Artificial Mussels: A New Tool for Monitoring Radionuclides in Aquatic Environments
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Chemical Analysis
4. Statistical Analysis
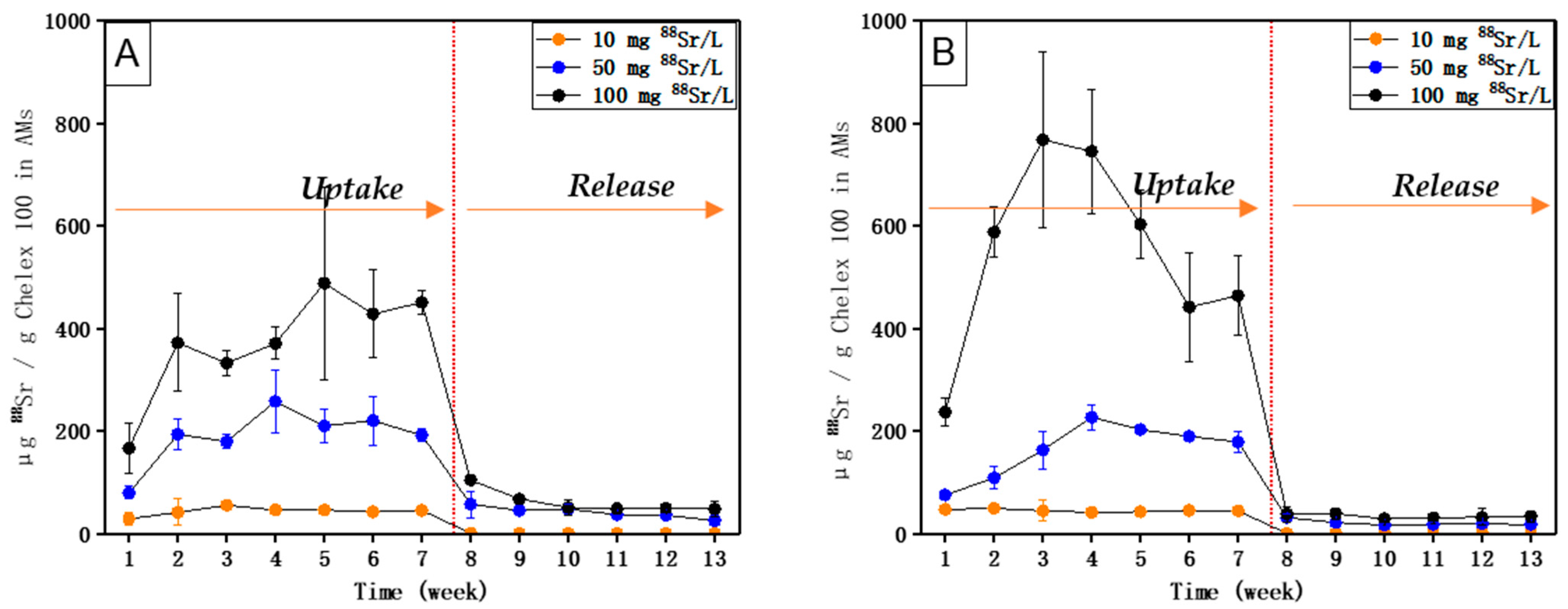
5. Results
6. Discussion
- The uptake and accumulation of 238U and 88Sr by AM (with Chelex 100), as well as the uptake and accumulation of 133Cs by AM (with molecular sieve 5 Å), are directly related to their respective concentrations in the external medium.
- The equilibrium of 238U could be reached within 8 weeks, and the equilibrium of 88Sr and 133Cs could be reached within 7 weeks.
- High concentration factors were found for 238U (1771), 88Sr (6710), and 133Cs (3675) upon exposure to their respective environmentally realistic concentrations, indicating that AMs with Chelex 100 can take up 238U and 88Sr, and AMs with molecular sieve 5 Å can take up 133Cs efficiently at low, environmentally realistic concentrations.
- 238U and 88Sr taken up by AMs (with Chelex 100) and 133Cs taken up by AMs (with molecular sieve 5 Å) can be released when their respective concentrations in the external medium become lower.
- The binding and release of 238U, 88Sr, and 133Cs were not significantly affected by the presence of the other two radionuclides in the external medium at all concentrations.
- Compared with 133Cs and 88Sr, 238U exhibited a relatively higher uptake rate upon exposure to both single and mixed solutions and also a longer time to reach equilibrium. The release of accumulated 238U was also much slower than that of 88Sr and 133Cs.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Drinhaus, J.; Harstrick, A.; Breustedt, B. An Autonomous Real-Time Detector System for Radionuclide Monitoring in Drinking Water Systems. SN Appl. Sci. 2021, 3, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, A.; Cha, Y.; Geddes, L.; Morley, K.M. Evaluation of Variability in Radionuclide Measurements in Drinking Water. J. Am. Water Works Assoc. 2011, 103, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinhauser, G.; Brandl, A.; Johnson, T.E. Comparison of the Chernobyl and Fukushima Nuclear Accidents: A Review of the Environmental Impacts. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 470–471, 800–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, M.; Takada, T.; Nagao, S.; Koike, T.; Shimada, K.; Hoshi, M.; Zhumadilov, K.; Shima, T.; Fukuoka, M.; Imanaka, T.; et al. An early survey of the radioactive contamination of soil due to the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant accident, with emphasis on plutonium analysis. Geochem. J. Jpn. 2012, 46, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miklavzic, U. Radionuclide Monitoring of Surface and Ground Water. Gas-Und Wasserfach 1993, 134, 574–576. [Google Scholar]
- Garnier-Laplace, J.; Adam, C.; Baudin, J.P. Experimental Kinetic Rates of Food-Chain and Waterborne Radionuclide Transfer to Freshwater Fish: A Basis for the Construction of Fish Contamination Charts. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2000, 39, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grate, J.W.; O’Hara, M.J.; Egorov, O.B.; Burge, S.R. Radionuclide Sensors and Systems for Environmental Monitoring. ECS Trans. 2009, 19, 301–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canu, I.G.; Laurent, O.; Pires, N.; Laurier, D.; Dublineau, I. Health effects of naturally radioactive water ingestion: The need for enhanced studies. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 1676–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, T.; Tomiya, A.; Enomoto, M.; Sato, T.; Morishita, D.; Izumi, S.; Niizeki, K.; Suzuki, S.; Morita, T.; Kawata, G. Radiological Impact of the Nuclear Power Plant Accident on Freshwater Fish in Fukushima: An Overview of Monitoring Results. J. Environ. Radioact. 2016, 151, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heldal, H.E.; Føyn, L.; Varskog, P. Bioaccumulation of 137Cs in Pelagic Food Webs in the Norwegian and Barents Seas. J. Environ. Radioact. 2003, 65, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, M.; Yokoduka, T. Radioactive Contamination of Fishes in Lake and Streams Impacted by the Fukushima Nuclear Power Plant Accident. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 482–483, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catsiki, V.A.; Florou, H. Study on the Behavior of the Heavy Metals Cu, Cr, Ni, Zn, Fe, Mn and 137Cs in an Estuarine Ecosystem Using Mytilus Galloprovincialis as a Bioindicator Species: The Case of Thermaikos Gulf, Greece. J. Environ. Radioact. 2006, 86, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metian, M.; Pouil, S.; Hédouin, L.; Oberhänsli, F.; Teyssié, J.L.; Bustamante, P.; Warnau, M. Differential Bioaccumulation of 134Cs in Tropical Marine Organisms and the Relative Importance of Exposure Pathways. J. Environ. Radioact. 2016, 152, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, K.S.; Mattson, K.M.; Kelly, D.G.; Bennett, L.G.I. Environmental Radionuclide Monitoring Programme. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2007, 271, 621–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.N.; Mao, S.Y. Application of High Resolution Gamma Ray Spectrometry in Measuring Radioactivities in Drinks in Hong Kong. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 1994, 45, 1031–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US EPA Method 900.0; Gross Alpha and Gross Beta Radioactivity in Drinking Water. EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 1980.
- DeVol, T.A. Radionuclide Sensors for Subsurface Water Monitoring; USDOE Office of Environmental Management Science Program (United States): Washington DC, USA, 2006; Volume DOE/ER/628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasyanovich, M.; Ekidin, A.; Trapeznikov, A.; Plataev, A. Analysis of Ultra-Low Radionuclide Concentrations in Water Samples with Baromembrane Method. Nucl. Eng. Technol. 2021, 53, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beals, D.M.; Crandall, B.S.; Fledderman, P.D. In-Situ Sample Preparation for Radiochemical Analyses of Surface Water. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2000, 243, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukada, H.; Nihira, S.; Watanabe, T.; Takeda, S. The 137Cs Activity Concentration of Suspended and Dissolved Fractions in Irrigation Waters Collected from the 80 Km Zone around TEPCO’s Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. J. Environ. Radioact. 2017, 178–179, 354–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enomoto, K.; Hoshina, H.; Kasai, N.; Kurita, K.; Ueki, Y.; Nagao, Y.; Yin, Y.-G.; Suzui, N.; Kawachi, N.; Seko, N. Flow Filtration/Adsorption and Simultaneous Monitoring Technologies of Radiocesium 137Cs in River Water. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 460, 141696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasutaka, T.; Tsuji, H.; Kondo, Y.; Suzuki, Y.; Takahashi, A.; Kawamoto, T. Rapid Quantification of Radiocesium Dissolved in Water by Using Nonwoven Fabric Cartridge Filters Impregnated with Potassium Zinc Ferrocyanide. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 792–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merz, S.; Shozugawa, K.; Steinhauser, G. Analysis of Japanese Radionuclide Monitoring Data of Food before and after the Fukushima Nuclear Accident. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 2875–2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noureddine, A.; Menacer, M.; Boudjenoun, R.; Benkrid, M.; Boulahdid, M.; Kadi-hanifi, M.; Lee, S.H.; Povinec, P.P. 137Cs in Seawater and Sediment along the Algerian Coast. Radioact. Environ. 2006, 8, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noureddine, A.; Benkrid, M.; Maoui, R.; Menacer, M.; Boudjenoun, R. Distribution of Natural Radioactivity, 137Cs, 90Sr, and Plutonium Isotopes in a Water Column and Sediment Core along the Algerian Coast. Sci. Technol. Nucl. Install. 2007, 048598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, F.P.; Oliveira, J.M.; Alberto, G. Factors Affecting 210Po and 210Pb Activity Concentrations in Mussels and Implications for Environmental Bio-Monitoring Programmes. J. Environ. Radioact. 2011, 102, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guendouzi, Y.; Soualili, D.L.; Boulahdid, M.; Eddalia, N.; Boudjenoun, M. Effect of Physiological Conditions and Biochemical Factors of Mussels Mytilus Galloprovincialis in Radioactivity Monitoring Programs along the Algerian Coast. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 46448–46457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrington, J.W.; Tripp, B.W.; Tanabe, S.; Subramanian, A.; Sericano, J.L.; Wade, T.L.; Knap, A.H. Edward D. Goldberg’s Proposal of “the Mussel Watch”: Reflections after 40 Years. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 110, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhelyazkov, G.; Yankovska-Stefanova, T.; Mineva, E.; Stratev, D.; Vashin, I.; Dospatliev, L.; Valkova, E.; Popova, T. Risk Assessment of Some Heavy Metals in Mussels (Mytilus Galloprovincialis) and Veined Rapa Whelks (Rapana Venosa) for Human Health. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 128, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assunta Meli, M.; Desideri, D.; Roselli, C.; Feduzi, L. Natural Radioactivity in the Mussel Mytilus Galloprovincialis Derived from the Central Adriatic Sea (Italy). J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 2008, 71, 1270–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollhöfer, A.; Brazier, J.; Humphrey, C.; Ryan, B.; Esparon, A. A Study of Radium Bioaccumulation in Freshwater Mussels, Velesunio Angasi, in the Magela Creek Catchment, Northern Territory, Australia. J. Environ. Radioact. 2011, 102, 964–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.S.S.; Lau, T.C.; Fung, W.K.M.; Ko, P.H.; Leung, K.M.Y. An “artificial Mussel” for Monitoring Heavy Metals in Marine Environments. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 145, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claassens, L.; Dahms, S.; Van Vuren, J.H.J.; Greenfield, R. Artificial Mussels as Indicators of Metal Pollution in Freshwater Systems: A Field Evaluation in the Koekemoer Spruit, South Africa. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 60, 940–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahms-Verster, S.; Baker, N.J.; Greenfield, R. A Multivariate Examination of ‘Artificial Mussels’ in Conjunction with Spot Water Tests in Freshwater Ecosystems. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 121763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degger, N.; Wepener, V.; Richardson, B.J.; Wu, R.S.S. Application of Artificial Mussels (AMs) under South African Marine Conditions: A Validation Study. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 63, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Rey, M.; Lau, T.C.; Gomes, T.; Maria, V.L.; Bebianno, M.J.; Wu, R. Comparison of Metal Accumulation between “Artificial Mussel” and Natural Mussels (Mytilus Galloprovincialis) in Marine Environments. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 63, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibria, G.; Lau, T.C.; Wu, R. Innovative ‘Artificial Mussels’ Technology for Assessing Spatial and Temporal Distribution of Metals in Goulburn–Murray Catchments Waterways, Victoria, Australia: Effects of Climate Variability (Dry vs. Wet Years). Environ. Int. 2012, 50, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labuschagne, M.; Wepener, V.; Nachev, M.; Zimmermann, S.; Sures, B.; Smit, N.J. The Application of Artificial Mussels in Conjunction with Transplanted Bivalves to Assess Elemental Exposure in a Platinum Mining Area. Water 2020, 12, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labuschagne, M.; Zimmermann, S.; Smit, N.J.; Erasmus, J.H.; Nachev, M.; Sures, B.; Wepener, V. Laboratory and Field Studies on the Use of Artificial Mussels as a Monitoring Tool of Platinum Exposure in the Freshwater Environment. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2021, 33, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, K.M.Y.; Furness, R.W.; Svavarsson, J.; Lau, T.C.; Wu, R.S.S. Field Validation, in Scotland and Iceland, of the Artificial Mussel for Monitoring Trace Metals in Temperate Seas. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2008, 57, 790–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Men, C.; Liu, R.; Xu, L.; Wang, Q.; Guo, L.; Miao, Y.; Shen, Z. Source-Specific Ecological Risk Analysis and Critical Source Identification of Heavy Metals in Road Dust in Beijing, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 388, 121763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ra, K.; Kim, J.-K.; Kim, K.-T.; Lee, S.-Y.; Kim, E.-S.; Lee, J.-M.; Wu, R.S.S. Application of the Artificial Mussel for Monitoring Heavy Metal Levels in Seawater of the Coastal Environments, Korea. J. Korean Soc. Mar. Environ. Energy 2014, 17, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Fernández, A.C.; Wu, R.S.S.; Lau, T.C.; Pérez-Bernal, L.H.; Sánchez-Cabeza, J.A.; Chiu, J.M.Y. A Comparative Study on Metal Contamination in Estero de Urias Lagoon, Gulf of California, Using Oysters, Mussels and Artificial Mussels: Implications on Pollution Monitoring and Public Health Risk. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 243, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genç, T.O.; Po, B.H.K.; Yılmaz, F.; Lau, T.-C.; Wu, R.S.S.; Chiu, J.M.Y.; Genç, T.O.; Po, B.H.K.; Yılmaz, F.; Lau, T.-C.; et al. Differences in Metal Profiles Revealed by Native Mussels and Artificial Mussels in Sarıçay Stream, Turkey: Implications for Pollution Monitoring. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2018, 69, 1372–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takata, H.; Aono, T.; Zheng, J.; Tagami, K.; Shirasaka, J.; Uchida, S. A Sensitive and Simple Analytical Method for the Determination of Stable Cs in Estuarine and Coastal Waters. Anal. Methods 2013, 5, 2558–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakaki, S.; Obata, H.; Tazoe, H.; Ishikawa, T. Precise and Accurate Analysis of Deep and Surface Seawater Sr Stable Isotopic Composition by Double-Spike Thermal Ionization Mass Spectrometry. Geochem. J. 2017, 51, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ma, Z.; Sun, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Cheng, H.; Xiao, J. U Concentration and 234U/238U of Seawater from the Okinawa Trough and Indian Ocean Using MC-ICPMS with SEM Protocols. Mar. Chem. 2017, 196, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araissi, M.; Ayed, I.; Elaloui, E.; Moussaoui, Y. Removal of Barium and Strontium from Aqueous Solution Using Zeolite 4A. Water Sci. Technol. 2016, 73, 1628–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kamash, A.M. Evaluation of Zeolite A for the Sorptive Removal of Cs+ and Sr2+ Ions from Aqueous Solutions Using Batch and Fixed Bed Column Operations. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 151, 432–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kamash, A.M.; Zaki, A.A.; El Geleel, M.A. Modeling Batch Kinetics and Thermodynamics of Zinc and Cadmium Ions Removal from Waste Solutions Using Synthetic Zeolite A. J. Hazard. Mater. 2005, 127, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, R.P.; Coker, E.N. Ion Exchange in Zeolites. In Studies in Surface Science and Catalysis; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2001; Volume 137, pp. 467–524. [Google Scholar]
- Marcus, Y. Ion Exchange | Isotope Separation. In Encyclopedia of Analytical Science; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 195–203. ISBN 9780081019832. [Google Scholar]



| 238U | 88Sr | 133Cs | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low-concentration mixture | 3 μg/L | 10 mg/L | 0.3 μg/L |
| Medium-concentration mixture | 15 μg/L | 50 mg/L | 1.5 μg/L |
| High-concentration mixture | 30 μg/L | 100 mg/L | 30 μg/L |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Y.; Chow, T.W.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Yu, P.K.N.; Ko, C.C.; Wu, R.S.S. Artificial Mussels: A New Tool for Monitoring Radionuclides in Aquatic Environments. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1309. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11071309
Yang Y, Chow TW, Zhang YQ, Yu PKN, Ko CC, Wu RSS. Artificial Mussels: A New Tool for Monitoring Radionuclides in Aquatic Environments. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2023; 11(7):1309. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11071309
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Yi, Tze W. Chow, Yi Q. Zhang, Peter K. N. Yu, Chi C. Ko, and Rudolf S. S. Wu. 2023. "Artificial Mussels: A New Tool for Monitoring Radionuclides in Aquatic Environments" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 11, no. 7: 1309. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11071309
APA StyleYang, Y., Chow, T. W., Zhang, Y. Q., Yu, P. K. N., Ko, C. C., & Wu, R. S. S. (2023). Artificial Mussels: A New Tool for Monitoring Radionuclides in Aquatic Environments. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 11(7), 1309. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11071309





_Kwan_Ngok_Yu.png)


