Rare Earth Elements in Shells of Black Sea Molluscs: Anomalies and Biogeochemical Implications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling Area and Sampled Molluscs
2.2. Analytical Sample Preparation
2.3. ICP-MS Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. REE Contents
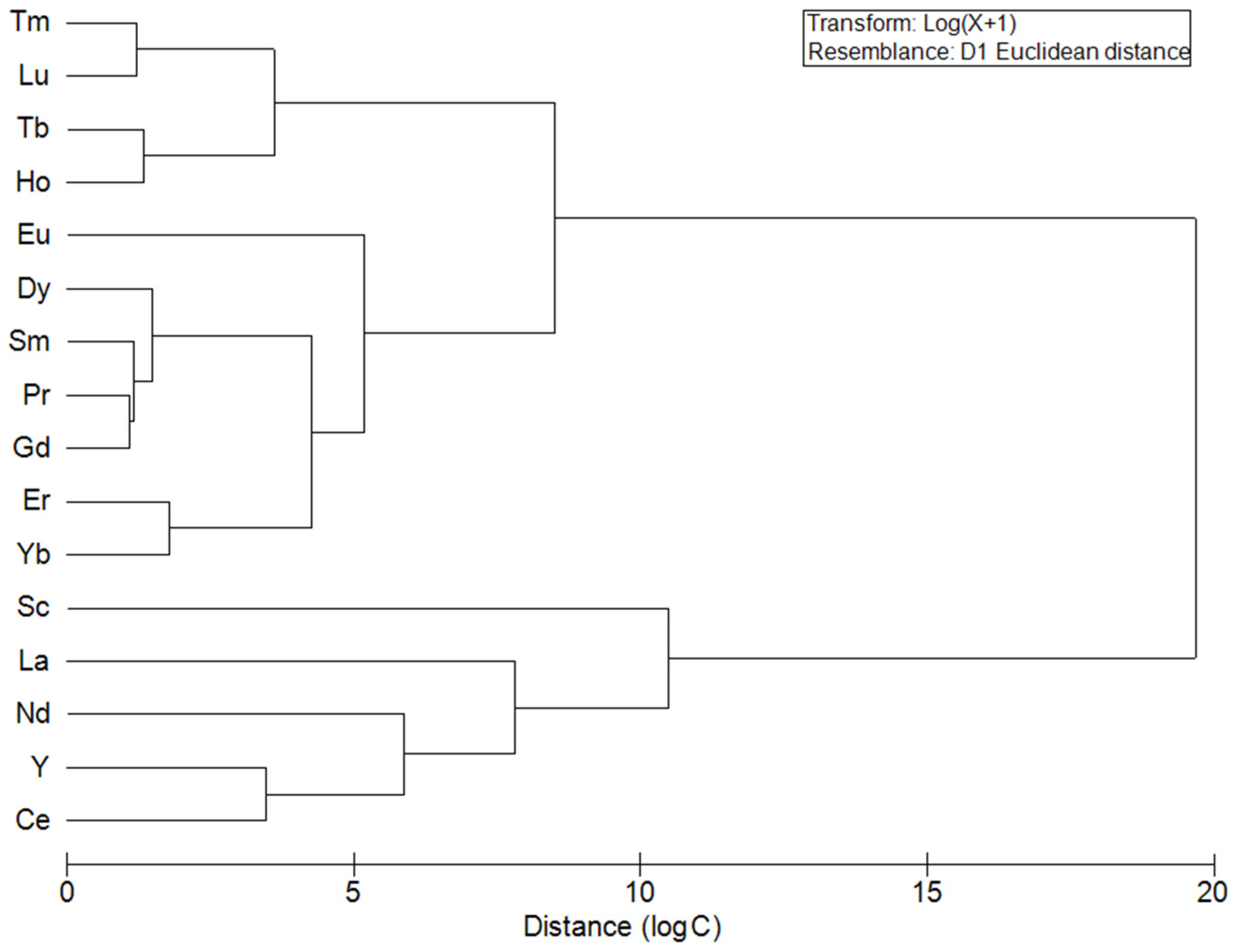
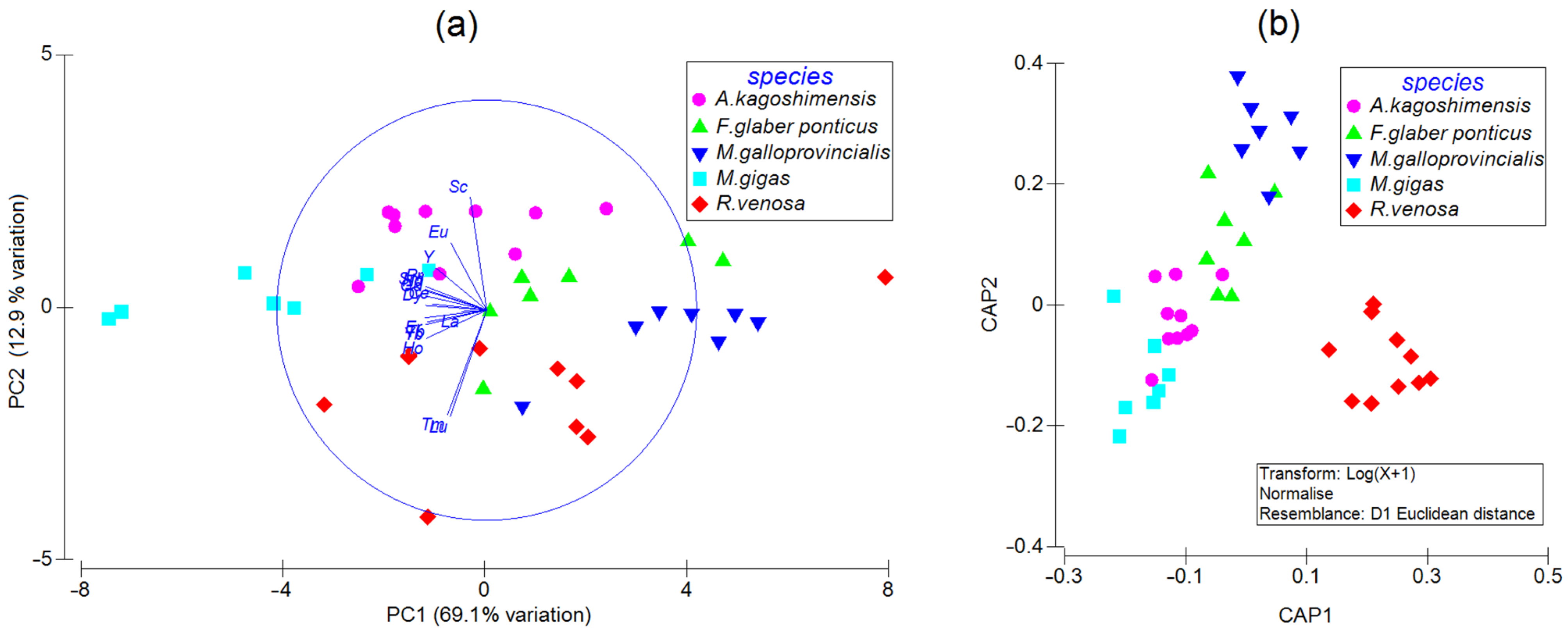
3.2. Multivariate Analysis of the REE Data
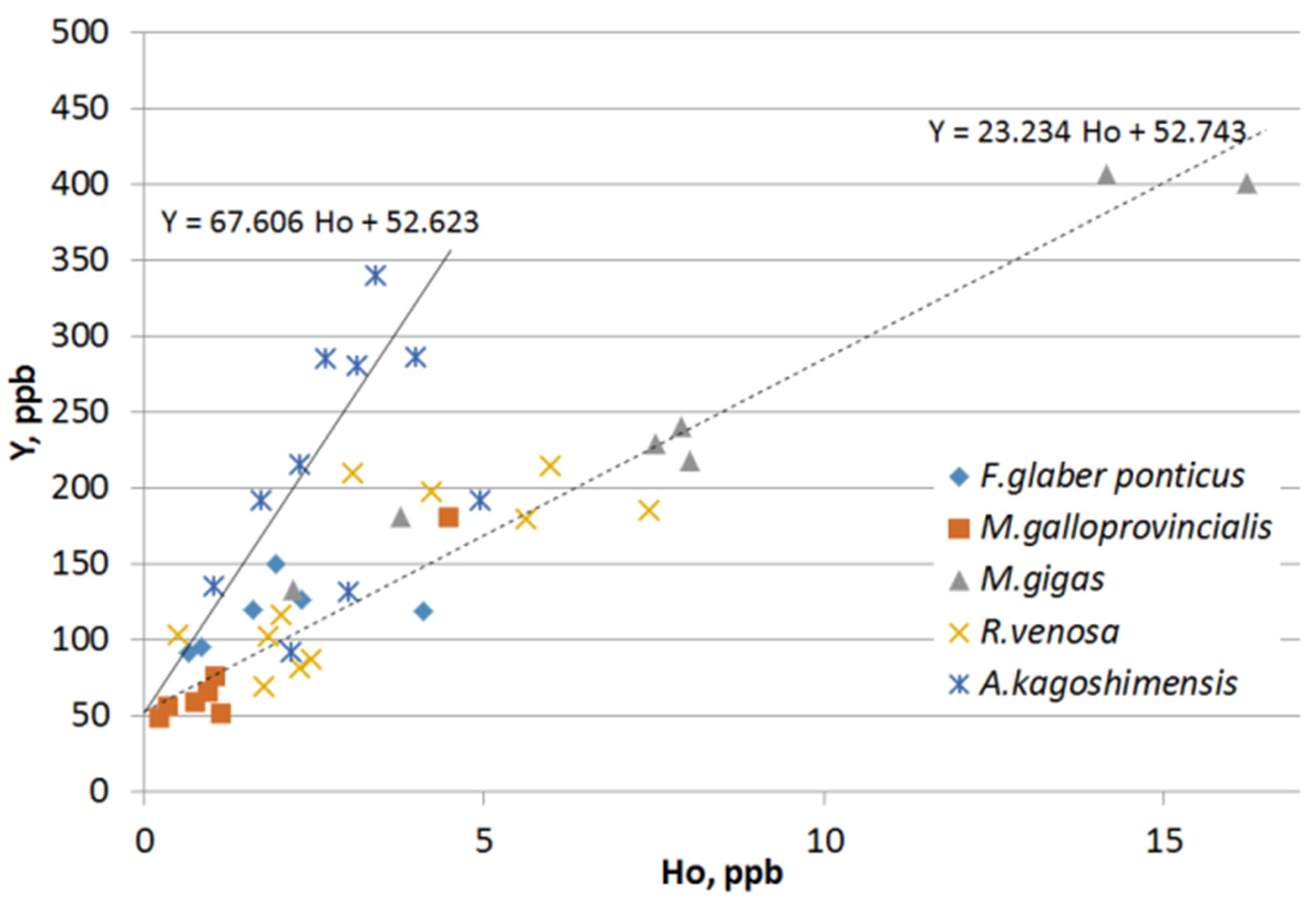
3.3. REE Enrichment, Anomalies and Characteristic Ratios
4. Discussion
4.1. REE Contents
4.2. Multivariate Analysis
4.3. REE Enrichment, Anomalies and Characteristic Ratios
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cheisson, T.; Schelter, E.J. Rare earth elements: Mendeleev’s bane, modern marvels. Science 2019, 363, 489–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damhus, T.; Hartshorn, R.M.; Hutton, A.T. Nomenclature of Inorganic Chemistry: IUPAC Recommendations; RSC Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Bau, M. Controls on the fractionation of isovalent trace elements in magmatic and aqueous systems: Evidence from Y/Ho, Zr/Hf, and lanthanide tetrad effect. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1996, 123, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squadrone, S.; Brizio, P.; Stella, C.; Mantia, M.; Battuello, M.; Nurra, N.; Sartor, R.M.; Orusa, R.; Robetto, S.; Brusa, F.; et al. Rare earth elements in marine and terrestrial matrices of Northwestern Italy: Implications for food safety and human health. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 660, 1383–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piper, D.Z.; Bau, M. Normalized rare earth elements in water, sediments, and wine: Identifying sources and environmental redox conditions. Am. J. Anal. Chem. 2013, 4, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhavaraju, J.; González-León, C.M. Depositional conditions and source of rare earth elements in carbonate strata of the Aptian-Albian Mural Formation, Pitaycachi section, northeastern Sonora, Mexico. Rev. Mex. Cienc. Geológicas 2012, 29, 478–491. [Google Scholar]
- Cicconi, M.R.; Losq, C.L.; Henderson, G.S.; Neuville, D.R. The redox behavior of rare earth elements. In Magma Redox Geochemistry; Moretti, R., Neuville, D.R., Keiling, A., Eds.; Geophysical Monograph Series; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 381–398. [Google Scholar]
- German, C.R.; Elderfield, H. Application of the Ce anomaly as a paleoredox indicator: The ground rules. Paleoceanogr. Paleoclimatol. 1990, 5, 823–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- German, C.R.; Holliday, B.P.; Elderfield, H. Redox cycling of rare earth elements in the suboxic zone of the Black Sea. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1991, 55, 3553–3558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, M.W.; Hood, A.V.; Shuster, A.; Greig, A.; Planavsky, N.J.; Reed, C.P. Oxygenation history of the Neoproterozoic to early Phanerozoic and the rise of land plants. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2017, 466, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellefroid, E.J.; Hood, A.V.S.; Hoffman, P.F.; Thomas, M.D.; Reinhard, C.T.; Planavsky, N.J. Constraints on Paleoproterozoic atmospheric oxygen levels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 8104–8109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Liu, X.-M.; Chen, J. Cerium anomaly as a tracer for paleo-oceanic redox conditions: A thermodynamics-based Ce oxidation modeling approach. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 927826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tostevin, R.; Shields, G.A.; Tarbuck, G.M.; He, T.; Clarkson, M.O.; Wood, R.A. Effective use of cerium anomalies as a redox proxy in carbonate-dominated marine settings. Chem. Geol. 2016, 438, 146–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, T.A.; Venancio, I.M.; Marques, E.D.; Figueiredo, T.S.; Nascimento, R.A.; Smoak, J.M.; Albuquerque, A.L.S.; Valeriano, C.M.; Silva-Filho, E.V. REE anomalies changes in bottom sediments applied in the Western Equatorial Atlantic since the last Interglacial. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 846976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elderfield, H. The oceanic chemistry of the rare-earth elements. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Sci. 1988, 325, 105–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Z.; Cui, G.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Liu, Q. Dissolved rare earth elements in the Northwest Pacific: Sources, water mass tracing, and cross-shelf fluxes. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1135113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippova, A.; Frank, M.; Kienast, M.; Rickli, J.; Hathorne, E.; Yashayaev, I.M.; Pahnke, K. Water mass circulation and weathering inputs in the Labrador Sea based on coupled Hf–Nd isotope compositions and rare earth element distributions. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2017, 199, 164–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hathorne, E.C.; Stichel, T.; Brück, B.; Frank, M. Rare earth element distribution in the Atlantic sector of the Southern Ocean: The balance between particle scavenging and vertical supply. Mar. Chem. 2015, 177, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Solsona, E.; Pena, L.D.; Paredes, E.; Pérez-Asensio, J.N.; Quirós-Collazos, L.; Lirer, F.; Cacho, I. Rare earth elements and Nd isotopes as tracers of modern ocean circulation in the central Mediterranean Sea. Prog. Oceanogr. 2020, 185, 102340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piepgras, D.J.; Jacobsen, S.B. The behavior of rare earth elements in seawater: Precise determination of variations in the North Pacific water column. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1992, 56, 1851–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozaki, Y.; Zhang, J.; Amakawa, H. The fractionation between Y and Ho in the marine environment. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1997, 148, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaram, V. Rare earth elements: A review of applications, occurrence, exploration, analysis, recycling, and environmental impact. Geosci. Front. 2019, 10, 1285–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depraiter, L.; Goutte, S. The role and challenges of rare earths in the energy transition. Resour. Policy 2023, 86, 104137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeili-Zare, M.; Amiri, O. 13—Rare earth–based compounds for solar cells. In Advanced Rare Earth-Based Ceramic Nanomaterials; Zinatloo-Ajabshir, S., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 365–393. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, M.K.; Raihan, G.A.; Akbar, M.A.; Kabir Rubel, M.H.; Ahmed, M.H.; Khan, M.I.; Hossain, S.; Sen, S.K.; Jalal, M.I.E.; El-Denglawey, A. Current applications and future potential of rare earth oxides in sustainable nuclear, radiation, and energy devices: A review. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2022, 4, 3327–3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Saji, S.E.; Yin, Z.; Zhang, H.; Du, Y.; Yan, C.-H. Rare-earth incorporated alloy catalysts: Synthesis, properties, and applications. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2005988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saviano, L.; Brouziotis, A.A.; Padilla Suarez, E.G.; Siciliano, A.; Spampinato, M.; Guida, M.; Trifuoggi, M.; Del Bianco, D.; Carotenuto, M.; Romano Spica, V.; et al. Catalytic activity of rare earth elements (REEs) in advanced oxidation processes of wastewater pollutants: A review. Molecules 2023, 28, 6185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas, J.; Lucas, P.; Le Mercier, T.; Rollat, A.; Davenport, W. Chapter 11—Rare Earths in Alloys and Metals. In Rare Earths; Lucas, J., Lucas, P., Le Mercier, T., Rollat, A., Davenport, W., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 181–189. [Google Scholar]
- Basu, B.; Banerjee, B. (Eds.) Rare Earth Elements: Processing, Catalytic Applications and Environmental Impact; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany; Boston, MA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Tommasi, F.; Thomas, P.J.; Pagano, G.; Perono, G.A.; Oral, R.; Lyons, D.M.; Toscanesi, M.; Trifuoggi, M. Review of rare earth elements as fertilizers and feed additives: A knowledge gap analysis. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 81, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyler, G. Rare earth elements in soil and plant systems—A review. Plant Soil 2004, 267, 191–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovaříková, M.; Tomášková, I.; Soudek, P. Rare earth elements in plants. Biol. Plant. 2019, 63, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastori, R.R.; Putnik, D.M.I.; Maksimović, I.V. Rare earth elements application in agriculture. Acta Agric. Serbica 2023, 28, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goecke, F.; Zachleder, V.; Vítová, M. Rare Earth Elements and Algae: Physiological effects, biorefinery and recycling. In Algal Biorefineries: Volume 2: Products and Refinery Design; Prokop, A., Bajpai, R.K., Zappi, M.E., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 339–363. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelnour, S.A.; Abd El-Hack, M.E.; Khafaga, A.F.; Noreldin, A.E.; Arif, M.; Chaudhry, M.T.; Losacco, C.; Abdeen, A.; Abdel-Daim, M.M. Impacts of rare earth elements on animal health and production: Highlights of cerium and lanthanum. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 672, 1021–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, H.; Sharma, A.; Sarkar, S.; Ojha, L.; Pal, R.P.; Mani, V. Perspectives for rare earth elements as feed additive in livestock—A review. Asian-Australas J. Anim. Sci. 2020, 33, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.L.; Rambeck, W.A. Rare earth elements—A new generation of growth promoters for pigs? Arch. Für Tierernaehrung 2000, 53, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ascenzi, P.; Bettinelli, M.; Boffi, A.; Botta, M.; De Simone, G.; Luchinat, C.; Marengo, E.; Mei, H.; Aime, S. Rare earth elements (REE) in biology and medicine. Rend. Lincei. Sci. Fis. E Nat. 2020, 31, 821–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faust, A. 4.5 Medical applications of rare earth compounds. In Rare Earth Chemistry; Pöttgen, R., Jüstel, T., Strassert, C.A., Eds.; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany; Boston, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 439–452. [Google Scholar]
- Du, X.; Graedel, T.E. Global in-use stocks of the rare earth elements: A first estimate. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 4096–4101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gwenzi, W.; Mangori, L.; Danha, C.; Chaukura, N.; Dunjana, N.; Sanganyado, E. Sources, behaviour, and environmental and human health risks of high-technology rare earth elements as emerging contaminants. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 299–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, P.; Valente, T.; Marques, R.; Prudêncio, M.I.; Pamplona, J. Rare earth elements—Source and evolution in an aquatic system dominated by mine-influenced waters. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 322, 116125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasavtseva, E.; Sandimirov, S.; Elizarova, I.; Makarov, D. Assessment of trace and rare earth elements pollution in water bodies in the area of rare metal enterprise influence: A case study—Kola Subarctic. Water 2022, 14, 3406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenga, T.; Gwenzi, W. Chapter 6—Anthropogenic rare earth elements in aquatic environments: Occurrence, behaviour, and fate. In Emerging Contaminants in the Terrestrial-Aquatic-Atmosphere Continuum: Occurrence, Health Risks and Mitigation; Gwenzi, W., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherland, 2022; pp. 87–102. [Google Scholar]
- De Baar, H.J.W.; Bacon, M.P.; Brewer, P.G.; Bruland, K.W. Rare earth elements in the Pacific and Atlantic Oceans. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1985, 49, 1943–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bau, M.; Dulski, P. Anthropogenic origin of positive gadolinium anomalies in river waters. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1996, 143, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alibo, D.S.; Nozaki, Y. Rare earth elements in seawater: Particle association, shale-normalization, and Ce oxidation. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1999, 63, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulaksız, S.; Bau, M. Rare earth elements in the Rhine River, Germany: First case of anthropogenic lanthanum as a dissolved microcontaminant in the hydrosphere. Environ. Int. 2011, 37, 973–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, N.; Hsu, H.S.; Liang, S.T.; Roldan, M.J.M.; Lee, J.S.; Ger, T.R.; Hsiao, C.D. An updated review of toxicity effect of the rare earth elements (REEs) on aquatic organisms. Animals 2020, 10, 1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martino, C.; Chianese, T.; Chiarelli, R.; Roccheri, M.C.; Scudiero, R. Toxicological impact of rare earth elements (REEs) on the reproduction and development of aquatic organisms using sea urchins as biological models. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piarulli, S.; Hansen, B.H.; Ciesielski, T.; Zocher, A.-L.; Malzahn, A.; Olsvik, P.A.; Sonne, C.; Nordtug, T.; Jenssen, B.M.; Booth, A.M.; et al. Sources, distribution and effects of rare earth elements in the marine environment: Current knowledge and research gaps. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 291, 118230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, S.; Mucci, A. Partitioning of rare earth elements (REEs) between calcite and seawater solutions at 25 °C and 1 atm, and high dissolved REE concentrations. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1995, 59, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, G.E.; Kamber, B.S. Rare earth elements in Holocene reefal microbialites: A new shallow seawater proxy. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2000, 64, 1557–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamber, B.S.; Webb, G.E.; Gallagher, M. The rare earth element signal in Archaean microbial carbonate: Information on ocean redox and biogenicity. J. Geol. Soc. 2014, 171, 745–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Porta, G.; Webb, G.E.; McDonald, I. REE patterns of microbial carbonate and cements from Sinemurian (Lower Jurassic) siliceous sponge mounds (Djebel Bou Dahar, High Atlas, Morocco). Chem. Geol. 2015, 400, 65–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Peng, Z.; Wei, G.; Chen, T.; Sun, W.; He, J.; Liu, G.; Chou, C.-L.; Shen, C.-C. Interannual variation of rare earth element abundances in corals from northern coast of the South China Sea and its relation with sea-level change and human activities. Mar. Environ. Res. 2011, 71, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherer, M.; Seitz, H. Rare-earth element distribution in Holocene and Pleistocene corals and their redistribution during diagenesis. Chem. Geol. 1980, 28, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, N.; Webb, G.E.; Zhao, J.-X.; Nguyen, A.D.; Lewis, S.E.; Lough, J.M. Coral-based high-resolution rare earth element proxy for terrestrial sediment discharge affecting coastal seawater quality, Great Barrier Reef. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2019, 254, 173–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Liu, G.; Han, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, J.; Yang, J.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D. Coral-based rare earth element proxy for hydrothermal fluid on the Yongxing Island, South China Sea. Ore Geol. Rev. 2023, 162, 105678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akagi, T.; Hashimoto, Y.; Fu, F.-F.; Tsuno, H.; Tao, H.; Nakano, Y. Variation of the distribution coefficients of rare earth elements in modern coral-lattices: Species and site dependencies. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2004, 68, 2265–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sholkovitz, E.; Shen, G.T. The incorporation of rare earth elements in modern coral. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1995, 59, 2749–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haley, B.A.; Klinkhammer, G.P.; Mix, A.C. Revisiting the rare earth elements in foraminiferal tests. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2005, 239, 79–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, M.R. Rare earth elements in foraminifera tests. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1985, 73, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborne, A.H.; Hathorne, E.C.; Schijf, J.; Plancherel, Y.; Böning, P.; Frank, M. The potential of sedimentary foraminiferal rare earth element patterns to trace water masses in the past. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2017, 18, 1550–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skinner, L.C.; Sadekov, A.; Brandon, M.; Greaves, M.; Plancherel, Y.; de la Fuente, M.; Gottschalk, J.; Souanef-Ureta, S.; Sevilgen, D.S.; Scrivner, A.E. Rare Earth Elements in early-diagenetic foraminifer ‘coatings’: Pore-water controls and potential palaeoceanographic applications. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2019, 245, 118–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zocher, A.-L.; Bau, M. Rare earth elements and yttrium in shells of invasive mussel species from temperate rivers in Central Europe: Comparison between C. fluminea, D. bugensis, and D. polymorpha. Chem. Geol. 2024, 648, 121878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouchi, V.; Godbillot, C.; Forest, V.; Ulianov, A.; Lartaud, F.; de Rafélis, M.; Emmanuel, L.; Verrecchia, E.P. Rare earth elements in oyster shells: Provenance discrimination and potential vital effects. Biogeosciences 2020, 17, 2205–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponnurangam, A.; Bau, M.; Brenner, M.; Koschinsky, A. Mussel shells of Mytilus edulis as bioarchives of the distribution of rare earth elements and yttrium in seawater and the potential impact of pH and temperature on their partitioning behavior. Biogeosciences 2016, 13, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Bi, R.; Sanganyado, E.; Zeng, X.; Li, W.; Lyu, Z.; Liu, J.; Li, P.; Du, H.; Liu, W.; et al. Rare earth elements in oysters and mussels collected from the Chinese coast: Bioaccumulation and human health risks. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 184, 114127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacMillan, G.A.; Chételat, J.; Heath, J.P.; Mickpegak, R.; Amyot, M. Rare earth elements in freshwater, marine, and terrestrial ecosystems in the eastern Canadian Arctic. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2017, 19, 1336–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bau, M.; Balan, S.; Schmidt, K.; Koschinsky, A. Rare earth elements in mussel shells of the Mytilidae family as tracers for hidden and fossil high-temperature hydrothermal systems. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2010, 299, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briant, N.; Le Monier, P.; Bruzac, S.; Sireau, T.; Araújo, D.F.; Grouhel, A. Rare earth element in bivalves’ soft tissues of French metropolitan coasts: Spatial and temporal distribution. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 81, 600–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chelyadina, N.S.; Kapranov, S.V.; Popov, M.A.; Smirnova, L.L.; Bobko, N.I. Rare earth elements in different body parts of the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis (Crimea, Black Sea) and assessment of associated human health risks from its consumption. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 195, 115462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapranov, S.V.; Karavantseva, N.V.; Bobko, N.I.; Ryabushko, V.I.; Kapranova, L.L. Element contents in three commercially important edible mollusks harvested off the southwestern coast of Crimea (Black Sea) and assessment of human health risks from their consumption. Foods 2021, 10, 2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapranov, S.V.; Kozintsev, A.F.; Bobko, N.I.; Ryabushko, V.I. Elements in soft tissues of the young Mediterranean mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis Lam. 1819 collected in Sevastopol Bay (Crimea, Black Sea): Effects of age, sex, location, and principal morphometric parameters. Animals 2023, 13, 1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akagi, T.; Edanami, K. Sources of rare earth elements in shells and soft-tissues of bivalves from Tokyo Bay. Mar. Chem. 2017, 194, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrat, J.-A.; Chauvaud, L.; Olivier, F.; Poitevin, P.; Rouget, M.-L. Trace elements in bivalve shells: How “vital effects” can bias environmental studies. Chem. Geol. 2023, 638, 121695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrat, J.-A.; Chauvaud, L.; Olivier, F.; Poitevin, P.; Bayon, G.; Ben Salem, D. Rare earth elements and yttrium in suspension-feeding bivalves (dog cockle, Glycymeris glycymeris L.): Accumulation, vital effects and pollution. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2022, 339, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Barrat, J.A.; Bayon, G.; Chauvaud, L.; Feng, D. Lanthanum anomalies as fingerprints of methanotrophy. Geochem. Perspect. Lett. 2020, 14, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merschel, G.; Bau, M. Rare earth elements in the aragonitic shell of freshwater mussel Corbicula fluminea and the bioavailability of anthropogenic lanthanum, samarium and gadolinium in river water. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 533, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueiredo, C.; Oliveira, R.; Lopes, C.; Brito, P.; Caetano, M.; Raimundo, J. Rare earth elements biomonitoring using the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis in the Portuguese coast: Seasonal variations. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 175, 113335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanana, H.; Turcotte, P.; André, C.; Gagnon, C.; Gagné, F. Comparative study of the effects of gadolinium chloride and gadolinium—Based magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent on freshwater mussel, Dreissena polymorpha. Chemosphere 2017, 181, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lachaux, N.; Otero-Fariña, A.; Minguez, L.; Sohm, B.; Rétif, J.; Châtel, A.; Poirier, L.; Devin, S.; Pain-Devin, S.; Gross, E.M.; et al. Fate, subcellular distribution and biological effects of rare earth elements in a freshwater bivalve under complex exposure. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 905, 167302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas, R.; Costa, S.; D Cardoso, C.E.; Morais, T.; Moleiro, P.; Matias, A.C.; Pereira, A.F.; Machado, J.; Correia, B.; Pinheiro, D.; et al. Toxicological effects of the rare earth element neodymium in Mytilus galloprovincialis. Chemosphere 2020, 244, 125457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leite, C.; Russo, T.; Pinto, J.; Polese, G.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Pretti, C.; Pereira, E.; Freitas, R. From the cellular to tissue alterations induced by two rare earth elements in the mussel species Mytilus galloprovincialis: Comparison between exposure and recovery periods. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 915, 169754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas, R.; Cardoso, C.E.D.; Costa, S.; Morais, T.; Moleiro, P.; Lima, A.F.D.; Soares, M.; Figueiredo, S.; Águeda, T.L.; Rocha, P.; et al. New insights on the impacts of e-waste towards marine bivalves: The case of the rare earth element Dysprosium. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 260, 113859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mestre, N.C.; Sousa, V.S.; Rocha, T.L.; Bebianno, M.J. Ecotoxicity of rare earths in the marine mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis and a preliminary approach to assess environmental risk. Ecotoxicology 2019, 28, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, M.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Solé, M.; Pereira, E.; Freitas, R. Salinity influences on the response of Mytilus galloprovincialis to the rare-earth element lanthanum. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 794, 148512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, M.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Solé, M.; Pereira, E.; Freitas, R. Threats of pollutants derived from electronic waste to marine bivalves: The case of the rare-earth element yttrium. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2023, 42, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Dang, D.H.; Wang, W.; Evans, R.D.; Wang, W.-X. Rare earth elements in the Pearl River Delta of China: Potential impacts of the REE industry on water, suspended particles and oysters. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 244, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrat, J.-A.; Bayon, G.; Carney, R.S.; Chauvaud, L. Rare earth elements as new biogeochemical proxies in deep-sea mussels. Chem. Geol. 2022, 610, 121102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rétif, J.; Zalouk-Vergnoux, A.; Briant, N.; Poirier, L. From geochemistry to ecotoxicology of rare earth elements in aquatic environments: Diversity and uses of normalization reference materials and anomaly calculation methods. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 856, 158890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrat, J.-A.; Bayon, G.; Lalonde, S. Calculation of cerium and lanthanum anomalies in geological and environmental samples. Chem. Geol. 2023, 615, 121202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marčeta, T.; Da Ros, L.; Marin, M.G.; Codognotto, V.F.; Bressan, M. Overview of the biology of Flexopecten glaber in the North Western Adriatic Sea (Italy): A good candidate for future shellfish farming aims? Aquaculture 2016, 462, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztürk, B. Non-Indigenous Species in the Mediterranean and the Black Sea; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Chemnitzer, R. Strategies for achieving the lowest possible detection limits in ICP-MS. Spectroscopy 2019, 34, 12–16. [Google Scholar]
- Hammer, Ø.; Harper, D.A.T.; Ryan, P.D. PAST: Paleontological statistics software package for education and data analysis. Palaeontol. Electron. 2001, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Mégevand, P. Games-Howell Post-Hoc Test for One-Way ANOVA. 2017. Available online: https://github.com/pierremegevand/games_howell (accessed on 21 March 2024).
- Clarke, K.R.; Gorley, R.N.; Somerfield, P.J.; Warwick, R.M. Change in Marine Communities: An Approach to Statistical Analysis and Interpretation, 3rd ed.; PRIMER-E: Plymouth, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, M.J.; Gorley, R.N.; Clarke, K. PERMANOVA+ for PRIMER: Guide to Software and Statistical Methods; PRIMER-E: Plymouth, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Reimann, C.; Caritat, P.D. Intrinsic flaws of element enrichment factors (EFs) in environmental geochemistry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 5084–5091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yongming, H.; Peixuan, D.; Junji, C.; Posmentier, E.S. Multivariate analysis of heavy metal contamination in urban dusts of Xi’an, Central China. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 355, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackermann, F. A procedure for correcting the grain size effect in heavy metal analyses of estuarine and coastal sediments. Environ. Technol. Lett. 1980, 1, 518–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komar, D.; Smuc, N.R.; Belak, Z.L.; Matešić, S.; Lojen, S.; Kniewald, G.; Vrhovnik, P.; Dolenec, T.; Dolenec, M. Geochemical characteristics and distribution of rare earth elements in makirina bay sediments (n. Dalmatia, Republic of Croatia). Geol. Maced. 2014, 28, 127–137. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, C.L. Riverine composition and estuarine geochemistry of particulate metals in China—Weathering features, anthropogenic impact and chemical fluxes. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2002, 54, 1051–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schropp, S.J.; Graham Lewis, F.; Windom, H.L.; Ryan, J.D.; Calder, F.D.; Burney, L.C. Interpretation of metal concentrations in estuarine sediments of Florida using aluminum as a reference element. Estuaries 1990, 13, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szefer, P.; Szefer, K.; Glasby, G.P.; Pempkowiak, J.; Kaliszan, R. Heavy-metal pollution in surficial sediments from the Southern Baltic sea off Poland. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A Environ. Sci. Eng. Toxicol. 1996, 31, 2723–2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto-Jiménez, M.; Páez-Osuna, F.; Morales-Hernández, F. Selected trace metals in oysters (Crassostrea iridescens) and sediments from the discharge zone of the submarine sewage outfall in Mazatlán Bay (southeast Gulf of California): Chemical fractions and bioaccumulation factors. Environ. Pollut. 2001, 114, 357–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merenkova, S.I.; Malakhova, L.V.; Ivanov, V.E.; Malakhova, T.V.; Bobko, N.I.; Kapranov, S.V. The geochemical features of sedimentation in Sevastopol Bay in the Holocene. Mosc. Univ. Geol. Bull. 2023, 78, 333–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenier, M.; Garcia-Solsona, E.; Lemaitre, N.; Trull, T.W.; Bouvier, V.; Nonnotte, P.; van Beek, P.; Souhaut, M.; Lacan, F.; Jeandel, C. Differentiating lithogenic supplies, water mass transport, and biological processes on and off the Kerguelen Plateau using rare earth element concentrations and neodymium isotopic compositions. Front. Mar. Sci. 2018, 5, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moermond, C.T.A.; Tijink, J.; van Wezel, A.P.; Koelmans, A.A. Distribution, speciation, and bioavailability of lanthanides in the Rhine-Meuse estuary, The Netherlands. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2001, 20, 1916–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elderfield, H.; Upstill-Goddard, R.; Sholkovitz, E.R. The rare earth elements in rivers, estuaries, and coastal seas and their significance to the composition of ocean waters. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1990, 54, 971–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sholkovitz, E.R. The aquatic chemistry of rare earth elements in rivers and estuaries. Aquat. Geochem. 1995, 1, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravera, O.; Cenci, R.; Beone, G.M.; Dantas, M.; Lodigiani, P. Trace element concentrations in freshwater mussels and macrophytes as related to those in their environment. J. Limnol. 2003, 62, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brookins, D.G. Aqueous geochemistry of rare earth elements. In Geochemistry and Mineralogy of Rare Earth Elements; Lipin, B.R., McKay, G.A., Eds.; Reviews in Mineralogy; The Mineralogaical Society of America: Washington, DC, USA, 1989; pp. 201–226. [Google Scholar]
- Feldstein, T.; Kashman, Y.; Abelson, A.; Fishelson, L.; Mokady, O.; Bresler, V.; Erel, Y. Marine molluscs in environmental monitoring. Helgol. Mar. Res. 2003, 57, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryabushko, V.I.; Kapranov, S.V.; Gureeva, E.V.; Bobko, N.I.; Barinova, S.S. Rare earth elements in the seagrass Zostera noltei and sediments from the Black Sea coast of Crimea. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelyadina, N.S.; Kapranov, S.V.; Popov, M.A.; Smirnova, L.L.; Bobko, N.I. Trace elements in the detoxifying and accumulating body parts of Mytilus galloprovincialis Lamark, 1819 (Crimea, Black Sea): Human health risks and effect of the sampling site location. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 61352–61369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryabushko, V.I.; Gureeva, E.V.; Kapranov, S.V.; Bobko, N.I.; Prazukin, A.V.; Nekhoroshev, M.V. Rare earth elements in brown algae of the genus Cystoseira (Phaeophyceae) (Black Sea). Eur. J. Phycol. 2022, 57, 433–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, I.d.S.; Brito, G.B.; dos Santos, G.L.; Santos, L.N.; Teixeira, L.S.G.; Araujo, R.G.O.; Korn, M.G.A. Multivariate data analysis of trace elements in bivalve molluscs: Characterization and food safety evaluation. Food Chem. 2019, 273, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Favretto, L.; Favretto, L.G.; Marletta, G.P.; Saitta, M. Principal component analysis: A chemometric aid for classification of polluted and unpolluted mussels. Anal. Chim. Acta 1989, 220, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forleo, T.; Zappi, A.; Melucci, D.; Ciriaci, M.; Griffoni, F.; Bacchiocchi, S.; Siracusa, M.; Tavoloni, T.; Piersanti, A. Inorganic elements in Mytilus galloprovincialis shells: Geographic traceability by multivariate analysis of ICP-MS data. Molecules 2021, 26, 2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricardo, F.; Génio, L.; Costa Leal, M.; Albuquerque, R.; Queiroga, H.; Rosa, R.; Calado, R. Trace element fingerprinting of cockle (Cerastoderma edule) shells can reveal harvesting location in adjacent areas. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricardo, F.; Mamede, R.; Bispo, R.; Santos, A.; Ferreira da Silva, E.; Patinha, C.; Calado, R. Cost-efficiency improvement of bivalves shells preparation when tracing their geographic origin through ICP-MS analysis of elemental fingerprints. Food Control 2020, 118, 107383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, B.J.; Fodrie, F.J.; McMillan, P.A.; Levin, L.A. Spatial and temporal variation in trace elemental fingerprints of mytilid mussel shells: A precursor to invertebrate larval tracking. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2005, 50, 48–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honig, A.; Etter, R.; Pepperman, K.; Morello, S.; Hannigan, R. Site and age discrimination using trace element fingerprints in the blue mussel, Mytilus edulis. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2020, 522, 151249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Struck, B.D.; Pelzer, R.; Ostapczuk, P.; Emons, H.; Mohl, C. Statistical evaluation of ecosystem properties influencing the uptake of As, Cd, Co, Cu, Hg, Mn, Ni, Pb and Zn in seaweed (Fucus vesiculosus) and common mussel (Mytilus edulis). Sci. Total Environ. 1997, 207, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunphy, B.J.; Millet, M.A.; Jeffs, A.G. Elemental signatures in the shells of early juvenile green-lipped mussels (Perna canaliculus) and their potential use for larval tracking. Aquaculture 2011, 311, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Furuta, N. Determination of rare earth elements (REEs) in airborne particulate matter (APM) collected in Tokyo, Japan, and a positive anomaly of europium and terbium. Anal. Sci. 2010, 26, 929–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, J.P.; Backeljau, T.; Chapelle, G. Shells from aquaculture: A valuable biomaterial, not a nuisance waste product. Rev. Aquac. 2019, 11, 42–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| A. kagoshimensis | F. glaber ponticus | M. galloprovincialis | M. gigas | R. venosa | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al | 3.3 × 105 (1.2 × 105–4.7 × 105) | 1.0 × 105 (4.6 × 104–4.1 × 105) | 3.2 × 104 (2.9 × 104–7.1 × 104) | 3.9 × 105 (2.2 × 105–8.0 × 105) | 1.7 × 105 (5.8 × 104–4.3 × 105) |
| Sc | 1043 (278–1387) a | 316 (270–488) a | 245 (224–336) b | 599 (505–966) b | 137 (BDL–330) c |
| Y | 204 (92–340) a | 119 (92–150) b | 56 (48–63) c | 229 (133–407) ab | 117 (69–215) ab |
| La | 252 (135–491) a | 224 (75–3039) ab | 70 (30–241) b | 370 (129–538) a | 228 (52–583) ab |
| Ce | 201 (58–282) a | 78 (12–121) b | 39 (38–55) b | 318 (150–720) a | 153 (74–293) a |
| Pr | 24 (8.7–34) a | 11 (3.9–14) b | 4.1 (2.1–7.5) b | 36 (17–89) a | 13 (6.0–31) ab |
| Nd | 91 (38–140) a | 39 (15–55) bc | 18 (11–24) c | 161 (90–379) a | 78 (24–119) ab |
| Sm | 21 (7.8–28) a | 9.3 (3.3–11) b | 3.5 (0.9–7.9) b | 35 (17–95) a | 12 (4.3–32) ab |
| Eu | 17 (8.1–24) ab | 9.4 (4.3–11) b | 12 (6.0–18) ab | 24 (14–39) a | 5.2 (BDL–9.6) b |
| Gd | 21 (8.5–31) a | 9.6 (3.4–13) b | 3.1 (1.3–6.4) b | 36 (16–84) a | 13 (6.9–32) ab |
| Tb | 2.7 (0.9–5.5) b | 1.6 (0.8–4.3) b | 0.9 (0.3–3.6) b | 10.4 (4.5–19) a | 1.6 (1.1–5.8) ab |
| Dy | 16 (6.5–22) a | 9.0 (3.5–11) b | 2.7 (1.9–6.7) b | 33 (20–77) a | 11 (7.2–25) ab |
| Ho | 2.9 (1.0–5.0) a | 1.8 (0.7–4.1) a | 0.8 (0.2–4.5) a | 7.9 (2.2–16) a | 2.5 (1.8–6.0) a |
| Er | 8.4 (2.9–13) ab | 5.3 (2.9–6.8) bc | 2.4 (1.3–6.2) c | 21 (8.8–53) a | 9.0 (3.4–16) ab |
| Tm | 1.2 (0.4–2.0) b | 1.3 (0.11–3.7) ab | 1.2 (1.0–4.5) ab | 2.5 (2.0–4.8) a | 3.8 (2.1–5.7) ab |
| Yb | 5.9 (3.1–9.4) ab | 4.4 (2.6–6.1) ab | 1.8 (0.71–5.3) b | 18 (5.6–32) a | 7.6 (3.4–12) ab |
| Lu | 0.86 (0.45–2.0) b | 1.4 (0.12–4.6) ab | 1.4 (1.2–4.4) ab | 2.6 (1.3–4.4) a | 2.6 (1.5–4.5) ab |
| ΣREE | 1913 | 840 | 461 | 1903 | 792 |
| A. kagoshimensis | F. glaber ponticus | M. galloprovincialis | M. gigas | R. venosa | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.17 | 6.51 | 12.23 | 7.61 | - * | |
| 3.90 | 6.45 | 8.16 | 4.94 | 17.61 | |
| 1.39 | 1.07 | 1.91 | 1.79 | 11.49 | |
| 1.36 | 1.07 | 1.73 | 1.62 | 3.19 | |
| 3.60 | 4.57 | 17.01 | 3.05 | 1.92 | |
| 3.69 | 4.43 | 16.20 | 2.98 | 1.92 | |
| 8.04 | 9.53 | 16.93 | 16.66 | 7.53 | |
| 82.73 | 81.64 | 93.63 | 35.84 | 43.02 | |
| 2.20 | 2.02 | 2.14 | 1.98 | 1.96 | |
| 1.12 | 1.17 | 1.18 | 1.04 | 1.03 | |
| 7.29 | 7.56 | 7.80 | 8.67 | 10.90 | |
| 8.86 | 10.06 | 8.81 | 10.21 | 15.57 | |
| 2.02 | 1.96 | 1.89 | 2.09 | 2.09 | |
| 2.04 | 2.44 | 1.84 | 0.96 | 1.41 | |
| 0.76 | 0.51 | 0.53 | 0.55 | 0.61 | |
| 0.77 | 0.44 | 0.50 | 0.44 | 0.51 | |
| 0.90 | 0.90 | 0.87 | 0.96 | 0.93 |
| Bivalves, Gastropod * | Bivalves | Glycymeris glycymeris | Placopecten magellanicus | Chemotrophic mussels | Bathymodiolus spp. | Chemotrophic mussels | Mytilus edulis | Mytilus edulis | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N Black Sea | Tokyo Bay | NW France Coast | Newfoundland, Atlantic | Deep Pacific and Atlantic | Mid-Atlantic Ridge | E Asia Pacific | NW France Coast | North Sea | |
| This Study | [76] | [78] | [77] | [91] | [71] | [79] | [79] | [68] | |
| Sc | 134–945 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Y | 55–259 | – | 36–357 | 12–78 | 6.9–94 | 10–116 | 3.6–62 | 6.0–24 | – |
| La | 95–319 | 19.6–104.3 | 26–175 | 19–103 | 13–97 | 8.5–153 | 5.4–1474 | 5.7–66 | 8.0–15 |
| Ce | 43–424 | 27.7–209 | 26–206 | 7.8–58 | 3.2–66 | 8.9–205 | 10–2487 | 4.9–64 | 7.6–13 |
| Pr | 4.7–50 | 2.07–27.2 | 4.2–26 | 2.3–12 | 0.8–12 | 1.8–27 | 1.2–224 | 0.8–6.8 | 1.3–2.5 |
| Nd | 18–219 | 6.5–121 | 17–106 | 8.8–50 | 2.4–44 | 7.5–100 | 4.7–814 | 3.6–34 | 5.4–11 |
| Sm | 4.0–47 | 0.750–27.0 | 3.6–20 | 1.5–8.9 | 0.4–9.0 | 1.5–24 | 0.7–128 | 0.7–7.1 | 1.2–2.5 |
| Eu | 8.4–25 | 0.135–4.62 | 0.9–5.1 | 0.3–1.9 | 0.10–55 | 0.5–296 | 0.2–31 | 0.17–1.6 | 0.3–0.7 |
| Gd | 3.8–48 | 0.97–31.5 | 4.7–27 | 1.8–10 | 0.6–14 | 1.7–24 | 0.9–139 | 1.0–7.8 | 2.1–3.8 |
| Tb | 1.3–12 | 0.114–4.44 | 0.6–3.7 | 0.2–1.3 | 0.06–1.7 | 0.2–3.0 | 0.1–19 | 0.1–1.0 | 0.2–0.5 |
| Dy | 3.7–43 | 0.790–28.0 | 3.4–21 | 1.1–7.9 | 0.4–8.4 | 1.4–14 | 0.6–102 | 0.5–5.2 | 1.2–2.4 |
| Ho | 1.4–8.5 | 0.191–6.03 | 0.7–4.5 | 0.2–1.7 | 0.10–1.9 | 0.3–2.4 | 0.1–18 | 0.09–1.0 | 0.2–0.4 |
| Er | 2.9–27 | 0.692–18.1 | 1.6–12 | 0.5–4.3 | 0.3–5.6 | 0.7–6.3 | 0.3–41 | 0.2–2.6 | 0.5–1.0 |
| Tm | 1.2–3.1 | 0.109–2.20 | – | - | – | – | – | – | – |
| Yb | 2.5–18 | 0.537–12.7 | 0.8–6.6 | 0.3–2.9 | 0.2–4.9 | 0–4.5 | 0.23–23 | 0.09–2.2 | 0–0.6 |
| Lu | 0.93–2.7 | 0.102–1.83 | 0.1–0.9 | 0.03–0.4 | 0.04–0.73 | 0–0.8 | 0.03–3.0 | 0.012–0.34 | 0.03–0.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kapranov, S.V.; Ryabushko, V.I.; Dikareva, J.D.; Kapranova, L.L.; Bobko, N.I.; Barinova, S. Rare Earth Elements in Shells of Black Sea Molluscs: Anomalies and Biogeochemical Implications. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 713. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12050713
Kapranov SV, Ryabushko VI, Dikareva JD, Kapranova LL, Bobko NI, Barinova S. Rare Earth Elements in Shells of Black Sea Molluscs: Anomalies and Biogeochemical Implications. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2024; 12(5):713. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12050713
Chicago/Turabian StyleKapranov, Sergey V., Vitaliy I. Ryabushko, Juliya D. Dikareva, Larisa L. Kapranova, Nikolay I. Bobko, and Sophia Barinova. 2024. "Rare Earth Elements in Shells of Black Sea Molluscs: Anomalies and Biogeochemical Implications" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 12, no. 5: 713. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12050713
APA StyleKapranov, S. V., Ryabushko, V. I., Dikareva, J. D., Kapranova, L. L., Bobko, N. I., & Barinova, S. (2024). Rare Earth Elements in Shells of Black Sea Molluscs: Anomalies and Biogeochemical Implications. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 12(5), 713. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12050713






