Simulation of Oil Spills in Inland Rivers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Oil Spill Simulation Methods
2.1. Flow Simulation
2.2. Oil Particle Model
3. Results of Two Oil Spill Accidents
3.1. Set-Up
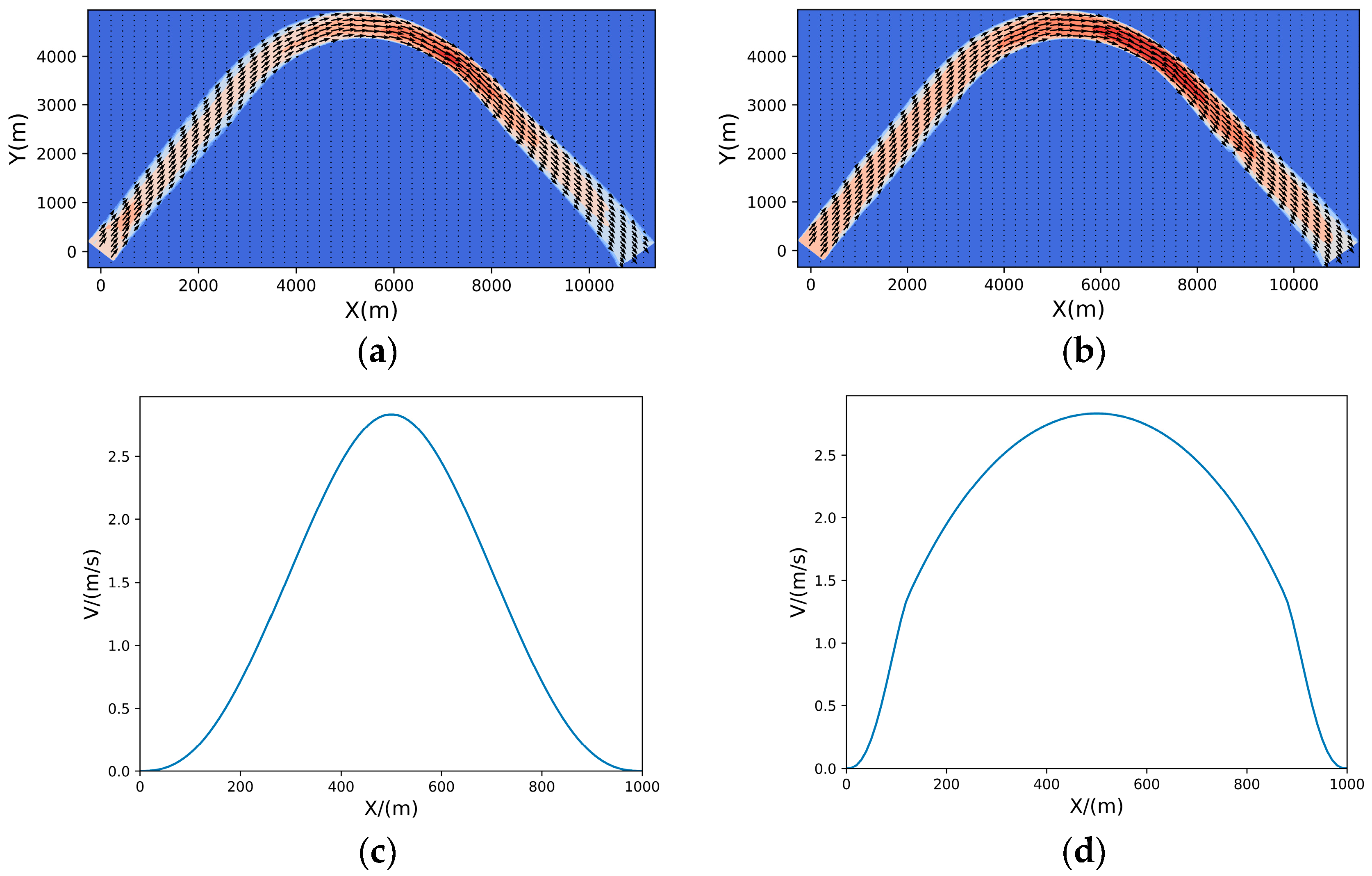
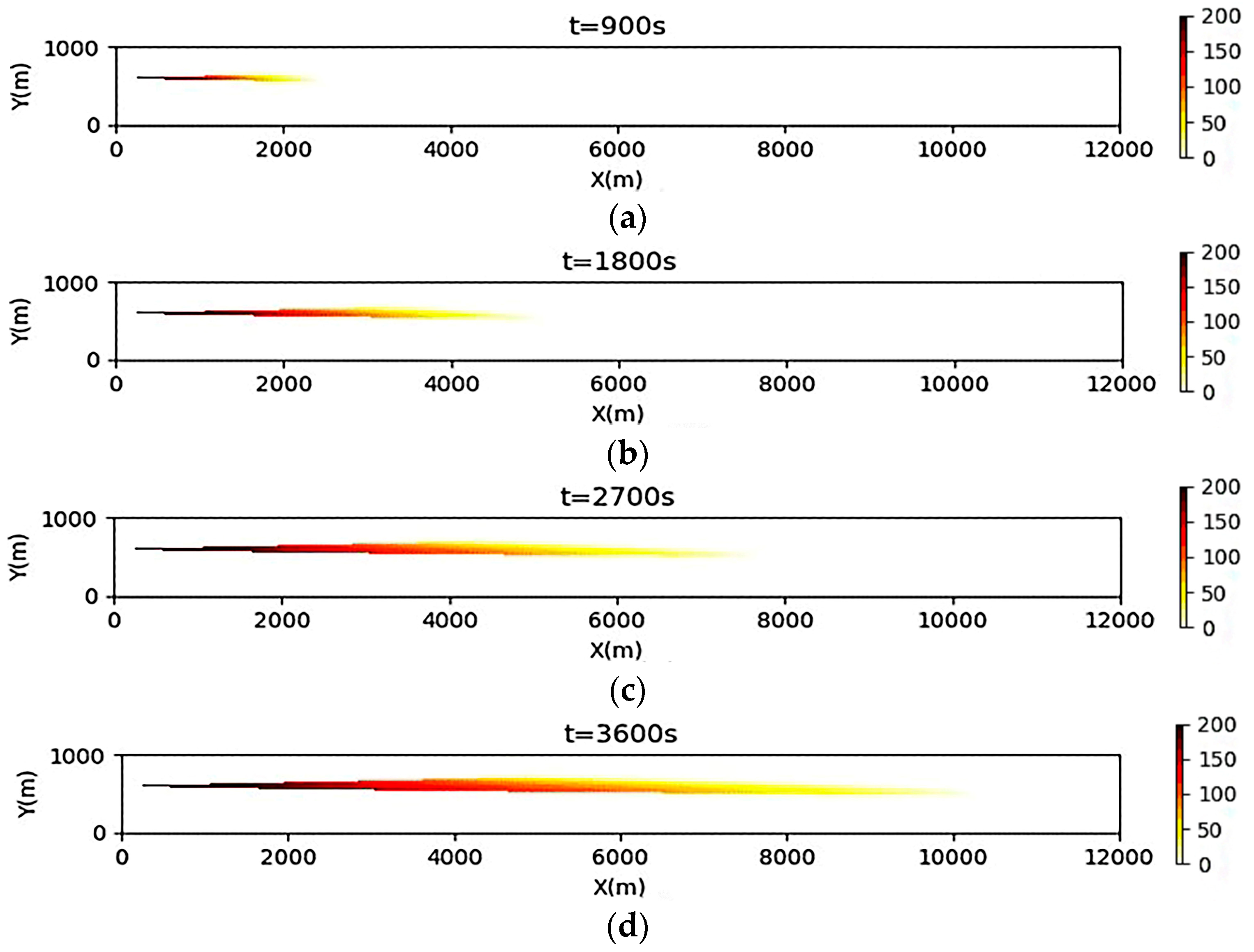
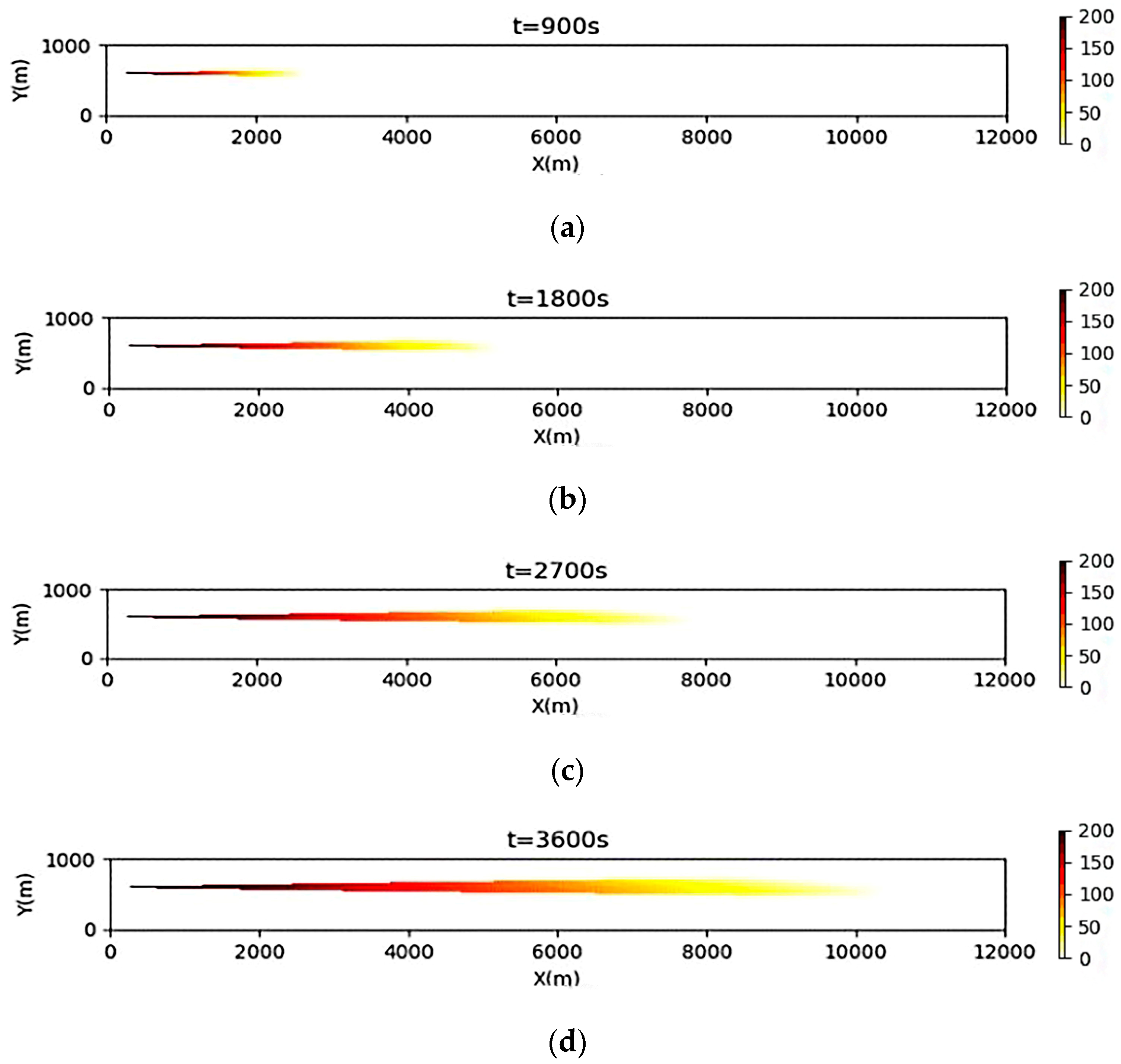
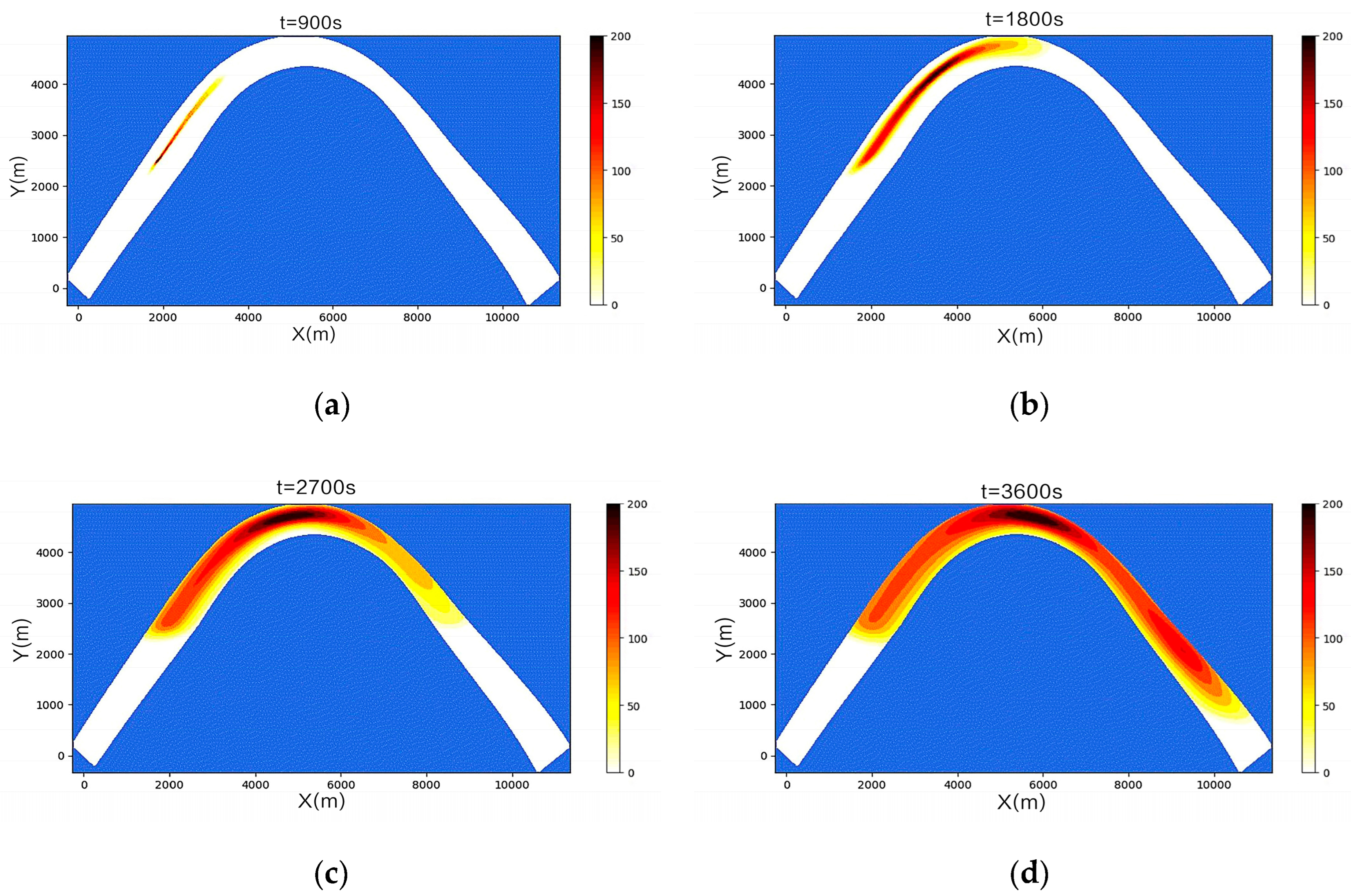
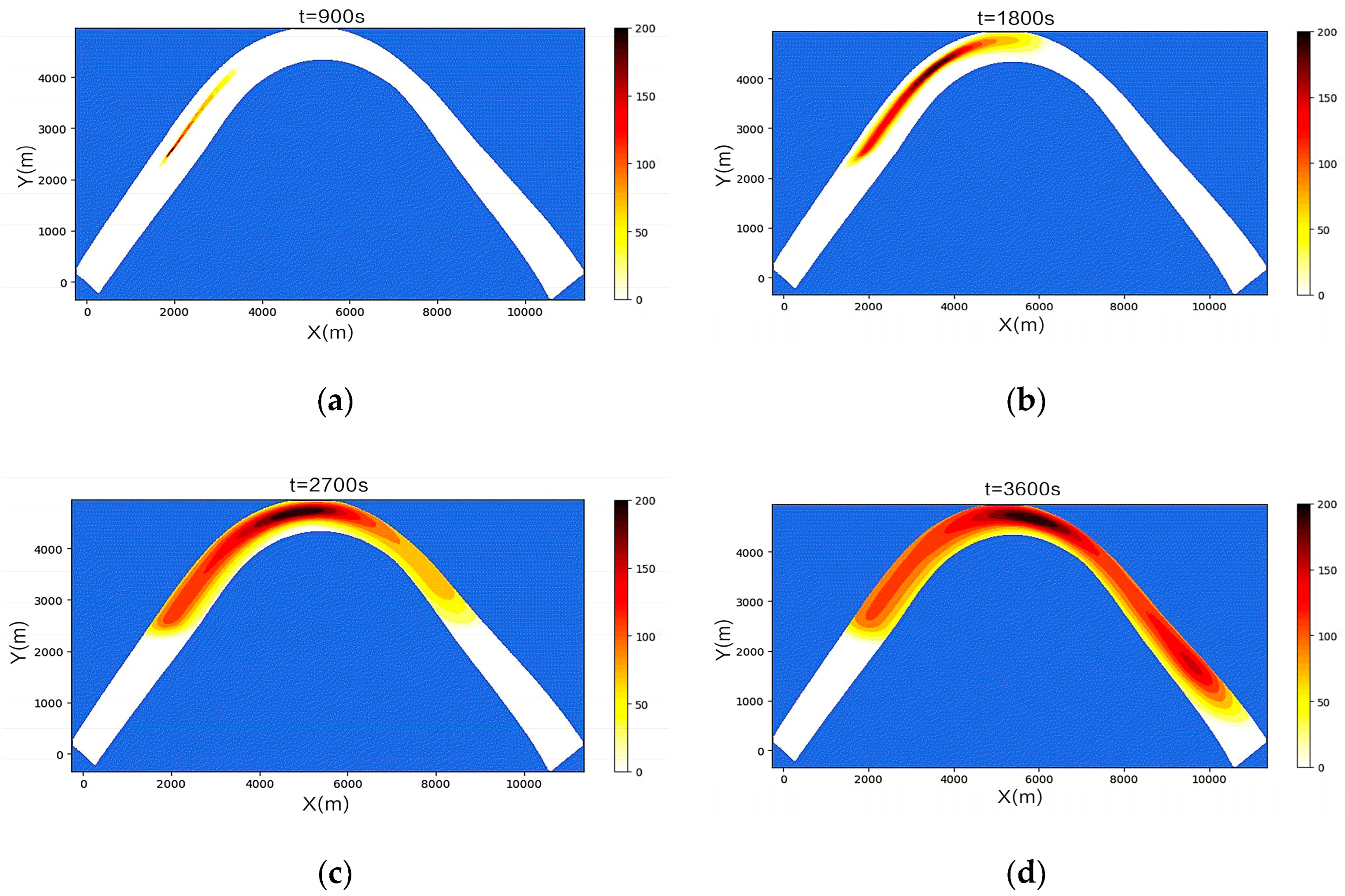
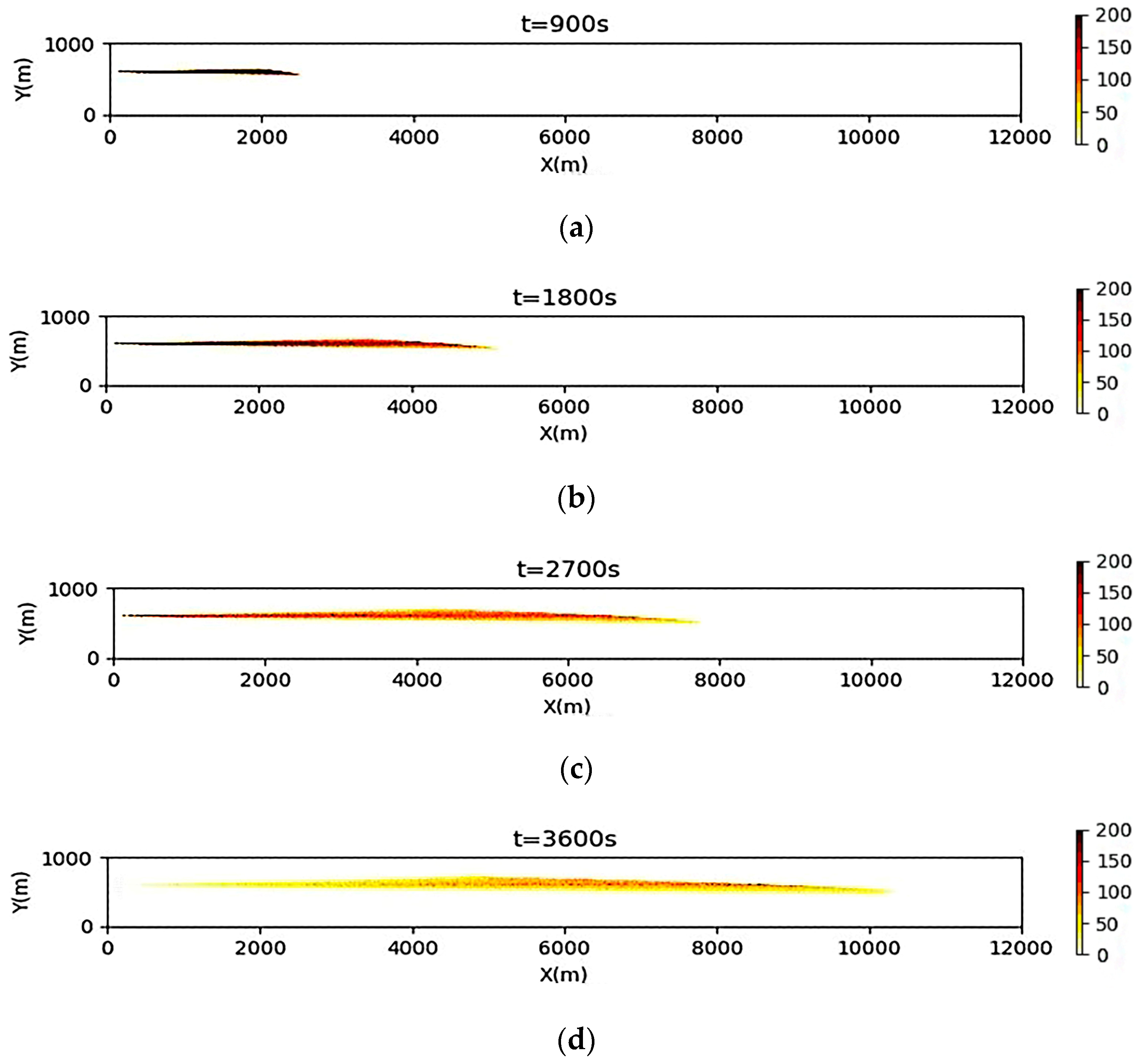
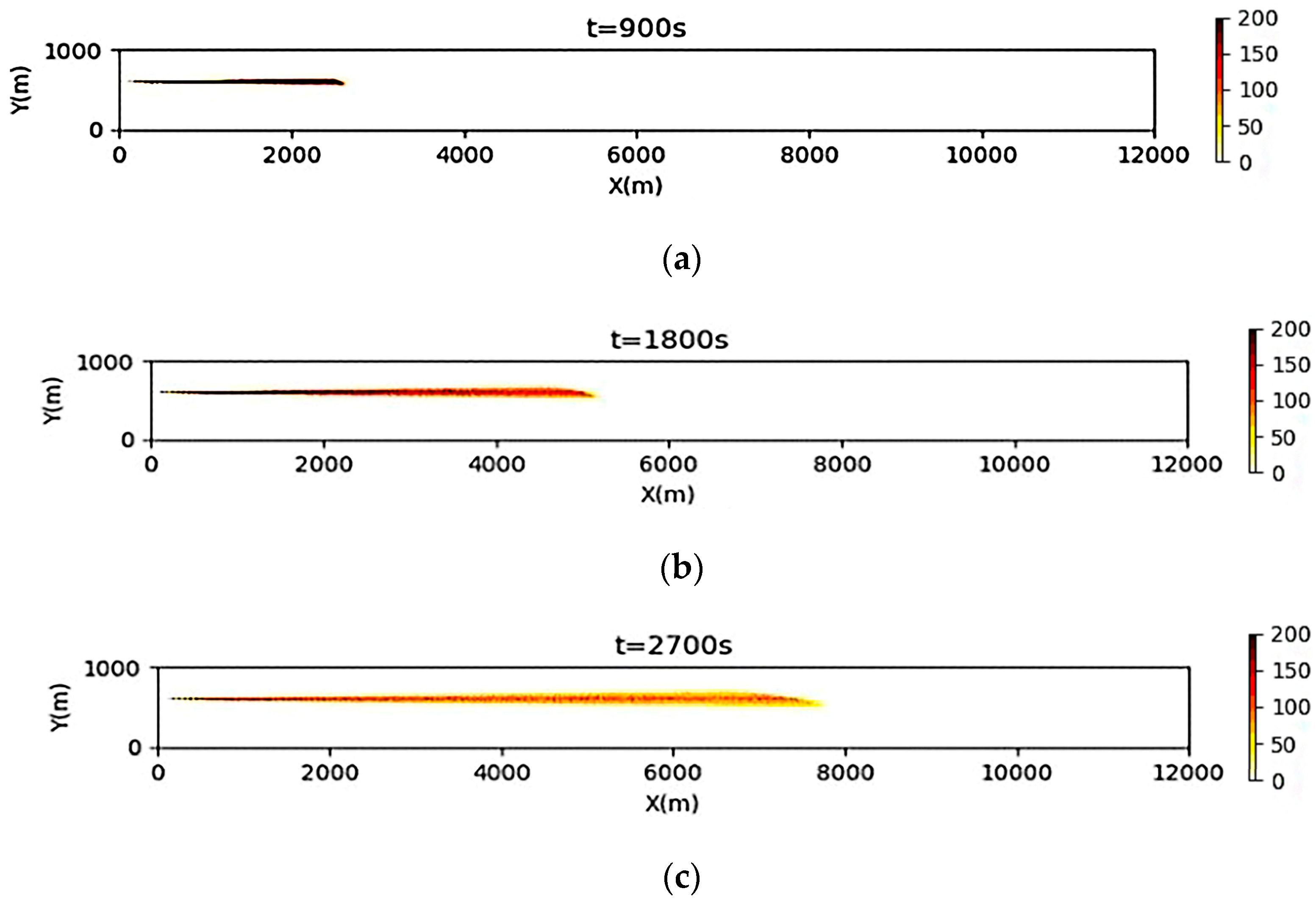
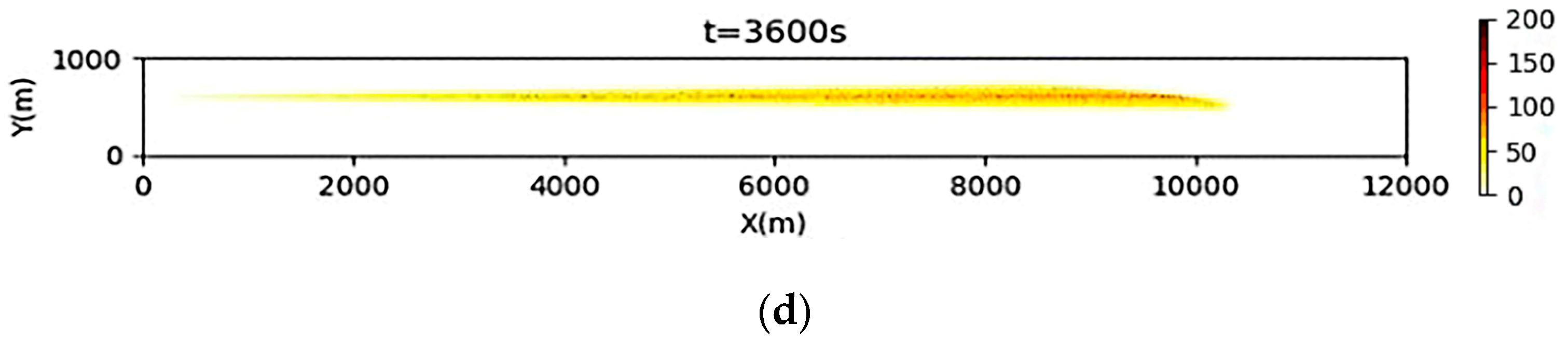
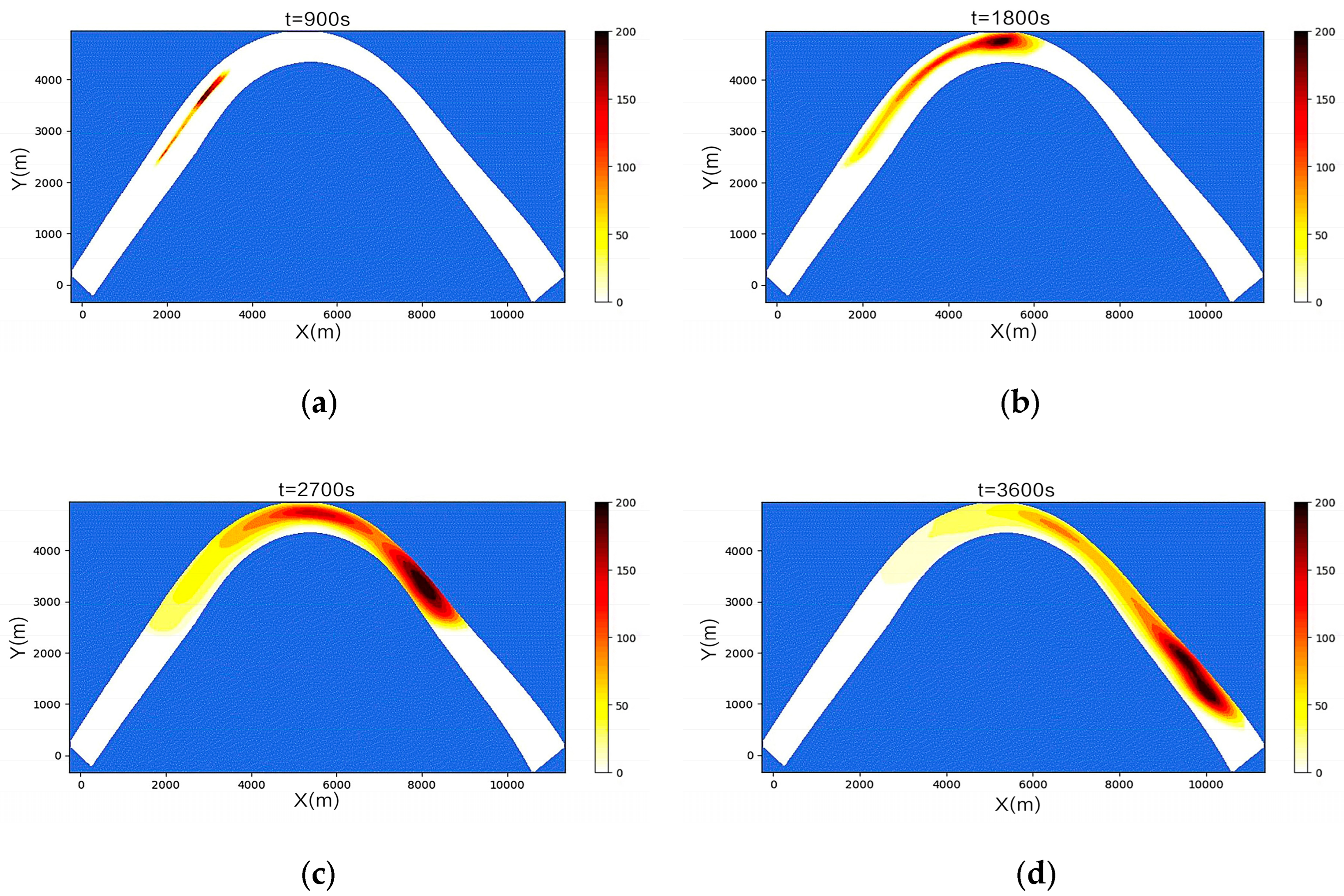
3.2. Simulation Results of a Continuous Oil Spill
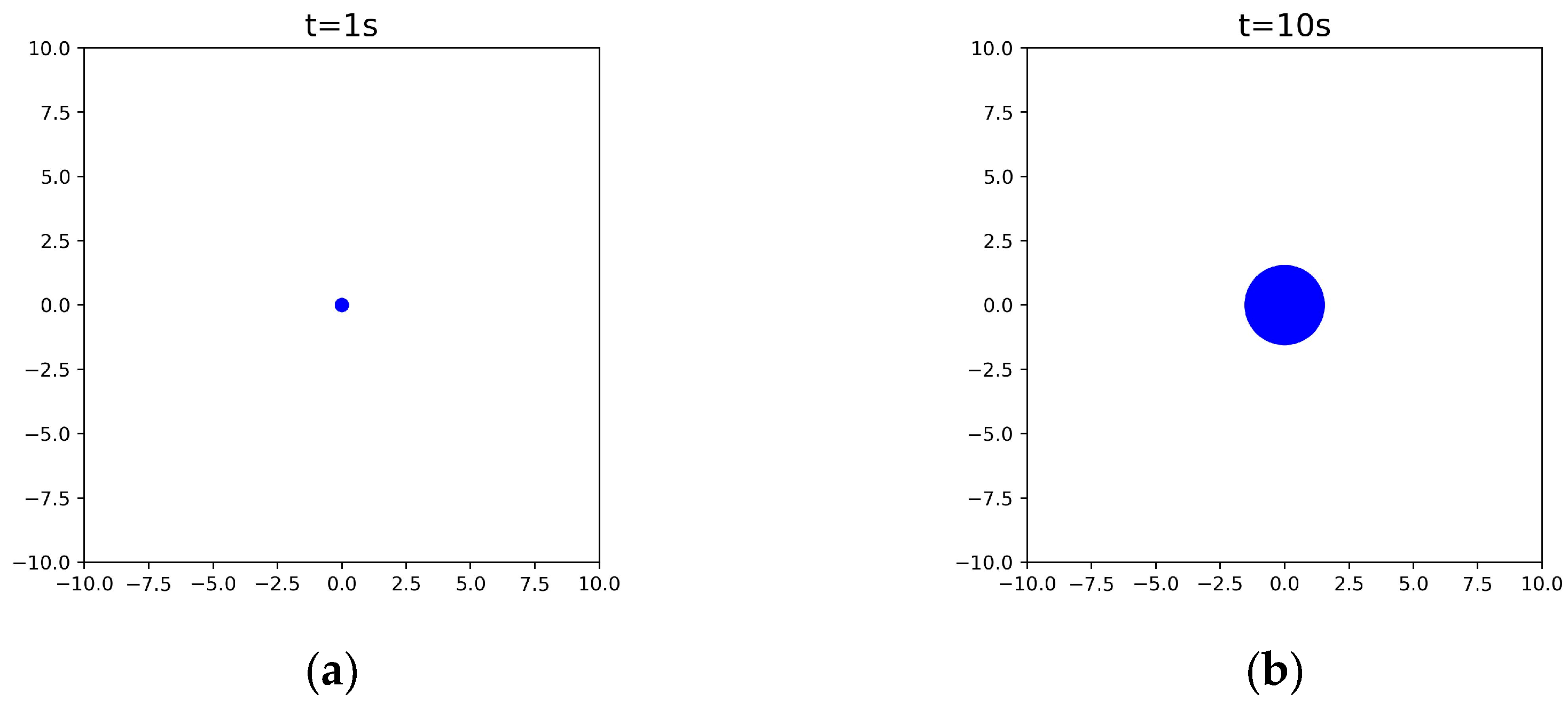
3.3. Simulation Results of a One-Time Oil Spill
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gan, L.; Yan, Z.; Zhang, L.; Liu, K.; Zheng, Y.; Zhou, C.; Shu, Y. Ship path planning based on safety potential field in inland rivers. Ocean Eng. 2022, 260, 111928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, F.; Gan, L.; Lee, P.T.-W.; Yin, J.; Chen, J. Path planning for ships assisted by the icebreaker in ice-covered waters in the Northern Sea Route based on optimal control. Ocean Eng. 2023, 267, 113182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayazit, O.; Kaptan, M. Evaluation of the risk of pollution caused by ship operations through bow-tie-based fuzzy Bayesian network. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 382, 135386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Y.; Wang, X.; Huang, Z.; Song, L.; Fei, Z.; Gan, L.; Xu, Y.; Yin, J. Estimating spatiotemporal distribution of wastewater generated by ships in coastal areas. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2022, 222, 106133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Chen, L.; Shu, Y.; Zhu, W. Evaluation model and management strategy for reducing pollution caused by ship collision in coastal waters. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2021, 203, 105446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Yu, Q.; Yuan, Z.; Yang, Z.; Shu, Y. A systematic analysis for maritime accidents causation in Chinese coastal waters using machine learning approaches. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2021, 213, 105859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Lee, K. Development and testing of a 2D offshore oil spill modeling tool (OSMT) supported by an effective calibration method. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 188, 114696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahkashan, S.; Wang, X.; Ya, M.; Chen, J.; Wu, Y.; Cai, Y.; Saleem, M.; Inam, A.; Aftab, J. Evaluation of marine sediment contamination by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons along the Karachi coast, Pakistan, 11 years after the Tasman Spirit oil spill. Chemosphere 2019, 233, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarlett, A.G.; Nelson, R.K.; Gagnon, M.M.; Holman, A.I.; Reddy, C.M.; Sutton, P.A.; Grice, K. MV Wakashio grounding incident in Mauritius 2020: The world’s first major spillage of Very Low Sulfur Fuel Oil. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 171, 112917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClenachan, G.; Turner, R.E. Disturbance legacies and shifting trajectories: Marsh soil strength and shoreline erosion a decade after the Deepwater Horizon oil spill. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 322, 121151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Di, Z.; Shi, J.; Shu, Y.; Wan, Z.; Song, L.; Zhang, W. Marine oil spill pollution causes and governance: A case study of Sanchi tanker collision and explosion. J. Cleaner Prod. 2020, 273, 122978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, Y.; Chen, J.; Wan, Z.; Shu, Y.; Xu, L.; Li, H.; Bai, Y.; Zheng, T. Crude oil maritime transportation: Market fluctuation characteristics and the impact of critical events. Energy Rep. 2020, 6, 518–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espedal, H.A. Satellite SAR oil spill detection using wind history information. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1999, 20, 49–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautama, B.G.; Longépé, N.; Fablet, R.; Mercier, G. Assimilative 2-D Lagrangian Transport Model for the Estimation of Oil Leakage Parameters From SAR Images: Application to the Montara Oil Spill. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 4962–4969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conceição, M.R.; de Mendonça, L.F.; Lentini, C.A.; da Cunha Lima, A.T.; Lopes, J.M.; de Vasconcelos, R.N.; Gouveia, M.B.; Porsani, M.J. SAR Oil Spill Detection System through Random Forest Classifiers. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huby, A.A.; Alubady, R.; Sagban, R. Oil Spill Segmentation from SAR Images Using Deep Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Symposium on Multidisciplinary Studies and Innovative Technologies (ISMSIT), Ankara, Turkey, 20–22 October 2022; pp. 282–287. [Google Scholar]
- Goyal, V.; Shukla, A. A New Optimized GA-RBF Neural Network Algorithm for Oil Spill Detection in SAR Images. In Advances in Computer, Communication and Computational Sciences, Proceedings of the IC4S 2019, Bangkok, Thailand, 11―12 October 2019; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 987–999. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.; Xu, J.; Wu, P.; Kong, P. Oil Spill Detection Based on Deep Convolutional Neural Networks Using Polarimetric Scattering Information From Sentinel-1 SAR Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 4204713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prants, S.V.; Budyansky, M.V.; Fayman, P.A.; Uleysky, M.Y.; Didov, A.A. Lagrangian Oil Spill Simulation in Peter the Great Bay (Sea of Japan) with a High-Resolution ROMS Model. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2023, 180, 551–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dąbrowska, E.; Kołowrocki, K. Stochastic determination of oil spill domain at Gdynia Port water area. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Information and Digital Technologies (IDT), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 18–19 January 2019; pp. 92–97. [Google Scholar]
- Ghaly, M.N.; Badr, N.E.; Omar, M.Y.; Amin, H.A. Risk Assessment of Oil Spills at Alexandria Port, Alexandria, Egypt. In Advanced Intelligent Systems for Sustainable Development (AI2SD’2019) Volume 3, Proceedings of the Advanced Intelligent Systems for Sustainable Development Applied to Environment, Industry and Economy, Marrakech, Morocco, 8–11 July 2019; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 569–585. [Google Scholar]
- Kvočka, D.; Žagar, D.; Banovec, P. A Review of River Oil Spill Modeling. Water 2021, 13, 1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Tong, S.; Wang, Y.; Xu, G. Modelling the oil spill transport in inland waterways based on experimental study. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 284, 117473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Wang, J.; Cao, Q.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X. Numerical Simulation of Crude Oil Spreading in a Complex River Channel. In Proceedings of the International Pipeline Conference, Online, 28–30 September 2020; p. V003T004A010. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Fingas, M.; Lambert, P.; Zeng, G.; Yang, C.; Hollebone, B. Characterization and identification of the Detroit River mystery oil spill (2002). J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1038, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Cunha, A.C.; De Abreu, C.H.M.; Crizanto, J.L.P.; Cunha, H.F.A.; Brito, A.U.; Pereira, N.N. Modeling pollutant dispersion scenarios in high vessel-traffic areas of the Lower Amazon River. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 168, 112404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y. Development of an oil spill model adaptable to exposure and submergence conversion of tidal flats: A case study in the Changjiang Estuary. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 171, 112715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.-S.; Cho, Y.-K.; Choi, B.-J.; Jung, K.T.; You, S.H. Improving a prediction system for oil spills in the Yellow Sea: Effect of tides on subtidal flow. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 68, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.-L.; Xu, J.-L.; Wang, L. Development of a vapor–liquid phase change model for volume-of-fluid method in FLUENT. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2012, 39, 1101–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopf, L. Turbulenz bei einem Flusse. Ann. Phys. 1910, 337, 777–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Launder, B.E.; Spalding, D.B. Lectures in Mathematical Models of Turbulence; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Shih, T.-H.; Zhu, J.; Lumley, J.L. A new Reynolds stress algebraic equation model. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 1995, 125, 287–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, M.; Aamo, O.M.; Daling, P.S. Quantitative analysis of alternate oil spill response strategies using OSCAR. Spill Sci. Technol. Bull. 1995, 2, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Board, T.R.; Council, N.R. Oil in the Sea III: Inputs, Fates, and Effects; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2003; p. 277. [Google Scholar]
- Fay, J.A. Physical Processes in the Spread of Oil on a Water Surface. Int. Oil Spill Conf. Proc. 1971, 1971, 463–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, N.; Zhang, C.; Hillel, D. Water properties☆. In Reference Module in Earth Systems and Environmental Sciences; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Poff, N.L. Section Introduction: Structures and Functions of Inland Water–Rivers. Encycl. Inland Waters 2022, 2, 235–236. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Xu, H.; Yin, J.; Du, S.; Liu, C.; Li, J.-y. Significance of the great protection of the Yangtze River: Riverine input contributes primarily to the presence of PAHs and HMs in its estuary and the adjacent sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 186, 114366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Woo, S.-H.; Lai, P.-L.; Chen, X. The economic impact of inland ports on regional development: Evidence from the Yangtze River region. Transp. Policy 2022, 127, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yang, D.; Chen, Y. Port integration on the Yangtze River: Does it follow an "interest balance" pattern? Transp. Policy 2021, 108, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Yang, Y.; Liu, S.; Gong, X.; Zhao, Y.; Jin, R.; Duan, H.; Jiang, P. A comparative study of green growth efficiency in Yangtze River Economic Belt and Yellow River Basin between 2010 and 2020. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 150, 110214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhao, Y. Synergy/trade-offs and differential optimization of production, living, and ecological functions in the Yangtze River economic Belt, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 147, 109925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adofo, Y.K.; Nyankson, E.; Agyei-Tuffour, B. Dispersants as an oil spill clean-up technique in the marine environment: A review. Heliyon 2022, 8, e10153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.; Wang, T.; Luo, Y.; Yang, D. Analysis of port pollutant emission characteristics in United States based on multiscale geographically weighted regression. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1131948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Zhang, A. Can government environmental regulation promote low-carbon development in heavy polluting industries? Evidence from China’s new environmental protection law. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2023, 99, 106991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivorra, B.; Gomez, S.; Carrera, J.; Ramos, A.M. A compositional Eulerian approach for modeling oil spills in the sea. Ocean Eng. 2021, 242, 110096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, Z.; Li, D.; Li, Y.; Chen, S.; Bu, S. Trajectory and weathering of oil spill in Daya bay, the South China sea. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 115562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Brimicombe, A.J.; Ralphs, M.P. Spatial data quality and sensitivity analysis in GIS and environmental modelling: The case of coastal oil spills. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2000, 24, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Tong, S.; Wang, Y. Establishment and application of oil spill model in inland waterway. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Hydraulic and Civil Engineering, ICHCE 2020, Xi’an, China, 11–13 December 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, H.; Si, H. Dynamic risk assessment of oil spill scenario for Three Gorges Reservoir in China based on numerical simulation. Saf. Sci. 2012, 50, 1112–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
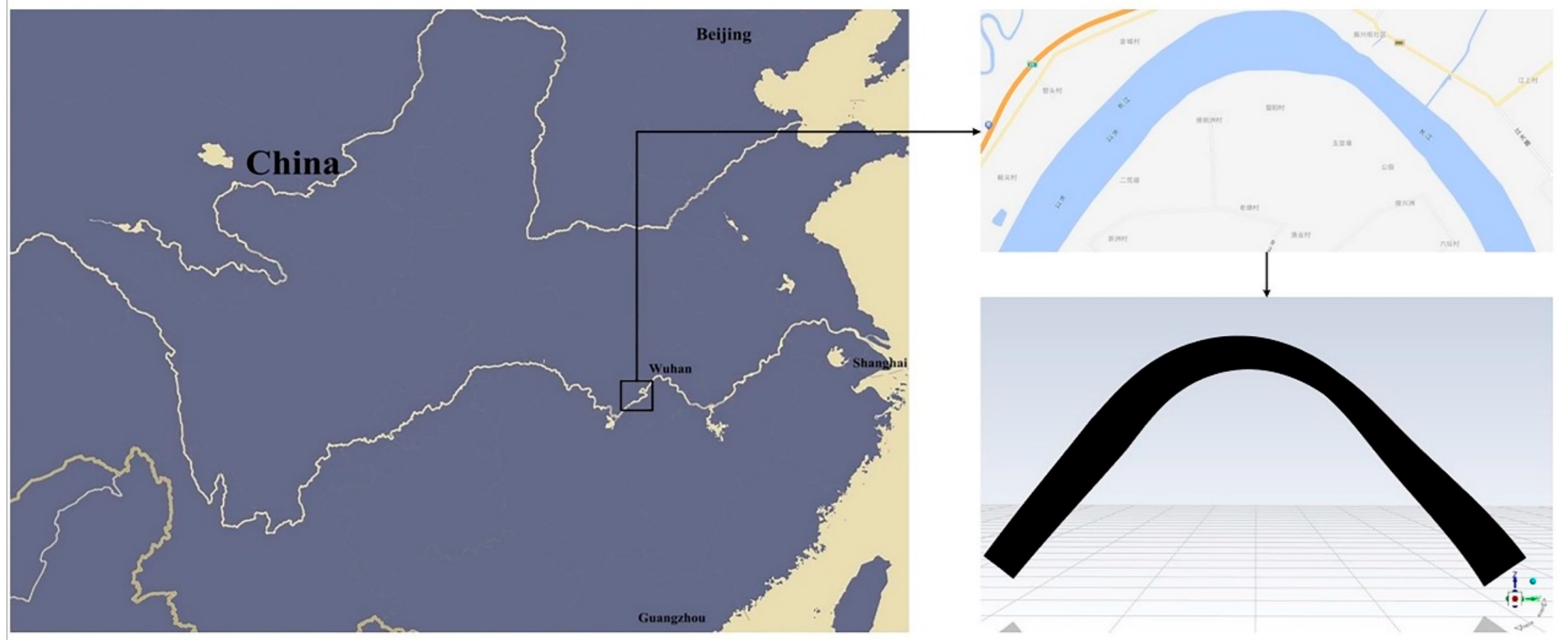
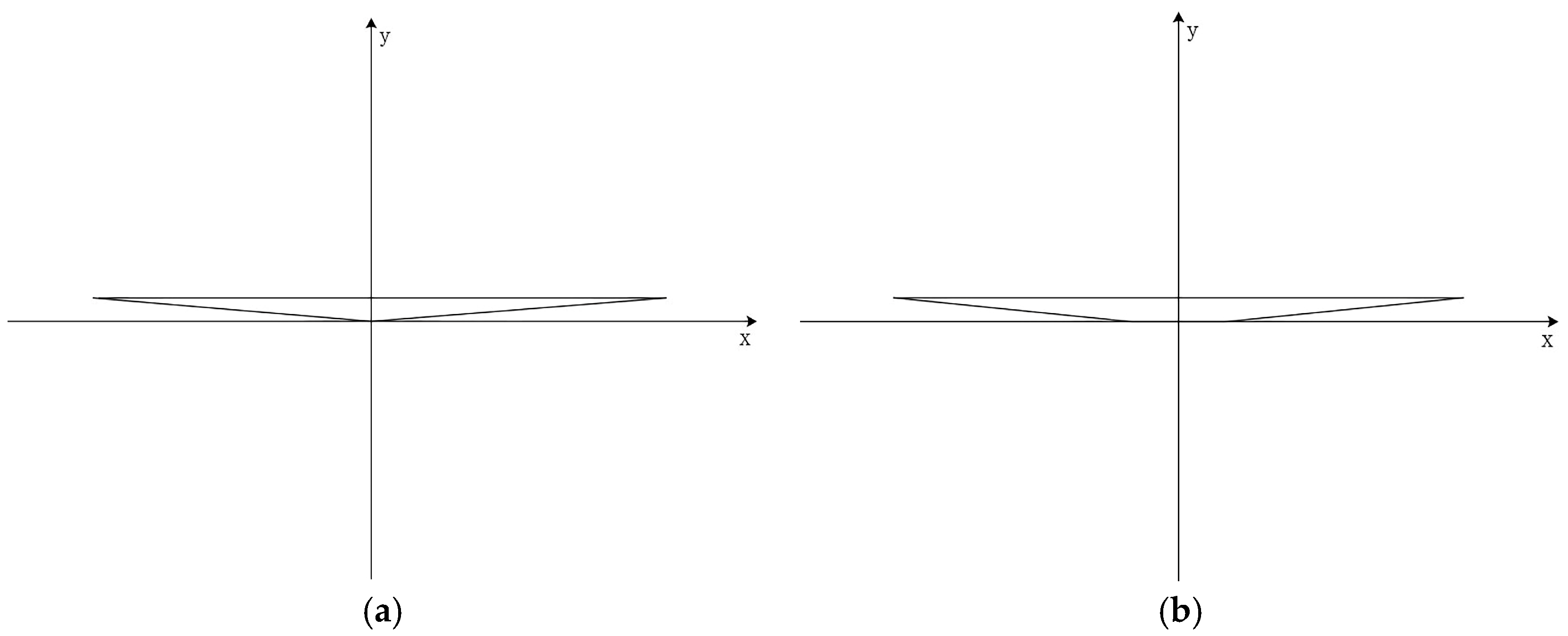

| Scenarios | Conditions | Channel Shapes | Cross-Sections |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Continuous | Straight | Triangular |
| 2 | Continuous | Straight | Trapezoidal |
| 3 | Continuous | Curved | Triangular |
| 4 | Continuous | Curved | Trapezoidal |
| 5 | One-time | Straight | Triangular |
| 6 | One-time | Straight | Trapezoidal |
| 7 | One-time | Curved | Triangular |
| 8 | One-time | Curved | Trapezoidal |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, C.; Yang, H.; Yu, G.; Deng, J.; Shu, Y. Simulation of Oil Spills in Inland Rivers. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11071294
Kang C, Yang H, Yu G, Deng J, Shu Y. Simulation of Oil Spills in Inland Rivers. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2023; 11(7):1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11071294
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Chenyang, Haining Yang, Guyi Yu, Jian Deng, and Yaqing Shu. 2023. "Simulation of Oil Spills in Inland Rivers" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 11, no. 7: 1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11071294
APA StyleKang, C., Yang, H., Yu, G., Deng, J., & Shu, Y. (2023). Simulation of Oil Spills in Inland Rivers. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 11(7), 1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11071294







