High-Resolution 3D Geological Modeling of Three-Phase Zone Coexisting Hydrate, Gas, and Brine
Abstract
:1. Introduction
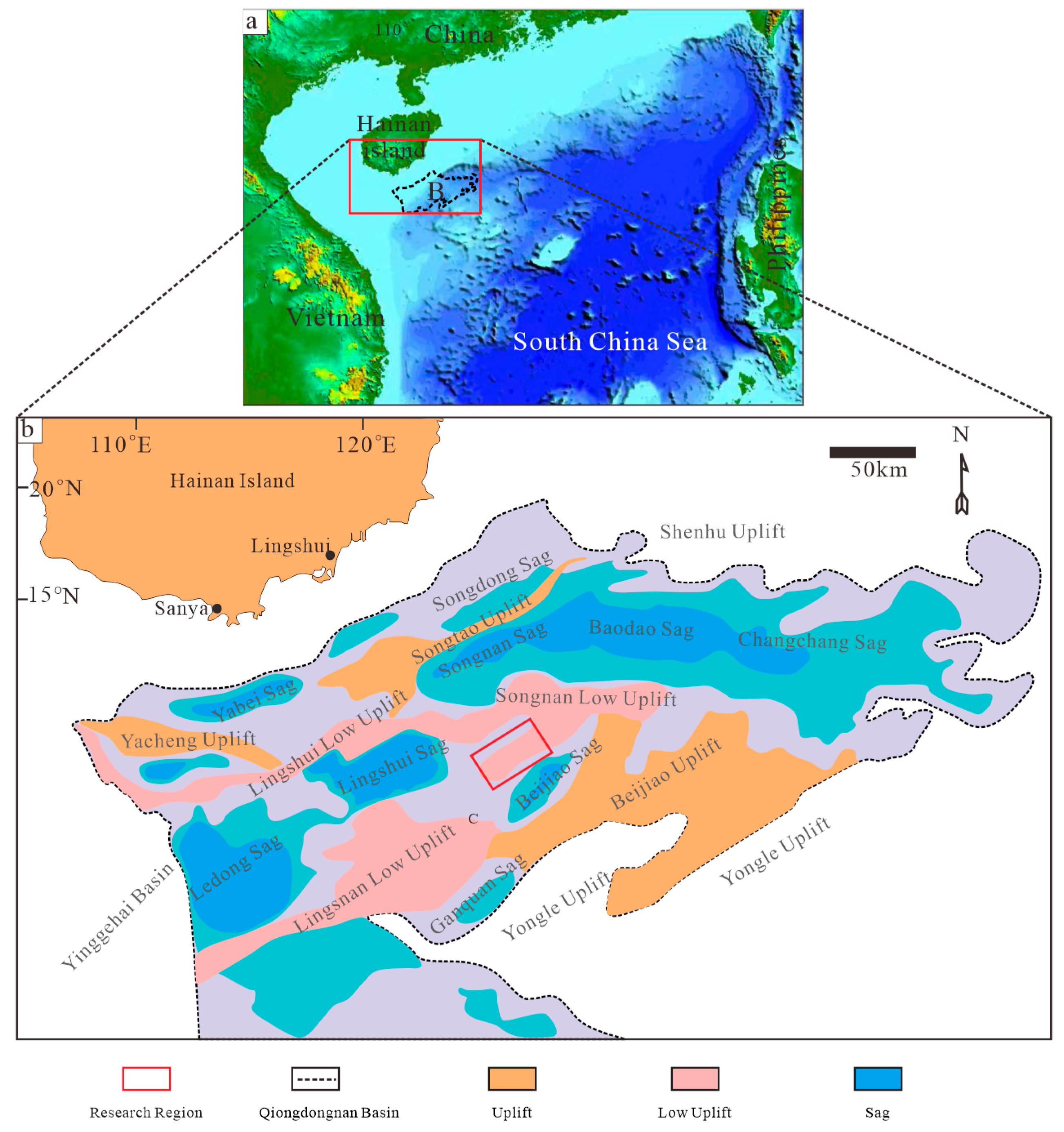
2. Geological Setting
2.1. Geologic Background
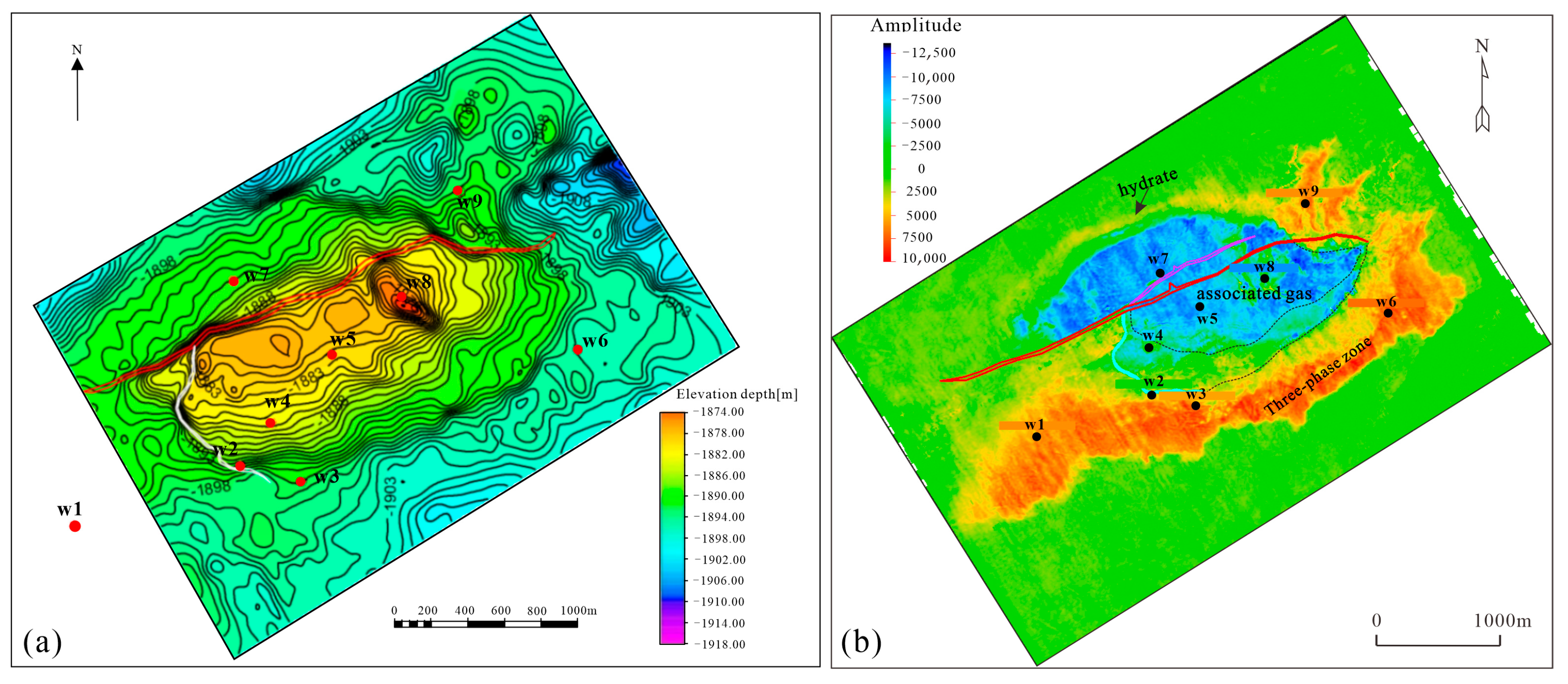
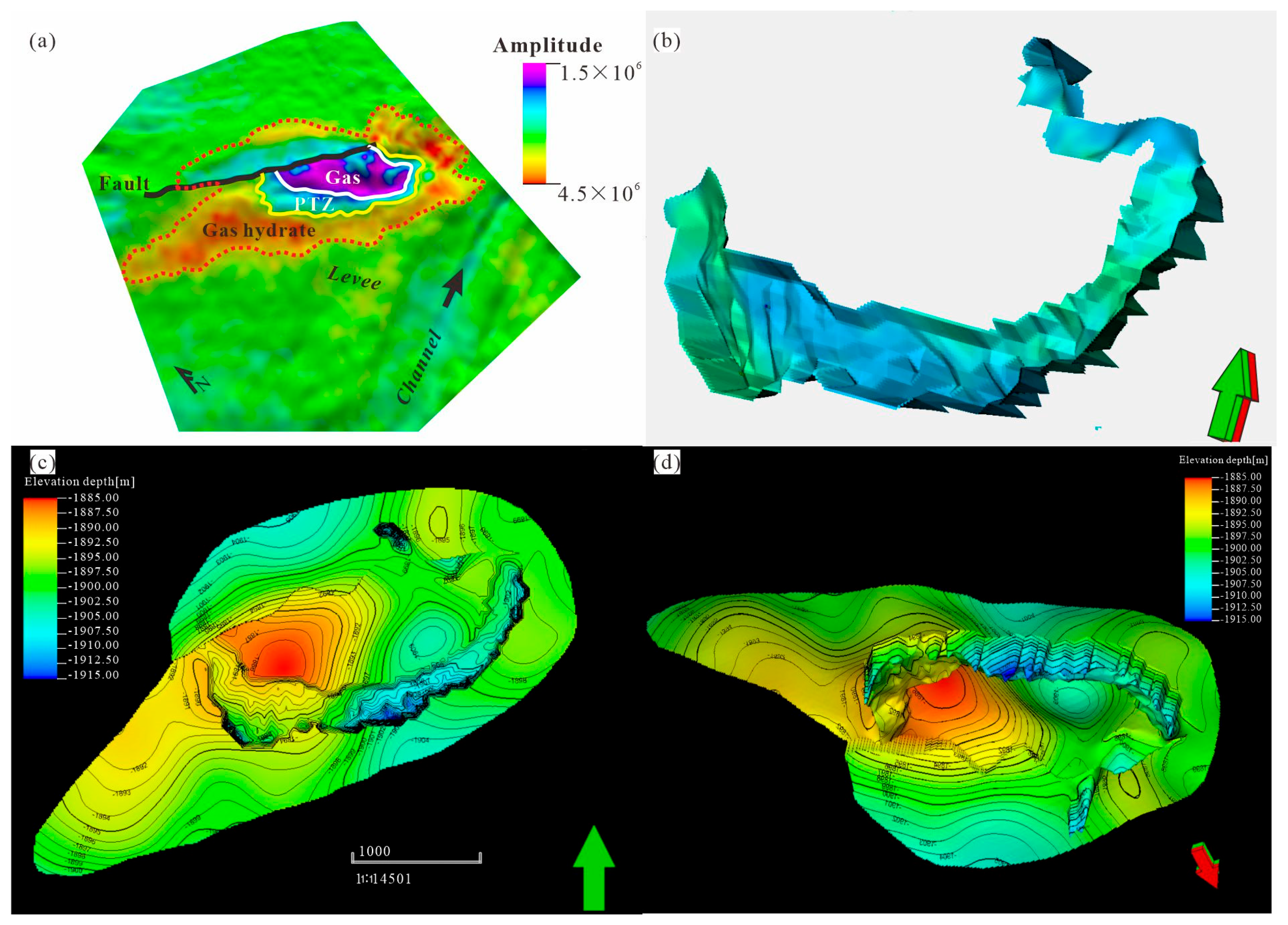
2.2. Distribution of Three-Phase Coexistence Zone
3. Material and Methods
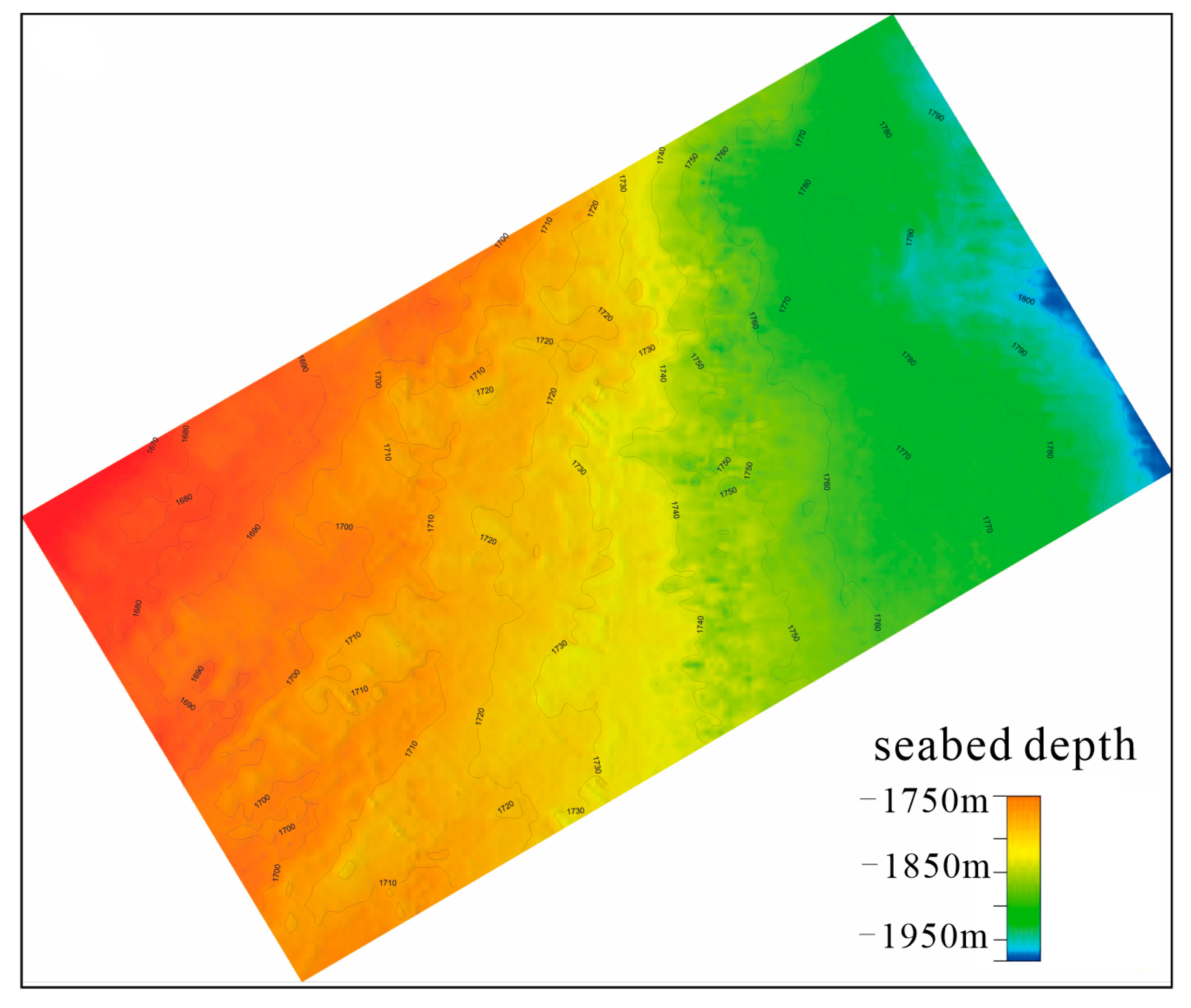
3.1. Data
3.2. Method
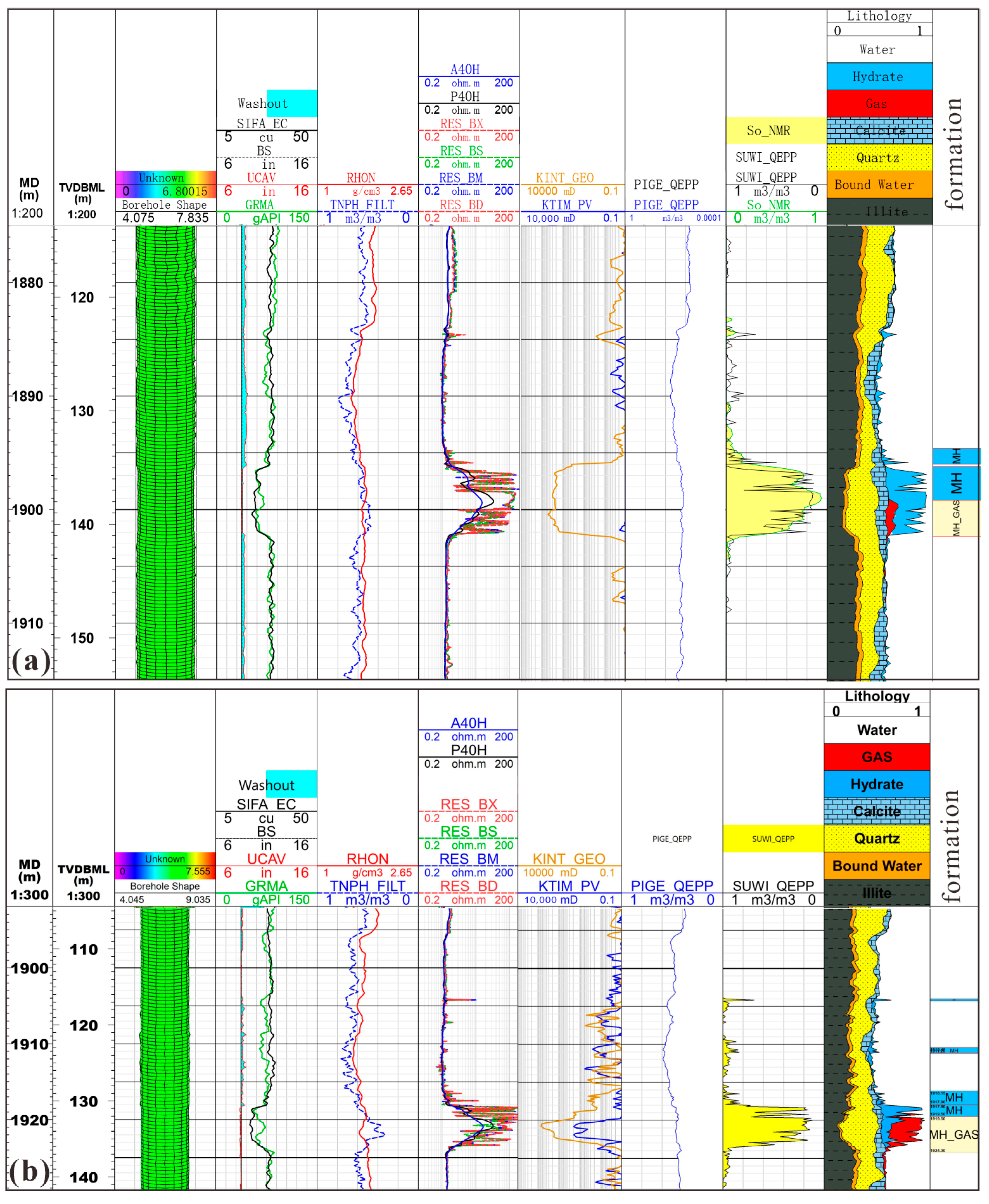
3.2.1. Logging Interpretation
3.2.2. Seismic Interpretation and Inversion
3.2.3. Geologic Modeling
- (1)
- The logging data from wells W1 to W9 have been subjected to correction processes. A band-pass filtering technique has been applied to reduce errors in the logging data, followed by environmental corrections. In sections lacking a density curve, a phase-controlled density prediction method has been utilized to estimate the density curve for subsequent calibration with seismic data [36].
- (2)
- A deep time conversion of the logging data has been executed, wherein non-equidistant logging data in the time domain have been interpolated to generate an equidistant curve. Following this resampling, a time sampling reflection coefficient sequence that corresponds with the seismic data has been derived.
- (3)
- A sand body distribution model has been developed through geostatistical methods, integrating lithological data derived from well information and seismic inversion.
- (4)
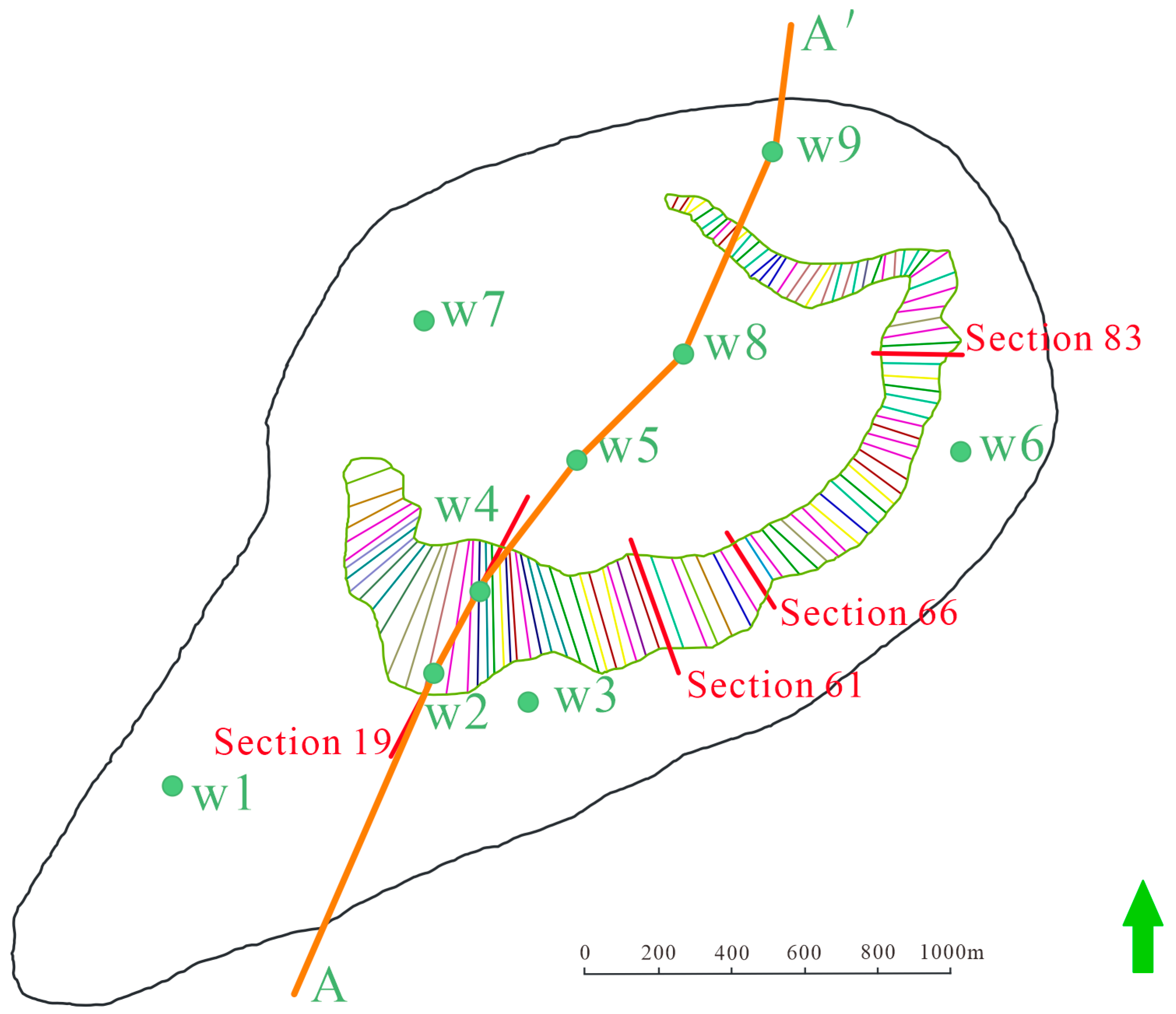
- The morphological plane model of the three-phase coexistence zone has been established within the study area. Section interpretation has been employed to mitigate the influence of intricate geological conditions on model accuracy. A total of 105 sections have been examined throughout the three-phase zone, leading to the development of porosity and saturation models for hydrate and free gas.
4. Results
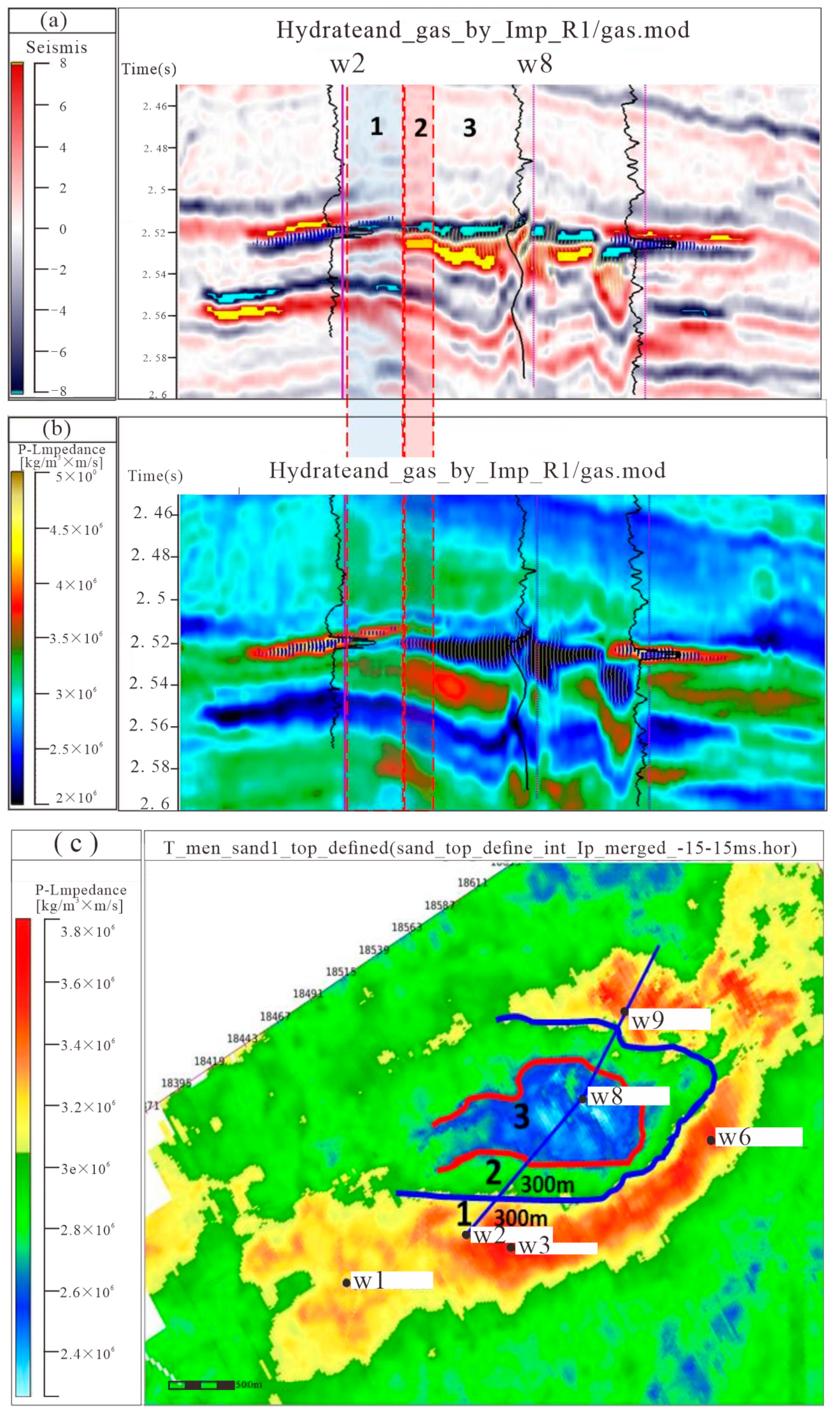
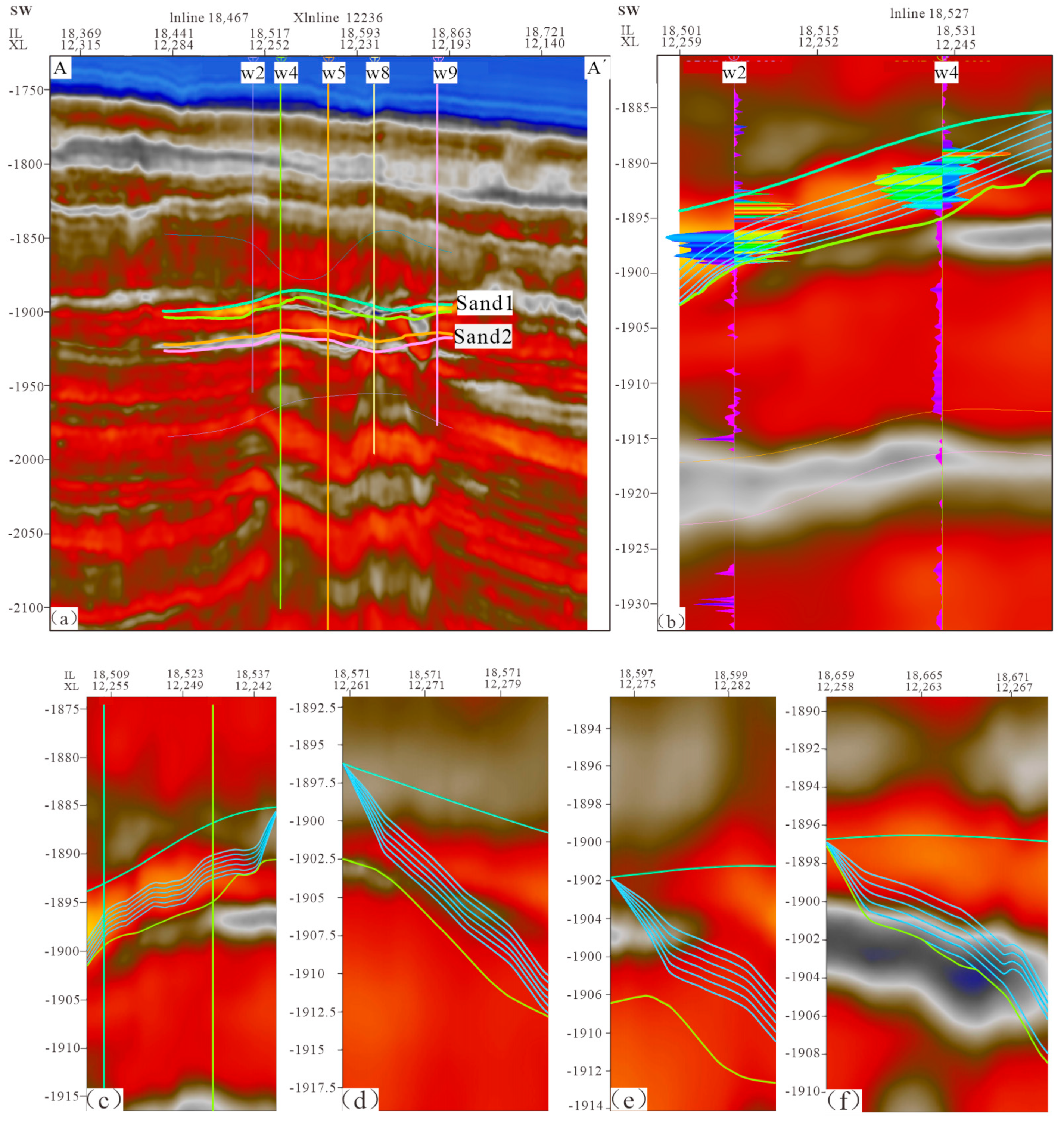
4.1. Well-Seismic Interpretation and Calibration of Three-Phase Coexistence Zone
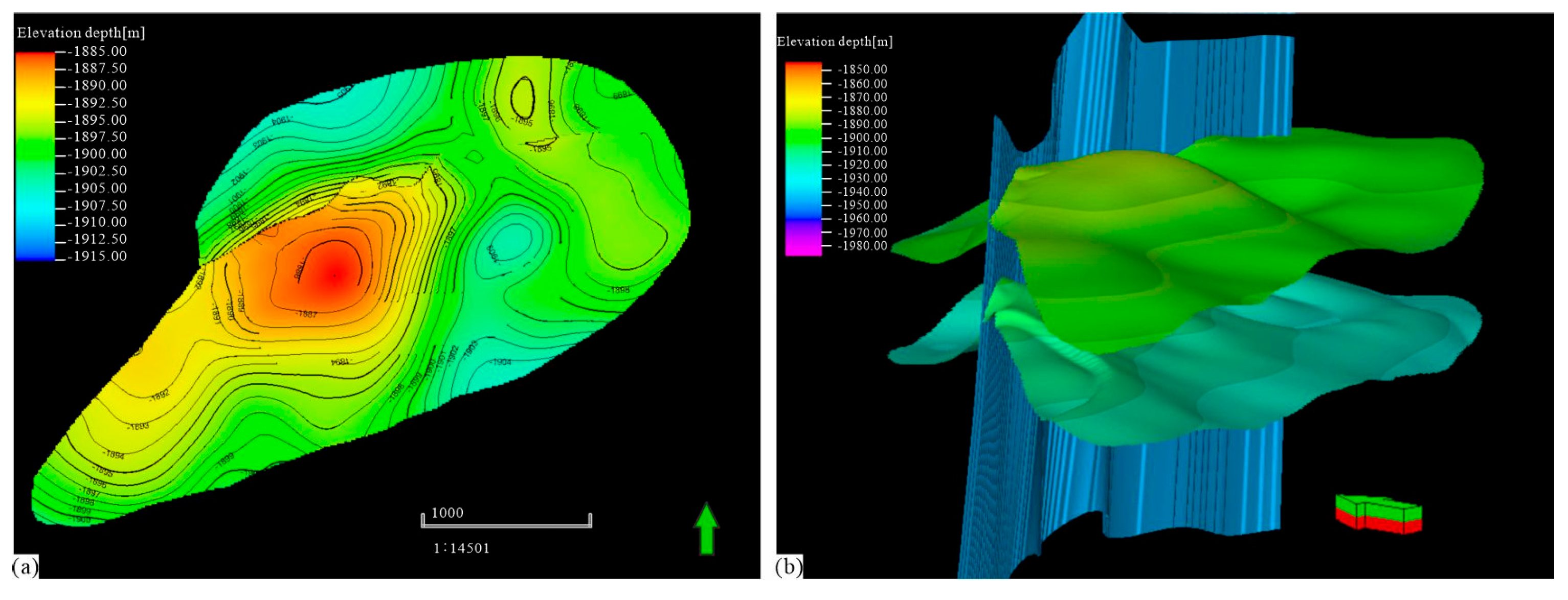
4.2. Structure Model
4.3. Fine Interpretation
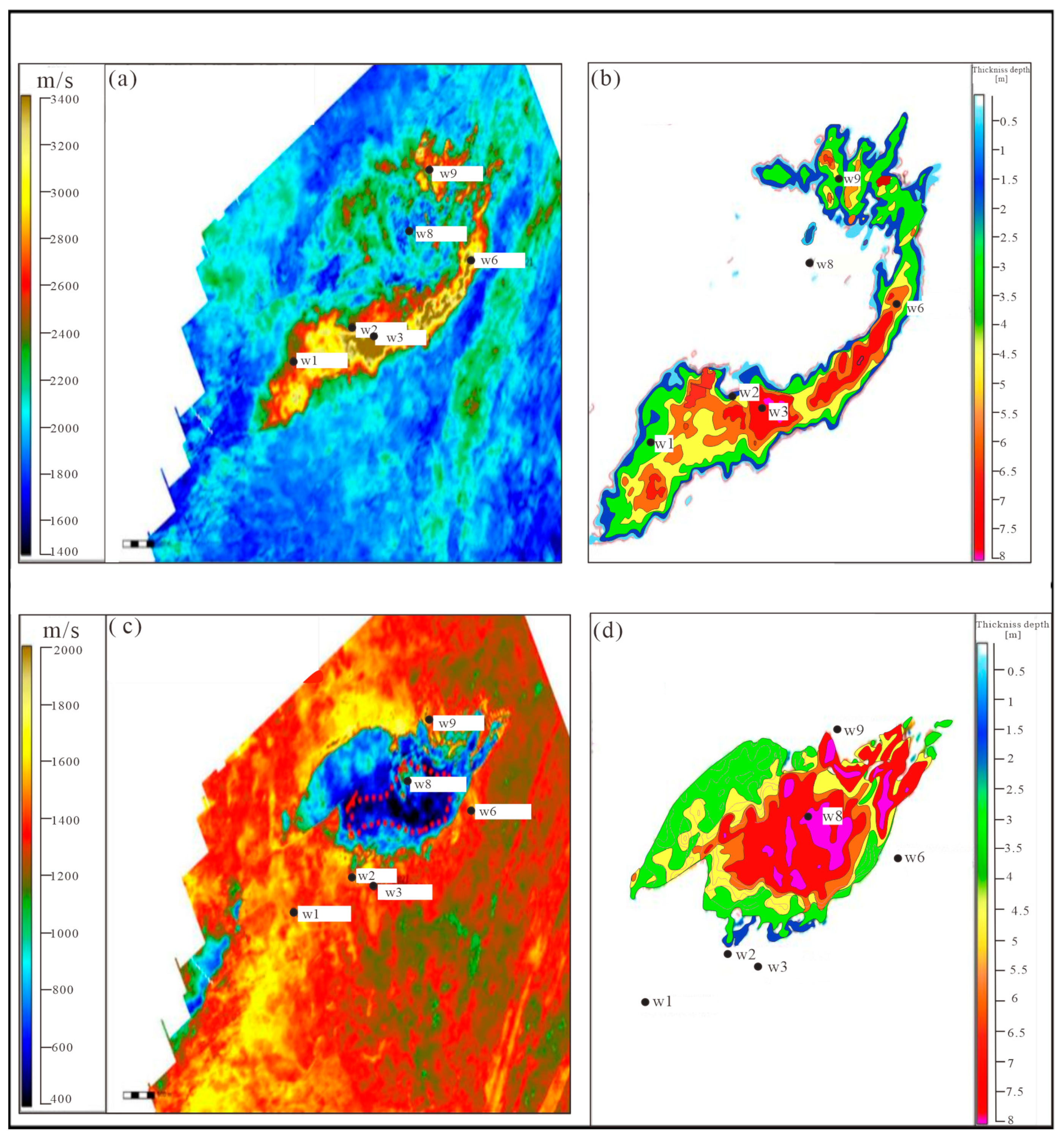
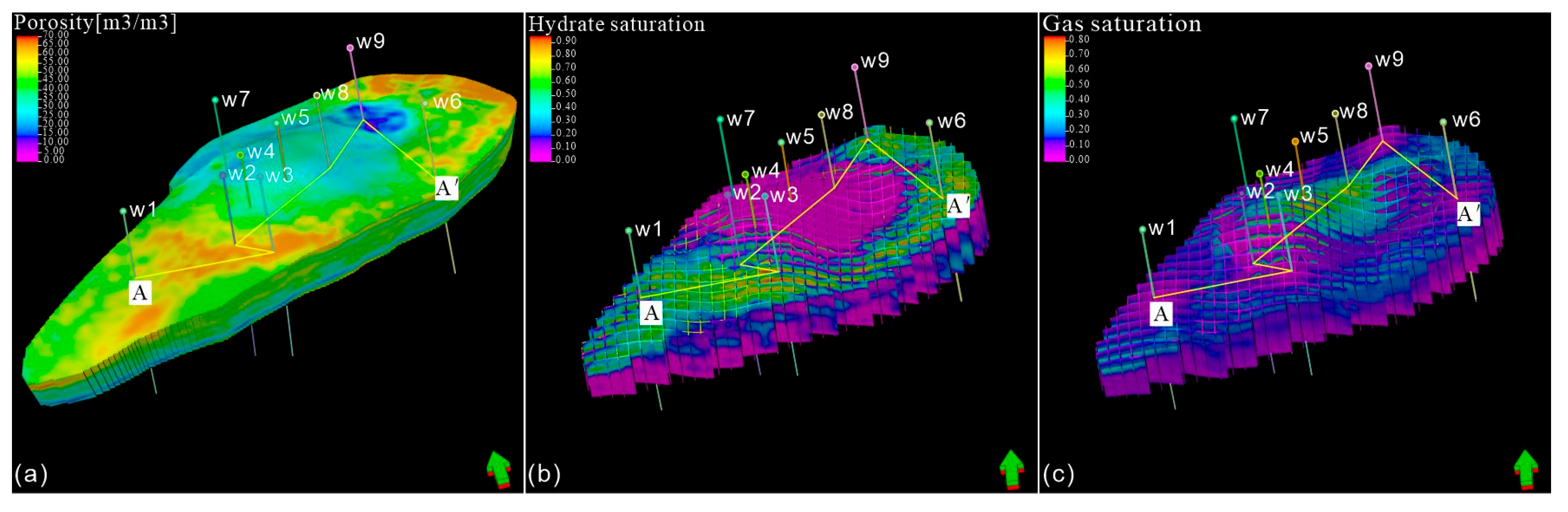
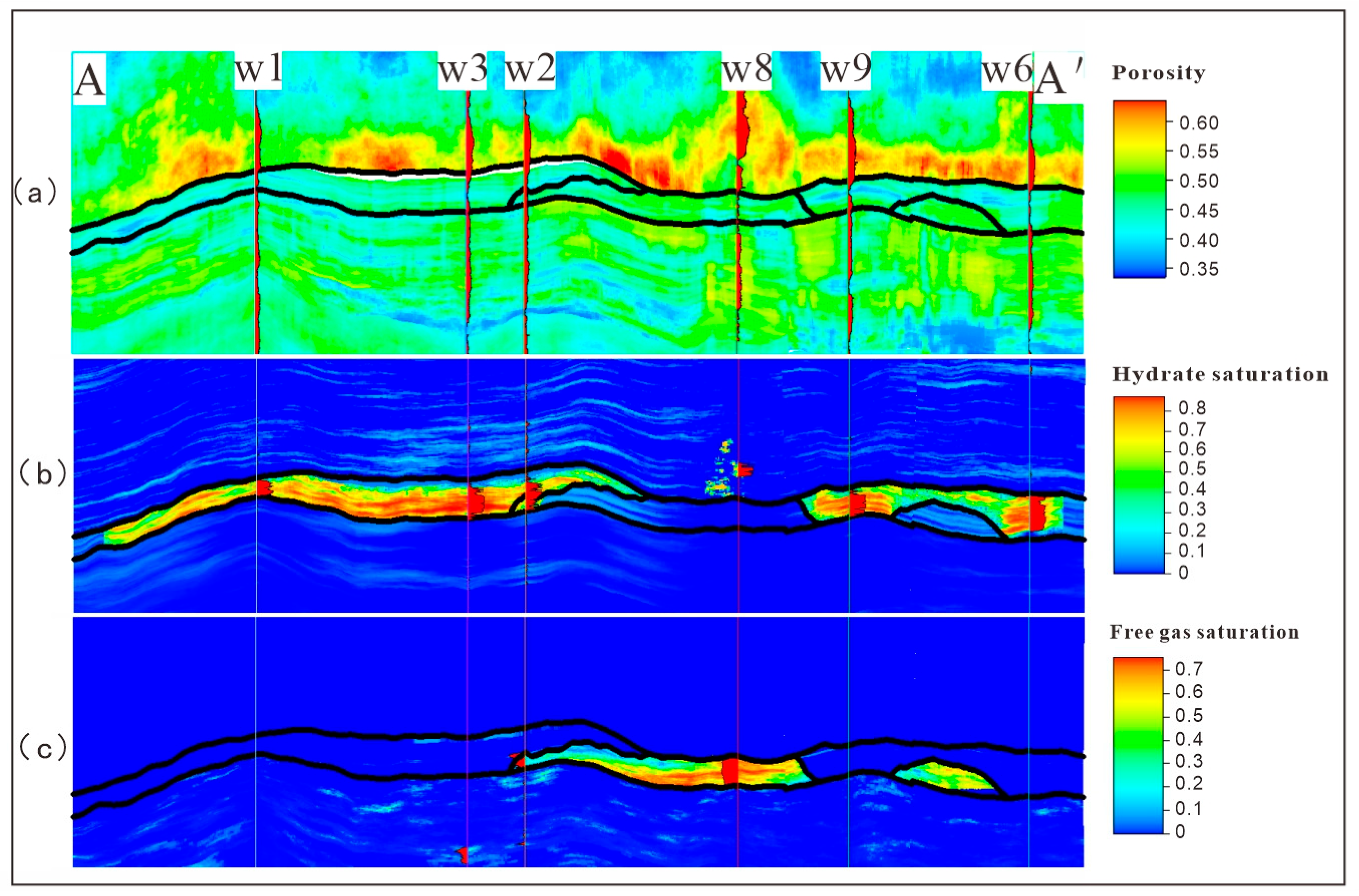
4.4. Attribute Model
5. Discussion
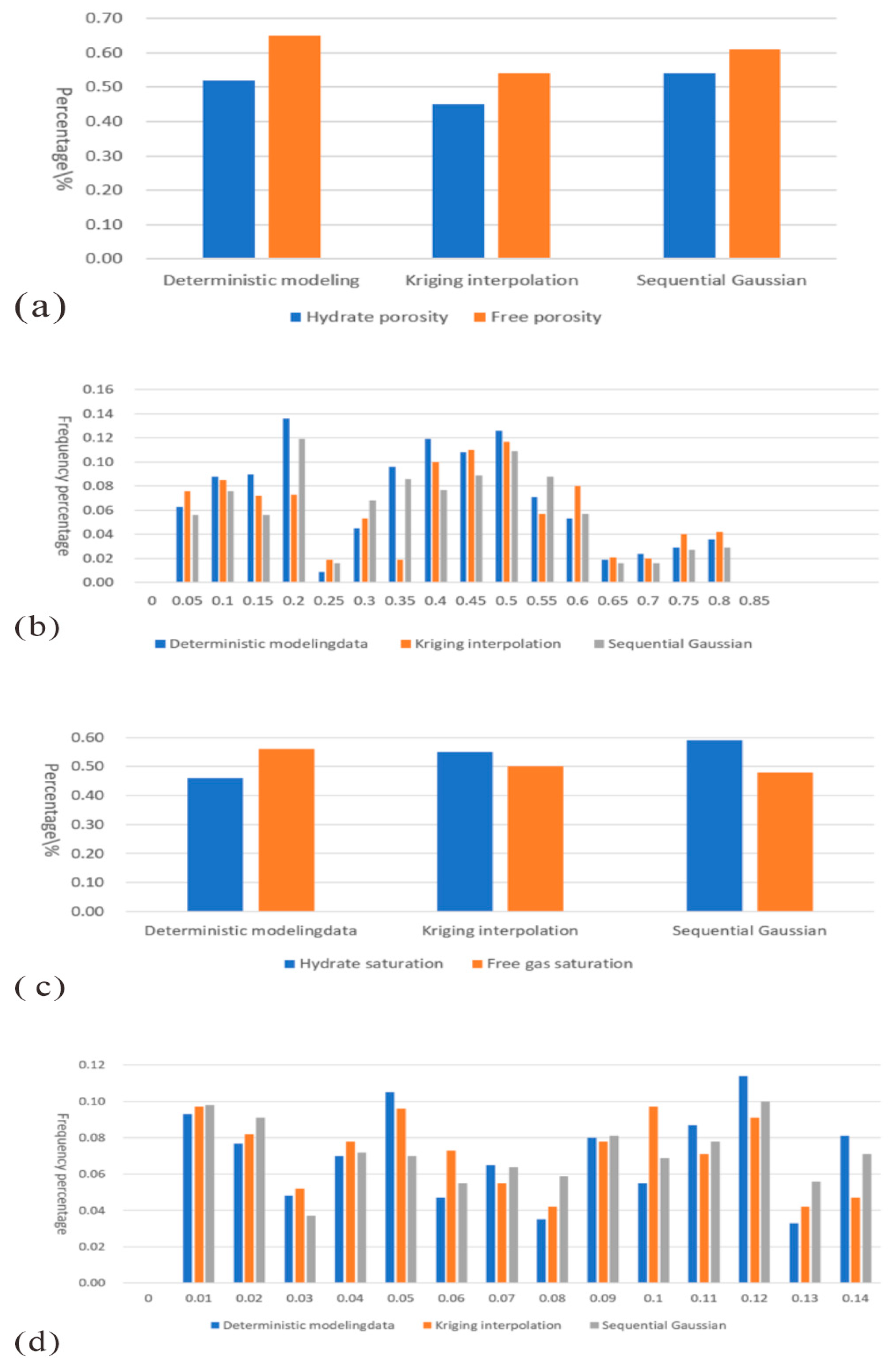
5.1. Error Analysis
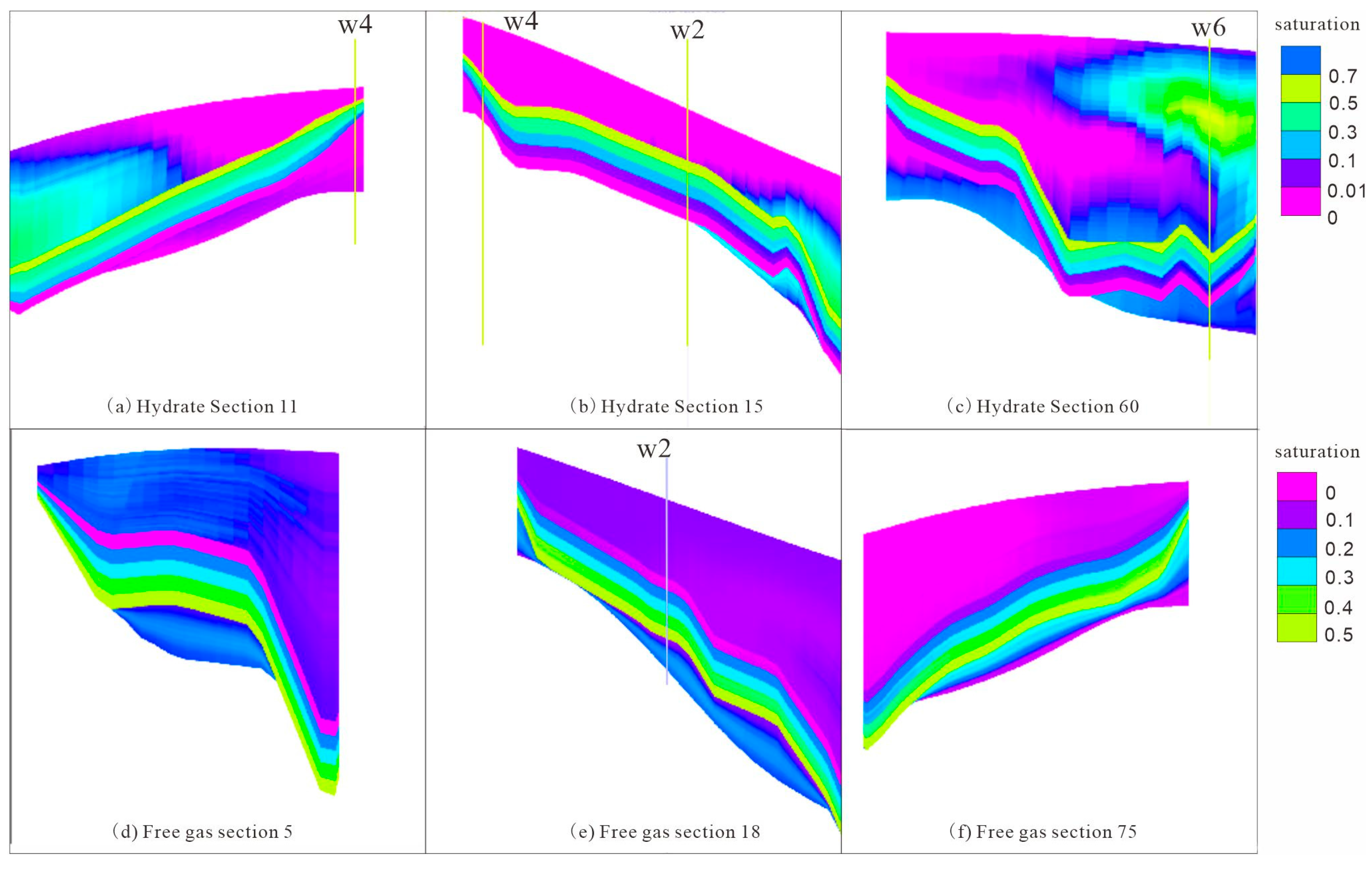
5.1.1. Verification of Distribution Patterns
5.1.2. Verification of Spatial Distribution of Parameters
5.2. Geological Implications
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ye, J.-L.; Qin, X.-W.; Xie, W.-W.; Lu, H.-L.; Ma, B.-J.; Qiu, H.-J.; Liang, J.-Q.; Lu, J.-A.; Kuang, Z.-G.; Lu, C.; et al. The second natural gas hydrate production test in the South China Sea. China Geol. 2020, 3, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Yu, X.; Liang, J.; Kuang, Z.; Wang, J. Geological modeling and favorable area prediction of natural gas hydrate in Shenhu sea area. Mar. Geol. Quat. Geol. 2014, 34, 117–126. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.-F.; Ye, J.-L.; Qin, X.-W.; Qiu, H.-J.; Wu, N.-Y.; Lu, H.-L.; Xie, W.-W.; Lu, J.-A.; Peng, F.; Xu, Z.-Q.; et al. The first offshore natural gas hydrate production test in South China Sea. China Geol. 2018, 1, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Liang, J.; Lu, J.; Qu, C.; Liu, B. New understanding of gas hydrate accumulation characteristics and main controlling factors in Shenhu area, northern South China Sea. Geol. Front. 2017, 24, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Liang, J.; Wang, H.; Su, X.; Song, H.; Jiang, S.; Zhu, Y.; LU, Z. Research progress of marine gas hydrate accumulation system. Mod. Geol. 2008, 3, 356–362. [Google Scholar]
- Dale, A.; Van Cappellen, P.; Aguilera, D.; Regnier, P. Methane efflux from marine sediments in passive and active margins: Estimations from bioenergetic reaction–transport simulations. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2008, 265, 329–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Sha, Z.; Meng, M.; Wang, X.; Xu, M.; Fang, Y. Characteristics and distribution of high saturation natural gas hydrate reservoirs in the Shenhu Sea. Geol. J. 2024, 98, 2641–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wu, S.; Liu, X.; Yang, S.; Guo, Y.; Li, Q. Estimation of Natural Gas Hydrate Resources in Shenhu Sea Area Based on Logging and Seismic Data. Adv. Geophys. 2010, 25, 1288–1297. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, J.; Wang, J.; Yang, C.; Kang, D.; Lu, J.; Liang, J. Geophysical characteristics of gas hydrate-bearing sediments in the eastern Pearl River Mouth Basin. Gas Ind. 2017, 37, 126–133. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, K.; Zheng, Y. Imulation and Comparison of Seismic Wave Fields in Natural Gas HydrateFormations. Adv. Mar. Sci. 2021, 39, 290–303. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Yin, X.; Luan, X. Seismic rock physical modelling for gas hydrate-bearing sediments. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2018, 61, 1261–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Cheng, B.; Wang, T.-G.; Simoneit, B.R.; Shi, S.; Wang, P. Monoterpanes as molecular indicators to diagnose depositional environments for source rocks of crude oils and condensates. Org. Geochem. 2014, 72, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, M.; Siddiqui, N.A.; Umar, M.; Usman, M.; Ahmed, N.; Rahman, A.H.A.; Zaidi, F.K. Aseismic and seismic impact on development of soft-sediment deformation structures in deep-marine sand-shaly Crocker fan in Sabah, NW Borneo. J. King Saud Univ.-Sci. 2021, 33, 101522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, M.; Siddiqui, N.A.; Ahmed, N.; Usman, M.; Umar, M.; Rahim, H.U.; Imran, Q.S. Facies Analysis and Sedimentary Architecture of Hybrid Event Beds in Submarine Lobes: Insights from the Crocker Fan, NW Borneo, Malaysia. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argentino, C.; Conti, S.; Fioroni, C.; Fontana, D. Evidences for Paleo-Gas Hydrate Occurrence: What We Can Infer for the Miocene of the Northern Apennines (Italy). Geosciences 2019, 9, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamaki, M.; Suzuki, K.; Fujii, T.; Sato, A. Prediction and validation of gas hydrate saturation distribution in the eastern Nankai Trough, Japan: Geostatistical approach integrating well-log and 3D seismic data. Interpretation 2016, 4, SA83–SA94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, Z.; Cook, A.; Ren, J.; Deng, W.; Cao, Y.; Cai, H. A Flat-Lying Transitional Free Gas to Gas Hydrate System in a Sand Layer in the Qiongdongnan Basin of the South China Sea. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2023, 50, e2023GL105744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, X.; Collett, T.S.; Li, S.; Kuang, Z.; Lu, Y.; Deng, W.; Yan, W.; Qian, J.; Jin, J. Characterization of a complex sand-rich gas hydrate reservoir system in the Indian marine continental margin with downhole log and seismic data. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2023, 155, 106370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerin, G.; Goldberg, D.; Meltser, A. Characterization of in situ elastic properties of gas hydrate-bearing sediments on the Blake Ridge. J. Geophys. Res. 1999, 104, 17781–17795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milkov, A.V.; Dickens, G.R.; Claypool, G.E.; Lee, Y.J.; Borowski, W.S.; Torres, M.E.; Xu, W.; Tomaru, H.; Tréhu, A.M.; Schultheiss, P. Co-existence of gas hydrate, free gas, and brine within the regional gas hydrate stability zone at Hydrate Ridge (Oregon margin): Evidence from prolonged degassing of a pressurized core. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2004, 222, 829–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paganoni, M.; Cartwright, J.A.; Foschi, M.; Shipp, R.C.; Van Rensbergen, P. Structure II gas hydrates found below the bottom-simulating reflector. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 5696–5706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecher, I.A.; Barnes, P.M.; Leah, I. International Ocean Discovery Program Expedition 372 Preliminary Report Creeping Gas Hydrate Slides and Hikurangi Lwd Disclaimer; Texan A&M University: College Station, TX, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, N.; Bohrmann, G.; Ruffine, L.; Pape, T.; Riboulot, V.; Colliat, J.; De Prunelé, A.; Dennielou, B.; Garziglia, S.; Himmler, T.; et al. Pockmark formation and evolution in deep water Nigeria: Rapid hydrate growth versus slow hydrate dissolution. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2014, 119, 2679–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.-W.; Survey, M.O.N.R.C.G.; Lu, J.-A.; Lu, H.-L.; Qiu, H.-J.; Liang, J.-Q.; Kang, D.-J.; Zhan, L.-S.; Lu, H.-F.; Kuang, Z.-G.; et al. Coexistence of natural gas hydrate, free gas and water in the gas hydrate system in the Shenhu Area, South China Sea. China Geol. 2020, 3, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Fan, X.; Yu, X.; Zhao, C.; He, Y.; Liang, J.; Su, P. Hierarchical modeling method and favorable zone prediction of hydrate reservoirs in Shenhu waters in continental slope of northern South China Sea. China Offshore Oil Gas 2019, 31, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, P.; He, J.; Liang, J.; Zhang, W. Natural gas hydrate migration and accumulation system and its controlling factors on northern deep water slope of the south China Sea. Mar. Geol. Front. 2017, 33, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Lei, X.; Zhang, X.; Sha, Z. Gas hydrate and associated free gas in the Dongsha Area of northern South China Sea. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2013, 39, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Lei, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, G. Heat flow derived from BSR and its implications for gas hydrate stability zone in Shenhu Area of northern South China Sea. Mar. Geophys. Res. 2012, 33, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Hutchinson, D.R.; Wu, S.; Yang, S.; Guo, Y. Elevated gas hydrate saturation within silt and silty clay sediments in the Shenhu area, South China Sea. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, B05102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Xiao, X.; Li, X. Geochemistry and origins of natural gases in the Yinggehai and Qiongdongnan basins, offshore South China Sea. Org. Geochem. 2003, 34, 1009–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Su, X.; Chen, F.; Li, Y. Primary discussion on accumulation conditions for sedimentation of gas hydrate and its distribution in south China sea. Earth Sci. Front. 2004, 11, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, M.; Liang, J.; Kuang, Z.; Ren, J.; He, Y.; Deng, W.; Gong, Y. Distribution characteristics of quaternary channel systems and their controlling factors in the Qiongdongnan Basin, South China Sea. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 902517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Z.; Jiang, J. Characteristics and Formation Mechanism of Faults in Qiongdongnan Basin. Mar. Geol. Quat. Geol. 2007, 27, 71–78. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, J.; Zhao, X.; Fan, Q.; Fang, X.; Song, P.; Xiang, Z. Preliminary study on depositional and reservoir characteristics of high-saturation gas hydrate worldwide. Mar. Geol. Front. 2023, 39, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Wang, J.; Liang, J.; Li, S.; Zeng, X.; Li, W. Depositional characteristics and accumulation model of gas hydrates in northern South China Sea. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2014, 56, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, M.; Carvajal, C.; Rodrigues, J.; Torres, A.; Aldana, M.; Sierra, J. Petrophysical seismic inversion conditioned to well-log data: Methods and application to a gas reservoir. Geophysics 2009, 74, O1–O15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, Y.; Siddiqui, N.A.; Morib, D.L.; Babasafari, A.A.; Ali, S.H.; Imran, Q.S.; Karaman, A. Cohesive approach for determining porosity and P-impedance in carbonate rocks using seismic attributes and inversion analysis. J. Pet. Explor. Prod. Technol. 2024, 14, 1173–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Gao, Y.; Hu, Z.; Xiong, T.; Feng, W.; Zhao, J.; Cheng, L. Multiple-point geostatistical simulation of outcrop based on UAV oblique photographic data: A case study of Shihezi Formation in Pingtou township, Lvliang city, Shanxi. Acta Pet. Sin. 2021, 42, 198–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, H.; Wang, J.; Deng, W.; Kuang, Z.; Li, T.; Lei, Z. High-Resolution 3D Geological Modeling of Three-Phase Zone Coexisting Hydrate, Gas, and Brine. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 2171. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12122171
Yu H, Wang J, Deng W, Kuang Z, Li T, Lei Z. High-Resolution 3D Geological Modeling of Three-Phase Zone Coexisting Hydrate, Gas, and Brine. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2024; 12(12):2171. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12122171
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Han, Ju Wang, Wei Deng, Zenggui Kuang, Tingwei Li, and Zhangshu Lei. 2024. "High-Resolution 3D Geological Modeling of Three-Phase Zone Coexisting Hydrate, Gas, and Brine" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 12, no. 12: 2171. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12122171
APA StyleYu, H., Wang, J., Deng, W., Kuang, Z., Li, T., & Lei, Z. (2024). High-Resolution 3D Geological Modeling of Three-Phase Zone Coexisting Hydrate, Gas, and Brine. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 12(12), 2171. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12122171





