Abstract
Ship biofouling is recognized as a significant pathway for the introduction and spread of invasive organisms. The in-water cleaning of ship hulls generates wastewater that includes antifouling paint residues and biofouling organisms, which inevitably leak into the marine environments, resulting in substantial adverse effects on marine ecosystems. To assess the impact of hull cleaning wastewater (HCW) on microalgae, we conducted microcosm experiments using HCW including attached microalgae. The experiments consisted of a total of 12 combined trials, including the following groups: ambient seawater as a control, the 5% HCW group (HCW), and the 5% HCW + nutrient addition group (HCW+N), conducted at temperatures of 15 and 20 °C, respectively. The Chl. a concentrations in the water column in the control group exhibited maximum values on day 1 (5.24 μg L−1 at 15 °C and 12.37 μg L−1 at 20 °C), but those of the treatments were at low levels, below 2 μg L−1 at both temperatures. On the other hand, the Chl. a concentrations on plastic plates were higher in the treatments than in the control group. Specifically, the Fv/Fm ratio in the water column, which indicates photosynthetic activity, was significantly higher in the control group compared to both the HCW and HCW+N groups at 15 and 20 °C (p < 0.05). This suggests that the growth of water column phytoplankton was inhibited following HCW inoculation. However, there were no significant differences in the Fv/Fm on plastic plates between the control and HCW treatment groups, implying that the periphyton maintained a high photosynthetic capacity even in the presence of HCW treatments. The elution of particulate copper in HCW was observed, which was considered as the main reason for the growth of phytoplankton. Our study results suggest that the runoff of HCW in the marine environment has a greater negative effect on phytoplankton than on periphyton, which can lead to changes in microalgae community composition and a decrease in productivity in the marine environment. Therefore, it is crucial to manage HCW runoff based on scientific assessments to minimize the ecological risks associated with the removal of biofilm or slime from ship biofouling during in-water hull cleaning.
1. Introduction
In aquatic ecosystems, the discharge of ballast water and the transportation of biofouling by international ships have been identified as major pathways for the introduction and spread of marine invasive species [1,2,3]. Consequently, there has been increasing pressure to impose stricter regulations on international shipping concerning the release of pollutants, including unwanted marine organisms, into the water. One such effort is led by the International Maritime Organization (IMO), which aims to minimize the transfer of invasive aquatic species through ships’ ballast water and sediments (BWM Convention). As a result, the International Ballast Waters Management Convention, officially known as “the International Convention for the Control and Management of Ships’ Ballast Water and Sediments”, was recently enacted (IMO, 2017). However, in the context of ship biofouling, management measures are still lacking (IMO, 2012). Fortunately, the biofouling guidelines established by the GloFouling Partnerships Project are a positive step in the broader initiatives taken by the IMO. These guidelines provide valuable recommendations on general measures to mitigate the risks associated with biofouling for all types of ships. They are directed at various stakeholders, including ship cleaning and maintenance operators, independent inspection organizations, ship repair, dry-docking and recycling facilities, and other relevant parties [4,5,6]. Therefore, the IMO Guidelines for the control and management of biofouling play an important role in reducing the spread of invasive species in marine ecosystems.
Marine biofouling organisms settle and grow on the immersed surfaces of ships or underwater structures, and form communities in various biogenic habitats [7]. This colonization process is particularly intense in coastal or shallow waters, as it is influenced by environmental factors such as temperature, salinity, and nutrient levels [1,8,9]. Biofouling typically occurs when a ship’s hull is submerged in water [1,10]. When organisms attach themselves to the ship’s hull, they increase frictional resistance on the immersed surface, resulting in reduced ship speed. Consequently, maintaining a certain speed requires higher fuel consumption, leading to the increased release of carbon dioxide and pollutants into the atmosphere [11,12]. These various biological, economic, and environmental threats induced by biofouling raise the need for regulation.
Recently, in-water hull cleaning, such as via the use of remote operated vehicles (ROVs) and scuba divers, has been applied as a method to overcome the cost and time limitations of the traditional dry-docking hull cleaning method [13]. The in-water hull cleaning process generates paint particles, including heavy metals and booster biocides applied to prevent biofouling, as well as attached organisms, as by-products [14]. In particular, in-water hull cleaning inevitably results in the leakage of the in-water hull cleaning wastewater (HCW) into the marine environment, requiring biological risk assessment and management of HCW. In particular, microalgae, which are small but important primary producers in the marine ecosystem, within HCW are more difficult to collect during the in-water hull cleaning process due to their size. Prior to implementing regulations and effective management strategies for ship hull biofouling, it is crucial to gather comprehensive scientific data and assess the potential risks of seawater contamination associated with in-water hull cleaning methods. To achieve this, the biofouling guidelines established by the GloFouling Partnerships Project provide valuable insights. One key tool utilized in these guidelines is the Infection Modes and Effects Analysis (IMEA), which assesses and ranks various sub-components of vessels based on their environmental suitability, the occurrence of marine organisms, and the likelihood of detection [15,16]. By conducting IMEA assessments for each ship, valuable information is obtained regarding the presence and abundance of marine organisms, measured through wet biomass analysis.
In response to the global issue, our study aims to provide scientific evidence related to the regulation and management of HCW by investigating the effects of HCW leakage on microalgae communities in the water. Specifically, we focused on the biological risk assessment and evaluated the potential regrowth ability of attached microalgae in seawater environments following in-water hull cleaning. The objectives of our study were threefold: (1) to assess the succession process of attached microalgae and the time-series attachment of detached microalgae after in-water cleaning; (2) to investigate the time-dependent concentration changes of biocides in HCW and their effects on microalgae; and (3) to determine the response of attached microalgal communities to temperature and nutrient conditions. The findings from our study will provide valuable insights for the management of HCW runoff, with the aim of effectively and reliably removing biofouling organisms from ship hulls in coastal waters and international port systems.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Field Sampling
Hull in-water cleaning was conducted by scuba divers on an international commercial ship at Busan New International ports, Korea, from 29 to 30 August 2022. Ship-specific details and log notes related to hull cleaning were obtained. Biological and environmental factors were examined in shipside harbor water. Water temperature, salinity, pH, and dissolved oxygen conditions were measured using YSI EXO2 Sonde probes (Yellow Springs, OH, USA) around cleaning site. During the collection process, divers attached 0.5 × 0.5 m quadrats to the hull surface using magnets and cleaned the surface using a hard brush (Figure 1a). The hard brush cleaning tool was connected to a tube, and the HCW was pumped to the land through a suction pump along with ambient seawater. This cleaning process was repeated ten times at regular intervals, covering the entire ship from the bow to the stern (Figure 1a). As a result, we collected 180 L of HCW from international commercial ships, which contained paints and microorganisms. The HCW was gently mixed, divided into 20 L bottles, and transferred to the laboratory.
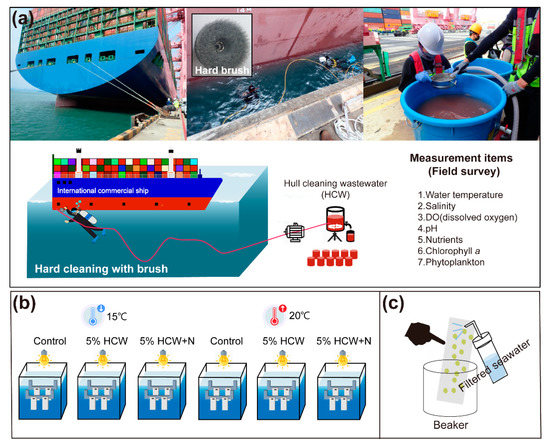
Figure 1.
Experimental design. Photos and schematic illustrating the procedure for in-water hull cleaning by a scuba diver using a hard brush, along with the collection of hull cleaning wastewater (HCW), and measurement items in-field (a). The top photos in (a) are, from left, the international commercial ship, in-water hull cleaning by divers, and HCW collection on land. Indoor microcosm experiments including the installation of plastic plates for the monitoring of attached and unattached microalgae, with three different experimental groups (control with ambient seawater around hull cleaning site, 5% HCW treatments, 5% HCW with nutrient addition treatment) under two temperature conditions (15 and 20 °C) (b). Schematic illustrating of sampling method for attached microalgae from plastic plates (c).
2.2. Microcosm Experiments
The microcosm experiments were conducted with three groups: (i) a control group with only ambient seawater around the in-water hull cleaning site; (ii) an HCW treatment group with 5% HCW (HCW); and (iii) a nutrient addition HCW treatment group with 5% HCW (HCW+N) (32 μM nitrate+nitrite, 2 μM phosphate, and 32 μM silicate were added on day 0). The experiments were performed in 10 L polypropylene (PP) boxes, and acrylic plastic plates (4 × 15 × 0.5 cm) were installed in each box to assess the potential for the reattachment of microalgae (Figure 1b,c). The experiments were carried out under two different temperature conditions (15 °C and 20 °C) with a 12 h light and 12 h dark photoperiod, providing a photon flux density of 250 μmol m−2 s−1. Environmental parameters, including temperature, salinity, pH, and dissolved oxygen (DO), were measured using YSI EXO2 Sonde probes (Yellow Springs, OH, USA). Water samples were collected using a 50 mL syringe and filtered through GF/F filters (diameter: 47 mm, pore size: 0.7 μm; Whatman, UK) for the analysis of dissolved inorganic nutrients (nitrate+nitrite, ammonia, phosphate, and silicate). To harvest the attached microalgae, two plastic plates from each PP box in each experimental group were sampled by cleaning with sterile filtered seawater (50 mL) while rubbing with sterilized nitrile gloves. Chlorophyll a (Chl. a) and Fv/Fm were measured using a PHYTO-PAM Phytoplankton Analyzer (Walz; PHYTO-ED, Effeltrich, Germany) for both phytoplankton in the water and periphyton on the plastic plates. The maximum quantum yield (Fv/Fm) was measured for each microcosm on days 1, 4, 7, 10, 14, and 22. Fv (variable fluorescence) was calculated as the difference between the fluorescence levels of Fo and Fm. Fo represents the minimum level of fluorescence emitted in the absence of photosynthetic light at open reaction centers, while Fm corresponds to the maximum fluorescence yield induced by a saturation light pulse at closed reaction centers of PSII.
For the community analysis of periphyton, a 30 mL sample from the plastic plate was filtered through a polycarbonate membrane filter (diameter: 47 mm, pore size: 0.22 µm; Isopore). Genomic DNA (gDNA) was then extracted from the filters using the DNeasy Plant Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) and quantified using Quant-IT PicoGreen (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA). To prepare a sequencing library, the V8 and V9 hypervariable regions of the 18S rRNA gene were amplified using Illumina Metagenomic Sequencing Library protocols. The input gDNA (2 ng) was PCR-amplified with 5× reaction buffer, 1 mM dNTP mix, and 500 nM each of the universal Illumina-tagged forward (V8f: 5′-ATAACAGGTCTGTGATGCCCT-3′) [17] and reverse (1510r: 5′-CCTTCYGCAGGTTCACCTAC-3′) [18] PCR primers, using Herculase II fusion DNA polymerase (Agilent Technologies, USA). The PCR cycle conditions were as follows: 30 s at 98 °C (initial denaturation); 32 cycles of 10 s at 95 °C, 30 s at 54 °C, and 45 s at 72 °C (amplification); and 10 min at 72 °C (final extension). The purified first PCR product was obtained using AMPure beads (Agencourt Bioscience, Beverly, MA, USA).
Following purification, 2 μL of the first PCR product was subjected to a second PCR amplification for final library construction using the NexteraXT Indexed Primer. The cycle conditions for the second PCR were the same as those for the first PCR, except that only 10 amplification cycles were performed. The second PCR product was purified using AMPure beads. The final purified product was quantified using qPCR following the qPCR Quantification Protocol Guide (KAPA Library Quantification kits for Illumina Sequencing Platforms) and assessed for quality using the TapeStation D1000 ScreenTape (Agilent Technologies, Waldbronn, Germany). Paired-end sequencing (2 × 300 bp) was carried out by Macrogen using the MiSeq™ platform (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA). Sequencing adaptors and barcodes were removed using Cutadapt [19]. To correct errors resulting from amplicon sequencing, the reads were filtered based on quality scores and then trimmed using the DADA2 package version 1.18.0 [20] in R software version 4.0.3 [21]. The forward and reverse reads were truncated at 250 bp and 200 bp, respectively. Filtering was performed to remove reads with an expected error of 2 or more base pairs. After merging the paired-end reads and correcting sequencing errors, PCR chimeric artifacts were removed using the consensus method of DADA2 to infer amplicon sequence variants (ASVs). The PR2 database v.4.14.0 [22], which contains the 18S rRNA gene sequences, was used as the training set for taxonomic classification using the assign Taxonomy function in the DADA2 package.
To count and identify microalgae, subsamples were gently mixed and loaded onto a Sedgewick–Rafter counting chamber. Phytoplankton in the water column and periphyton on the plastic plates were counted using a light microscope (Carl Zeiss; 37081 Göttingen, Germany) at 200× magnification, and identification was performed at 400× magnification.
2.3. Chemical Analysis
To analyze the dissolved metals, a sample was filtered through a filter with a pore size of 0.45 µm and then acidified to a pH below 2 using nitric acid (HNO3). The SeaFAST SP3 system (Elemental Scientific, Omaha, NE, USA) was employed to remove the seawater matrix and pre-concentrate the metals, and an inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer (ICP-MS, Thermo Scientific, Bremen, Germany) was utilized for analysis. The system was calibrated using standard solutions ranging from 0.05 to 40 µg L−1 for each element. The processed samples were injected, and the peak areas corresponding to different elements were quantified based on the standard calibrations. For the analysis of the particulate phase, particles collected on MCE membrane filter paper with a pore size of 0.45 µm were transferred to a Teflon digestion vessel and digested with 0.9 mL of HNO3, 0.9 mL of HF, and 0.2 mL of HClO4. After the reaction, the residue was dissolved in 1% HNO3 and analyzed using ICP-MS. The methods used for metal analysis were described in detail in a previous study by Soon et al. [23].
2.4. Statistical Analysis
To assess the effect of HCW on microalgae, the non-parametric Kruskal–Wallis test with Bonferroni correction for post hoc pairwise comparisons (p = 0.017, corresponding to p < 0.05/3) was performed to compare Chl. a concentrations and Fv/Fm in the water columns and plastic plates across the different experimental groups. The Mann–Whitney U-test was performed to compare Chl. a concentrations, Fv/Fm, and dissolved metal concentrations between the different temperatures (15 °C vs. 20 °C). Statistical significance was defined as a p-value less than 0.05. All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS version 17.0 (SPSS, Inc., Chicago, IL, USA).
3. Results
3.1. Abiotic Factors and Fate of Metal in Microcosms
The initial abiotic factors were measured as follows: temperature (21.6 °C), salinity (34.3), dissolved oxygen (6.87 mg L−1), and pH (8.12). In the 15 °C treatment, the initial temperature was adjusted to 15 °C from 21.6 °C on day 2 in all three microcosm groups, and it was subsequently maintained within a similar range (Figure 2a). In the 20 °C treatment, the temperature was well regulated at 20 °C in all three microcosms (Figure 2b). Salinity exhibited a similar temporal increasing pattern between the 15 °C and 20 °C treatments, possibly due to evaporation over time (Figure 2d). The DO levels ranged from 6.8 to 9.5 mg L−1 in the 15 °C treatment and from 6.8 to 8.2 mg L−1 in the 20 °C treatment. Relatively high DO levels were recorded between days 2 and 7, with the peak DO level observed in the HCW+N treatment of the 15 °C treatment on day 7 (Figure 2e,f). The pH levels ranged from 8.14 to 8.48 in the 15 °C treatment and from 8.13 to 8.62 in the 20 °C treatment, showing similar patterns in both temperature treatments. The pH was relatively high between day 7 and 10, gradually decreasing towards the later period (Figure 2g,h).

Figure 2.
Temporal changes in environmental factors at 15 °C (left) and 20 °C (right). Each panel represents the following parameters: temperature (a,b), salinity (c,d), dissolved oxygen (e,f), and pH (g,h). The error bars represent the variation in duplicates.
The concentrations of heavy metals, including chromium (Cr), manganese (Mn), iron (Fe), cobalt (Co), nickel (Ni), copper (Cu), zinc (Zn), arsenic (As), cadmium (Cd), lead (Pb), and barium (Ba), are presented in Table 1. Except for Cu, the concentrations of most of the dissolved heavy metals on day 22 were higher than those of HCW stock on day 0 in all experimental groups. In addition, the dissolved Cu concentrations at 15 °C and 20 °C were 6.60 ± 0.07 μg L−1 and 7.39 ± 1.29 μg L−1 in the control group, 22.34 ± 0.77 μg L−1 and 36.68 ± 0.39 μg L−1 in the HCW, and 33.37 ± 2.13 μg L−1 and 48.69 ± 3.90 μg L−1 in the HCW+N. The particulate HCW stock on day 0 had higher concentrations compared to the dissolved HCW stock, particularly for Fe (2715 ± 90 μg L−1), Cu (4264 ± 92 μg L−1), Zn (146 ± 8 μg L−1), and Pb (32 ± 1 μg L−1). The concentrations of Cr, Mn, Co, Ni, As, and Cd in the particulate HCW were significantly higher compared to the dissolved HCW, with Cr showing an 18-fold increase, Mn showing a 3-fold increase, Co showing a 6-fold increase, Ni showing a 2-fold increase, As showing a 5-fold increase, and Cd showing a 29-fold increase at 15 °C. At 20 °C, a similar trend in heavy metal concentrations was observed, but the difference between 15 °C and 20 °C was not substantial (p > 0.05; Mann–Whitney U-test). Regarding the dissolved heavy metals, when comparing temperatures within the same microcosm treatments, most metals, including Ni, Cu, Zn, As, Cd, Pb, and Ba, exhibited higher concentrations at 20 °C compared to 15 °C. However, there were exceptions where Cr and Co did not show significant differences. Additionally, in the control group, the concentrations of Mn and Fe at 15 °C were higher than those at 20 °C. In contrast, at 20 °C, the concentrations of Mn, Co, Ni, and Zn in the HCW group were higher compared to those in the HCW+N group.

Table 1.
Heavy metal concentration in dissolved phase of hull cleaning wastewater (HCW) stock solution on day 0 and different experimental groups on day 22, and in the particulate phase of HCW stock solution on day 0 from in-water cleaning by scuba divers.
3.2. Biotic Factors in Microcosms
The total chlorophyll a (Chl. a), which is used as an indicator of algal biomass and growth, exhibited different patterns over time between the water column and the plastic plate. In the control group of the water column, there were two peaks: 5.24 μg L−1 at 15 °C and 12.37 μg L−1 at 20 °C on day 1 (Figure 3a). In particular, after reaching the maximum Chl. a concentration at 20 °C, there was a significant decrease with increasing culture time. On the other hand, at 15 °C, the Chl. a levels remained consistently high between day 1 and 14. Furthermore, throughout the experimental period, the Chl. a concentrations in the control group were consistently higher compared to those in the HCW and HCW+N treatments at both temperatures.
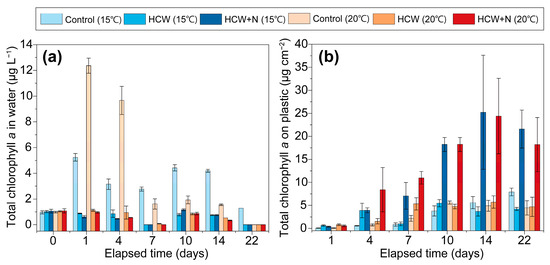
Figure 3.
Temporal changes in total chlorophyll a in the water column (a) and on plastic plates (b) at different temperature levels (15 °C = blue colors; 20 °C = red colors) for the control group (light color), HCW treatment (medium color), and HCW+N treatment (deep color). The error bars represent the variation in duplicates.
On the plastic plates, the control group exhibited relatively low levels of Chl. a compared to both the HCW and HCW+N treatments. At 15 °C, Chl. a ranged from 0.38 μg cm−2 to 25.23 μg cm−2, while at 20 °C, it ranged from 0.54 μg cm−2 to 24.40 μg cm−2. In the control group at both temperatures, Chl. a remained at low levels from day 1 to day 7, gradually increasing until the last day of the experiment. In the HCW group at 15 °C, the first peak of Chl. a occurred on day 4 at 3.90 μg cm−2, followed by a second peak of 5.47 μg cm−2 on day 10, and then reached 4.22 μg cm−2 on the final day. At 20 °C, the first peak of Chl. a was observed on day 7 at 5.33 μg cm−2, followed by a second peak on day 14, and it finally reached 4.70 μg cm−2 on the last day. In the HCW+N group, at both 15 °C and 20 °C, Chl. a gradually increased from day 1 to day 14, reaching the maximum values of 25.23 μg cm−2 and 24.40 μg cm−2, respectively, on day 15. Throughout the experimental period, the Chl. a in the HCW+N treatment was consistently 3.5 to 4.0 times higher than that of the HCW treatment at both temperatures. Overall, there was a similar time series change in Chl. a between the control and HCW treatments, but the Chl. a in the HCW+N treatment showed significantly higher levels compared to the HCW treatment at both 15 °C and 20 °C.
The comparative analysis of total Chl. a and Fv/Fm is presented in Figure 4. In the water column, the concentration of Chl. a was significantly higher in the control group (3.51 ± 0.15 μg L−1 at 15 °C and 4.52 ± 0.40 μg L−1 at 20 °C) compared to both the HCW group (0.55 ± 0.11 μg L−1 at 15 °C and 0.59 ± 0.19 μg L−1 at 20 °C) and the HCW+N group (0.50 ± 0.04 μg L−1 at 15 °C and 0.46 ± 0.04 μg L−1 at 20 °C) (p < 0.01; Kruskal–Wallis test). However, on the plastic plates, the HCW+N group (12.74 ± 4.56 μg cm−2) exhibited a higher concentration of Chl. a compared to the control group (3.13 ± 0.54 μg cm−2; p < 0.01) and the HCW group (3.15 ± 0.52 μg cm−2; p < 0.05) in the 15 °C treatment. Similarly, in the 20 °C treatment, the HCW+N group (13.47 ± 3.12 μg cm−2) showed a higher Chl. a concentration compared to the control group (3.00 ± 0.59 μg cm−2; p < 0.001) and the HCW group (3.81 ± 0.71 μg cm−2; p < 0.05) (Figure 4a,b). There was no significant difference in total Chl. a in the water column between the same experimental conditions under different temperature conditions (Mann-Whitney U-test, p > 0.05). Similarly, the Fv/Fm values in the water column were higher in the control group (0.50 ± 0.05 at 15 °C and 0.39 ± 0.03 at 20 °C) compared to both the HCW group (0.13 ± 0.04 at 15 °C and 0.20 ± 0.05 at 20 °C) and the HCW+N group (0.15 ± 0.01 at 15 °C and 0.13 ± 0.01 at 20 °C) (p < 0.05) (Figure 4c,d). However, there were no significant differences in Fv/Fm values on the plastic plates between the control group and both treatments at 15 °C and 20 °C (p > 0.05).

Figure 4.
Boxplot of total chlorophyll a (a,b) and Fv/Fm (c,d) in the water column (left side) and on the plastic plate (right side) for the control, HCW, and HCW+N treatments at different temperature levels during the entire experiment. Asterisks indicate significant differences between treatments (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001).
3.3. Phytoplankton and Periphyton Community in Microcosms
Overall, in the control group’s water column, the phytoplankton communities were predominantly composed of diatoms, specifically Pseudo-nitzschia spp. and Cylindrotheca spp., at both 15 °C and 20 °C. However, in the HCW and HCW+N treatments, the abundances of phytoplankton in the water column remained relatively low until day 7, indicating that they did not adapt well to the presence of HCW (Figure 5). The diatom Pseudo-nitzschia spp. accounted for 0.08 × 105 to 1.00 × 105 cells L−1 at 15 °C and 0.08 to 2.58 × 105 cells L−1 at 20 °C, and subsequently, Cylindrotheca species became dominant (maximum density: 1.85 × 105 cells L−1 at 15 °C and 2.48 × 105 cells L−1 at 20 °C) during the middle and later stages of the experiment. In the HCW and HCW+N treatments, although a clear dominant species succession trend was not observed in the initial stages, Halamphora spp. consistently maintained a low abundance throughout the experiment. In contrast, on the plastic plates, the attached microalgal communities in the control group were mainly dominated by Cylindrotheca, while in the HCW and HCW+N treatments, Halamphora spp. dominated. In the 15 °C treatment, the abundance of Cylindrotheca spp. in the control group gradually increased, reaching 0.63 × 106 cells cm−2 on day 10, and then rapidly increased to a maximum abundance of 8.45 × 106 cells cm−2 on day 14. On the plastic plates of the HCW and HCW+N experiments, the abundance of Halamphora spp. followed a similar time series pattern in both groups. The maximum abundances of attached microalgae in the HCW and HCW+N treatments were 5.75 × 106 cells cm−2 and 13.3 × 106 cells cm−2, respectively, on day 14 (Figure 5c). Similarly, at 20 °C, although the time series patterns of the attached microalgal communities were similar between the HCW and HCW+N treatments, the abundance in the HCW+N treatment was higher than that in the HCW treatment, indicating that the periphyton were able to grow more rapidly under high nutrient conditions.
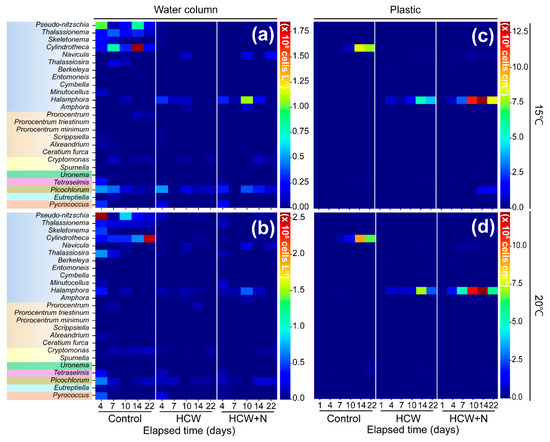
Figure 5.
Temporal changes in total microalgae abundance (at the genus level) in the water column ((a,b); ×105 cells L−1) and on the plastic plates ((c,d); ×106 cells cm−2) at 15 °C (above) and 20 °C (below) in the control, HCW, and HCW+N treatments. The background colors of each genus text represent different phytoplankton groups: light blue = Bacillariophyceae; light orange = Dinophyceae; light yellow = Cryptophyceae; green = Oligohymenophorea; pink = Chlorodendrophyceae; brown = Trebouxiophyceae; light sky = Euglenophyceae; dark orange = Thermococcaceae.
The attached microalgal communities showed similar trends to those seen in the microscopic analysis, except for minor small-sized cells. Halamphora spp. was predominantly present on the plates in most microcosms, except in the control group. Consistent with the microscopic analysis, at the initial stage of 15 °C, Halamphora spp. had a relative abundance of 53% in HCW, while Tetraselmis dominated with 27% in HCW+N. This trend became more pronounced at 20 °C, where Berkeleya spp. replaced Halamphora spp. in HCW and HCW+N, accounting for 22% and 31%, respectively, while Halamphora spp. accounted for 30% and 29%, respectively. In the later stages, Halamphora spp. exhibited a high relative abundance of 53% and 50% at 15 °C for HCW and HCW+N, respectively, and 49% in HCW at 20 °C, becoming the predominant species in most cases. Additionally, in the control group at 20 °C, on day 4, Skeletonema and Picochlorum accounted for 24% and 21%, respectively (Figure 6).
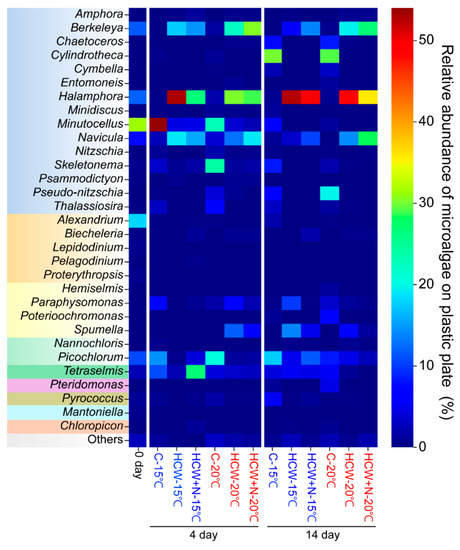
Figure 6.
Temporal changes (day 0, day 4, and day 14) in the relative abundance (%) of the attached microalgal community (at the genus level) on the plastic plate at different temperature levels in the control, HCW, and HCW+N treatments (background colors of each genus text: light blue = Bacillariophyceae; light orange = Dinophyceae; light yellow = Cryptophyceae; light green = Trebouxiophyceae; green = Chlorodendrophyceae; pink = Dictyochophyceae; brown = Thermococcaceae; light sky = Mamiellophyceae; dark orange = Chloropicophyceae; grey = others).
4. Discussion
The majority of in-water hull cleaning machines typically use rotating brushes operated by scuba divers and remotely operated vehicles (ROVs) to remove biofouling. However, during the cleaning process, biofouling organisms and antifouling (AF) paint can be released into the water column, potentially causing negative impacts on marine ecosystems. In particular, the release of biofouling organisms raises concerns about the potential dispersal of alien species to other biological regions. Antifouling paints are commonly used on commercial ships to prevent the growth of biofouling organisms, allowing the ships to maintain optimal performance while spending extended periods in seawater. However, the biocides present in these paints can slowly leach out into the surrounding seawater as it penetrates the paint surface [24,25]. Furthermore, if effluent release during the in-water cleaning process is not properly managed, the biocides in antifouling paint can have a significant impact on aquatic organisms. In order to assess the potential effects of biocides, including heavy metals, in antifouling paint on unattached and attached microalgae, as well as to understand the succession process of attached algae over time under different nutrient and water temperature conditions, we designed our microcosm study using the effluent from in-water hull cleaning. Prior to conducting this study, we conducted an assessment using HCW from the research vessel (R/V) Isabu of the Korea Institute of Ocean Science and Technology (KIOST). The assessment involved using iron attachment plates coated with antifouling paint as the attached substrates (Unpublished data). Our preliminary results indicate that the applied antifouling paint significantly inhibited the regrowth of biofouling microorganisms due to the leaching of metals and biocides mixtures from the iron plates. This suggests that the newly applied antifouling paint severely damaged the microalgae. As an alternative approach, we evaluated the time series attachment characteristics of attached microalgae using acrylic plastic plates without any biocides constituents. Through this alternative approach associated with the IMEA method, we can assess the potential regrowth ability of attached microalgae and obtain valuable information to predict the natural impact on marine microorganisms during the in-water hull cleaning process, which is relevant to biological risk assessment.
It is well established that certain heavy metals found in antifouling paints, such as lead, copper, and zinc, not only impact marine organisms directly, but also pose ecosystem risks due to their potential for bioaccumulation [26]. In particular, the paint particulate associated with wastewater effluent from in-water hull cleaning can lead to the release of dissolved heavy metals into the surrounding environment over time under natural conditions [23,27]. These dissolved heavy metals can have significant impacts on marine organisms, due to the leaching of metals from sinking paint particles onto the bottom sediment [28,29]. In our study, we compared the levels of particulate heavy metals and dissolved heavy metals in the HCW generated during in-water hull cleaning using microcosm experiments. Our results show that while the concentrations of particulate-associated heavy metals remained extremely high, the levels of dissolved heavy metals remained relatively low. Considering the dose of HCW, the initial concentrations of dissolved Cu in the 5% HCW and HCW+N treatments should have been one fifth of level in the stock solution of HCW on day 0. Interestingly, at the end of the microcosm experiment (22 days later), the concentration of dissolved heavy metals was estimated to be higher than the initial concentration (Table 1), suggesting a gradual elution of metals from particulate during the incubation period, leading to a significant shift towards the dissolved phase. This phenomenon aligns with the findings of Soon et al. [23,27], who demonstrated that particles in wastewater effluents can be effectively reduced by up to 90% using a filtration system with an 8 μm mesh size. This implies that the settled paint particulate including heavy metals present in bottom sediments can pose a threat to benthic marine organisms in areas where in-water cleaning using scuba and ROV is conducted without capture systems. In our study, the particulate fragments including paints and biofouling organisms in HCW stocks obtained during in-water hull cleaning suggest the sedimentation of these particles into the sub-marine sediment (Table 1; Figure 6). Indeed, such paint particles can continuously release dissolved heavy metals into the seabed over a prolonged period, potentially exerting negative effects on macrofauna in the Busan International Port of Korea, which is situated in close proximity to the dry dock [29]. High levels of heavy metals have been observed in the vicinity of the dry dock in Yeongdo, Busan, resulting from their leaching during ship hull cleaning activities using hydroblasting [22,27,29]. According to the ecosystem health assessment of benthos conducted by Kim et al. [29], the density and biomass of benthic macroinvertebrates were significantly lower in the vicinity of Yeongdo, Busan, where the concentrations of heavy metals remained high due to effluent from ship hull cleaning by hydroblasting [23,27]. These findings highlight the potential risks associated with both in-water cleaning and dry-dock cleaning, particularly in areas close to biofouling cleaning activities using hydroblasting methods. As a result, if the dredging of polluted sediments is not carried out, the heavy metal contaminants can gradually be released into the seabed, particularly in enclosed inner bays, leading to a significant and chronic impact on the surrounding marine organisms and ecosystems. Therefore, during in-water cleaning and dry-dock cleaning processes, the mixtures of paint and biocides, along with other harmful chemical contaminants, have the potential to be released into the marine environment. This can create localized “hotspots” of chemical contamination within port systems. Consequently, the proper management of hull cleaning wastewater (HCW) during in-water cleaning is crucial to minimize the risk associated with the removal of biofouling from ships.
The microbial community, including microalgae, is known to be highly sensitive to metal contamination [30,31,32]. It is well-established that paint and biocide mixtures in wastewater can be significantly toxic to marine organisms, with the degree of toxicity depending on the specific chemical composition [26,30,33]. In the present study, the concentrations of metals in the particulate phase were relatively high, with Cu (4264 ± 92 μg L−1), Fe (2715 ± 90 μg L−1), Zn (146 ± 8 μg L−1), and Pb (32 ± 1 μg L−1) being the most prominent. After the microcosm experiments, the concentration of dissolved Cu was found to be the highest, followed by Zn. These two heavy metals, Cu and Zn, are commonly used in antifouling paints [34,35,36], and previous studies by Soon et al. [23,27] also reported their high abundance in HCW, which is consistent with our findings. The concentration of dissolved Fe, compared to the initial concentration, remained relatively low in the later stages of the experiment, indicating the rapid uptake of dissolved Fe by microalgae. As highlighted in the reference [37,38], Fe is a crucial metal for microalgae growth, primarily through biological uptake. This suggests that the elevated levels of dissolved Cu and Zn were primarily due to the elution of these metals from the particulate form present in the paint, emphasizing the importance of developing capture systems in ship hull cleaning processes conducted by ROVs. These cleaning systems play a vital role in minimizing the release of paint particulate matter and various microalgal species into the marine environment, considering the potential risks associated with the wastewater.
The microalgae in the water column of the control group exhibited rapid growth on day 2, while the microalgae in both HCW treatment groups remained at low levels on day 7. Notably, the Fv/Fm in the water column, which indicates photosynthetic activity, was significantly higher in the control group compared to both the HCW and HCW+N treatments at both 15 and 20 °C (p < 0.05). This suggests that the photosynthetic activity of phytoplankton in the water column was inhibited after the inoculation of HCW, leading to the inhibition of their growth (Figure 3). However, on the plastic plates, the Chl. a concentrations (indicative of the biomass of attached microalgae) of HCW treatments showed a marked increase, particularly in the HCW+N treatment. Interestingly, unlike phytoplankton in water column, there were no significant differences in the Fv/Fm ratio of the attached microalgae on the plastic plates between the control and HCW treatments (p > 0.01; Figure 4). This implies that the periphyton community, such as benthic diatoms, had a high photosynthetic capacity even in the presence of HCW containing biocides. Therefore, our findings suggest that phytoplankton in the water column can be negatively affected by HCW, while the periphyton is not severely affected by HCW. Furthermore, this negative effect on phytoplankton community can alter the composition of the microalgae community. When the distribution scale of microalgae (phytoplankton—water column, periphyton—attached substance) in the marine environment is considered, the phytoplankton in the water column contributes more to productivity [39], indicating that the negative impacts of HCWs can lead to reduced productivity in the marine environments.
Overall, the water column microalgae in the control group were predominantly composed of diatoms, such as Pseudo-nitzschia spp. and Cylindrotheca spp. The Pseudo-nitzschia spp. exhibited relatively high abundance during the initial to middle stages, but decreased towards the late stage. In contrast, C. closterium showed a lower abundance during the initial to middle stages, but gradually increased towards the late stage. The rapid growth of Pseudo-nitzschia spp. is typically associated with the introduction of nitrogen sources in coastal waters [40,41,42,43]. In our mesocosm study, similar to previous findings, Pseudo-nitzschia spp. exhibited rapid growth during the initial stage, but gradually declined as the nutrient levels decreased. On the other hand, Cylindrotheca species are capable of thriving even in low-nutrient environments [43,44]. The biomass of Cylindrotheca in the control group remained low in the water column. On the plastic plates, the attached benthic microalgae in the control group were exclusively composed of C. closterium. These attached microalgae gradually increased in abundance during the middle stage (day 7) and reached maximum densities in the late stages at 15 and 20 °C. This indicates that C. closterium is capable of thriving under conditions of low to moderate nutrient levels in the absence of attached microalgae. On the other hand, in the treatment groups (HCW, HCW+N), the benthic diatom Halamphora gradually increased towards the late stage even in the water column. In addition, in the NGS analysis, the three diatoms Halamphora, Berkeleya, and Navicula also constituted an average of 12, 11, and 8% in HCW stock, respectively. Unlike the control group (below 4%), the composition ratios of these three diatoms on the plastic plates were 41 ± 11% in Halamphora, 19 ± 7% in Berkeleya, and 15 ± 7% in Navicula on average, on days 4 and 14 in the treatments. In particular, Halamphora dominated on the plastic plates in the HCW and HCW+N treatments, suggesting the possibility of the reattachment and regrowth of these diatoms, mainly Halamphora, originating from ship hulls. Our microcosm study suggests that the periphyton community released during in-water hull cleaning may have the potential to reattach and grow under favorable nutrient conditions of coastal waters and port systems.
In summary, our microcosm study confirmed that the growth of phytoplankton was inhibited by in-water HCW effluent, while periphyton was not significantly affected. In the water column, phytoplankton showed a relatively high sensitivity to the biocide mixtures including heavy metals present in the HCW compared to periphyton. Considering the elution from particulate metals in HCW as a cause of these microalgae fluctuations, a potential risk to phytoplankton growth may arise if HCW is continuously discharged into inner bays and coastal waters. Through our microcosm study, we found that the toxicity of HCW can lead to changes in the composition of phytoplankton communities, resulting in a negative impact on productivity. Additionally, the reattachment and growth of certain attached microalgae have been observed, raising concerns about biosecurity risks. Therefore, it is crucial to implement management strategies to mitigate ecological risks to aquatic microorganisms during the in-water cleaning of ship biofouling, considering the release of harmful chemical contaminants into the marine environment. Particularly, careful attention should be paid to the accumulation of heavy metals in microorganisms, as they can be transferred to higher trophic levels.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.K.L. and S.H.B.; methodology, Y.K.L. and S.H.B.; validation, M.K. and S.H.B.; formal analysis, Y.K.L., T.K. and J.N.Y.; investigation, Y.K.L., T.K. and J.N.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.K.L. and S.H.B.; writing—review and editing, Y.K.L. and S.H.B.; visualization, Y.K.L., C.H.L. and S.H.B.; supervision, S.H.B.; project administration, K.S.; funding acquisition, K.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the Korea Institute of Marine Science & Technology Promotion (KIMST) funded by the Ministry of Oceans and Fisheries (No. 20220357, Land/sea-based input and fate of microplastics in the marine environment; and No. 20210651, Techniques development for the management and evaluation of biofouling on ship hulls).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge the captains of the international commercial ships for their invaluable contributions in making the sampling process possible.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ruiz, G.M.; Fofonoff, P.W.; Carlton, J.T.; Wonham, M.J.; Hines, A.H. Invasion of coastal marine communities in North America: Apparent patterns, processes, and biases. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 2000, 31, 481–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, I.C.; Brown, C.W.; Sytsma, M.D.; Ruiz, G.M. The role of containerships as transfer mechanisms of marine biofouling species. Biofouling 2009, 25, 645–655. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Davidson, I.C.; Scianni, C.; Minton, M.S.; Ruiz, G.M. A history of ship specialization and consequences for marine invasions, management and policy. J. Appl. Ecol. 2018, 55, 1799–1811. [Google Scholar]
- Tamburri, M.N.; Davidson, I.C.; First, M.R.; Scianni, C.; Newcomer, K.; Inglis, G.J.; Georgiades, E.T.; Barnes, J.M.; Ruiz, G.M. In-water cleaning and capture to remove ship biofouling: An initial evaluation of efficacy and environmental safety. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 437. [Google Scholar]
- Schultz, M.P. Effects of coating roughness and biofouling on ship resistance and powering. Biofouling 2007, 23, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, M.; Bendick, J.; Holm, E.; Hertel, W. Economic impact of biofouling on a naval surface ship. Biofouling 2011, 27, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scianni, C.; Georgiades, E. Vessel in-water cleaning or treatment: Identification of environmental risks and science needs for evidence-based decision making. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, S.H.; Kim, D.; Kim, Y.O.; Son, M.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, M.; Park, B.S. Seasonal changes in abiotic environmental conditions in the Busan coastal region (South Korea) due to the Nakdong River in 2013 and effect of these changes on phytoplankton communities. Cont. Shelf Res. 2019, 175, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Lee, M.; Lim, Y.K.; Kim, Y.J.; Baek, S.H. Occurrence characteristics of harmful and non-harmful algal species related to coastal environments in the southern sea of Korea. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2019, 70, 794–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Department of Agriculture [DOA]; Department of the Environment [DOE]; New Zealand Ministry for Primary Industries [MPI]. Antifouling and in-Water Cleaning Guidelines; Department of Agriculture: Canberra, Australia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Champ, M.A. A review of organotin regulatory strategies, pending actions, related costs and benefits. Sci. Total Environ. 2000, 258, 21–71. [Google Scholar]
- Shtykova, L.; Fant, C.; Handa, P.; Larsson, A.; Berntsson, K.; Blanck, H.; Simonsson, R.; Nyden, M.; Harelind, H.I. Adsorption of antifouling booster biocides on metal oxide nanoparticles: Effect of different metal oxides and solvents. Prog. Org. Coat. 2009, 64, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiades, E.; Kluza, D. Evidence-based decision making to underpin the thresholds in New Zealand’s craft risk management standard: Biofouling on vessels arriving to New Zealand. Mar. Technol. Soc. J. 2017, 51, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dafforn, K.A.; Lewis, J.A.; Johnston, E.L. Antifouling strategies: History and regulation, ecological impacts and mitigation. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 453–465. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Keith, R.H. Identifying hazards in complex ecological systems. Part 1: Fault-tree analysis for biological invasions. Biol. Invasions 2002, 4, 235–249. [Google Scholar]
- Keith, R.H. Identifying hazards in complex ecological systems. Part 2: Infection modes and effects analysis for biological invasions. Biol. Invasions 2002, 4, 251–261. [Google Scholar]
- Bradley, I.M.; Pinto, A.J.; Guest, J.S. Design and evaluation of Illumina MiSeq-compatible, 18S rRNA gene-specific primers for improved characterization of mixed phototrophic communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 5878–5891. [Google Scholar]
- Amaral-Zettler, L.A.; McCliment, E.A.; Ducklow, H.W.; Huse, S.M. A method for studying protistan diversity using massively parallel sequencing of V9 hypervariable regions of small-subunit ribosomal RNA genes. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet J. 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. 2021. Available online: http://www.r-project.org (accessed on 13 September 2022).
- Guillou, L.; Bachar, D.; Audic, S.; Bass, D.; Berney, C.; Bittner, L.; Boutte, C.; Burgaud, G.; de Vargas, C.; Decelle, J. The Protist Ribosomal Reference database (PR2): A catalog of unicellular eukaryote small sub-unit rRNA sequences with curated taxonomy. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 41, D597–D604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soon, Z.Y.; Jung, J.H.; Loh, A.; Yoon, C.; Shin, D.; Kim, M. Seawater contamination associated with in-water cleaning of ship hulls and the potential risk to the marine environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 171, 112694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katranitsas, A.; Castritsi-Catharios, J.; Persoone, G. The effects of a copper-based antifouling paint on mortality and enzymatic activity of a non-target marine organisms. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2003, 46, 1491–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warnken, J.; Dunn, R.J.K.; Teasdale, P.R. Investigation of recreational boats as a source of copper at anchorage sites using time-integrated diffusive gradients in thin film and sediment measurements. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2004, 49, 833–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Chung, J.; Lee, Y.W. Cu and Zn concentrations in seawater and marine sediments along Korean coasts from the perspective of antifouling agents. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2018, 101, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soon, Z.Y.; Jung, J.H.; Yoon, C.; Kang, J.H.; Kim, M. Characterization of hazards and environmental risks of wastewater effluents from ship hull cleaning by hydroblasting. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 123708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, N.S.; Hong, S.H.; An, J.G.; Shin, K.H.; Shim, W.J. Distribution of butyltins and alternative antifouling biocides in sediments from shipping and shipbuilding areas in South Korea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 95, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.O.; Shim, W.J.; Baek, S.H.; Choi, J.W.; Kim, D.; Choi, H.W. Coastal Ecosystem Health Assessment in Korea: Busan Case Study. Ocean Sci. J. 2019, 54, 165–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Dai, Z.; Zhao, H.; Hu, L.; Dahlgren, R.A.; Xu, J. Heavy metal effects on multitrophic level microbial communities and insights for ecological restoration of an abandoned electroplating factory site. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 327, 121548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molino, C.; Angeletti, D.; Oldham, V.E.; Goodbody-Gringley, G.; Buck, K.N. Effect of marine antifouling paint particles waste on survival of natural Bermuda copepod communities. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 149, 110492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, L.E.; Sunda, W.G.; Guillard, R.R.L. Reduction of marine phytoplankton reproduction rates by copper and cadmium. J. Exp. Mar. Bio. Ecol. 1986, 96, 225–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.; Choi, Y.; Soon, Z.Y.; Kim, M.; Jang, M.C.; Seo, J.Y.; Shin, K.; Jung, J.H. Chemical hazard of robotic hull in-water cleaning discharge on coastal embryonic fish. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 253, 114653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ytreberg, E.; Karlsson, J.; Eklund, B. Comparison of toxicity and release rates of Cu and Zn from anti-fouling paints leached in natural and artificial brackish seawater. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 2459–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ytreberg, E.; Bighiu, M.A.; Lundgren, L.; Eklund, B. XRF measurements of tin, copper and zinc in antifouling paints coated on leisure boats. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 213, 594–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagerström, M.; Ytreberg, E.; Wiklund, A.K.E.; Granhag, L. Antifouling paints leach copper in excess–study of metal release rates and efficacy along a salinity gradient. Water Res. 2020, 186, 116383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, S.H.; Lee, M.; Kim, Y.B. Spring phytoplankton community response to an episodic windstorm event in oligotrophic waters offshore from the Ulleungdo and Dokdo islands, Korea. J. Sea Res. 2018, 132, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, L.E. Minimum iron requirements of marine phytoplankton and the implications for the biogeochemical control of new production. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1991, 36, 1756–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankenbach, S.; Ezequiel, J.; Plecha, S.; Goessling, J.W.; Vaz, L.; Kühl, M.; Dias, J.M.; Vaz, N.; Serôdio, J. Synoptic spatio-temporal variability of the photosynthetic productivity of microphytobenthos and phytoplankton in a tidal estuary. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 170. [Google Scholar]
- Cochlan, W.P.; Herndon, J.; Kudela, R.M. Inorganic and organic nitrogen uptake by the toxigenic diatom Pseudo-nitzschia australis (Bacillariophyceae). Harmful Algae 2008, 8, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loureiro, S.; Jauzein, C.; Garcés, E.; Collos, Y.; Camp, J.; Vaqué, D. The significance of organic nutrients in the nutrition of Pseudo-nitzschia delicatissima (Bacillariophyceae). J. Plankton. Res. 2009, 31, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, S.H.; Kim, D.; Son, M.; Yun, S.M.; Kim, Y.O. Seasonal distribution of phytoplankton assemblages and nutrient-enriched bioassays as indicators of nutrient limitation of phytoplankton growth in Gwangyang Bay, Korea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf. Sci. 2015, 163, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magaletti, E.; Urbani, R.; Sist, P.; Ferrari, C.R.; Cicero, A.M. Abundance and chemical characterization of extracellular carbohydrates released by the marine diatom Cylindrotheca fusiformis under N-and P-limitation. Eur. J. Phycol. 2004, 39, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.N.; Lim, Y.K.; Baek, S.H. Time-series response of water column phytoplankton and periphyton on attachment plates following nutrient addition during summer in mesocosms. J. Appl. Phycol. 2023, 35, 1301–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).