The Role of Tide and Wind in Modulating Density Stratification in the Pearl River Estuary during the Dry Season
Abstract
1. Introduction
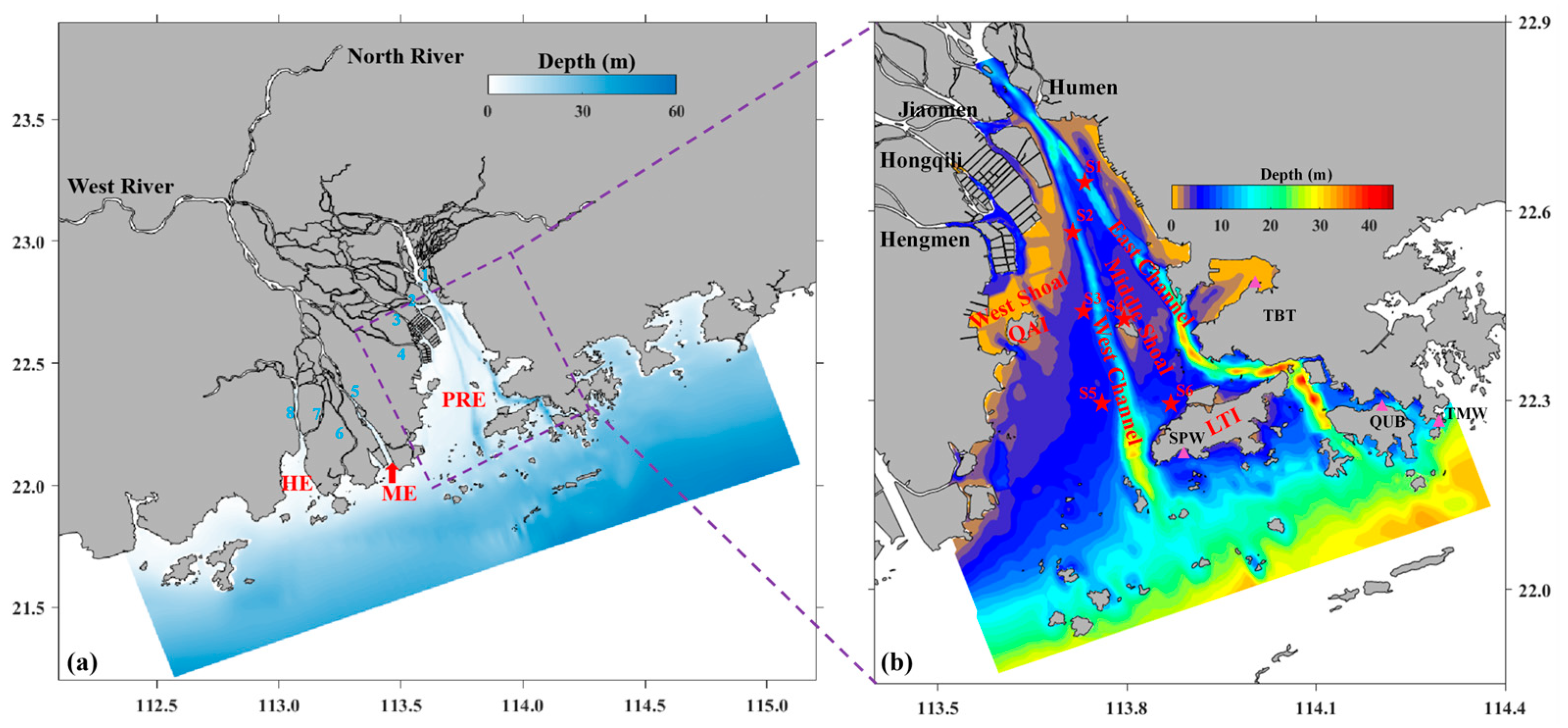
2. Regional Settings
3. Methods
3.1. Numerical Model
3.2. Model Setup
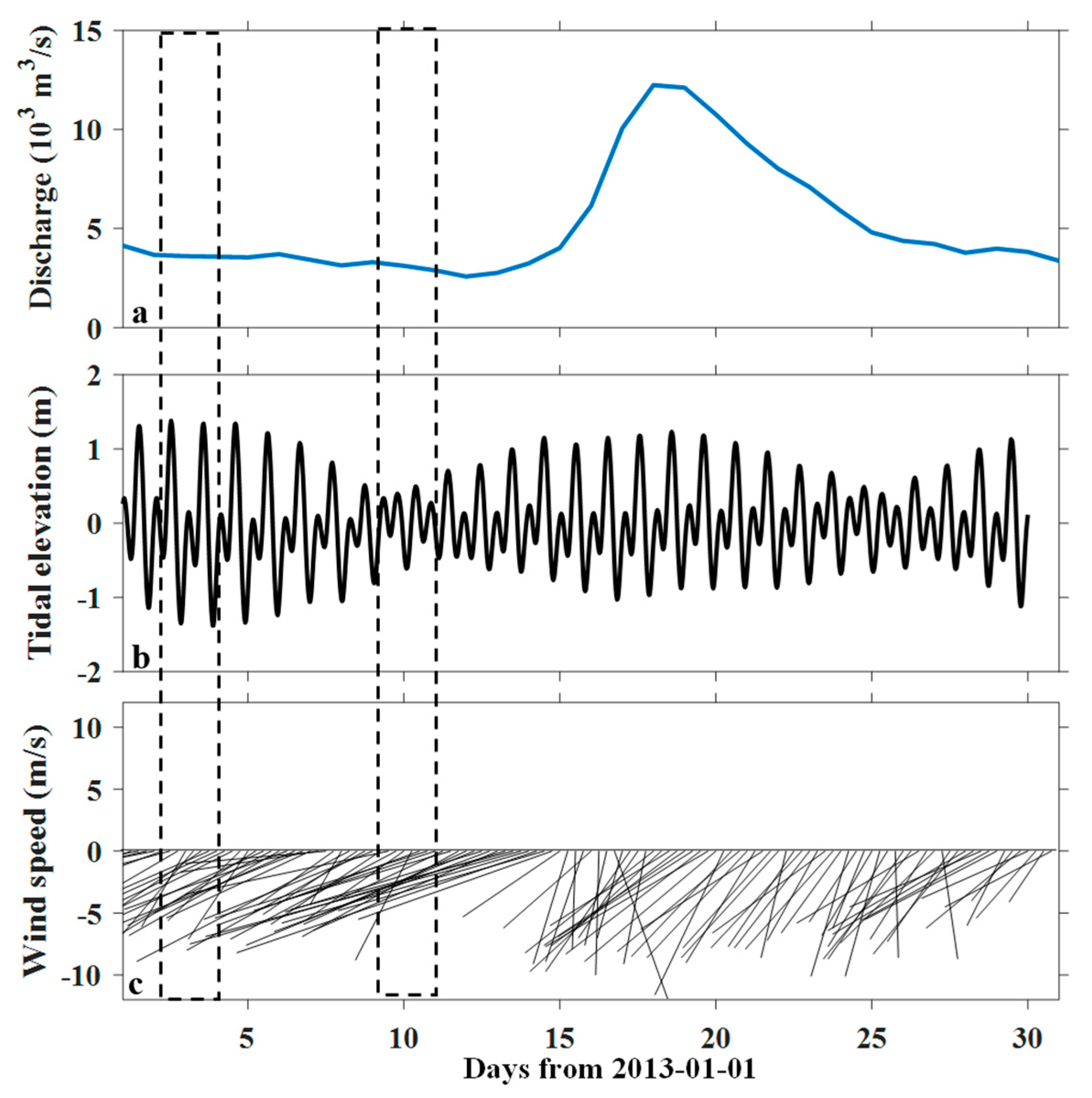
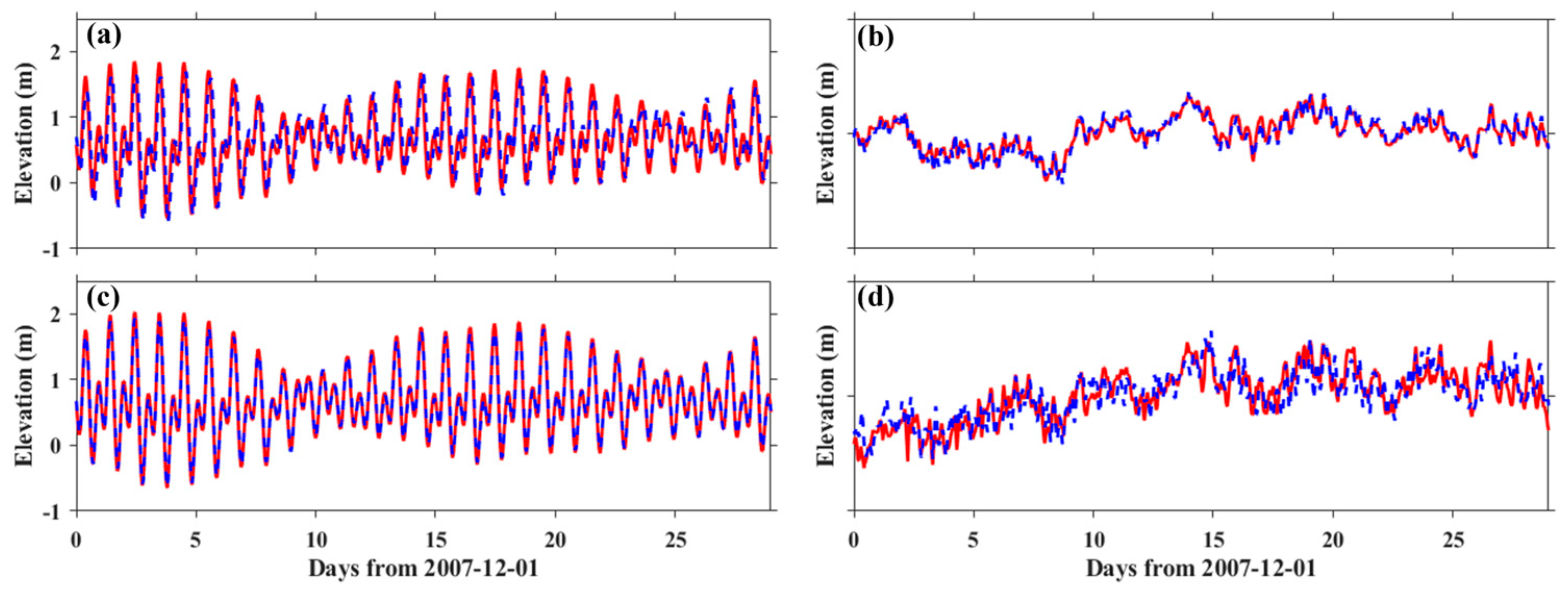
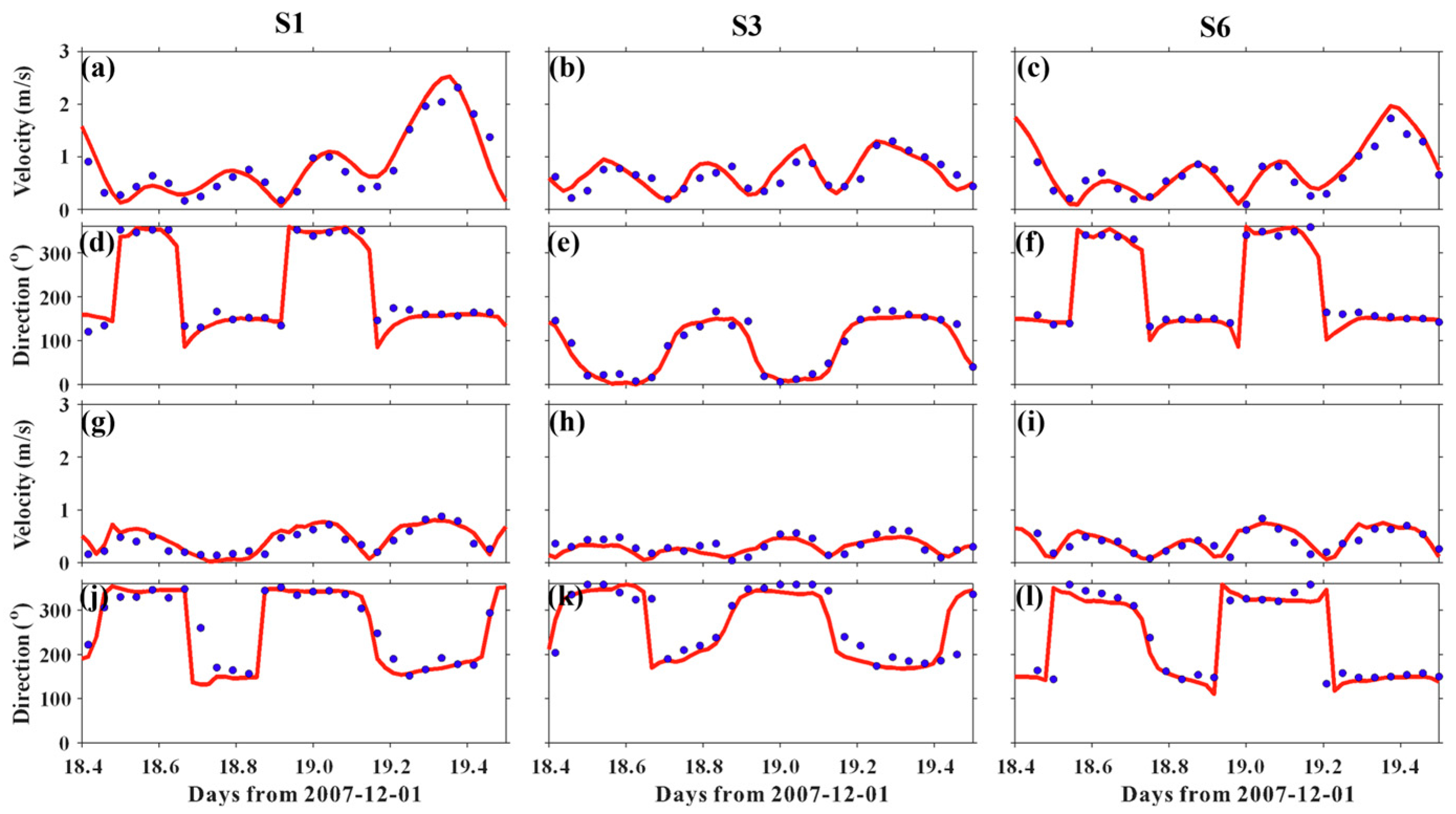
3.3. Model Calibration
4. Results
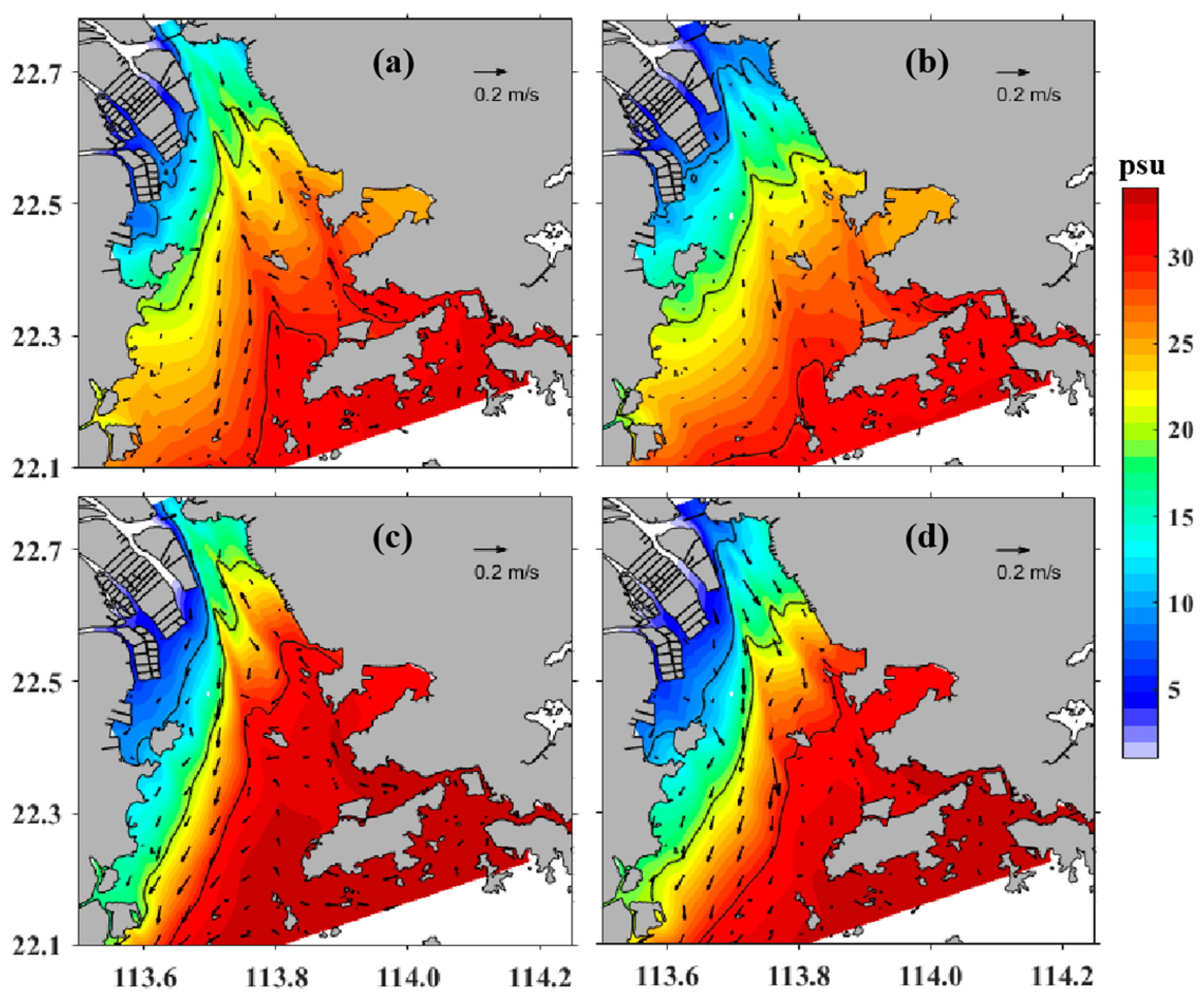
4.1. Water Exchage
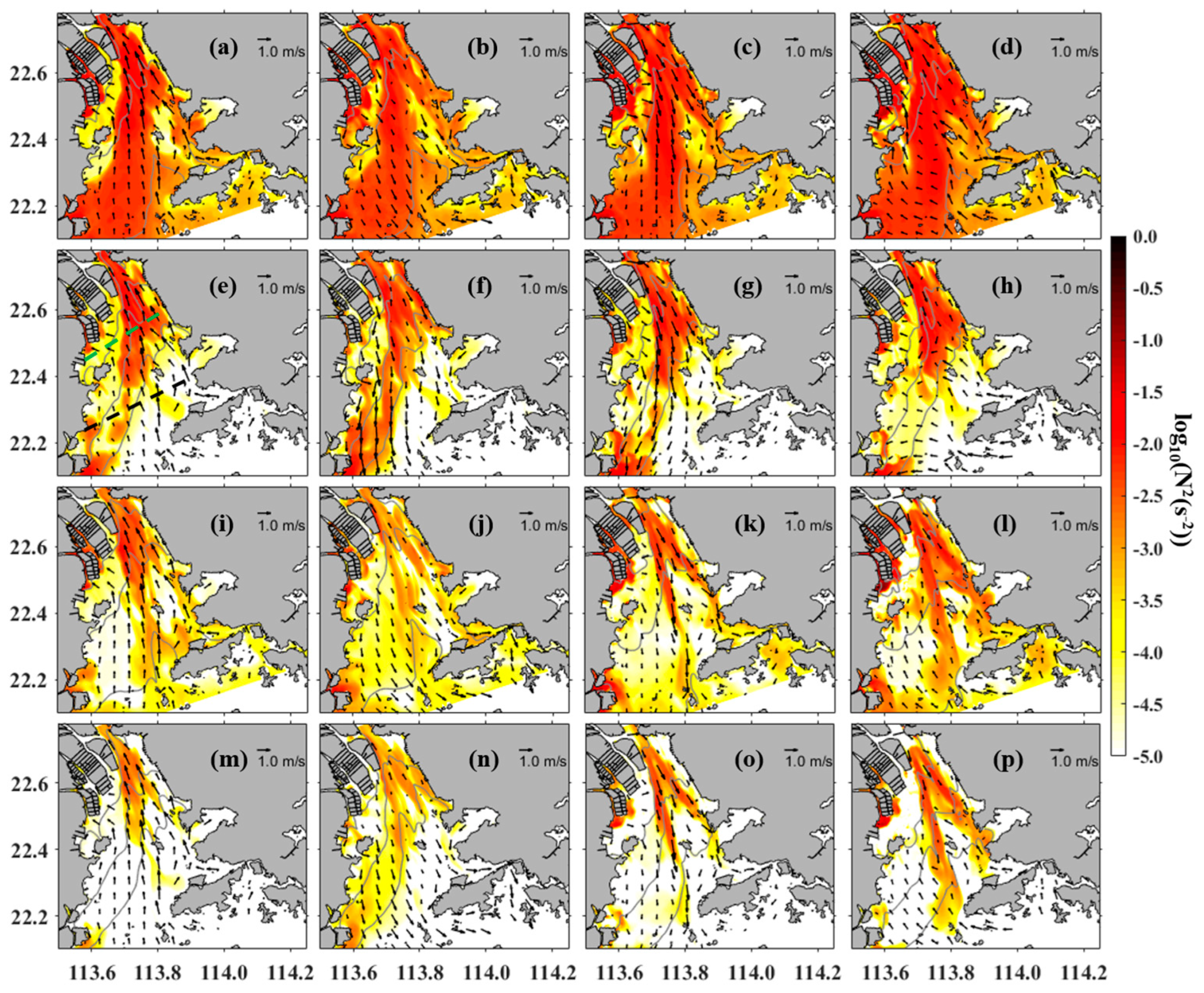
4.2. Intra-Tidal Variation in Stratification
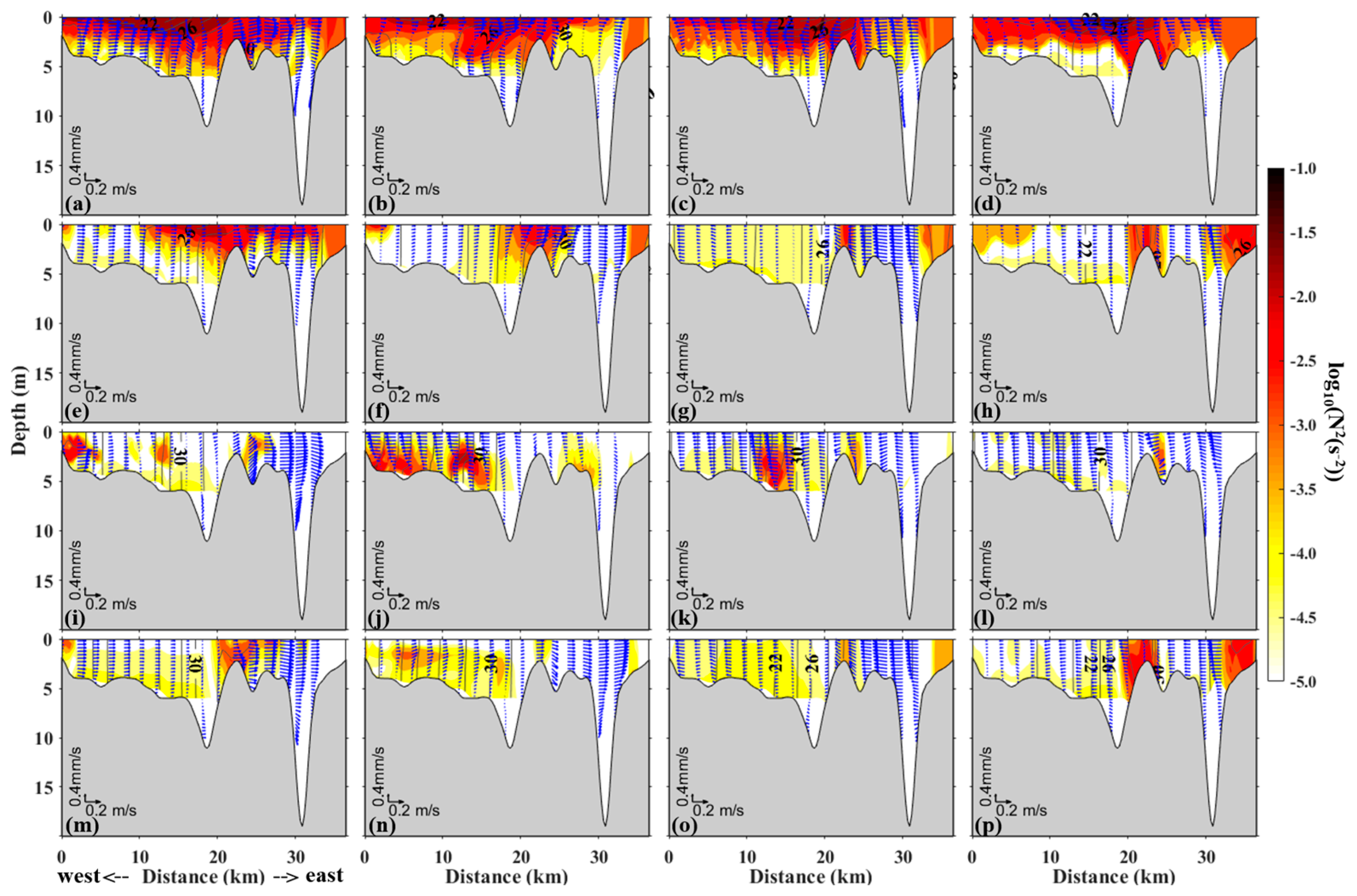
4.3. Transverse Distribution of Stratification
5. Discussion
5.1. Wind Modulation on Water Transport
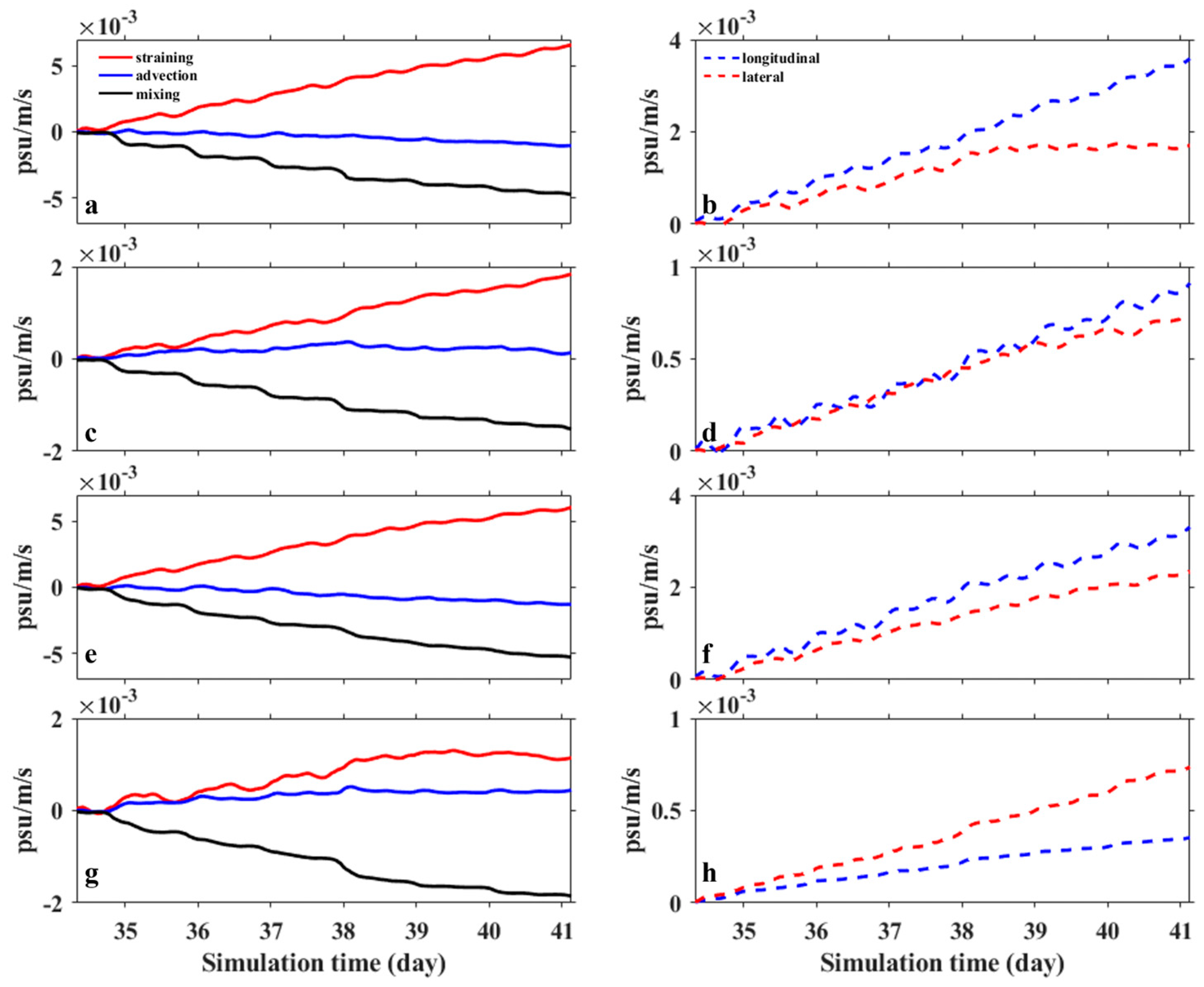
5.2. Controlling Factors in Stratification
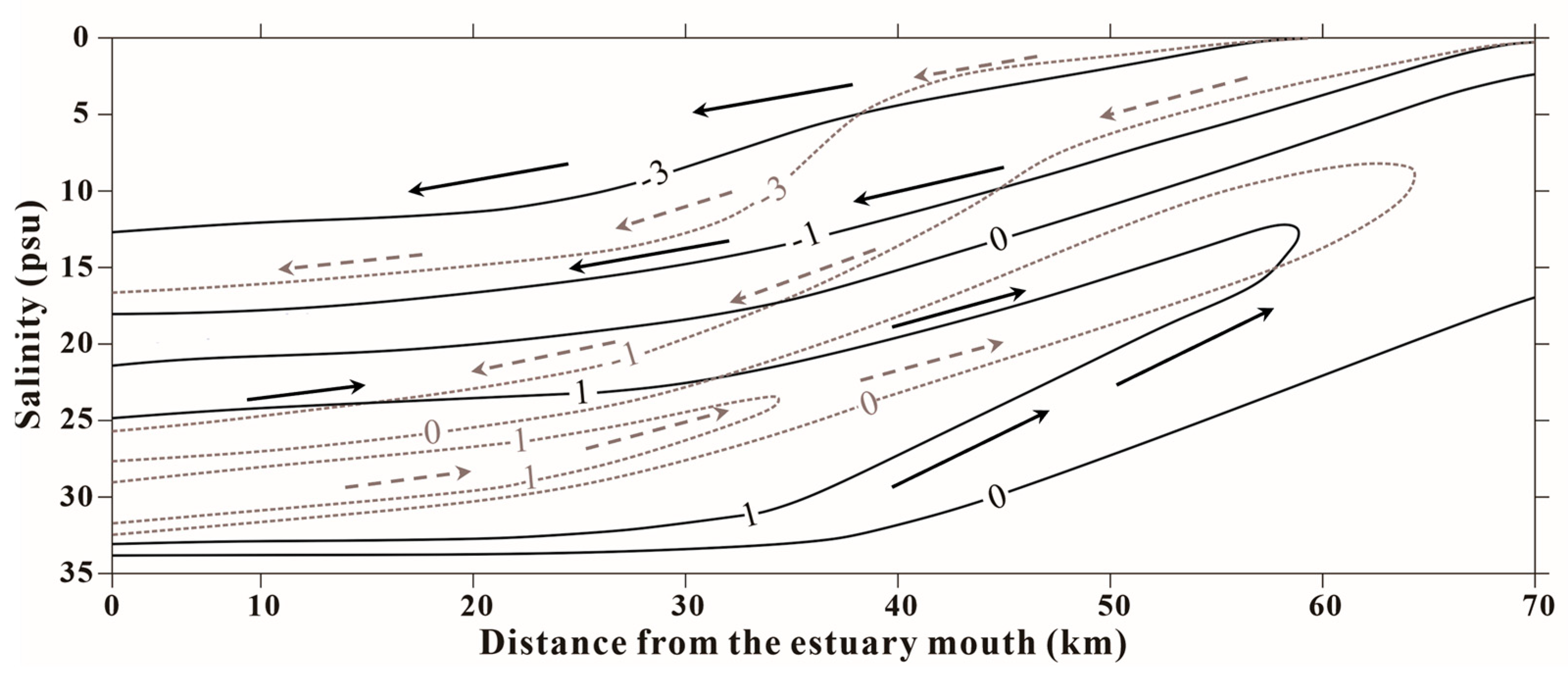
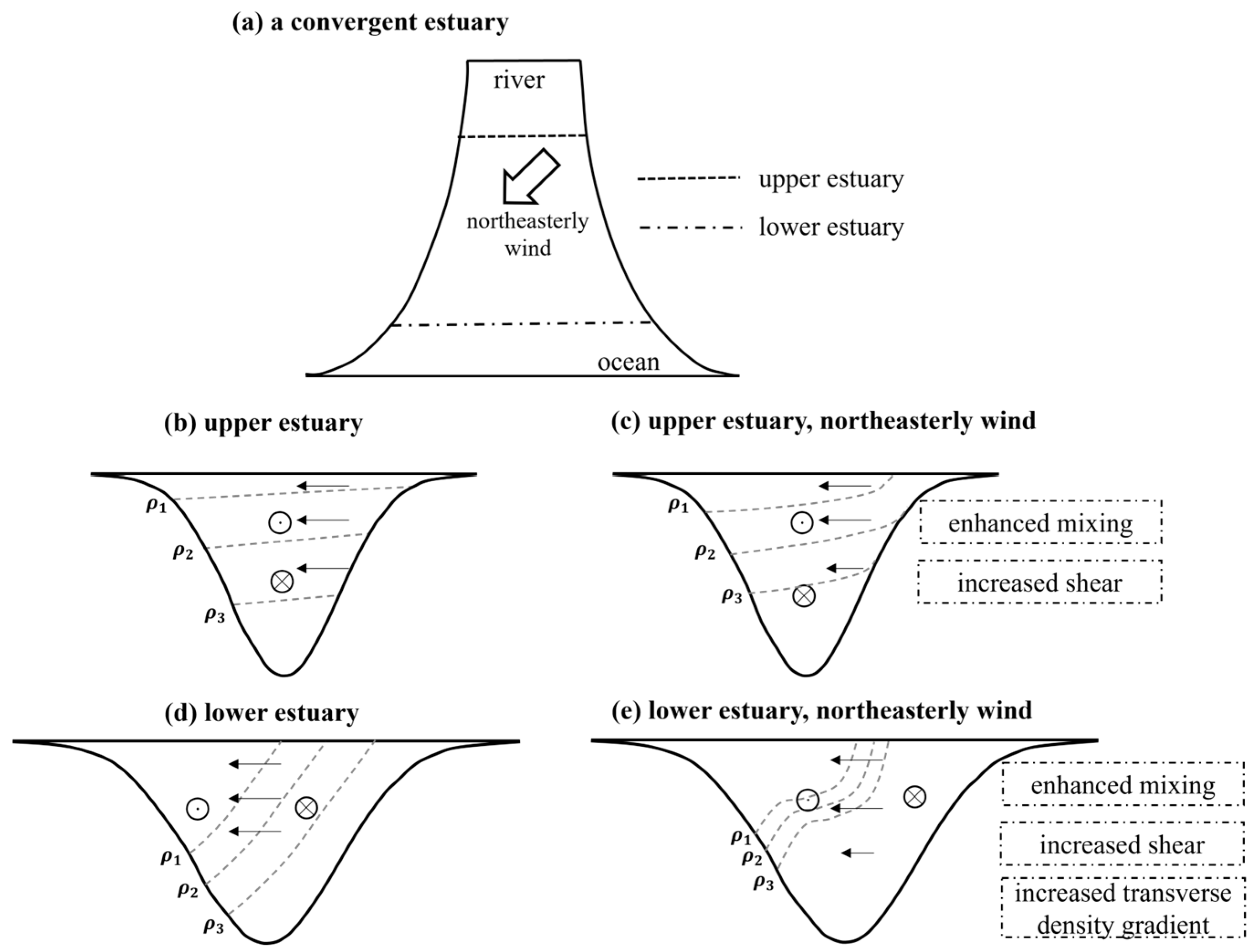
5.3. Conceptual Diagram and Comparisons with Other Estuaries
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hansen, D.V.; Rattray, M. Gravitational circulation in straits and estuaries. J. Mar. Res. 1966, 23, 104–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geyer, W.R. The importance of suppression of turbulence by stratification on the estuarine turbidity maximum. Estuaries 1993, 16, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codiga, D.L. Density stratification in an estuary with complex geometry: Driving processes and relationship to hypoxia on monthly to inter-annual timescales. J. Geophys Res. Ocean 2012, 117, C12004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, J.H.; Brown, J.; Matthews, J.; Allen, G. Tidal straining, density currents, and stirring in the control of estuarine stratification. Estuaries 1990, 13, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burchard, H.; Hofmeister, R. A dynamic equation for the potential energy anomaly for analysing mixing and stratification in estuaries and coastal seas. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2008, 77, 679–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, X.; Shi, J.Z.; Hu, G.D.; Xiong, L.B. Circulation and mixing along the North Passage in the Changjiang River estuary, China. J. Mar. Syst. 2015, 148, 213–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, J.H.; Williams, E.; Brasseur, L.H.; Brubaker, J.M. The impact of tidal straining on the cycle of turbulence in a partially stratified estuary. Cont. Shelf Res. 2005, 25, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garel, E.; Pinto, L.; Santos, A.; Ferreira, O. Tidal and river discharge forcing upon water and sediment circulation at a rock-bound estuary (Guadiana estuary, Portugal). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2009, 84, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becherer, J.; Stacey, M.T.; Umlauf, L.; Burchard, H. Lateral circulation generates flood tide stratification and estuarine exchange flow in a curved tidal inlet. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2015, 45, 638–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; He, Q.; Shen, J. Modeling lateral circulation and its influence on the along–channel flow in a branched estuary. Ocean Dyn. 2018, 68, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scully, M.E.; Friedrichs, C.; Brubaker, J. Control of estuarine stratification and mixing by wind-induced straining of the estuarine density field. Estuaries 2005, 28, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.N.; Sanford, L.P. Axial wind effects on stratification and longitudinal salt transport in an idealized, partially mixed estuary. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2009, 39, 1905–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, M. Effects of winds on stratification and circulation in a partially mixed estuary. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2012, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.H.; Wang, H.V.; Shen, J.; Valle-Levinson, A.; Teng, Y.C. A modeling study on the response of Chesapeake Bay to hurricane events of Floyd and Isabel. Ocean Model. 2012, 49–50, 22–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valle-Levinson, A. Density-driven exchange flow in terms of the kelvin and Ekman numbers. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2008, 113, C04001. [Google Scholar]
- Tilburg, C.E.; Houghton, R.W.; Garvine, R.W. Mixing of a dye tracer in the Delaware plume: Comparison of observations and simulations. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2007, 112, C12004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geyer, W.R. Influence of wind on dynamics and flushing of shallow estuaries. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1997, 44, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giddings, S.N.; MacCready, P. Reverse estuarine circulation due to local and remote wind forcing, enhanced by the presence of along–coast estuaries. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2017, 122, 10184–10205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Wu, C.Y.; Bao, Y. Dynamic structure of Humen estuary of the Pearl River. Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Sunyatsen 2006, 45, 105–109, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Gong, W.P.; Chen, L.H.; Zhang, H.; Yuan, L.R.; Chen, Z.Y. Plume dynamics of a lateral river tributary influenced by river discharge from the estuary head. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2020, 125, e2019JC015580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Zhang, H.; Guo, L.C.; Huang, W.H.; Gong, W.P. Estimation of riverine sediment fate and transport timescales in a wide estuary with multiple sources. J. Mar. Syst. 2021, 214, 103448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, W.F.; Pan, J.Y.; Devlin, A.T. Impact of tides and winds on estuarine circulation in the pearl river estuary. Cont. Shelf Res. 2018, 168, 68–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Q.W.; Shi, P.; Yin, K.D.; Gan, J.P.; Qi, Y.Q. Tides and tidal currents in the Pearl River estuary. Cont. Shelf Res. 2004, 24, 1797–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arifin, R.R.; James, S.C.; de Alwis Pitts, D.A.; Hamlet, A.F.; Sharma, A.; Fernando, H.J.S. Simulating the thermal behavior in Lake Ontario using EFDC. J. Great Lakes Res. 2016, 42, 511–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.B.; Shen, J. Transport of riverine material from multiple rivers in the Chesapeake Bay: Important control of estuarine circulation on the material distribution. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeoscience 2017, 122, 2998–3013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Lin, J. Modeling study of the influences of tide and stratification on age of water in the tidal James River. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2006, 68, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumberg, A.F.; Mellor, G.L. A description of a three-dimensional coastal ocean circulation model. In Three-Dimensional Coastal Ocean Models, Coastal and Estuarine Science; Heaps, N.S., Ed.; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 1987; Volume 3, pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Mellor, G.L.; Yamada, T. Development of a turbulence closure model for geophysical fluid problems. Rev. Geophys. 1982, 20, 851–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galperin, B.; Kantha, L.; Hassid, S.; Rosati, A. A quasi-equilibrium turbulent energy model for geophysical flows. J. Atmos. Sci. 1988, 45, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamrick, J.M. User’s Manual for the Environmental Fluid Dynamics Computer Code; Department of Physical Sciences, School of Marine Science, Virginia Institute of Marine Science, College of William and Mary: Williamsburg, VA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Hu, S.A.; Cheng, W.C.; Zhu, L.; Chen, Y.R.; Liu, J.H.; Gong, W.P.; Li, Y.N.; Li, S.T. Response of freshwater transport during typhoons with wave-induced mixing effects in the Pearl River Estuary, China. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2021, 258, 107439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, A.H. Skill scores based on the mean square error and their relationships to the correlation coefficient. Mon. Weather Rev. 1988, 116, 637–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Cheng, W.C.; Chen, L.H.; Zhang, H.; Gong, W.P. Transport of riverine sediment from different outlets in the pearl river estuary during the wet season. Mar. Geol. 2019, 415, 105957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.R.; Weidemann, A.; Arnone, R.; Davis, C.O. Chesapeake Bay outflow plume and coastal upwelling events: Physical and optical properties. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2001, 106, 11613–11622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitney, M.M.; Garvine, R.W. Simulating the Delaware bay buoyant outflow: Comparison with observations. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2006, 6, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geyer, W.R.; Maccready, P. The estuarine circulation. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2014, 46, 175–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacCready, P. Calculating estuarine exchange flow using isohaline coordinates. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2011, 41, 1116–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayson, M.D.; Gross, E.S.; Hetland, R.D.; Fringer, O.B. Using an isohaline flux analysis to predict the salt content in an unsteady estuary. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2017, 47, 2811–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.N.; Geyer, W.R.; Ralston, D.K.; Lerczak, J.A. Estuarine exchange flow quantified with isohaline coordinates: Contrasting long and short estuaries. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2012, 42, 748–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scully, M.E.; Geyer, W.R. The role of advection, straining, and mixing on the tidal variability of estuarine stratification. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2012, 42, 855–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Lin, J.; Wang, D. Numerical study on salinity stratification in the Pamlico river estuary. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2008, 80, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharples, J.; Simpson, J.H.; Brubaker, J.M. Observations and modelling of periodic stratification in the upper York River Estuary, Virginia. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1994, 38, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neilson Gertz, R.F. A simple model for water level and stratification in ringkøbing fjord, a shallow, artificial estuary. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2005, 63, 235–248. [Google Scholar]
- Restrepo, J.C.; Schrottke, K.; Bartholomae, A.; Ospino, S. Estuarine and sediment dynamics in a microtidal tropical estuary of high fluvial discharge: Magdalena river (Colombia, south America). Mar. Geol. 2018, 398, 86–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Wang, K. Changjiang river plume and suspended sediment transport in Hangzhou bay. Cont. Shelf Res. 1989, 9, 93–111. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Zhu, J.; Ho Choi, B. Links between saltwater intrusion and subtidal circulation in the Changjiang Estuary: A model-guided study. Cont. Shelf Res. 2010, 30, 1891–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valle-Levinson, A.; Li, C.Y.; Royer, T.; Atkinson, L. Flow patterns at the Chesapeake Bay entrance. Cont. Shelf Res. 1998, 18, 1157–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, D.J.; Jay, D.A. Interfacial mixing in a highly stratified estuary 1. Characteristics of mixing. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2003, 108, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prestininzi, P.; Montessori, A.; La Rocca, M.; Sciortino, G. Simulation of arrested salt wedges with a multi-layer Shallow Water Lattice Boltzmann model. Adv. Water Resour. 2016, 96, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Model Cases | River Discharge | Tidal Elevation | Wind |
|---|---|---|---|
| Case 1 | 3800~12,000 m3/s, daily measured data in upstream tributaries | The tidal range varies from 0.68 to 2.70 m, driven by 11 harmonic tidal constituents extracted from [31]. | × |
| Case 2 | Averaged wind: 6.9 m/s with a direction of 248°, obtained from the Climate Forecast System Reanalysis (NCEP, https://climatedataguide.ucar.edu/climate-data/climate-forecast-system-reanalysis-cfsr (accessed on 12 June 2021)) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, L.; Sheng, J.; Pang, L. The Role of Tide and Wind in Modulating Density Stratification in the Pearl River Estuary during the Dry Season. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 1241. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12081241
Zhu L, Sheng J, Pang L. The Role of Tide and Wind in Modulating Density Stratification in the Pearl River Estuary during the Dry Season. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2024; 12(8):1241. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12081241
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Lei, Jiangchuan Sheng, and Liwen Pang. 2024. "The Role of Tide and Wind in Modulating Density Stratification in the Pearl River Estuary during the Dry Season" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 12, no. 8: 1241. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12081241
APA StyleZhu, L., Sheng, J., & Pang, L. (2024). The Role of Tide and Wind in Modulating Density Stratification in the Pearl River Estuary during the Dry Season. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 12(8), 1241. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12081241





