Abstract
Pile running during the installation of offshore large diameter pipe piles poses a significant challenge to construction safety and pile bearing capacity. This paper proposes a deep learning (DL)-based method for predicting pile running occurrences. Utilizing a dataset of pile installation records collected from various construction sites, the DL model was trained and tested. The predictive capacity of the DL model was compared with conventional analytical methods, demonstrating its superior performance in terms of accuracy and robustness. Additionally, the SHAP (SHapley Additive exPlanations) method was employed for the sensitivity analysis of the model’s input variables, and the resultant importance ranking agreed well with the findings of existing studies, thus enhancing the reliability and interpretability of the model’s predictions.
1. Introduction
The foundation of many offshore structures, including wind turbines and oil and gas platforms [1,2,3], relies on driven open-ended steel pipe piles. With offshore structures growing heavier, they often necessitate large-diameter pipe piles (LDPPs) to withstand the loads from the structure’s weight, wind, and waves. To ensure seamless pile driving without on-site splicing and to streamline the installation process, LDPPs are frequently fabricated as single segments. This approach not only enhances installation efficiency, but also reduces the risk of premature refusal [4,5].
However, due to their considerable length and weight, LDPPs are susceptible to a potential issue during the pile driving process, known as pile running. This phenomenon occurs when the pile unexpectedly penetrates the seabed under its own weight at an uncontrolled speed. Pile running can lead to various consequences, such as damage to the hydraulic control system of the driving hammer or even loss of the hammer into the water. Moreover, it can result in inaccuracies in the target penetration depth and the designed elevation of the pile, which, in turn, may affect the pile’s bearing capacity. Pile running is not uncommon in offshore engineering practice, particularly in carbonate soils [6,7] or layered seabeds with alternating strong and weak layers [8], where the soil resistance to driving can abruptly decrease during pile driving and become significantly smaller than the submerged weight of the pile. Therefore, accurately predicting the occurrence of pile running has significant practical importance in offshore engineering.
Considerable research has been devoted to predicting the occurrence of pile running. For instance, Yan et al. [9] proposed a predictive method based on the limit equilibrium of pile weight and soil resistance, yielding promising results in practical applications. Sun et al. [10,11,12] introduced static-equilibrium-based methods for predicting pile running, where dynamic skin friction of the pile is determined from the degradation of static skin friction. Zhao et al. [5] conducted larger deformation finite element analysis to simulate the pile running phenomenon on layered soil. In these methods, predicting pile running relies on comparing the pile weight with soil resistance. However, accurately calculating the resistance is challenging and influenced by numerous factors, including the complex material properties of soil layers, the diameter and wall thickness of the pile, and pile–soil interactions such as interface degradation, soil remolding during driving, and soil plugging effects [13]. Furthermore, most contemporary methods are essentially empirical and inherently involve various subjective assumptions and simplifications. Therefore, they may only be applicable under some specific conditions and have limited predictive accuracy in practical engineering.
In recent years, the rapid advancement of artificial intelligence technology and computing resources has introduced the deep learning (DL) method [14,15] as a powerful alternative across various traditional domains. The DL model excels in feature extraction and mapping, enabling the direct modelling of complex nonlinear relationships from training data without relying on theoretical assumptions. Consequently, it often yields superior predictive performance compared to conventional methods. Moreover, as additional training data become available, the DL model can be iteratively fine-tuned and improved, enhancing its adaptability and dynamic predictive modeling capability [16].
The DL method has found successful applications in geotechnical engineering, including deriving constitutive modeling of soil [17], predicting pile settlements [18] and bearing capacities [19], assessing landslide failure susceptibility [20], and more [21,22]. Demonstrating remarkable accuracy and robustness, the DL model has proven its effectiveness in various areas. This study extends the application of the DL method to the prediction of pile running. Utilizing a comprehensive dataset collected from different construction sites in China, the DL model was trained and tested. To assess its performance, the results were compared with conventional methods, where pile running occurrence was determined by comparing pile weight with soil resistance. Furthermore, sensitivity analysis of the model’s input variables was conducted to enhance interpretability.
The remainder of the paper is organized as follows: Section 2 provides a brief introduction to the dataset, the development procedure of the DL model, and the formulations of the conventional methods; Section 3 evaluates the predictive performance of the DL model and analyzes the sensitivity of the input variables; Section 4 concludes this paper.
2. Methodology
2.1. Dataset
Experimental data from practical engineering projects involving LDPPs were employed to train and test the DL model. This dataset, encompassing information on 17 piles, was collected from six construction sites associated with offshore wind power projects in China. It includes the geometrical characteristics of each pile and the soil properties of the layered seabed.
The geometrical characteristics consisted of the diameter (D), length (l), and weight (w) of the piles. Figure 1 illustrates the relationships between D, l, and w for these piles. It reveals variations in diameter ranging from 5.5 m to over 9 m, lengths spanning from 65 m to beyond 100 m, and weights ranging from 600 tons to 1800 tons. This diversity underscores the wide range of geometrical specifications observed in the piles considered in this study.
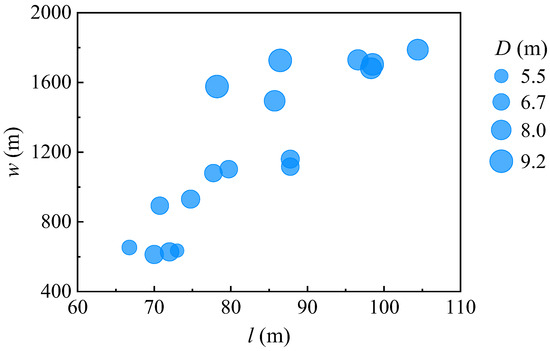
Figure 1.
Pile dimensions: length vs. weight; diameter indicated by point size.
The soil layer properties were determined through laboratory tests and piezocone penetrometer test (CPTu). Table 1 provides an example of the laboratory test results for soil samples obtained at a construction site, detailing the soil type of each layer, depth of the bottom of the layer (d), submerged unit weight (), relative density (Dr), friction angle (φ), and undrained shear strength (cu). φ and cu were determined from direct shear test and unconsolidated–undrained triaxial tests, respectively. It could be observed that the soil profile was mainly composed of mud, silty clay, and silty sand. Through CPTu, the cone tip resistance (qc), side friction resistance (fs), and pore water pressure (u) were measured during the penetration process.

Table 1.
The soil properties for a construction site.
Experimental data corresponding to each pile were divided into segments with a fixed depth interval of 0.02 m. The input variables for the DL model comprised the diameter and weight of the piles, along with soil properties obtained from laboratory tests and CPTu. The DL model’s output was an index indicating the occurrence of pile running at a specific depth. A value of unity signified that the pile running was expected, whereas a value of 0 indicated that the pile running was not anticipated.
Before inputting data into DL models, preprocessing is typically necessary. Normalization is a widely adopted technique used to rescale data from different variables to the same scale, which has been shown to reduce computational costs and improve the convergence of DL models [23]. The following equation was used to rescale the data to the range of [0, 1]:
where x is the data sequence before normalization, is the data sequence after normalization, and max(x) and min(x) are the maximum and minimum values of the data sequence, respectively.
The dataset is typically divided into three parts: training set, validation set, and test set. The training set is primarily used to optimize the trainable parameters of the model, enabling it to capture the underlying patterns and relationships within the data. The validation set is used to fine-tune the model’s configuration, aiding in preventing overfitting and optimizing the model’s generalization capabilities. Finally, the test set, which is completely separate from the training and validation process, is used to assess the final predictive performance of the trained model. In this study, the data from each pile were alternately used as the test set, while the remaining data were utilized as the training and validation set.
2.2. DL Model Development
In this study, the multilayer perceptron (MLP) was chosen as the architecture for the DL model. The MLP is the most basic type of neural network, comprising a three-block architecture—an input layer, hidden layers, and an output layer—as depicted in Figure 2. There can be one or multiple hidden layers, which determines the depth of the network. Each layer contains a set of neurons serving as the processing units. Each neuron gathers information from all neurons in the preceding layer and propagates its outputs to all the neurons in the succeeding layer, which can be mathematically expressed as follows:
where the superscript l denotes the layer index, and Wl and bl are the weight matrix and bias vector, respectively. x1 and xL represent the input and output layers, respectively. f is the activation function, introducing nonlinear properties into the network to model complex relationships.
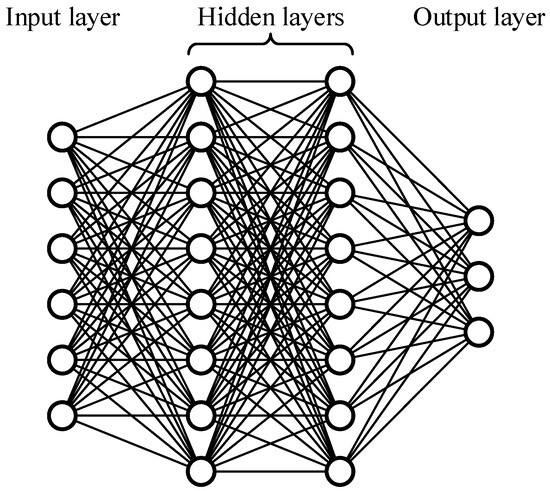
Figure 2.
The architecture of the MLP.
Despite its simplicity and efficiency, the MLP remains one of the most commonly used DL models [21,24], widely applied in various domains such as pattern recognition, regression analysis, and predictive modeling [25,26,27,28]. Although its predictive capacity may not match that of more sophisticated DL architectures, the MLP demonstrates remarkable generalization capabilities and high adaptability to dataset with limited sizes [29].
Prior to training, the model’s hyperparameters, which control its configuration and training procedure, must be assigned. In this study, a grid search was performed over the main hyperparameters that are critical to the predictive capacity of the model, such as the number of layers and neurons per layer. Other hyperparameters were set to their most commonly used values. The optimal hyperparameters are summarized in Table 2. The MLP model comprised three hidden layers, each containing 64 neurons. The rectified linear unit (ReLU) [30] was chosen as the activation function for these layers, a widely adopted activation function in DL.

Table 2.
The hyperparameters for the DL model.
Training a DL model is an optimization process, where the trainable parameters (i.e., weights and biases) are iteratively updated to minimize the discrepancy between predicted and true values. This discrepancy is quantified by a loss function, and the mean squared error (MSE) is selected as the loss function:
where n is the dimension of the output, and yi are the predicted and true values, respectively. The Adam optimizer is chosen to update trainable parameters, implementing an adaptive stochastic optimization method that is robust and well-suited for various DL problems [31].
To mitigate overfitting, a regularization strategy, called early stopping [32], is employed. During training, the model’s performance is evaluated on both the training and validation sets. When the validation error begins to plateau or increase, it indicates that the model has reached its optimal generalization capacity. Any further training is likely to lead to overfitting, prompting the training process to stop. The patience was set to 20 in this study; corresponding loss curves for the model on the training and validation sets are presented in Figure 3. The training loss steadily decreased, while the validation loss initially mirrored the training loss but subsequently plateaus, indicating potential for overfitting. The application of early stopping leads to termination of the training process at about 300 epochs.
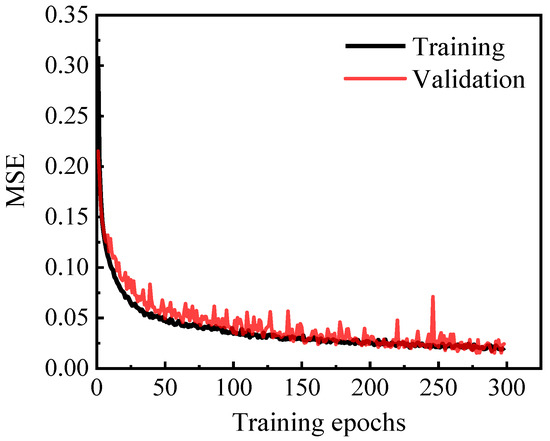
Figure 3.
The training and validation loss.
2.3. Traditional Methods
To further evaluate the predictive capacity of the DL model, its accuracy was compared with the traditional methods, where the occurrence of pile running is judged by comparing the weight of the pile with soil resistance. The following methods are used to calculate soil resistance: API [33], ICP-05 [34], UWA-05 [35], and UWA-13 [36]. Notably, the ICP-05 and UWA-05 methods are applicable only to sandy soil, while the UWA-13 method is designed for clayey soil. Thus, for layered soils containing both sand and clay, two hybrid methods are adopted: one combining ICP-05 and UWA-13, and the other combining UWA-05 and UWA-13.
In the API method, the unit shaft resistance, τf, and unit tip resistance, qt, for clayey soil are calculated as follows:
where cu is the undrained shear strength of the soil and α is the shaft friction factor for clay, given by the following equation:
where ψ is a strength factor calculated as follows:
where is the in situ vertical effective stress at the specific depth.
For sandy soil, the τf and qt can be calculated as follows:
where β is the shaft friction factor for sand given by:
where φ is the internal friction angle of soil and δf is the interface friction angle.
In the ICP-05 method, τf and qt are calculated as follows:
where a and b are loading factors, and are set as 1.0 for pile under compression; qc is the cone tip resistance measured from CPTu; pa = 100 kPa is the atmospheric pressure; h is the distance of the point from the pile tip; R* is the equivalent radius for the open-ended pile, and can be obtained from Equation (10); is the area ratio; and qc,avg is the average value of qc measured over the 1.5 pile diameter range, both above and below the pile tip.
where D and Di are the outer and inner diameters of the pipe pile, respectively.
In the UWA-05 method, τf and qt are calculated as follows:
where is the average qc obtained from the Dutch method [37], and Ar,eff is the effective area ratio, calculated as follows:
In the UWA-13 method, qt is obtained from Equation (9), while τf is calculated as follows:
where qct is the corrected cone resistance, calculated as follows:
3. Performance
3.1. Predictive Accuracy
This section focuses on the predictive accuracy of the DL model on the test data. Notably, each pile in the dataset is alternately employed as the test set to assess the predictive capacity of the DL model.
Figure 4 illustrates the distribution of predictive accuracy on the test data using a boxplot. It is evident that the MLP significantly outperforms the other methods and exhibits superior accuracy. The mean accuracy of the MLP is approximately 0.89, contrasted with the considerably lower accuracy of around 0.4 observed from the other methods, demonstrating the exceptional predictive capacity of the MLP. Additionally, the MLP offers a narrower accuracy distribution compared to the other methods, as indicated by the range from the minimum to the maximum of the box, while the other methods exhibit wider distribution. A wider distribution signifies a higher degree of variability, indicating that the method is more sensitive to the conditions of construction sites. Therefore, the MLP not only offers higher accuracy, but also better applicability and robustness.
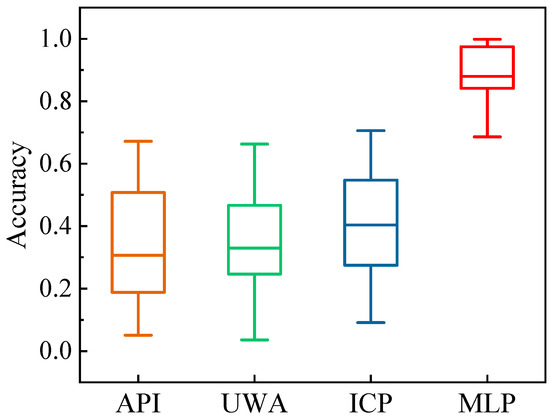
Figure 4.
Distribution of the predictive accuracy.
Figure 5 presents the prediction of pile running occurrence for two pile cases, where the dots denote that pile running occurred at the corresponding depth. The predictions of the MLP align well with the test data at different depths, demonstrating the superior predictive capacity of the DL model. The DL model can accurately reproduce both the initial pile running caused by the pile’s own weight and the surface weak soil layer, as well as pile running incidences during the driving process. In contrast, traditional methods tend to underestimate the likelihood of pile running occurrence and are only applicable at the early stage of the pile installation.
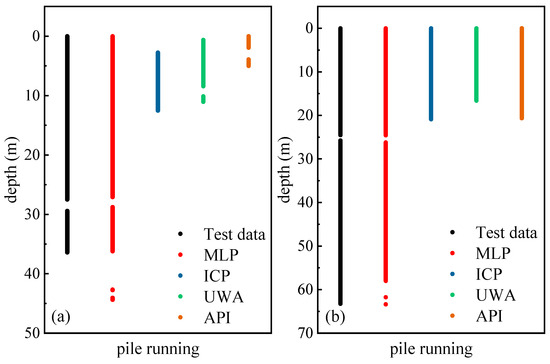
Figure 5.
Prediction of pile running: (a) pile example 1; (b) pile example 2. Dots indicate occurrence.
However, it is important to recognize that the DL model’s accuracy and generalizability is highly dependent on the quality and diversity of the training data. The model may not perform as well when applied to construction sites with soil properties or conditions that significantly differ from those in the training dataset. Furthermore, while the DL model demonstrates superior performance in predicting pile running occurrences, it may require substantial computational resources for training and may not be as easily interpretable as traditional methods, which could be a limitation in practical applications where transparency and explainability are crucial.
3.2. Sensitivity Analysis
The sensitivity of each input variable was analyzed using the SHAP (SHapley Additive exPlanations) method [38], which provides a unified measure of variable importance based on game theory principles to interpret the predictions of a machine learning model. Each input variable is assigned a value, known as the SHAP value, to quantify its specific contribution to the model’s prediction.
By analyzing the SHAP values, one can gain a comprehensive understanding of how each input variable influences the model’s output. This is particularly valuable in DL models. Due to the complex architecture of DL models, interpreting the relationship between inputs and outputs is challenging [39], rendering DL models as black boxes. The SHAP method offers a viable approach to dissect the model, facilitating a detailed exploration of the importance of each input variable. This enhances the interpretability of the model and provides insights into the underlying patterns and relationships within the data that the model has learned. Such analysis is crucial for building trust in the model’s predictions and ensuring that the model’s decisions align with the established domain knowledge.
Figure 6 illustrates the mean SHAP value for different input variables. It is evident that the penetration depth (d) and weight (w) of the pile are the two most critical variables in determining the occurrence of pile running. This is logical because the total resistance of the soil is directly influenced by the penetration depth of the pile, and a greater difference between the pile weight and soil resistance would result in a higher risk of pile running. Additionally, the diameter of the pile (D) exhibits a high SHAP value, as the size of the diameter significantly influences the soil plugging effect, which has a considerable impact on the bearing capacity and drivability of the pile [40]. Furthermore, variables measured from the CPTu, such as the cone tip resistance (qc), side friction resistance (fs), and the pore water pressure (u), are the least important variables. This can be attributed to the close correlation between the soil parameters and the CPTu data [41,42], leading to information redundancy and lower SHAP values. These results demonstrate that the SHAP method reliably ranks the importance of the input variables, which is in alignment with the findings of existing studies in the field.
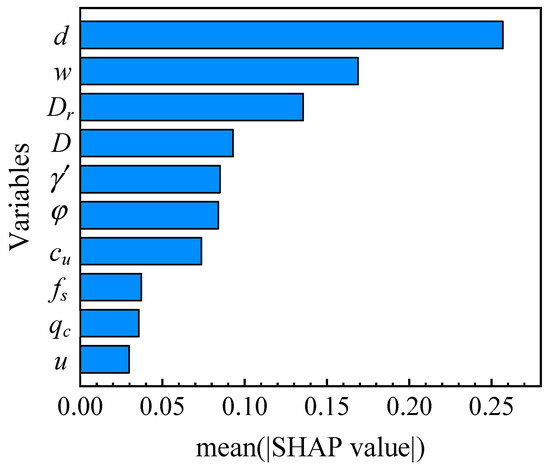
Figure 6.
The mean SHAP value for different input variables.
4. Conclusions
This paper introduces a DL-based framework for predicting the occurrence of pile running. The model was trained and tested using a comprehensive dataset comprising 17 pile driving cases collected from practical construction sites. The input variables included geometrical information of the pile and soil properties obtained from laboratory tests and CPTu. Comparative analysis was conducted to evaluate the predictive performance of the model against traditional methods, in which three distinct formulations were utilized to calculate soil resistance. Additionally, the SHAP method was employed to analyze the importance of the input variables.
The DL model demonstrated a high level of accuracy in predicting pile driving occurrences, surpassing traditional methods in terms of both predictive accuracy and robustness under varying conditions. Additionally, the SHAP method has proven effective in conducting sensitivity analysis, offering a reliable ranking of variable importance that aligns well with established domain knowledge, thereby enhancing the interpretability of the model.
Despite these successes, it is noteworthy that the model’s performance is significantly influenced by the quality and representativeness of the training data. The current dataset may not fully capture the variability of real-world conditions, which could limit the model’s applicability to untested scenarios. Future work could focus on expanding the dataset to include a broader range of soil types and construction scenarios.
The successful integration of the DL model into the prediction of pile driving not only improves the predictive accuracy, but also suggests its potential for broader applications within the field of geotechnical engineering, such as the prediction of soil settlement and assessment of slope stability.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.H. and R.S.; methodology, B.H. and R.S.; software, B.H. and Q.G.; validation, B.H., R.S. and Q.G.; formal analysis, B.H. and Q.G.; investigation, B.H.; resources, B.H.; data curation, B.H. and R.S.; writing—original draft preparation, Q.G. and Y.Y.; writing—review and editing, B.H. and R.S.; visualization, Q.G.; supervision, B.H. and R.S.; project administration, B.H. and R.S.; funding acquisition, B.H. and R.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Power China Huadong Engineering Corporation Limited and the Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 52271294).
Data Availability Statement
The data used or analyzed in this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
Author B.H. and R.S. were employed by the company Huadong Engineering Corporation Limited. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Randolph, M.F. Science and empiricism in pile foundation design. Geotechnique 2003, 53, 847–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randolph, M.; Cassidy, M.; Gourvenec, S.; Erbrich, C. Challenges of offshore geotechnical engineering. In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, Osaka, Japan, 12–16 September 2005; pp. 123–176. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.X.; Gao, Y.Y.; Jardine, R.J.; Guo, W.B.; Wang, D. Large deformation finite-element simulation of displacement-pile installation experiments in sand. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2020, 146, 04020044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Tian, Y.H.; Zhou, Y.R.; Jiang, B.F.; Wang, J.B. Premature refusal of large-diameter, deep-penetration piles on an offshore platform. Appl. Ocean Res. 2013, 42, 55–59. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Wang, L.; Sun, L.Q.; Tian, Y.H.; Reul, O.; Chen, Q.Z. Pile running in layered soils. China Ocean Eng. 2023, 37, 829–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senders, M.; Banimahd, M.; Zhang, T.; Lane, A. Piled foundations on the North West Shelf. Aust. Geomech. 2013, 48, 149–160. [Google Scholar]
- Banimahd, M.; Chow, F.C.; Tyler, S.; Senders, M.; Stewart-Wynne, R. In Hold-back anchor piles with free fall potential on the Australian north-west shelf. In Proceedings of the Offshore Site Investigation Geotechnics 8th International Conference Proceeding, London, UK, 12–14 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Dover, A.R.; Davidson, J. Large diameter steel pipe piles running under self weight in soft clay: Predicted vs. observed behavior—Richmond San-Rafael Bridge seismic retrofit. In Proceedings of the 11th Triennial International Conference on Ports, San Diego, CA, USA, 25–28 March 2007; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, S.W.; Jia, Z.L.; Liu, W.B.; Li, J. Research on the large diameter and supper long pile running under self-weight in the ocean engineering. J. Coast. Res. 2015, 73, 809–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.Q.; Wang, Y.D.; Guo, W.; Yan, S.W.; Chu, J.; Liu, X.Q. Case study on pile running during the driving process of large-diameter pipe piles. Mar. Georesources Geotechnol. 2018, 36, 709–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.Q.; Shi, J.; Zhang, Y.R.; Feng, X.W.; Tian, Y.H.; Wang, R. Analytical method for predicting pile running during driving. Appl. Ocean Res. 2022, 125, 103234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.Q.; Jia, T.Q.; Yan, S.W.; Guo, W.; Ren, Y.X.; Lei, Z.M. Prediction of pile running during the driving process of large diameter pipe piles. Ocean Eng. 2016, 128, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeNicola, A.; Randolph, M.F. The plugging behaviour of driven and jacked piles in sand. Geotechnique 1997, 47, 841–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidhuber, J. Deep learning in neural networks: An overview. Neural Netw. 2015, 61, 85–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.P.; Fuhg, J.N.; Weissenfels, C.; Wriggers, P. A machine learning based plasticity model using proper orthogonal decomposition. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2020, 365, 113008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibagahi, G.; Bamdad, A. A neural network framework for mechanical behavior of unsaturated soils. Can. Geotech. J. 2003, 40, 684–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pooya Nejad, F.; Jaksa, M.B.; Kakhi, M.; McCabe, B.A. Prediction of pile settlement using artificial neural networks based on standard penetration test data. Comput. Geotech. 2009, 36, 1125–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Walia, B.S. Performance evaluation of nature-inspired algorithms for the design of bored pile foundation by artificial neural networks. Neural Comput. Appl. 2017, 28, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieu Tien, B.; Tsangaratos, P.; Viet-Tien, N.; Ngo Van, L.; Phan Trong, T. Comparing the prediction performance of a Deep Learning Neural Network model with conventional machine learning models in landslide susceptibility assessment. Catena 2020, 188, 104426. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.G.; Li, H.R.; Li, Y.Q.; Liu, H.L.; Chen, Y.M.; Ding, X.M. Application of deep learning algorithms in geotechnical engineering: A short critical review. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2021, 54, 5633–5673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.G.; Gu, X.; Tang, L.B.; Yin, Y.P.; Liu, D.S.; Zhang, Y.M. Application of machine learning, deep learning and optimization algorithms in geoengineering and geoscience: Comprehensive review and future challenge. Gondwana Res. 2022, 109, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Bottou, L.; Orr, G.B.; Muller, K.R. Efficient backprop. Neural Netw. Tricks Trade 1998, 1524, 9–50. [Google Scholar]
- Baghbani, A.; Choudhury, T.; Costa, S.; Reiner, J. Application of artificial intelligence in geotechnical engineering: A state-of-the-art review. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2022, 228, 103991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiblee, M.; Kalra, P.K.; Chandra, B. Time series prediction with multilayer perceptron (MLP): A new generalized error based approach. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neuro-Information Processing, Berlin, Heidelberg, 10 July 2009; pp. 37–44. [Google Scholar]
- Abiodun, O.I.; Jantan, A.; Omolara, A.E.; Dada, K.V.; Umar, A.M.; Linus, O.U.; Arshad, H.; Kazaure, A.A.; Gana, U.; Kiru, M.U. Comprehensive review of artificial neural network applications to pattern recognition. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 158820–158846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamalov, F. Forecasting significant stock price changes using neural networks. Neural Comput. Appl. 2020, 32, 17655–17667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.H.; Ruan, S.J.; Huang, T.Q.; Zhou, H.Y.; Zhang, S.H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.Y.; Huang, Z.; Liu, Y. A lightweight multi-layer perceptron for efficient multivariate time series forecasting. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2024, 288, 111463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Yin, Z.Y.; Jin, Y.F. State-of-the-art review of machine learning applications in constitutive modeling of soils. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2021, 28, 3661–3686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, V.; Hinton, G.E. Rectified linear units improve restricted boltzmann machines. In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning, Haifa, Israel, 21–24 June 2010; pp. 807–814. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), San Diego, CA, USA, 7–9 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Y.; Rosasco, L.; Caponnetto, A. On early stopping in gradient descent learning. Constr. Approx. 2007, 26, 289–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- API. Recommend Practice 2GEO Geotechnical and Foundation Design Considerations, 1st ed.; American Petroleum Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Jardine, R.; Chow, F.; Overy, R.; Standing, J. ICP Design Methods for Driven Piles in Sands and Clays; Thomas Telford: London, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Lehane, B.; Schneider, J.A.; Xu, X.T. The UWA-05 method for prediction of axial capacity of driven piles in sand. In Proceedings of the Frontiers in Offshore Geotechnics, Perth, Australia, 19–21 September 2005; pp. 683–689. [Google Scholar]
- Lehane, B.M.; Li, Y.; Williams, R. Shaft capacity of displacement piles in clay using the cone penetration test. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2013, 139, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmertmann, J.H. Guidelines for Cone Penetration Test: Performance and Design; Federal Highway Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 1978.
- Lundberg, S.M.; Lee, S.I. A unified approach to interpreting model predictions. In Proceedings of the 31st Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS 2017), Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; pp. 4768–4777. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, X.; Guo, J.; Song, B.; Cai, B.; Sun, H.; Zhang, Z. Interpretability for reliable, efficient, and self-cognitive DNNs: From theories to applications. Neurocomputing 2023, 545, 126267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehane, B.M.; Gavin, K.G. Base resistance of jacked pipe piles in sand. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2001, 127, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.; Cai, G.; Liu, S.; Puppala, A.J.; Chen, R. In-situ evaluation of undrained shear strength from seismic piezocone penetration tests for soft marine clay in Jiangsu, China. Transp. Geotech. 2019, 20, 100253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.; Congress, S.S.C.; Cai, G.; Puppala, A.J.; Dong, X.; Du, Y. Empirical correlations of soil parameters based on piezocone penetration tests (CPTU) for Hong Kong-Zhuhai-Macau Bridge (HZMB) project. Transp. Geotech. 2021, 30, 100605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).