Unsupervised Learning-Based Optical–Acoustic Fusion Interest Point Detector for AUV Near-Field Exploration of Hydrothermal Areas
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- Fuse module incorporating the FPN into UnsuperPoint for better sensor fusion;
- (2)
- Depth module designed to ensure a uniform distribution of interest points in depth for better localization accuracy;
- (3)
- Unsupervised training strategy including an auto-encoder framework, a ground truth depth generation framework, and a mutually supervised framework designed to enable unsupervised training of the new modules;
- (4)
- Non-rigid feature filter with which the camera data encoder filters out features from non-rigid structural objects, mitigating the interference caused by the smoke emitted from active vents in hydrothermal areas;
2. Related Works
2.1. IPD for Underwater SLAM
2.2. Deep Learning Based IPD
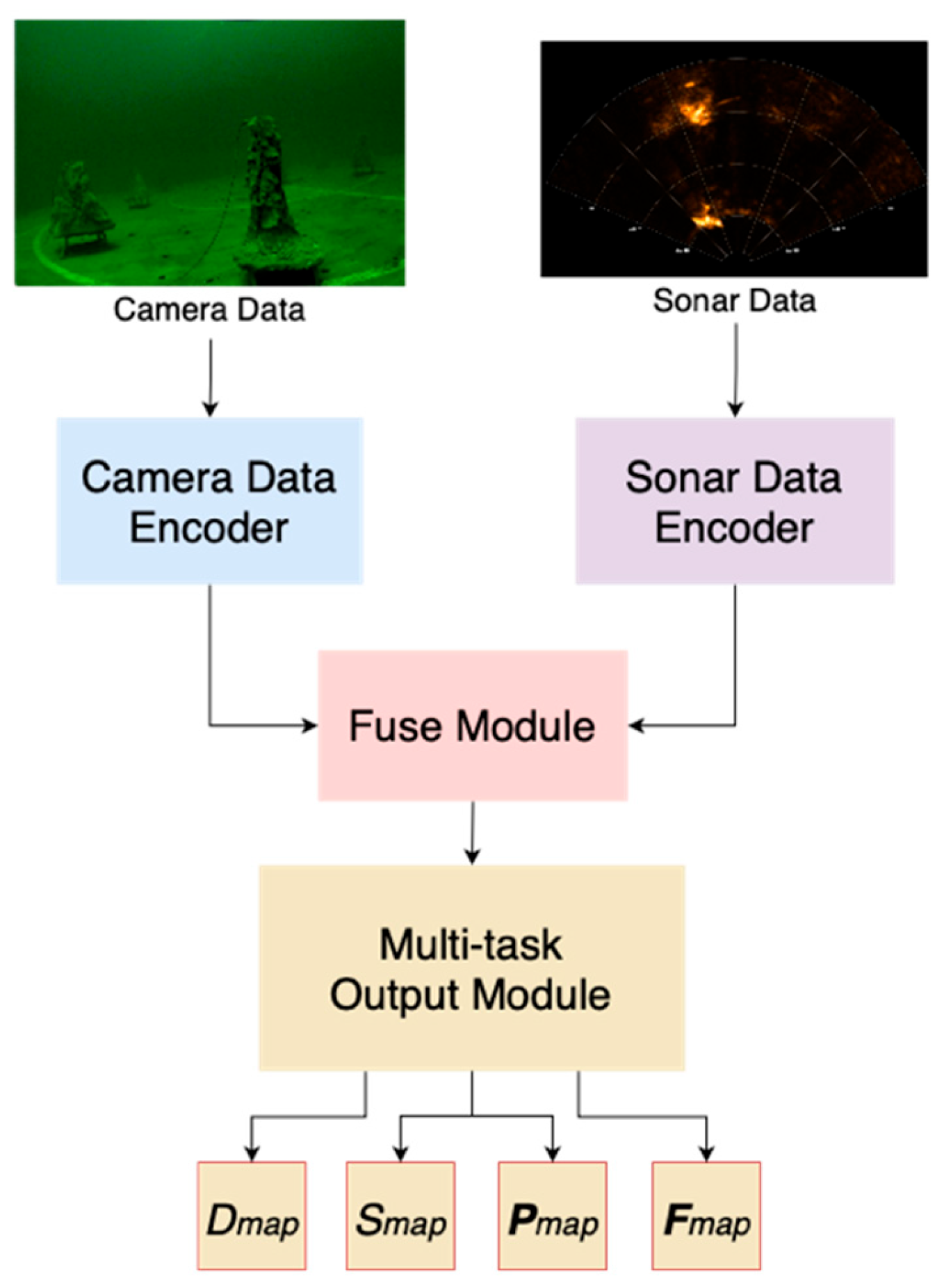
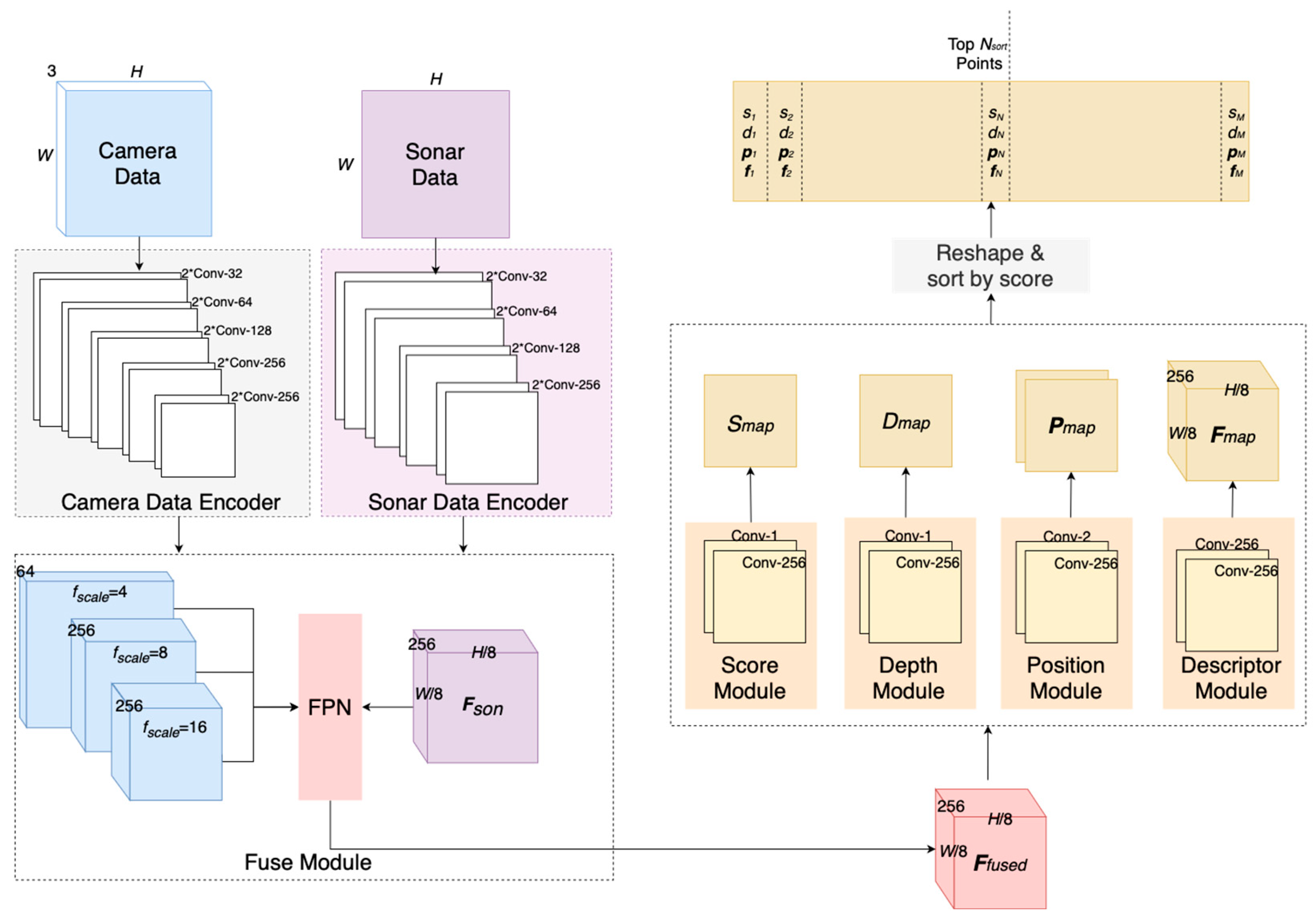
3. Network Architecture
3.1. Data Encoders
3.1.1. Backbone
3.1.2. Camera Data Encoder
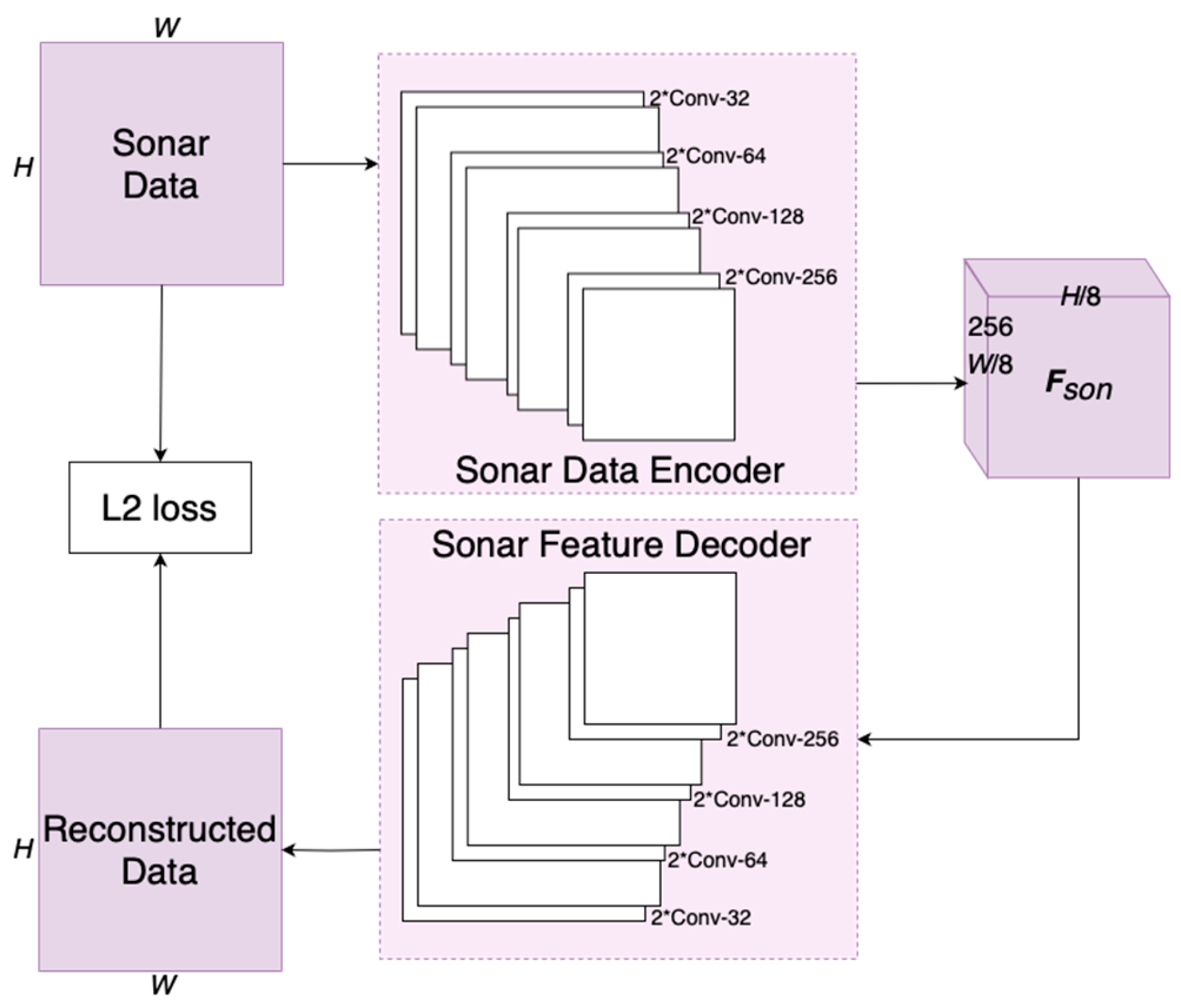
3.1.3. Sonar Data Encoder
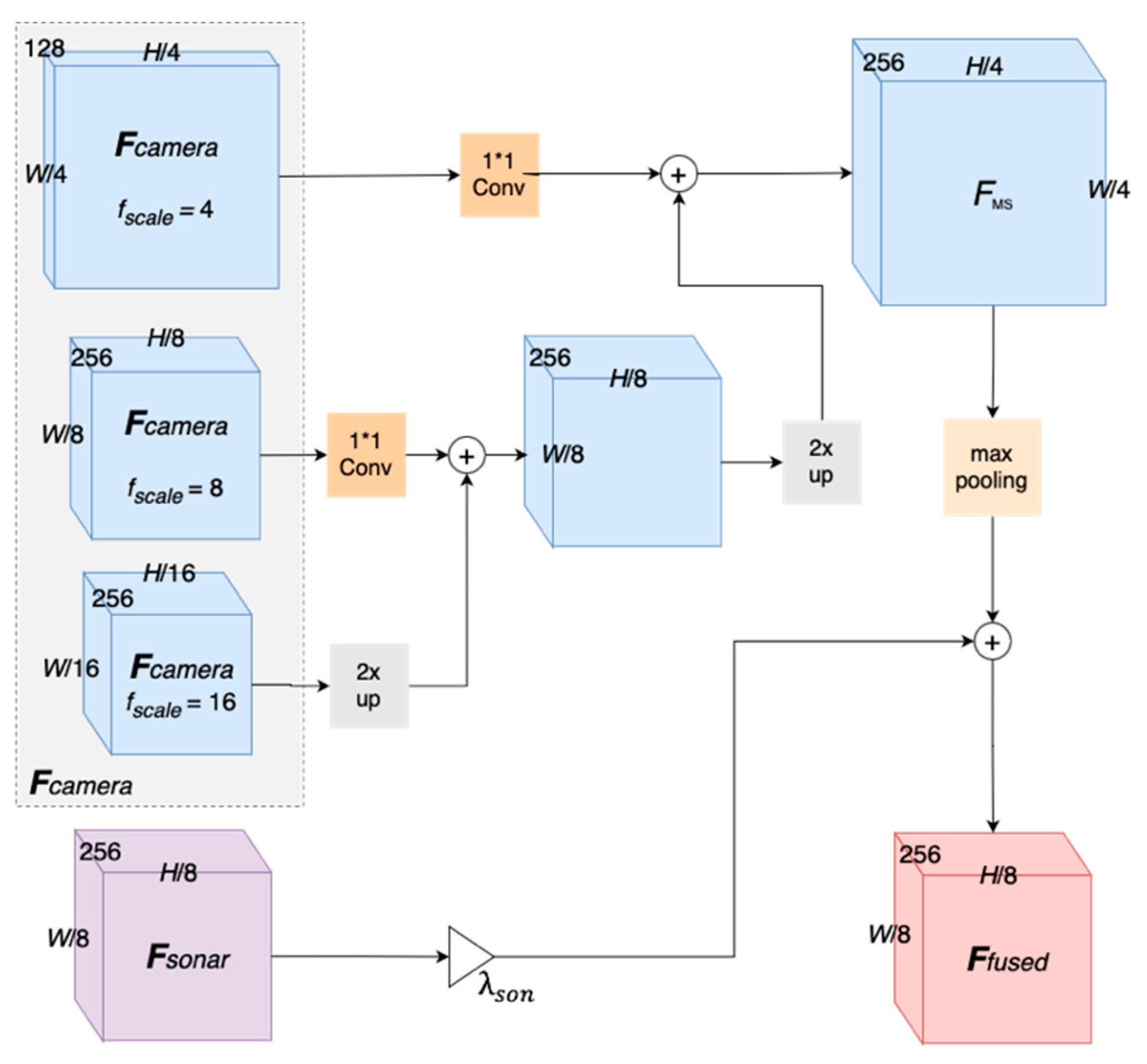
3.2. Fuse Module
3.3. Position Module
3.4. Depth Module
3.5. Score Module
3.6. Descriptor Module
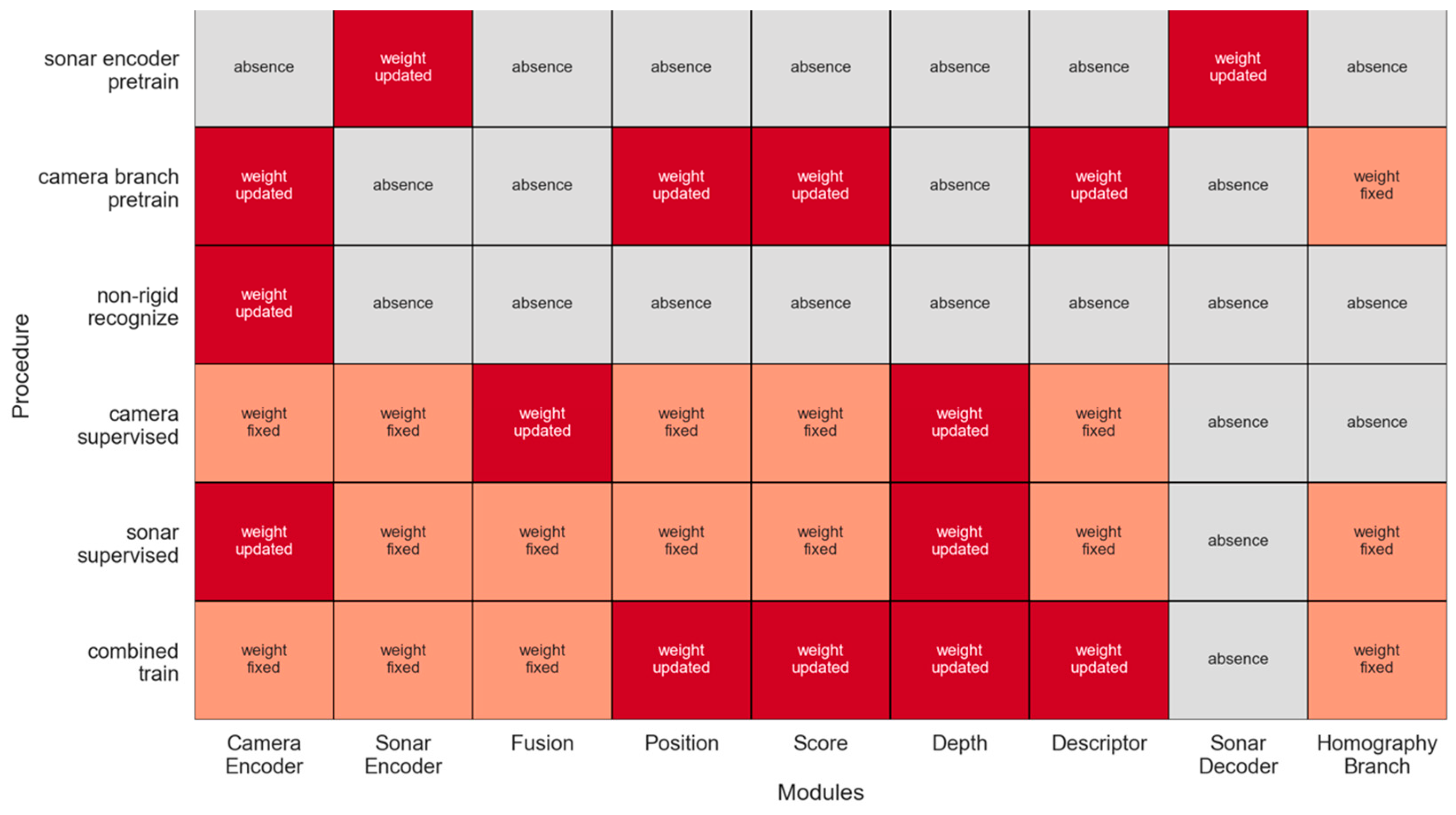
4. Self-Supervised Framework
4.1. Ground Truth Generation
4.1.1. Homography-Based Self-Supervised Framework
4.1.2. Depth Ground-Truth Generation
4.2. Sonar Encoder Pertain Based on Auto-Encoder
4.3. Non-Rigid Feature Removal Training Framework
4.4. Mutually Supervised Framework Based on Sensor Differences
4.4.1. Camera-Supervised Framework
4.4.2. Sonar-Supervised Framework
5. Loss Functions
6. Experiments and Results
6.1. Data Collection
6.2. Datasets
6.3. Training Details
- (1)
- Transfer Learning for Camera Data Encoder in Underwater Environments:
- (2)
- Training for Non-Rigid Interest Points Removal:
- (3)
- Pretraining for Sonar Data Encoder:
- (4)
- Mutually Supervised Training:
- (5)
- Final Training for the Entire Model:
6.4. Results
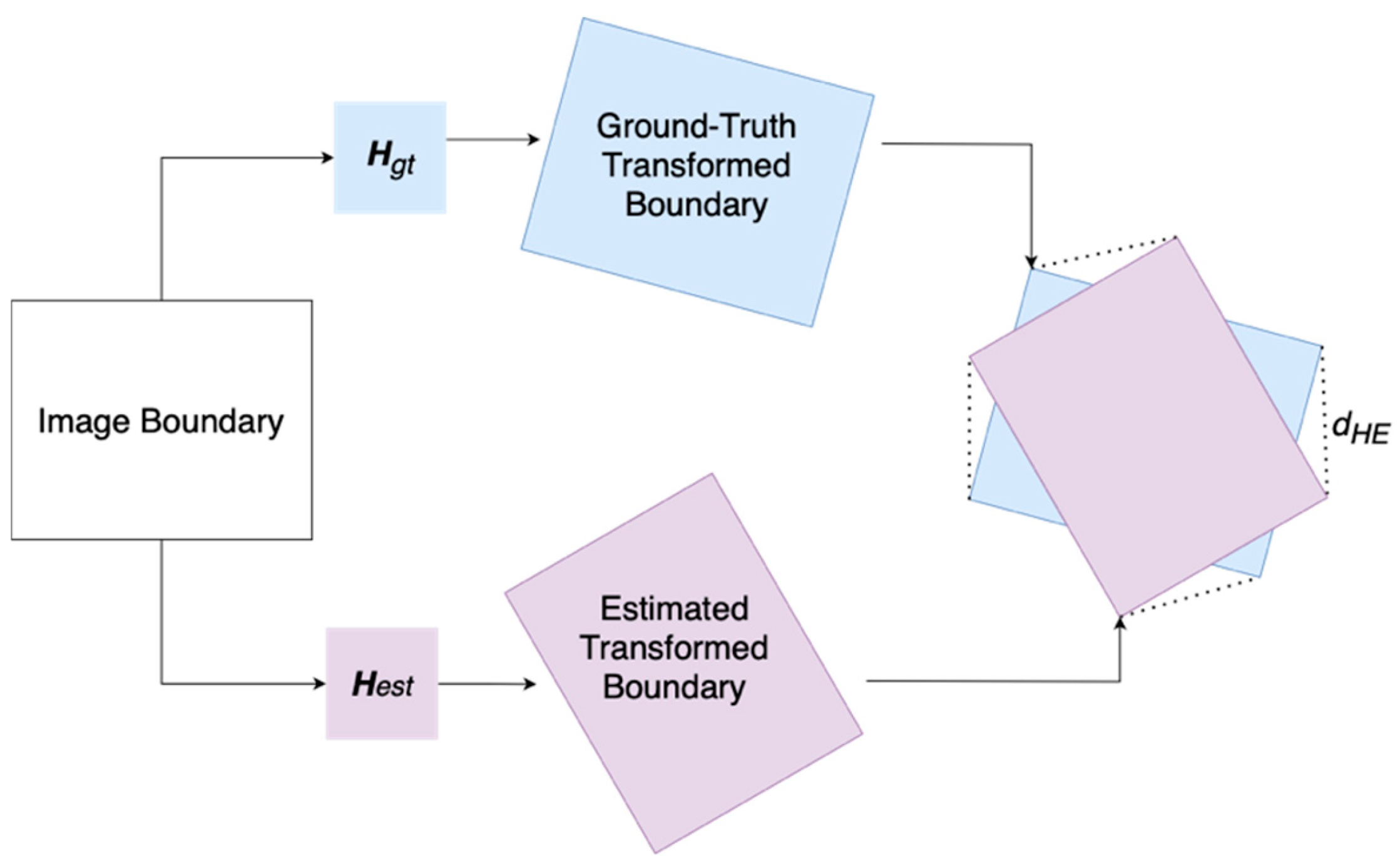
6.4.1. Metix
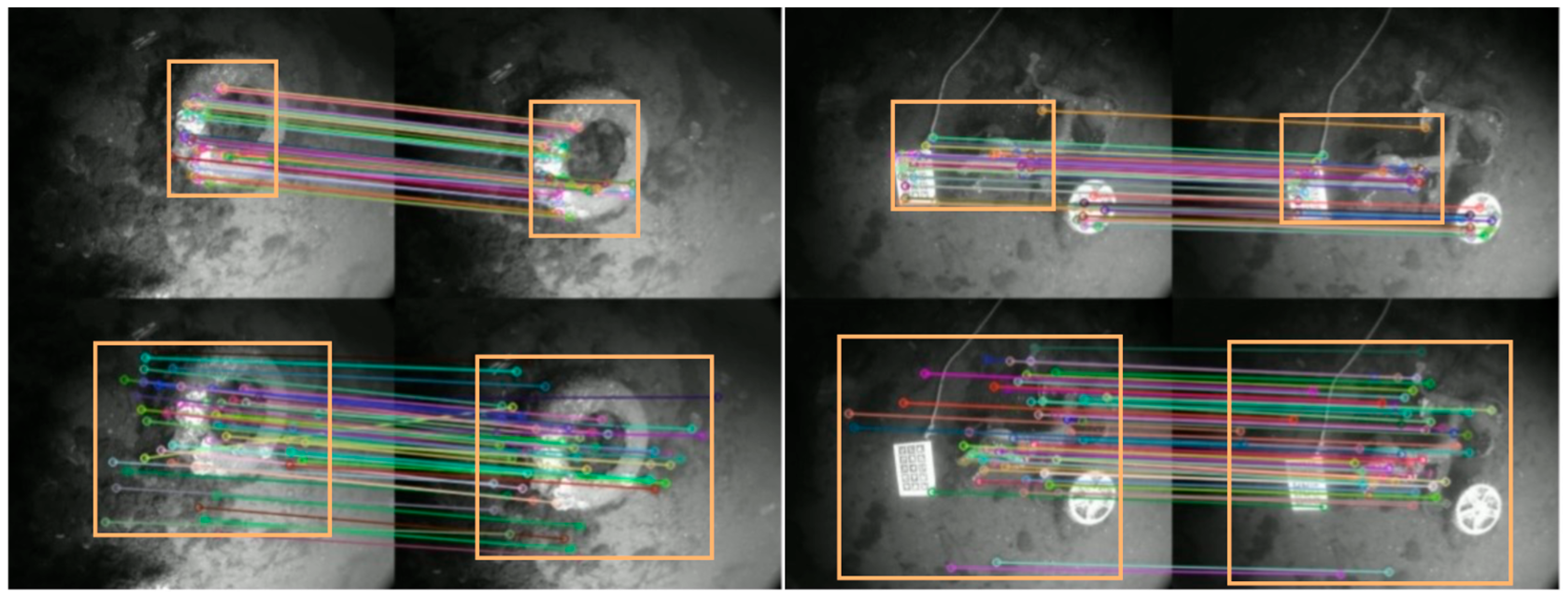
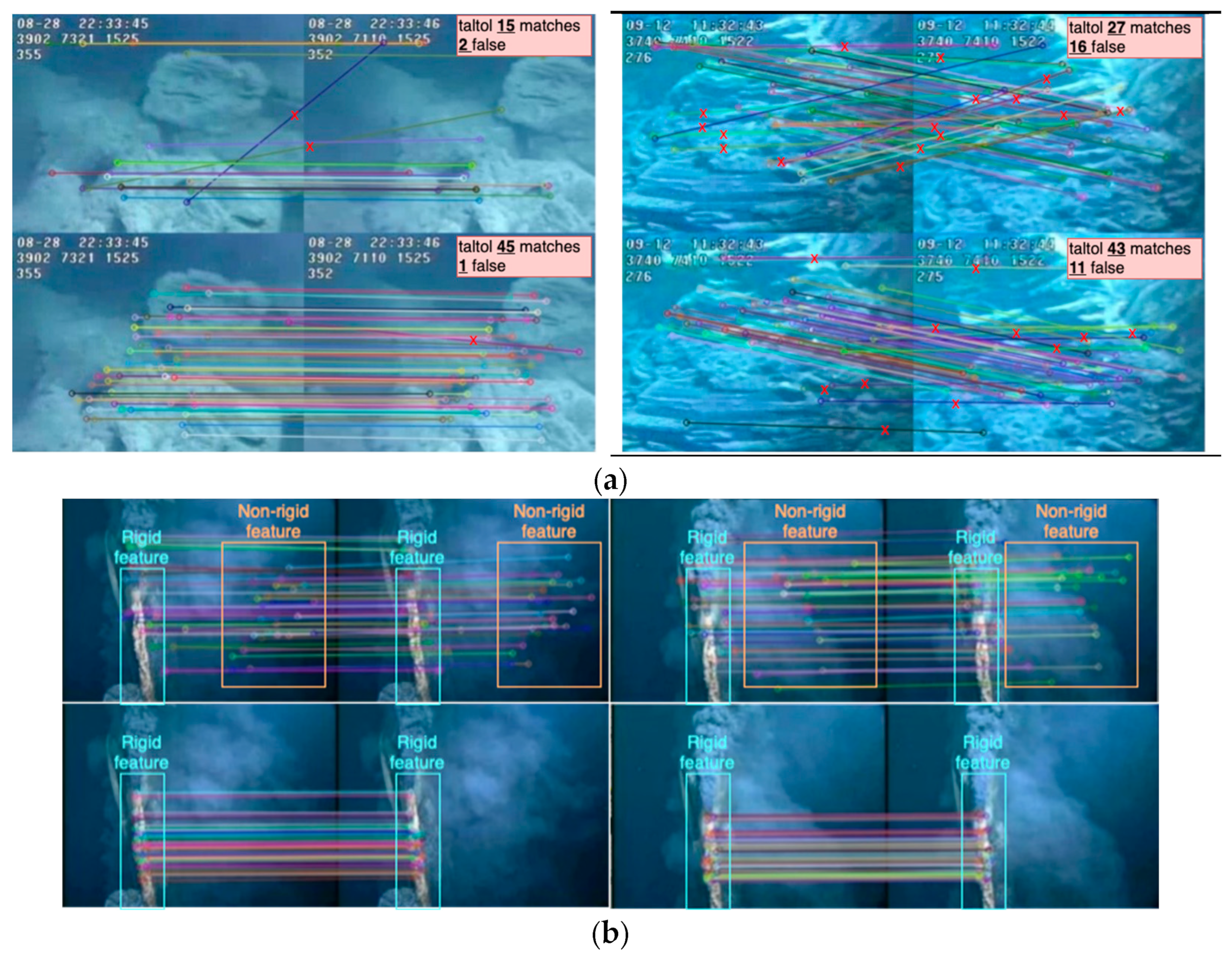
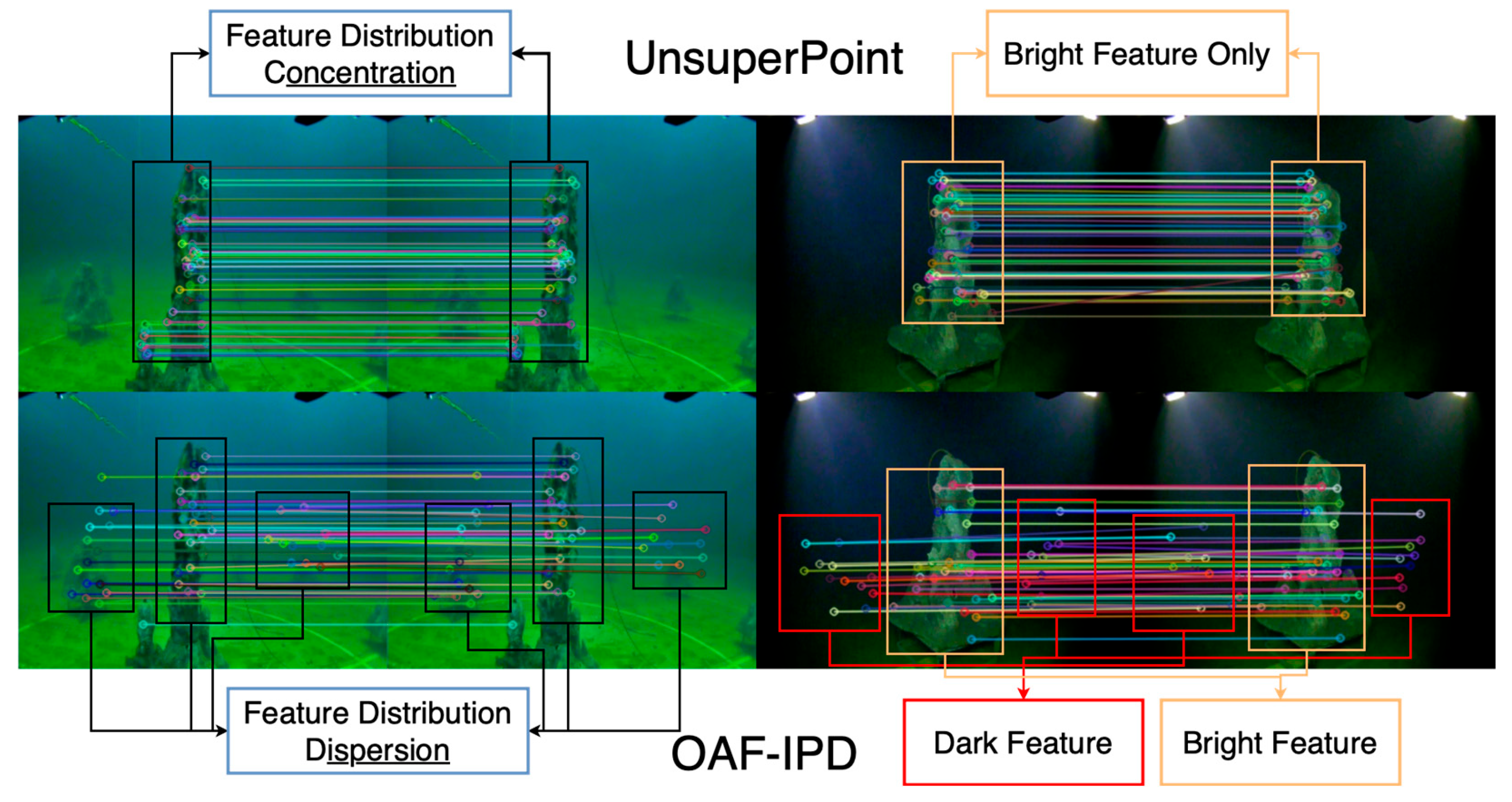
6.4.2. Detector Evaluation
6.4.3. Descriptor Evaluation
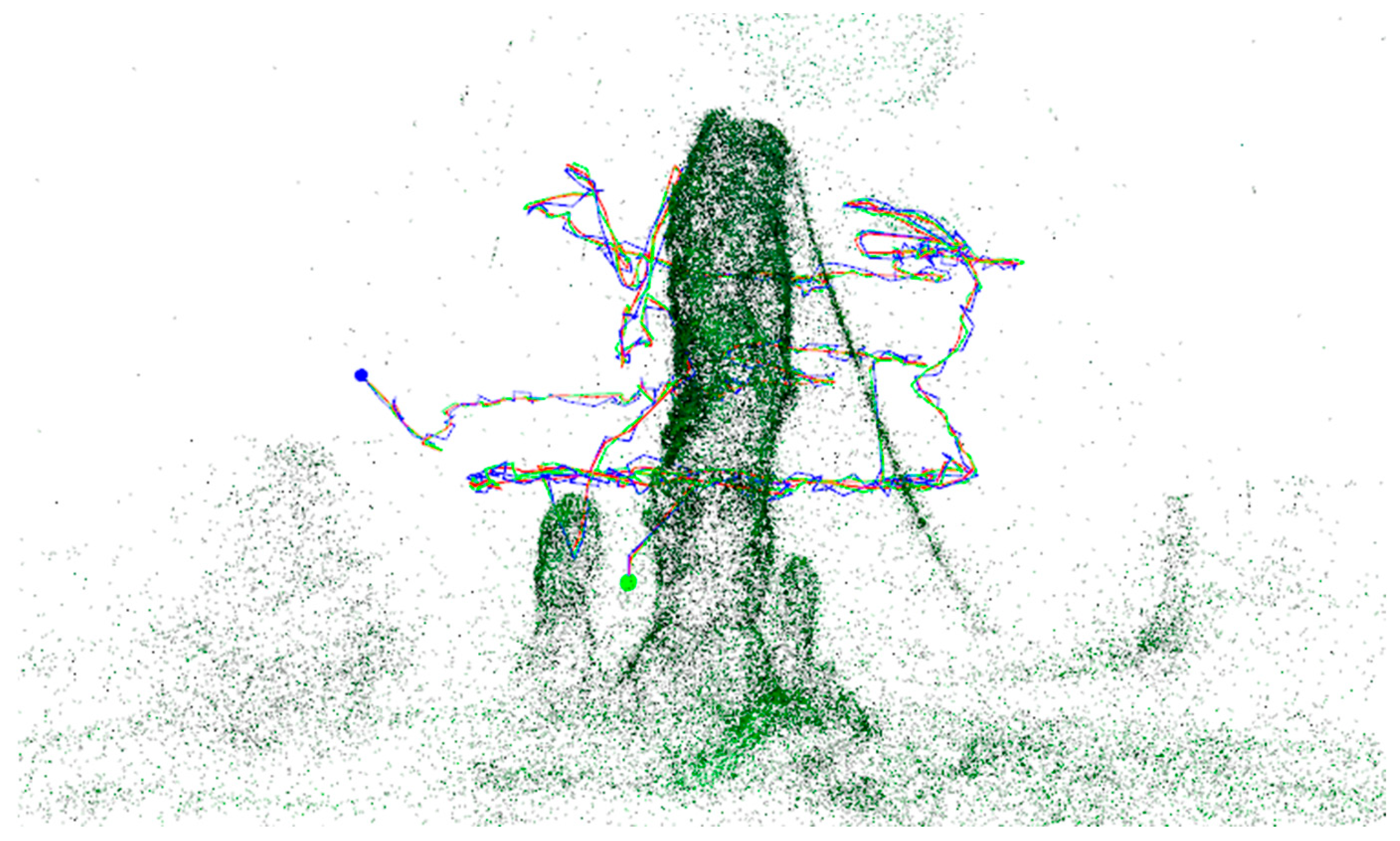
6.4.4. Localization Accuracy Evaluation
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Humphris, S.E.; Tivey, M.K.; Tivey, M.A. The Trans-Atlantic Geotraverse hydrothermal field: A hydrothermal system on an active detachment fault. Deep Sea Res. Part II 2015, 121, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Scott, S.D. Possible contribution of a metal-rich magmatic fluid to a sea-floor hydrothermal system. Nature 1996, 383, 420–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Li, Y.; Wang, R.; Cong, Z.; Gong, Y. AUV robust bathymetric simultaneous localization and mapping. Ocean Eng. 2018, 166, 336–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloesch, M.; Omari, S.; Hutter, M.; Siegwart, R. Robust visual inertial odometry using a direct EKF-based approach. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Hamburg, Germany, 28 September–2 October 2015; pp. 298–304. [Google Scholar]
- Germain, H.; Lepetit, V.; Bourmaud, G. Neural Reprojection Error: Merging feature learning and camera pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Sarlin, P.-E.; Unagar, A.; Larsson, M.; Germain, H.; Toft, C.; Larsson, V.; Pollefeys, M.; Lepetit, V.; Hammarstrand, L.; Kahl, F.; et al. Back to the Feature: Learning robust camera localization from pixels to pose. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Q.; Sattler, T.; Leal-Taixé, L. Patch2Pix: Epipolar-guided pixel-level correspondences. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Quattrini Li, A.; Coskun, A.; Doherty, S.M.; Ghasemlou, S.; Jagtap, A.S.; Modasshir, M.; Rahman, S.; Singh, A.; Xanthidis, M.; O’Kane, J.M.; et al. Experimental comparison of open source vision-based state estimation algorithms. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Experimental Robotics (ISER), Tokyo, Japan, 3–8 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Burguera, A.; Bonin-Font, F.; Font, E.G.; Torres, A.M. Combining deep learning and robust estimation for outlier-resilient underwater visual graph SLAM. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, B.; Rahman, S.; Kalaitzakis, M.; Cain, B.; Johnson, J.; Xanthidis, M.; Karapetyan, N.; Hernandez, A.; Li, A.Q.; Vitzilaios, N.; et al. Experimental comparison of open source visual-inertial based state estimation algorithms in the underwater domain. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Macau, China, 4–8 November 2019; pp. 7227–7233. [Google Scholar]
- Joe, H.; Cho, H.; Sung, M.; Kim, J.; Yu, S.-C. Sensor fusion of two sonar devices for underwater 3D mapping with an AUV. Auton. Robot. 2021, 45, 543–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Zhu, S.; Liang, Y.; Mu, Z.; Song, W. Visual-pressure fusion for underwater robot localization with online initialization. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 6, 8426–8433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, S.; Quattrini Li, A.; Rekleitis, I. SVIn2: A multi-sensor fusion-based underwater SLAM system. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2022, 41, 1022–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, D.G. Distinctive image features from Scale-Invariant keypoints. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2004, 60, 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bay, H.; Ess, A.; Tuytelaars, T.; Van Gool, L. Speeded-Up robust features (SURF). Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2008, 110, 346–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rublee, E.; Rabaud, V.; Konolige, K.; Bradski, G.R. ORB: An efficient alternative to SIFT or SURF. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Barcelona, Spain, 6–13 November 2011; pp. 2564–2571. [Google Scholar]
- Mur-Artal, R.; Montiel, J.M.M.; Tardos, J.D. ORB-SLAM: A versatile and accurate monocular SLAM system. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2015, 31, 1147–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, K.M.; Trulls, E.; Lepetit, V.; Fua, P. LIFT: Learned invariant feature transform. In Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; pp. 467–483. [Google Scholar]
- DeTone, D.; Malisiewicz, T.; Rabinovich, A. Superpoint: Self-supervised interest point detection and description. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 224–236. [Google Scholar]
- Christiansen, P.H.; Kragh, M.F.; Brodskiy, Y.; Karstoft, H. UnsuperPoint: End-to-end Unsupervised Interest Point Detector and Descriptor. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.-Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature Pyramid Networks for Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, A.; Eustice, R. Pose-graph visual SLAM with geometric model selection for autonomous underwater ship hull inspection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), St. Louis, MO, USA, 11–15 October 2009; pp. 1559–1565. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, J.; Xia, Q. An Overview of Underwater Vision Enhancement: From Traditional Methods to Recent Deep Learning. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaderberg, M.; Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A.; Kavukcuoglu, K. Spatial transformer networks. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), Montreal, QC, Canada, 7–12 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ioffe, S.; Szegedy, C. Batch Normalization: Accelerating Deep Network Training by Reducing Internal Covariate Shift. In Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), Lille, France, 6–11 July 2015; pp. 448–456. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Delving deep into rectifiers: Surpassing human-level performance on imagenet classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 13–16 December 2015; pp. 1026–1034. [Google Scholar]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully Convolutional Networks for Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Schonberger, J.L.; Frahm, J.-M. Structure-from-Motion Revisited. COLMAP. Available online: https://colmap.github.io (accessed on 18 July 2023).
- Lindenberger, P.; Sarlin, P.-E.; Larsson, V.; Pollefeys, M. Pixel-Perfect Structure-from-Motion with Featuremetric Refinement. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 5987–5997. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrera, M.; Creuze, V.; Moras, J.; Trouvé-Peloux, P. AQUALOC: An underwater dataset for visual–inertial–pressure localization. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2019, 38, 1549–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NOAA Ocean Exploration. Available online: https://oceanexplorer.noaa.gov (accessed on 18 July 2023).
- PMEL Earth-Ocean Interactions Program. Available online: https://www.pmel.noaa.gov/eoi/chemocean.html (accessed on 18 July 2023).
- InterRidge Vents Database. Available online: https://vents-data.interridge.org (accessed on 18 July 2023).
- Paszke, A.; Gross, S.; Chintala, S.; Chanan, G. Pytorch, version 0.3; The Linux Foundation: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), San Diego, CA, USA, 7–9 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- DeTone, D. Superpoint. Available online: https://github.com/MagicLeapResearch/SuperPointPretrainedNetwork (accessed on 18 July 2023).
- Ono, Y. Lf-net. Available online: https://github.com/vcg-uvic/lf-net-release (accessed on 18 July 2023).
- Schmid, C.; Mohr, R.; Bauckhage, C. Evaluation of interest point detectors. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2000, 37, 151–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischler, M.A.; Bolles, R.C. Random sample consensus: A paradigm for model fitting with applications to image analysis and automated cartography. Commun. ACM 1981, 24, 381–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, C.; Elvira, R.; Rodriguez, J.J.G.; Montiel, J.M.M.; Tardos, J.D. ORB-SLAM3: An accurate open-source library for visual, visual–inertial, and multimap SLAM. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2021, 37, 1874–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
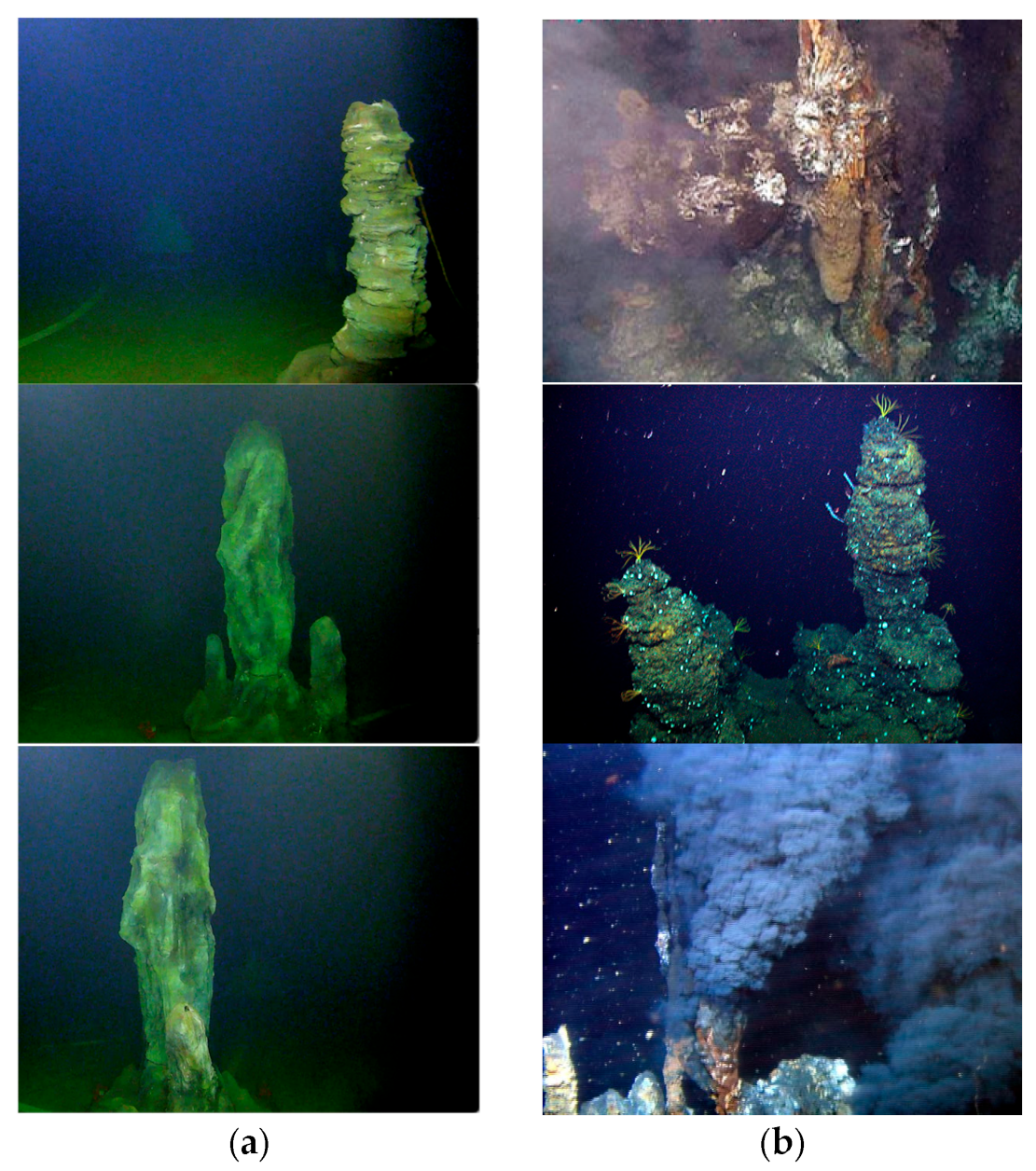


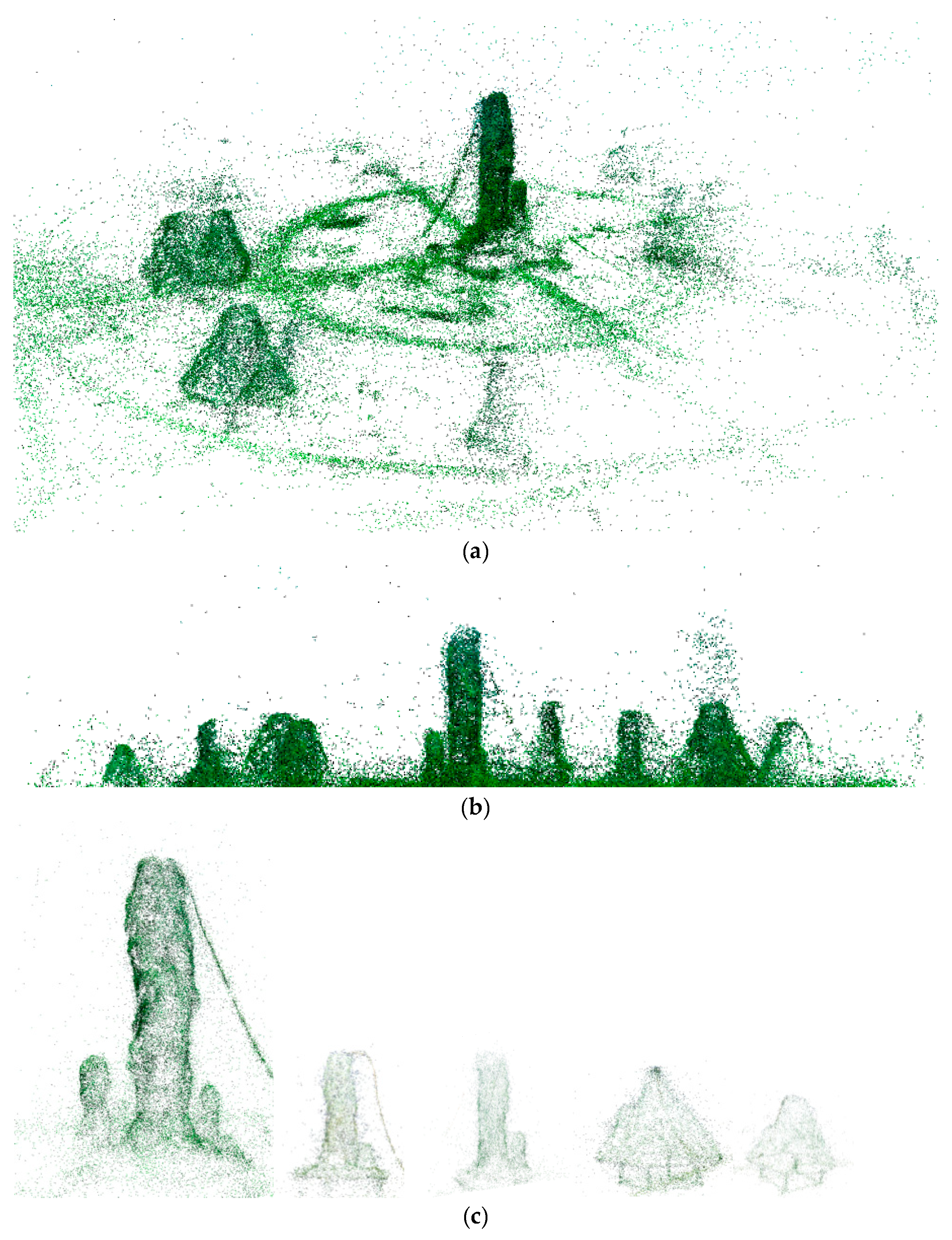




| Scene | Sensor Type | Number of Sequences | Number of Data Units |
|---|---|---|---|
| Swimming pool | Camera | 3 | 536 |
| Harbor | Camera | 3 | 6225 |
| Archaeological | Camera | 3 | 3470 |
| Hydrothermal area | Camera | 9 | 729 |
| Experimental pool | camera and sonar | 10 | 15,185 |
| Total | - | 28 | 19,920 |
| Datasets | Data Composition | Data Source | Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Underwater images dataset | Image sequences | AQUALOC Hydrothermal area data | Camera encoder pretrain IPD evaluation |
| Sonar dataset | Sonar data | Pool experiment | Sonar encoder pretrain |
| Non-rigid feature dataset | Image sequences | Hydrothermal area data | Non-rigid feature removal training framework |
| OA combined dataset | Camera–sonar combined data | Pool experiment | Mutually supervised training SLAM evaluation |
| Detectors | Repeatability | Localization error | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 240 × 320 | 480 × 640 | 240 × 320 | 480 × 640 | |
| ORB | 0.527 | 0.543 | 1.438 | 1.434 |
| SURF | 0.477 | 0.454 | 1.132 | 1.259 |
| SIFT | 0.455 | 0.429 | 0.836 | 1.03 |
| SuperPoint | 0.644 | 0.581 | 1.096 | 1.199 |
| UnsuperPoint | 0.637 | 0.613 | 0.829 | 0.983 |
| OAF-IPD (optical only) | 0.640 | 0.603 | 0.826 | 0.974 |
| Detectors | Repeatability | Localization Error | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 240 × 320 | 480 × 640 | 240 × 320 | 480 × 640 | |
| ORB | 0.510 | 0.525 | 1.468 | 1.464 |
| SURF | 0.460 | 0.435 | 1.162 | 1.289 |
| SIFT | 0.440 | 0.415 | 0.866 | 1.060 |
| SuperPoint | 0.625 | 0.560 | 1.126 | 1.229 |
| UnsuperPoint | 0.620 | 0.595 | 0.859 | 1.013 |
| OAF-IPD | 0.649 | 0.623 | 0.715 | 0.762 |
| Descriptor | 240 × 320 300 Points | 480 × 640 1000 Points | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HE | MS | HE | MS | |||||
| ε = 1 | ε = 3 | ε = 5 | ε = 1 | ε = 3 | ε = 5 | |||
| ORB | 0.142 | 0.456 | 0.562 | 0.227 | 0.281 | 0.602 | 0.700 | 0.223 |
| SURF | 0.404 | 0.712 | 0.747 | 0.276 | 0.435 | 0.735 | 0.801 | 0.221 |
| SIFT | 0.606 | 0.842 | 0.872 | 0.297 | 0.503 | 0.817 | 0.867 | 0.262 |
| SuperPoint | 0.487 | 0.840 | 0.878 | 0.319 | 0.510 | 0.814 | 0.901 | 0.269 |
| UnsuperPoint | 0.530 | 0.839 | 0.907 | 0.402 | 0.483 | 0.820 | 0.904 | 0.376 |
| OAF-IPD (optical only) | 0.557 | 0.854 | 0.918 | 0.412 | 0.509 | 0.853 | 0.900 | 0.392 |
| Descriptor | 240 × 320 300 Points | 480 × 640 1000 Points | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HE | MS | HE | MS | |||||
| ε = 1 | ε = 3 | ε = 5 | ε = 1 | ε = 3 | ε = 5 | |||
| ORB | 0.120 | 0.418 | 0.522 | 0.211 | 0.258 | 0.563 | 0.657 | 0.208 |
| SURF | 0.381 | 0.675 | 0.706 | 0.260 | 0.412 | 0.696 | 0.759 | 0.206 |
| SIFT | 0.433 | 0.704 | 0.831 | 0.281 | 0.481 | 0.778 | 0.825 | 0.247 |
| SuperPoint | 0.465 | 0.802 | 0.837 | 0.303 | 0.487 | 0.775 | 0.859 | 0.255 |
| UnsuperPoint | 0.507 | 0.801 | 0.866 | 0.386 | 0.461 | 0.701 | 0.862 | 0.302 |
| OAF-IPD | 0.562 | 0.859 | 0.923 | 0.417 | 0.512 | 0.857 | 0.911 | 0.397 |
| No. | Length of Trajectory (m) | Number of Frames | Completion Rate (%) | Average Error in the Completed Trial (m) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ORB | OAF-IPD | ORB | OAF-IPD | |||
| 1 | 105 | 1867 | 100 | 100 | 0.18 | 0.15 |
| 2 | 240 | 3421 | 100 | 100 | 0.17 | 0.13 |
| 3 | 327 | 3343 | 100 | 100 | 0.24 | 0.13 |
| 4 | 43 | 633 | 100 | 100 | 0.19 | 0.19 |
| 5 | 363 | 5423 | 100 | 100 | 0.22 | 0.24 |
| 6 | 87 | 1242 | 60 | 100 | 0.94 | 0.37 |
| 7 | 118 | 1747 | 13 | 100 | 1.3 | 0.43 |
| 8 | 148 | 2379 | - | 90 | - | 0.44 |
| 9 | 292 | 3090 | - | 86 | - | 0.45 |
| 10 | 449 | 4453 | - | 93 | - | 0.32 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wan, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y. Unsupervised Learning-Based Optical–Acoustic Fusion Interest Point Detector for AUV Near-Field Exploration of Hydrothermal Areas. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 1406. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12081406
Liu Y, Xu Y, Zhang Z, Wan L, Li J, Zhang Y. Unsupervised Learning-Based Optical–Acoustic Fusion Interest Point Detector for AUV Near-Field Exploration of Hydrothermal Areas. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2024; 12(8):1406. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12081406
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yihui, Yufei Xu, Ziyang Zhang, Lei Wan, Jiyong Li, and Yinghao Zhang. 2024. "Unsupervised Learning-Based Optical–Acoustic Fusion Interest Point Detector for AUV Near-Field Exploration of Hydrothermal Areas" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 12, no. 8: 1406. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12081406
APA StyleLiu, Y., Xu, Y., Zhang, Z., Wan, L., Li, J., & Zhang, Y. (2024). Unsupervised Learning-Based Optical–Acoustic Fusion Interest Point Detector for AUV Near-Field Exploration of Hydrothermal Areas. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 12(8), 1406. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12081406






