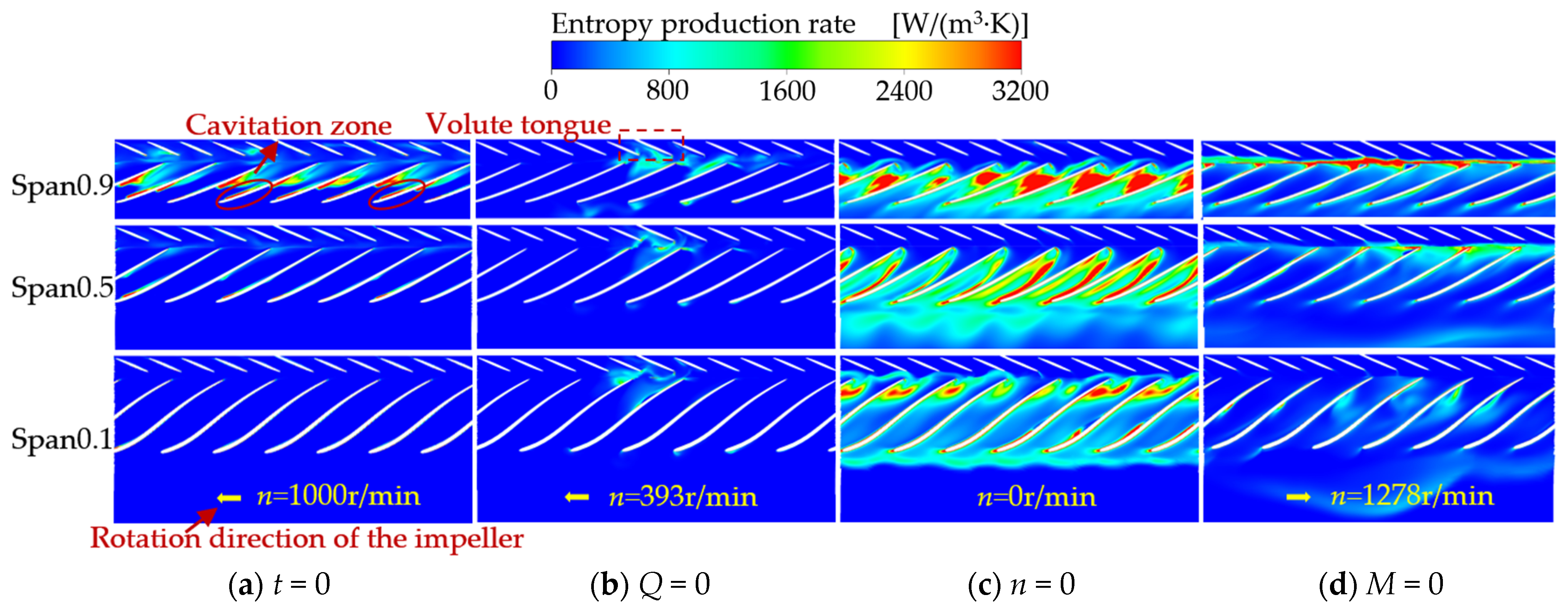
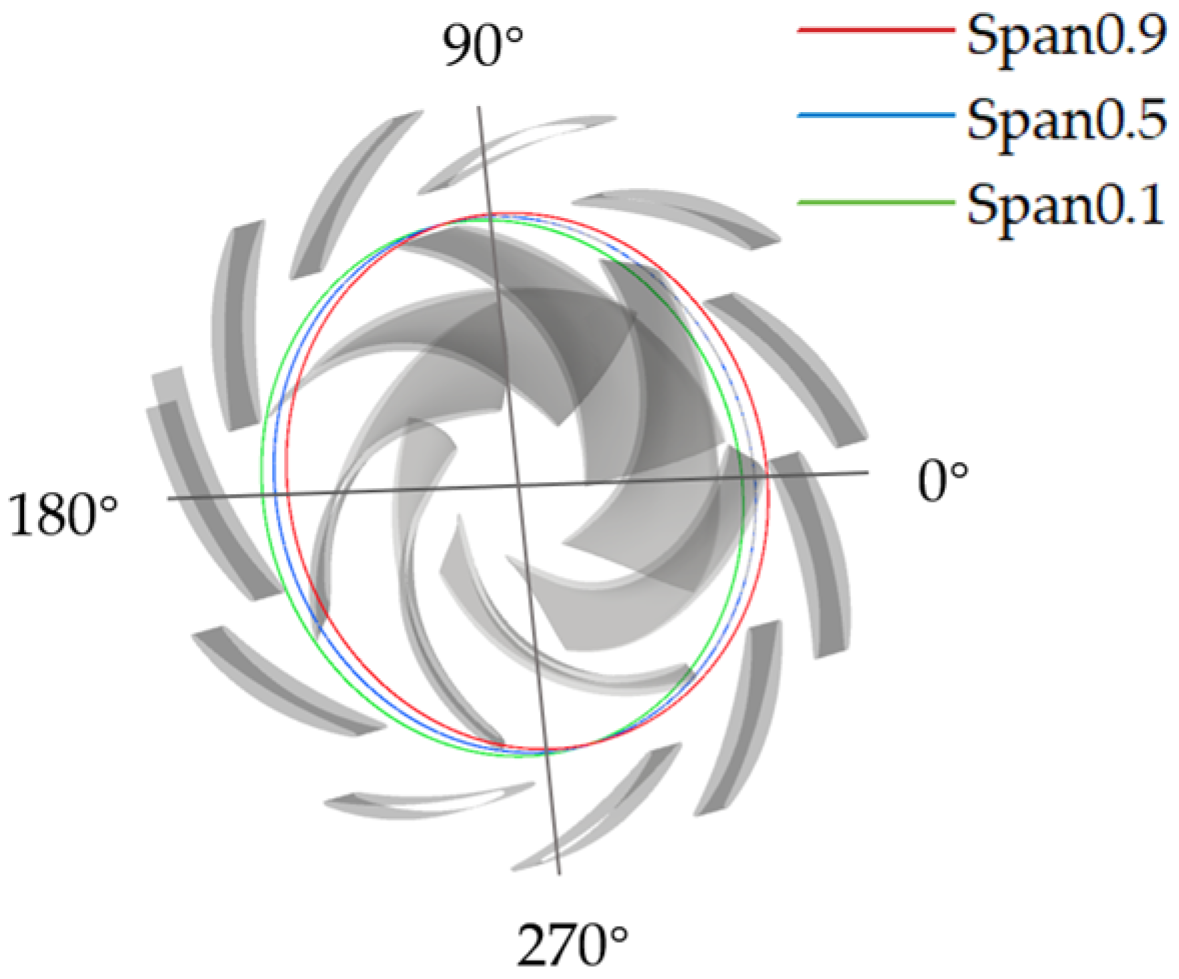
4.3.3. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Local Entropy Production
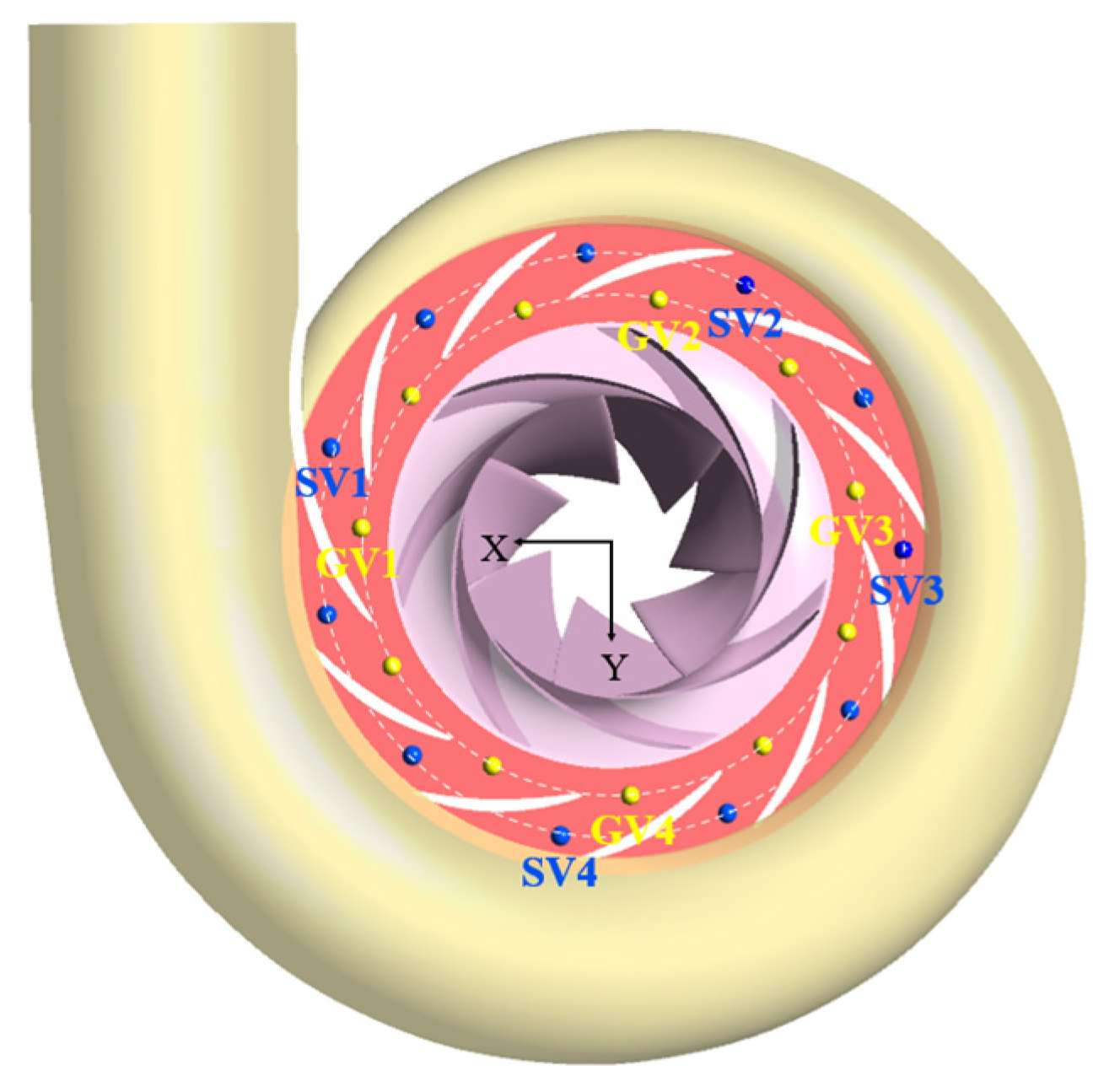
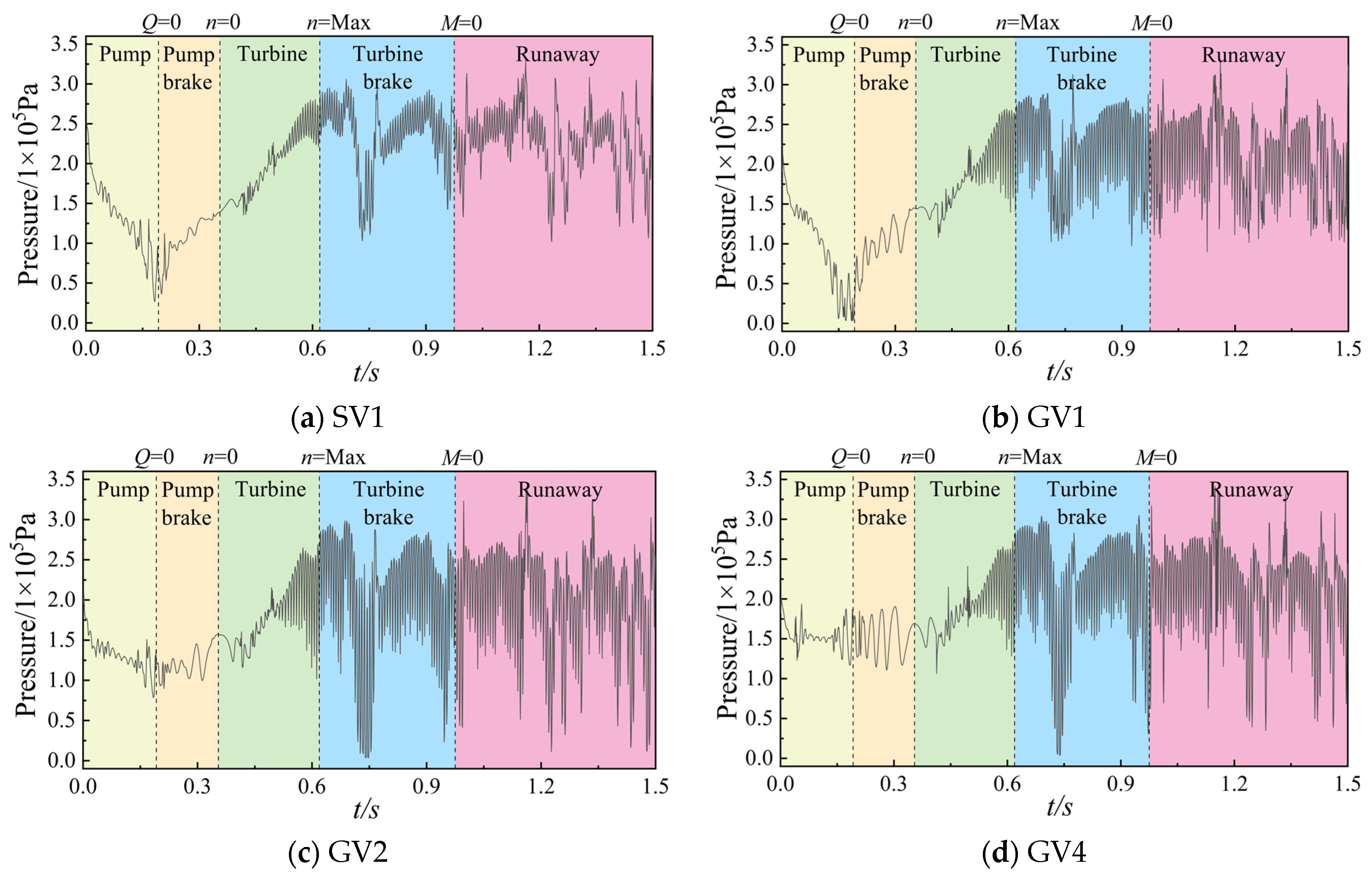
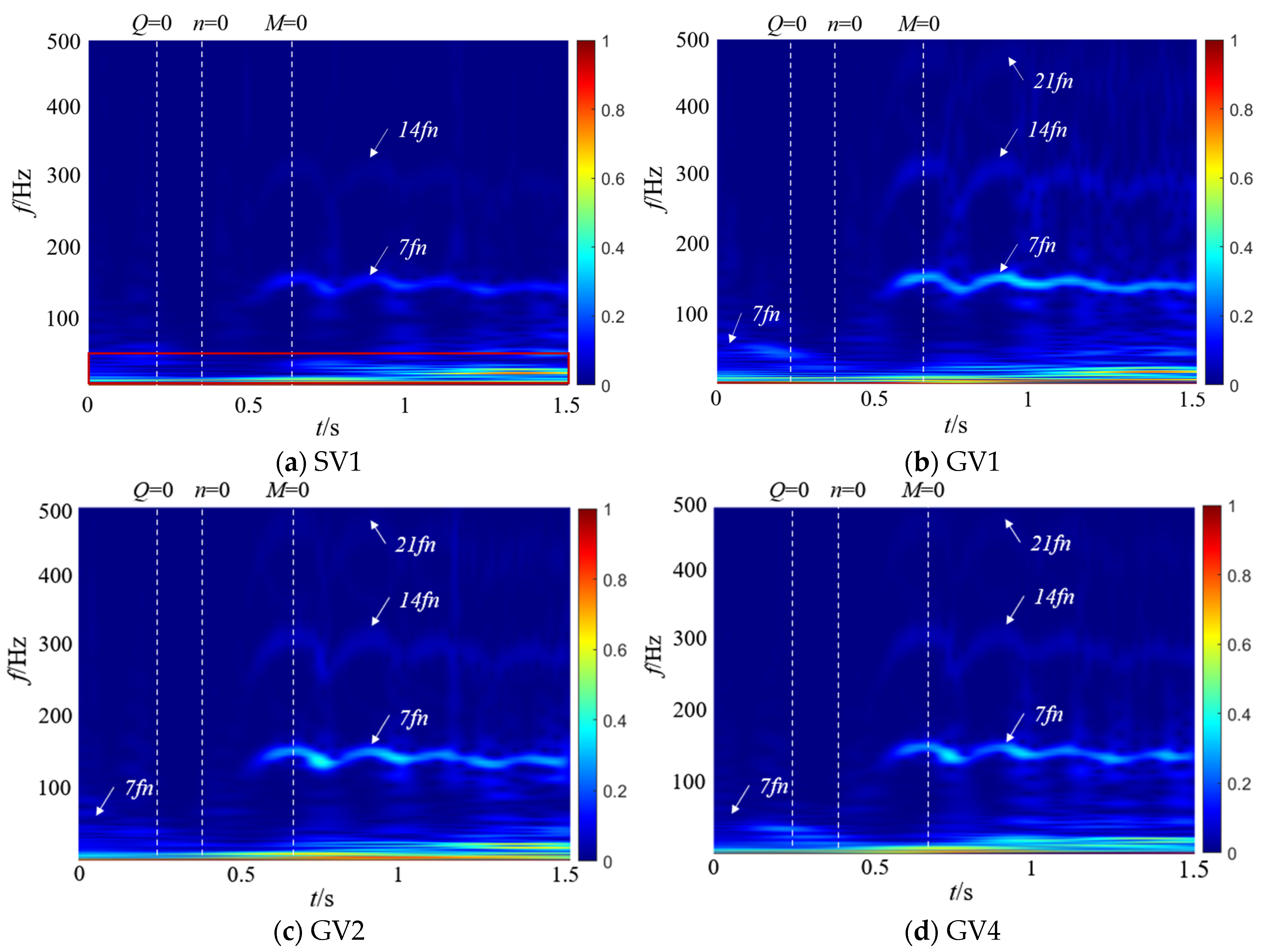
4.4. Time–Frequency Analysis of Pressure Pulsation
5. Conclusions and Outlook
- (1)
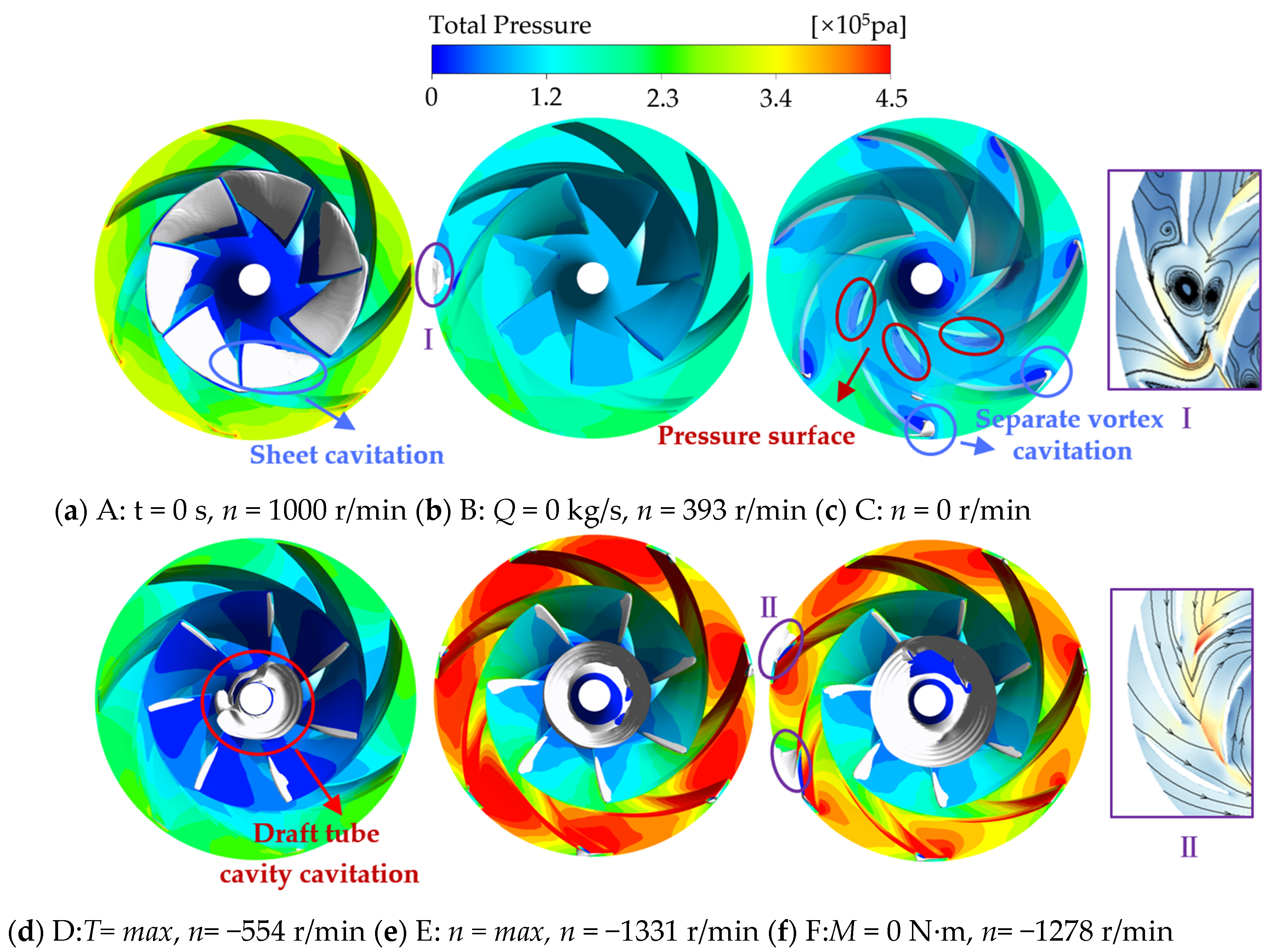
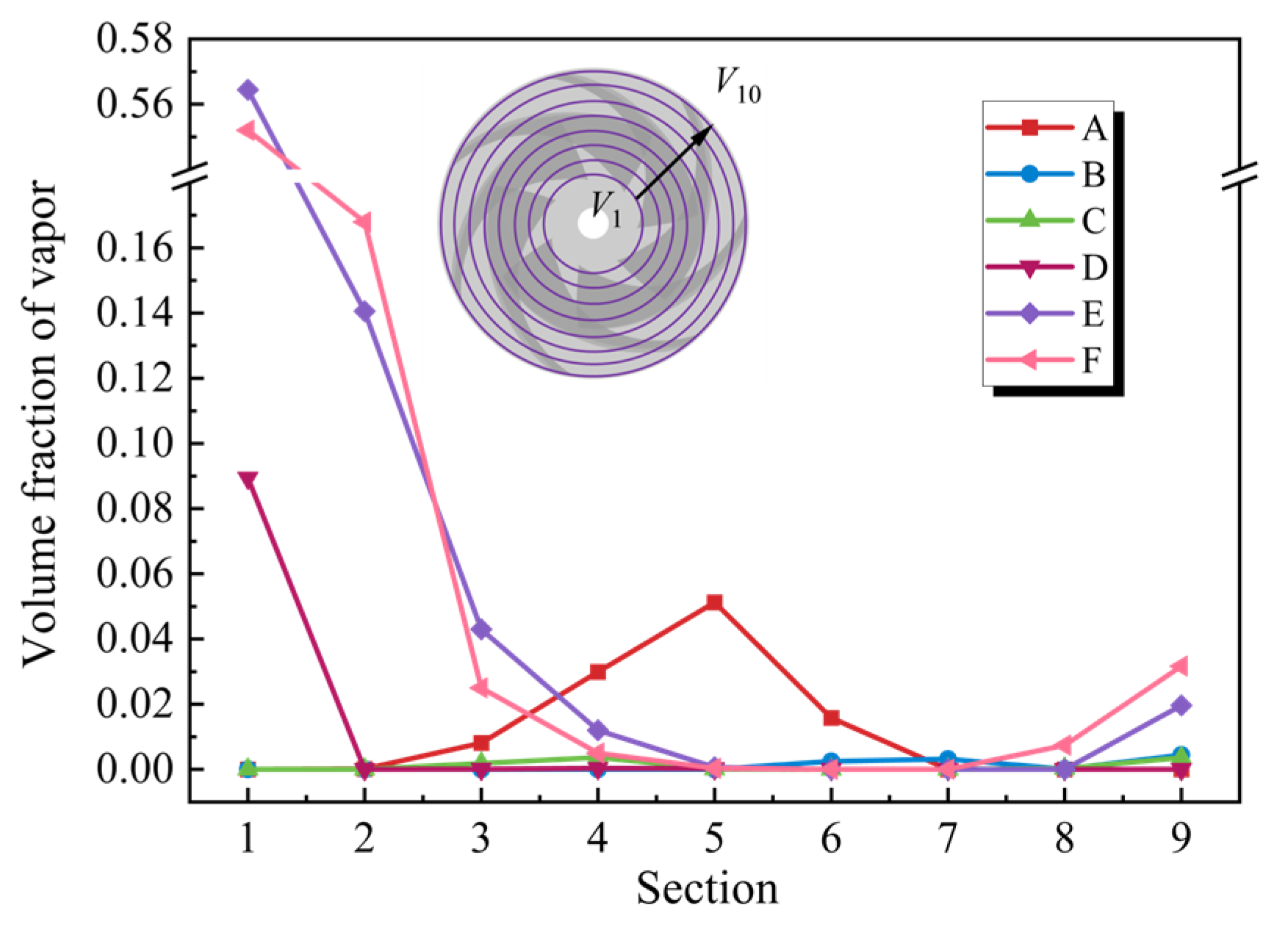
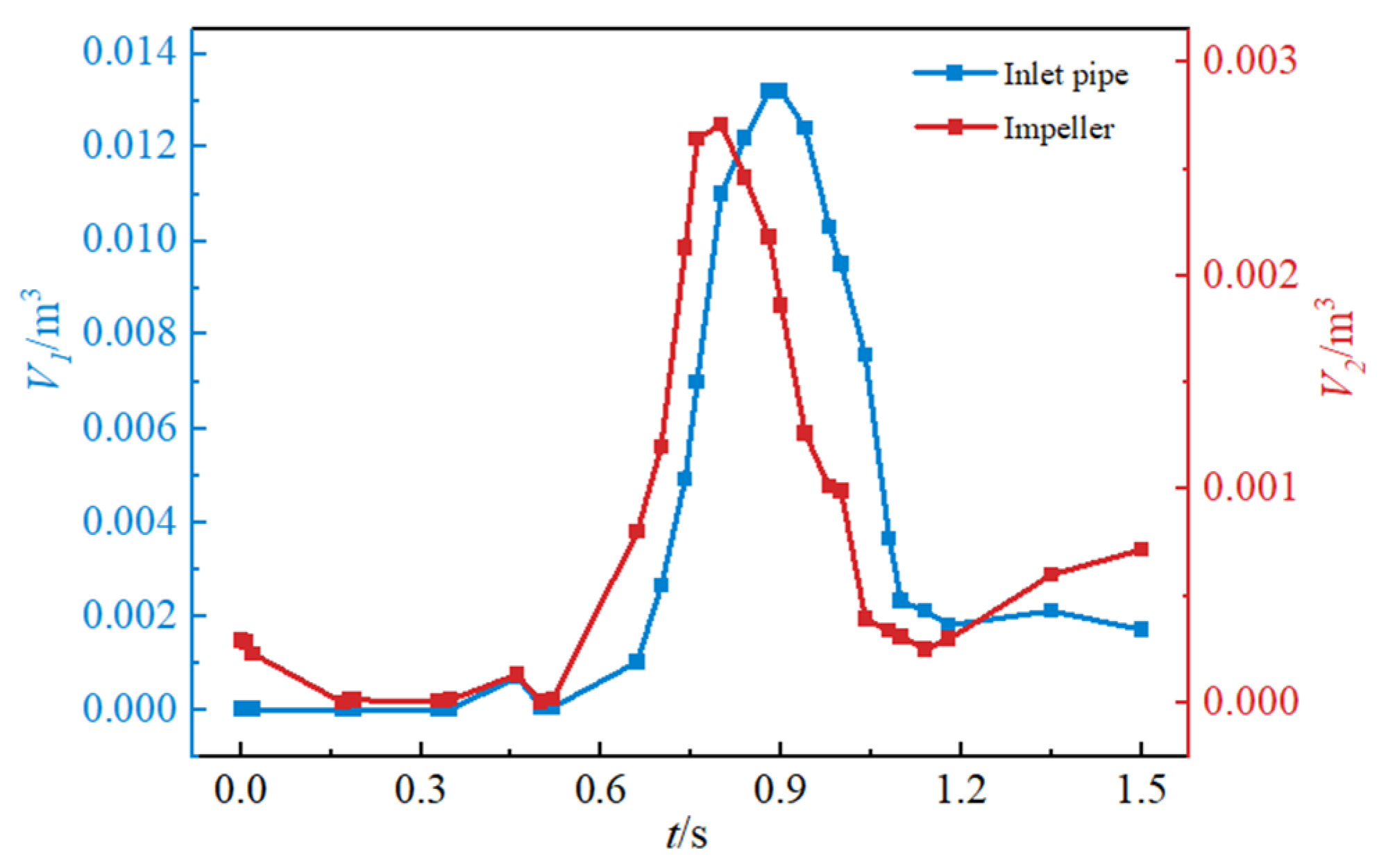
- Following the power-off process of the LVCP, the external characteristic parameters undergo drastic changes, transitioning through multiple unstable operating conditions until runaway mode are reached, with the rotational speed ultimately stabilizing at 1.25nrel. During the transitional moment, the interaction of reversal vortices, separation vortices, and their induced secondary flows collectively disrupts the internal flow patterns within the pump. This hydrodynamic instability, manifested as abrupt flow field transitions, subsequently initiates intricate cavitation phenomena. During the initial power-off phase, inverted-triangular sheet cavitation develops on blade surfaces. As operating conditions transition, flow angle mismatch induces separation vortex cavitation, while under runaway conditions, the draft tube vortex rope propagates upstream, triggering distinct cavity-type cavitation structures. There is a strong coupling relationship between the cavitation morphology at different phases of the transient process and the dynamic characteristics of the impeller.
- (2)
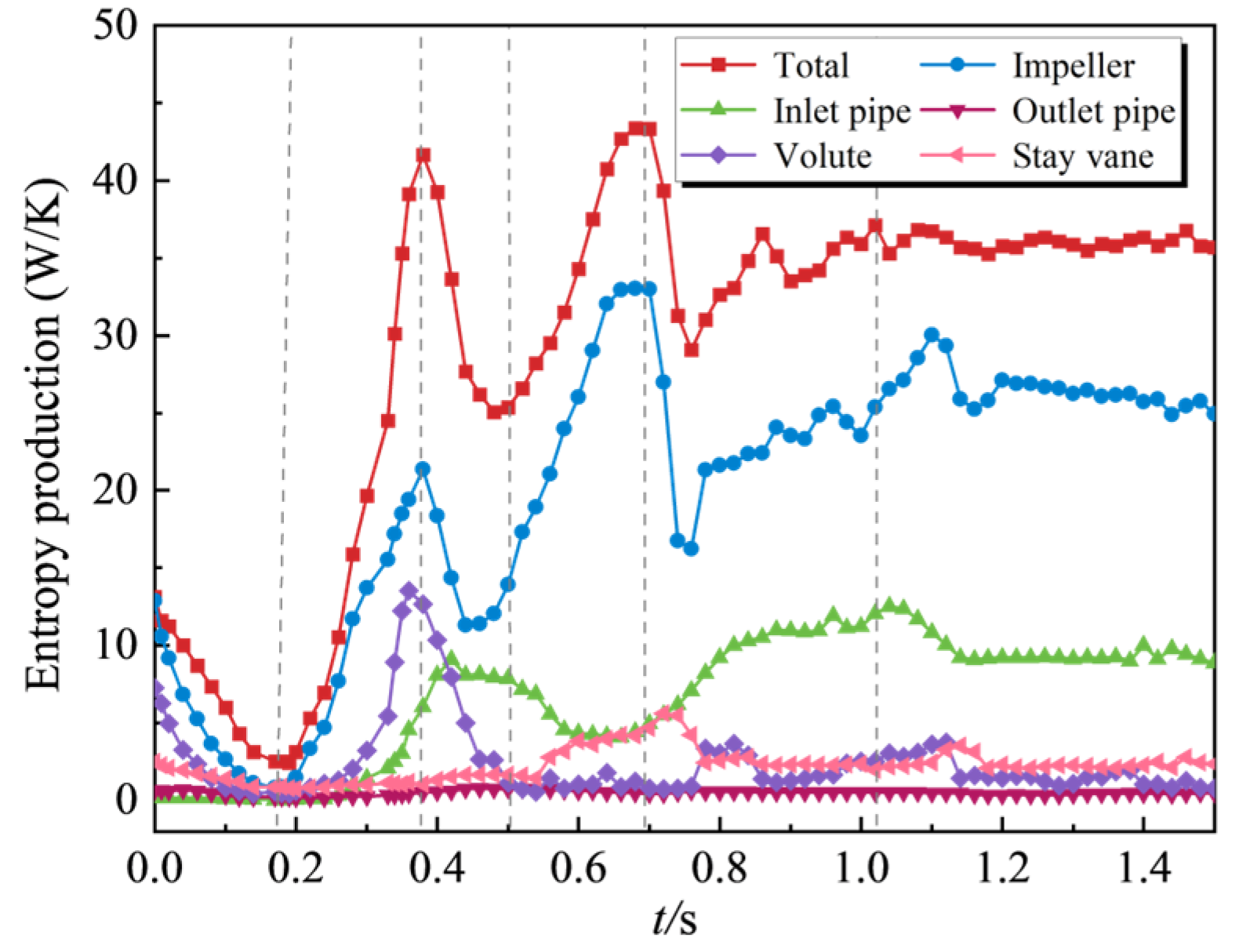
- The transient process exhibits significant entropy production fluctuations. Unsteady flow patterns within the flow field demonstrate strong correlations with energy dissipation characteristics. During the initial shutdown phase, microjet formation from collapsing cavitation bubbles induces steep velocity gradient amplification in the flow field. This hydrodynamic intensification drives an exponential rise in entropy production rate within the cavitation collapse core zones, while cavitation exacerbates the flow complexity in the wake region. As the process proceeds, the separation vortices caused by the mismatch of the liquid flow angle and the induced cavitation of the separation vortices lead to a large amount of energy dissipation. The entropy production rate in the draft tube of the turbine mode increases sharply, and the high entropy production rate area corresponds to the recirculation vortex and the wake vortex band area. The pressure gradient change caused by the vortex is the main reason for energy dissipation. The fluid near the wall of the draft tube is squeezed by the draft water vortex band, resulting in an increase in shear stress and thus an increase in energy dissipation.
- (3)
- This study demonstrates that pressure pulsations induced by cavitation collapse and vortex system evolution are key factors influencing transient process stability. The main frequency of pressure pulsation exhibits dynamic variation with the shaft frequency, while its amplitude demonstrates a negative correlation with the cross-sectional area of the volute. Cavitation collapse, in conjunction with flow separation, recirculation, and other vortex-related phenomena, forms an unstable excitation source that induces low-frequency, high-amplitude pressure pulsations. During the runaway process, the pressure amplitude of LVCP reaches its peak value, and the pressure fluctuations become significantly more intense. This extreme pulsation, coupled with the potential for structural system resonance, represents a critical factor impacting the operational safety and stability of the unit.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| D1, D2 | Impeller inlet, outlet diameter (mm) |
| Hd | Design, Simulated, Experiment head (m) |
| HCFD | Simulated head (m) |
| HEXP | Experiment head (m) |
| J | The moment of inertia of the impeller and the motor rotor (kg·m2) |
| Qdes | Design flow rates (m3/s) |
| M | Impeller torque (N·m) |
| Z1, Z2 | Number of impeller, stay vane blades |
| fn | Impeller rotational frequency |
| ns | Specific speed |
| n | Rotational speed (r/min) |
| ui, uj, uk | Velocity components in x, y, z-direction (m/s) |
| pin, pout | The inlet and outlet pressure of the pump (Pa) |
| Fc | Condensation coefficient |
| Fe | Evaporation coefficient |
| μm | Laminar dynamic viscosity of mixture (Pa·s) |
| μt | Turbulent eddy viscosity (Pa·s) |
| μeff | The effective dynamic viscosity of the mixture (Pa·s) |
| ρm | mixed phase densities (kg/m3) |
| ρl | Liquid densities (kg/m3) |
| ρv | vapor densities (kg/m3) |
| fHT | The total error of the head |
| fηs | The comprehensive efficiency error of the test bench |
| αv | Vapor volume fraction |
| αnuc | Volume fraction of vapor nuclei contained in a unit liquid |
| ω | Rotational angular velocity (rad/s) |
| σ | Cavitation number |
| η | Efficiency (%) |
| Wall entropy production (W/K) | |
| Averaged velocity entropy production (W/K) | |
| Pulsating velocity entropy production (W/K) | |
| Rb | Mean radius of cavity (m) |
| , | Evaporation and condensation rates of the liquid and vapor phases |
Abbreviations
| LVCP | Large volute centrifugal pump |
| UDF | User-Defined Function |
| CFD | Computational Fluid Dynamics |
| SST | Shear stress transport |
| CWT | Continuous Wavelet Transform |
References
- Zsiborács, H.; Baranyai, N.; Vincze, A.; Zentkó, L.; Birkner, Z.; Máté, K.; Pintér, G. Intermittent renewable energy sources: The role of energy storage in the European power system of 2040. Electronics 2019, 8, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, H.; Yin, X.; Jiang, W. Towards the integration of distributed renewables: Operation analysis of pumped storage system under off-design condition based on CFD. Appl. Energy 2024, 355, 122217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Z.; Liu, S. Flow-induced instabilities in pump-turbines in China. Engineering 2017, 3, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rode, B.; Kumar, A. Unstable pressure fluctuations in the vaneless space of high-head reversible pump-turbines—A systematic review. J. Energy Storage 2023, 72, 108397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torii, D.; Nagahara, T.; Okihara, T. Suppression of the secondary flow in a suction channel of a large centrifugal pump. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2013, 52, 032005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kye, B.; Park, K.; Choi, H.; Lee, M.; Kim, J. Flow characteristics in a volute-type centrifugal pump using large eddy simulation. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2018, 72, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W.; Huang, R.; Jiang, Z.; Li, X.; Zhu, Z.; Luo, X. Instability analysis under part-load conditions in centrifugal pump. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2019, 33, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duplaa, S.; Coutier-Delgosha, O.; Dazin, A.; Bois, G. X-ray measurements in a cavitating centrifugal pump during fast start-ups. J. Fluids Eng. 2013, 135, 041204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walseth, E.; Nielsen, T.; Svingen, B. Measuring the dynamic characteristics of a low specific speed pump-turbine model. Energies 2016, 9, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Yang, J.; Zeng, W.; Yang, J. Transient pressure analysis of a prototype pump turbine: Field tests and simulation. J. Fluids Eng. 2018, 140, 071102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Tong, J.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, H.; Zhou, W.; Jia, X.; Ou, L. Experimental analysis of radial centrifugal pump shutdown. Fluid Dyn. Mater. Process. 2024, 20, 725–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirag, T.; Gunnar, D. Interaction between trailing edge wake and vortex rings in a Francis turbine at runaway condition: Compressible large eddy simulation. Phys. Fluids 2018, 30, 075101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Xia, L.; Meng, W.; Liu, K.; Zhang, X. Evolutions of flow patterns and pressure fluctuations in a prototype pump-turbine during the runaway transient process after pump-trip. Renew. Energy 2020, 152, 1149–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, K.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhou, D.; Dai, J.; Maxime, B.; Yu, A. Numerical simulation of transient flow in a shaft extension tubular pump unit during runaway process caused by power failure. Renew. Energy 2020, 154, 1153–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Ge, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, G.; Wu, G.; Lu, J.; Luo, X. Numerical investigation on characteristics of transient process in centrifugal pumps during power failure. Renew. Energy 2021, 170, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, W.; Zhou, L.; Wang, Z. Analysis of flow characteristics and cavitation in the vanes of a reversible pump-turbine in pump mode. J. Energy Storage 2023, 68, 107690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Song, Y.; Lin, S.; Wang, H.; Qin, Y.; Wei, X. Effect mechanism of cavitation on the hump characteristic of a pump-turbine. Renew. Energy 2021, 167, 369–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghan, A.; Shojaeefard, M.; Roshanaei, M. Exploring a new criterion to determine the onset of cavitation in centrifugal pumps from energy-saving standpoint; experimental and numerical investigation. Energy 2024, 293, 130681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liu, D.; Wang, Y.; Wu, X.; Wang, J.; Du, H. Experimental investigation and numerical analysis of unsteady attached sheet cavitating flows in a centrifugal pump. J. Hydrodyn. 2013, 25, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Yuan, J.; Yuan, S.; Giovanni, P.; D’Agostino, L.; Huang, P.; Li, X. Numerical and experimental analysis of flow phenomena in a centrifugal pump operating under low flow rates. J. Fluids Eng. 2015, 137, 011102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Zhang, D.; Shen, X.; Pan, Q.; Pang, Q.; Lu, Q. Investigation on flow instability in the hump region of the large vertical centrifugal pump under cavitation based on proper orthogonal decomposition. Phys. Fluids 2024, 36, 115134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Tan, L. Cavitation-vortex-pressure fluctuation interaction in a centrifugal pump using bubble rotation modified cavitation model under partial load. J. Fluids Eng.-Trans. ASME 2020, 142, 051206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Li, D.; Wang, H.; Cheng, Y.; Wei, X. Hydraulic fluctuations during the pump power-off runaway transient process of a pump turbine with consideration of cavitation effects. J. Hydrodyn. 2021, 33, 1162–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Xin, L.; Yao, L.; Zhang, S. Flow characteristics analysis of load rejection transition process in pumped storage unit based on cavitation model. J. Appl. Fluid Mech. 2024, 17, 1735–3572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Hang, J.; Bai, L.; Krzemianowski, Z.; El-Emam, M.; Yaseer, E.; Agarwal, R. Application of entropy production theory for energy losses and other investigation in pumps and turbines: A review. Appl. Energy 2022, 318, 119211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Shen, X.; Shi, L.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, X.; van Esch, B. Numerical investigation of hump characteristic improvement in a large vertical centrifugal pump with special emphasis on energy loss mechanism. Energy 2023, 273, 127163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kock, F.; Herwig, H. Local entropy production in turbulent shear flows: A high-Reynolds number model with wall functions. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2004, 47, 2205–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jiang, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Si, Q. Entropy generation analysis for the cavitating head-drop characteristic of a centrifugal pump. J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2018, 232, 4637–4646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Xiao, Y.; Jiang, L.; Li, M. A numerical investigation on energy characteristics of centrifugal pump for cavitation flow using entropy production theory. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2023, 201, 123591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Z.; Feng, J.; Wu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, G.; Luo, X. Numerical analysis on characteristics of transient process in centrifugal pumps during power failure under large flow initial condition. Chin. J. Hydrodyn. 2022, 37, 452–458. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Y.; Xu, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Qi, C. Research on energy loss characteristics of pump-turbine during abnormal shutdown. Processes 2022, 10, 1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, W.; Pavesi, G.; Yuan, S.; Pei, J. Research on the mechanism of severe unsteadiness of PAT braking condition during the power failure. Renew. Energy 2024, 232, 121019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, X.; Cheng, H.; Ji, B.; Arndt, R.; Peng, X. Large eddy simulation and Euler-Lagrangian coupling investigation of the transient cavitating turbulent flow around a twisted hydrofoil. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2018, 100, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, H.; Kim, K. Effects of the cross-sectional area of a volute on suction recirculation and cavitation in a centrifugal pump. J. Fluids Eng. 2022, 142, 051204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menter, F. Review of the shear-stress transport turbulence model experience from an industrial perspective. Int. J. Comput. Fluid Dyn. 2009, 23, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Bayeul-Laine, A.; Coutier-Delgosha, O. Numerical investigations on unsteady vortical flows and separation-induced transition over a cycloidal rotor at low Reynolds number. Energy Convers. Manag. 2022, 266, 115812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Zhang, D.; Gao, H.; Shen, X.; Pan, Q.; Pang, Q.; Lu, Q. Transient flow characteristics and energy loss investigation in a desalination energy recovery device under rotor system axial sliding conditions: Focusing on the turbine side. Phys. Fluids 2025, 37, 015196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Liu, H.; Kan, K.; Hui, X.; Feng, J.; Aboule, L. Analysis of hydraulic characteristics during low head start-up transition of pumped storage units based on entropy production theory. J. Energy Storage 2024, 102, 114042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Xu, X. Energy conversion characteristic within impeller of low specific speed centrifugal pump. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2011, 42, 75–81. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Guo, H.; Zhang, C.; Shen, J.; Pei, J.; Yuan, S. Transient characteristics of PAT in micro pumped hydro energy storage during abnormal shutdown process. Renew. Energy 2023, 209, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Parameter | Prototype Machine Value | Model Machine Value |
|---|---|---|
| Design flow rate Qdes (m3/s) | 9.6 | 0.294 |
| Rotational speed n (r/min) | 375 | 1000 |
| Design head Hd (m) | 75 | 27.4 |
| Impeller inlet diameter D1 (mm) | 1382 | 312 |
| Impeller outlet diameter D2 (mm) | 2020 | 456 |
| Number of impeller blades Z1 | 7 | 7 |
| Number of stay vanes Z2 | 11 | 11 |
| Item | Steady | Unsteady |
|---|---|---|
| Turbulence model | SST k-ω model | SST k-ω model |
| Inlet boundary | Total pressure (0.25 atm) | Total pressure (0.25 atm) |
| Outlet boundary | Volumetric flow rate (Qdes) | Total pressure (2.82 atm) |
| Impeller speed | 1000 r/min | Variable |
| Wall condition | No-slip wall | No-slip wall |
| Interface condition | Frozen Rotor | Transient Rotor stator |
| Pressure–velocity coupling algorithm | Coupled | Coupled |
| Convection term discretization | Second-order | Second-order |
| Maximum residual value | 10−5 | 10−5 |
| Time step | / | 5 × 10−4 s |
| Total calculation time | / | 1.5 s |
| Maximum number of iterations | 1500 | 20 (each time step) |
| Item | Volute | Impeller | Vaned Diffuser | Inlet Pipe | Outlet Pipe | Chamber |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mesh number (×106) | 2.21 | 1.92 | 1.98 | 0.62 | 0.52 | 0.98 |
| Minimum mesh quality | 0.4 | 0.64 | 0.66 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.7 |
| Items | Q (m3/s) | n (r/min) | M (N·m) | H (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Experimental | 0.101 | 699.3 | 0.019 | 7.8 |
| Simulation | 0.099 | 687.6 | 0.070 | 7.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pang, Q.; Zhang, D.; Yang, G.; Shen, X.; Pan, Q.; Geng, L.; Lu, Q. A Study on Energy Loss and Transient Flow Characteristics of a Large Volute Centrifugal Pump During Power-Off Process Under Cavitation Conditions. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 1973. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13101973
Pang Q, Zhang D, Yang G, Shen X, Pan Q, Geng L, Lu Q. A Study on Energy Loss and Transient Flow Characteristics of a Large Volute Centrifugal Pump During Power-Off Process Under Cavitation Conditions. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(10):1973. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13101973
Chicago/Turabian StylePang, Qingzhao, Desheng Zhang, Gang Yang, Xi Shen, Qiang Pan, Linlin Geng, and Qinghui Lu. 2025. "A Study on Energy Loss and Transient Flow Characteristics of a Large Volute Centrifugal Pump During Power-Off Process Under Cavitation Conditions" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 10: 1973. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13101973
APA StylePang, Q., Zhang, D., Yang, G., Shen, X., Pan, Q., Geng, L., & Lu, Q. (2025). A Study on Energy Loss and Transient Flow Characteristics of a Large Volute Centrifugal Pump During Power-Off Process Under Cavitation Conditions. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(10), 1973. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13101973








