Trawling-Induced Sedimentary Dynamics in Submarine Canyons of the Gulf of Palermo (SW Mediterranean Sea)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.1.1. Geological Setting
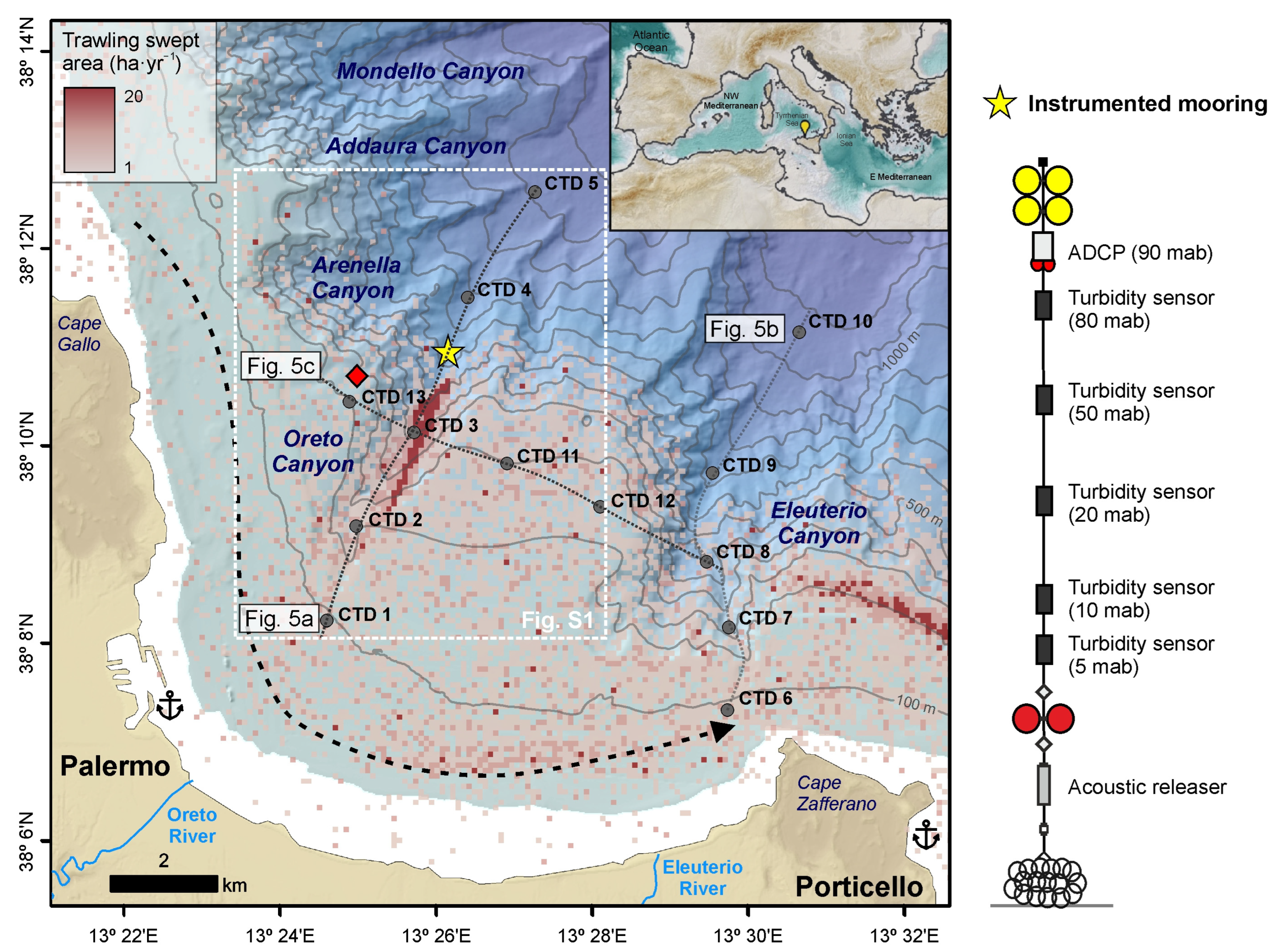
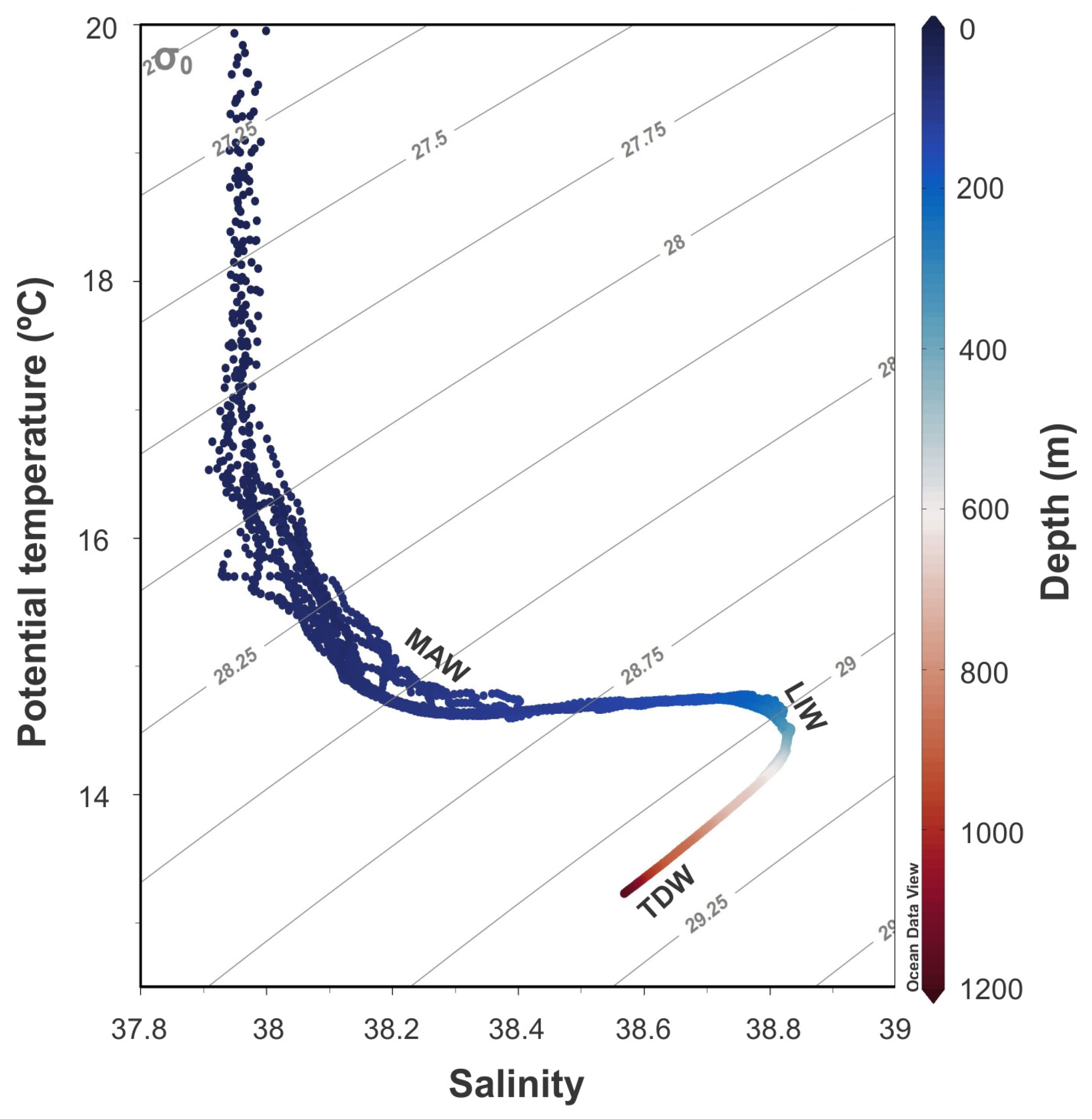
2.1.2. Oceanographic Setting
2.1.3. Bottom Trawling Grounds
2.2. Sampling
2.3. Field Data Analyses
2.3.1. Mooring Data
2.3.2. CTD Data
2.4. Ancillary Data
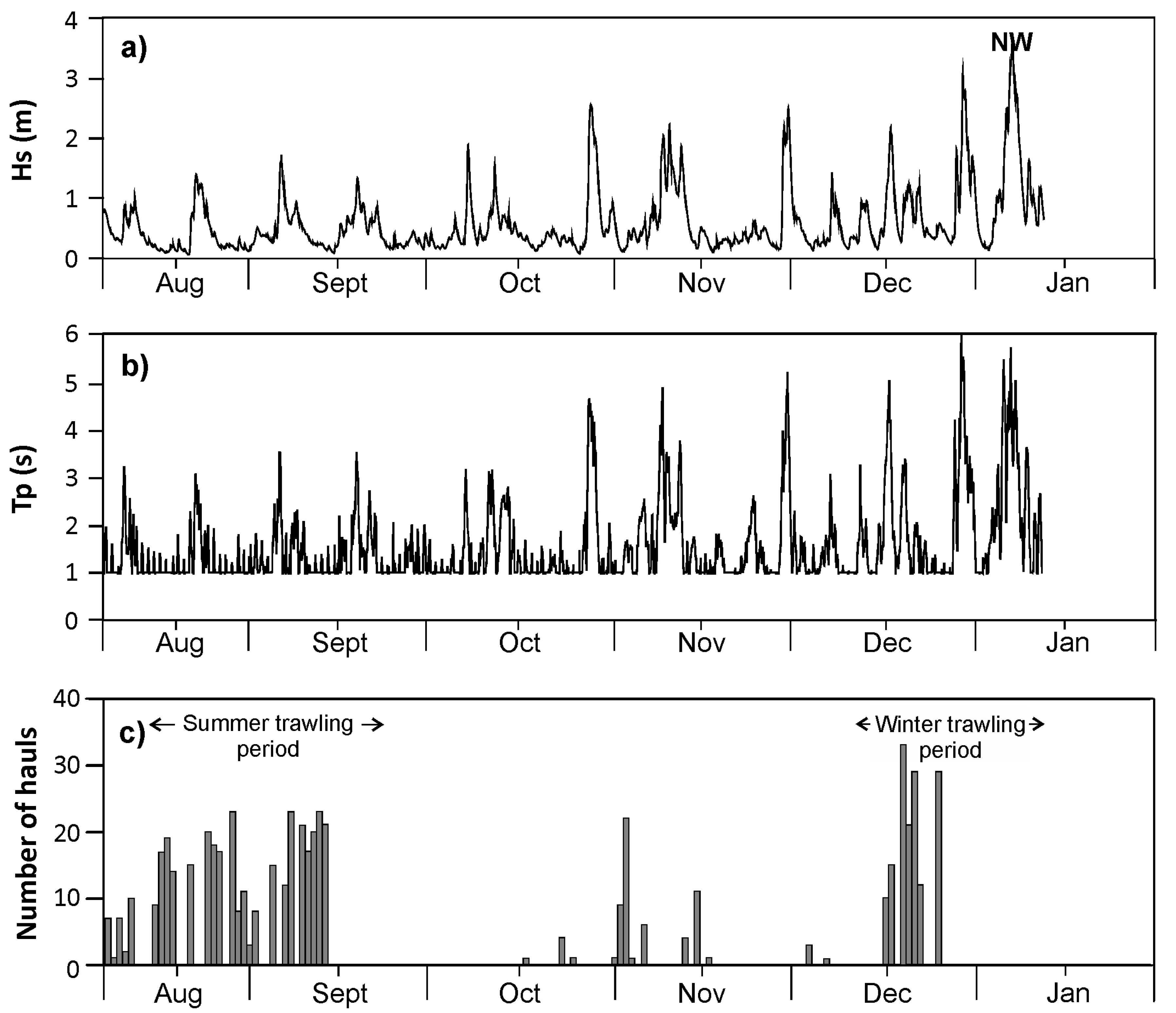
2.4.1. Wave Conditions
2.4.2. Fishing Effort
3. Results
3.1. Forcing Conditions
3.1.1. Wave Regime
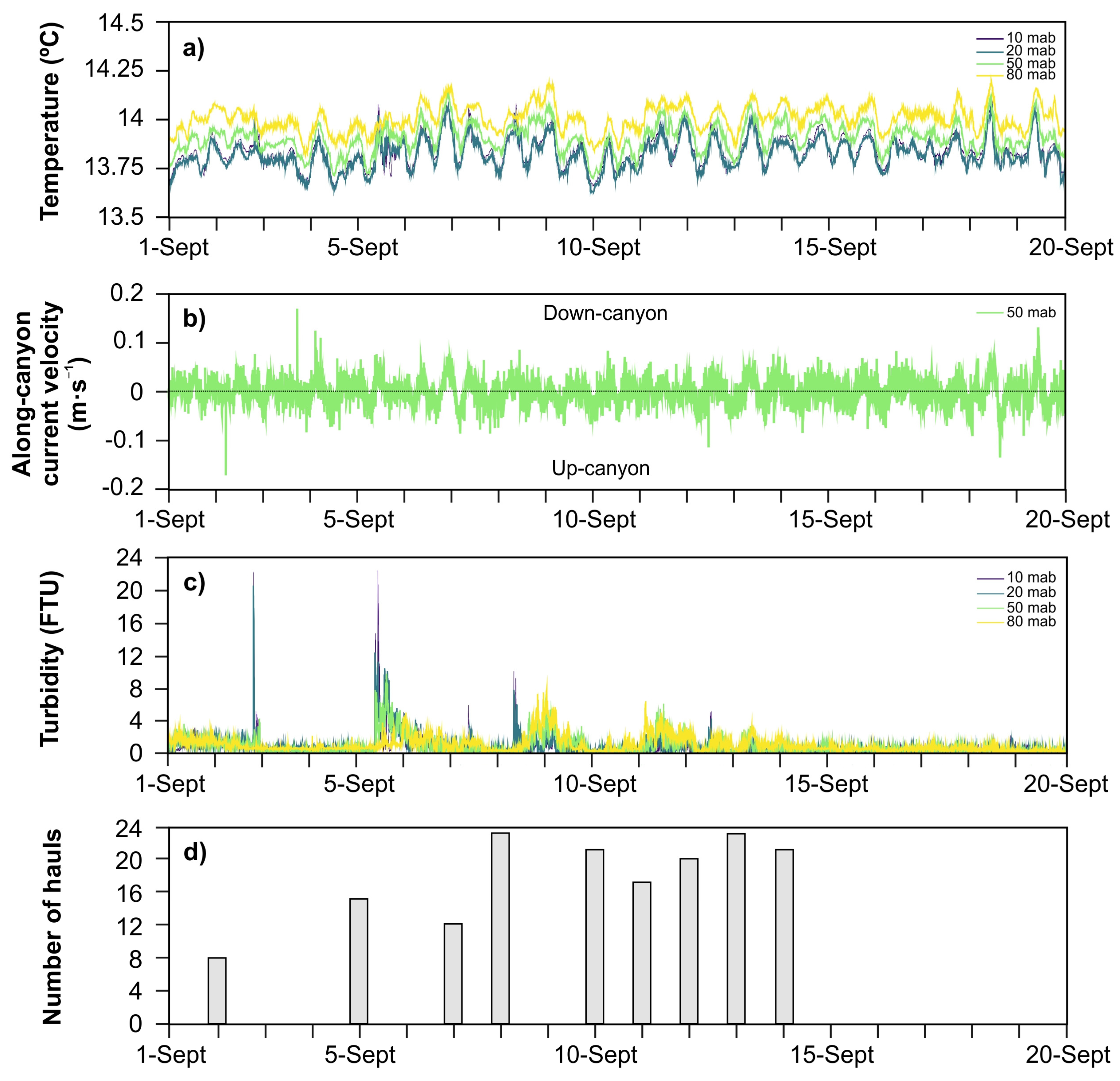
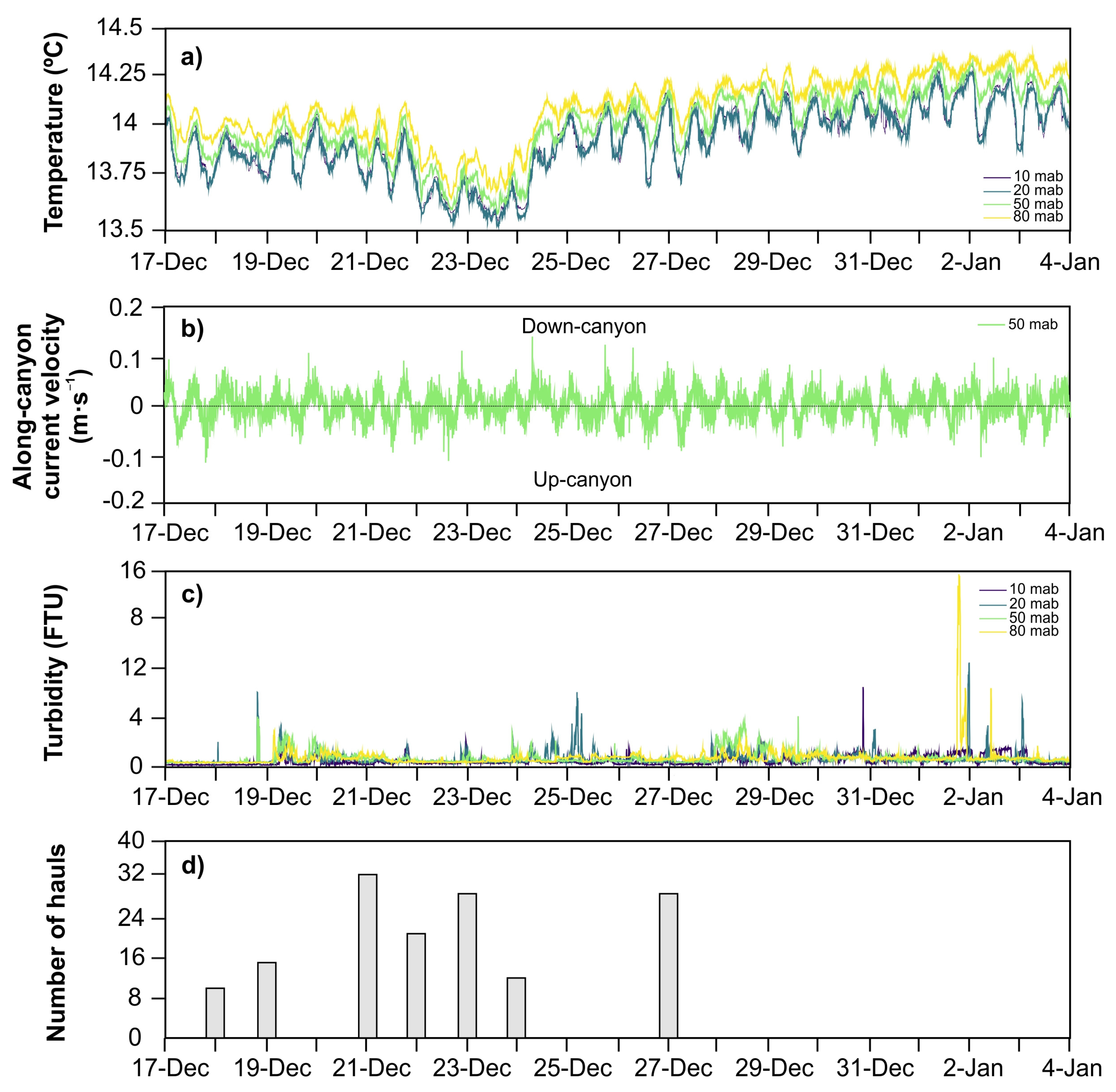
3.1.2. Bottom Trawling Activity
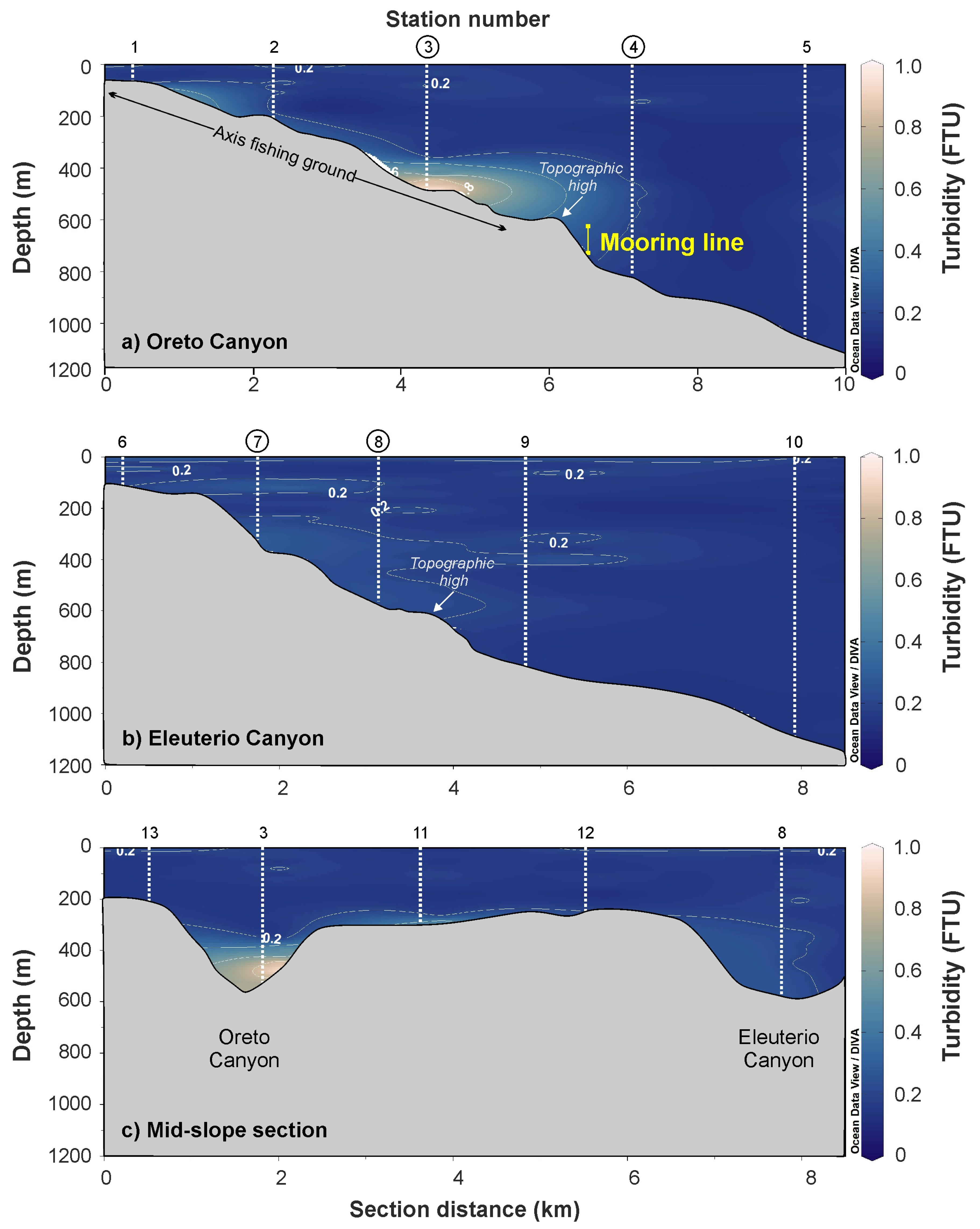
3.2. Hydrographic and Turbidity Structure in Oreto and Eleuterio Canyons
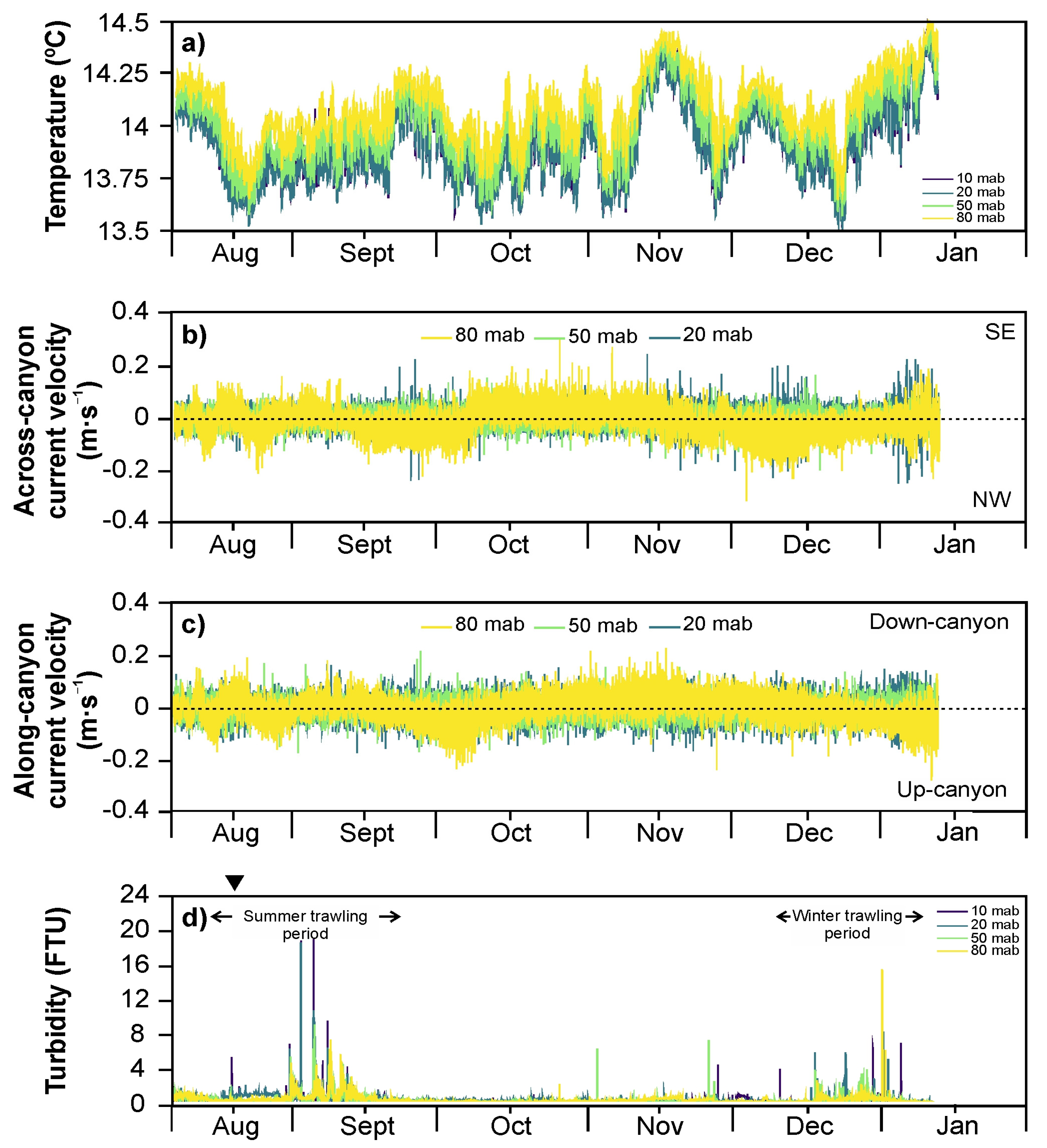
3.3. Time Series of Temperature, Currents, and Turbidity in the Oreto Canyon
4. Discussion
4.1. Role of Bottom Trawling as a Contemporary Mechanism of Sediment Resuspension
4.2. Role of Water Masses and Current Variability as a Mechanism of Suspended Sediment Transport
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Harris, P.T.; Whiteway, T. Global distribution of large submarine canyons: Geomorphic differences between active and passive continental margins. Mar. Geol. 2011, 285, 69–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, S.E.; Durrieu de Madron, X. A review of the role of submarine canyons in deep-ocean exchange with the shelf. Ocean Sci. 2009, 5, 607–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Stigter, H.C.; Jesus, C.C.; Boer, W.; Richter, T.O.; Costa, A.; van Weering, T.C. Recent sediment transport and deposition in the Lisbon-Setúbal and Cascais submarine canyons, Portuguese continental margin. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2011, 58, 2321–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talling, P.J. On the triggers, resulting flow types and frequencies of subaqueous sediment density flows in different settings. Mar. Geol. 2014, 352, 155–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puig, P.; Palanques, A.; Martín, J. Contemporary sediment-transport processes in submarine canyons. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2014, 6, 53–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porter, M.; Inall, M.E.; Hopkins, J.; Palmer, M.R.; Dale, A.C.; Aleynik, D.; Barth, J.A.; Mahaffey, C.; Smeed, D.A. Glider observations of enhanced deep water upwelling at a shelf break canyon: A mechanism for cross-slope carbon and nutrient exchange. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2016, 121, 7575–7588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Leo, F.C.; Smith, C.R.; Rowden, A.A.; Bowden, D.A.; Clark, M.R. Submarine canyons: Hotspots of benthic biomass and productivity in the deep sea. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2010, 277, 2783–2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Leo, F.C.; Vetter, E.W.; Smith, C.R.; Rowden, A.A.; McGranaghan, M. Spatial scale-dependent habitat heterogeneity influences submarine canyon macrofaunal abundance and diversity off the Main and Northwest Hawaiian Islands. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2014, 104, 267–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetter, E.W.; Smith, C.R.; De Leo, F.C. Hawaiian hotspots: Enhanced megafaunal abundance and diversity in submarine canyons on the oceanic islands of Hawaii. Mar. Ecol. 2010, 31, 183–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Arcaya, U.; Ramirez-Llodra, E.; Aguzzi, J.; Allcock, A.L.; Davies, J.S.; Dissanayake, A.; Harris, P.; Howell, K.; Huvenne, V.A.I.; Macmillan-Lawler, M.; et al. Ecological Role of Submarine Canyons and Need for Canyon Conservation: A Review. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrugio, H. A refugium for the spawners of exploited Mediterranean marine species: The canyons of the continental slope of the Gulf of Lion. In Mediterranean Submarine Canyons: Ecology and Governance; Würtz, M., Ed.; International Union for Conservation of Nature: Gland, Switzerland, 2012; pp. 45–50. [Google Scholar]
- O’Neill, F.G.; Summerbell, K. The mobilization of sediment by demersal otter trawls. Mar. Pollut. Mar. 2011, 62, 1088–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín, J.; Puig, P.; Palanques, A.; Ribó, M. Trawling-induced daily sediment resuspension in the flank of a Mediterranean submarine canyon. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2014, 104, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, J.; Puig, P.; Masqué, P.; Palanques, A.; Sánchez-Gómez, A. Impact of bottom trawling on deep-sea sediment properties along the flanks of a submarine canyon. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neill, F.G.; Ivanovic, A. The physical impact of towed demersal fishing gears on soft sediments. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2016, 73, i5–i14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depestele, J.; Ivanovic, A.; Degrendele, K.; Esmaeili, M.; Polet, H.; Roche, M.; Summerbell, K.; Teal, L.R.; Vanelslander, B.; O’Neill, F.G. Measuring and assessing the physical impact of beam trawling. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2016, 73, i15–i26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, E.; Johnson, M.P.; Wilson, A.M.; Gerritsen, H.D.; Kiriakoulakis, K.; Allcock, A.L.; White, M. Bottom trawling at Whittard Canyon: Evidence for seabed modification, trawl plumes and food source heterogeneity. Prog. Oceanogr. 2018, 169, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanques, A.; Martín, J.; Puig, P.; Guillén, J.; Company, J.B.; Sardà, F. Evidence of sediment gravity flows induced by trawling in the Palamós (Fonera) submarine canyon (northwestern Mediterranean). Deep Sea Res. I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2006, 53, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, J.; Palanques, A.; Puig, P. Near-bottom horizontal transfer of particulate matter in the Palamós Submarine Canyon (NW Mediterranean). J. Mar. Res. 2007, 65, 193–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puig, P.; Canals, M.; Company, J.B.; Martín, J.; Amblas, D.; Lastras, G.; Palanques, A. Ploughing the deep sea floor. Nature 2012, 489, 286–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chronis, G.; Lykousis, V.; Georgopoulos, D.; Zervakis, V.; Stavrakakis, S.; Poulos, S. Suspended particulate matter and nepheloid layers over the southern margin of the Cretan Sea (NE Mediterranean): Seasonal distribution and dynamics. Prog. Oceanogr. 2000, 46, 163–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A.M.; Kiriakoulakis, K.; Raine, R.; Gerritsen, H.D.; Blackbird, S.; Allcock, A.L.; White, M. Anthropogenic influence on sediment transport in the Whittard Canyon, NE Atlantic. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 101, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arjona-Camas, M.; Puig, P.; Palanques, A.; Emelianov, M.; Durán, R. Evidence of trawling-induced resuspension events in the generation of nepheloid layers in the Foix submarine canyon (NW Mediterranean). J. Mar. Syst. 2019, 196, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arjona-Camas, M.; Puig, P.; Palanques, A.; Durán, R.; White, M.; Paradis, S.; Emelianov, M. Natural vs. trawling-induced water turbidity and suspended sediment transport variability within the Palamós Canyon (NW Mediterranean). Mar. Geophys. Res. 2021, 42, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, J.; Puig, P.; Palanques, A.; Masqué, P.; García-Orellana, J. Effect of commercial trawling on the deep sedimentation in a Mediterranean submarine canyon. Mar. Geol. 2008, 252, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puig, P.; Martín, J.; Masqué, P.; Palanques, A. Increasing sediment accumulation rates in La Fonera (Palamós) submarine canyon axis and their relationship with bottom trawling activities. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 8106–8113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradis, S.; Puig, P.; Masqué, P.; Juan-Díaz, X.; Martín, J.; Palanques, A. Bottom trawling along submarine canyons impacts deep sedimentary regimes. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paradis, S.; Puig, P.; Sánchez-Vidal, A.; Masqué, P.; García-Orellana, J.; Calafat, A.; Canals, M. Spatial distribution of sedimentation-rate increases in Blanes Canyon caused by technification of bottom trawling fleet. Prog. Oceanogr. 2018, 169, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradis, S.; Masqué, P.; Puig, P.; Juan-Diaz, X.; Gorelli, G.; Company, J.B.; Palanques, A. Enhancement of sedimentation rates in the Foix Canyon after the renewal of trawling fleets in the early XXIst century. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2018, 132, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo Iacono, C.; Sulli, A.; Agate, M.; Lo Presti, V.; Pepe, F.; Catalano, R. Submarine canyon morphologies in the Gulf of Palermo (Southern Tyrrhenian Sea) and possible implications for geo-hazard. Mar. Geophys. Res. 2011, 32, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo Iacono, C.; Sulli, A.; Agate, M. Submarine canyons of north-western Sicily (Southern Tyrrhenian Sea): Variability in morphology, sedimentary processes, and evolution on a tectonically active margin. Deep-Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2014, 104, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradis, S.; Lo Iacono, C.; Masqué, P.; Puig, P.; Palanques, A.; Russo, T. Evidence of large increases in sedimentation rates due to fish trawling in submarine canyons of the Gulf of Palermo (SW Mediterranean). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 172, 112861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palanques, A.; Paradis, S.; Puig, P.; Masqué, P.; Lo Iacono, C. Effects of bottom trawling on trace metal contamination of sediments along the submarine canyons of the Gulf of Palermo (southwestern Mediterranean). Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 814, 152658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Leonardo, R.; Bellanca, A.; Capotondi, L.; Cundy, A.; Neri, R. Possible impacts of Hg and PAH contamination on benthic foraminiferal assemblages: An example from the Sicilian coast, Central Mediterranean. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 388, 168–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzo, S.; Basile, S.; Caruso, A.; Cosentino, C.; Tranchina, L.; Brai, M. Dating of a sediment Core by 210Pbex method and pb pollution chronology in the Palermo gulf (Italy). Water Air Soil Pollut. 2009, 202, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannina, G.; Viviani, G. Water quality modelling for ephemeral rivers: Model development and parameter assessment. J. Hydrol. 2010, 393, 186–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tranchina, L.; Basile, S.; Brai, M.; Caruso, A.; Cosentino, C.; Miccichè, S. Distribution of heavy metals in marine sediments of Palermo Gulf (Sicily, Italy). Water Air Soil Pollut. 2008, 191, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiocci, F.L.; Ridente, D. Regional-scale seafloor mapping and geohazard assessment. The experience from the Italian project MaGIC (Marine Geohazards along the Italian Coasts). Mar. Geophys. Res. 2011, 32, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Vara, A.; Parras-Berrocal, I.M.; Izquierdo, A.; Sein, D.V.; Cabos, W. Climate change signal in the ocean circulation of the Tyrrhenian Sea. Earth Syst. Dynam. 2002, 13, 303–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinardi, N.; Masetti, E. Variability of the large scale general circulation of the Mediterranean Sea from observations and modelling: A review. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2000, 158, 153–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astraldi, M.; Gasparini, G.P.; Vetrano, A.; Vignudelli, S. Hydrographic characteristics and interannual variability of water masses in the central Mediterranean: A sensitivity test for long-term changes in the Mediterranean Sea. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2002, 49, 661–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millot, C. Circulation in the western Mediterranean Sea. J. Mar. Syst. 1999, 20, 423–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparnocchia, S.; Gasparini, G.P.; Astraldi, M.; Borghini, M.; Pistek, P. Dynamics and mixing of the Eastern Mediterranean outflow in the Tyrrhenian basin. J. Mar. Syst. 1999, 20, 301–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, A.R.; Leslie, W.G.; Thecharis, A.; Lascaratos, A. Mediterranean Sea circulation. Encycl. Ocean Sci. 2001, 1, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budillon, G.; Gasparini, G.P.; Schroeder, K. Persistence of an eddy signature in the central Tyrrhenian basin. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2009, 56, 713–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astraldi, M.; Gasparini, G.P. The seasonal characteristics of the circulation in the Tyrrhenian Sea. Seas. Interannual Var. West. Mediterr. Sea 1994, 46, 661–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetrano, A.; Napolitano, E.; Iacono, R.; Schroeder, K.; Gasparini, G.P. Tyrrhenian Sea circulation and water mass fluxes in spring 2004: Observations and model results. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2010, 115, C06023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacono, R.; Napolitano, E.; Marullo, S.; Artale, V.; Vetrano, A. Seasonal variability of the Tyrrhenian Sea surface geostrophic circulation as assessed by altimeter data. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2013, 43, 1710–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhein, M.; Send, U.; Klein, B.; Krahmann, G. Interbasin deep water exchange in the western Mediterranean. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1999, 104, 23495–23508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuda, J.L.; Etope, G.; Millot, C.; Favali, P.; Calcara, M.; Smriglio, G.; Boschi, E. Warming, salting and origin of the Tyrrhenian Deep Water. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 4-1–4-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millot, C. Another description of the Mediterranean Sea outflow. Prog. Oceanogr. 2009, 66, 231–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falco, P.; Trani, M.; Zambianchi, E. Water mass structure and deep mixing processes in the Tyrrhenian Sea: Results from the VECTOR project. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2016, 113, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menna, M.; Poulain, P.M.; Ciani, D.; Doglioli, A.; Notarstefano, G.; Gerin, R.; Rio, M.H.; Santoleri, R.; Gauci, A.; Drago, A. New insights of the Sicily Channel and southern Tyrrhenian Sea variability. Water 2019, 11, 1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Istituto Idrografico della Marina. Atlante della Correnti Superficiali dei Mari Italiani; Istituto Idrografico della Marina: Genoa, Italy, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Solomon, O.M.; Larson, D.R.; Paulter, N.G. Comparison of some algorithms to estimate the low and high state level of pulses. In Proceedings of the IMTC 2001, Proceedings of the 18th IEEE Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference. Rediscovering Measurement in the Age of Informatics (Cat. No.01CH 37188), Budapest, Hungary, 21–23 May 2001; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2001; Volume 1, pp. 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalkan, E. spikeRemoval. MATLAB Central File Exchange. 2024. Available online: https://www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/69614-spikeremoval (accessed on 1 May 2024).
- Carlson, D.F.; Muscarella, P.A.; Gildor, H.; Lipphardt, B.L.; Fredj, E. How useful are progressive vector diagrams for studying coastal ocean transport? Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods 2010, 8, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlitzer, R. Ocean Data View. 2010. Available online: https://odv.awi.de (accessed on 19 October 2022).
- Troupin, C.; Barth, A.; Sirjacobs, D.; Ouberdous, M.; Brankart, J.M.; Brasseur, P.; Rixen, M.; Alvera-Azcárate, A.; Belounis, M.; Capet, A.; et al. Generation of analysis and consistent error fields using the Data Interpolating Variational Analysis (DIVA). Ocean Model. 2012, 52, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korres, G.; Ravdas, M.; Zacharioudaki, A.; Denaxa, D.; Sotiropoulou, M. Mediterranean Sea Waves Reanalysis (CMEMS Med-Waves, MedWAM3 System), version 1; [Data Set]; Copernicus Monitoring Environment Marine Service (CMEMS): Ramonville-Saint-Agne, France, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korres, G.; Ravdas, M.; Zacharioudaki, A. Mediterranean Sea Waves Hindcast (CMEMS MED-Waves); [Data Set]; Copernicus Monitoring Environment Marine Service (CMEMS): Ramonville-Saint-Agne, France, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Commission regulation (EC) No. 2244/2003 of 18 December 2003 laying down detailed provisions regarding satellite-based Vessel Monitoring Systems. Off. J. Eur. Union 2003, L333, 17–27. Available online: http://data.europa.eu/eli/reg/2003/2244/oj (accessed on 19 October 2022).
- Lambert, G.I.; Jennings, S.; Hiddink, J.G.; Hintzen, N.T.; Hinz, H.; Kaiser, M.J.; Murray, L.G. Implications of using alternative methods of vessel monitoring system (VMS) data analysis to describe fishing activities and impacts. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2012, 69, 682–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, T.; D’Andrea, L.; Parisi, A.; Cataudella, S. VMSbase: An R-package for VMS and logbook data management and analysis in fisheries ecology. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, E.T.; Jiménez, A.A. Vulnerability assessment to coastal storms at a regional scale. Coast. Eng. 2008, 5, 4154–4166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradis, S.; Pusceddu, A.; Masqué, P.; Puig, P.; Moccia, D.; Russo, T.; Lo Iacono, C. Organic matter contents and degradation in a highly trawled area during fresh particle inputs (Gulf of Castellammare, southwestern Mediterranean). Biogeosciences 2019, 16, 4307–4320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linders, T.; Nilsson, P.; Wikström, A.; Sköld, M. Distribution and fate of trawling-induced resuspension sediments in a marine protected area. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2018, 75, 785–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierini, S. Topographic Rossby modes in the Strait of Sicily. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1996, 101, 6429–6440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flexas, M.M.; Durrieu de Madron, X.; Garcia, M.A.; Canals, M.; Arnau, P. Flow variability in the Gulf of Lions during the MATER HFF experiment (March–May 1997). J. Mar. Syst. 2002, 33, 197–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanques, A.; García-Ladona, E.; Gomis, D.; Martín, J.; Macros, M.; Pascual, A.; Puig, P.; Gili, J.M.; Emelianov, M.; Montserrat, S.; et al. General patterns of circulation, sediment fluxes and ecology of the Palamós (La Fonera) submarine canyon, northwestern Mediterranean. Prog. Oceanogr. 2005, 66, 89–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puig, P.; Palanques, A.; Orange, D.L.; Lastras, G.; Canals, M. Dense shelf water cascades and sedimentary furrow formation in the Cap de Creus Canyon, northwestern Mediterranean Sea. Cont. Shelf Res. 2008, 28, 2017–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Haren, G.; Gostiaux, L. Large internal waves advection in very weakly stratified deep Mediterranean waters. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaldo, D.; Orlic, M.; Carniel, S. Framing Continental Shelf Waves in the southern Adriatic Sea, a further flushing factor beyond dense water cascading. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sammari, C.; Millot, C.; Prieur, L. Aspects of the seasonal and mesoscale variabilities of the Northern Current in the western Mediterranean Sea inferred from the PROLIG-2 and PROS-6 experiments. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 1995, 42, 893–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribó, M.; Puig, P.; van Haren, H. Hydrodynamics over the Gulf of Valencia continental slope and their role in sediment transport. Deep Sea Res. Part I Res. Oceanogr. Pap. 2015, 95, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPhee-Shaw, E.E.; Kunze, E. Boundary layer intrusions from a sloping bottom: A mechanism for generating intermediate nepheloid layers. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2002, 107, 3-1–3-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPhee-Shaw, E.E. Boundary-interior exchange: Reviewing the idea that internal-wave mixing enhances lateral dispersal near continental margins. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2006, 53, 42–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, K.; Gunn, R.; Wilcox, C.; Hardesty, B.D. Understanding causes of gear loss provides a sound basis for fisheries management. Mar. Policy. 2018, 96, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Haren, H.; Millot, C. Rectiliniar and circular inertial motions in the Western Mediterranean Sea. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2004, 51, 1441–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosegood, P.; van Haren, H. Near-bed solibores over the continental slope in the Faroe-Shetland Channel. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2004, 51, 2943–2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.T.; Wang, Y.H.; Lee, I.H.; Hsu, R.T. Quantifying tidal signatures of the benthic nepheloid layer in Gaoping Submarine Canyon in Southern Taiwan. Mar. Geol. 2010, 27, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arjona-Camas, M.; Lo Iacono, C.; Puig, P.; Russo, T.; Palanques, A. Trawling-Induced Sedimentary Dynamics in Submarine Canyons of the Gulf of Palermo (SW Mediterranean Sea). J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 1050. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12071050
Arjona-Camas M, Lo Iacono C, Puig P, Russo T, Palanques A. Trawling-Induced Sedimentary Dynamics in Submarine Canyons of the Gulf of Palermo (SW Mediterranean Sea). Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2024; 12(7):1050. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12071050
Chicago/Turabian StyleArjona-Camas, Marta, Claudio Lo Iacono, Pere Puig, Tommaso Russo, and Albert Palanques. 2024. "Trawling-Induced Sedimentary Dynamics in Submarine Canyons of the Gulf of Palermo (SW Mediterranean Sea)" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 12, no. 7: 1050. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12071050
APA StyleArjona-Camas, M., Lo Iacono, C., Puig, P., Russo, T., & Palanques, A. (2024). Trawling-Induced Sedimentary Dynamics in Submarine Canyons of the Gulf of Palermo (SW Mediterranean Sea). Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 12(7), 1050. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12071050






