LSTM-Based Predefined-Time Model Predictive Tracking Control for Unmanned Surface Vehicles with Disturbance and Actuator Faults
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- A novel model predictive optimization control framework has been developed by incorporating contraction constraints derived from a predefined-time Lyapunov function into the optimization problem. This formulation ensures that the resulting control inputs guarantee predefined-time convergence of tracking errors while substantially enhancing the control performance of MPC.
- (2)
- Leveraging the inherent capability of LSTM neural networks to model temporal dependencies in sequential data, oceanic disturbances can be accurately forecasted. Integrating these predictions into the control strategy substantially improves system robustness, enabling reliable operation in highly dynamic marine environments.
- (3)
- By integrating a predefined-time fault observer into the model predictive control architecture, precise fault information can be ascertained within a predefined-time interval. This strategic incorporation of temporal fault observation enhances the system’s transient performance while ensuring robust fault-tolerant capabilities, thereby extending operational viability across a broader spectrum of fault scenarios.
2. Problem Statement
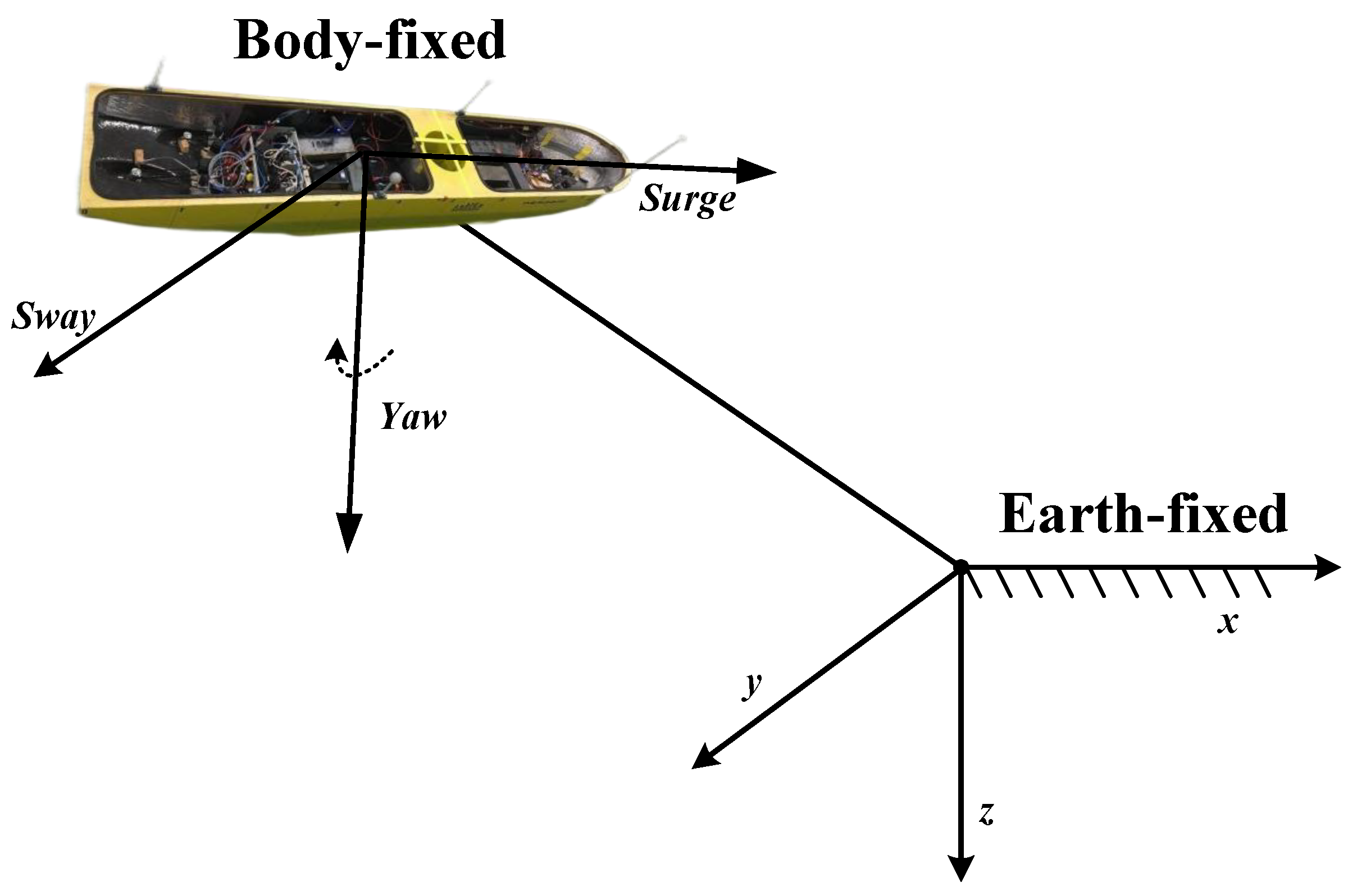
2.1. USVs Model
2.2. The Fault Model of USVs
2.3. Control Objective
3. Design of the Auxiliary Control System
3.1. LSTM Network
3.2. Predefined-Time Fault Observer
4. Main Results
5. Predefined-Time Model Predictive Control for USVs
5.1. Design of the Optimization Problem
5.2. Stability and Feasibility Analysis for the PTMPC
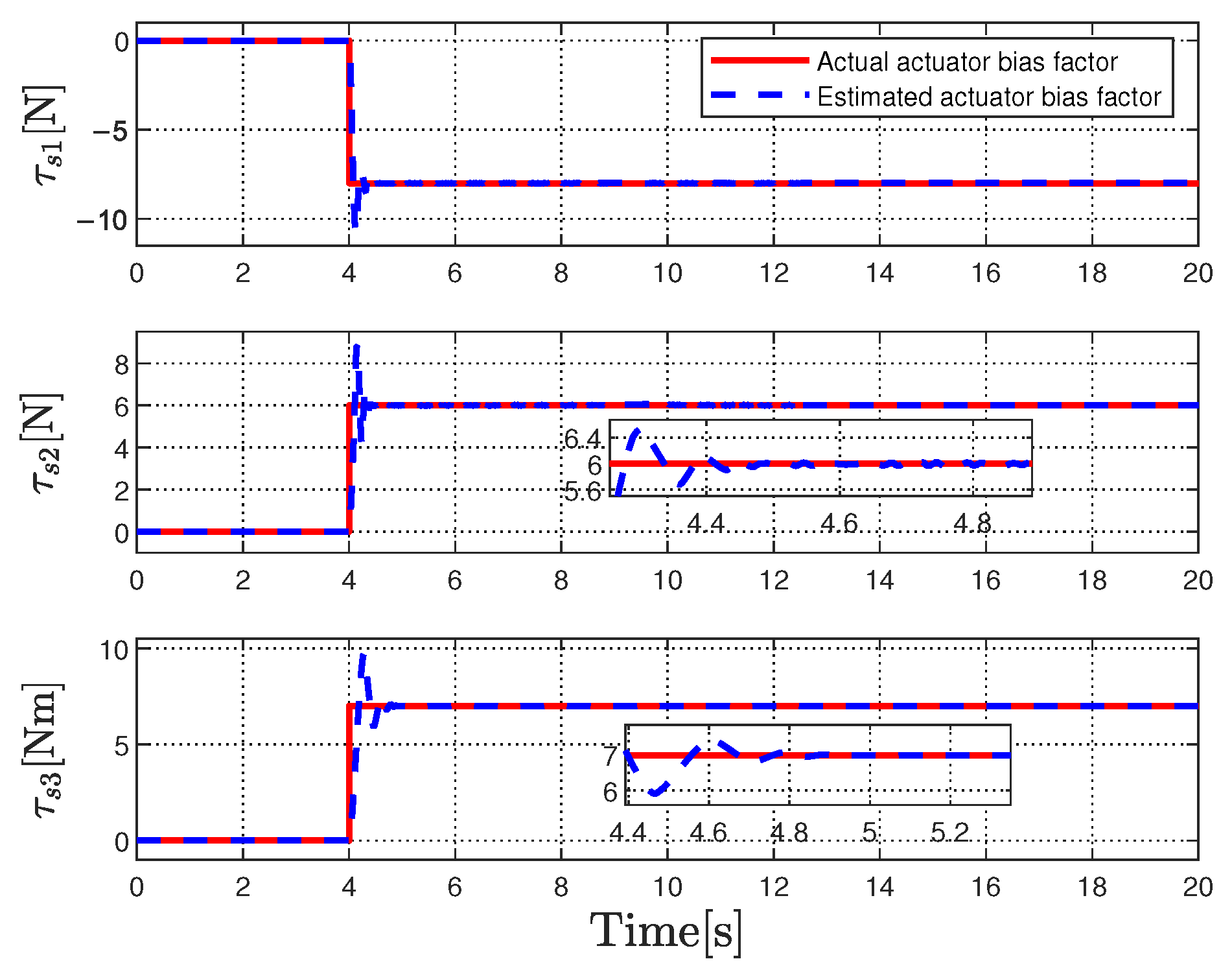
6. Simulation Results
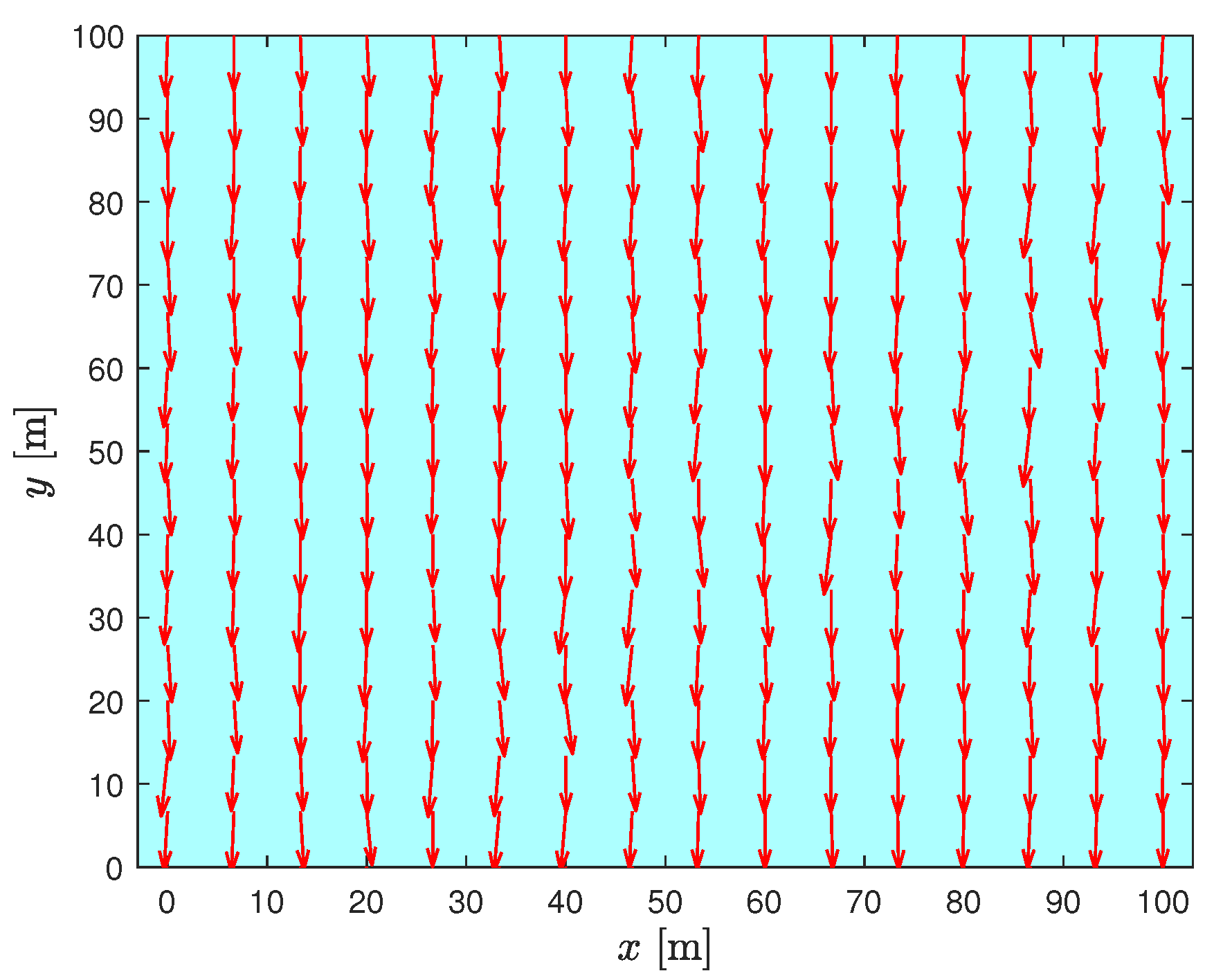
6.1. System Parameter Selection
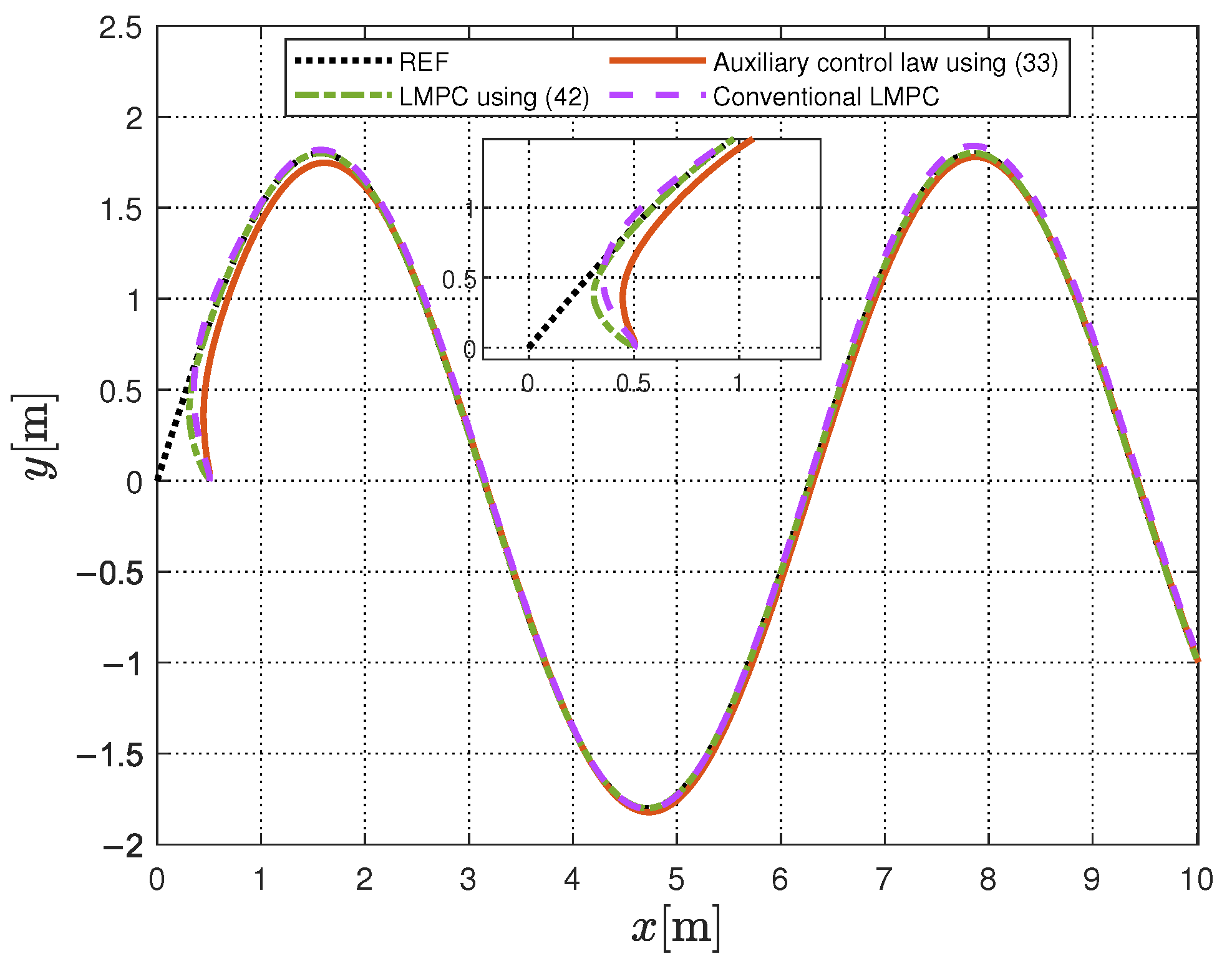
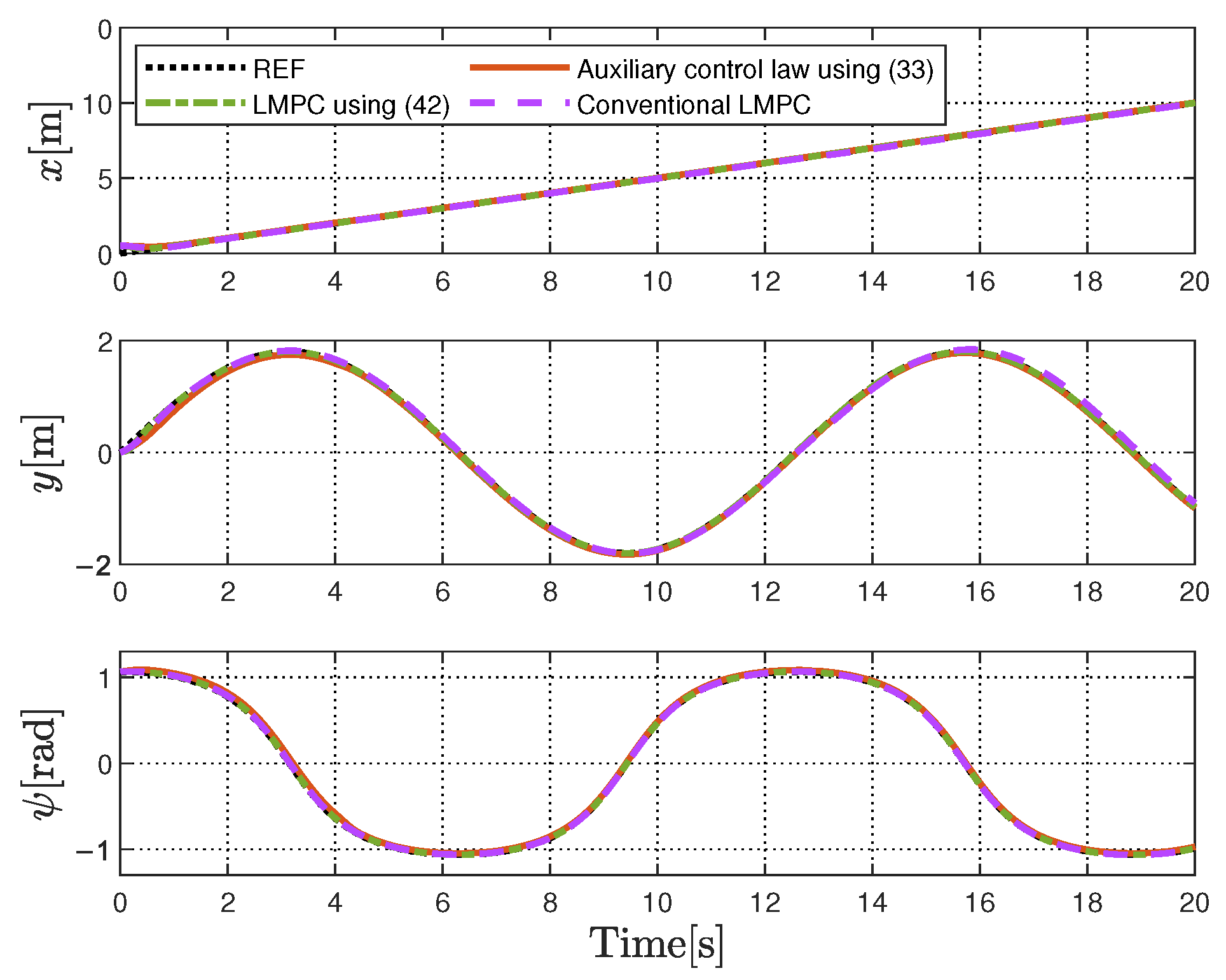
6.2. Tracking Performance Validation
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wei, H.; Shi, Y. MPC-based Motion Planning and Control Enables Smarter and Safer Autonomous Marine Vehicles: Perspectives and a Tutorial Survey. IEEE CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2023, 10, 8–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, D.; Han, Q.L. An Overview of Recent Advances in Coordinated Control of Multiple Autonomous Surface Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2021, 17, 732–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, L.Y.; Zhang, H.; Guo, G.; Li, H. Quantized Sliding Mode Control of Unmanned Marine Vehicles: Various Thruster Faults Tolerated With a Unified Model. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2021, 51, 2012–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tee, K.; Ge, S. Control of fully actuated ocean surface vessels using a class of feedforward approximators. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2006, 14, 750–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguiar, A.P.; Hespanha, J.P. Trajectory-Tracking and Path-Following of Underactuated Autonomous Vehicles With Parametric Modeling Uncertainty. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2007, 52, 1362–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, L.Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, T.S.; Lin, B.; Chen, C.L.P. Fault Tolerant Control for Dynamic Positioning of Unmanned Marine Vehicles Based on T-S Fuzzy Model with Unknown Membership Functions. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2021, 70, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Li, Y.; Lv, M.; Tong, S. Adaptive Backstepping Control for Underactuated 6-DoF USV with Uncertain Dynamics. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 2024, 9, 7476–7484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Park, J.H.; Zhang, B.; Song, X. Event-Triggered Adaptive Practical Fixed-Time Trajectory Tracking Control for Unmanned Surface Vehicle. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2021, 68, 436–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Wang, X.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, H.T.; Zhao, F.; Zhu, L.; He, Y. Adaptive Optimal Surrounding Control of Multiple Unmanned Surface Vessels via Actor-Critic Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2025, 36, 12173–12186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Ye, Z.; Feng, G.; Li, H. Intelligent Event-Based Fuzzy Dynamic Positioning Control of Nonlinear Unmanned Marine Vehicles Under DoS Attack. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2022, 52, 13486–13499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fossen, T.I. Handbook of Marine Craft Hydrodynamics and Motion Control; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Magni, L.; Raimondo, D.; Scattolini, R. Regional Input-to-State Stability for Nonlinear Model Predictive Control. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2006, 51, 1548–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scokaert, P.; Mayne, D.; Rawlings, J. Suboptimal model predictive control (feasibility implies stability). IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 1999, 44, 648–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Linnemann, A. Toward infinite-horizon optimality in nonlinear model predictive control. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2002, 47, 679–682. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, C.; Shi, Y.; Buckham, B. Trajectory Tracking Control of an Autonomous Underwater Vehicle Using Lyapunov-Based Model Predictive Control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 5796–5805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Shen, C.; Shi, Y. Distributed Lyapunov-Based Model Predictive Formation Tracking Control for Autonomous Underwater Vehicles Subject to Disturbances. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2021, 51, 5198–5208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.; Wang, S. Fault Diagnosis of Air Handling Units in an Auditorium Using Real Operational Labeled Data across Different Operation Modes. J. Comput. Civ. Eng. 2025, 39, 04025065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S. Automated fault diagnosis detection of air handling units using real operational labelled data and transformer-based methods at 24-hour operation hospital. Build. Environ. 2025, 282, 113257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, L.Y.; Liu, Y.P.; Wu, Z.J.; Shen, C. Learning-Based Guidance and Control Codesign for Underactuated Autonomous Surface Vehicles: Theory and Experiment. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2025, 72, 3927–3936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Deng, H.; Wu, J.; Xu, J. A Cooperative Hunting Method for Multi-USVs Based on Trajectory Prediction by OR-LSTM. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2024, 73, 18087–18101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, F.; Guan, C.; Steyskal, F. LOS Guidance for Fuzzy Adaptive Fault-Tolerant Path Following Control of USV With Side-Slip Compensation and Actuator Fault. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2025, 11, 6875–6886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, S.; Zhou, H.; Li, Y. Neural Network Event-Triggered Formation Fault-Tolerant Control for Nonlinear Multiagent Systems With Actuator Faults. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2023, 53, 7571–7582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Liu, M.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, E. Adaptive Fault Estimation for Unmanned Surface Vessels with a Neural Network Observer Approach. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2021, 68, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Sun, L.; Xie, L. Error-Constrained LOS Path Following of a Surface Vessel With Actuator Saturation and Faults. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2018, 48, 1794–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corradini, M.L.; Monteriu, A.; Orlando, G. An Actuator Failure Tolerant Control Scheme for an Underwater Remotely Operated Vehicle. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2011, 19, 1036–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, N.; Wang, D.; Peng, Z.; Liu, L. Observer-Based Finite-Time Control for Distributed Path Maneuvering of Underactuated Unmanned Surface Vehicles With Collision Avoidance and Connectivity Preservation. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2021, 51, 5105–5115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, J.; Hua, C.; Li, J. Saturation-Tolerant Adaptive Fixed-Time Control of Underactuated Surface Vessel With Improved Given Performances. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 2024, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Wang, J.; Cheng, D. Adaptive finite-time control of nonlinear systems with parametric uncertainty. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2006, 51, 858–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, H.; Li, T.; Xu, K. Adaptive Neural Fixed-Time Control for Uncertain Nonlinear Systems. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2024, 71, 637–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becerra, H.M.; Vázquez, C.R.; Arechavaleta, G.; Delfin, J. Predefined-Time Convergence Control for High-Order Integrator Systems Using Time Base Generators. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2018, 26, 1866–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Han, T.; Xiao, B.; Yan, H. Predefined-Time Bipartite Time-Varying Formation Tracking Control of Networked Autonomous Surface Vehicles via Hierarchical Control Approach. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2024, 73, 9536–9545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fossen, T.I. Marine Control Systems: Guidance, Navigation, and Control of Ships, Rigs, and Underwater Vehicles; Marine Cybernetics: Trondheim, Norway, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Hao, L.Y.; Che, W.W. Bi-LSTM-Based Resilient Data-Driven Integral Sliding Mode Control for UMVs Under Hybrid Attacks. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2025, 26, 6702–6714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Huang, Z.; Diao, R.; Zhang, J.; Hou, B.; Wu, C.; Sun, F.; Lan, T. A Machine Learning-Based SVG Parameter Identification Framework Using Hardware-in-the-Loop Testbed. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2024, 39, 6849–6860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Hu, C.; Ou, T.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, Y. Intelligent GRU-RIC Position-Loop Feedforward Compensation Control Method With Application to an Ultraprecision Motion Stage. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2024, 20, 5609–5621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Xu, J. A New Adaptive Predefined Time Sliding Mode Control for Nonlinear Systems. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2024, 71, 2094–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skjetne, R.; Fossen, T.I.; Kokotović, P.V. Adaptive maneuvering, with experiments, for a model ship in a marine control laboratory. Automatica 2005, 41, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, Y.; Hao, L.-Y.; Atajan, H. LSTM-Based Predefined-Time Model Predictive Tracking Control for Unmanned Surface Vehicles with Disturbance and Actuator Faults. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 1914. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13101914
Zhou Y, Hao L-Y, Atajan H. LSTM-Based Predefined-Time Model Predictive Tracking Control for Unmanned Surface Vehicles with Disturbance and Actuator Faults. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(10):1914. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13101914
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Yuxing, Li-Ying Hao, and Hudayberenov Atajan. 2025. "LSTM-Based Predefined-Time Model Predictive Tracking Control for Unmanned Surface Vehicles with Disturbance and Actuator Faults" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 10: 1914. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13101914
APA StyleZhou, Y., Hao, L.-Y., & Atajan, H. (2025). LSTM-Based Predefined-Time Model Predictive Tracking Control for Unmanned Surface Vehicles with Disturbance and Actuator Faults. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(10), 1914. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13101914






