Marine Plastic Drift from the Mekong River to Southeast Asia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Met-Ocean Forcing
2.2. The ROMS Model
2.3. The OpenDrift Model Framework
2.4. Experimental Design
3. Results
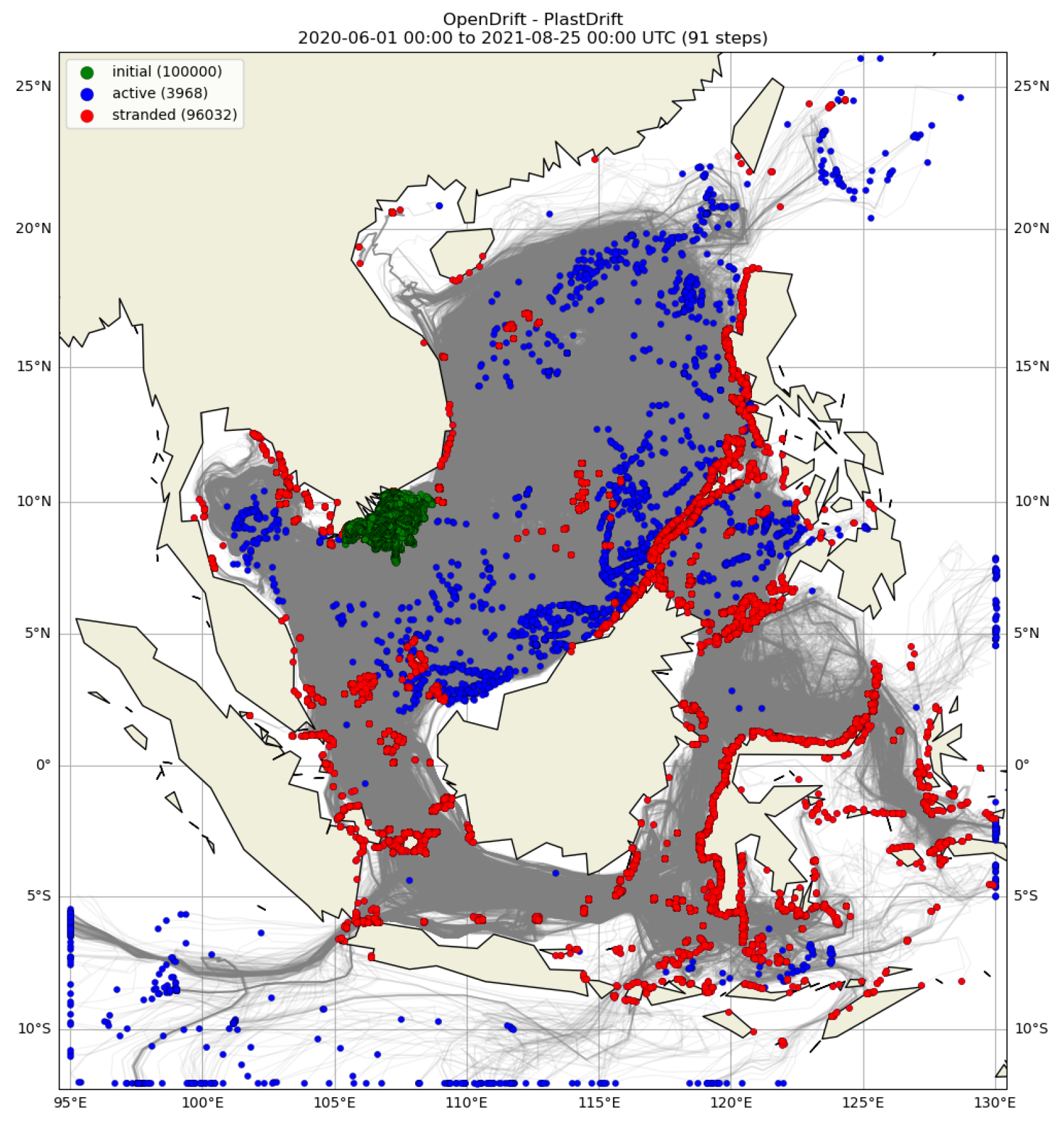
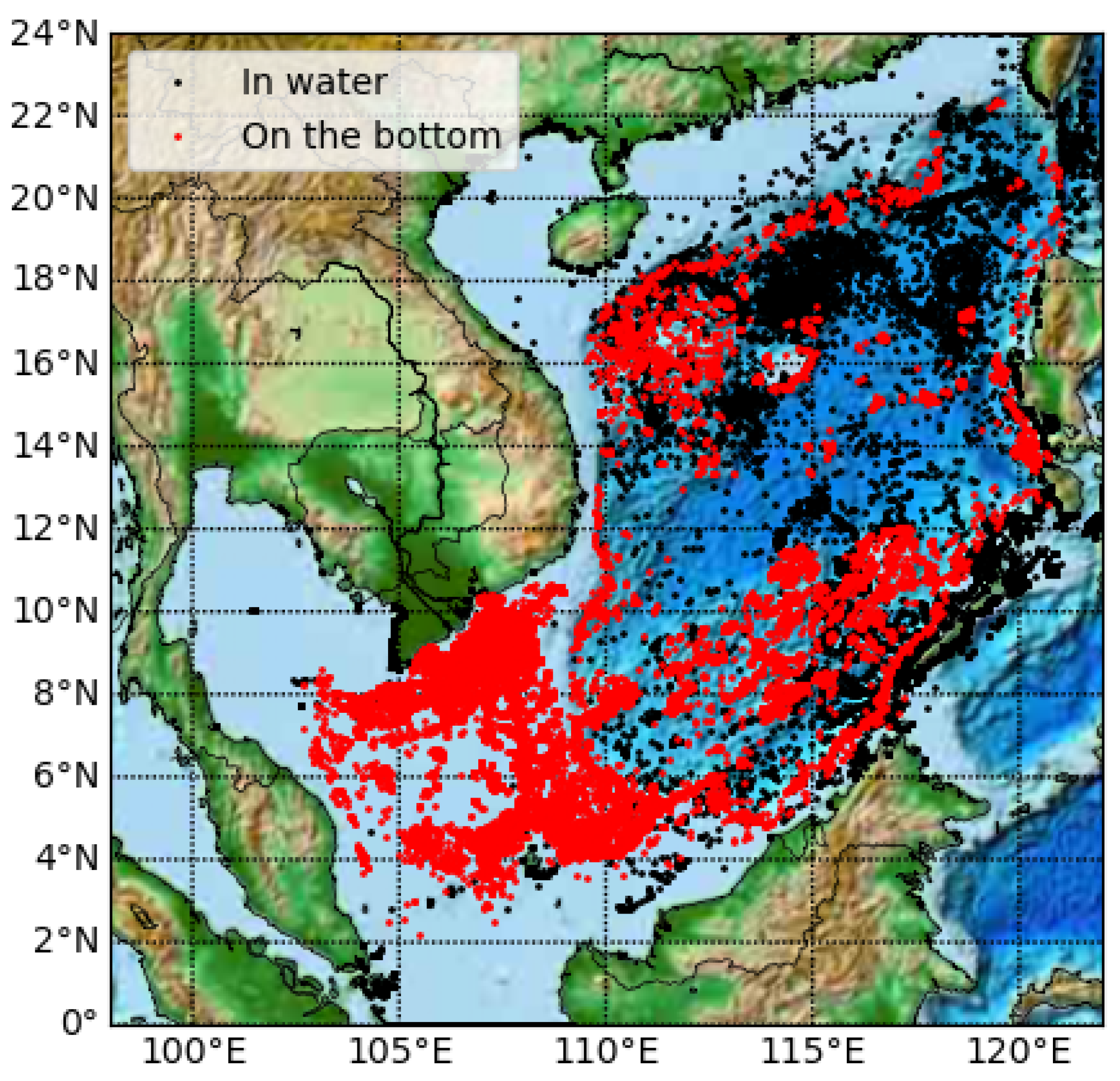
3.1. Trajectory of Marine Plastic Drift
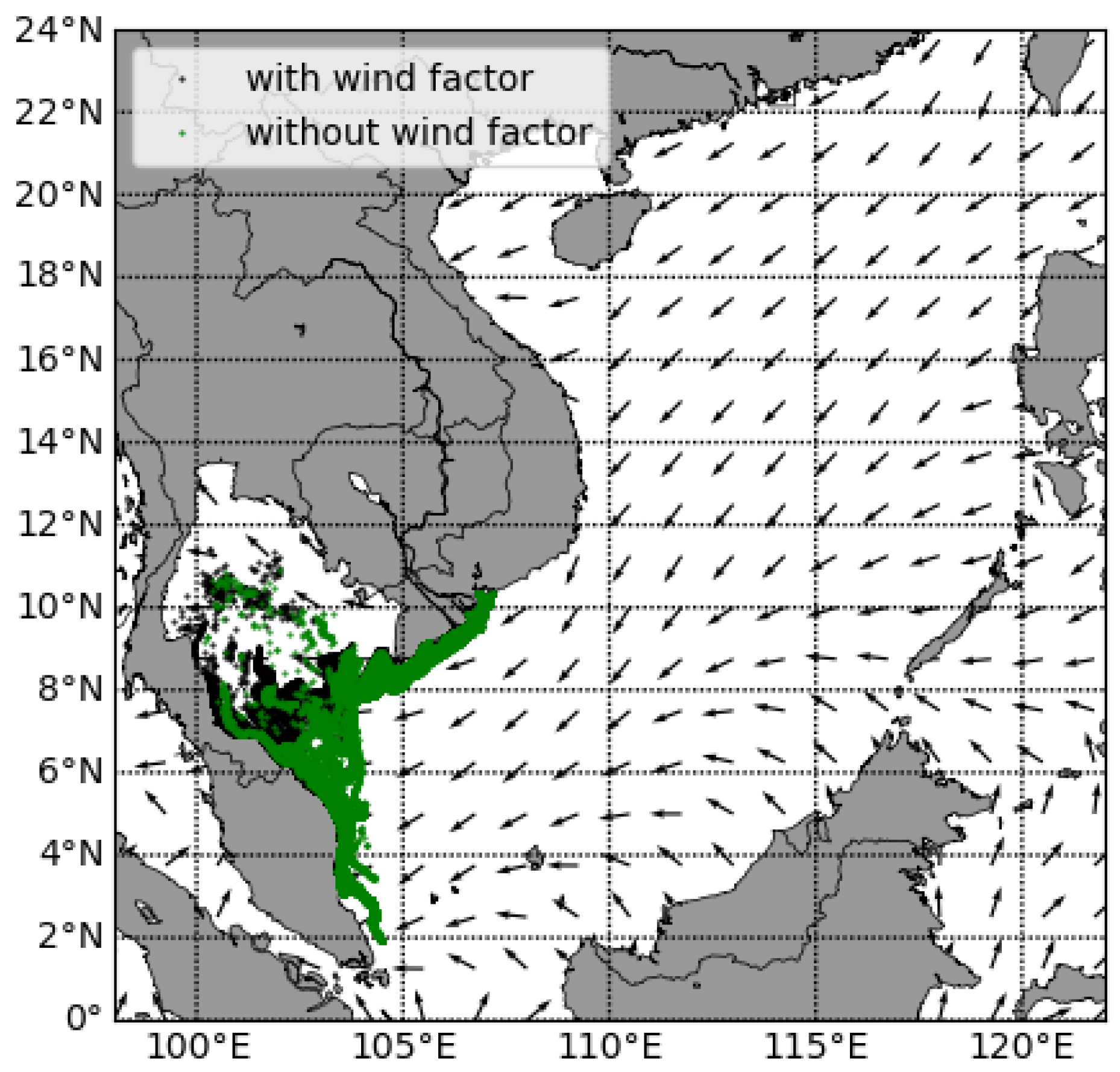
3.2. The Seasonal Drift Pattern and the Influence of Wind Drift
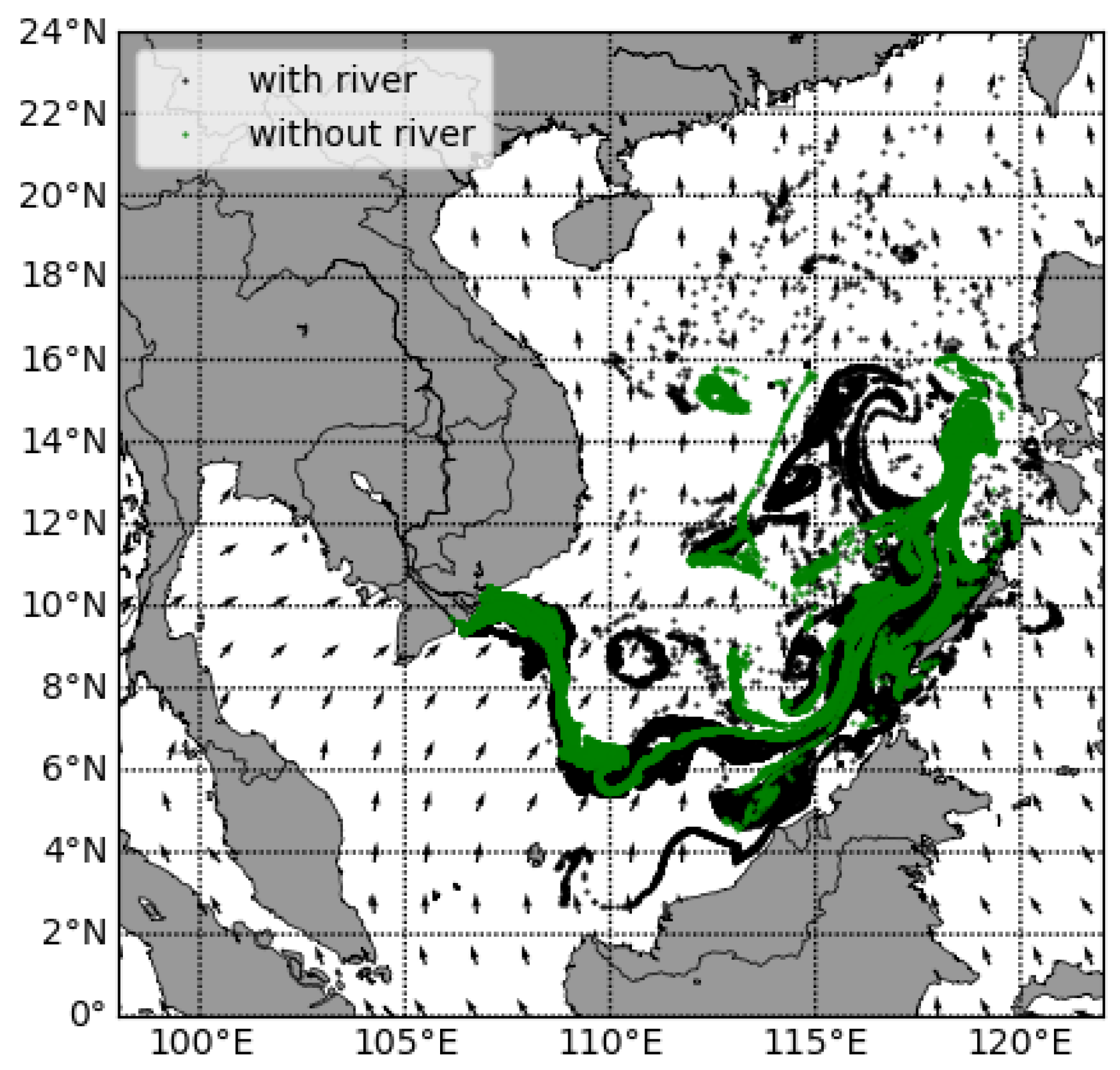
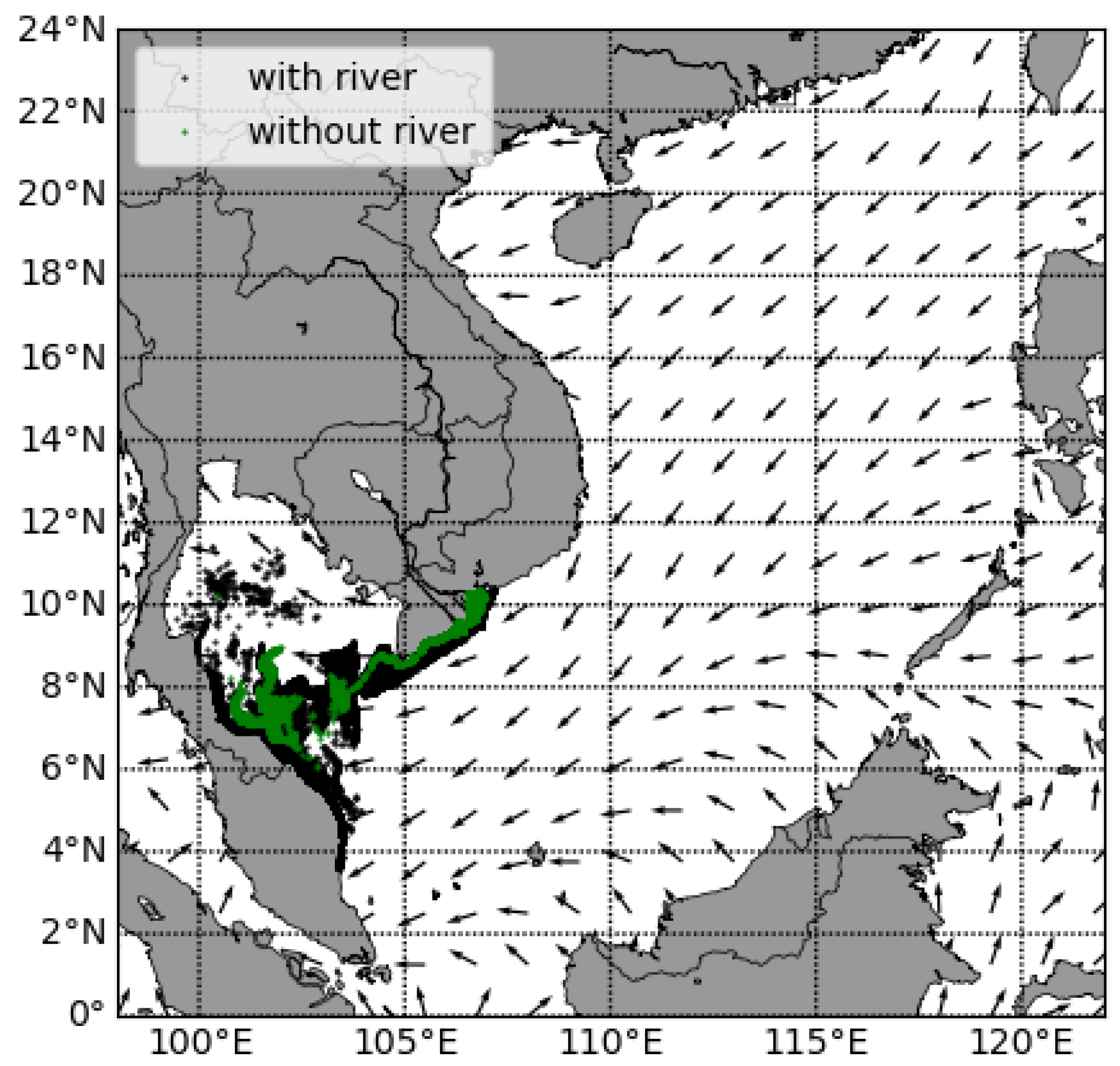
3.3. The Influence of the Mekong River
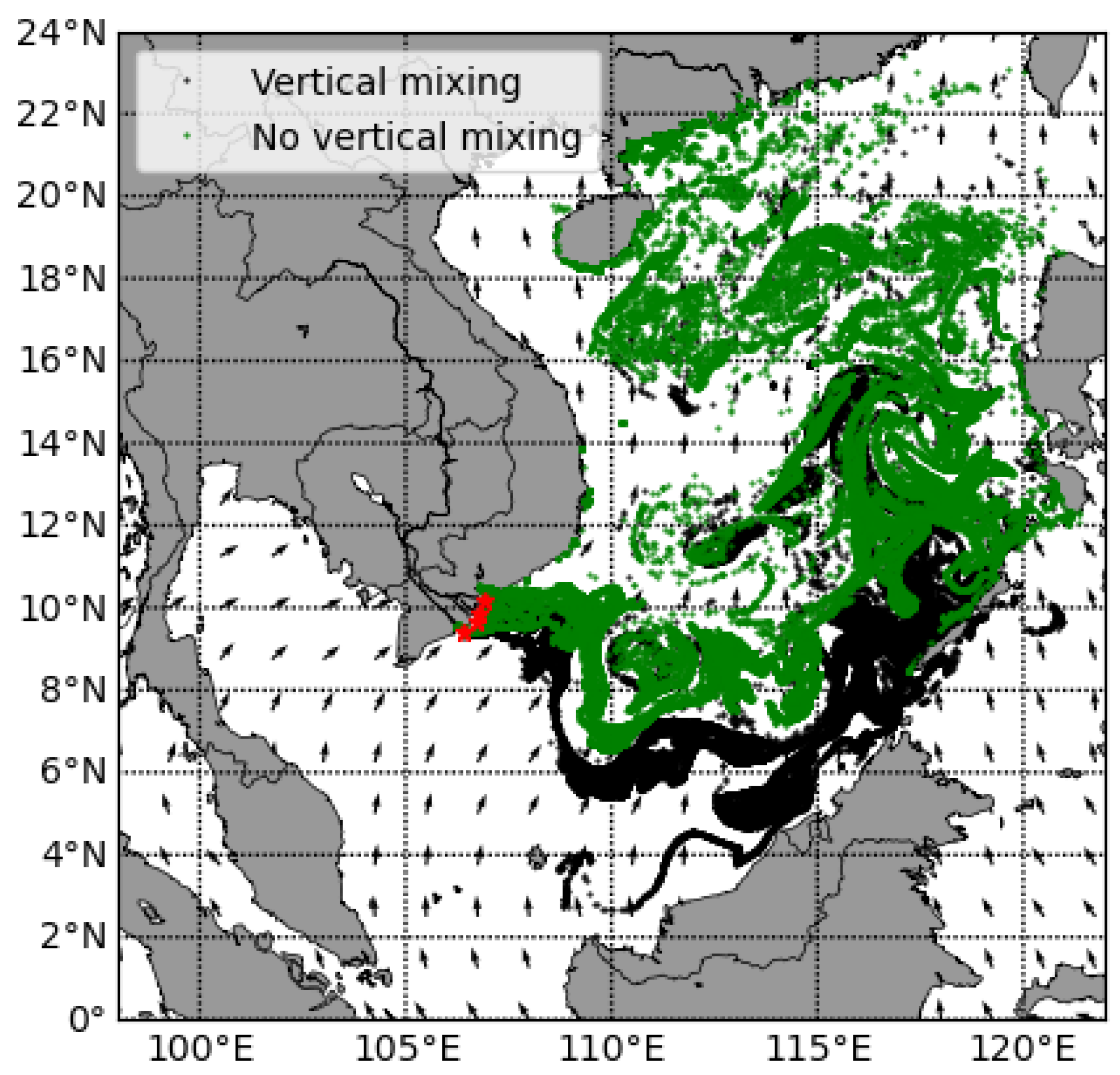
3.4. Vertical Mixing
3.5. The Influence of Sinking Rates
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- The plastic drift is highly seasonal. During the summer, the plastic particles from the Mekong river drift to the east and the northeast, and in the winter they drift to the southwest. This is because the South China Sea is influenced by the strong monsoon system, in which the southwesterly wind prevails in summer, and the northeasterly wind dominates in the winter.
- The river flow plays a role in dispersing plastic waste. Specifically, the Mekong river disperses plastics efficiently in both summer and winter.
- The effect of wind drift on plastic drift depends on the wind speed and direction. This influence is significant in winter because of strong wind. Additionally, wind drift and vertical mixing can have combined effects on the trajectory of marine plastics. More specifically, when the wind drift is enabled and vertical mixing is disabled, the plastic particles stay on the surface and are more exposed and driven by wind drift.
- Sinking rates have a great influence on where plastics end up. With a terminal velocity of 2 m/d, plastics drift to most parts of theSCS and beyond, and many remain suspended in deep waters. With a terminal velocity of 5 m/d, most plastic particles deposit right at the Mekong river.
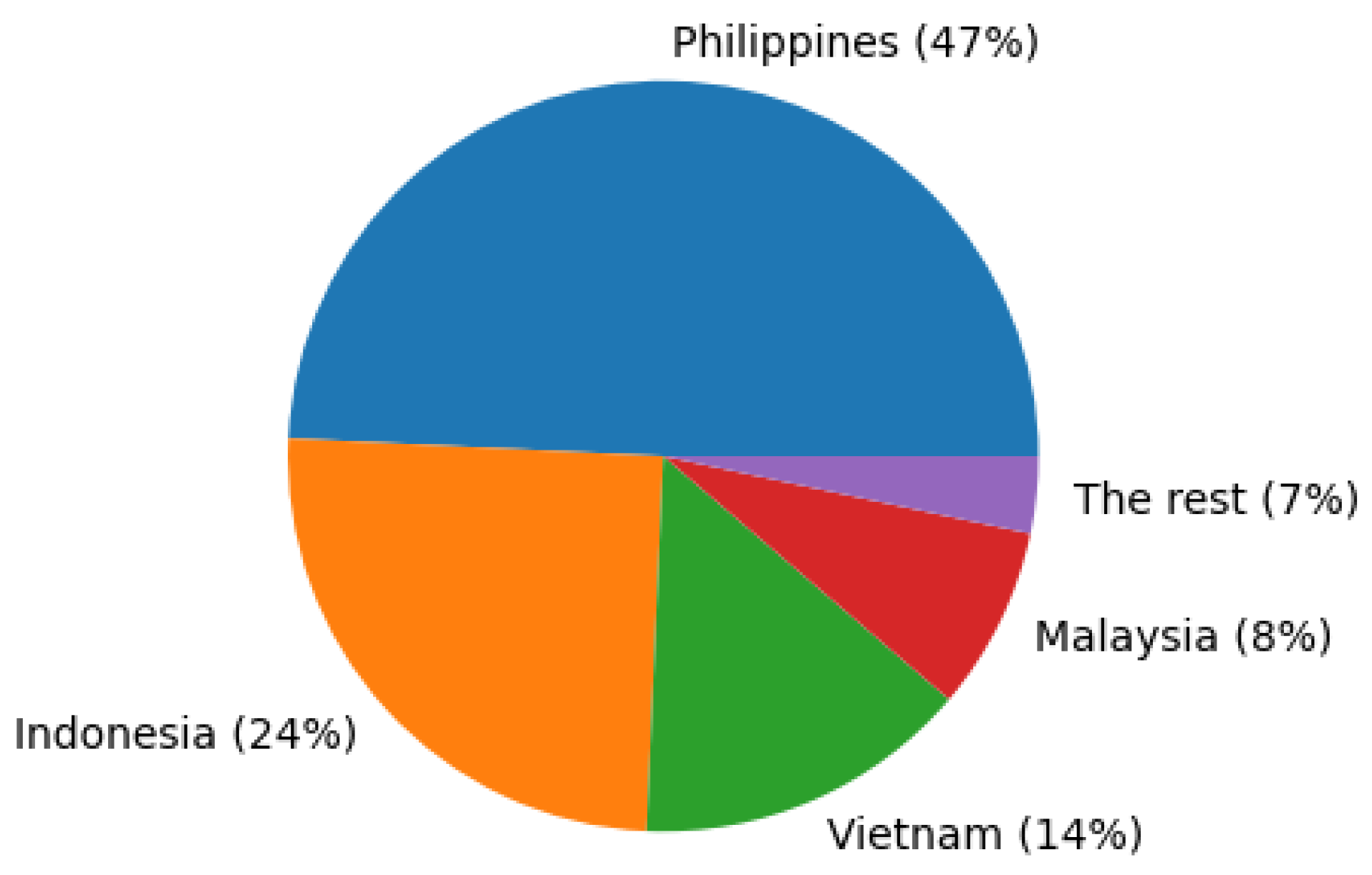
- The Philippines is most vulnerable to marine plastic pollution from the Mekong river because plastic waste mainly drifts to the sea in the summer following the flood season and the southwesterly monsoon will then transport the plastics toward the Philippines. Indonesia is also a major destination of marine plastics from the Mekong river, because of its very large size with many seas and straits.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CMEMS | The Copernicus Marine Environment Monitoring Service |
| (the Coper-nicus Marine Service) | |
| ECMWF | The European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts |
| MET | Norwegian Meteorological Institute |
| MP(s) | Micro-plastic(s) |
| SCS | South China Sea |
| SEA | Southeast Asia |
| VNMHA | The Vietnam Meteorological and Hydro-logical Administration |
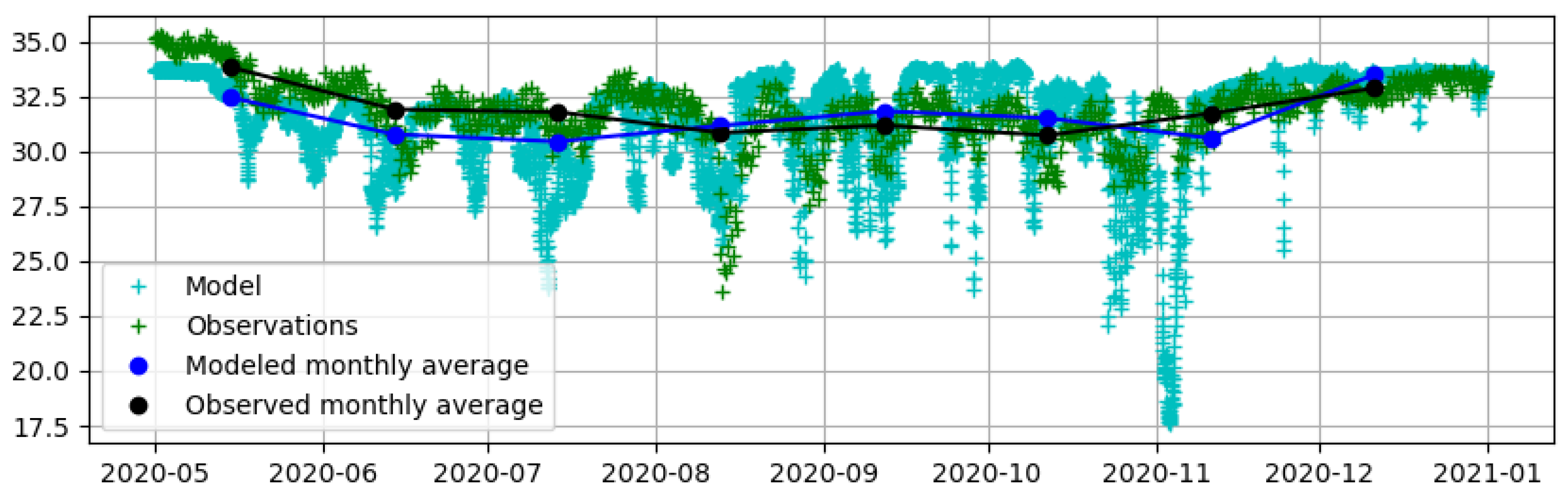
Appendix A
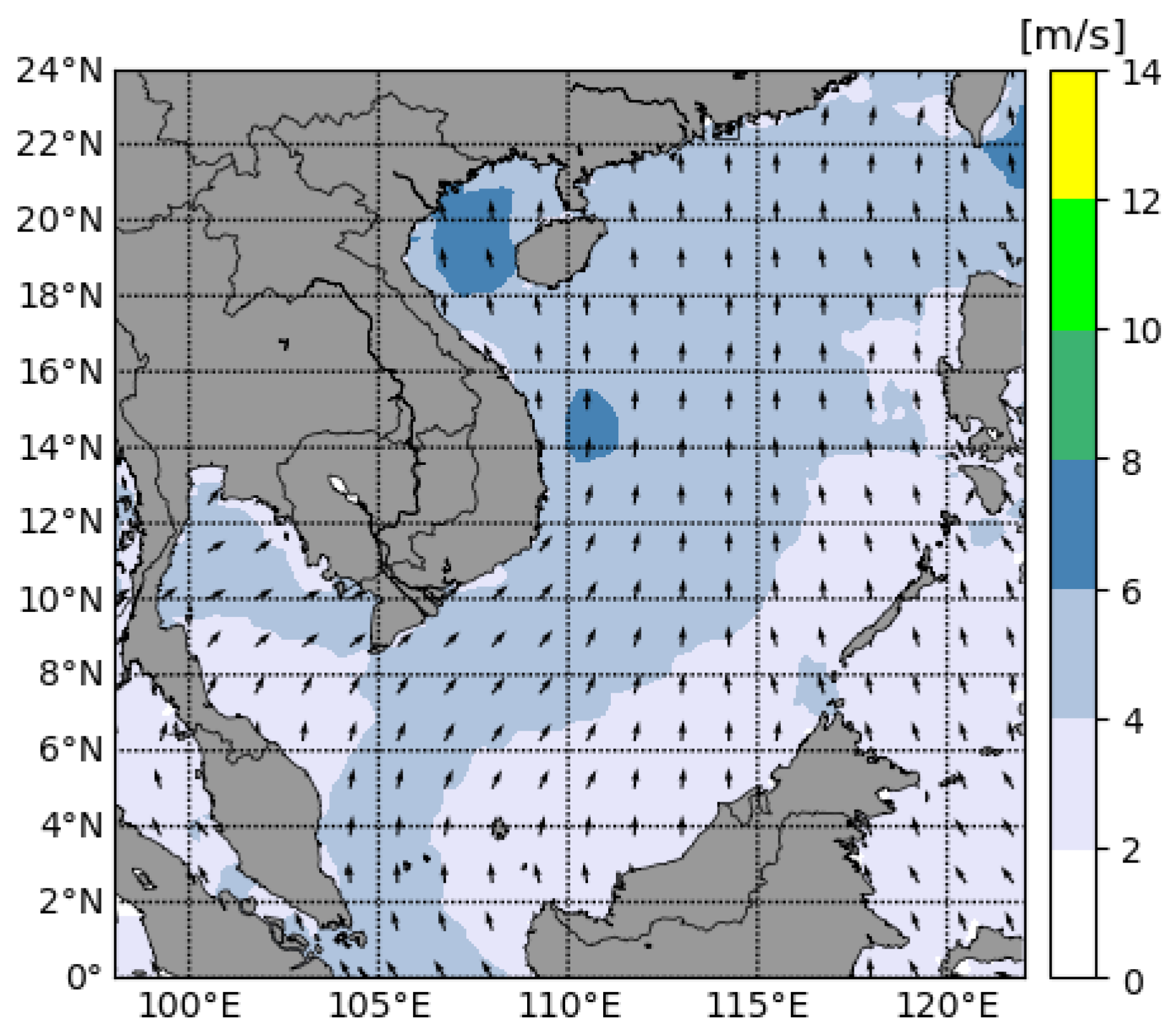
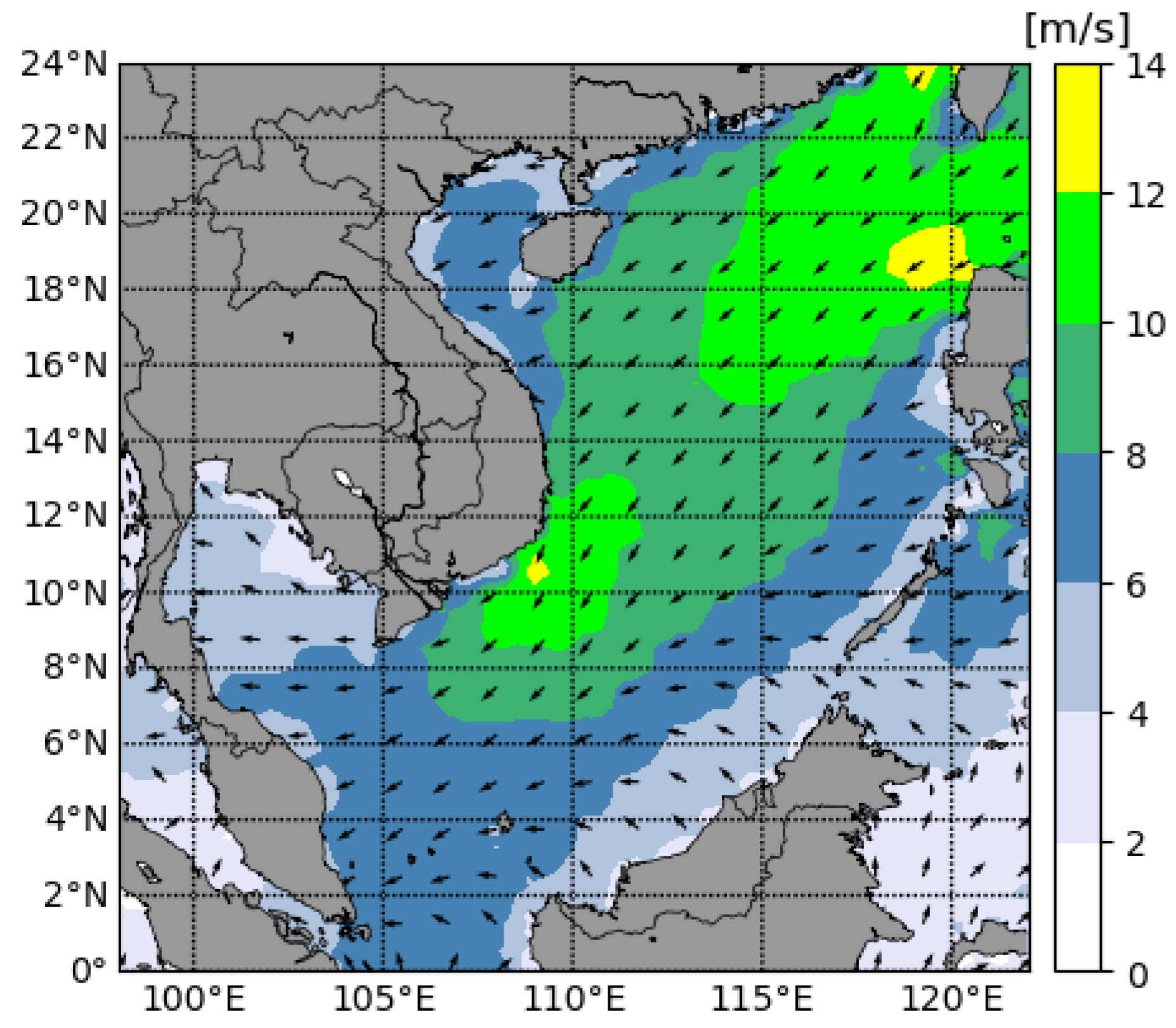
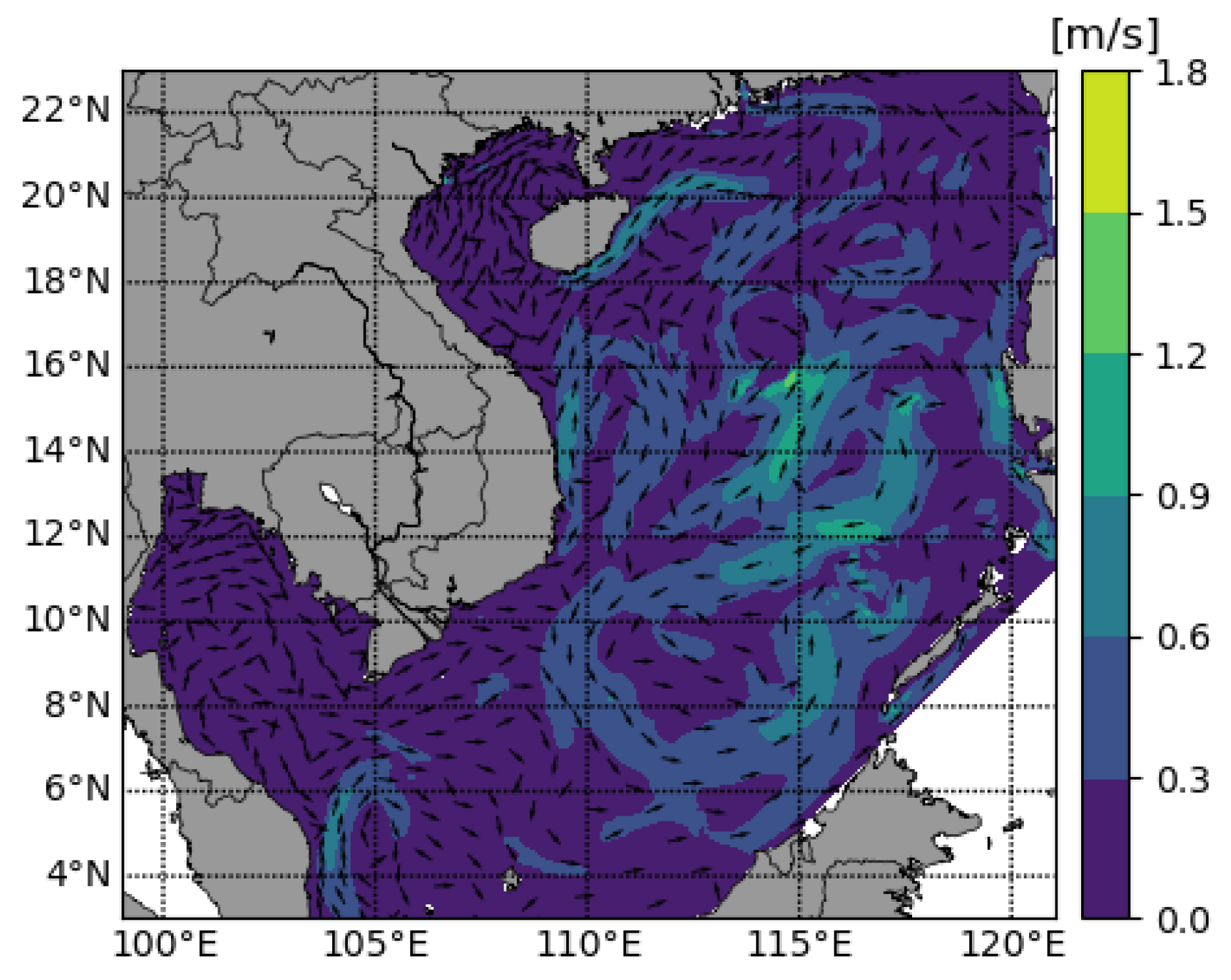
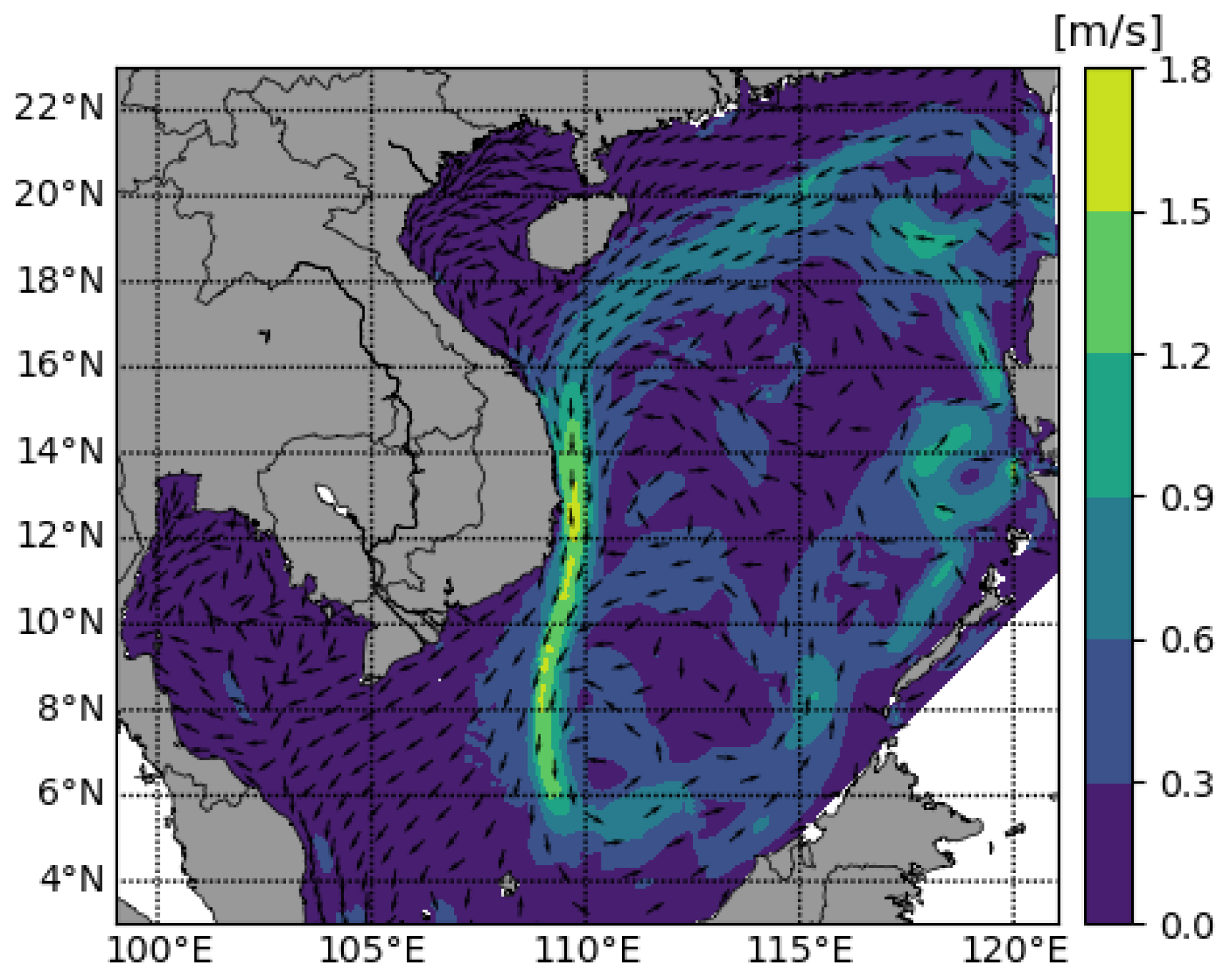

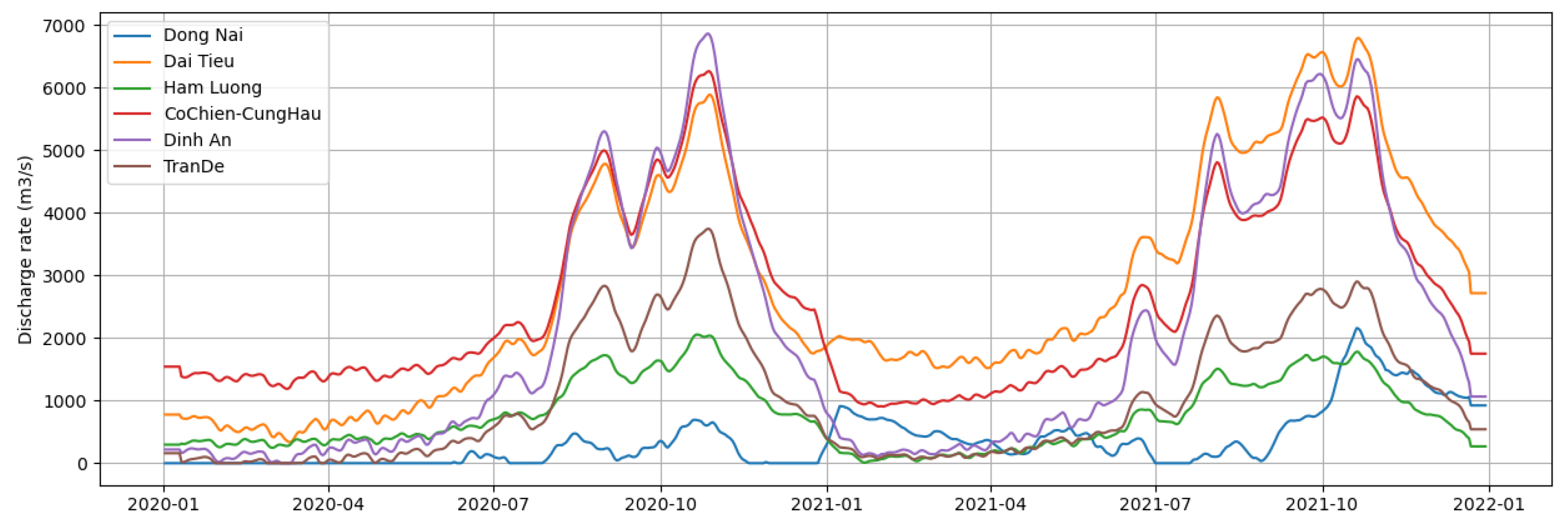


References
- Zhang, P.; Wei, S.S.; Zhang, J.B.; Ou, Z.; Yang, Y.Q.; Wang, M.Y. Occurrence, composition, and relationships in marine plastic debris on the first long beach adjacent to the land-based source, south China sea. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Fang, C.; Chen, Z.; Chen, G. Regional cooperation in marine plastic waste cleanup in the south china sea region. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Allgeier, A.; Yin, D.; Hollert, H. Leaching of endocrine disrupting chemicals from marine microplastics and mesoplastics under common life stress conditions. Environ. Int. 2019, 130, 104938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jambeck, J.R.; Geyer, R.; Wilcox, C.; Siegler, T.R.; Perryman, M.; Andrady, A.; Narayan, R.; Law, K.L. Plastic waste inputs from land into the ocean. Science 2015, 347, 768–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, P.T.; Tamelander, J.; Lyons, Y.; Neo, M.L.; Maes, T. Taking a mass-balance approach to assess marine plastics in the South China Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 171, 112708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haberstroh, C.J.; Arias, M.E.; Yin, Z.; Sok, T.; Wang, M.C. Plastic transport in a complex confluence of the Mekong River in Cambodia. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 095009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.-z.; Wang, W.-z.; Li, Y.S.; Li, C.W. Current characteristics of the South China Sea. In Oceanology of China Seas; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1994; pp. 39–47. [Google Scholar]
- van der Mheen, M.; Pattiaratchi, C.; Cosoli, S.; Wandres, M. Depth-Dependent Correction for Wind-Driven Drift Current in Particle Tracking Applications. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erftemeijer, P.L.; Van Beek, J.K.; Ochieng, C.A.; Jager, Z.; Los, H.J. Eelgrass seed dispersal via floating generative shoots in the Dutch Wadden Sea: A model approach. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2008, 358, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Hénaff, M.; Kourafalou, V.H.; Paris, C.B.; Helgers, J.; Aman, Z.M.; Hogan, P.J.; Srinivasan, A. Surface evolution of the deepwater horizon oil spill patch: Combined effects of circulation and wind-induced drift. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 7267–7273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagestad, K.F.; Röhrs, J. Prediction of ocean surface trajectories using satellite derived vs. modeled ocean currents. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 223, 130–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hole, L.R.; de Aguiar, V.; Dagestad, K.F.; Kourafalou, V.H.; Androulidakis, Y.; Kang, H.; Le Hénaff, M.; Calzada, A. Long term simulations of potential oil spills around Cuba. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 167, 112285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hole, L.R.; Dagestad, K.F.; Röhrs, J.; Wettre, C.; Kourafalou, V.H.; Androulidakis, Y.; Kang, H.; Hénaff, M.L.; Garcia-Pineda, O. The Deepwater horizon oil slick: Simulations of river front effects and oil droplet size distribution. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2019, 7, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukulka, T.; Proskurowski, G.; Morét-Ferguson, S.; Meyer, D.W.; Law, K.L. The effect of wind mixing on the vertical distribution of buoyant plastic debris. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooi, M.; Reisser, J.; Slat, B.; Ferrari, F.F.; Schmid, M.S.; Cunsolo, S.; Brambini, R.; Noble, K.; Sirks, L.A.; Linders, T.E.; et al. The effect of particle properties on the depth profile of buoyant plastics in the ocean. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Röhrs, J.; Dagestad, K.F.; Asbjørnsen, H.; Nordam, T.; Skancke, J.; Jones, C.E.; Brekke, C. The effect of vertical mixing on the horizontal drift of oil spills. Ocean Sci. 2018, 14, 1581–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Int-Veen, I.; Nogueira, P.; Isigkeit, J.; Hanel, R.; Kammann, U. Positively buoyant but sinking: Polymer identification and composition of marine litter at the seafloor of the North Sea and Baltic Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 172, 112876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, J.; Chase, Z.; Zhang, J.; Holl, M.M.; Willis, K.; Williams, A.; Hardesty, B.D.; Wilcox, C. Microplastic Pollution in Deep-Sea Sediments From the Great Australian Bight. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazey, F.M.; Ryan, P.G. Biofouling on buoyant marine plastics: An experimental study into the effect of size on surface longevity. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 210, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Sebille, E.; Aliani, S.; Law, K.L.; Maximenko, N.; Alsina, J.M.; Bagaev, A.; Bergmann, M.; Chapron, B.; Chubarenko, I.; Cózar, A.; et al. The physical oceanography of the transport of floating marine debris. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 023003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Li, D.; Sun, Y.; Zheng, X.; Peng, X.; Zheng, K.; Hu, B.; Luo, X.; Mai, B. Plastic debris in marine birds from an island located in the South China Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 149, 110566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokes, G.G. On the theory of oscillatory waves. Trans. Camb. Philos. Soc. 1847, 8, 441–455. [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser, D.; Estelmann, A.; Kowalski, N.; Glockzin, M.; Waniek, J.J. Sinking velocity of sub-millimeter microplastic. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 139, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalski, N.; Reichardt, A.M.; Waniek, J.J. Sinking rates of microplastics and potential implications of their alteration by physical, biological, and chemical factors. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 109, 310–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E.U. Copernicus Marine Service Information, Global Ocean 1/12° Physics Analysis and Forecast Updated. 2014. Available online: https://data.marine.copernicus.eu/product/GLOBAL_ANALYSISFORECAST_PHY_001_024/description (accessed on 23 April 2023). [CrossRef]
- Le Traon, P.Y.; Reppucci, A.; Fanjul, E.A.; Aouf, L.; Behrens, A.; Belmonte, M.; Bentamy, A.; Bertino, L.; Brando, V.E.; Kreiner, M.B.; et al. From observation to information and users: The Copernicus Marine Service Perspective. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ECMWF. The European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts. 2022. Available online: https://www.ecmwf.int/en/forecasts/accessing-forecasts/ (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Ehard, B.; Malardel, S.; Dörnbrack, A.; Kaifler, B.; Kaifler, N.; Wedi, N. Comparing ECMWF high-resolution analyses with lidar temperature measurements in the middle atmosphere. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2018, 144, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haiden, T.; Janousek, M.; Vitart, F.; Ben Bouallegue, Z.; Ferranti, L.; Prates, F.; Richardson, D. Evaluation of ECMWF Forecasts, Including the 2020 Upgrade; ECMWF Technical Memorandum; European Centre for Medium Range Weather Forecasts: Reading, UK, 2021; Volume 880, pp. 1–54. [Google Scholar]
- Thuy, N.; Tien, T.; Wettre, C.; Hole, L. Monsoon-Induced Surge during High Tides at the Southeast Coast of Vietnam: A Numerical Modeling Study. Geosciences 2019, 9, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egbert, G.D.; Erofeeva, S.Y. Efficient Inverse Modeling of Barotropic Ocean Tides. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2002, 19, 183–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doan, Q.T. Application MIKE 11 model on simulation and calculation for saltwater intrusion in Southern region. Sci. Tech. Hydrometeorol. J. 2016, 1, 39–46. [Google Scholar]
- EFAS. The European Flood Awareness System. 2022. Available online: https://www.efas.eu/en/data-access (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- OpenDrift. OpenDrift—Open Source Framework for Ocean Trajectory Modelling. 2020. Available online: https://opendrift.github.io/ (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Dagestad, K.F.; Röhrs, J.; Breivik, O.; Ådlandsvik, B. OpenDrift v1.0: A generic framework for trajectory modelling. Geosci. Model Dev. 2018, 11, 1405–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.E.; Dagestad, K.F.; Breivik, Ø.; Holt, B.; Röhrs, J.; Christensen, K.H.; Espeseth, M.; Brekke, C.; Skrunes, S. Measurement and modeling of oil slick transport. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2016, 121, 7759–7775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gérigny, O.; Pedrotti, M.L.; El Rakwe, M.; Brun, M.; Pavec, M.; Henry, M.; Mazeas, F.; Maury, J.; Garreau, P.; Galgani, F. Characterization of floating microplastic contamination in the bay of Marseille (French Mediterranean Sea) and its impact on zooplankton and mussels. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 175, 113353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visser, A.W. Using random walk models to simulate the vertical distribution of particles in a turbulent water column. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1997, 158, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekman, V.W. On the Influence of the Earth’s Rotation on Ocean-Currents; Almqvist & Wiksells boktryckeri, A.-B.: Uppsala, Sweden, 1905. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen Manh, D. Marine Plastic Drift from the Mekong River to Southeast Asia. Master’s Thesis, The University of Bergen, Bergen, Norway, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Cushman-Roisin, B. Introduction to Geophysical Fluid Dynamics: Physical and Numerical Aspects, 2nd ed.; International Geophysics Series; Academic: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; Volume 101. [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser, D.; Kowalski, N.; Waniek, J.J. Effects of biofouling on the sinking behavior of microplastics. Environ. Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 124003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Models | Parameters | Resolution | Vertical | Temporal |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ECMWF | Wind velocity | 1/8 | 10 m | 3 h |
| ROMS | Ocean current (inside SCS) | 1–7 km | 20 layers | Hourly |
| CMEMS | Ocean current (outside SCS) | 1/12° | −0.47 m | Daily |
| Models | Parameters | Resolution | Vertical | Temporal |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ECMWF | Wind velocity | 1/8° | 10 m | 3 h |
| Sea level pressure | - | - | - | |
| Cloud cover | - | - | - | |
| Precipitation | - | - | - | |
| Air temperature | - | 2 m | - | |
| Dew-point temperature | - | 2 m | - | |
| CMEMS | 3D current | (−)5000 -> (−)0.5 m | Daily | |
| 3D temperature | - | - | - | |
| 3D salinity | - | - | - | |
| Sea surface height | - | - | ||
| Mike 11 | discharge rate | Daily | ||
| (Mekong mouths) | ||||
| EFAS | discharge rate | Daily | ||
| (other mouths) | ||||
| OSU TPXO 8.1 | Harmonic tides | 13 constituents |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, D.M.; Hole, L.R.; Breivik, Ø.; Nguyen, T.B.; Pham, N.K. Marine Plastic Drift from the Mekong River to Southeast Asia. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 925. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11050925
Nguyen DM, Hole LR, Breivik Ø, Nguyen TB, Pham NK. Marine Plastic Drift from the Mekong River to Southeast Asia. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2023; 11(5):925. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11050925
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Dung M., Lars R. Hole, Øyvind Breivik, Thuy B. Nguyen, and Ngoc Kh. Pham. 2023. "Marine Plastic Drift from the Mekong River to Southeast Asia" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 11, no. 5: 925. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11050925
APA StyleNguyen, D. M., Hole, L. R., Breivik, Ø., Nguyen, T. B., & Pham, N. K. (2023). Marine Plastic Drift from the Mekong River to Southeast Asia. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 11(5), 925. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11050925







