Maritime Traffic Knowledge Discovery via Knowledge Graph Theory
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
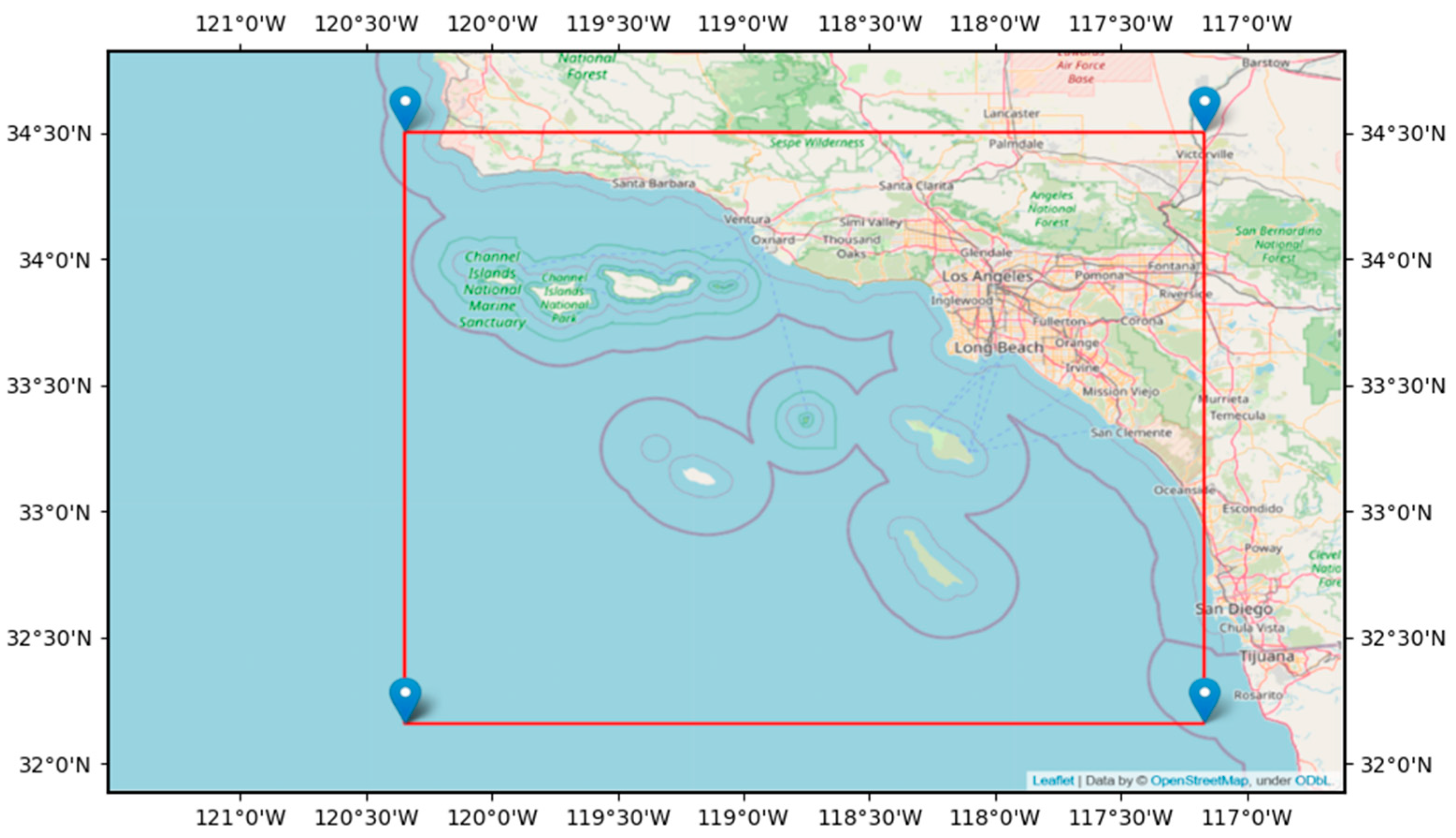
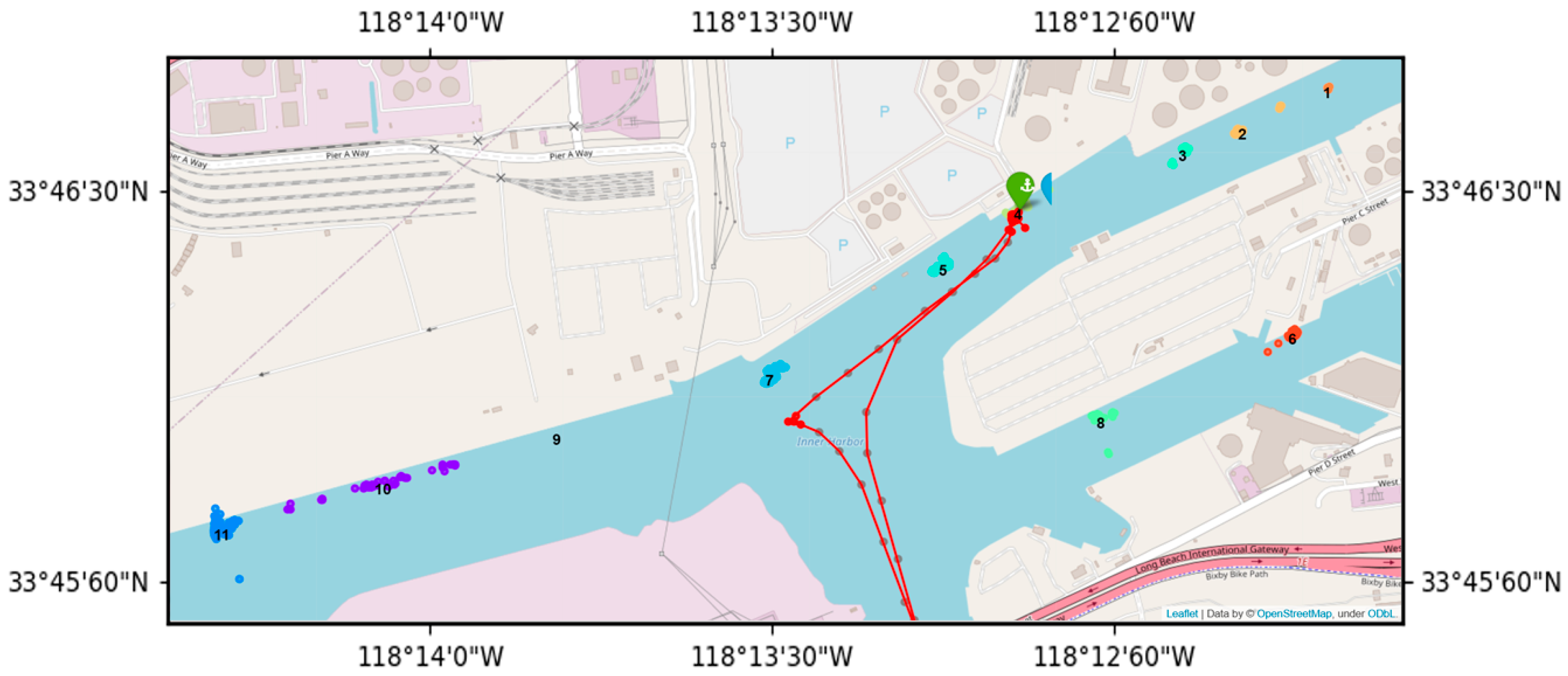
2.1. Research Area
2.2. Methodology
2.2.1. AIS Data Preprocessing
2.2.2. Vessel Navigation Knowledge Discovery
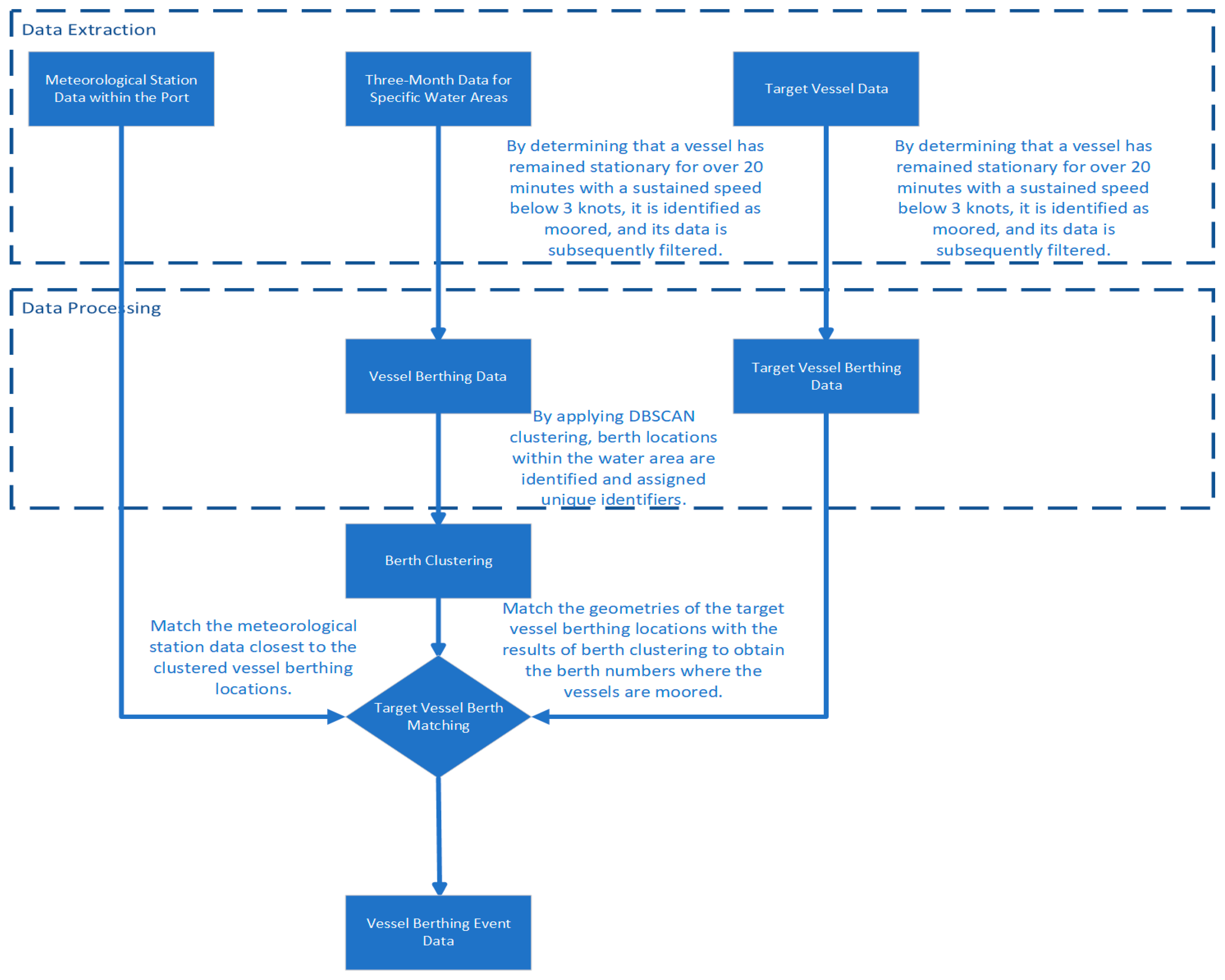
2.2.3. Berth Knowledge Discovery for Vessels
3. Results
3.1. Definitions of Vessel Navigation Entities and Relationships
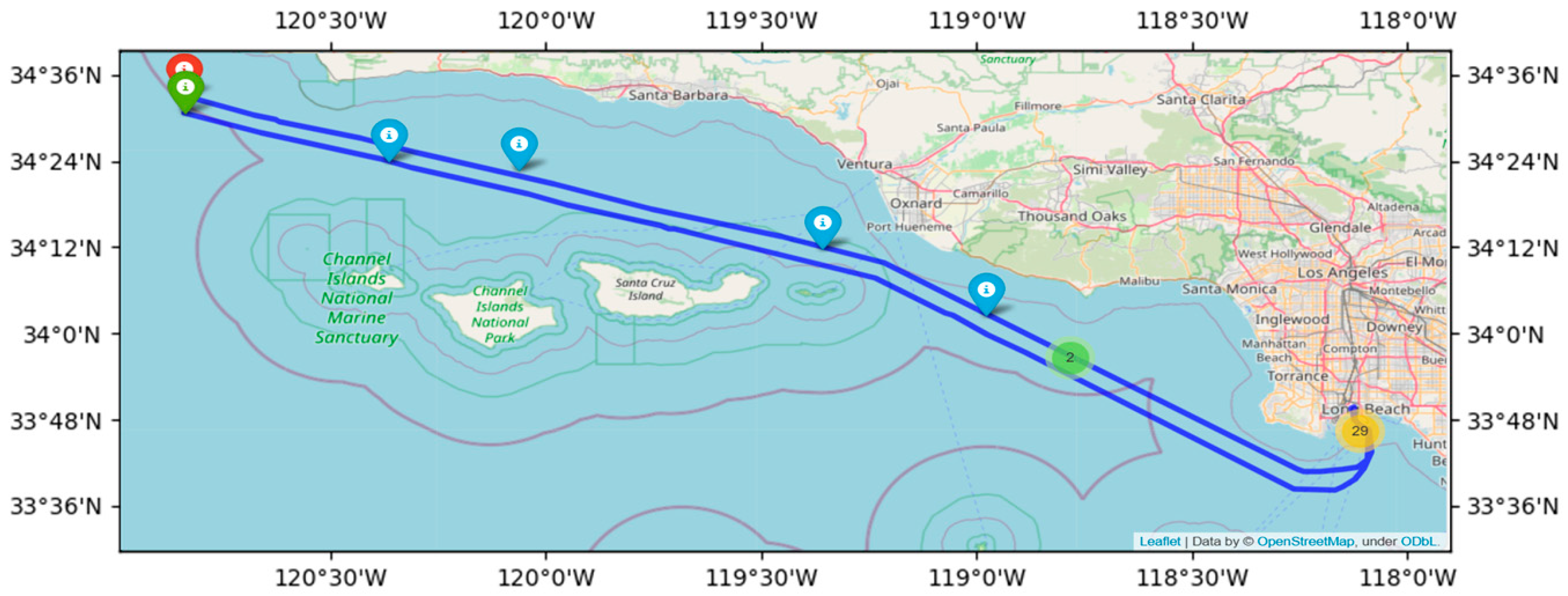
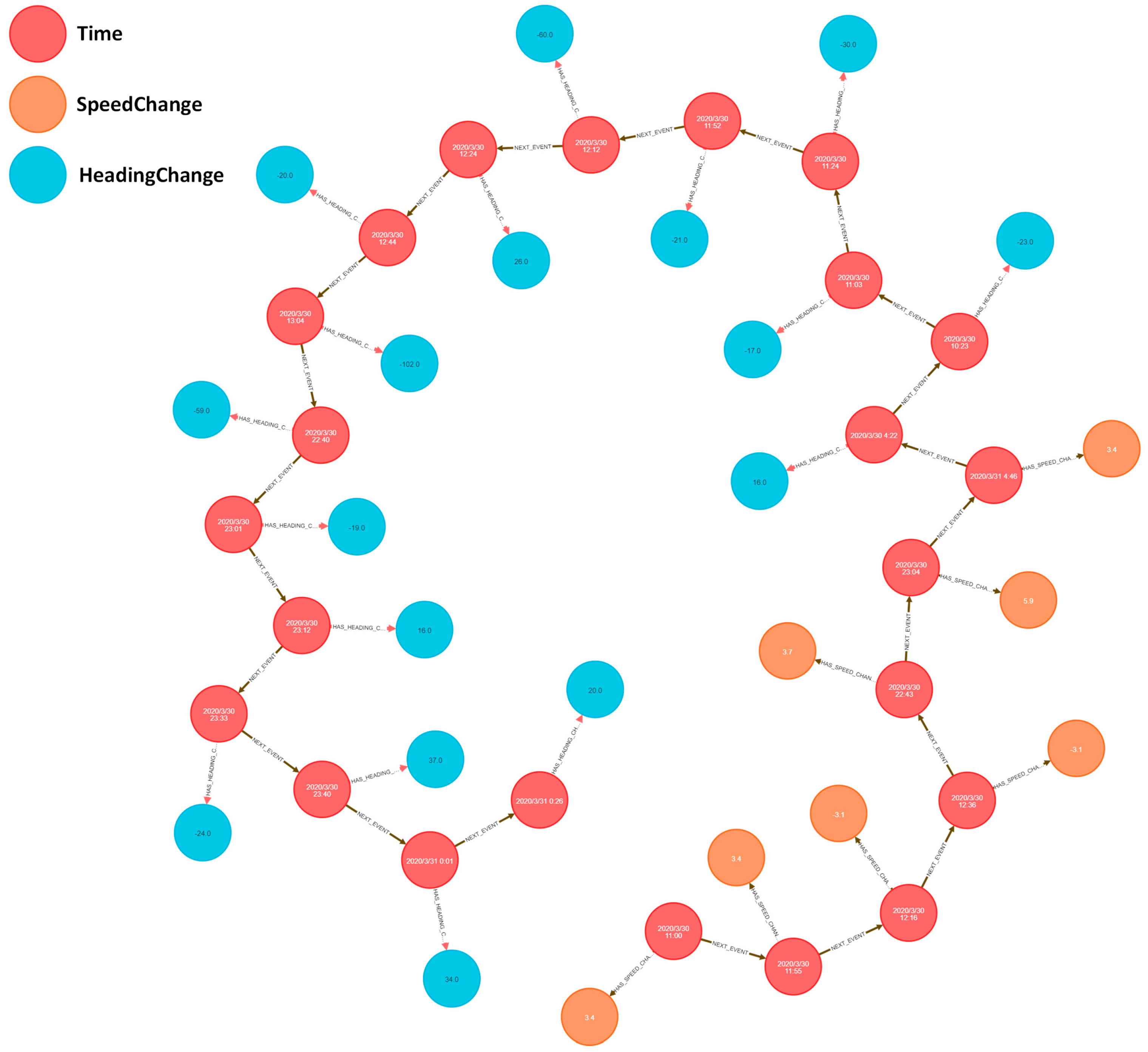
3.1.1. Extraction of Vessel Speed and Course Change Events
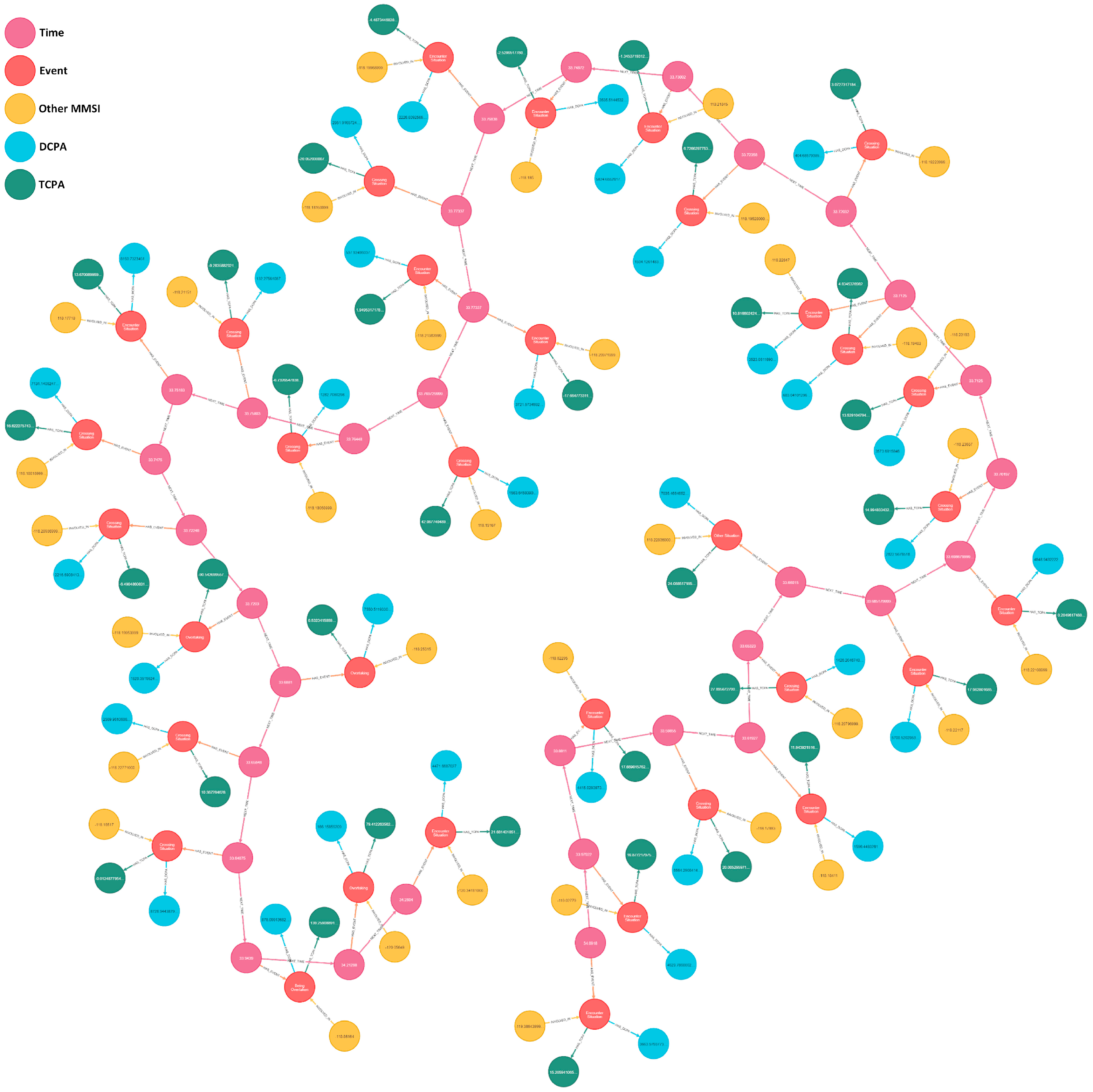
3.1.2. Extraction of Vessel Encounter Events
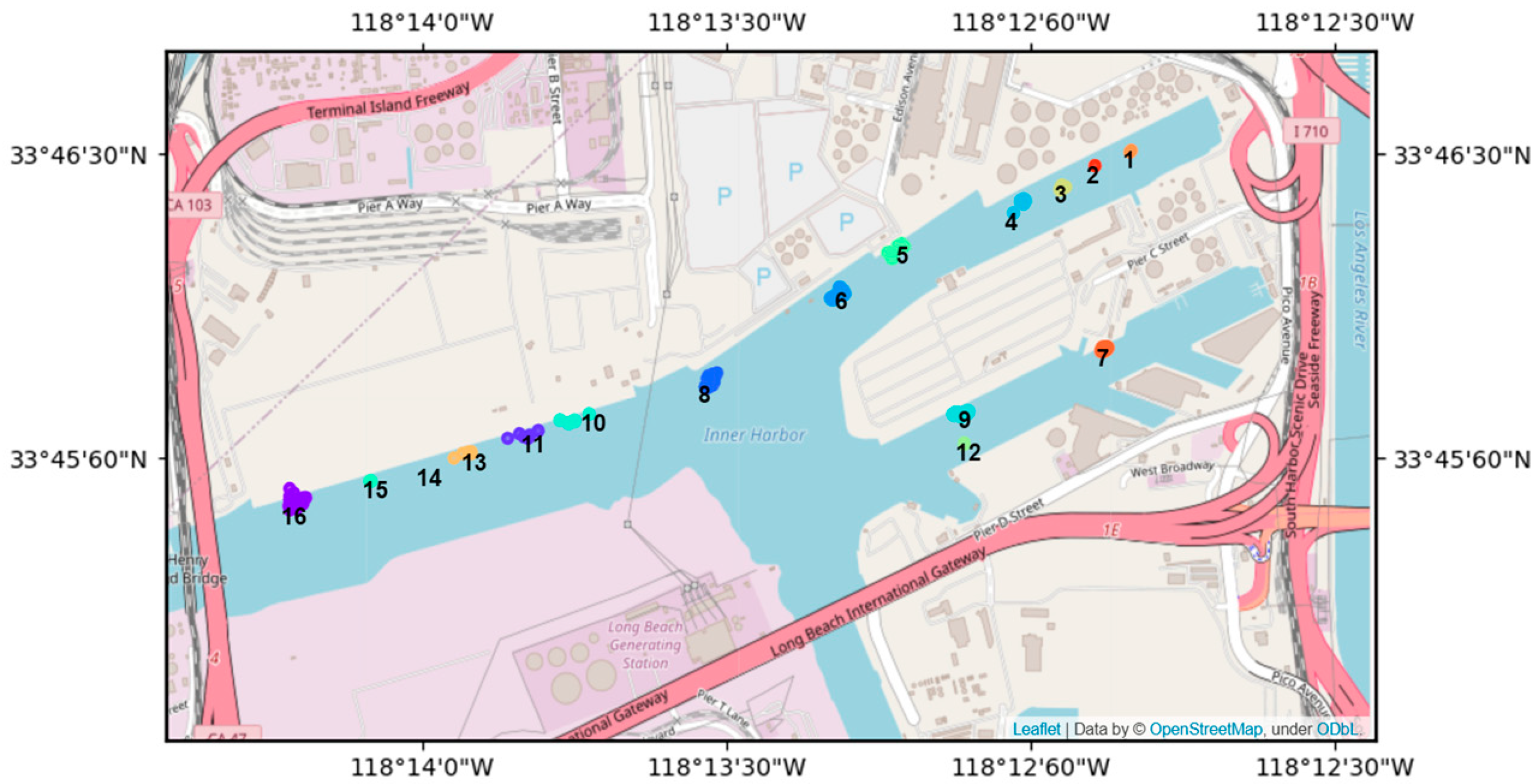
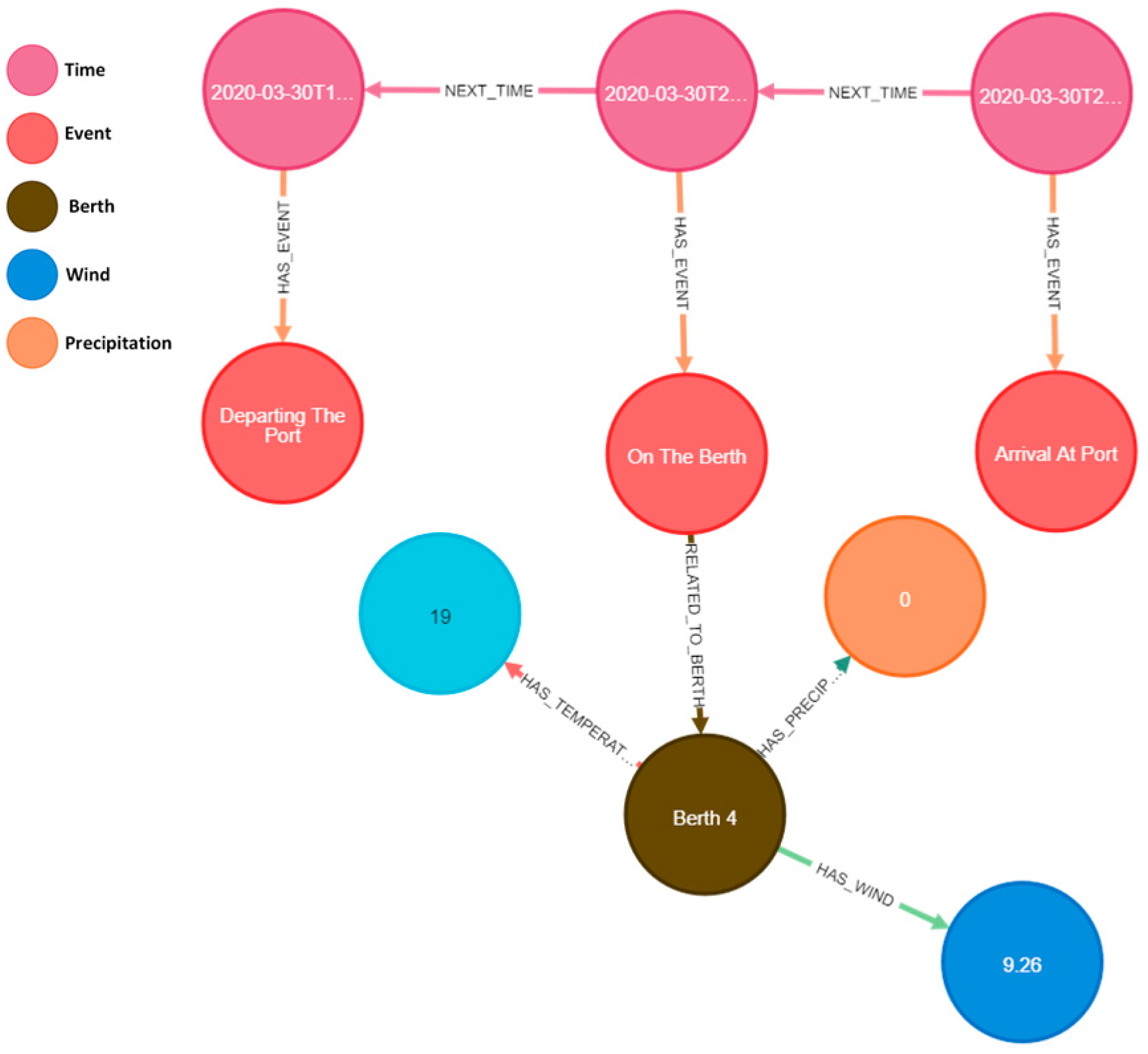
3.1.3. Extraction of Vessel Berthing Events
4. Discussion
4.1. Maritime Traffic Knowledge Construction
4.2. Maritime Traffic Knowledge Discovery
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xin, X.; Liu, K.; Loughney, S.; Wang, J.; Li, H.; Ekere, N.; Yang, Z. Multi-scale collision risk estimation for maritime traffic in complex port waters. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2023, 240, 109554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, T.; Youn, I.H. Collision Risk Situation Clustering to Design Collision Avoidance Algorithms for Maritime Autonomous Surface Ships. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.Q.; Chen, W.P.; Wu, B.; Wu, H.F.; Xian, J.F. Ship visual trajectory exploitation via an ensemble instance segmentation framework. Ocean Eng. 2024, 313, 119368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Huang, L.W.; He, Y.X.; Wang, B.; Chen, J.H.; Tian, Y.F.; Zhao, X.Y. A real-time multi-ship collision avoidance decision-making system for autonomous ships considering ship motion uncertainty. Ocean Eng. 2023, 278, 114205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Zhou, L.; Zhao, X.; Shao, B. Research on ship collision avoidance path planning based on modified potential field ant colony algorithm. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2023, 235, 106482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipiak, D.; Wecel, K.; Strózyna, M.; Michalak, M.; Abramowicz, W. Extracting Maritime Traffic Networks from AIS Data Using Evolutionary Algorithm. Bus. Inf. Syst. Eng. 2020, 62, 435–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Ma, J.W. Ship Navigation Behavior Prediction Based on AIS Data. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 47997–48008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Park, H.J.; Shin, W.; Park, D.; Han, S.W. WAY: Estimation of Vessel Destination in Worldwide AIS Trajectory. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2023, 59, 5961–5977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, I.L.; Lee, M.C.; Nieh, C.Y.; Huang, J.C. Ship Classification Based on AIS Data and Machine Learning Methods. Electronics 2024, 13, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.J.; Chen, J.H.; Geng, J.J.; Ye, J.; Yan, T.; Shi, J.; Xu, J.H. Monitoring and evaluation of ship operation congestion status at container ports based on AIS data. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2023, 245, 106836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Afflisio, E.; Braca, P.; Willett, P. Malicious AIS Spoofing and Abnormal Stealth Deviations: A Comprehensive Statistical Framework for Maritime Anomaly Detection. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2021, 57, 2093–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Chen, L.; Chen, P.; Negenborn, R.R.; van Gelder, P.H.A.J.M. Ship collision avoidance methods: State-of-the-art. Saf. Sci. 2020, 121, 451–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, B.; Perera, L.P. Ship behavior prediction via trajectory extraction-based clustering for maritime situation awareness. J. Ocean Eng. Sci. 2022, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Guo, S. Event-triggered adaptive finite time trajectory tracking control for an underactuated vessel considering unknown time-varying disturbances. Transp. Saf. Environ. 2023, 5, tdac078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, J.; Roh, M.I.; Lee, H.W. Quantitative calculation method of the collision risk or collision avoidance in ship navigation using the CPA and ship domain. J. Comput. Des. Eng. 2021, 8, 894–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Perera, L.P.; Batalden, B.-M. Localized advanced ship predictor for maritime situation awareness with ship close encounter. Ocean Eng. 2024, 306, 117704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wu, H.; Han, B.; Liu, W.; Montewka, J.; Liu, R.W. Orientation-aware ship detection via a rotation feature decoupling supported deep learning approach. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 125, 106686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, M.R.; Niu, B.; Hu, Q. SARGAN: A Novel SAR Image Generation Method for SAR Ship Detection Task. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 28500–28512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, L.; Xiao, J.R. Ellipse Polar Encoding for Oriented SAR Ship Detection. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 3502–3515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.Q.; Wu, B.; Xie, L.; Teixeira, A.P.; Yan, X.P. A Novel Ship Speed and Heading Estimation Approach Using Radar Sequential Images. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 24, 11107–11120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Chu, X.M.; Deng, L.; Lei, J.Y.; He, W.; Królczyk, G.; Li, Z. A new multi-sensor fusion approach for integrated ship motion perception in inland waterways. Measurement 2022, 200, 111630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.W.; Liu, Y.C.; Gunawan, B.A.; Bucknall, R. Practical Moving Target Detection in Maritime Environments Using Fuzzy Multi-sensor Data Fusion. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 2021, 23, 1860–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.H.; Zuo, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, W.J.; Li, T.S. STMGF-Net: A Spatiotemporal Multi-Graph Fusion Network for Vessel Trajectory Forecasting in Intelligent Maritime Navigation. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2024, 25, 21367–21379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Li, X.C.; Yin, J.J.; Liang, W.; Hu, Y.P. Adaptive multi-source data fusion vessel trajectory prediction model for intelligent maritime traffic. Knowl. -Based Syst. 2023, 277, 110799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Tang, J.; Yuan, C.; Gao, F.; Ding, X. Examining the characteristics between time and distance gaps of secondary crashes. Transp. Saf. Environ. 2023, 6, tdad014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Z.; Cheng, S.Y.; Chen, J.; Liang, X.Z.; Xiong, F.Y.; Zhang, N.Y. Relphormer: Relational Graph Transformer for Knowledge Graph Representations. Neurocomputing 2024, 566, 127044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.Y.; Xia, F.; Naseriparsa, M.; Osborne, F. Knowledge Graphs: Opportunities and Challenges. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2023, 56, 13071–13102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, N.N.; Song, D.D.; Liao, L.J. Knowledge graph embedding with concepts. Knowl. -Based Syst. 2019, 164, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.Q.; Liu, J.; Wu, M.M.; Abbas, S.; Hu, W.; Wei, B.F.; Zheng, Q.H. Representation learning over multiple knowledge graphs for knowledge graphs alignment. Neurocomputing 2018, 320, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.L.; Zhou, W.X.; Zheng, P.J.; Liu, G.Y. A Novel Approach for the Analysis of Ship Pollution Accidents Using Knowledge Graph. Sustainability 2024, 16, 5296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.X.; Zhang, L.M.; Zhong, Z.G. A Novel Method for Constructing Spatiotemporal Knowledge Graph for Maritime Ship Activities. Electronics 2023, 12, 3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.T.; Xu, R.Q.; Lu, W.P.; Mayer, W.; Ning, D.; Duan, Y.C.; Zeng, X.; Feng, Z.W. Multi-Modal Spatio-Temporal Knowledge Graph of Ship Management. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 9393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamasauskaite, G.; Groth, P. Defining a Knowledge Graph Development Process Through a Systematic Review. ACM Trans. Softw. Eng. Methodol. 2023, 32, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knatz, G. Port mergers: Why not Los Angeles and Long Beach? Res. Transp. Bus. Manag. 2018, 26, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, B.M.; Liu, J.G.; Ye, X.H.; Gong, Y.; Chen, J.H. Data-driven approach for port resilience evaluation. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2024, 186, 103570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.L.; Han, P.H.; Zhu, M.D.; Osen, O.; Zhang, H.X.; Li, G.Y. AIS Data-Based Hybrid Predictor for Short-Term Ship Trajectory Prediction Considering Uncertainties. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2024, 25, 20268–20279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, M.; Cao, Y.; Cheng, X. Research of AIS Data-Driven Ship Arrival Time at Anchorage Prediction. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 24, 12740–12746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.S.; Huang, J.Q.; Lei, J.L.; Kong, L.H.; Lv, Y.B.; Lin, Z.L.; Chen, G.H.; Khan, M.K. AISChain: Blockchain-Based AIS Data Platform With Dynamic Bloom Filter Tree. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 24, 2332–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciancalepore, S.; Tedeschi, P.; Aziz, A.; Di Pietro, R. Auth-AIS: Secure, Flexible, and Backward-Compatible Authentication of Vessels AIS Broadcasts. IEEE Trans. Dependable Secur. Comput. 2022, 19, 2709–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brcko, T.; Luin, B. A Decision Support System Using Fuzzy Logic for Collision Avoidance in Multi-Vessel Situations at Sea. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M.D.; Sadeghi, Z.; Matwin, S. Exploring autoregression patterns for automatic vessel type classification. J. Supercomput. 2024, 80, 9532–9553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.W.; Wong, Y.D.; Tan, K.H.; Wang, N.X.; Yuen, K.F. Real-time prediction and detection of contacts between vessels and facilities based on AIS: A multivariate time-series classification approach. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 257, 125109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.H.; Bai, X.W. Prospects for improving shipping companies? profit margins by quantifying operational strategies and market focus approach through AIS data. Transp. Policy 2022, 128, 138–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Yan, D.W.; Yan, M.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Y.B. An Unscented Kalman Filter Online Identification Approach for a Nonlinear Ship Motion Model Using a Self-Navigation Test. Machines 2022, 10, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, S.; Chen, S.; Chen, Q.; Liu, K. Research on the navigational risk of liquefied natural gas carriers in an inland river based on entropy: A cloud evaluation model. Transp. Saf. Environ. 2023, 6, tdad018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.F.; Ma, J.; He, M.R.; Su, Y.D.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, Q. Motion primitives learning of ship-ship interaction patterns in encounter situations. Ocean Eng. 2022, 247, 110708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.Q.; Zhen, R.; Liu, J.L. Fuzzy logic-based modeling method for regional multi-ship collision risk assessment considering impacts of ship crossing angle and navigational environment. Ocean Eng. 2022, 259, 111847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Arnesen, M.J.; Fagerholt, K.; Gjestvang, M.; Thun, K. A two-phase heuristic for an in-port ship routing problem with tank allocation. Comput. Oper. Res. 2018, 91, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Mondo, G.; Peng, P.; Gensel, J.; Claramunt, C.; Lu, F. Leveraging Spatio-Temporal Graphs and Knowledge Graphs: Perspectives in the Field of Maritime Transportation. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



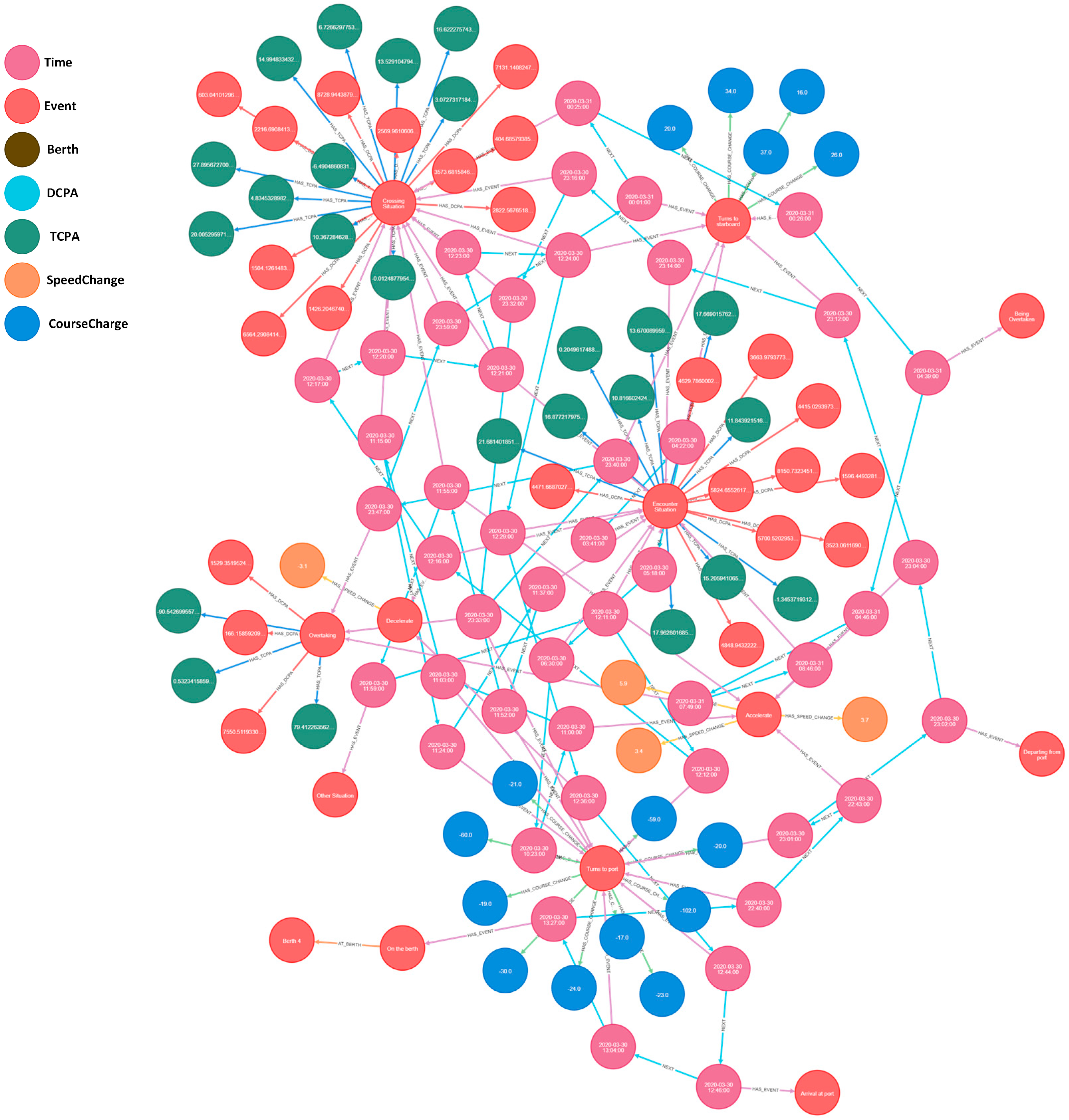
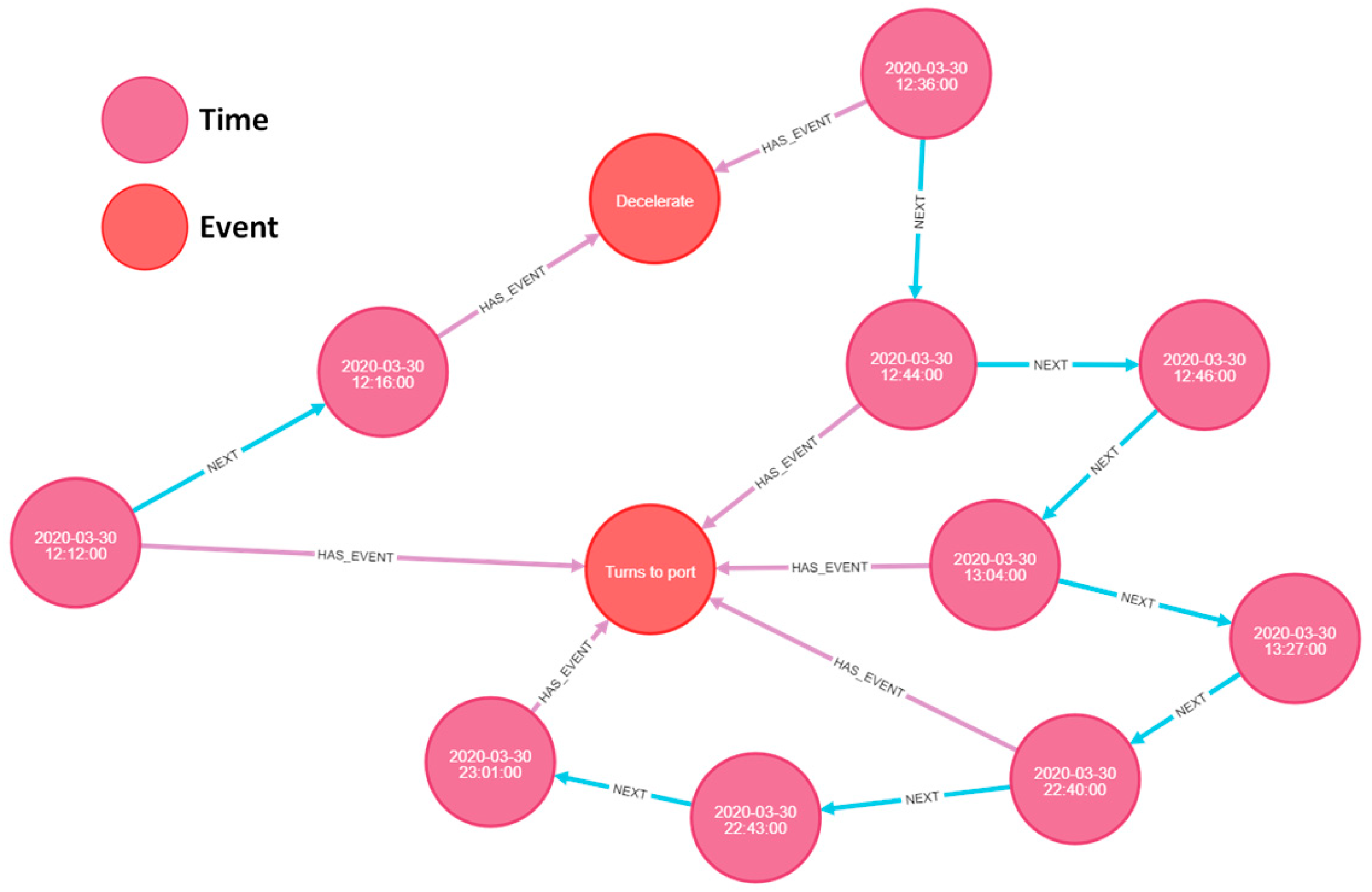
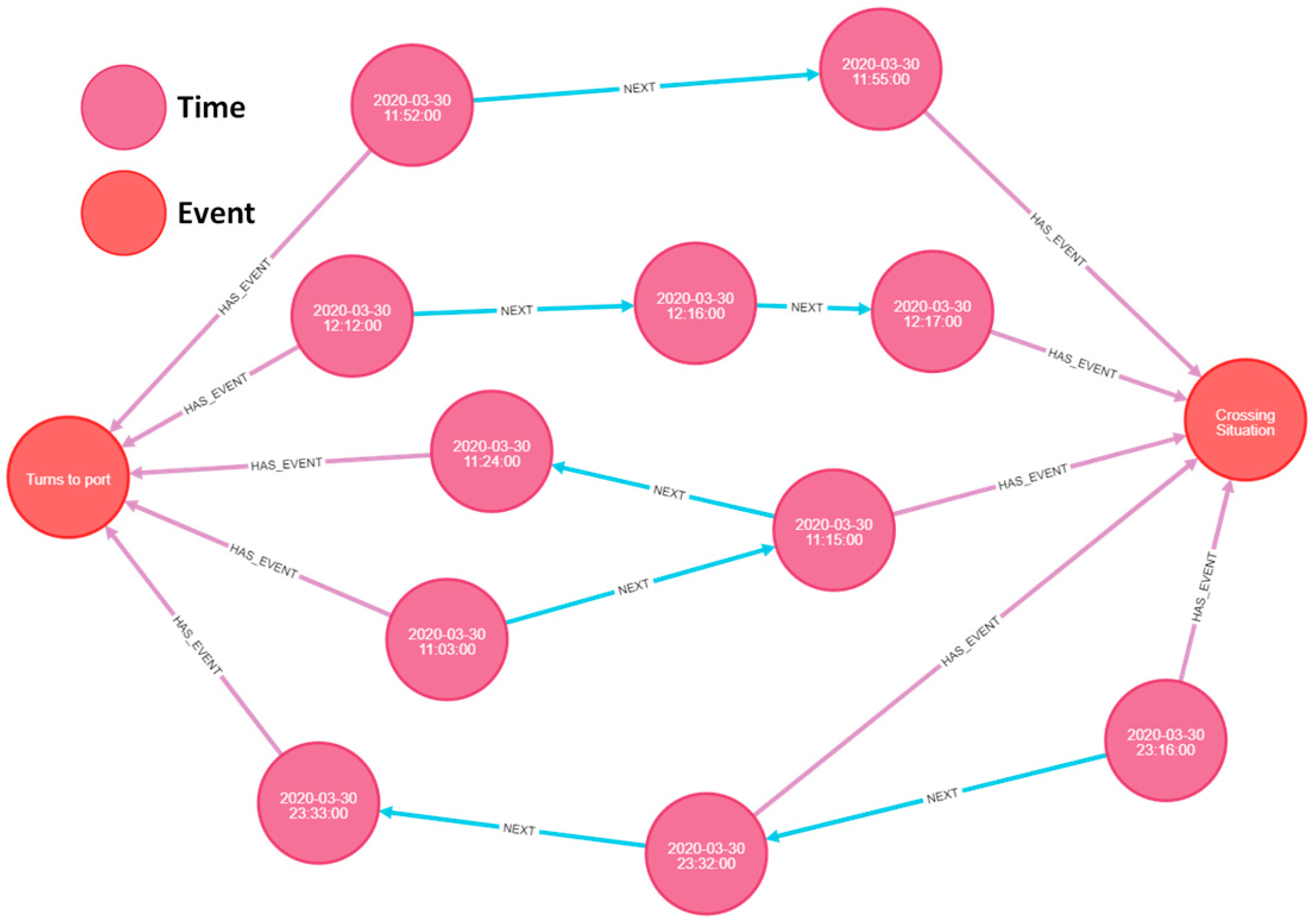
| Static Information | Dynamic Information |
|---|---|
| MMSI | UTC |
| ship name | longitude |
| call sign | latitude |
| maximum static draught | COG |
| vessel length | SOG |
| vessel width | heading |
| vessel type | Status |
| Transceiver Class |
| Ship Type | AIS Main Ship Type Codes |
|---|---|
| Special-purpose ships | 50–59 |
| Passenger ships | 60–69 |
| Cargo ships | 70–79 |
| Oil tankers | 80–89 |
| Other types of ships | 90–99 |
| Entities | Attribute |
|---|---|
| Ship | MMSI, Vessel Type, Vessel Width, Vessel Length, Maximum Static Draught, COG, SOG |
| Navigation Event | Crossing Encounter, Head-on Encounter, Overtaking, Vessel Acceleration, Vessel Deceleration, Port Turn, Starboard Turn, Berthing, Departure from Berth |
| Berth | Berth Number |
| Weather Conditions | Wind speed, Wind Direction, Temperature, Precipitation Amount |
| Time | UTC |
| Node Labels | Relationship Types |
|---|---|
| Event | NEXT_EVENT |
| Speed Change | HAS_ Speed_ Change |
| Heading Change | HAS_ Heading_ Change |
| Node Labels | Relationship Types |
|---|---|
| Time | NEXT_TIME |
| Other MMSI | INVOLVED_IN |
| Event | HAS_EVENT |
| DCPA | HAS_DCPA |
| TCPA | HAS_TCPA |
| Node Labels | Relationship Types |
|---|---|
| Berth | RELATED_TO_BERTH |
| Temperature | HAS_TEMPERATURE |
| Wind | HAS_WIND |
| Precipitation | HAS_PRECIPITATION |
| Time | NEXT_TIME |
| Event | HAS_EVENT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, S.; Xu, J.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Postolache, O. Maritime Traffic Knowledge Discovery via Knowledge Graph Theory. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 2333. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12122333
Li S, Xu J, Chen X, Zhang Y, Zheng Y, Postolache O. Maritime Traffic Knowledge Discovery via Knowledge Graph Theory. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2024; 12(12):2333. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12122333
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Shibo, Jiajun Xu, Xinqiang Chen, Yajie Zhang, Yiwen Zheng, and Octavian Postolache. 2024. "Maritime Traffic Knowledge Discovery via Knowledge Graph Theory" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 12, no. 12: 2333. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12122333
APA StyleLi, S., Xu, J., Chen, X., Zhang, Y., Zheng, Y., & Postolache, O. (2024). Maritime Traffic Knowledge Discovery via Knowledge Graph Theory. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 12(12), 2333. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12122333








