Movement Behavior of the Dusky Grouper Epinephelus marginatus (Lowe, 1834) in Early Life Stages
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Figueiredo, J.L.; Menezes, N.A. Manual de Peixes Marinhos do Brasil; Museu de Zoologia da Universidade de São Paulo: São Paulo, Brasil, 1980; 90 p. [Google Scholar]
- Menezes, N.A.; Buckup, P.A.; Figueiredo, J.L.; de Moura, R.L. Catálogo das Espécies de Peixes Marinhos do Brasil; Museu de Zoologia da Universidade de São Paulo: São Paulo, Brasil, 2003; 159 p. [Google Scholar]
- Ruangpanit, N.; Boonliptanon, P.; Kongkumnerd, J. Progress in the propagation and larval rearing of the grouper Epinephelus malabaricus. In Proceedings of the Seminar on Grouper Culture, Songkla, Thailand, 30 November–1 December 1993; pp. 32–44. [Google Scholar]
- IUCN, International Union for Conservation of Nature Red List of Threatened Species. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org (accessed on 12 January 2021).
- Pierre, S.; Gaillard, S.; Pré-Vot-Dálvise, N.; Aubert, J.; Rostaining-Capaillon, O.; Leung-Tack, D.; Grillasca, J.-P. Grouper aquaculture: Asian success and Mediterranean trials. Aquatic Conserv Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2008, 18, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, M.E.; Quental, H.; Barradas, A.; Pousão-Ferreira, P.; Cabrita, E.; Engrola, S. Rearing larvae of dusky grouper, Epinephelus marginatus (Lowe, 1834), (Pisces: Serranidae) in a semi-extensive mesocosm. Sci. Mar. 2009, 73 (Suppl. S1), 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glamuzina, B.; Skaramuca, B.; Glavić, N.; Kožul, V. Preliminary studies on reproduction and early life stages in rearing trials with dusky grouper, Epinephelus marginatus (Lowe, 1834). Aquac. Res. 1998, 29, 769–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glamuzina, B.; Skaramuca, B.; Glavić, N.; Kožul, V.; Dulčić, J.; Kraljević, M. Egg and early larval development of laboratory reared dusky grouper, Epinephelus marginatus (Lowe, 1834) (Pisces, Serranidae). Sci. Mar. 1998, 62, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuiman, L.A. Special considerations of fish eggs and larvae. In Fishery Science: The Unique Contributions of Early Life Stages; Fuiman, L.A., Werner, R.G., Eds.; Blackwell Science: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002; pp. 1–32. [Google Scholar]
- Balon, E.K. Types of feeding in the ontogeny of fish and the life-history model. Environ. Biol. Fish. 1986, 16, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cushing, D.H. Plankton production and year-class strength in fish populations: An update of the match/mismatch hypothesis. Adv. Mar. Biol. 1990, 26, 250–293. [Google Scholar]
- Blaxter, J.H.S. Visual thresholds and spectral sensitivity of herring larvae. J. Exp. Biol. 1968, 48, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaxter, J.H.S. Development of Sense organs and Behaviour of Teleost Larvae with Special Reference to Feeding and Predator Avoidance. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1986, 115, 98–114. [Google Scholar]
- Hunter, J.R. Swimming and feeding behavior of larval anchovy Engraulis mordax. U. S. Fish Bull. 1972, 70, 821–838. [Google Scholar]
- Munk, P.; Kiørboe, T. Feeding behaviour and swimming activity of larval herring (Clupea harengus) in relation to density of copepod nauplii. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1985, 24, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahjoub, M.-S.; Souissi, S.; Schmitt, F.G.; Nan, F.-H.; Hwang, J.S. Anisotropy and shift of sear behavior in Malabar grouper (Epinephelus malabaricus) larvae in response to prey availability. Hydrobiologia 2011, 666, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahjoub, M.-S.; Dur, G.; Souissi, S.; Schmitt, F.G.; Hwang, J.S. Multifractal anisotropic swimming: The optimal foraging behavior of grouper larvae. J. Fish Biol. 2016, 88, 1835–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fui, C.F.; Miura, A.; Nakagawa, Y.; Kato, K.; Sakamoto, W.; Takiis, K.; Myashita, S.; Senoo, S. Aeration rate adjustment at night to prevent sinking syndrome-related death in the tiger grouper Epinephelus fuscoguttatus (Perciformes: Serranidae) larvae. Aquac. Res. 2014, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Kerber, C.E.; Silva, H.K.A.; Santos, P.; Sanches, E. Reproduction and Larviculture of Dusky Grouper Epinephelus marginatus (Lowe 1834) in Brazil. J. Agriculture Sci. Technol. B 2012, 2, 229–234. [Google Scholar]
- Russo, T.; Boglione, C.; De Marzi, P.; Cataudella, S. Feeding preferences of the dusky grouper (Epinephelus marginatus, Lowe 1834) larvae reared in semi-intensive conditions: A contribution addressing the domestication of this species. Aquaculture 2009, 289, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peck, M.A.; Hufnagl, M. Can IBMs tell us why most larvae die in the sea? Model sensitivities and scenarios reveal research needs. J. Mar. Systems. 2012, 93, 77–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staaterman, E.; Paris, C.B. Modelling larval fish navigation: The way forward. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2014, 71, 918–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, S.S.; Ma, N.L.; Jusoh, A.; Ambak, M.A. A study on the optimal tank design and feed type to the growth of marble goby (Oxyeleotris marmorata Bleeker) and reduction of waste in a recirculating aquaponic system. Desalin. Water Treat. 2013, 52, 1044–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joan Holt, G. Larval Fish Nutrition; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; 436 pp. [Google Scholar]
- Strickler, J.R.; Hwang., J.-S. Matched Spatial Filters in Long Working Distance Microscopy of Phase Objects. In Focus on Multidimensional Microscopy; Cheng, P.C., Hwang, P.P., Wu, J.L., Wang, G., Kim, H., Eds.; World Scientific Publishing Pte. Ltd.: River Edge, NJ, USA, 1999; pp. 217–239. [Google Scholar]
- Katz, J.; Sheng, J. Applications of holography in fluid mechanics and particle dynamics. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2010, 42, 531–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecht, E. Optics, 4th ed.; Addison-Wesley: New York, NY, USA, 2002; 698p. [Google Scholar]
- Ghiglieno, F.; Baldasso, L.F.; Goçalo, C.G.; Aquino, N.; Lopes, R.M. Ergonomic digital holography for oceanographic applications. In Proceedings of the 3rd EOS Topical Meeting on Blue Photonics–Optics in the Sea (Blue Photonics 3), Royal Netherlands Institute for Sea Research, Texel, The Netherlands, 20 March 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Rollin, B.E.; Kessel, M.L. Guidelines for the treatment of animals in behavioural research and teaching. Anim. Behav. 1998, 55, 251–257. [Google Scholar]
- Hunter, J.R. Feeding Ecology and Predation of Marine Fish Larvae. In Marine Fish Larvae: Morphology, Ecology and Relation to Fisheries; Lasker, R., Ed.; Washington Sea Grant Program: Washington, DC, USA, 1984; pp. 34–77. [Google Scholar]
- Doi, M.; Toledo, J.D.; Golez, M.S.N.; de los Santos, M.; Ohno, A. Preliminary investigation of feeding performance of larvae of early red spotted grouper, Epinephelus coioides, reared with mixed zooplankton. Hydrobiology 1997, 358, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, T.; Pulcini, D.; Bruner, E.; Cataudella, S. Shape and Size variation: Growth and development of the dusky grouper (Epinephelus marginatus, Lowe, 1834). J. Morphol. 2009, 270, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altmann, J. Observational study of behavior: Sampling Methods. Behaviour 1974, 49, 227–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weihs, D. Energetic significance of changes in swimming modes during growth of larval anchovy, Engraulis mordax. U. S. Fish. Bull. 1980, 77, 597–604. [Google Scholar]
- Eaton, R.C.; DiDomenico, R. Role of the Teleost Escape Response during Development. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1986, 115, 128–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batty, R.S.; Blaxter, J.H.S. The effect of temperature on the burst swimming performance of fish larvae. J. Exp. Biol. 1992, 170, 187–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuiman, L.A.; Batty, R.S. What a drag it is getting cold: Partitioning the physical and physiological effects of temperature on fish swimming. J. Exp. Biol. 1997, 200, 1745–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Videler, J.J.; Weihs, D. Energetic advantages of burst-and-coast swimming of fish at high speeds. J. Exp. Biol. 1982, 97, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, C.M. Age and Growth. In Fishery Science: The Unique Contributions of Early Life Stages; Fuiman, L.A., Werner, R.G., Eds.; Blackwell Science: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002; pp. 33–63. [Google Scholar]
- Browman, H.I.; St-Pierre, J.F.; Skiftesvik, A.B.; Racca, R.G. Behaviour of Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) larvae: An attempt to link maternal condition with larval quality. In The Big Fish Bang, Proceedings of the 26th Annual Larval Fish Conference, Os, Norway, 22–26 July 2002; Browman, H.I., Skiftesvik, A.B., Eds.; Institute of Marine Research: Bergen, Norway, 2003; pp. 71–95. [Google Scholar]
- Masuda, R. Ontogeny of anti-predator behavior in hatchery-reared jack mackerel Trachurus japonicus larvae and juveniles: Patchiness formation, swimming capability, and interaction with jellyfish. Fish. Sci. 2006, 72, 1225–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesney, E.J. Foraging behavior of bay anchovy larvae Anchoa mitchilli. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2008, 362, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govoni, J.J.; Boehlert, G.W.; Watanabe, Y. The physiology of digestion in fish larvae. Environ. Biol. Fish. 1986, 16, 59–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobcroft, J.M.; Pankhurst, P.M. Sensory organ development cultured striped trumpeter larvae Latris lineata: Implications for feeding behavior. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2003, 54, 669–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frederich, B.; Adriaens, D.; Vandewalle, P. Ontogenetic shape changes in Pomacentridae (Teleostei, Perciformes) and their relationships with feeding strategies: A geometric morphometric approach. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2008, 95, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukai, Y.; Lim, L.S.; Saad, S. Retinomotor response in larvae of brown-marbled grouper, Epinephelus fuscoguttatus. J. Fish. and Aquati. Sci. 2012, 7, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehtiniem, I.M. Swim or hide: Predator cues cause species specific reactions in young fish larvae. J. Fish Biol. 2005, 66, 1285–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coughlin, D.J.; Strickler, J.R.; Sanderson, B. Swimming and search behavior in clownfish, Amphiprion perideraion, larvae. Anim. Behav. 1992, 44, 427–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skiftesvik, A.B. Changes in behaviour at onset of exogenous feeding in marine fish larvae. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1992, 49, 1570–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, R.; Bellwood, D.R.; Job, S.D. Development of swimming abilities in reef fish larvae. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2000, 202, 163–173. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, R.; Bellwood, D.R. Effects of feeding on the sustained swimming abilities of late-stage larval Amphiprion melanopus. Coral Reefs 2001, 20, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munk, P. Foraging behavior of larval cod (Gadus morhua) influenced by prey density and hunger. Mar. Biol. 1995, 122, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, R.; Shoji, J.; Aoyama, M.; Tanaka, M. Chub mackerel larvae fed fish larvae can swim faster than those fed rotifers and Artemia nauplii. Fish. Sci. 2002, 68, 320–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, T.J.; Crowder, L.B.; Rice, J.A.; Marschall, E.A. Larval size and recruitment mechanisms in fishes: Toward a conceptual framework. Can. J. Fish. Aquati Sci. 1988, 45, 1657–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drucker, E.G.; Lauder, G.V. Locomotor forces on a swimming fish: Three-dimensional vortex wake dynamics quantified using digital particle image velocimetry. J. Exp. Biol. 1999, 202, 2393–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leis, J.M.; Yerman, M.N. Behavior of larval butterflyfishes (Teleostei: Chaetodontidae) at settlement on coral reefs. Copeia. 2012, 2012, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fashingbauer, M.C.; Tuttle, L.J.; Robinson, H.E.; Strickler, J.R.; Hartline, D.K.; Lenz, P.H. Predatory posture and performance in a precocious larval fish targeting evasive copepods. J. Exp. Biol. 2019, 222, jeb191411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borla, M.A.; Palecek, B.; Budick, S.; O’malley, D.M. Prey capture by larval zebrafish: Evidence for fine axial motor control. Brain Behav. Evol. 2002, 60, 207–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eve Robinson, H.; Strickler, J.R.; Henderson, M.J.; Hartline, D.K.; Lenz, P.H. Predation strategies of larval clownfish capturing evasive copepod prey. Mar. Ecol. Progr. Ser. 2019, 614, 125–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, K.; Johnson, N.; Beaulieu, W.; Cathcart, E.; Tirrell, G.; Colin, S.P.; Gemmell, B.J.; Dabiri, J.O.; Costello, J.H. Bending rules for animal propulsion. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahjoub, M.-S.; Souissi, S.; Michalec, F.-G.; Schmitt, F.G.; Hwang, J.-S. Swimming kinematics of Eurytemora affinis (Copepoda, Calanoida) reproductive stages and differential vulnerability to predation of larval Dicentrarchus labrax (Teleosti, Perciformes). J. Plankton Res. 2011, 33, 1095–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, R.C.; Bombardieri, R.A.; Meyer, D.L. The Mauthner-Initiated Startle Response in Teleost Fish. J. Exp. Biol. 1977, 66, 65–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazzola, M.; Van Rees, W.M.; Koumoutsakos, P. C-start: Optimal start of larval fish. J. Fluid. Mech. 2012, 698, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benítez-Santana, T.; Juarez-Carrillo, E.; Betancor, M.B.; Torrecillas, S.; Caballero, M.J.; Izquierdo, M.S. Increased Mauthner cell activity and escaping behavior in seabream fed long-chain PUFA. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 107, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Pankhurst, P.M.; Montgomery, J.C.; Pankhurst, N.W. Growth, development and behaviour of artificially reared larval Pagrus auratus (Bloch & Schneider, 1801) (Sparidae). Mar. Freshw. Res. 1991, 42, 391–398. [Google Scholar]
- Hjort, J. Fluctuations in the Great Fisheries of Northern Europe Viewed in the Light of Biological Research. Rapports et Procès-verbaux des Reunions, Conseil International pour l’Exploration de la Mer; ICES: Bergen, Norway, 1914; Volume 20, pp. 1–228. [Google Scholar]
- Strickler, J.R.; Udvadia, A.J.; Marino, J.; Radabaugh, N.; Ziarek, J.; Nihongi, A. Visibility as a factor in the copepod-planktivorous fish relationship. Sci. Mar. 2005, 69 (Suppl. S1), 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yúfera, M. Feeding behavior in larval fish. 2011. In Larval Fish Nutrition, Holt, G.J., Ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 285–305. [Google Scholar]
- Carassou, L.; Ponton, D. Relative importance of water column vs zooplankton variables in the determination of late-stage larval fish assemblage structure in coastal waters of a coral reef lagoon. Sci. Mar. 2009, 73 (Suppl. S1), 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, R.M.; Katsuragawa, M.; Dias, J.F.; Montú, M.A.; Muelbert, J.H.; Gorri, C.; Brandini, F.P. Zooplankton and ichthyoplankton distribution on the southern Brazilian shelf: An overview. Sci. Mar. 2006, 70, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, C.M. Connectivity and management of Caribbean coral reefs. Science 1997, 278, 1454–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leis, J.M. Are larvae of demersal fishes plankton or nekton? Adv. Mar. Biol. 2006, 51, 57–141. [Google Scholar]
- Houde, E.D. Emerging from Hjort’s shadow. J. Northwest Atl. Fish. Sci. 2008, 41, 53–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goçalo, C.G.; Katsuragawa, M.; Silveira, I.C.A. Patterns of distribution and abundance of larval Phosichthyidae in the Southeastern Brazilian Waters. Braz. J. Oceanogr. 2011, 59, 213–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhuang, X.; Qu, M.; Zhang, X.; Ding, S. A comprehensive description and evolutionary analysis of 22 grouper (Perciformes, Epinephelidae) Mitochondrial Genomes with Emphasis on Two Novel Genome Organizations. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aride, P.H.R.; Gomes, M.F.S.; Azevedo, D.G.; Sangali, G.R.; Silva, A.C.F.; Lavander, H.D.; Faggio, C. Dusky grouper Epinephelus marginatus growth and survival when exposed to different photoperiods. Fishes 2021, 6, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
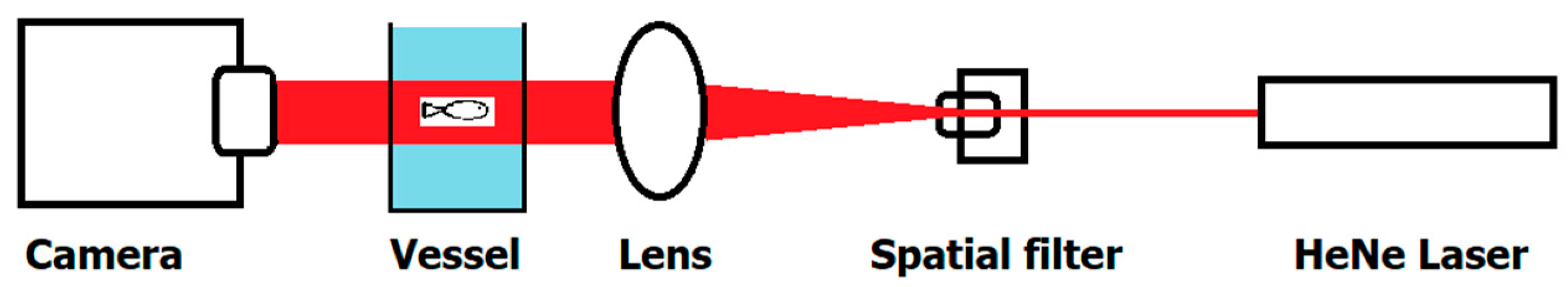
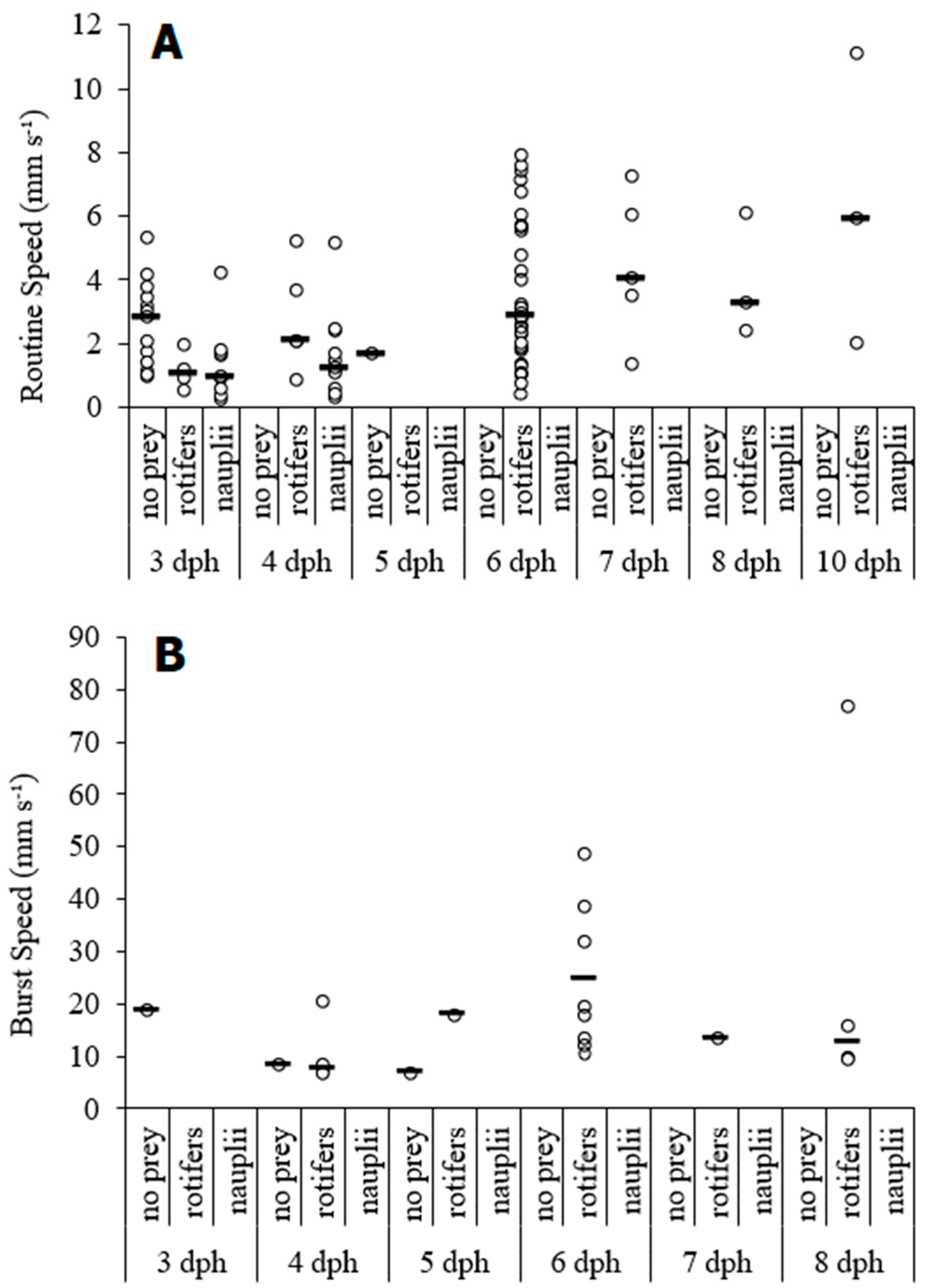
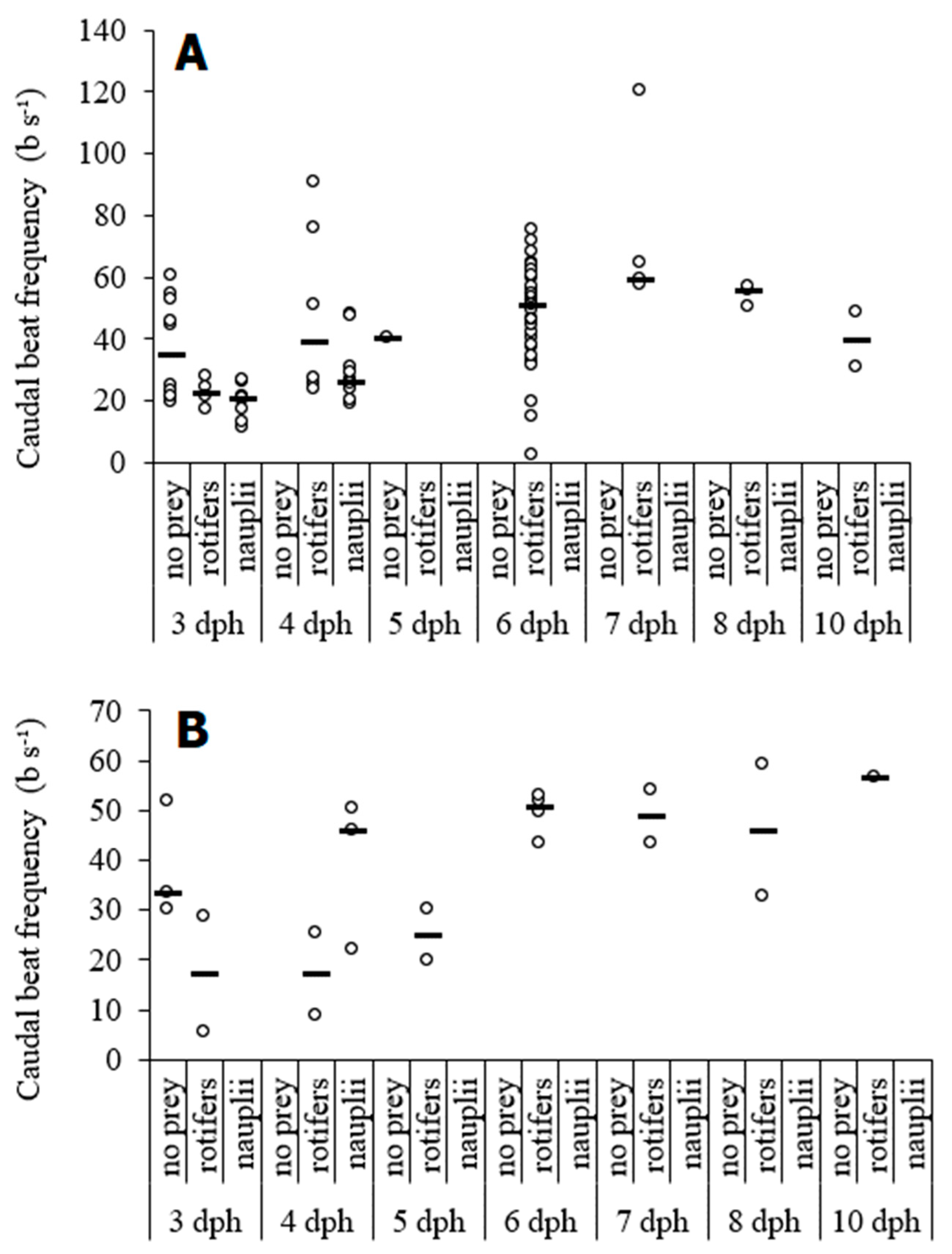
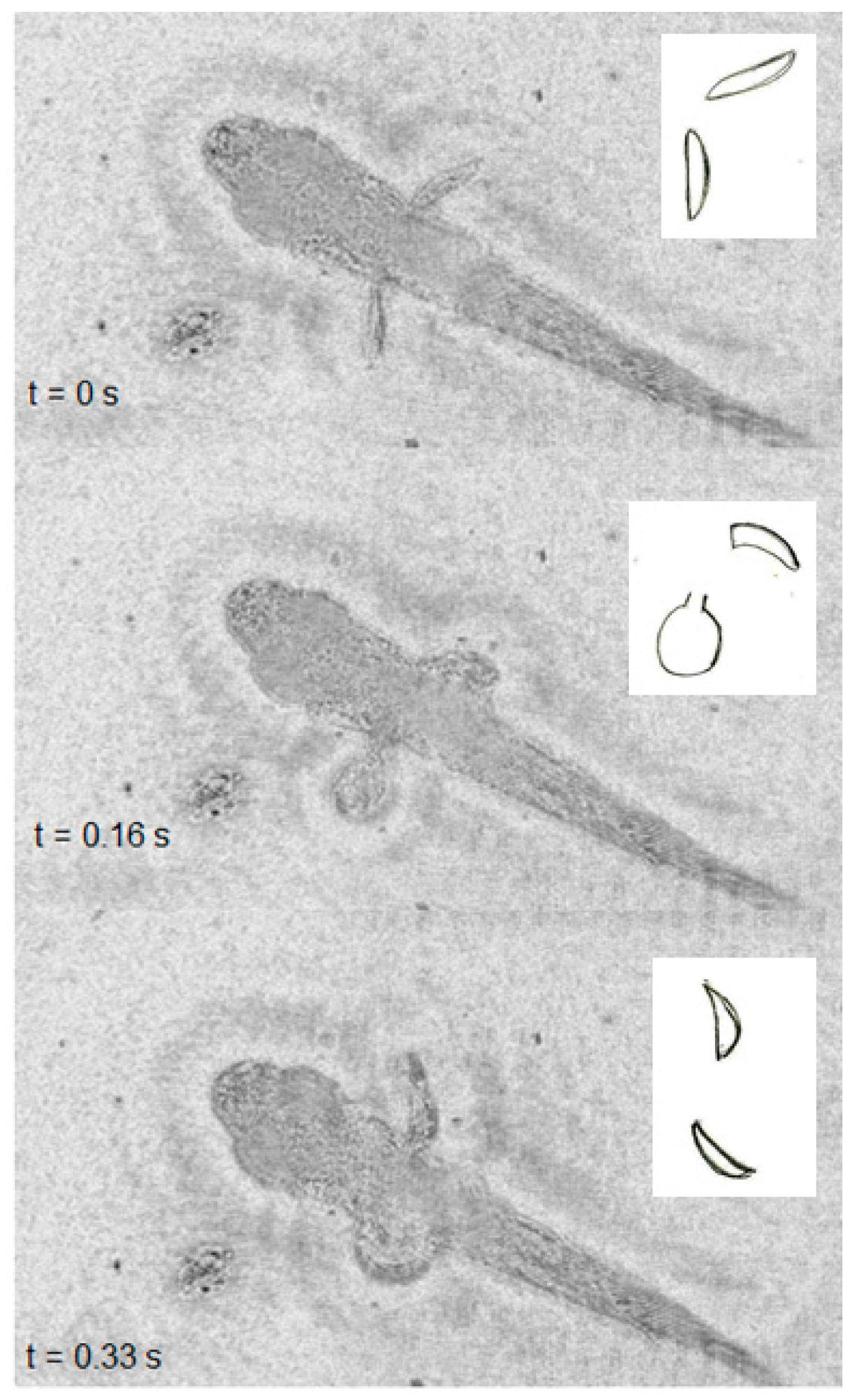
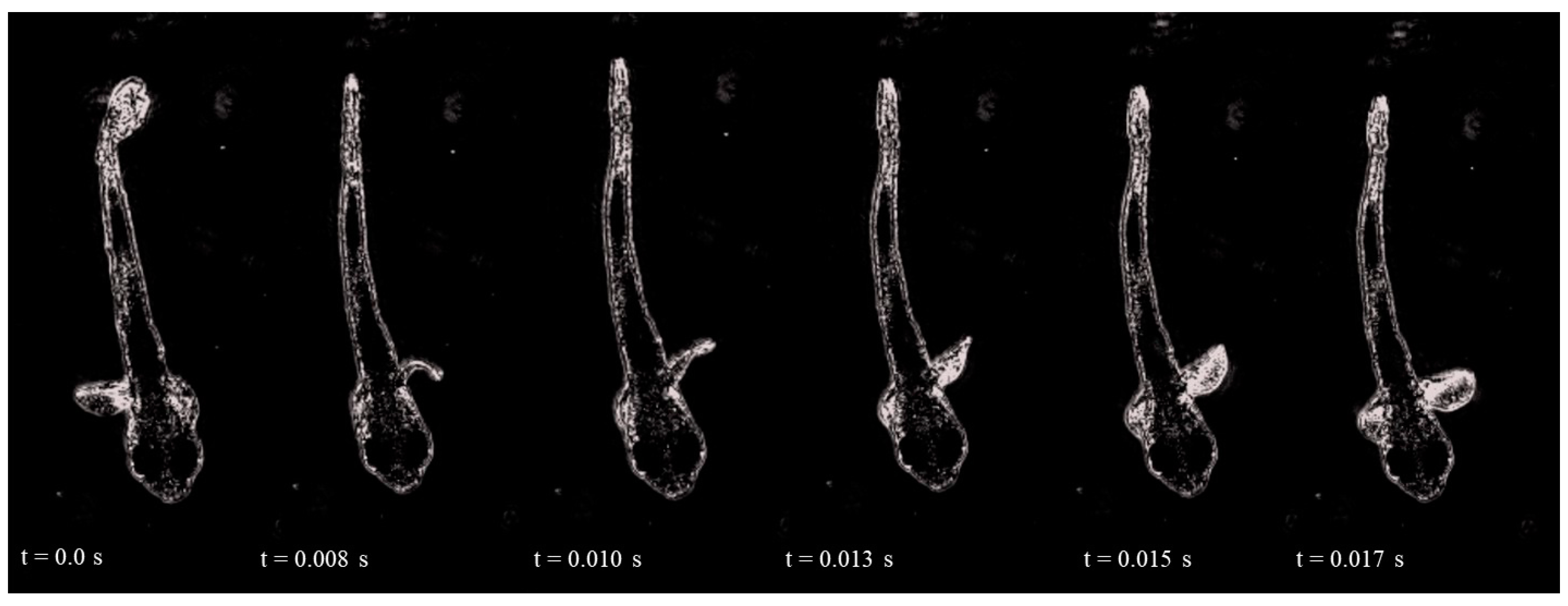
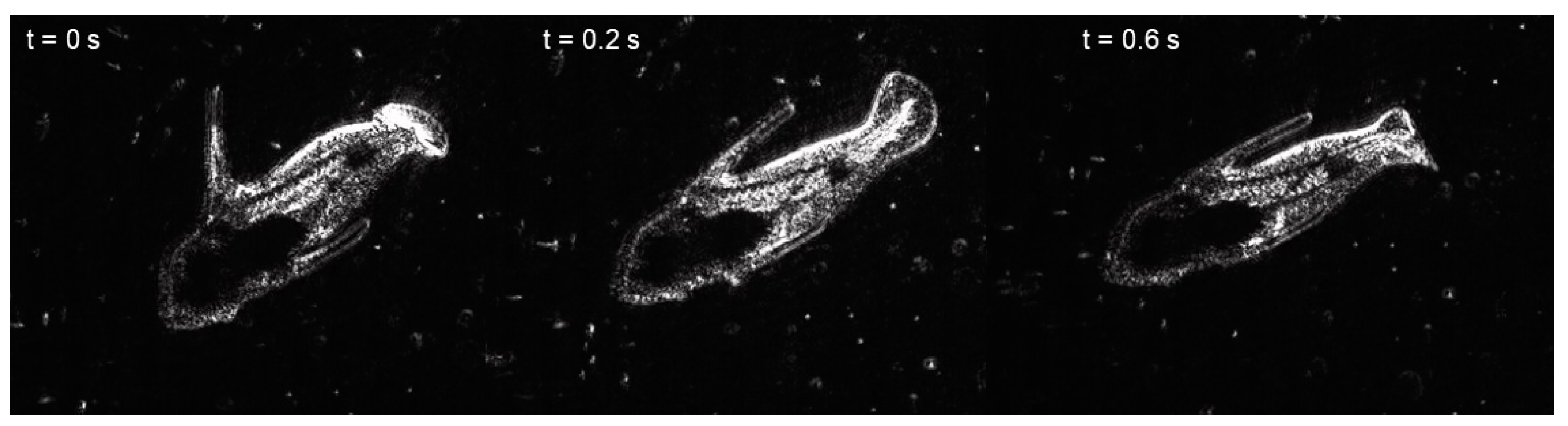
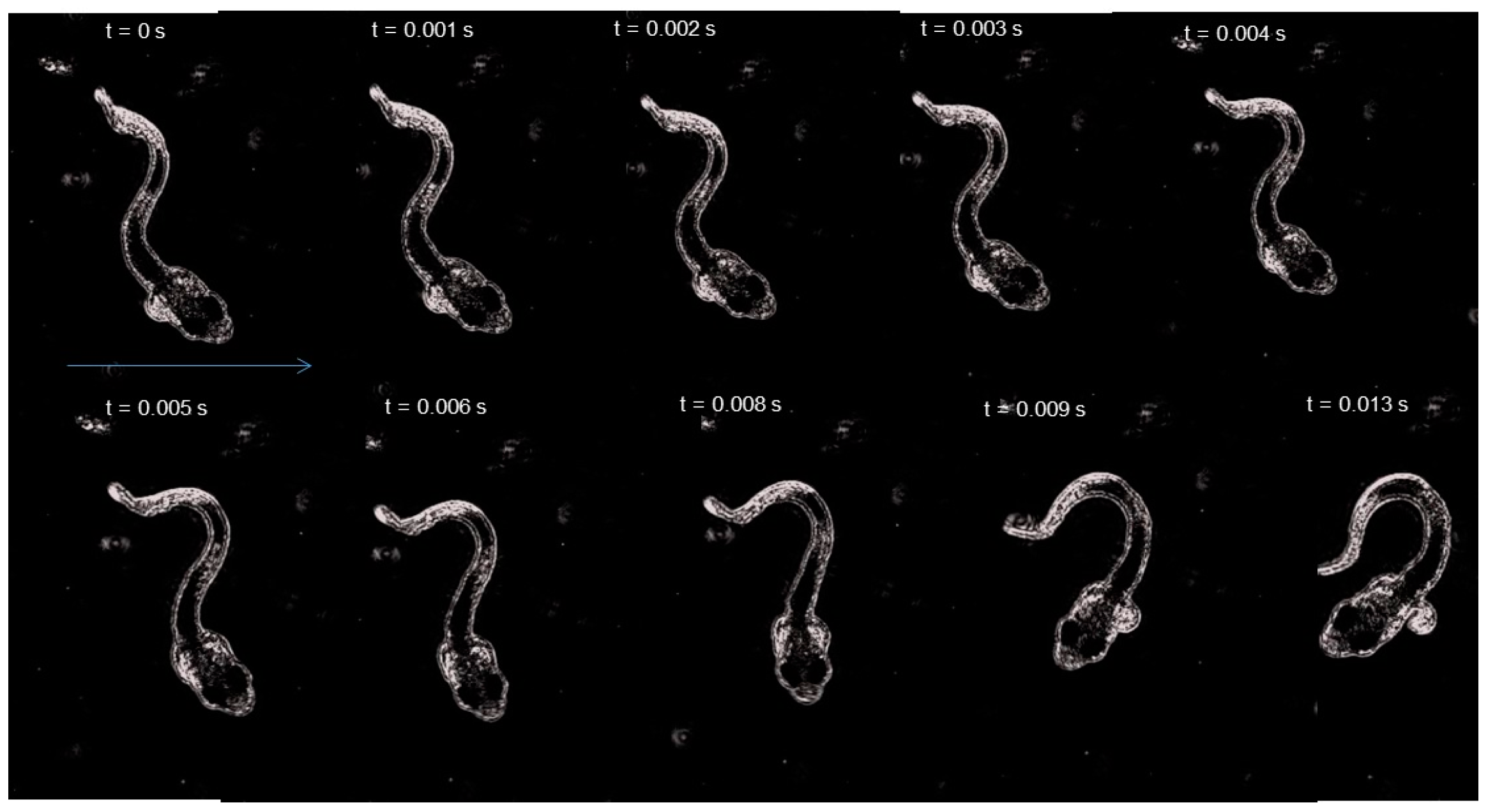
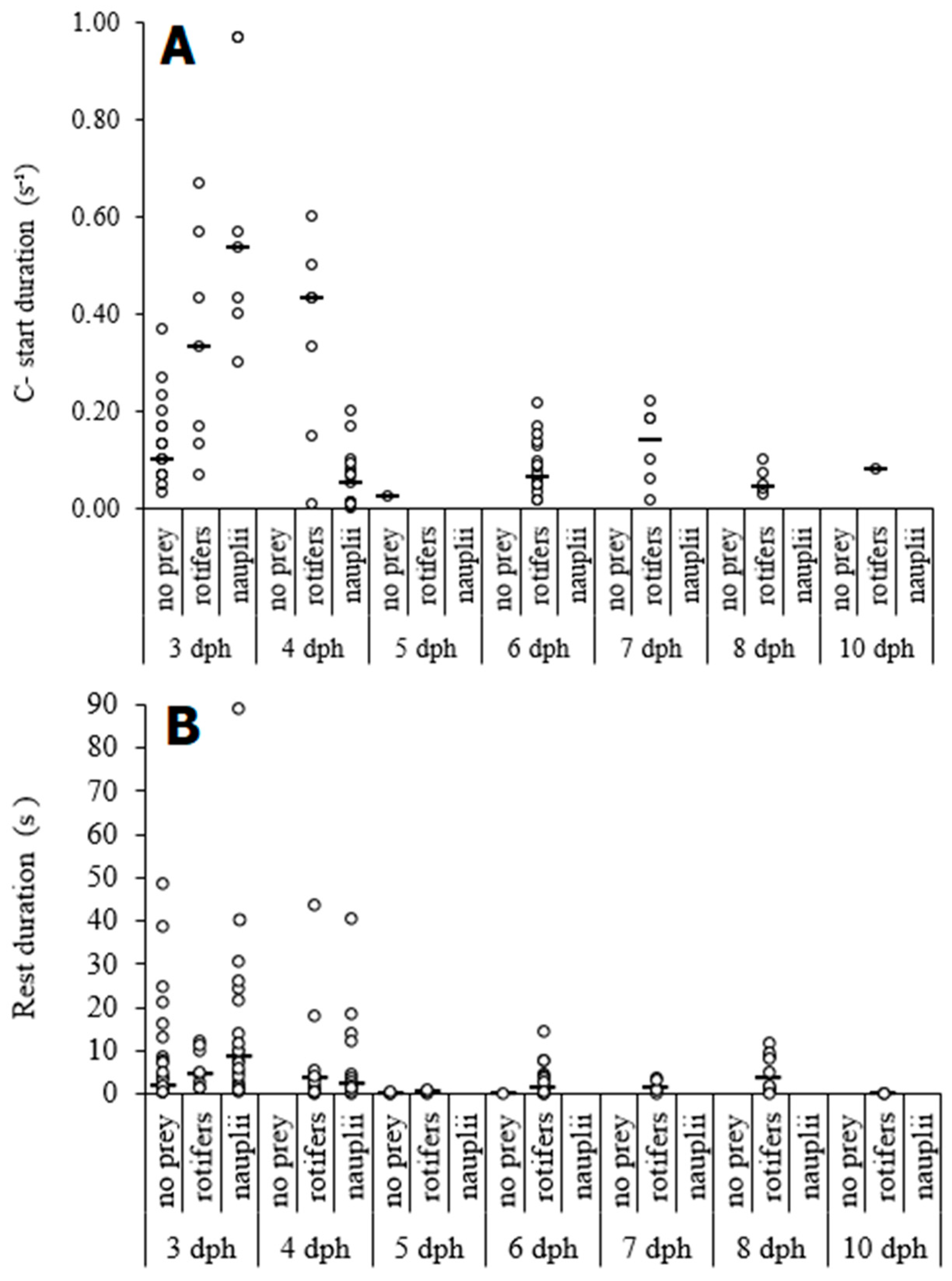
| dph | Size (mm) | Routine Speed (BL s−1) | # | Burst Speed (BL s−1) | # |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 2.0 ± 0.0 | 1.0 ± 0.7 | 26 | 9.2 ± 0.0 | 1 |
| 4 | 2.0 ± 0.0 | 1.0 ± 0.8 | 16 | 5.3 ± 3.3 | 5 |
| 5 | 2.0 ± 0.0 | 0.8 ± 0.0 | 1 | 6.4 ± 4.3 | 2 |
| 6 | 2.8 ± 0.0 | 1.3 ± 0.8 | 35 | 8.7 ± 5.1 | 8 |
| 7 | 3.0 ± 0.1 | 1.5 ± 0.8 | 5 | 4.4 ± 0.0 | 1 |
| 8 | 3.1 ± 0.0 | 1.3 ± 0.6 | 3 | 9.1 ± 10.7 | 4 |
| 10 | 3.9 ± 0.0 | 1.6 ± 1.2 | 3 | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Goçalo, C.G.; Lopes, R.M. Movement Behavior of the Dusky Grouper Epinephelus marginatus (Lowe, 1834) in Early Life Stages. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 1068. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12071068
Goçalo CG, Lopes RM. Movement Behavior of the Dusky Grouper Epinephelus marginatus (Lowe, 1834) in Early Life Stages. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2024; 12(7):1068. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12071068
Chicago/Turabian StyleGoçalo, Cássia Gongora, and Rubens M. Lopes. 2024. "Movement Behavior of the Dusky Grouper Epinephelus marginatus (Lowe, 1834) in Early Life Stages" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 12, no. 7: 1068. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12071068
APA StyleGoçalo, C. G., & Lopes, R. M. (2024). Movement Behavior of the Dusky Grouper Epinephelus marginatus (Lowe, 1834) in Early Life Stages. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 12(7), 1068. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12071068







