Temperature Structure Inversion of Mesoscale Eddies in the South China Sea Based on Deep Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- We construct a dataset for the inversion of the subsurface temperature structure of mesoscale eddies by combining SSH, SST, and subsurface temperature reanalysis data. This dataset offers practical support, particularly for studying mesoscale eddies in the South China Sea.
- (2)
- Using a data-driven approach and deep learning technology, we build a network (Dual_EddyNet) that establishes the relationships between the sea surface and subsurface, incorporating multiple sources of sea surface data. As a result, we reconstruct the three-dimensional temperature field of mesoscale eddies within a depth of 1000 m in the South China Sea, significantly improving the inversion accuracy.
- (3)
- Based on the proposed Dual_EddyNet method, we investigate the trends in the three-dimensional temperature fields at different depths for cyclonic and anticyclonic mesoscale eddies in the South China Sea, with a focus on the impact of the SST and SSH.
2. Data and Data Preprocessing
2.1. Data
2.2. Data Preprocessing
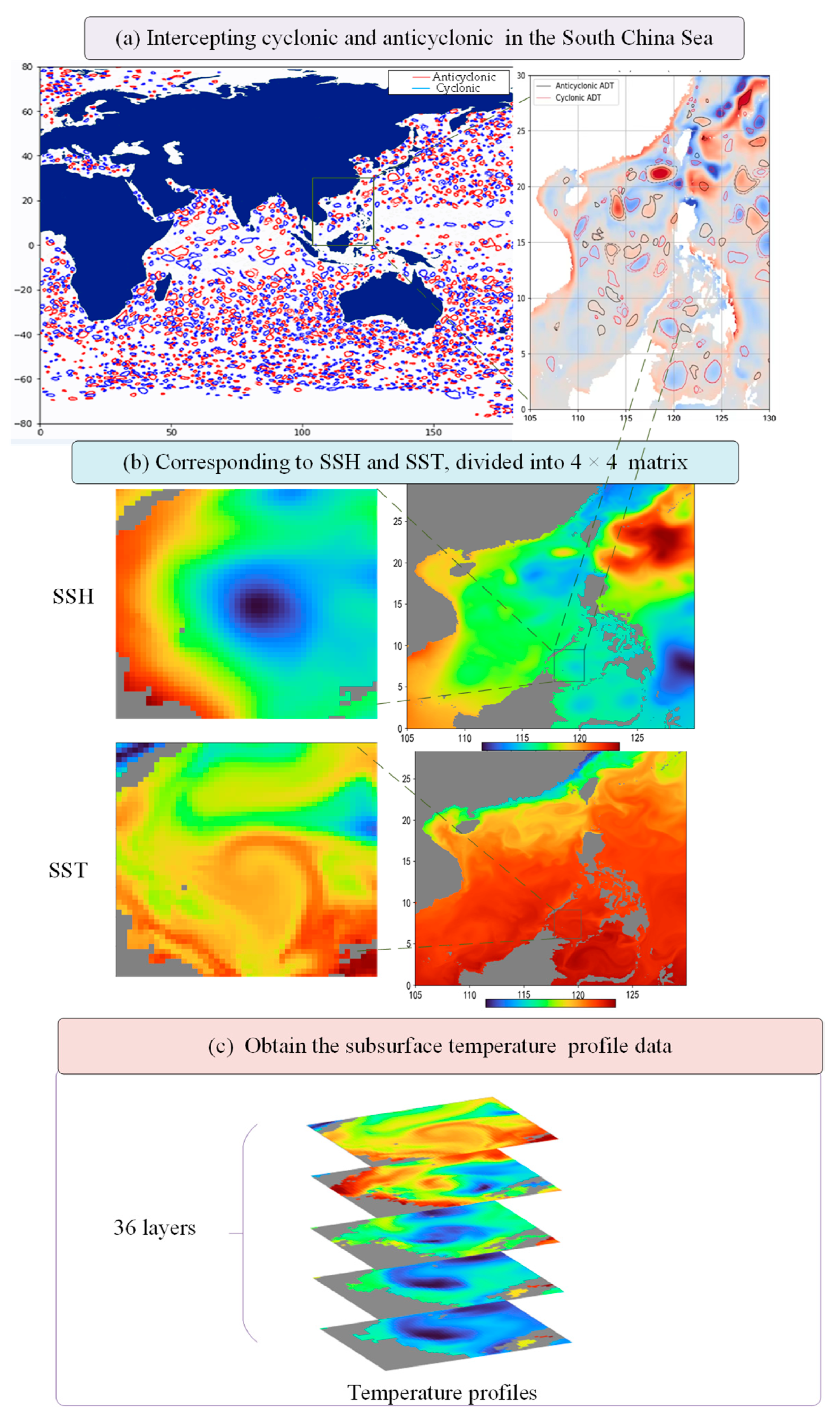
- (a)
- The South China Sea region (0–30° N, 105–130° E) is selected. Critical information, such as the coordinates and time of the eddy center, is extracted from the AVISO mesoscale eddy dataset and separate cyclonic and anticyclonic eddy datasets.
- (b)
- The corresponding sea surface position coordinates are identified based on the eddy center coordinates and time. A 4 × 4 matrix is defined with the coordinates as the center, and sea surface information (SSH and SST) is extracted from the Copernicus reanalysis data within the specified region, establishing the relationship mapping between mesoscale eddies and the sea surface.
- (c)
- Subsurface temperature profile information is obtained within the corresponding region from the Copernicus reanalysis data. We select the first 36 layers of data (0–1000 m) as the ground truth data.
3. Method
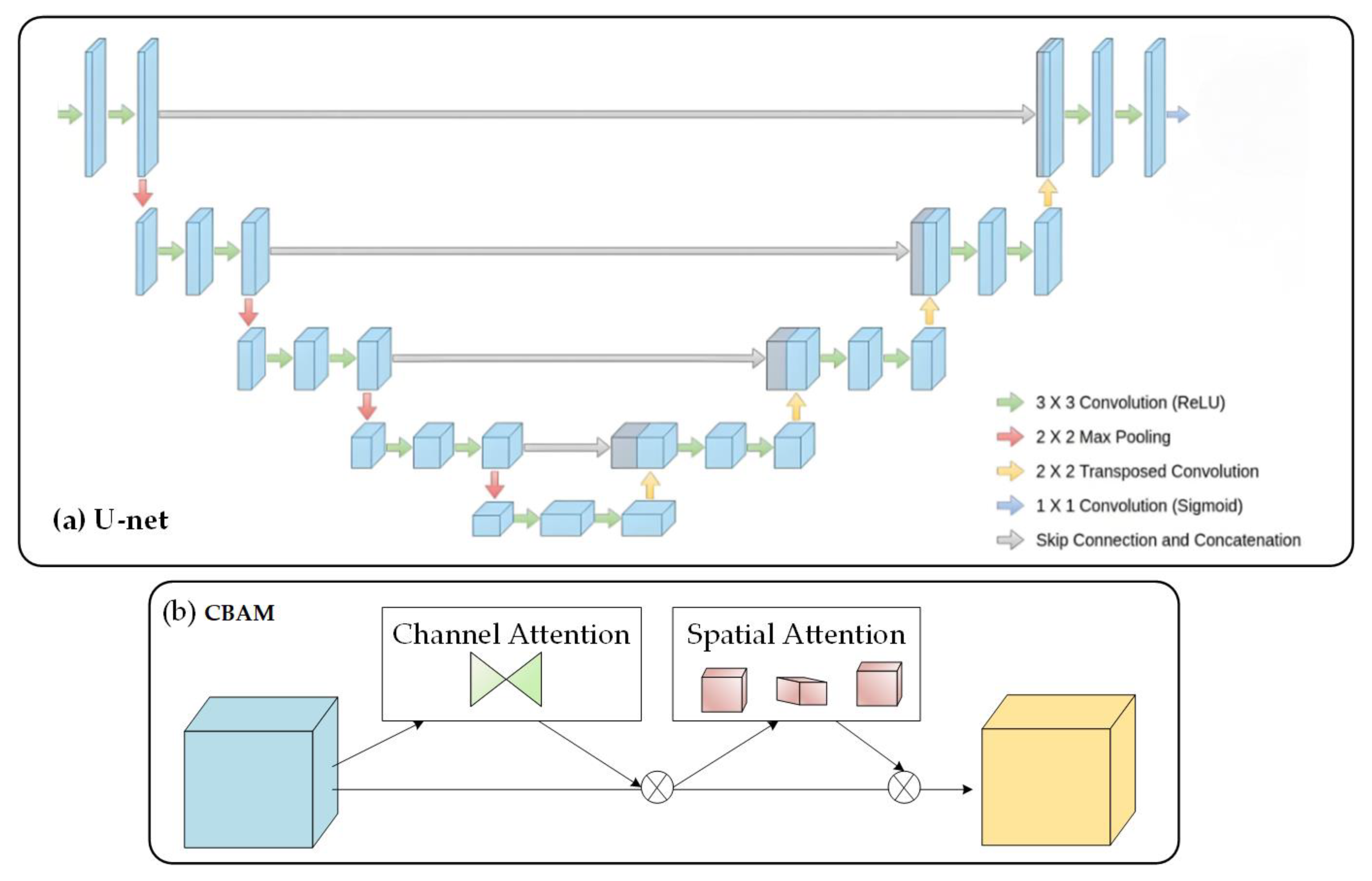
3.1. Convolutional Neural Networks
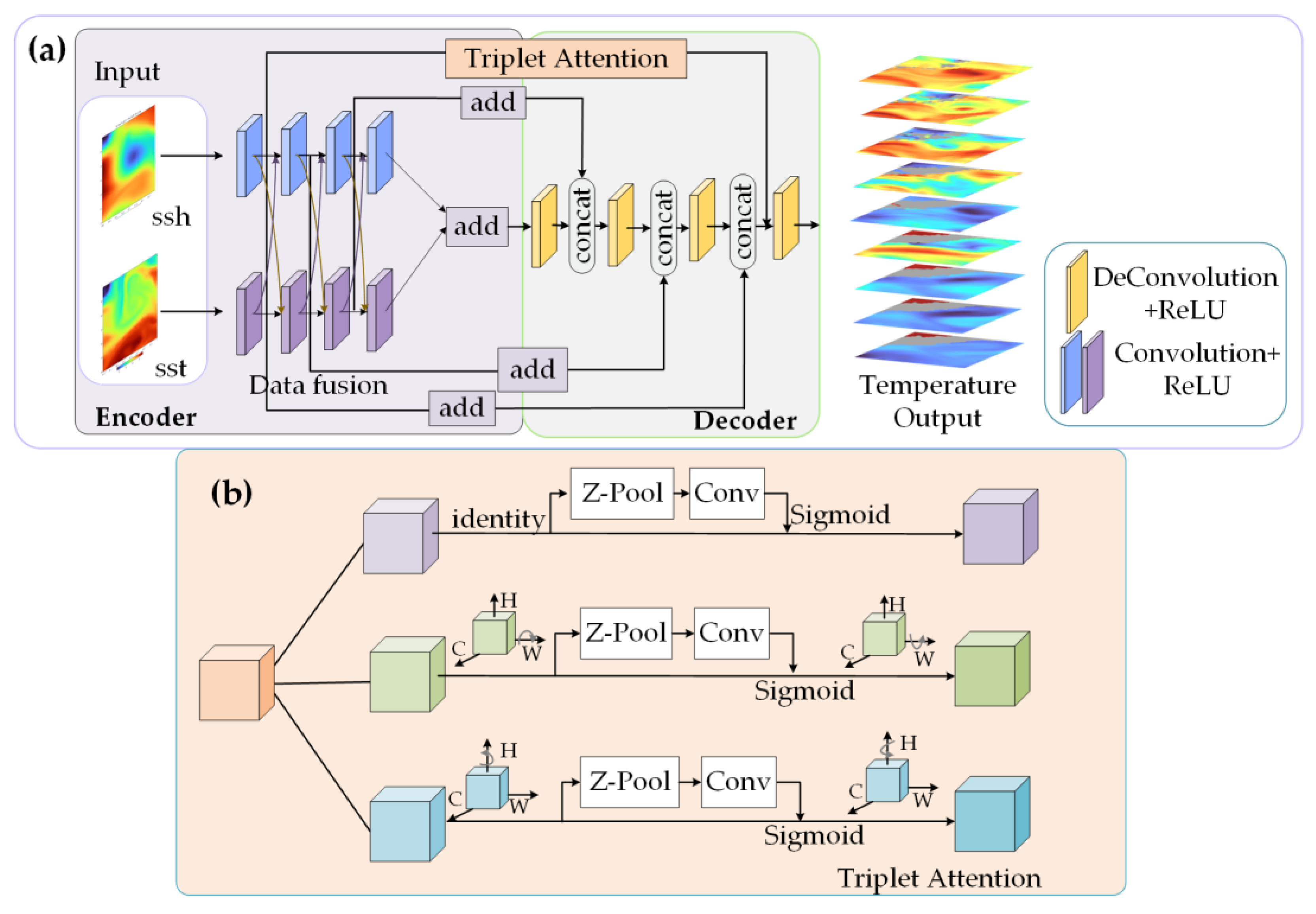
3.2. The Overall Architecture of the Model
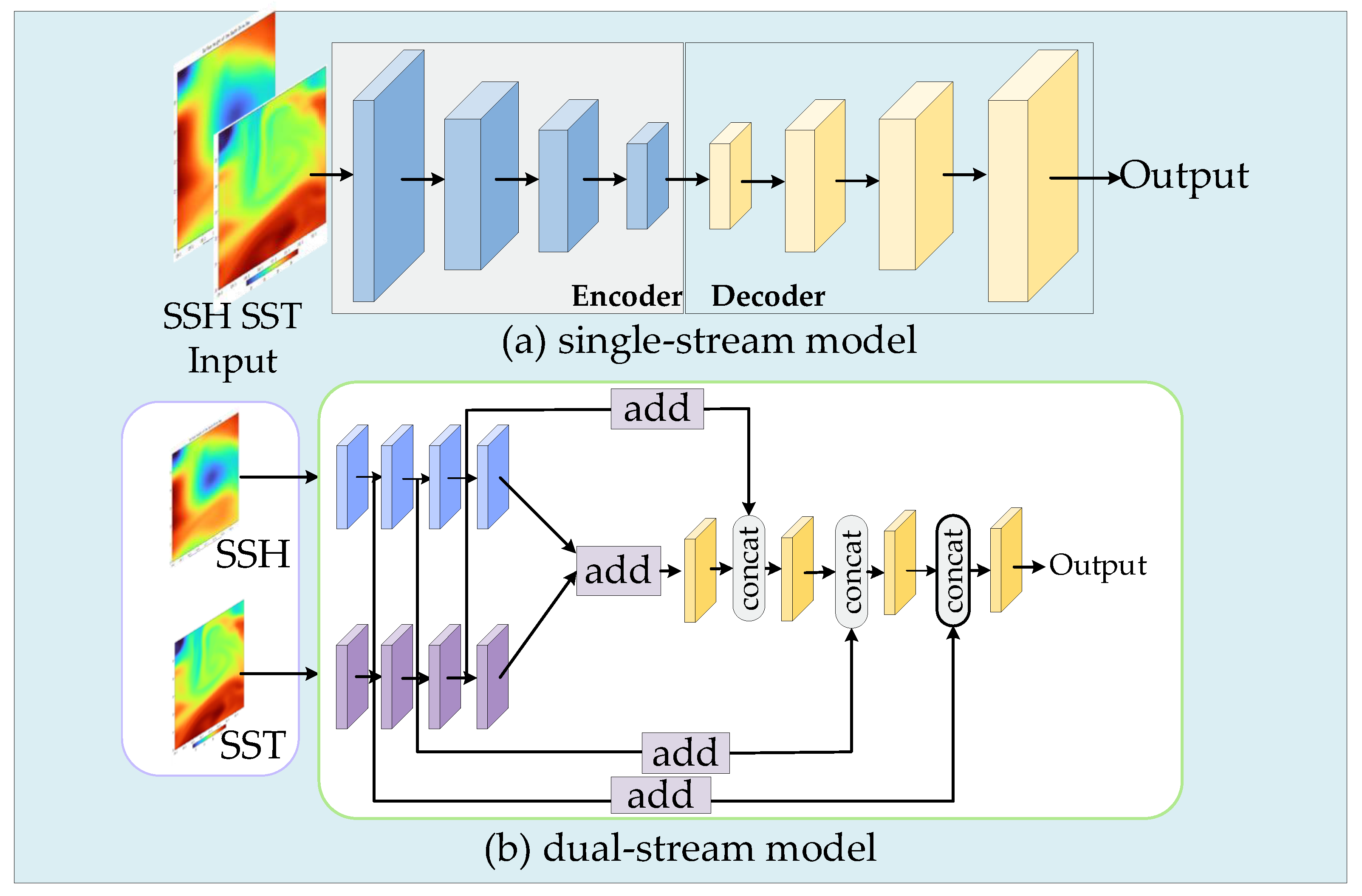
3.3. Comparison of Single-Stream and Dual-Stream Models
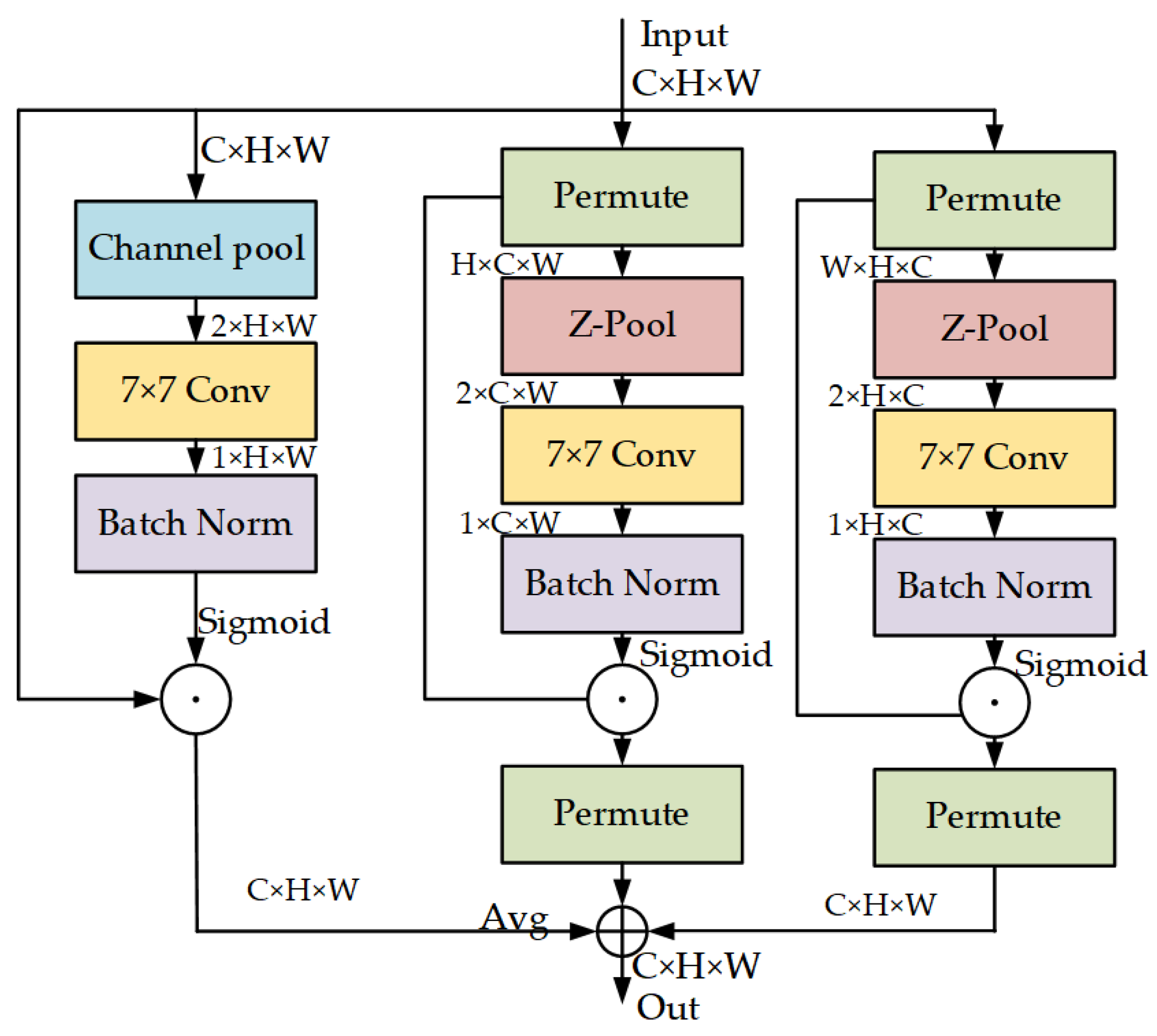
3.4. Triplet Attention
4. Experiments
4.1. Evaluation Metrics
4.2. Experimental Results
4.2.1. Comparison of Input of Different Variables
4.2.2. Comparison of Different Model
4.2.3. Ablation Experiments
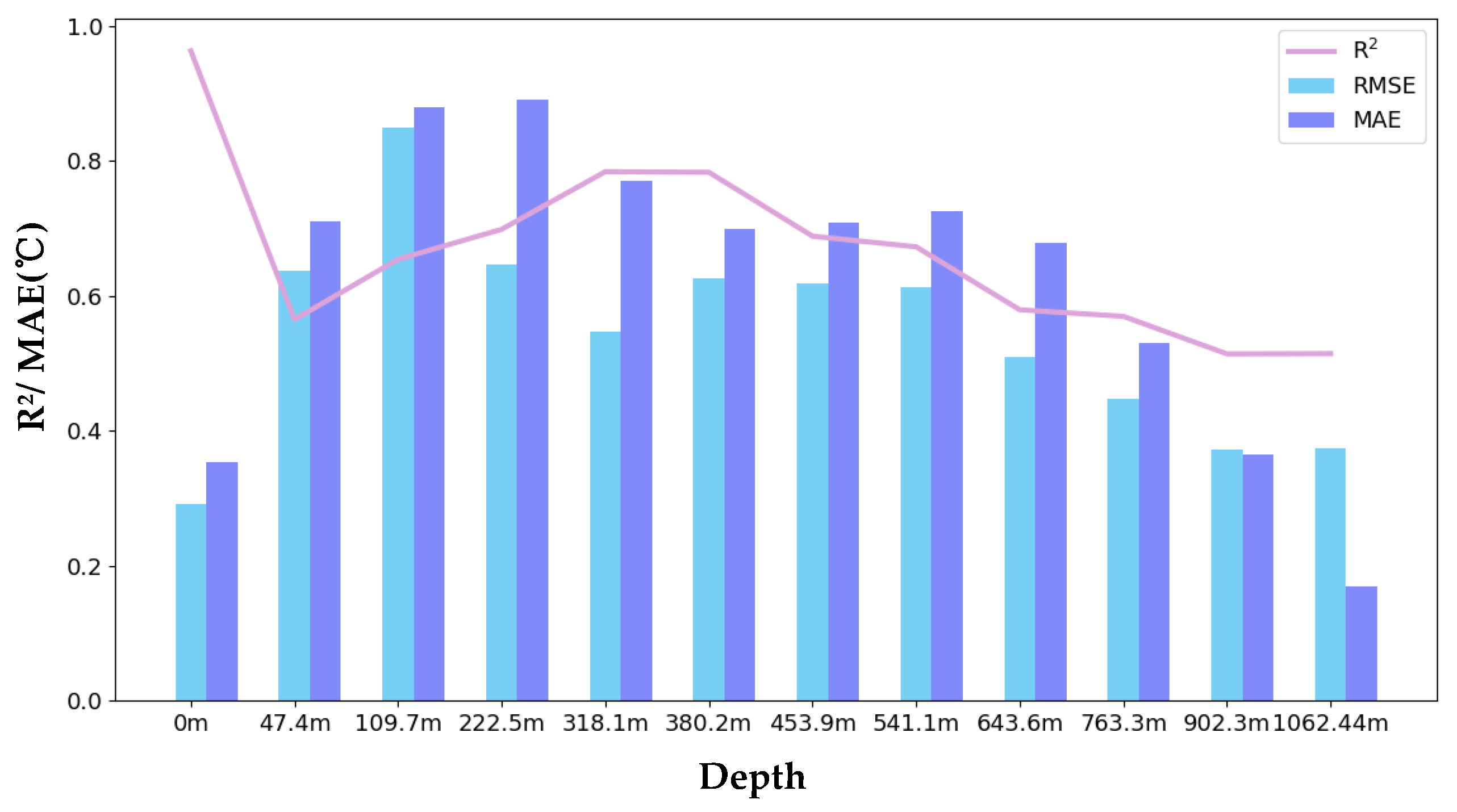
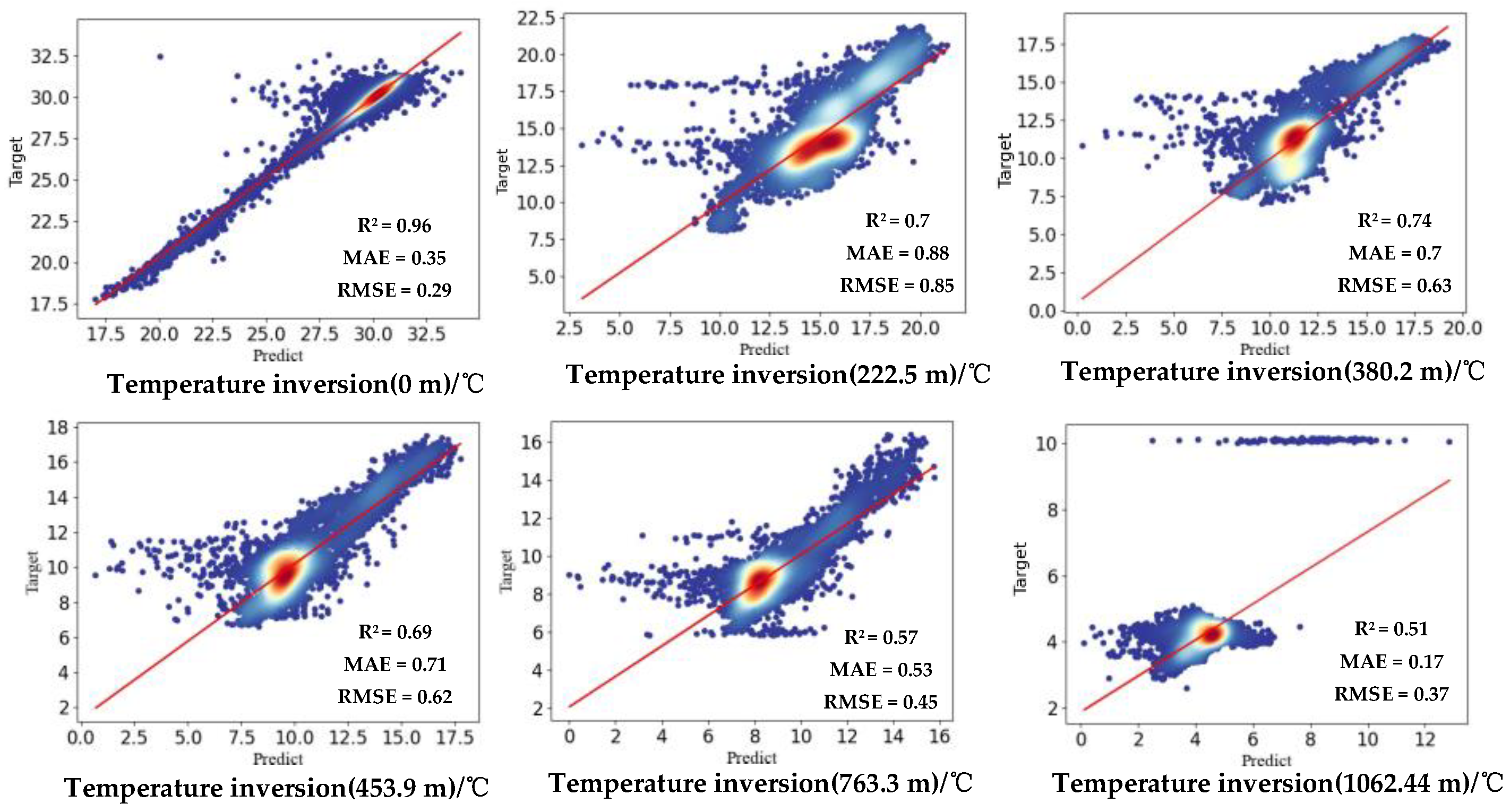
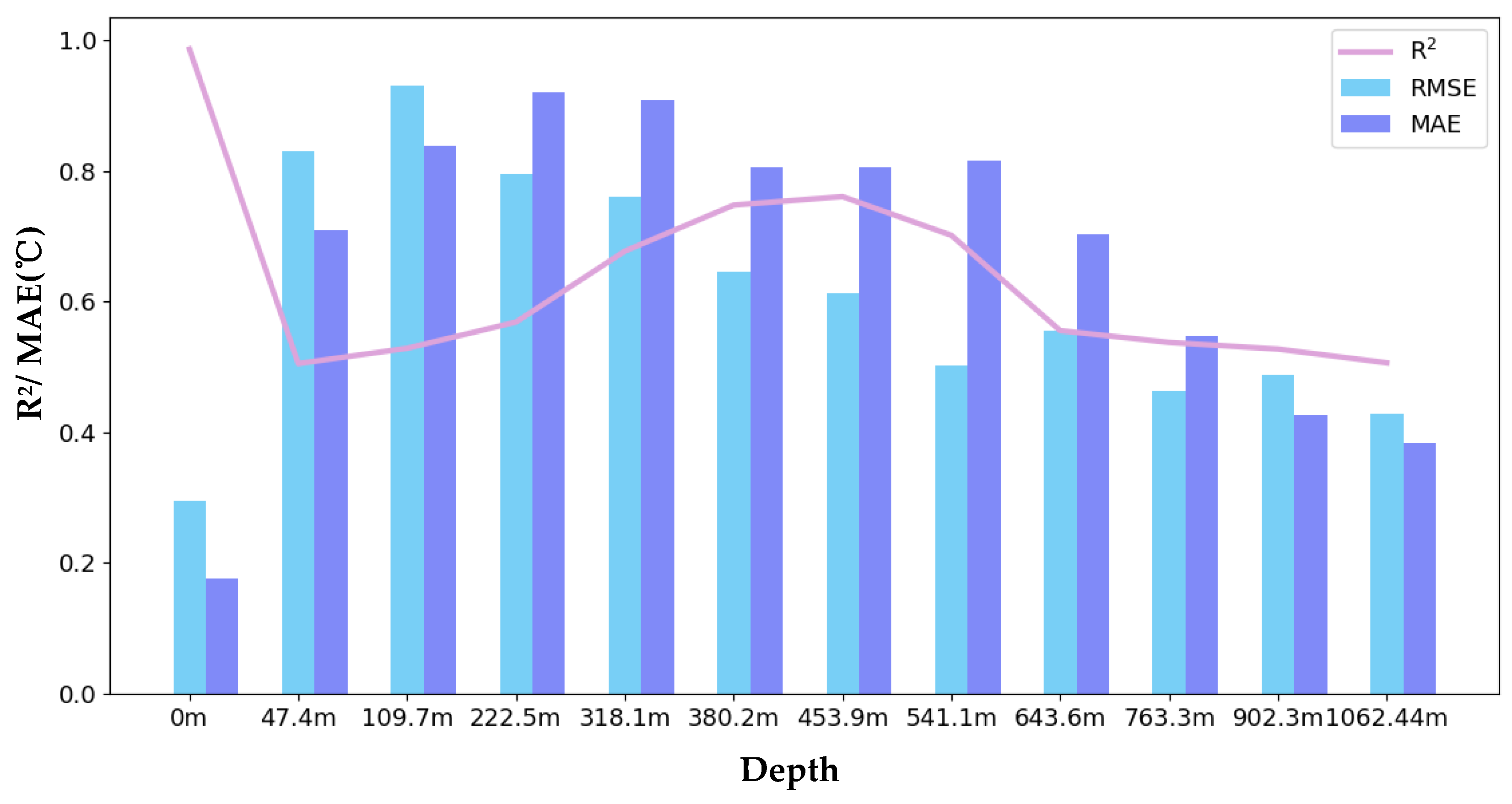
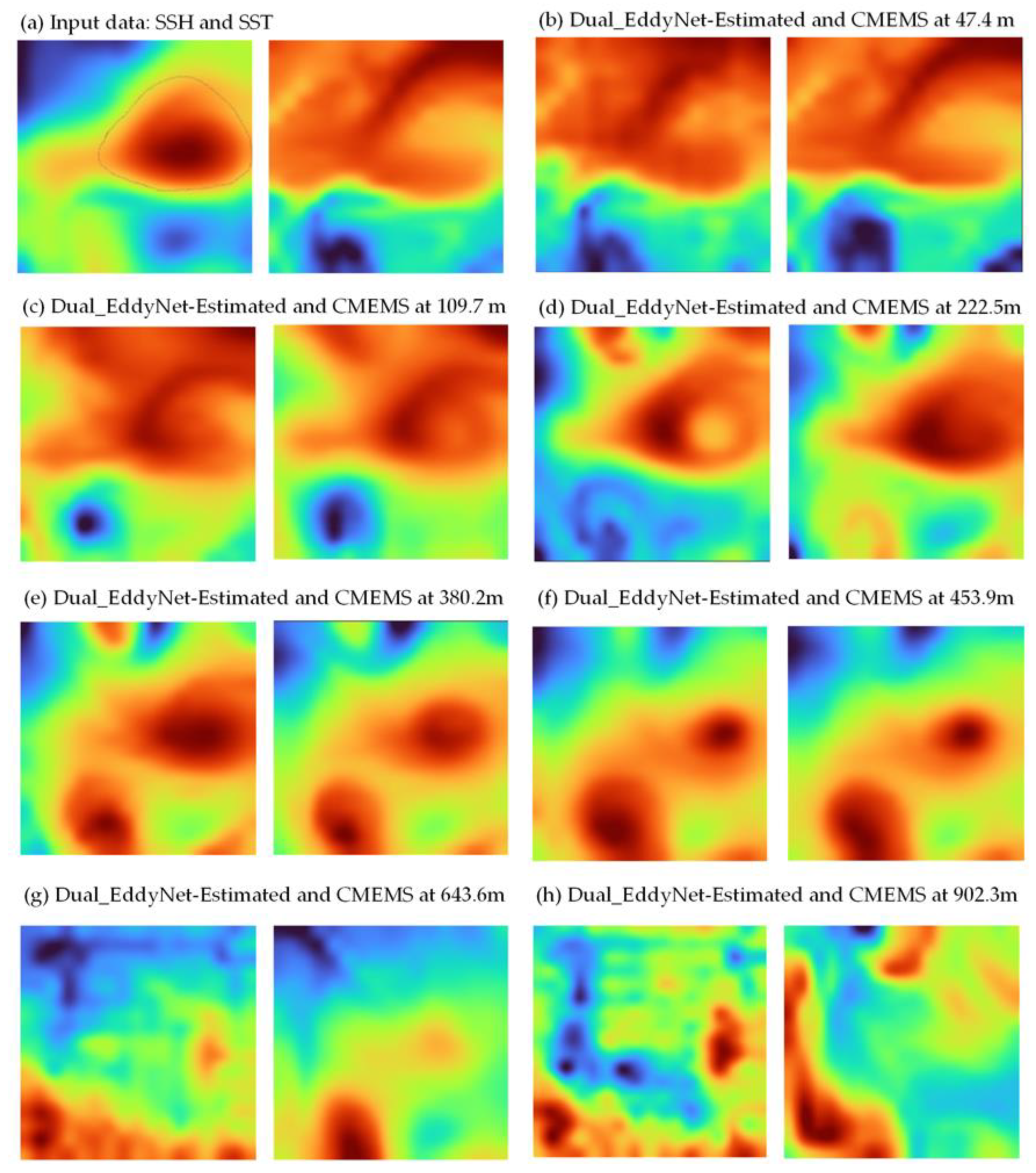
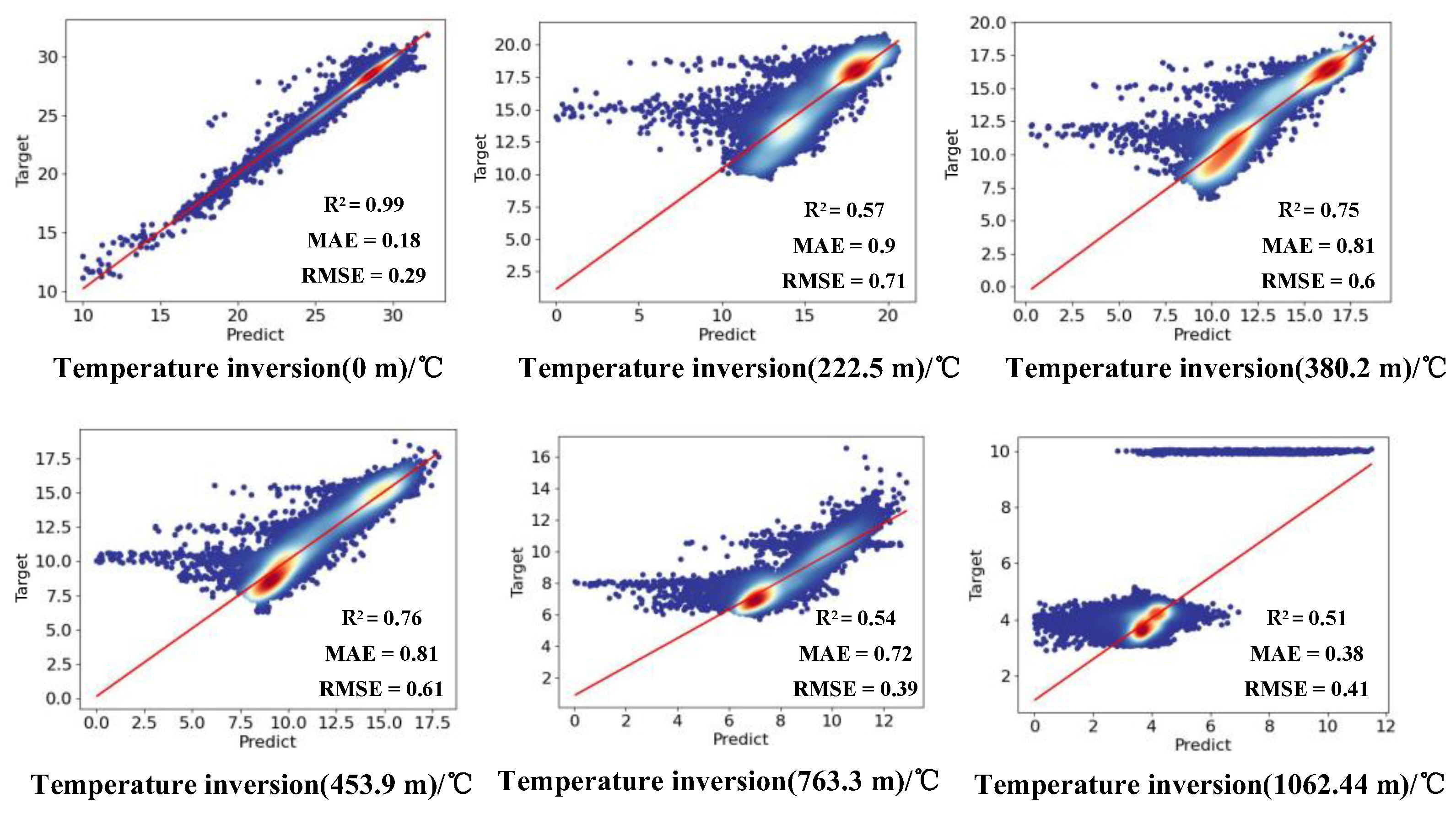
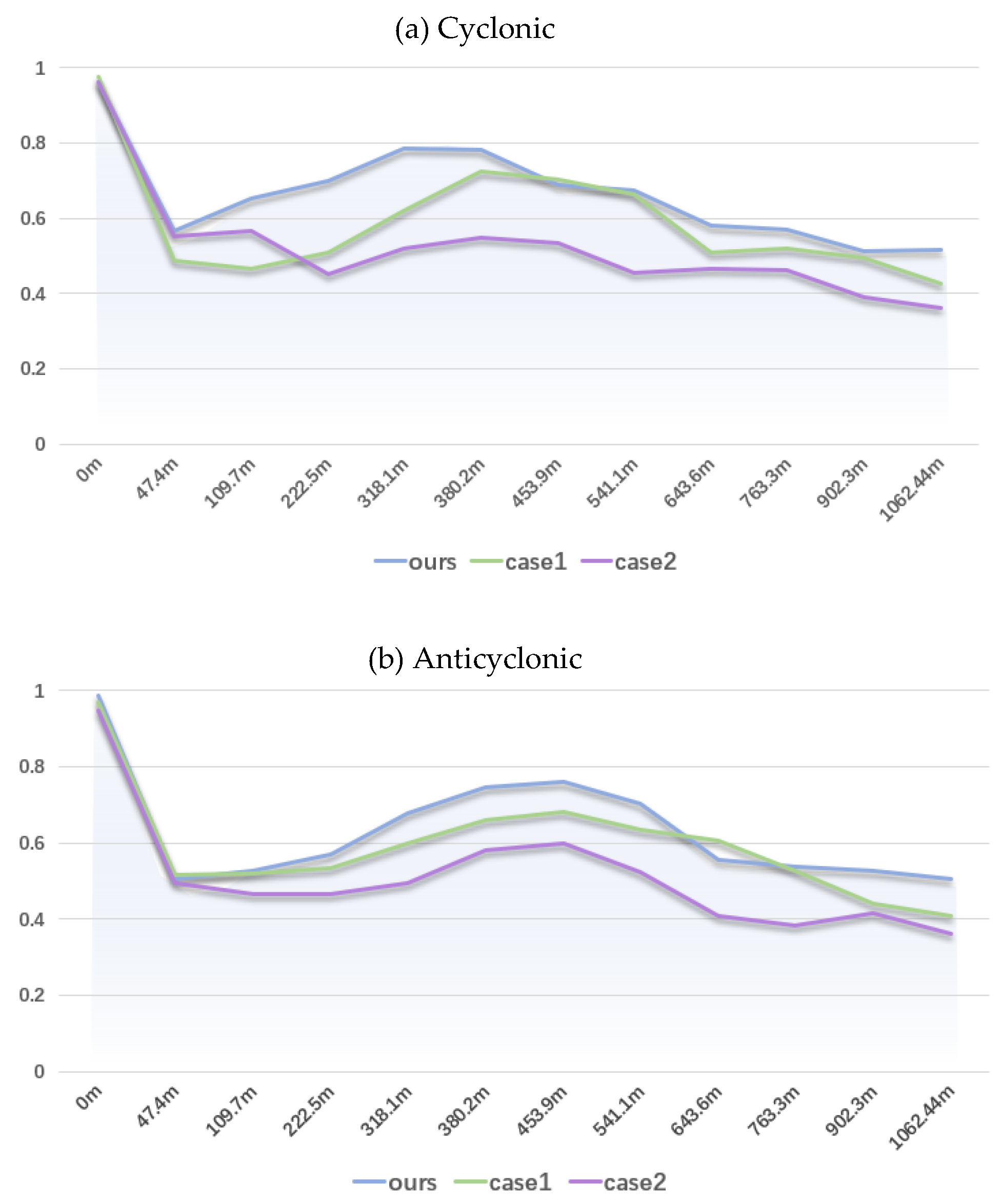
4.3. Results and Analyses
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Manso-Narvarte, I.; Rubio, A.; Jordà, G.; Carpenter, J.; Merckelbach, L.; Caballero, A. Three-Dimensional Characterization of a Coastal Mode-Water Eddy from Multiplatform Observations and a Data Reconstruction Method. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moschos, E.; Barboni, A.; Stegner, A. Why do inverse eddy surface temperature anomalies emerge? The case of the Mediterranean Sea. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenger, I.; Gruber, N.; Knutti, R.; Münnich, M. Imprint of Southern Ocean eddies on winds, clouds and rainfall. Nat. Geosci. 2013, 6, 608–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelton, D.B.; Schlax, M.G.; Samelson, R.M.; de Szoeke, R.A. Global observations of large oceanic eddies. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L15606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaube, P.; Chelton, D.B.; Samelson, R.M.; Schlax, M.G.; O’Neill, L.W. Satellite observations of mesoscale eddy-induced Ekman pumping. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2015, 45, 104–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, P.; Fu, Z.; Hu, L.; Wu, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, F. 3D-EddyNet: A Novel Approach for Identifying Three-Dimensional Morphological Features of Mesoscale Eddies in the Ocean. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaube, P.; Chelton, D.B.; Strutton, P.G.; Behrenfeld, M.J. Satellite observations of chlorophyll, phytoplankton biomass, and Ekman pumping in nonlinear mesoscale eddies. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2013, 118, 6349–6370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGillicuddy Jr, D.J.; Robinson, A.; Siegel, D.; Jannasch, H.; Johnson, R.; Dickey, T.; McNeil, J.; Michaels, A.; Knap, A. Influence of mesoscale eddies on new production in the Sargasso Sea. Nature 1998, 394, 263–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Gan, J.; Sun, Z.; Zhu, J.; Dai, M. Observed three-dimensional structure of a cold eddy in the southwestern South China Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2011, 116, C05016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Lin, X.; Liu, Y.; Nencioli, F.; Chao, Y.; Guan, Y.; Chen, D.; Dickey, T.; McWilliams, J.C. Three-dimensional oceanic eddy analysis in the Southern California Bight from a numerical product. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2012, 117, C00H14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.; Hwang, J.; Park, J.; Jang, C.J.; Jo, Y.-H. Reconstructed 3-D ocean temperature derived from remotely sensed sea surface measurements for mixed layer depth analysis. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Swain, D.; Weller, R. Estimation of ocean subsurface thermal structure from surface parameters: A neural network approach. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L20308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Jagadeesh, P.; Lin, I.-I.; Hsu, J.-Y. A neural network approach to estimate tropical cyclone heat potential in the Indian Ocean. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2012, 9, 1114–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Wu, X.; Yan, X.-H.; Kidwell, A. Estimation of subsurface temperature anomaly in the Indian Ocean during recent global surface warming hiatus from satellite measurements: A support vector machine approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 160, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Li, W.; Yan, X.H. Retrieving temperature anomaly in the global subsurface and deeper ocean from satellite observations. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2018, 123, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Feng, Y.; Zhao, X.; Sun, C.; Hong, F.; Liu, C. A convolutional neural network using surface data to predict subsurface temperatures in the Pacific Ocean. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 172816–172829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosne, G.; Maze, G.; Tandeo, P. Coupling oceanic observation systems to study mesoscale ocean dynamics. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1910.08573. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Gong, X.; Guo, X.; Xing, X.; Lu, K.; Gao, H.; Gong, X. Improved Perceptron of Subsurface Chlorophyll Maxima by a Deep Neural Network: A Case Study with BGC-Argo Float Data in the Northwestern Pacific Ocean. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Wang, J.; Peng, C.; Gao, C.; Yu, G.; Sang, N. Bisenet: Bilateral segmentation network for real-time semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 325–341. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, H.; Xu, Q.; Cheng, Y.; Yin, X.; Fan, K. Reconstructing three-dimensional salinity field of the South China Sea from satellite observations. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1168486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Yan, C.; Zhuang, W.; Zhang, W.; Yan, X.H. Reconstruction of Three-Dimensional Temperature and Salinity Fields From Satellite Observations. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2021, 126, e2021JC017605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinehut, S.; Dhomps, A.-L.; Larnicol, G.; Le Traon, P.-Y. High resolution 3-D temperature and salinity fields derived from in situ and satellite observations. Ocean Sci. 2012, 8, 845–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Qiu, Y.; Ni, X.; Lin, W.; Aung, C. Three-Dimensional Climatological Structures of the Arabian Sea Eddies and Eddy-Induced Flux. J. Ocean Univ. China 2023, 22, 874–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Tian, J.; Qiu, B.; Zhao, W.; Chang, P.; Wu, D.; Wan, X. Observed 3D structure, generation, and dissipation of oceanic mesoscale eddies in the South China Sea. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Q.; Tian, Y.; Sang, Q.; Liu, S.; Yu, J.; Wang, X. A deep learning model for joint prediction of three-dimensional ocean temperature, salinity and flow fields. In Proceedings of the 2021 6th International Conference on Automation, Control and Robotics Engineering (CACRE), Dalian, China, 15–17 July 2021; pp. 573–577. [Google Scholar]
- Buongiorno Nardelli, B. A deep learning network to retrieve ocean hydrographic profiles from combined satellite and in situ measurements. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelton, D.B.; Schlax, M.G.; Samelson, R.M. Global observations of nonlinear mesoscale eddies. Prog. Oceanogr. 2011, 91, 167–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelton, D.B.; Gaube, P.; Schlax, M.G.; Early, J.J.; Samelson, R.M. The influence of nonlinear mesoscale eddies on near-surface oceanic chlorophyll. Science 2011, 334, 328–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegliasco, C.; Busché, C.; Faugère, Y. Mesoscale Eddy Trajectory Atlas META3.2 Delayed-Time All Satellites. CNES 2022. Available online: https://www.aviso.altimetry.fr/en/data/products/value-added-products/global-mesoscale-eddy-trajectory-product/meta3-2-dt.html (accessed on 3 March 2024). [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, C.; Liu, Q. Observation of an anti-cyclonic mesoscale eddy in the subtropical northwestern Pacific Ocean from altimetry and Argo profiling floats. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2020, 39, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Q.; Zhai, X.; LaCasce, J.; Chen, D.; Marshall, D. Full-depth eddy kinetic energy in the global ocean estimated from altimeter and Argo observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2023, 50, e2023GL103114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Boser, B.; Denker, J.S.; Henderson, D.; Howard, R.E.; Hubbard, W.; Jackel, L.D. Backpropagation applied to handwritten zip code recognition. Neural Comput. 1989, 1, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Commun. ACM 2017, 60, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2015, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Gao, Z.; Hou, F.; Sun, J. Learning the Spatiotemporal Evolution Law of Wave Field Based on Convolutional Neural Network. J. Ocean Univ. China 2022, 21, 1109–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kweon, I.S. Cbam: Convolutional block attention module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Misra, D.; Nalamada, T.; Arasanipalai, A.U.; Hou, Q. Rotate to attend: Convolutional triplet attention module. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Virtual, 5–9 January 2021; pp. 3139–3148. [Google Scholar]
- Stegner, A.; Le Vu, B.; Dumas, F.; Ghannami, M.A.; Nicolle, A.; Durand, C.; Faugere, Y. Cyclone-anticyclone asymmetry of eddy detection on gridded altimetry product in the Mediterranean Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2021, 126, e2021JC017475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, L.; Yuan, C.; Sun, X.; Chen, X.; Wei, Z.; Gao, Z. Physics-informed deep operator learning based on reduced-order modeling for retrieving the ocean interior density from the surface. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2024, 129, e2023JC019941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Dataset | Source | Variable | Temporal Resolution | Spatial Resolution | Time Period |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| META 3.2 DT | AVISO | latitude, longitude, time amplitude | Daily | 0.25° × 0.25° | 1 January 1993–9 February 2022 |
| Reanalysis data | Copernicus | SSH, SST, temperature profile | Daily | 0.083° × 0.083° | 1 January 1993–26 December 2023 |
| Input | Model | R2 | MAE | Explained_Variance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSH | Cyclonic | 0.73 | 2.17 | 73.17% |
| SSH, SST | Cyclonic | 0.82 | 1.17 | 81.57% |
| SSH | Anticyclonic | 0.82 | 1.9 | 90.39% |
| SSH, SST | Anticyclonic | 0.94 | 0.86 | 94.73% |
| Input | Model | R2 | MAE | Explained Variance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cyclonic | Single-stream | 0.82 | 1.17 | 81.57% |
| Cyclonic | Dual-stream | 0.89 | 1.01 | 90.50% |
| Anticyclonic | Single-stream | 0.94 | 0.86 | 94.73% |
| Anticyclonic | Dual-stream | 0.94 | 0.82 | 94.80% |
| Dual Stream | Attention | Data Fusion | R2 | MAE | Explained Variance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| √ | 0.89 | 1.01 | 90.50% | ||
| √ | √ | 0.89 | 0.97 | 90.69% | |
| √ | √ | √ | 0.91 | 0.59 | 91.44% |
| Dual Stream | Attention | Data Fusion | R2 | MAE | Explained Variance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| √ | 0.94 | 0.82 | 94.80% | ||
| √ | √ | 0.94 | 0.79 | 94.96% | |
| √ | √ | √ | 0.95 | 0.57 | 95.25% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huo, J.; Yang, J.; Geng, L.; Liu, G.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Cui, W. Temperature Structure Inversion of Mesoscale Eddies in the South China Sea Based on Deep Learning. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 723. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12050723
Huo J, Yang J, Geng L, Liu G, Zhang J, Wang J, Cui W. Temperature Structure Inversion of Mesoscale Eddies in the South China Sea Based on Deep Learning. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2024; 12(5):723. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12050723
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuo, Jidong, Jungang Yang, Liting Geng, Guangliang Liu, Jie Zhang, Jichao Wang, and Wei Cui. 2024. "Temperature Structure Inversion of Mesoscale Eddies in the South China Sea Based on Deep Learning" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 12, no. 5: 723. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12050723
APA StyleHuo, J., Yang, J., Geng, L., Liu, G., Zhang, J., Wang, J., & Cui, W. (2024). Temperature Structure Inversion of Mesoscale Eddies in the South China Sea Based on Deep Learning. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 12(5), 723. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12050723







