Lightweight Multi-Scales Feature Diffusion for Image Inpainting Towards Underwater Fish Monitoring
Abstract
1. Introduction
- LMF-Diffusion is proposed. Employing LMF-Diffusion models for image inpainting tasks has shown promising results in underwater fish image inpainting, producing results that closely resemble real images.
- Within LMF-Diffusion, MCA is integrated to allow the model to effectively capture distant dependencies among pixels and extract features from images at various scales and orientations.
- To reduce parameters, depthwise separable convolutions are used. Models trained using LMF-Diffusion possess only of the parameters compared to the guided diffusion model.
2. Related Work
2.1. Image Inpainting
2.2. Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models
2.3. Attention Mechanisms
3. Materials and Methods
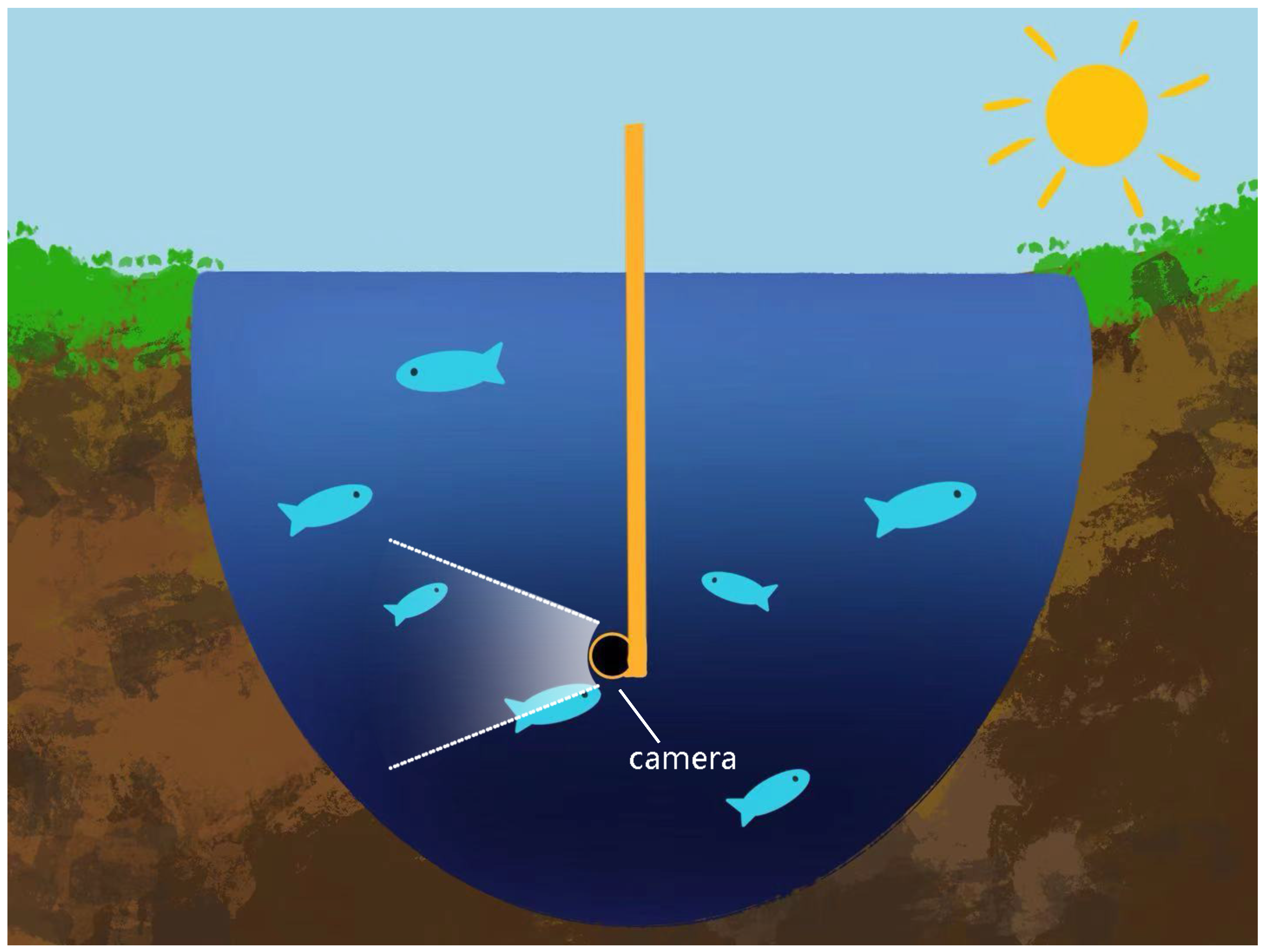
3.1. Koi Dataset
3.2. LMF-Diffusion
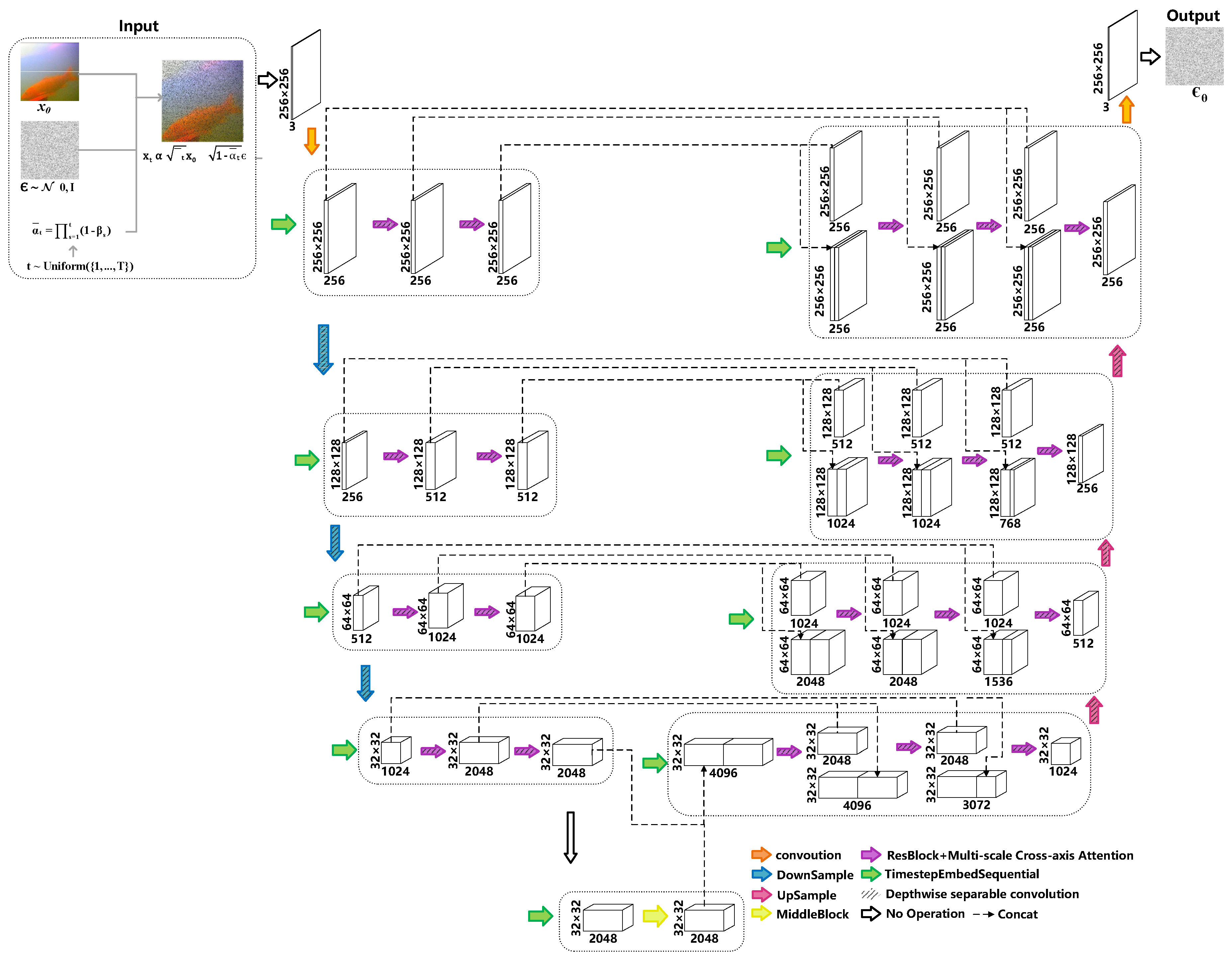
3.2.1. LMF-Diffusion Model Architecture
| Algorithm 1 Training LMF-Diffusion model |
|
3.2.2. Multi-Scale Cross-Axis Attention (MCA)
3.2.3. Depthwise Separable Convolution
4. Experiments Setup
4.1. Experimental Platform and Parameters
4.2. Evaluation Metrics
4.3. Mask Settings
5. Results
5.1. Hyperparameter Optimization
5.2. The Results of Ablation Studies
5.3. Comparison with Other Methods
5.4. Inpainting Obscured Fish Images
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, G.; Chen, Q.; Yoshida, T.; Teravama, K.; Mizukami, Y.; Li, Q.; Kitazawa, D. Detection of Bluefin Tuna by Cascade Classifier and Deep Learning for Monitoring Fish Resources. In Global Oceans 2020: Singapore—U.S. Gulf Coast; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Han, F.; Zhu, J.; Liu, B.; Zhang, B.; Xie, F. Fish Shoals Behavior Detection Based on Convolutional Neural Network and Spatiotemporal Information. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 126907–126926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Gu, Y.Q.; Li, C.; Cong, R.; Shao, F. Underwater Image Enhancement Quality Evaluation: Benchmark Dataset and Objective Metric. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2022, 32, 5959–5974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, P.; Wu, J.; Porikli, F.M.; Li, C. Underwater Image Enhancement With Hyper-Laplacian Reflectance Priors. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2022, 31, 5442–5455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, W. Underwater image enhancement method via multi-feature prior fusion. Appl. Intell. 2022, 52, 16435–16457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Reda, F.A.; Shih, K.J.; Wang, T.C.; Tao, A.; Catanzaro, B. Image Inpainting for Irregular Holes Using Partial Convolutions. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, B.; Lapedriza, A.; Khosla, A.; Oliva, A.; Torralba, A. Places: A 10 Million Image Database for Scene Recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2018, 40, 1452–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Luo, P.; Wang, X.; Tang, X. Deep Learning Face Attributes in the Wild. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 3730–3738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doersch, C.; Singh, S.; Gupta, A.; Sivic, J.; Efros, A.A. What makes Paris look like Paris? Commun. ACM 2015, 58, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, N.; Zhang, L.; Du, B.; Tao, D. Recurrent Feature Reasoning for Image Inpainting. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 7757–7765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Liu, X.; Bai, S.; Wang, L.; Liu, A.; Tao, D.; Hancock, E.R. Regionwise Generative Adversarial Image Inpainting for Large Missing Areas. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2023, 53, 5226–5239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazeri, K.; Ng, E.; Joseph, T.; Qureshi, F.Z.; Ebrahimi, M. EdgeConnect: Generative Image Inpainting with Adversarial Edge Learning. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1901.00212. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, Z.; Tang, Q.; Azizi, S.; Jang, D.; Xu, Z. Contextual Residual Aggregation for Ultra High-Resolution Image Inpainting. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 7505–7514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Lin, Z.; Yang, J.; Shen, X.; Lu, X.; Huang, T.S. Generative Image Inpainting with Contextual Attention. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 5505–5514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Lin, Z.L.; Yang, J.; Zhang, J.; Shechtman, E.; Lu, H. High-Resolution Image Inpainting with Iterative Confidence Feedback and Guided Upsampling. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2005.11742. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Lin, Z.; Yang, J.; Shen, X.; Lu, X.; Huang, T. Free-Form Image Inpainting With Gated Convolution. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 4470–4479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Liu, D.; Xu, S.; Li, H. Generating Diverse Structure for Image Inpainting With Hierarchical VQ-VAE. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 10770–10779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Fu, J.; Chao, H.; Guo, B. Aggregated Contextual Transformations for High-Resolution Image Inpainting. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2023, 29, 3266–3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugmayr, A.; Danelljan, M.; Romero, A.; Yu, F.; Timofte, R.; Gool, L.V. RePaint: Inpainting using Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 11451–11461. [Google Scholar]
- Oktay, O.; Schlemper, J.; Folgoc, L.L.; Lee, M.J.; Heinrich, M.P.; Misawa, K.; Mori, K.; McDonagh, S.G.; Hammerla, N.Y.; Kainz, B.; et al. Attention U-Net: Learning Where to Look for the Pancreas. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.03999. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, K.; Zhang, E.; Xia, M.; Weng, L.; Lin, H. MCANet: A Multi-Branch Network for Cloud/Snow Segmentation in High-Resolution Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, A.G.; Zhu, M.; Chen, B.; Kalenichenko, D.; Wang, W.; Weyand, T.; Andreetto, M.; Adam, H. MobileNets: Efficient Convolutional Neural Networks for Mobile Vision Applications. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.04861. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Yao, L.; Chen, L.; Cai, D.; He, X.; Liu, W. CrossFormer: A Versatile Vision Transformer Based on Cross-scale Attention. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2108.00154. [Google Scholar]
- Pathak, D.; Krähenbühl, P.; Donahue, J.; Darrell, T.; Efros, A.A. Context Encoders: Feature Learning by Inpainting. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 2536–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Chan, T.F. Mathematical Models for Local Nontexture Inpaintings. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 2002, 62, 1019–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Yan, C.; Yang, H.; Bai, L.; Zhou, J.; Hancock, E.R. Adaptive hash retrieval with kernel based similarity. Pattern Recognit. J. Pattern Recognit. Soc. 2018, 75, 136–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.; Ram, S.; Rodríguez, J.J. Image Inpainting Using Nonlocal Texture Matching and Nonlinear Filtering. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2019, 28, 1705–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Wei, Y.; Yang, Z.; Wei, W. Image inpainting algorithm based on TV model and evolutionary algorithm. Soft Comput. 2014, 20, 885–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridevi, G.; Kumar, S.S. Image Inpainting Based on Fractional-Order Nonlinear Diffusion for Image Reconstruction. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. Cssp 2019, 38, 3802–3817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Su, Y.; Zou, L.; Wang, Y.; Jing, P.; Wang, Z.J. Sparsity-Based Image Inpainting Detection via Canonical Correlation Analysis With Low-Rank Constraints. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 49967–49978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, J.; Zhou, Y. The research of image inpainting algorithm using self-adaptive group structure and sparse representation. Clust. Comput. 2019, 22, 7593–7601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, T.B.; Mann, B.; Ryder, N.; Subbiah, M.; Kaplan, J.; Dhariwal, P.; Neelakantan, A.; Shyam, P.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; et al. Language Models are Few-Shot Learners. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2005.14165. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, C.; Cham, T.J.; Cai, J. Pluralistic Image Completion. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 1438–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Cui, J.; Sheng, Y.; Dong, Y.; Xu, Y. Large Scale Image Completion via Co-Modulated Generative Adversarial Networks. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2103.10428. [Google Scholar]
- Richardson, E.; Alaluf, Y.; Patashnik, O.; Nitzan, Y.; Azar, Y.; Shapiro, S.; Cohen-Or, D. Encoding in Style: A StyleGAN Encoder for Image-to-Image Translation. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 2287–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Shen, L.; Wang, H.; Yao, Y.; Zhao, G. Finger vein image inpainting using neighbor binary-wasserstein generative adversarial networks (NB-WGAN). Appl. Intell. Int. J. Artif. Intell. Neural Netw. Complex Probl.-Solving Technol. 2022, 52, 9996–10007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Dong, X.; Li, T.; Zhang, F.; Qian, H.; Chen, G. Parallel adaptive guidance network for image inpainting. Appl. Intell. Int. J. Artif. Intell. Neural Netw. Complex Probl.-Solving Technol. 2023, 53, 1162–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, H.; Liu, L.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, K.; Xia, R.; Xie, J. Research on image Inpainting algorithm of improved GAN based on two-discriminations networks. Appl. Intell. Int. J. Artif. Intell. Neural Netw. Complex Probl.-Solving Technol. 2021, 51, 3460–3474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Zhang, G.; Yang, Z.; Liu, W. Multi-scale patch-GAN with edge detection for image inpainting. Appl. Intell. Int. J. Artif. Intell. Neural Netw. Complex Probl.-Solving Technol. 2023, 53, 3917–3932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, J.; Jain, A.; Abbeel, P. Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.11239. [Google Scholar]
- Sohl-Dickstein, J.N.; Weiss, E.A.; Maheswaranathan, N.; Ganguli, S. Deep Unsupervised Learning using Nonequilibrium Thermodynamics. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1503.03585. [Google Scholar]
- Dhariwal, P.; Nichol, A. Diffusion Models Beat GANs on Image Synthesis. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2105.05233. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Sohl-Dickstein, J.; Kingma, D.P.; Kumar, A.; Ermon, S.; Poole, B. Score-Based Generative Modeling through Stochastic Differential Equations. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Virtual Event, 3–7 May 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Dockhorn, T.; Vahdat, A.; Kreis, K. Score-Based Generative Modeling with Critically-Damped Langevin Diffusion. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2112.07068. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, J.; Wu, J.; Chen, H.; Ma, M. MapGen-Diff: An End-to-End Remote Sensing Image to Map Generator via Denoising Diffusion Bridge Model. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawar, B.; Elad, M.; Ermon, S.; Song, J. Dendenoisingoising Diffusion Restoration Models. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2201.11793. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Li, X.; Zhu, X.; Li, J.; Guo, S. Spatial Downscaling of Sea Surface Temperature Using Diffusion Model. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esser, P.; Rombach, R.; Blattmann, A.; Ommer, B. ImageBART: Bidirectional Context with Multinomial Diffusion for Autoregressive Image Synthesis. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 3518–3532. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Sun, H.; Tang, T.; Sun, Y.; He, Q.; Lei, L.; Ji, K. Leveraging Visual Language Model and Generative Diffusion Model for Zero-Shot SAR Target Recognition. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.A.; Wang, G.; Gao, K.; Li, H. A Gated Convolution and Self-Attention-Based Pyramid Image Inpainting Network. J. Circuits Syst. Comput. 2022, 31, 2250208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Isola, P.; Efros, A.A.; Shechtman, E.; Wang, O. The Unreasonable Effectiveness of Deep Features as a Perceptual Metric. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 586–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Name | Configure |
|---|---|
| CPU | Intel(R) Core (TM) i9-10850K CPU @ 3.60 GHZ (Intel Corporation, Santa Clara, CA, USA) |
| GPU | Nvidia GeForce RTX 3090 (Nvidia Corporation, Santa Clara, CA, USA) |
| Operating system | Ubuntu 20.04.6 LTS |
| CUDA | 10.1 |
| CUDNN | 8.0.5 |
| Python | 3.7.6 |
| Learning Rate | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 × | 1 × | 1 × | 1 × | |
| PSNR | 14.962 | 24.505 | 28.812 | 26.641 |
| LPIPS | 0.425 | 0.165 | 0.116 | 0.148 |
| Batch Size | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 16 | 32 | 64 | 128 | 256 | 512 | |
| PSNR | 24.861 | 26.966 | 25.977 | 28.812 | 25.782 | 27.661 |
| LPIPS | 0.150 | 0.135 | 0.142 | 0.116 | 0.159 | 0.132 |
| Model | Params (M) | Mask Settings | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fish | Thin | Thick | Half | ||||||
| PSNR↑ | LPIPS↓ | PSNR↑ | LPIPS↓ | PSNR↑ | LPIPS↓ | PSNR↑ | LPIPS↓ | ||
| Guided diffusion model | 932.08 | 28.461 | 0.121 | 36.137 | 0.070 | 33.879 | 0.087 | 24.775 | 0.192 |
| + DSC | 486.86 | 28.617 | 0.119 | 36.138 | 0.071 | 33.832 | 0.089 | 24.571 | 0.199 |
| + MCA | 899.74 | 29.342 | 0.112 | 36.109 | 0.069 | 33.984 | 0.084 | 24.573 | 0.194 |
| Our architecture | 454.53 | 28.812 | 0.116 | 36.154 | 0.068 | 33.965 | 0.084 | 24.761 | 0.192 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Jiang, X.; Chen, C.; Li, Y. Lightweight Multi-Scales Feature Diffusion for Image Inpainting Towards Underwater Fish Monitoring. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 2178. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12122178
Wang Z, Jiang X, Chen C, Li Y. Lightweight Multi-Scales Feature Diffusion for Image Inpainting Towards Underwater Fish Monitoring. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2024; 12(12):2178. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12122178
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zhuowei, Xiaoqi Jiang, Chong Chen, and Yanxi Li. 2024. "Lightweight Multi-Scales Feature Diffusion for Image Inpainting Towards Underwater Fish Monitoring" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 12, no. 12: 2178. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12122178
APA StyleWang, Z., Jiang, X., Chen, C., & Li, Y. (2024). Lightweight Multi-Scales Feature Diffusion for Image Inpainting Towards Underwater Fish Monitoring. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 12(12), 2178. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12122178






