Abstract
Maritime traffic is increasing more and more, creating more complex navigation environments for ships. Ship trajectory prediction based on historical AIS data is a vital method of reducing navigation risks and enhancing the efficiency of maritime traffic control. At present, employing machine learning or deep learning techniques to construct predictive models based on AIS data has become a focal point in ship trajectory prediction research. This paper systematically evaluates various trajectory prediction methods, spanning classical machine learning approaches and emerging deep learning techniques, to uncover their respective merits and drawbacks. In this work, a variety of studies were investigated that applied different algorithms in ship trajectory prediction, including regression models (RMs), artificial neural networks (ANNs), Kalman filtering (KF), and random forests (RFs) in machine learning, along with deep learning such as convolutional neural networks (CNNs), recurrent neural networks (RNNs), long short-term memory (LSTM), gate recurrent unit (GRU) networks, and sequence-to-sequence (Seq2seq) networks. The performance of predictive models based on different algorithms in trajectory prediction tasks was graded and analyzed. Among the existing studies, deep learning methods exhibit significant performance and considerable potential application value for maritime traffic systems, which can be assessed by future work on ship trajectory prediction research.
1. Introduction
The maritime sector has grown significantly in the last several years. The shipping sector has witnessed the emergence of a new technical innovation known as Shipping 4.0 due to the growing popularization and use of cloud computing and the Internet of Things (IOT) [1,2]. According to statistics, every day, over 50,000 different ships navigate the ocean [3]. This number is anticipated to rise further as the world’s shipping industry expands, and a new generation of maritime autonomous surface ships (MASSs) is emerging quickly as well [4]. The marine transportation industry is facing new challenges as a result of the rise in the number of maritime shipping vessels. The importance of ensuring ship navigation safety, particularly in preventing collision accidents, has grown [5]. A vital piece of technology for securing the safety of ship navigation is trajectory prediction. It can not only improve the efficiency of maritime traffic control but also help determine the location of maritime targets [6]. Precise navigation disaster prevention requires a thorough understanding of sailing ship trajectories. The process of estimating a ship’s future position using navigational data is called ship trajectory prediction. It is crucial for route planning [7], preventing ship collisions [8,9,10,11], autonomous navigation [12,13], and identifying unusual traffic patterns.
Recent studies have demonstrated that the technology used to predict ship trajectories mostly relies on historical trajectory data and the movement characteristics of ships [14,15]. For the former, the future positions of ships are estimated based on kinematic equations, projecting the trajectory based on the motion characteristics of the vessel. It is exceedingly challenging to estimate trajectory based on ship motion characteristics in real-world applications due to the randomness and uncertainty of a ship’s movement in this process, as well as the influence of ambient elements [16].
For the latter approach, ship trajectory prediction based on historical trajectories has become the mainstream method. A ship’s trajectory when sailing on the ocean has distinct features. Similar movement trajectories are typically observed in ships operating in the same water area. By using their previous data as a guide, it is feasible to effectively improve trajectory prediction thanks to trajectory feature precision [14]. Installed on ships, the Automatic Identification System (AIS) is a self-reporting monitoring system that logs a ship’s navigational activity in real-time and delivers records for additional analysis. These records include several types of information, including locations, routes, timestamps, and IDs. Currently, the International Convention for the Safety of Life at Sea (SOLAS) requires international sailing ships above 300 gross tonnage and all passenger ships to install AIS systems. The AIS system has steadily surpassed other data sources as the primary source for ship trajectory prediction and marine traffic analysis because of its high sampling rate, extensive coverage, and convenience [14,17,18,19,20,21,22,23].
The development of artificial intelligence (AI) has promoted the advancement of data processing and data mining technology. Artificial intelligence has unique advantages in making predictions using large-scale data of the same type. In this domain of ship trajectory prediction, a range of machine learning and deep learning techniques have been utilized in trajectory prediction studies utilizing AIS historical data, including Kalman filtering (KF), support vector regression (SVR), and back propagation (BP) networks, Gaussian process regression (GPR), and random forests (RFs), as well as convolutional neural networks (CNNs), recurrent neural networks (RNNs), long short-term memory (LSTM), gated recurrent unit (GRU) networks, and Sequence-to-Sequence (Seq2seq) networks. In Table 1, different methods that have been applied in ship trajectory prediction are listed.

Table 1.
Artificial intelligence methods in ship trajectory prediction applications.
AI technology has demonstrated significant practical value in ship trajectory prediction, with the methods presented in Table 1 performing well during testing. However, the flexibility and durability of these techniques in various settings are still questioned. Researchers have conducted systematic reviews of some trajectory prediction methods based on artificial intelligence, but there are still some research gaps. In the field of ship trajectory prediction, there is still a need for further research to analyze the advantages and disadvantages of prediction methods based on principles and further determine their applicable scenarios. This article aims to conduct a review of the existing ship trajectory prediction methods, summarize the advantages and disadvantages of different methods, analyze their applicability in various scenarios, and provide valuable guidance for research and applications in related fields. The subsequent sections of this paper are organized as follows: The second and third sections provide a systematic review of commonly employed machine learning and deep learning methods. The fourth section presents a summary of the research findings in this article.
2. Machine Learning-Based Methods
Machine learning is the scientific study of algorithms and statistical models that enable computers to learn how to process data more efficiently from data without explicit programming [24]. Machine learning has different algorithms to solve different data problems [25]. For ship trajectory prediction, a ship’s motion trajectory at a certain time in the future is mainly analyzed from the ship’s speed, position, acceleration, sailing direction, and other data. Many machine learning methods are now being used in ship trajectory prediction [26]. It is mainly divided into methods using regression models and those using neural network algorithm models. Regression models include the linear regression model (LRM), autoregressive model (AR), support vector regression (SVR), and GPR. Neural network algorithm models include artificial neural networks (ANNs), Kalman filtering (KF), and random forests (RFs).
2.1. Regression Models
The particular use of a machine learning technique in a regression problem is known as a regression model. A continuous output variable Y will regress close to the actual value on multiple input variables [27], achieving the goal of prediction. The main task of a regression problem is to train a computer on the basis of available data [28] so that the program can map the input to the corresponding output result. When using regression models to predict ship trajectory, it is necessary to train the model to map the AIS data related to ship movement to the corresponding position information at a future time.
2.1.1. Linear Regression Model
The linear regression model (LRM) is the classical regression prediction model and can realize the linear prediction of ship trajectory in real-time and directly by modeling the regression function as the linear combination of ship motion data. The linear regression model can be used to predict a ship’s future trajectory in a short time. The real-time characteristic of linear regression models can be used for collision warning for ship motion.
In order to simulate ship motion, Neri et al. [29] investigated a short–term time domain algorithm that took into account plane motion and used a three–degrees–of–freedom model. Simple and accurate linear regression trajectory prediction was achieved by entering the propeller speed, rudder angle, and initial conditions (starting location/direction and linear/rotational speed) and then outputting the ship position and direction after a predetermined amount of time. The researchers applied the method to the Costa Concordia shipwreck and implemented the proposed model as a maneuvering predictor in real–time. It was found that the predictor could predict the position of the ship 40 s in advance according to a certain command sequence. Figure 1 shows a comparison between the predicted ship’s position and the actual position of the Costa Concordia during two different tests near the Giglio Rock, with the first conducted minutes before impact and the second conducted seconds before impact, as shown in Figure 1a,b. The parameters xg and yg and the coordinate g are the absolute errors between predicted and actual values. The solid and dashed lines, labeled Act, show the ship’s position at the current time step and 20 s later, while the black dashed line (Sim) represents the portion of the recorded maneuver that was simulated for validation. The results showed that the predictor could predict the rock impact about 20 s ahead, giving it a chance to avoid the impact and correct the helmsman’s mistake.
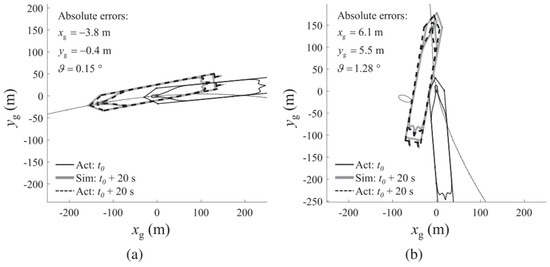
Figure 1.
Predicts the position of the two movements of the Costa Concordia: (a) left turn; (b) Giglio rock impact [29].
In order to better analyze ship motion, Burger and Neil [30] expanded the linear regression model (LRMAC). They proposed using historical AIS motion data in the manner of manufactured ground process spatial maps to predict ship trajectories. This method allowed for nonlinear trajectory prediction and had the advantages of low algorithm complexity, easy programming, and accurate prediction results. LRM has good performance in short-term trajectory prediction and can realize the real-time prediction of motion trajectory. However, LRM is prone to overfitting and the error is large in long-term trajectory prediction, which greatly limits the application range of the linear regression model in the field of ship trajectory prediction.
2.1.2. Support Vector Regression
Support vector regression (SVR) is a kind of regression prediction model that combines support vector machines and regression prediction to make sequence predictions. It is appropriate for small sample training and has excellent global optimal fitting performance. Many scholars have optimized the support vector regression model and applied it in the domain of ship trajectory prediction. For example, Chen et al. [31] presented a support vector regression model based on the dimensional learning grey wolf optimizer (DLGWO-SVR). GWO’s mobile search procedure was optimized by the application of the dimension learning hunting method, and the selection and updating process could prevent GWO from falling into the local optimal solution. At last, the updated GWO’s ideal parameters were replaced in the SVR model. Figure 2 shows the prediction results of different MMSI ships using DLGWO-SVR. The graphic illustrates that the anticipated trajectory essentially parallels or corresponds to the original track, and some minor distance differences will not affect the actual operation of personnel.

Figure 2.
Trajectory prediction of five ships using DLGWO-SVR [31].
Predictive models can easily get trapped in local optima, which can have a negative impact on the results of ship trajectory prediction. Liu et al. [32] proposed a support vector regression model using an adaptive chaotic differential evolution algorithm for parameter optimization (ACDE-SVR). The AIS data’s speed, heading, time stamp, latitude, and longitude were chosen as sample features, and ship location data were processed using the wavelet threshold denoising technique. By optimizing the model’s internal parameters, the ACDE algorithm raised the convergence rate and prediction accuracy of the model. Nevertheless, the offline model put forward in this work was predicated on the idea that all samples were collected simultaneously and that, once trained, the model could not be altered. The AIS data used by the model were periodically gathered based on speed and heading. The prediction error would rise if the freshly acquired AIS data and the initial sample data differed significantly.
Liu et al. [33] attempted to address the issue of applying conventional least squares support vector regression to intricate multi-feature prediction scenarios. They proposed a model named SM-OMLSSVR that utilized a selection mechanism to achieve online multi-output. From a single result of the traditional least squares support vector regression model, the model generated several outputs. Then, to address the issue of poor real-time performance, an iterative approach was employed to lower the high computational complexity of matrix inversion. They determined which online model to use based on the features of various trajectories. To lessen the effect of a significant increase in the number of fresh samples on the computational complexity, the first examples that had the least impact on the model were removed. Figure 3 shows the trajectory prediction results of the model after training it with the ship trajectory data that were randomly extracted from the AIS data of Tianjin Port. There is also a comparison diagram of model prediction error between this and other trajectory prediction models.

Figure 3.
SM-OMLSSVR model predicts ship trajectory [33]: (a) the sailing direction of a ship; (b) comparison of the prediction errors obtained using four models; (c) predicted vs actual trajectories obtained using the online multiple outputs LSSVR trajectory prediction model based on SM and (d) the offline multiple outputs LSSVR model.
Figure 3a shows the randomly extracted ship track AIS data of MMSI 412326162. The ship’s sailing direction is indicated by the black arrow, the data utilized to train the model are represented by the red cross, and the green circle represents the test set data. Figure 3b presents a comparison between online model prediction error with the traditional LSSVR model, RNN-LSTM model, and BP neural network model. Figure 3c,d show the predicted ship trajectory using online and offline modes, respectively. The findings demonstrate that the effectiveness and precision of the traditional LSSVR model were improved significantly on the basis of real-time prediction.
The SVR model can achieve high-precision ship trajectory prediction, but it usually faces the challenge of parameter selection and the problem of high operation costs, which restrict its development in real-time prediction.
2.1.3. Other Regression Models
LRM and SVR can effectively complete tasks, and other regression models also perform well in ship trajectory prediction, such as autoregressive prediction (AR) and Gaussian process regression (GPR). Qiang et al. [34] used the AR model to predict ship motion, offering a ship stabilization platform model predictive control approach based on ship motion prediction. A better option than Bayesian linear regression is Gaussian process regression (GPR). Chen et al. [35] proposed a sparse GPR model to assist intelligent navigation. In contrast to parameter identification, the Gaussian process regression model does not require knowledge of a ship’s dynamics prior to model construction. Compared to the parametric model, it yields more accurate motion prediction. The similarity-based sparse method resolves the problem that the kernel method has challenges with when it comes to learning from huge sample data. It can replace the information from a huge sample with very little data used. As a result, the model’s generalization is increased. The suggested model’s validity was confirmed using a ship’s experimental data. The findings demonstrate that a large dataset may be learned using sparse Gaussian process regression with similarity, yielding ship motion prediction results that are more accurate than those obtained from a parameterized model. Furthermore, the suggested model maintains the correct ship speed and trajectory information in the event of sensor signal loss, and the motion trajectory’s highest forecast error within 100 s is only 0.59 m. However, the performance of the model is limited by the dataset used—it is hard to improve the predictive accuracy without more training data.
To improve the GPR model, Rong et al. [36] presented a non–parametric Bayesian model built on the Gaussian process. The model breaks down ship motion prediction into longitudinal and lateral orientations. Lateral and longitudinal motion are independent of each other. Historical AIS data can be used to obtain the acceleration distributions along the longitudinal direction and applied to describe the uncertainty of the ship’s position in this direction based on the acceleration. The ship trajectory uncertainty in the lateral direction is modeled using a Gaussian process perpendicular to the route centerline. Moreover, during Gaussian process modeling, to reduce the computing burden, the authors used a sequential Cholesky decomposition approach. In order to verify the model, the author extracted AIS data for the past three months from the Traffic Separation Scheme off Cape Roca in the southbound traffic lane. The model was applied to predict the ship trajectories. Figure 4a shows the AIS trajectory data of an individual ship on the lane; Figure 4b gives the trajectory prediction with uncertainty calculated by the GP model. Based on actual AIS data, the results show that the ship positions were well within the 95% probability prediction interval determined by the GP model.

Figure 4.
AIS trajectory of an individual ship [36]. (a) AIS trajectory of an individual ship, (b) trajectory prediction with uncertainty by the GP model.
After that, Rong et al. [23] established a combination prediction model of LRM and GPR to forecast a ship’s trajectory and destination during navigation, respectively. When the method was used for all ships operating in a study region, it can anticipate the positions of ships over a lengthy period of time and offer information on marine traffic 10, 30, and 60 min ahead of time. This technique might help maritime authorities create plans to increase navigation safety and boost the effectiveness of maritime traffic surveillance. Figure 5a shows an example, according to the model prediction results. There is a 44.4% chance that the ship is going to Lisbon and a 55.6% chance that it is going to Setubal. Rather than providing a precise geographic position of the ship’s location along the ship route, Figure 5b,c display a range of coordinates labeled with probabilities, creating a probabilistic area. The precision of this trajectory prediction is, nevertheless, limited. While long-term prediction is made possible by merging marine traffic networks with a vessel trajectory prediction model, the method’s reliance on ship destination prediction findings limits the precision of trajectory prediction.

Figure 5.
Two ship routes compatible with the ship’s position (a), ship position prediction with uncertainty (b), and prediction uncertainty contour and actual ship position (c) [23].
On the other hand, as a complete system that uses decision trees, random forest (RF) has also been used extensively in ship trajectory prediction studies. Karatas et al. [37] studied problems about arrival time, arrival port, and next location prediction with decision tree-based approaches. Zhang et al. [38] proposed a universal RF-based model for vessel destination prediction that is powered by AIS data. This model measures and uses the similarity between a vessel’s current and past trajectories to forecast the destination. To achieve the effective prediction of ship speed over the ground (SOG), Abebe et al. [39] investigated a variety of machine learning regression techniques, including polynomial regression, decision tree regressors, random forest regressors, extra trees regressors, gradient-boosting regressors, and gradient-boosting regressors (GBRs) with hyperparameter-tuned parameters. Model validation was used to assess the computing time and accuracy of each technique using actual ship route data, and the most accurate and efficient method was verified for a range of ship types and ship routes.
Trajectory prediction methods based on regression models have significant effects. However, they have significant limitations in practical applications. To date, the widespread application of artificial neural networks (ANNs) provides a new option.
2.2. Neural Networks
Artificial neural networks (ANNs) are the first model to simulate how the brain processes sensory information [40]. Due to the back-propagation algorithm [41], an artificial neural network is able to learn from examples and adaptively adjust internal parameters to solve different types of problems.
2.2.1. Artificial Neural Network
ANNs and their upgraded models are now frequently used in the area of ship trajectory prediction. Volkova et al. [42] employed experimental data of a vessel’s actual movement in the Neva River’s fairway to construct and train neural networks with various architectures and activations. This study demonstrates that neural network training can be performed with a ship’s movement coordinates and yet produce accurate results for future positions. Zhou et al. [43] proposed a technique for predicting the navigation trajectory of ships that combines data from a ship’s automated identification system with a back propagation (BP) neural network. In order to predict a future ship navigation trajectory, the BP neural network is trained by using the characteristic values of the ship’s navigation behavior at three consecutive moments as input and the characteristic values of the ship’s navigation behavior at the fourth moment as output. Zissis et al. [44] employed ANNs to extend the predictive capacity of vessel traffic monitoring information systems (VTMIS). The model had the ability to forecast vessel activity in real-time with no computing overhead. Researchers trained and tested their ANN by using AIS data from vessel MMSI 239923000 in the Aegean Sea region of Greece. Figure 6a,b report on future (15 min ahead) latitude and longitude predictions for a vessel, while Figure 6c,d show future (4 h ahead) latitude and longitude predictions.
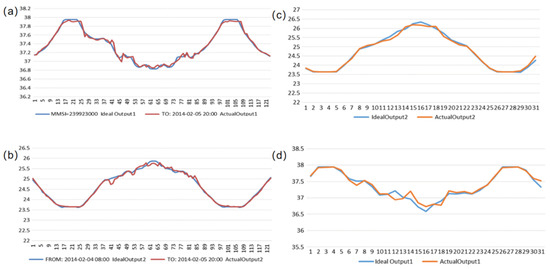
Figure 6.
Evaluation results regarding predictions for the vessel MMSI 239923000 using ANN [44]: (a) latitude and (b) longitude predictions 15 min ahead; (c) latitude and (d) longitude predictions 4 h ahead.
In a similar study, Simsir and Ertugrul [45] developed a method of navigation and early warning that involved predicting a vessel’s position three minutes ahead of time, particularly during turning points. This method predicts the future coordinates of a vessel navigating in narrow waterways using ANNs. Some experiments have been conducted in Istanbul Strait. Figure 7a shows the turning points in the strait. Figure 7b shows a three–minute–ahead prediction of the model and the real positions of the vessel. Figure 7c provides a comparison of the predicted and actual courses. The results demonstrate that the suggested prediction method employing an artificial neural network can detect separation line violations three minutes in advance. As a result, it may be used as an early warning and guiding system to alert ship crew members and VTS operators to potentially harmful circumstances before they arise.

Figure 7.
Using ANN to predict three-minute-ahead position of vessel in Istanbul Strait [45]: (a) turning points in Istanbul Strait; (b) 3 min ahead prediction with TANN and real positions; (c) error analysis between prediction and real course.
In addition to the above algorithms, Xu et al. [46] researched a model based on a BP neural network. The ship’s course and speed, along with the difference in latitude and longitude, were used by the model as input and output, respectively. The network was trained to capture the ship motion law at time n using the last N training samples under the same time step and then predicted the ship position at n + 1. Chen et al. [47] presented a framework for reconstructing an ensemble ship’s trajectory that combined a prediction module with a data quality check approach. The suggested methodology incorporated data denoising, trajectory separation, and raw AIS data normalization. Following this, the framework used the ANN to estimate the ship’s trajectory.
Prediction models based on ANNs have good prediction accuracy but lack generalization ability. Some scholars have also researched ship trajectory prediction using improved neural network models. Borkowski [48] presented a ship trajectory prediction algorithm that makes use of the process of the fusion of navigational data. A generalized regression neural network (GRNN) was utilized by the technique, which could be used to forecast a ship’s course as well as that of another.
Łącki [49] presented a neural network model based on neuroevolution to build the intelligent ship maneuvering prediction system (Figure 8). The system mimicked the method by which an ANN-created autonomous control unit learned. When a vessel was moving in restricted seas, the control unit calculated the values of the necessary parameters by observing input signals. The findings demonstrate that the investigated model of ship maneuvering in tight waters performs better and is more complicated when artificial neural networks based on the modified NEAT method are used.

Figure 8.
Algorithm of prediction system with neuroevolutionary method [49].
Valsamis et al. [50] implemented a ship trajectory online predictive service that handles data streams using conventional, multi-scan, pre-trained models. According to the research, a well-trained model that produces predictions with a high degree of accuracy may very well be able to satisfy a predictive service’s need for real-time reaction without requiring retraining or compromising accuracy.
The above studies prove that using neural networks for ship trajectory prediction can obtain satisfactory accuracy and stability. However, the large number of parameters involved in neural network models, along with their poor interpretability, still raises questions about their reliability. Additionally, the structure of neural networks introduces high computational and spatial complexity, posing challenges for training and application.
2.2.2. Hybrid of Neural Networks and Other Algorithms
Due to the limitations of neural networks, researchers have put effort into addressing issues and simultaneously broadening the application scope of neural networks with a hybrid approach of neural networks and other algorithms.
In order to interpret large amounts of AIS data and utilize it to develop ship routes, Wen et al. [51] suggested a research framework. They combined DBSCAN with an artificial neural network that could automatically create a ship’s path between ports using a vast amount of AIS data. The technique could automatically generate a ship’s path based on its various dimensions. In the research of Gan et al. [52], the well-known K-Means clustering approach was used to first group the historical trajectories. Next, ANN models were constructed to forecast the trajectories of the ships using the above clustering results together with other known factors (such as ship speed, loading capacity, self-weight, maximum power, and water level). With an accuracy of more than 70%, the created model agreed well with the real data. Additionally, it assisted in producing the best traffic orders for Yangtze River traffic management. In order to achieve ship trajectory smoothing and prediction, Zhao et al. [53] proposed an ensemble machine learning framework to predict the tendency of ship trajectory fluctuation and eliminate outliers from raw AIS data (see Figure 9a). To suppress the AIS data outliers, the ensemble framework used the empirical mode decomposition (EMD) model to split the raw AIS data into low- and high-frequency components. An ANN model was employed to complete the ship trajectory prediction task. Figure 9b shows the AIS data distribution for a case, while Figure 9c gives the outlier removal performance.
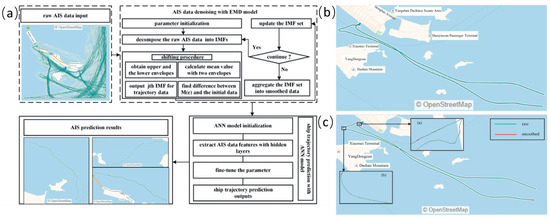
Figure 9.
Schematic overview of the ensemble framework (a), AIS data outlier removal performance for a case (b), and statistical indicator distributions (c) [53].
Due to issues with low accuracy and simple trapping in the local optimum of BP neural networks, Zheng et al. [54] proposed an enhanced sparrow search algorithm (SSA) based on sine chaos mapping to optimize a BP neural network for the trajectory prediction of inland river vessels. The technique used sine chaos mapping to create a sine–BP model and set thresholds and weights for neural networks. Then, in order to solve the optimal solutions of the neural network weights and thresholds, a sine–SSA–BP model was constructed using the sparrow search algorithm (SSA). The suggested model successfully mitigated the issue of population intelligence algorithms’ propensity to be premature and enhanced the initialized population of uniform distribution. Figure 10 is the model framework diagram of the sine–SSA–BP model. Figure 11 shows a comparison of trajectory prediction in two different scenarios using sine–SSA–BP, SSA-BP, LSTM, and SVM. According to the test results, the sine–SSA–BP neural network outperformed the traditional LSTM and SVM in terms of prediction accuracy and stability, particularly when it came to turning prediction, which was in good accord with the actual ship navigation trajectory.
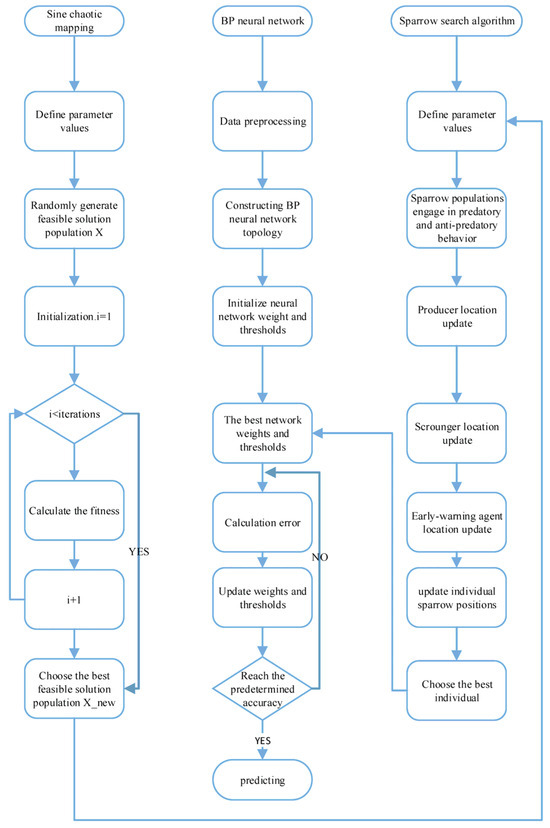
Figure 10.
Sine–SSA–BP model framework diagram [54].
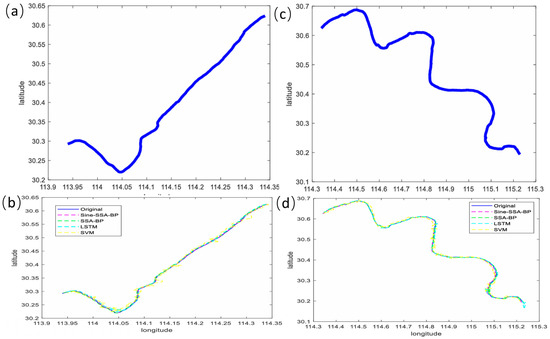
Figure 11.
Comparison of trajectory prediction of different models in two different scenarios [54]: (a,b) the original trajectory of two different scenarios; (c,d) comparison of trajectory prediction of different models in two scenarios.
Papadimitrakis et al. [55] focused on surface vessel automated collision avoidance. For the purpose of the collision avoidance task, they demonstrated a multi-ship MPC controller that used RBF obstacle trajectory prediction models that were trained using actual AIS data. The model adopted a radial basis function (RBF) neural network to predict the nonlinear trajectory of an obstructed ship, which could be used for collision avoidance in busy ports or waterways. Using straight-line obstacle ship trajectory prediction models for a genuine simulation example for the Port of Miami, the approach was compared to an MPC controller. The response of the MPC controller using RBF and straight-line prediction models (MPC-RBFP and MPC-SLP) is displayed in Figure 12a,b.

Figure 12.
The response of different MPC controllers. Subfigures (a1–a4) refer to the MPC-SLP scheme, while (b1–b4) to the MPC-RBFP scheme [55].
Kanazaw et al. [56] developed a multiple-output hybrid predictor (MHP) and improved its architecture. Using information from onboard sensors, the MHP was able to anticipate one long-horizon event at a time. An extended time series of future command assumptions was transformed by researchers into a fixed-length, model-based, projected vessel state, which was then incorporated into the inputs of a black-box error compensator. This concept is resistant to extended control horizons and multidimensional commands and has really improved the MHP’s predictive decision-making process by assessing the performance of future command assumptions.
To obtain accurate forecasts, Xiao et al. [57] combined particle filtering, physical motion modeling, and machine learning in an efficient manner. They demonstrated a thorough process for utilizing AIS data to forecast a vessel’s trajectory and navigational status. A number of important research findings were also included in their study to address the main difficulties with vessel trajectory and the navigating state prediction problem. These included the adaptive training window determination for the learning process and an efficient knowledge storage and searching algorithm designed to shorten the query time for retrieving waterway patterns.
On the subject of ship trajectory prediction, developing a sophisticated model that accurately captures a system and its interactions with dynamic environments has always been difficult. Wang et al. [58] suggested a hybrid modeling approach that created a representative model with a high degree of predictive capacity by combining previous knowledge about ship dynamic effects into a data-driven calibrator. To demonstrate the idea, full-scale experiments and simulations of the model were carried out on the research vessel Gunnerus. Gunnerus’s consecutive motions while at sea are seen in Figure 13a. Figure 13b illustrates how the thruster turning angle and ship direction changed during maneuvering. The forecasted outcomes are displayed in Figure 13c. It is believed that there was a good enough match between the hybrid projections and the ship’s actual trajectory.

Figure 13.
Gunnerus’s actual ship trajectory and prediction result [58]: (a) execute zigzag maneuver; (b) azimuth turning angle and ship heading during maneuvering; (c) hybrid predictions in comparison with model predictions in real life.
In addition, in order to accomplish near real-time (NRT) trajectory prediction of a large number of ships, Xiao et al. [59] proposed a concurrent processing cluster method. The method combined concurrent processing clustering with neural networks to empower advanced trajectory forecasting for hundreds of vessels in NRT. Rhodes et al. [60] created an improved, neurobiologically inspired algorithm for situation awareness that learned motion pattern models dynamically from real-time tracking data, allowing the models to perform effectively even under changing circumstances.
2.3. Other Machine Learning Methods
Kalman filtering allows for the analysis, inference, and computation of multiple uncertain results, resulting in relatively accurate results. Perera et al. [61] proposed integrating intelligent features into VTMIS. In order to estimate vessel states and anticipate vessel trajectories, they created the extended Kalman filter (EKF). A ship’s predicted trajectory during a circular maneuver is shown in Figure 14. Figure 14b shows the vascular velocity components in the x– and y–directions for the estimated and real values. Figure 14c shows the tangential acceleration and the normal acceleration of the estimated and real values.
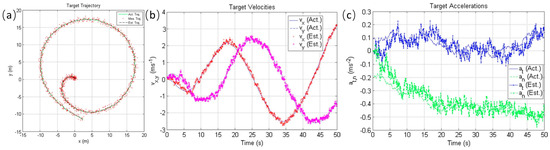
Figure 14.
Ship trajectory prediction using EKF [61]: (a) navigational trajectories; (b) vessel velocity conditions; (c) vessel acceleration conditions.
One major application of ship trajectory prediction is the intelligent route planning of unmanned surface vehicles (USVs). For the safe operation of unmanned surface vehicles (USVs), Liu et al. [62] suggested a predictive path-planning algorithm based on the Kalman filter. A USV’s position and the trajectories of other moving ships are predicted by the algorithm, which then evaluates the risk of a collision. The results of the study indicate that the algorithms are capable of handling intricate traffic conditions, and the resulting practical path is appropriate for both manned and unmanned vessels.
Xie et al. [63] looked into the use of a Kalman filter with discrete wavelet analysis in short-term traffic volume forecasting to increase the prediction accuracy of short-term traffic volumes. The original data were split up into several approximate and detailed data using discrete wavelet decomposition analysis. This allowed the denoised data to be subjected to the Kalman filter model, which increased prediction accuracy. Jaskólski [64] presented a Kalman filtering algorithm to increase the potential for tracking and monitoring ship motion in fairways and the TSS (Traffic Separation Scheme). The application of the Kalman filter reduced the coordinate mean error to 10 m. Murray and Perera [65] developed a technique that used historical AIS data to forecast a vessel’s future course. The approach used machine learning techniques to assess previous ship behavior in a certain geographic area and extrapolate commonalities in pertinent trajectory segments. These similarities showed patterns of past conduct that could be indicative of the chosen vessel’s potential future behavior. The chosen vessel was then assigned to a behavior mode, and a trajectory in relation to this mode was forecast.
To achieve a practical and appropriate steering angle, Zheng et al. [66] proposed a decision-making approach for ship collision avoidance based on enhanced cultural particle swarm during the decision-making process. The ship trajectory was smoothed and predicted in the study by the authors using the Kalman filter. Second, by integrating the COLREGs and the encounter state of the ship, the steering angle direction and the ship’s estimated danger degree were ascertained using the fuzzy distribution approach. Ultimately, the cultural particle swarm optimization method determined the ship’s ideal steering angle, enabling decision-making for ship collision avoidance.
One of the main problems with ship trajectory prediction is long-term trajectory prediction. For ocean vessels, no long-term, fine-grained trajectory prediction techniques have been offered. An innovative, long-term trajectory prediction system for ocean vessels, known as long-term vessel trajectory prediction (L-VTP), was proposed by Liu et al. [67] using a K-order multivariate Markov chain model and several sailing-related factors. L-VTP builds several state-transition matrices for trajectory prediction based on the quantitative uncertainty analysis of trajectories by utilizing multiple sailing-related characteristics to achieve trajectory prediction. Figure 15 shows the performance of a three-order improved Markov model with temporal division. The authors chose three vessels and compared their original trajectory with the predicted trajectory.
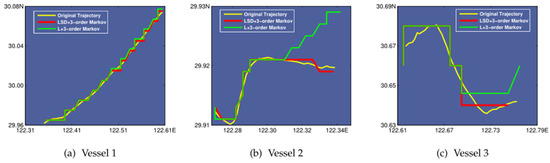
Figure 15.
Ship trajectory prediction of three ships using L-VTP [67].
Apart from the aforementioned methods, researchers have employed additional machine learning methods to predict ship trajectories. These methods include the single point neighbor search (SPNS) [68], second-order rational Bézier curve coefficients estimation [69], and a predictive collision avoidance method for underactuated surface vessels [70] based on an improved beetle antennae search (BAS) algorithm.
3. Deep Learning-Based Methods
Machine learning methods perform well in ship trajectory prediction, and related works have made some achievements. However, models based on machine learning algorithms have high computational complexity and lack generalization and robustness. There are still deficiencies in the prediction accuracy and applicability of machine learning methods in different applications. Deep learning provides appropriate mechanisms to predict vessel trajectories. To this end, scholars have tried to use deep learning methods with more powerful learning abilities. The advantage of deep learning is that it can efficiently process complex and dynamic data, which gives it remarkable performance in ship trajectory prediction.
3.1. Convolutional Neural Networks
One common deep learning-based neural network is the convolutional neural network (CNN). It introduces a convolution module for feature extraction and achieves higher predictive performance, while the number of neural network parameters is reduced effectively. However, CNNs do not have the ability to learn from sequences, so most researchers use graph neural networks (GNNs) for ship trajectory prediction.
Feng et al. [6] suggested the Improved Social-STGCNN (IS-STGCNN) (Figure 16). The IS-STGCNN preprocessed the original AIS trajectory data in the input layer using invalid data elimination, trajectory similarity screening, and trajectory division to extract the coordinate data (i.e., latitude and longitude) of ships. The spatial–temporal graph representation layer then took care of organizing and processing the data. The ship coordinate data were used to generate a spatiotemporal graph. Subsequently, positive and negative samples were collected by social sampling and fed into an encoder to update the graph’s nodes’ vector representation. Next, the encoder built a latent representation of all ships in the region (STGCNN) using the spatio-temporal graph CNN. The decoder then employed the time-extrapolator CNN (TXP-CNN) to predict the trajectory and the MPC to correct the anticipated trajectory in order to ensure the kinematic viability of ships. Finally, the corrected predicted ship trajectory was obtained. A comparative comparison of the predicted trajectories in birds-eye view in three video frames produced by IS-STGCNN and Social-STGCNN is shown in Figure 17. The lines with red hollow circles represent the ground truths, while the lines with yellow hollow triangles represent the method’s results. Experiments show that IS-STGCNN performs better in real-time performance and trajectory prediction accuracy than Social-STGCNN and other state-of-the-art prediction models.

Figure 16.
Structure of IS-STGCNN [6].

Figure 17.
Qualitative comparisons of predicted trajectories in bird view of three frames of video by both Social-STGCNN and IS-STGCNN. [6].
The combination of CNNs and recurrent neural networks (RNNs) is another method to use CNN for ship trajectory prediction. A novel, attention-based, residual CNN-LSTM trajectory prediction model was built by Lu et al. [71]. Two layers of residual CNNs were used in the model to extract spatial characteristics, and two two-layer bidirectional LSTMs were used to extract temporal features from the residual CNN output. The model was given a boost in convergence speed and stability by adding the Ranger optimizer. In comparison to the current prediction model, the study demonstrated that the attention-based residual CNN-LSTM ship trajectory prediction model could obtain higher prediction accuracy and a better prediction effect.
3.2. Recurrent Neural Networks
Recurrent neural networks (RNNs) can mine temporal and semantic information from AIS raw data and are useful for processing sequential data. However, RNNs only have short-term memory because of diminishing gradients and gradient explosion; more research has focused on using LSTM for trajectory prediction.
3.2.1. LSTM
A deep learning approach for regional trajectory prediction was proposed by Murray and Perera [72]. With this architecture, it is possible to estimate a vessel’s trajectory in less than a second for the next five to thirty minutes. It also looked into breaking down regional ship behavior into local models by using contemporary deep learning architectures. Attention-based sequence-to-sequence models made up the local prediction models. Trajectories were successfully predicted globally by the framework.
Long short-term memory (LSTM) is a variant of RNNs; it introduces a “forget gate” into the structure of RNNs (Figure 18). LSTM can effectively filter key features, perform selective memory, and, to some extent, resolve the issue of disappearing gradients. In order to anticipate a ship’s trajectory, an LSTM cyclic neural network was used to learn the ship’s motion law based on its current surroundings and time [73]. This concept guaranteed that the established model complied with the actual logic in addition to avoiding the laborious modeling process involved in the standard method [73].
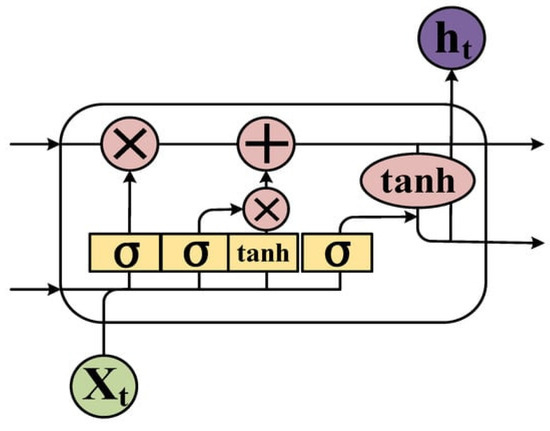
Figure 18.
The structure of an LSTM cell.
Many integrated LSTM models have been proposed by scholars to tackle complicated trajectory problems. Qian et al. [74] used an LSTM network model as the technical foundation for creating an inland river ship trajectory prediction model. Given that the number of hidden-layer neurons, learning rate, and other critical hyperparameters of the present LSTM model are hard to figure out, a genetic algorithm (GA) was developed to optimize LSTM networks’ critical hyperparameters. The GA-LSTM prediction model had strong practical application value in the intelligent navigation of inland river ships as it could reduce the impact of hyperparameter parameters on the accuracy of ship trajectory prediction.
In order to predict future ship trajectories in complicated settings, Wang et al. [75] proposed the STPGL model, which used an encoder–decoder structure (Figure 19) and covered a spatio-temporal awareness graph attention network (GAT) based on LSTM. The kinematic sequence properties of every ship were extracted from historical trajectories in the temporal dimension by the historical encoder using an LSTM. The spatial dimension of the interaction features between several ships using GAT was summarized by the interactive encoder. Subsequently, the two characteristics were combined and supplied to the decoder module in order to deduce the future paths of vessels. The experimental findings show that the STPGL model may significantly increase the accuracy of ship trajectory predictions over the short, medium, and long term. It performs exceptionally well and has a particular benchmark for the development of unmanned ship collision avoidance.

Figure 19.
The overall framework of the STPGL model [75].
Gao et al. [14] addressed the limitations of multi-step prediction. By merging the benefits of TPNet and LSTM, they presented an easy-to-implement approach appropriate for real-time analysis in their study. The technique is known as multi-step prediction LSTM (MP-LSTM), and Figure 20 illustrates the method’s technological roadmap. The main concept is that cubic spline interpolation is used to perform multi-step predictions on the start, support, and destination points. Among these, a trained LSTM model generates the support point, and historical data generates the destination point, which helps to maintain a low degree of error. The suggested method can achieve higher prediction accuracy than several conventional approaches for a dataset and the four fundamental navigation states—straight-line, turning, acceleration, and deceleration—according to a thorough review of the case study. Furthermore, the approach can also attain a sufficient level of prediction accuracy even after the time to be anticipated has passed.
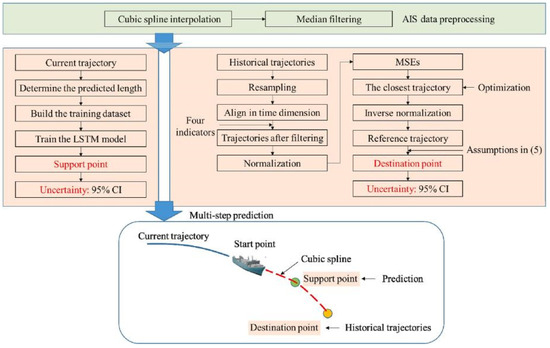
Figure 20.
The technical roadmap of the MP-LSTM [14].
To predict multiple trajectories, Ma et al. [76] proposed a novel trajectory representation method to extract common aspects of various trajectories utilizing a sequence of AIS data points. The suggested technique is predicated on a hierarchical clustering methodology. The Euclidean metric was employed by the authors in this work to quantify the similarity between two points or clusters. This technique allowed for the representation of numerous trajectories as shared feature points with an identical optimum number. Both the LSTM and RNN performed well on various trajectory prediction tasks in the experiments.
On the other hand, Venskus et al. [77] expanded on earlier studies in the area of anomalous marine traffic detection. Their research looked at and suggested an LSTM autoencoder-based approach for predicting vessel trajectory and assessing prediction region. The technique can be used to detect unusual marine traffic. A new cooperative collision avoidance system for inland ships was created by Hammedi et al. [78] while maintaining data security and privacy. The system employs the ConvLSTM model to predict ships’ positions since it is the most efficient and most robust. Based on numerical data, the suggested system is able to identify collisions with a high accuracy rate above 92% under various conditions.
To enhance the awareness of the surroundings in intersecting waterways and avoid traffic accidents, accumulated long short-term memory (ALSTM), a recurrent neural network architecture first described by Ma et al. [79], was used. The method uses skip connections and an adaptive memory module to get around the drawbacks of the traditional LSTM (Figure 21). By providing a high-level depiction of the erratic and varied motions of individual ships, ALSTM helps to relate different ship motion patterns and intents. The suggested model was tested and trained with excellent results on a naturalistic dataset in order to validate it.

Figure 21.
Framework based on proposed ALSTM architecture for the intent prediction of vessels [79].
Ship trajectory analysis seldom uses contextual data in present systems and procedures. The common compression algorithm was enhanced by Mehri et al. [80] by merging contextual data from several trajectory mining and prediction stages. Contextual information was then used to verify the logical consistency of the curvilinear technique, and a context-aware long short-term memory (CLSTM) network was built to account for contextual variables such as vessel types. Via a recursive feedback loop, the innovative prediction technique, which draws on the strengths of the deep learning LSTM network and the curvilinear model, can improve prediction accuracy while preserving logical coherence. Figure 22 shows the framework and graphic for predicting vessel behavior. According to the conducted experiments, the context-aware trajectory prediction technique performs 15.68% better in terms of prediction accuracy and beats the standard LSTM network in terms of convergence velocity and oscillation amplitude.

Figure 22.
The framework of CLSTM (a) and schematic of vessel behavior prediction (b) [80].
3.2.2. Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory
The traditional LSTM model solely takes into account historical data patterns while producing maritime traffic data. In cases where a ship undergoes large movement state changes, such as abrupt changes in maneuvering direction and speed, the model may yield clearly biased results. The LSTM model’s drawback can be lessened by the Bi-LSTM model. The Bi-LSTM model learns intrinsic features from the outputs of both the forward layer and the feedback layer, which consists of a forward layer and feedback layer (with basic LSTM units) to obtain final training and prediction results. Using a bidirectional LSTM (Bi-LSTM) model, Chen et al. [81] forecasted a ship’s trajectory and used the data prediction findings to further examine the tendency of trajectory fluctuation.
Moreover, to improve prediction performance, density-based spatial clustering of applications with noise (DBSCAN) was utilized by Park et al. [82] to identify a ship trajectory pattern. They used a technique called spectral clustering, which can show similarities between different trajectories. The similarity was determined by the distance between the longest common subsequences (LCSS). Next, a ship trajectory prediction model was created utilizing bidirectional long short-term memory (Bi-LSTM). In the study, Bi-LSTM was determined to have the highest prediction accuracy when compared to LSTM and GRU.
The quality of AIS data is essential for ship trajectory prediction. It was discovered that instances of missing AIS data were common in the interior river regions. Zhong et al. [83] concentrated on the prediction and restoration of inland ship trajectories. In order to restore AIS trajectory data, a deep learning technique based on bi-directional long short-term memory recurrent neural networks (BLSTM-RNNs) was presented and used. For two different Yangtze River reaches (Chongqing and Wuhan), the effectiveness of BLSTMRNNs and their equivalents (linear interpolation and ANNs) was tested and assessed (Figure 23). The results from the BLSTM-RNNs were more promising than those of the linear and non-linear approaches, with lower RMSE and MAPE but greater R2. Using the BLSTM-RNN model, ship trajectories with several missing points could be successfully recovered.
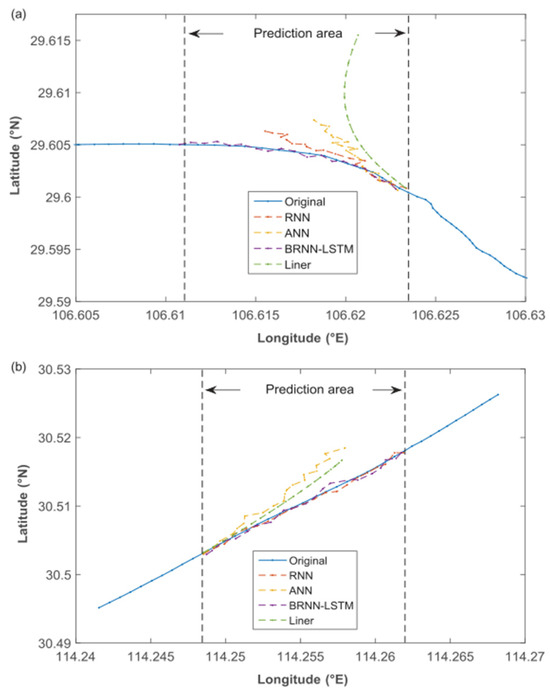
Figure 23.
Ship trajectory restoration by applying different methods for multiple missing points. (a) Meandering reach at Chongqing. (b) Straight reach at Wuhan [83].
By constructing a BiLSTM-RNN, Gao et al. [84] also created an online real-time ship behavior prediction model (Figure 24). The model can be used for online parameter change and sequential AIS date and time characteristics. By using LSTM units and both forward and backward propagation to update the weights, the BiLSTM-RNN is able to increase prediction precision and contextual relevance. This method can help a human operator make better decisions to stay out of harm’s way and help them comprehend the complex surroundings at sea.

Figure 24.
Batch-training diagram (a) and flowchart (b) of BiLSTM-RNN [84].
The attention mechanism has advanced significantly in the domains of natural language and image processing in recent years, which helps deep learning models perform better. Wang and Fu [85] introduced the attention mechanism to ship trajectory prediction. They proposed a model based on attention in bidirectional long short-term memory recurrent neural networks (BLSTMs) (Figure 25). The model combined the attention mechanism and recurrent neural networks to predict the trajectory of a ship. By including the attention mechanism, the ship prediction offset could be significantly decreased and the trajectory of the ship could be predicted with more accuracy. Furthermore, it was possible to fit the attention mechanism model quickly.

Figure 25.
Attention in bidirectional recurrent neural networks [85].
A recurrent encoder–decoder architecture was introduced by Capobianco et al. [4] to solve the trajectory prediction issue when complicated mobility patterns are present. The input sequence was mapped into a sequential context representation by the encoder, a BiLSTM-RNN. Subsequently, the series of encoder hidden states was combined with the context representations using an attention-based aggregation function. Ultimately, the decoder LSTM network received the motion pattern descriptor and each context representation in order to produce the output sequence. A multilayered structure can be present in encoder and decoder networks to enhance internal representation learning.
3.2.3. GRU
The GRU model performs similarly to LSTM but is computationally cheaper [86]. It improves upon LSTM’s drawbacks and can successfully lower the overfitting risk by using fewer parameters. Therefore, many scholars choose to construct recurrent neural networks for trajectory prediction using GRUs. Han et al. [87] developed a short-term real-time trajectory coordinate point prediction method based on a gated recurrent unit (GRU) recurrent neural network, approaching this from the perspectives of historical trajectory data and real-time trajectory data. The GRU neural network’s parameters were adaptively updated online and flight positions were predicted in real-time using the real-time trajectory data.
Suo et al. [88] presented a deep learning framework and a GRU model to predict ship trajectories. By using AIS ship data and the density-based spatial clustering of applications with noise (DBSCAN) technique, the framework was able to determine the main trajectories. After that, a symmetric, segmented-path, distance-based trajectory information correction technique was used to optimize incoming trajectories and remove the impact of a lot of redundant data. Subsequently, the GRU model underwent training in order to forecast ship trajectories in real-time. As seen in Figure 26a, the optimum trajectory set was produced by the DBSCAN trajectory clustering. Trajectories were essentially categorized into three categories: north–south routes, crossing waterways, and incoming waterways. Figure 26b,c show the ship track and the GRU model’s predicted course using historical AIS data from Zhangzhou Port, China. According to the trials, the vessel trajectory prediction model based on the GRU model offered a more computationally economical approach while maintaining a good prediction accuracy comparable to that of LSTM.

Figure 26.
A detailed representation of the ship’s real trajectory and predicted trajectory using the GRU model [88]: (a) trajectory clusters by DBSCAN; (b) visualization of the vessel’s real trajectory and predicted trajectory that uses the GRU model and (c) a detailed representation.
In order to better address the issue of ship navigation behavior prediction in port water and enhance the safety of vessel berthing, Wang et al. [89] established a vessel berthing trajectory prediction model based on a bidirectional GRU (Figure 27). This model aimed to address the challenging problem of predicting the movement trend of vessels in crowded port water. The berthing trajectory data of hundreds of containers in port waters were tested using the Bi-GRU model. The outcomes demonstrate that the Bi-GRU model prediction has a lower error and higher accuracy. The model can be modified and used in the future to investigate ship anomaly detection, including grounding warning, collision avoidance, and oversight by vessel traffic services.

Figure 27.
Structure of bidirectional GRU neural network [89].
Conversely, Bao et al. [90] presented a high-precision ship track prediction model (Figure 28) that combined a bidirectional gate recurrent unit (MHA-BiGRU) with a multi-head attention mechanism. Notably, the addition of a multi-head attention mechanism improved forecast accuracy by computing the correlation between AIS data characteristics, actively learning cross-time synchronization between the hidden layers of ship track sequences, and weighting the result differently depending on the input criterion.
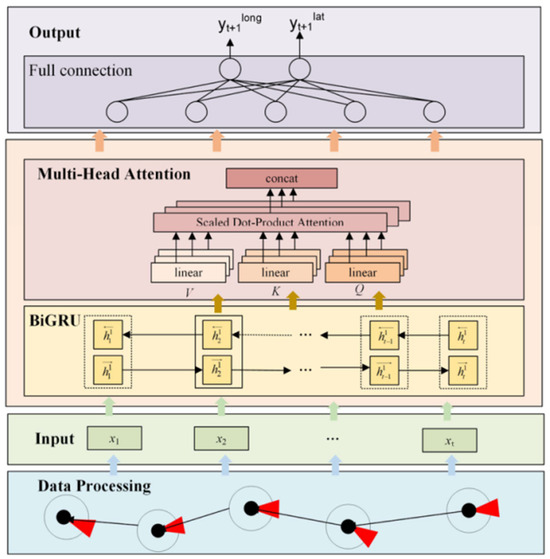
Figure 28.
Schematic diagram of the MHA-BiGRU [90].
Figure 29 indicates the comparative prediction results for the longitude and latitude of eight methods. In comparison to prior comparative tests, the MHA-BiGRU model has higher applicability, accuracy, and validity, as evidenced by its lowest loss, RMSE, and MAE values.
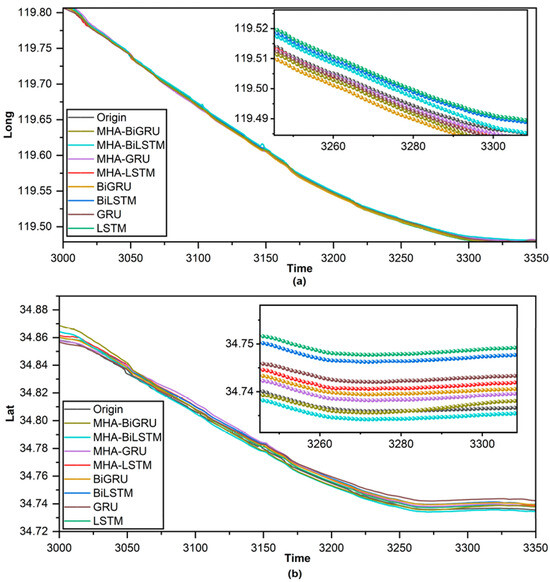
Figure 29.
Comparative prediction results: (a) predicted longitude; (b) predicted latitude [90].
Lin et al. [91] introduced a temporal convolutional network (TCN) into the field of ship trajectory prediction and upgraded it, proposing the Tiered–TCN (TTCN) because TCN gives high temporal memory ability and has demonstrated greater performance in time series prediction in recent years. Then, TTCN, the attention mechanism, and the GRU network were combined to create the TTCN–Attention–GRU (TTAG) hybrid model for trajectory prediction. High accuracy prediction impact was obtained by optimizing the benefits of each module. The TTAG model’s structure is depicted in Figure 30. The input layer, Tiered–TCN layer, attention layer, reshape layer, GRU layer, and dense layer were the six layers that made up the model. The vectors of the Tiered–TCN layer’s output were assigned varying weights by the attention layer. Following the reshape layer’s dimension change on the features, the GRU layer collected more data features. To achieve the ultimate prediction, feature integration was then completed using the dense layer.
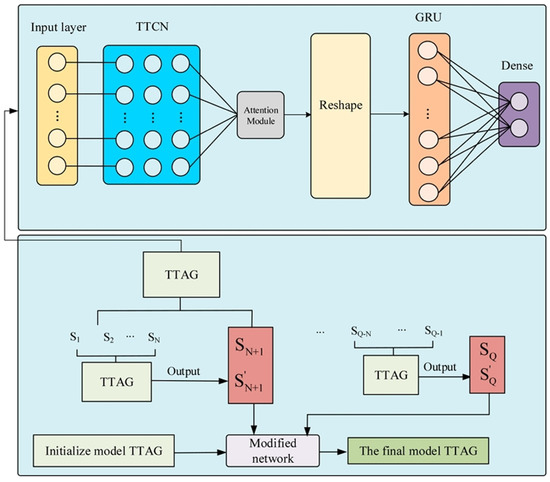
Figure 30.
The structure of the TTAG model [91].
3.2.4. Seq2seq
Speech recognition, machine translation, and other applications involving variable length input and output sequences have made extensive use of the sequence-to-sequence model. Its main concept is to use a cyclic neural network to transfer a variable length input sequence to a variable length output sequence [92,93]. One of the encoding–decoding structures (Figure 31) that can map an input sequence to an output sequence with different lengths is the sequence-to-sequence model.

Figure 31.
Seq2seq model [94].
The needs for real–time navigation are not fully supported by current models. An expanded Seq2seq model was given by You et al. [94] with the aim of predicting short–term vessel motions. The strategy is predicated on incoming AIS data, with the primary objective being the provision of a forecast system to prevent vessel collisions. The primary unique feature of the method is that it considers the irregular sampling of AIS data while simultaneously improving vessel navigation predictions by utilizing contextual and previous navigation data. As illustrated in Figure 32a, the model incorporates the features of both the Seq2Seq model and the spatiotemporal sequence data. The primary components of the real–time Seq2Seq prediction model are two RNN modules. In order to help predict future ship AIS trajectories, this model can be thought of as a process that involves encoding previous ship AIS trajectory input data, extracting trajectory features, and then decoding the features. For evaluation, the authors used actual AIS data from the Yangzi River’s Chongqing and Wuhan portions as representative experimental locations. The enlarged Seq2Seq model has acceptable stability on various ship channels, as seen in Figure 32b.
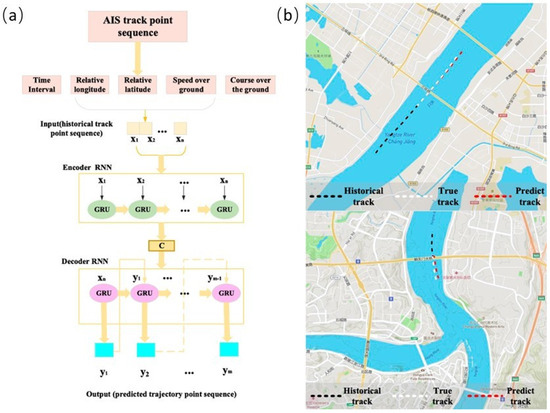
Figure 32.
Seq2Seq neural network model (a) and forecast result (b) [94].
The majority of research concentrates more on extracting temporal aspects of ship trajectories while ignoring the spatial connections between trajectory points because of the strong temporal relationship in the context of trajectory sequences. In order to facilitate the simultaneous extraction of temporal and spatial features of ship trajectories, Wu et al. [95] proposed a trajectory prediction model that integrates the convolutional LSTM (convLSTM) and sequence-to-sequence (Seq2Seq) models, as shown in Figure 33, thereby improving the prediction accuracy.
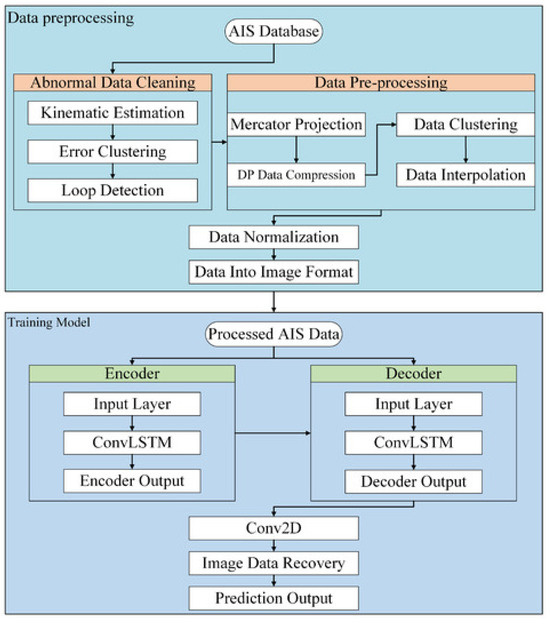
Figure 33.
ConvLSTM–seq2seq model design flow chart [95].
3.3. Other Deep Learning Models
In addition to the studies mentioned above, other deep learning methods can also be applied to ship trajectory prediction. Murray and Perera [20] proposed a novel dual linear autoencoder method to predict the future trajectory of a ship. Two linear autoencoders were used in this method. The chosen vessel’s future trajectory could be predicted using the latent representation of the history trajectories provided by the forward linear autoencoder. A latent representation of the previous behavior of the historical trajectories was provided by the backward linear autoencoder. To estimate the forward latent representation of the chosen vessel, latent interpolation was carried out based on a similarity measure evaluated in the latent space of the backward linear autoencoder. This estimate could then be encoded to produce a trajectory forecast.
Zhang et al. [96] applied generative adversarial networks (GANs) to ship collision avoidance. The suggested video-based early warning system had three primary components: trajectory anomaly detection and prediction, vessel trajectory data augmentation, and vessel placement (Figure 34). Initially, a real-time, homograph-based vessel positioning method was used to achieve vessel placement. To improve the historical trajectories, particularly the aberrant trajectories, trajectory generative adversarial networks with multiple critics (TGANs-MC) were suggested as a second option. Third, a dual-task network was used to forecast the trajectories of boats involved in warning of vessel–vessel collisions and identify vessels with aberrant trajectories for warning of vessel–bridge collisions.

Figure 34.
The framework for warning of ship collisions [96].
Transformer models currently perform exceptionally well in time series forecasting, computer vision, and natural language processing. Transformer models have great structural advantages in representing sequential problems, but they do not use the recursive method of recurrent neural networks. These benefits make it possible to model ship trajectory prediction with high performance. A deep learning vessel trajectory prediction technique combining discretized meteorological data (TripleConvTransformer) was presented by Huang et al. [97]. In order to capture multiscale information, the model consisted of three modules: global convolution, local convolution, and trend convolution. These modules were based on the simplified transformer model. TripleConvTransformer had some advantages in the network architecture and was capable of extracting features in all dimensions. According to the experimental findings, TripleConvTransformer produced impressive trajectory prediction outcomes for forecasting latitude and longitude. Nevertheless, there is not a confidence index in the current model.
4. Conclusions
In conclusion, the shipping industry has experienced rapid growth in past years, coupled with the introduction of MASS. This has led to increasingly complex maritime traffic environments, posing new challenges for ship route planning, navigation safety, and traffic control. Accurate ship trajectory prediction emerges as a pivotal tool to address these challenges effectively. With the advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) technology, its applications in trajectory prediction have shown significant value. Constructing predictive models utilizing machine learning and deep learning methods for ship trajectory prediction has garnered widespread attention.
Given the need for developing intelligent maritime traffic systems in the future, this paper provided a comprehensive review of the application of different mathematical models and algorithms in ship trajectory prediction to reveal their advantages and disadvantages as well as fitness in different scenarios involving complicated maritime traffic. In machine learning approaches, regression models offer easy access to future ship positions but with limited prediction accuracy, while predictive models based on neural network algorithms achieve high precision in trajectory prediction tasks but come with a large number of parameters and high computational complexity.
In deep learning methods, convolutional neural networks (CNNs) effectively extract features from trajectory data but are not suitable for handling sequential data. However, recurrent neural networks (RNNs) efficiently extract spatio-temporal features from AIS historical data and accurately predict future trajectories in real-time. The introduction of attention mechanisms has also improved the performance of prediction models. It is noteworthy that the performance of seq2seq models in ship trajectory prediction is not as favorable as in other applications.
This research provides guidance for related fields such as maritime vessel anomaly detection, collision avoidance warning systems, route planning, and traffic control. In future studies, trajectory prediction will become one of the key technologies for achieving safe autonomous navigation. To address diverse maritime navigation environments, future research will focus on improving prediction accuracy, real-time performance, and model generalization capabilities.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.B., H.C. and W.Z.; methodology, J.B., H.C. and W.Z.; model, J.B., H.C., K.B. and P.W.; validation, J.B., W.Z. and H.C.; formal analysis, K.B. and P.W.; investigation, J.B. and W.Z.; resources, W.Z; writing—original draft preparation, J.B.; writing—review and editing, W.Z.; visualization, K.B. and P.W.; supervision, W.Z.; project administration, W.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (grant number 2022YFB3207400) and the Tianjin Transportation Technology Development Plan Project (grant number 2023-47) and the Tianjin Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 22JCQNJC00290).
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing is not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Hermann, M.; Pentek, T.; Otto, B. Design Principles for Industrie 4.0 Scenarios. In Proceedings of the 2016 49th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences (HICSS), Koloa, HI, USA, 5–8 January 2016; pp. 3928–3937. [Google Scholar]
- Jan Rødseth, L.P.P.Ø.; Mo, B. Big Data in Shipping—Challenges and Opportunities. In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Computer and IT Applications in the Maritime Industries—COMPIT’16, Lecce, Italy, 9–11 May 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kisialiou, Y.; Gribkovskaia, I.; Laporte, G. Robust supply vessel routing and scheduling. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2018, 90, 366–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capobianco, S.; Millefiori, L.M.; Forti, N.; Braca, P.; Willett, P. Deep Learning Methods for Vessel Trajectory Prediction Based on Recurrent Neural Networks. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2021, 57, 4329–4346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akyuz, E. A hybrid accident analysis method to assess potential navigational contingencies: The case of ship grounding. Saf. Sci. 2015, 79, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Cao, G.; Xu, H.; Ge, S.S. IS-STGCNN: An Improved Social spatial-temporal graph convolutional neural network for ship trajectory prediction. Ocean Eng. 2022, 266, 112960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Zhu, Y.; Soares, C.G. Uncertainty modelling and dynamic risk assessment for long-sequence AIS trajectory based on multivariate Gaussian Process. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2023, 230, 108963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Chen, L.; Chen, P.; Negenborn, R.R.; van Gelder, P.H.A.J.M. Ship collision avoidance methods: State-of-the-art. Saf. Sci. 2020, 121, 451–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansen, T.A.; Perez, T.; Cristofaro, A. Ship Collision Avoidance and COLREGS Compliance Using Simulation-Based Control Behavior Selection With Predictive Hazard Assessment. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2016, 17, 3407–3422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Wu, B.; Wang, Y. Autonomous decision-making scheme for multi-ship collision avoidance with iterative observation and inference. Ocean Eng. 2020, 197, 106873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, X.; Liu, K.; Loughney, S.; Wang, J.; Yang, Z. Maritime traffic clustering to capture high-risk multi-ship encounters in complex waters. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2023, 230, 108936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, L.P.; Ferrari, V.; Santos, F.P.; Hinostroza, M.A.; Soares, C.G. Experimental Evaluations on Ship Autonomous Navigation and Collision Avoidance by Intelligent Guidance. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2015, 40, 374–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polvara, R.; Sharma, S.; Wan, J.; Manning, A.; Sutton, R. Obstacle Avoidance Approaches for Autonomous Navigation of Unmanned Surface Vehicles. J. Navig. 2017, 71, 241–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.-W.; Zhu, Y.-S.; Zhang, J.-F.; He, Y.-K.; Yan, K.; Yan, B.-R. A novel MP-LSTM method for ship trajectory prediction based on AIS data. Ocean Eng. 2021, 228, 108956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.W.; Liang, M.; Nie, J.; Lim, W.Y.B.; Zhang, Y.; Guizani, M. Deep Learning-Powered Vessel Trajectory Prediction for Improving Smart Traffic Services in Maritime Internet of Things. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2022, 9, 3080–3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Jiao, H.; Yang, Z. AIS data-driven ship trajectory prediction modelling and analysis based on machine learning and deep learning methods. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2023, 175, 103152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schöller, T.T.E.F.E.T.; Becktor, J.B.; Hansen, P.N. Trajectory Prediction for Marine Vessels using Historical AIS Heatmaps and Long Short-Term Memory Networks. IFAC-Pap. 2021, 54, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abebe, M.; Noh, Y.; Kang, Y.-J.; Seo, C.; Kim, D.; Seo, J. Ship trajectory planning for collision avoidance using hybrid ARIMA-LSTM models. Ocean Eng. 2022, 256, 111527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yuan, H.; Xiao, C.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Q. Hybrid-driven vessel trajectory prediction based on uncertainty fusion. Ocean. Eng. 2022, 248, 110836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, B.; Perera, L.P. A dual linear autoencoder approach for vessel trajectory prediction using historical AIS data. Ocean Eng. 2020, 209, 107478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, L.-Z.; Wall, A.; Mao, Z.; Yan, X.-P.; Wang, J. A novel method for restoring the trajectory of the inland waterway ship by using AIS data. Ocean Eng. 2015, 110, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Mou, J.; Chen, L.; Chen, P. Improved kinematic interpolation for AIS trajectory reconstruction. Ocean Eng. 2021, 234, 109256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, H.; Teixeira, A.P.; Soares, C.G. Maritime traffic probabilistic prediction based on ship motion pattern extraction. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2022, 217, 108061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahesh, B. Machine Learning Algorithms—A Review. Int. J. Sci. Res. 2020, 9, 381–386. [Google Scholar]
- Jordan, M.I.; Mitchell, T.M. Machine learning: Trends, perspectives, and prospects. Science 2015, 349, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, G. Generating bunkering statistics from AIS data: A machine learning approach. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2021, 155, 102495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.-C.; Ko, K.-M.; Shu, M.-H.; Hsu, B.-M. Application and comparison of several machine learning algorithms and their integration models in regression problems. Neural Comput. Appl. 2019, 32, 5461–5469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Yan, X.; Tsai, C.L. Linear regression. WIREs Comput. Stat. 2012, 4, 275–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neri, P. Time-domain simulator for short-term ship manoeuvring prediction: Development and applications. Ships Offshore Struct. 2018, 14, 249–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, C.N. An Extension of the Linear Regression Model for Improved Vessel Trajectory Prediction Utilising a Priori AIS Information; University of Stellenbosch: Stellenbosch, South Africa, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, S.; Suo, Y.; Zheng, M.; Wang, P. Ship Track Prediction Based on DLGWO-SVR. Sci. Program. 2021, 2021, 9085617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Shi, G.; Zhu, K. Vessel Trajectory Prediction Model Based on AIS Sensor Data and Adaptive Chaos Differential Evolution Support Vector Regression (ACDE-SVR). Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Shi, G.; Zhu, K. Online Multiple Outputs Least-Squares Support Vector Regression Model of Ship Trajectory Prediction Based on Automatic Information System Data and Selection Mechanism. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 154727–154745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, H.; Jin, S.; Feng, X.; Xue, D.; Zhang, L. Model Predictive Control of a Shipborne Hydraulic Parallel Stabilized Platform Based on Ship Motion Prediction. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 181880–181892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Wang, W.; Xue, Y. Identification of Ship Dynamics Model Based on Sparse Gaussian Process Regression with Similarity. Symmetry 2021, 13, 1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, H.; Teixeira, A.P.; Soares, C.G. Ship trajectory uncertainty prediction based on a Gaussian Process model. Ocean Eng. 2019, 182, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krogh, A. What are artificial neural networks? Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 195–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rumelhart, D.E.; Hinton, G.E.; Williams, R.J. Learning representations by back-propagating errors. Nat. Biotechnol. 1986, 323, 533–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkova, T.A.; Balykina, Y.E.; Bespalov, A. Predicting Ship Trajectory Based on Neural Networks Using AIS Data. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, S. Ship Trajectory Prediction Based on BP Neural Network. J. Artif. Intell. 2019, 1, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zissis, D.; Xidias, E.K.; Lekkas, D. Real-time vessel behavior prediction. Evol. Syst. 2015, 7, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simsir, U.; Ertugrul, S. Prediction of manually controlled vessels’ position and course navigating in narrow waterways using Artificial Neural Networks. Appl. Soft Comput. 2009, 9, 1217–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Liu, X.; Yang, X. Ship Trajectory Online Prediction Based on BP Neural Network Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference of Information Technology, Computer Engineering and Management Sciences, Nanjing, China, 24–25 September 2011; pp. 103–106. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Ling, J.; Yang, Y.; Zheng, H.; Xiong, P.; Postolache, O.; Xiong, Y. Ship Trajectory Reconstruction from AIS Sensory Data via Data Quality Control and Prediction. Math. Probl. Eng. 2020, 2020, 7191296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borkowski, P. The Ship Movement Trajectory Prediction Algorithm Using Navigational Data Fusion. Sensors 2017, 17, 1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacki, M. Intelligent Prediction of Ship Maneuvering, TransNav. the Int. J. Mar. Navig. Saf. Sea Transp. 2016, 10, 511–516. [Google Scholar]
- Valsamis, A.; Tserpes, K.; Zissis, D.; Anagnostopoulos, D.; Varvarigou, T. Employing traditional machine learning algorithms for big data streams analysis: The case of object trajectory prediction. J. Syst. Softw. 2017, 127, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Sui, Z.; Zhou, C.; Xiao, C.; Chen, Q.; Han, D.; Zhang, Y. Automatic ship route design between two ports: A data-driven method. Appl. Ocean Res. 2020, 96, 102049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, S.L.S.; Li, K.; Deng, J.; Cheng, T. Ship trajectory prediction for intelligent traffic management using clustering and ANN. In Proceedings of the 2016 UKACC 11th International Conference on Control (CONTROL), IEEE, Belfast, UK, 31 August–2 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Lu, J.; Chen, X.; Yan, Z.; Yan, Y.; Sun, Y. High-fidelity data supported ship trajectory prediction via an ensemble machine learning framework. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2022, 586, 126470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Li, L.; Qian, L.; Cheng, B.; Hou, W.; Zhuang, Y. Sine-SSA-BP Ship Trajectory Prediction Based on Chaotic Mapping Improved Sparrow Search Algorithm. Sensors 2023, 23, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadimitrakis, M.; Stogiannos, M.; Sarimveis, H.; Alexandridis, A. Multi-Ship Control and Collision Avoidance Using MPC and RBF-Based Trajectory Predictions. Sensors 2021, 21, 6959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanazawa, M.; Skulstad, R.; Li, G.; Hatledal, L.I.; Zhang, H. A Multiple-Output Hybrid Ship Trajectory Predictor With Consideration for Future Command Assumption. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 27124–27135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Fu, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Liu, R.W.; Liu, Z.; Goh, R.S.M. Big Data Driven Vessel Trajectory and Navigating State Prediction With Adaptive Learning, Motion Modeling and Particle Filtering Techniques. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 3696–3709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Li, G.; Hatledal, L.I.; Skulstad, R.; Aesoy, V.; Zhang, H. Incorporating Approximate Dynamics Into Data-Driven Calibrator: A Representative Model for Ship Maneuvering Prediction. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2022, 18, 1781–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Zhang, L.; Fu, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, J.T.; Goh, R.S.M. Concurrent Processing Cluster Design to Empower Simultaneous Prediction for Hundreds of Vessels’ Trajectories in Near Real-Time. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2020, 51, 1830–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, N.A.B.B.J.; Zandipour, M. Probabilistic Associative Learning of Vessel Motion Patterns at Multiple Spatial Scales for Maritime Situation Awareness. In Proceedings of the 2007 10th International Conference on Information Fusion, IEEE, Quebec, QC, Canada, 9–12 July 2007; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Karataş, G.B.; Karagoz, P.; Ayran, O. Trajectory pattern extraction and anomaly detection for maritime vessels. Internet Things 2021, 16, 100436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Bin, J.; Wang, W.; Peng, X.; Wang, R.; Halldearn, R.; Liu, Z. AIS data driven general vessel destination prediction: A random forest based approach. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2020, 118, 102729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abebe, M.; Shin, Y.; Noh, Y.; Lee, S.; Lee, I. Machine Learning Approaches for Ship Speed Prediction towards Energy Efficient Shipping. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, L.P.; Oliveira, P.; Soares, C.G. Maritime Traffic Monitoring Based on Vessel Detection, Tracking, State Estimation, and Trajectory Prediction. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2012, 13, 1188–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, W.; Song, R.; Bucknall, R. Predictive navigation of unmanned surface vehicles in a dynamic maritime environment when using the fast marching method. Int. J. Adapt. Control Signal Process. 2015, 31, 464–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, Z. Short-Term Traffic Volume Forecasting Using Kalman Filter with Discrete Wavelet Decomposition. Comput. -Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2007, 22, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaskólski, K. Automatic Identification System (AIS) Dynamic Data Estimation Based on Discrete Kalman Filter (KF) Algorithm. Sci. J. Pol. Nav. Acad. 2017, 211, 71–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, B.; Perera, L.P. Ship behavior prediction via trajectory extraction-based clustering for maritime situation awareness. J. Ocean Eng. Sci. 2022, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Shang, Z.; Guo, S.; Du, Y.; Dolezel, P. A Decision-Making Method for Ship Collision Avoidance Based on Improved Cultural Particle Swarm. J. Adv. Transp. 2021, 2021, 8898507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Guo, S.; Feng, Y.; Hong, F.; Huang, H.; Guo, Z. L-VTP: Long-Term Vessel Trajectory Prediction Based on Multi-Source Data Analysis. Sensors 2019, 19, 4365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hexeberg, S.; Flåten, A.L.; Eriksen, B.-O.H.; Brekke, E.F. AIS-based vessel trajectory prediction. In Proceedings of the 2017 20th International Conference on Information Fusion (Fusion), Xi’an, China, 10–13 July 2017; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, A.; Walczak, S. Maritime Autonomous Surface Ship’s Path Approximation Using Bézier Curves. Symmetry 2020, 12, 1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Chu, X.; Zheng, M.; Liu, C. Ship predictive collision avoidance method based on an improved beetle antennae search algorithm. Ocean Eng. 2019, 192, 106542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Lin, R.; Zou, H. A Novel CNN-LSTM Method for Ship Trajectory Prediction. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 23rd IEEE International Conference on High Performance Computing and Communications (HPCC-2021); 7th IEEE International Conference on Data Science and Systems (IEEE DSS-2021); 19th IEEE International Conference on Smart City (SmartCity); 7th International Conference on Dependability in Sensor, Cloud & Big Data Systems & Application (HPCC/DSS/SmartCity/DependSys), Haikou, China, 17–19 December 2021; pp. 2431–2436. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, B.; Perera, L.P. An AIS-based deep learning framework for regional ship behavior prediction. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2021, 215, 107819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Ni, G.; Xu, Y. Ship Trajectory Prediction based on LSTM Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 5th Information Technology and Mechatronics Engineering Conference (ITOEC), IEEE, Chongqing, China, 12–14 June 2020; pp. 1356–1364. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, L.; Zheng, Y.; Li, L.; Ma, Y.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, D. A New Method of Inland Water Ship Trajectory Prediction Based on Long Short-Term Memory Network Optimized by Genetic Algorithm. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 4073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Xing, H. A novel method for ship trajectory prediction in complex scenarios based on spatio-temporal features extraction of AIS data. Ocean Eng. 2023, 281, 114846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Zuo, Y.; Li, T.; Lambert, A. Vessel Navigation Behavior Analysis and Multiple-Trajectory Prediction Model Based on AIS Data. J. Adv. Transp. 2022, 2022, 6622862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venskus, J.; Treigys, P.; Markevičiūtė, J. Unsupervised marine vessel trajectory prediction using LSTM network and wild bootstrapping techniques. Nonlinear Anal. Model. Control 2021, 26, 718–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammedi, W.; Brik, B.; Senouci, S.M. Toward Optimal MEC-Based Collision Avoidance System for Cooperative Inland Vessels: A Federated Deep Learning Approach. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 24, 2525–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Jia, C.; Shu, Y.; Liu, K.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, Y. Intent prediction of vessels in intersection waterway based on learning vessel motion patterns with early observations. Ocean Eng. 2021, 232, 109154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehri, S.; Alesheikh, A.A.; Basiri, A. A Contextual Hybrid Model for Vessel Movement Prediction. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 45600–45613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wei, C.; Zhou, G.; Wu, H.; Wang, Z.; Biancardo, S.A. Automatic Identification System (AIS) Data Supported Ship Trajectory Prediction and Analysis via a Deep Learning Model. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Jeong, J.; Park, Y. Ship Trajectory Prediction Based on Bi-LSTM Using Spectral-Clustered AIS Data. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.; Jiang, Z.; Chu, X.; Liu, L. Inland Ship Trajectory Restoration by Recurrent Neural Network. J. Navig. 2019, 72, 1359–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Shi, G.; Li, S. Online Prediction of Ship Behavior with Automatic Identification System Sensor Data Using Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory Recurrent Neural Network. Sensors 2018, 18, 4211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Fu, Y. Ship Trajectory Prediction Based on Attention in Bidirectional Recurrent Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2020 5th International Conference on Information Science, Computer Technology and Transportation (ISCTT), Shenyang, China, 13–15 November 2020; pp. 529–533. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, C.G.J.; Cho, K.; Bengio, Y. Empirical Evaluation of Gated Recurrent Neural Networks on Sequence Modeling. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.3555v1. [Google Scholar]
- Han, P.; Wang, W.; Shi, Q.; Yang, J. Real-time Short-Term Trajectory Prediction Based on GRU Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/AIAA 38th Digital Avionics Systems Conference (DASC), San Diego, CA, USA, 8–12 September 2019; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Suo, Y.; Chen, W.; Claramunt, C.; Yang, S. A Ship Trajectory Prediction Framework Based on a Recurrent Neural Network. Sensors 2020, 20, 5133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Ren, H.; Li, H. Vessel trajectory prediction based on AIS data and bidirectional GRU. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Computer Vision, Image and Deep Learning (CVIDL), Chongqing, China, 10–12 July 2020; pp. 260–264. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, K.; Bi, J.; Gao, M.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, W. An Improved Ship Trajectory Prediction Based on AIS Data Using MHA-BiGRU. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Yue, W.; Huang, J.; Wan, J. Ship Trajectory Prediction Based on the TTCN-Attention-GRU Model. Electronics 2023, 12, 2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; Wang, Y.; Fang, Y.; Xiao, W. Abstract Text Summarization with a Convolutional Seq2seq Model. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xiao, W. Keyphrase Generation Based on Deep Seq2seq Model. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 46047–46057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, L.; Xiao, S.; Peng, Q.; Claramunt, C.; Han, X.; Guan, Z.; Zhang, J. ST-Seq2Seq: A Spatio-Temporal Feature-Optimized Seq2Seq Model for Short-Term Vessel Trajectory Prediction. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 218565–218574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Chen, P.; Chen, L.; Mou, J. Ship Trajectory Prediction: An Integrated Approach Using ConvLSTM-Based Sequence-to-Sequence Model. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wu, G. A warning framework for avoiding vessel-bridge and vessel-vessel collisions based on generative adversarial and dual-task networks. Comput. Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2021, 37, 629–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Chen, Q.; Wang, D.; Wang, M.; Wu, X.; Huang, X. TripleConvTransformer: A deep learning vessel trajectory prediction method fusing discretized meteorological data. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 1012547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).